Evaluating Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Myeloperoxidase as Biomarkers in Severe Osteoarthritis Patients: A Biostatistical Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Transparency
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Ethical Considerations
2.5. Sample Collection and Processing
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
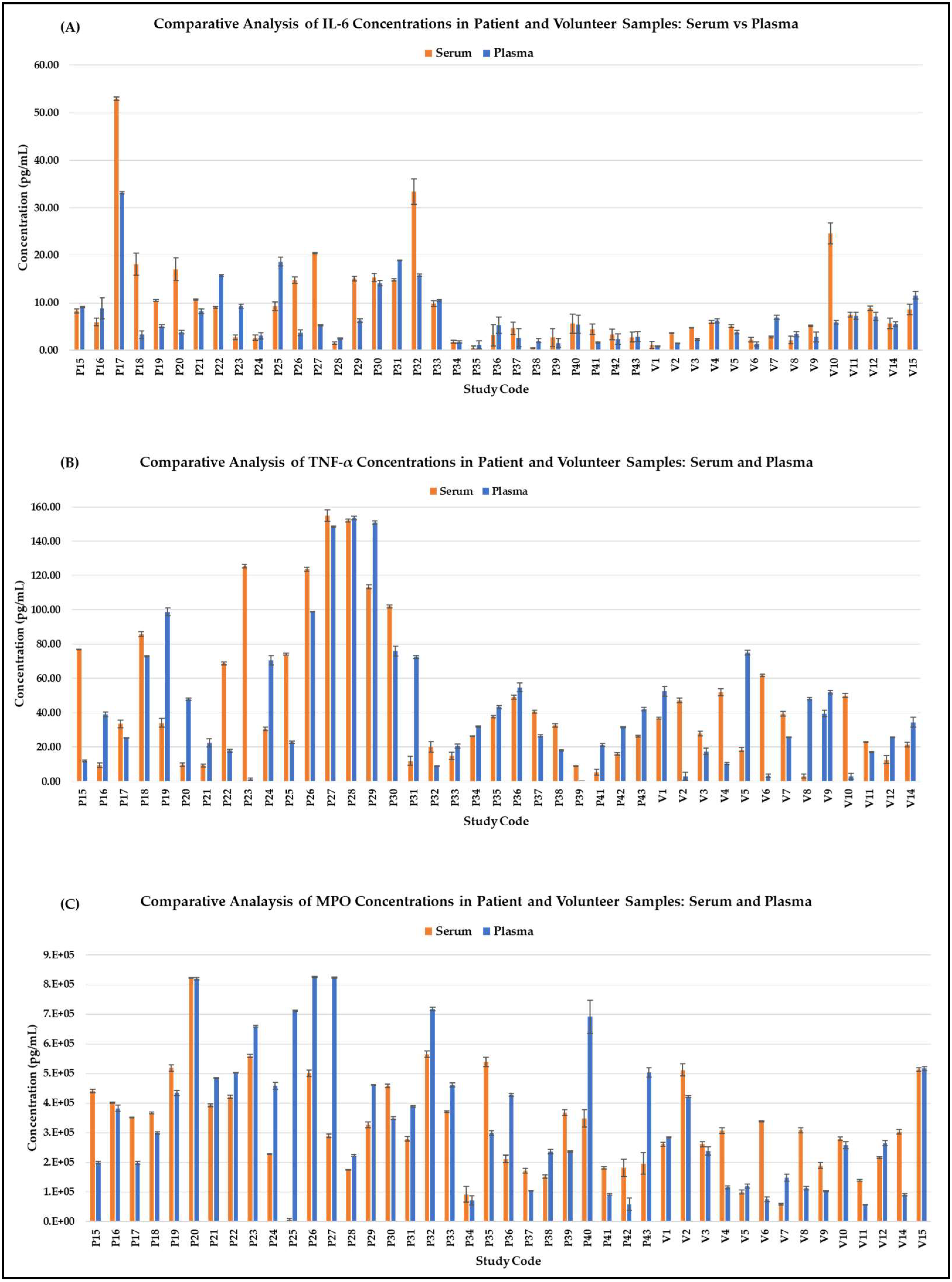
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Analysis
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | MPO (pg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Serum | Plasma | Serum | Plasma | Serum | Plasma |
| Patient | 10.42 ± 11.07 | 7.67± 7.22 | 54.67 ± 44.40 | 48.60 ± 44.62 | 3.42 × 105 ± 1.73 × 105 | 4.18 × 105 ± 2.32 × 105 |
| Volunteer | 6.31± 5.76 | 4.78± 2.99 | 30.26 ± 17.21 | 28.21 ± 22.78 | 2.70 × 105 ± 1.32 × 105 | 2.01 × 105 ± 1.37 × 105 |
3.2. Statistical Analysis
| Mann–Whitney U Test | Blood Samples (Serum vs. Plasma) | Grouping (Patients vs. Volunteers) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | p | Statistic | p | |
| ZIL-6 | 807 | 0.310 | 659 | 0.160 |
| ZTNF-α | 822 | 0.481 | 570 | 0.045 |
| ZMPO | 897 | 0.817 | 457 | 0.001 |
3.3. Sample Type Effects
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
| Variable | Source | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr(>F) | Observations Deleted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIL-6 | Grouping | 1 | 1240 | 1240 | 2.01 | 0.16 | 1 |
| Residuals | 84 | 51,757 | 616 | ||||
| ZTNF-α | Grouping | 1 | 2463 | 2463 | 4.20 | 0.044 * | 2 |
| Residuals | 83 | 48,707 | 587 | ||||
| ZMPO | Grouping | 1 | 6674 | 6674 | 12.10 | 8 × 10−4 *** | 1 |
| Residuals | 84 | 46,324 | 551 |
| Variable | Source | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr(>F) | Observations Deleted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIL-6 | Ranked_Age | 1 | 1027 | 1027 | 1.63 | 0.21 | 1 |
| Gender | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.97 | ||
| Grouping | 1 | 262 | 262 | 0.42 | 0.52 | ||
| Residuals | 82 | 51,707 | 631 | ||||
| ZTNF-α | Ranked_Age | 1 | 2572 | 2572 | 4.48 | 0.037 * | 2 |
| Gender | 1 | 1983 | 1983 | 3.46 | 0.067 | ||
| Grouping | 1 | 140 | 140 | 0.24 | 0.623 | ||
| Residuals | 81 | 46,475 | 574 | ||||
| ZMPO | Ranked_Age | 1 | 3928 | 3928 | 6.97 | 0.0099 ** | 1 |
| Gender | 1 | 40 | 40 | 0.07 | 0.7902 | ||
| Grouping | 1 | 2847 | 2847 | 5.05 | 0.0272 * | ||
| Residuals | 82 | 46,182 | 563 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, E.; van Caam, A.; van der Kraan, P.M. Obesity and osteoarthritis, more than just wear and tear: Pivotal roles for inflamed adipose tissue and dyslipidaemia in obesity-induced osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Batt, M. An update on the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 59, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, W.J.; Iman, R.L. Analysis of covariance using the rank transformation. Biometrics 1982, 38, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, L.; Hagen, K.; Bijlsma, J.; Andreassen, O.; Christensen, P.; Conaghan, P.; Doherty, M.; Geenen, R.; Hammond, A.; Kjeken, I.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the non-pharmacological core management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Culbreth, G.T.; Haile, L.M.; Rafferty, Q.; Lo, J.; Fukutaki, K.G.; Cruz, J.A.; Smith, A.E.; Vollset, S.E.; Brooks, P.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990–2020 and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e508–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, W.J.; Iman, R.L. Rank Transformations as a Bridge between Parametric and Nonparametric Statistics. Am. Stat. 1981, 35, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; L. Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, M.E.; Davis, C.S.; Koch, G.G. Categorical Data Analysis Using SAS, 3rd ed.; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Steyerberg, E.W. FRANK E. HARRELL, Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications, to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis, 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer. Biometrics 2016, 72, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, T.M.; Erickson, S.; Allison, D.B. Rank-based inverse normal transformations are increasingly used, but are they merited? Behav. Genet. 2009, 39, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ouyang, H.; Dass, C.; Xu, J. Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 15040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, S.S.; Abu Amin, S.R.; Baharuddin, H.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, V.K.M.; Mohamad Yahaya, N.H.; Tai, C.C.; Tan, M.P. A Malaysian Delphi consensus on managing knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, B.; Staines, K.A. New developments in osteoarthritis and cartilage biology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanicka-Wojtas, D.; Kurpas, D. Personalised Medicine—Implementation to the Healthcare System in Europe (Focus Group Discussions). J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsdal, M.; Michaelis, M.; Ladel, C.; Siebuhr, A.; Bihlet, A.; Andersen, J.; Guehring, H.; Christiansen, C.; Bay-Jensen, A.; Kraus, V. Disease-modifying treatments for osteoarthritis (DMOADs) of the knee and hip: Lessons learned from failures and opportunities for the future. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Thudium, C.S.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Maleitzke, T.; Geissler, S.; Duda, G.N.; Winkler, T. Biomarkers for osteoarthritis: Current status and future prospects. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. J. 2023, 37, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernotiene, E.; Bagdonas, E.; Kirdaite, G.; Bernotas, P.; Kalvaityte, U.; Uzieliene, I.; Thudium, C.S.; Hannula, H.; Lorite, G.S.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; et al. Emerging Technologies and Platforms for the Immunodetection of Multiple Biochemical Markers in Osteoarthritis Research and Therapy. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 572977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Henrotin, Y. Biomarkers of Osteoarthritis: A Review of Recent Research Progress on Soluble Biochemical Markers, Published Patents and Areas for Future Development. Recent Pat. Biomark. 2011, 1, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegertjes, R.; van de Loo, F.A.J.; Blaney Davidson, E.N. A roadmap to target interleukin-6 in osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2681–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uciechowski, P.; Dempke, W.C.M. Interleukin-6: A Masterplayer in the Cytokine Network. Oncology 2020, 98, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swärd, P.; Frobell, R.; Englund, M.; Roos, H.; Struglics, A. Cartilage and bone markers and inflammatory cytokines are increased in synovial fluid in the acute phase of knee injury (hemarthrosis)—A cross-sectional analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stannus, O.; Jones, G.; Cicuttini, F.; Parameswaran, V.; Quinn, S.; Burgess, J.; Ding, C. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 20, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.A.-O.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.A.-O.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.A.-O.; Lee, S.A.-O.X.; Yang, S.A.-O. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estee, M.M.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Page, M.J.; Wluka, A.E.; Wang, Y. Efficacy of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in hand osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2023, 5, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, E.; Yaghmour, K.M.; Khan, W.S. The effects of TNF-alpha inhibition on cartilage: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attur, M.; Krasnokutsky, S.; Zhou, H.; Samuels, J.; Chang, G.; Bencardino, J.; Rosenthal, P.; Rybak, L.; Huebner, J.L.; Kraus, V.B.; et al. The combination of an inflammatory peripheral blood gene expression and imaging biomarkers enhance prediction of radiographic progression in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratani, Y. Myeloperoxidase: Its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 640, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Hawkins, C.L. The Role of Myeloperoxidase in Biomolecule Modification, Chronic Inflammation, and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 957–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Myeloperoxidase as an Active Disease Biomarker: Recent Biochemical and Pathological Perspectives. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, P.; Harsulkar, A.; Märtson, A.A.-O.; Suutre, S.; Märtson, A.; Koks, S.A.-O. Mast Cells Differentiated in Synovial Fluid and Resident in Osteophytes Exalt the Inflammatory Pathology of Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranstam, J. Why the P-value culture is bad and confidence intervals a better alternative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.A.; Degen, A.N.; Antunes, F.T.T.; da Rosa, L.G.; Ferraz, A.G.; Wiilland, E.; Vieira, L.B.; de Souza, A.H. Benefits of electroacupuncture and a swimming association when compared with isolated protocols in an osteoarthritis model. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 12, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S. Hip and Knee Surgeries. Available online: https://www.hipandkneesurgery.ie/ (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Madry, H. Surgical therapy in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellgren, J.H.; Lawrence, J.S. Radiological Assessment of Osteo-Arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1957, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.D.; Sassoon, A.A.; Fernando, N.D. Classifications in Brief: Kellgren-Lawrence Classification of Osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, V.B.; McDaniel, G.; Huebner, J.L.; Stabler, T.V.; Pieper, C.F.; Shipes, S.W.; Petry, N.A.; Low, P.S.; Shen, J.; McNearney, T.A.; et al. Direct In Vivo evidence of activated macrophages in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofat, N.; Ejindu, V.; Heron, C.; Harrison, A.; Koushesh, S.; Assi, L.; Kuttapitiya, A.; Whitley, G.S.; Howe, F.A. Biomarkers in Painful Symptomatic Knee OA Demonstrate That MRI Assessed Joint Damage and Type II Collagen Degradation Products Are Linked to Disease Progression. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, C.C.; Cihan, M.; Yücel, D.; Serdar, M.A. Sample size, power and effect size revisited: Simplified and practical approaches in pre-clinical, clinical and laboratory studies. Biochem. Medica 2021, 31, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaHammam, A.S.; Almeneessier, A.S. Recent Evidence on the Impact of Ramadan Diurnal Intermittent Fasting, Mealtime, and Circadian Rhythm on Cardiometabolic Risk: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaing, T.T.; Compston, J.E. Biochemical markers of bone turnover—Uses and limitations. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dığın, F.A.-O.; Kızılcık Özkan, Z.; Kalaycı, E. Intensive Care Experiences of Postoperative Patients. J. Patient Exp. 2022, 9, 23743735221092489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kao, C.-C.; Liang, H.-W.; Wu, H.-T. Validity of the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) recommended performance-based tests of physical function in individuals with symptomatic Kellgren and Lawrence grade 0–2 knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.S.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, S.K.; Won, Y.; Son, Y.O.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Critical role for arginase II in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogera, S.; Jansen, M.A.-O.; Bay-Jensen, A.A.-O.; Frederiksen, P.; Karsdal, M.A.; Thudium, C.S.; Mastbergen, S.C. Relevance of Biomarkers in Serum vs. Synovial Fluid in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Ezquerro, F.; Marcon Alfieri, F.; Vilas Boas, L.; Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Chen, J.; Özçakar, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Rizzo Battistella, L.A.-O. Serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines in painful knee osteoarthritis and sensitization. Int. J. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 329792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, K.M.; Zhu, S.; Mavropalias, G.; Carrino, J.A.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J. Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic outlooks for arthrofibrosis. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, W.H.; Lepus, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Raghu, H.; Mao, R.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Sokolove, J. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverwood, V.; Blagojevic-Bucknall, M.; Jinks, C.; Jordan, J.L.; Protheroe, J.; Jordan, K.P. Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östlind, E.; Ekvall Hansson, E.; Eek, F.; Stigmar, K. Experiences of activity monitoring and perceptions of digital support among working individuals with hip and knee osteoarthritis—A focus group study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabey, T.; Honsawek, S. Cytokines as biochemical markers for knee osteoarthritis. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, A.K.; Rawle, R.A.; Adams, E.; Greenwood, M.C.; Bothner, B.; June, R.K. Application of global metabolomic profiling of synovial fluid for osteoarthritis biomarkers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Wu, J.P.; Kirk, T.B.; Carrino, J.A.; Xiang, C.; Xu, J. High-resolution measurements of the multilayer ultra-structure of articular cartilage and their translational potential. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Swift, B.J.; Becker, T.; Squelch, A.; Wang, A.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, W.; Zheng, M.; et al. High-resolution study of the 3D collagen fibrillary matrix of Achilles tendons without tissue labelling and dehydrating. J. Microsc. 2017, 266, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coleman, L.J.; Byrne, J.L.; Edwards, S.; O’Hara, R. Evaluating Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Myeloperoxidase as Biomarkers in Severe Osteoarthritis Patients: A Biostatistical Perspective. LabMed 2025, 2, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020008
Coleman LJ, Byrne JL, Edwards S, O’Hara R. Evaluating Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Myeloperoxidase as Biomarkers in Severe Osteoarthritis Patients: A Biostatistical Perspective. LabMed. 2025; 2(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleColeman, Laura Jane, John L. Byrne, Stuart Edwards, and Rosemary O’Hara. 2025. "Evaluating Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Myeloperoxidase as Biomarkers in Severe Osteoarthritis Patients: A Biostatistical Perspective" LabMed 2, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020008
APA StyleColeman, L. J., Byrne, J. L., Edwards, S., & O’Hara, R. (2025). Evaluating Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha, and Myeloperoxidase as Biomarkers in Severe Osteoarthritis Patients: A Biostatistical Perspective. LabMed, 2(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020008






