Performance Study of Anticoagulants and Animal Blood for Establishment of In Vitro Blood Circulation Loop System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Blood Acquisition and Anticoagulant
2.3. Observation of Red Blood Cells
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Initial Erythrocyte Cell Number Among the Animal Species
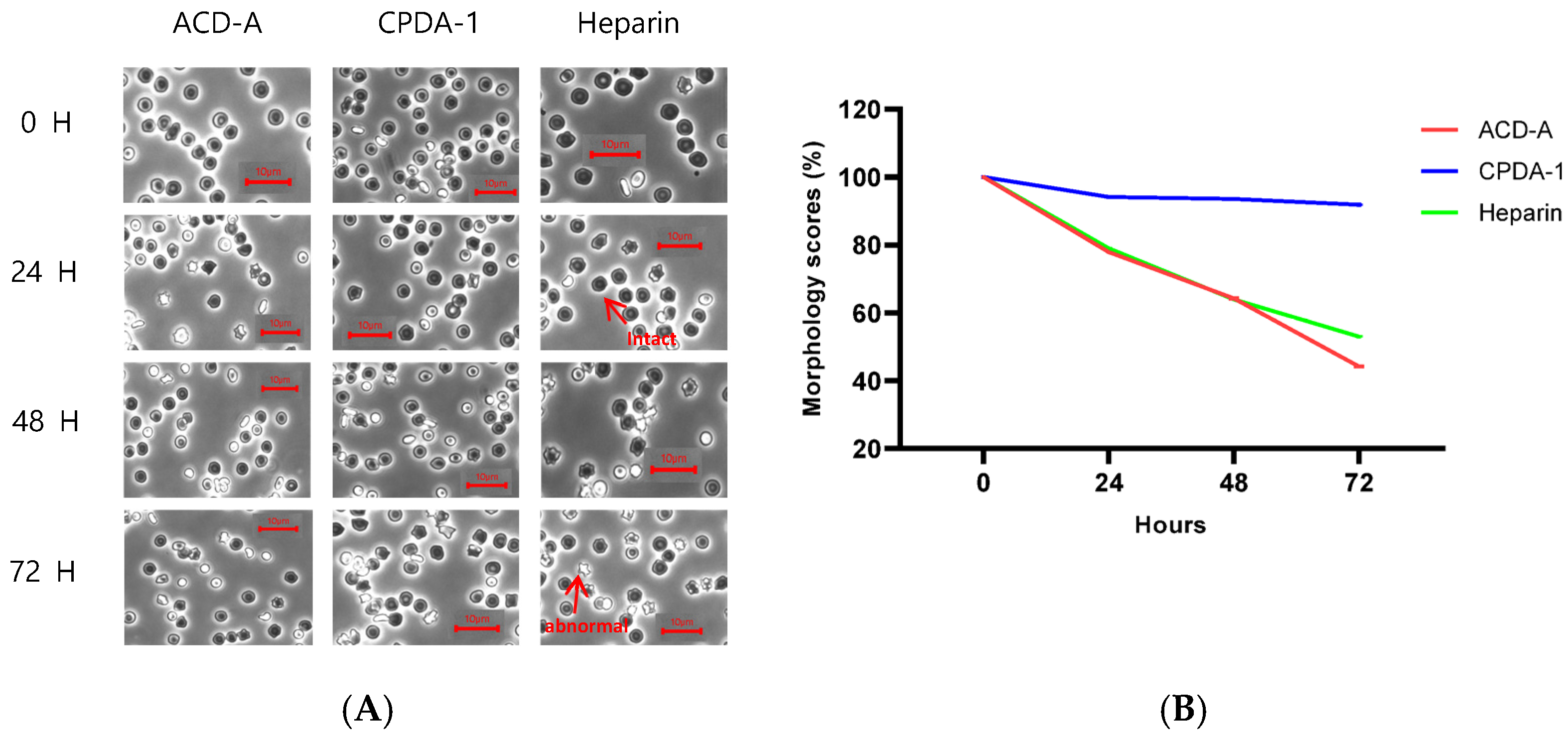
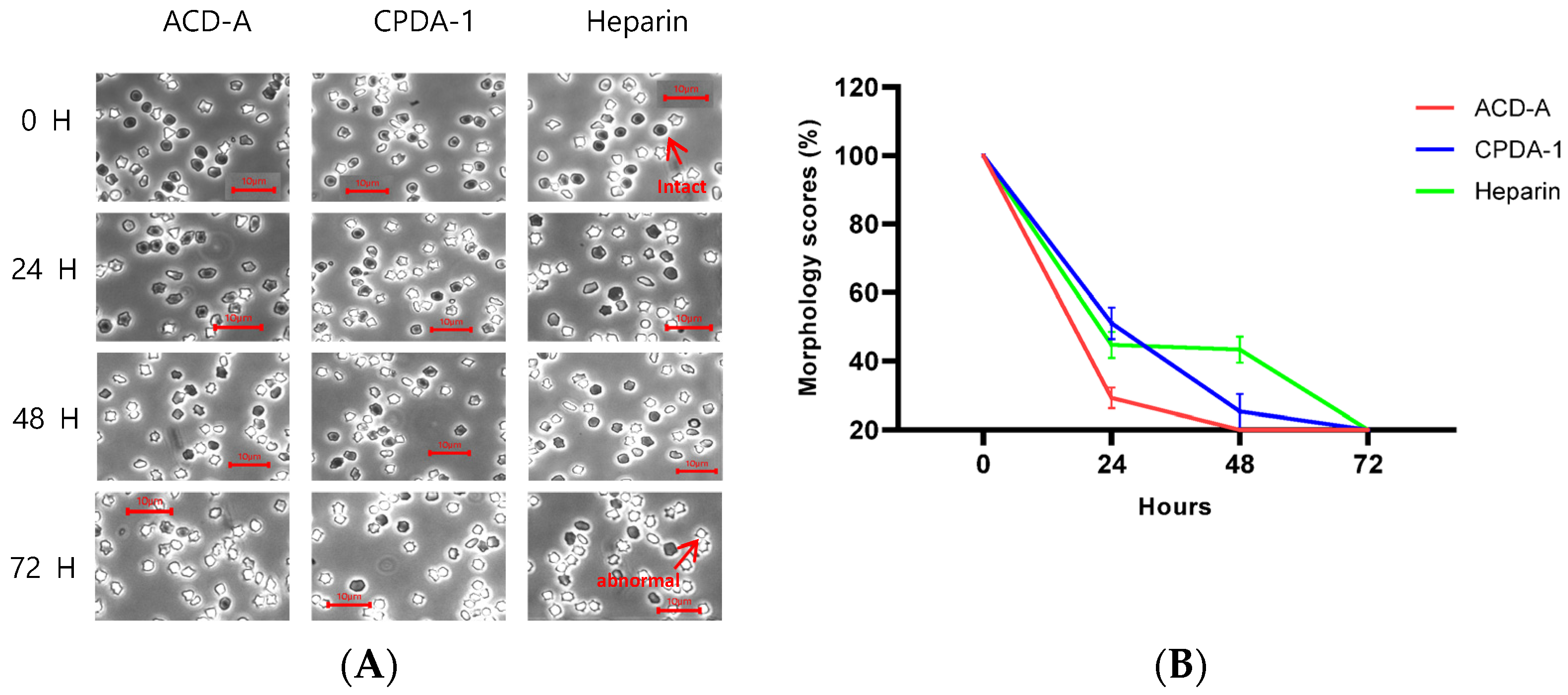
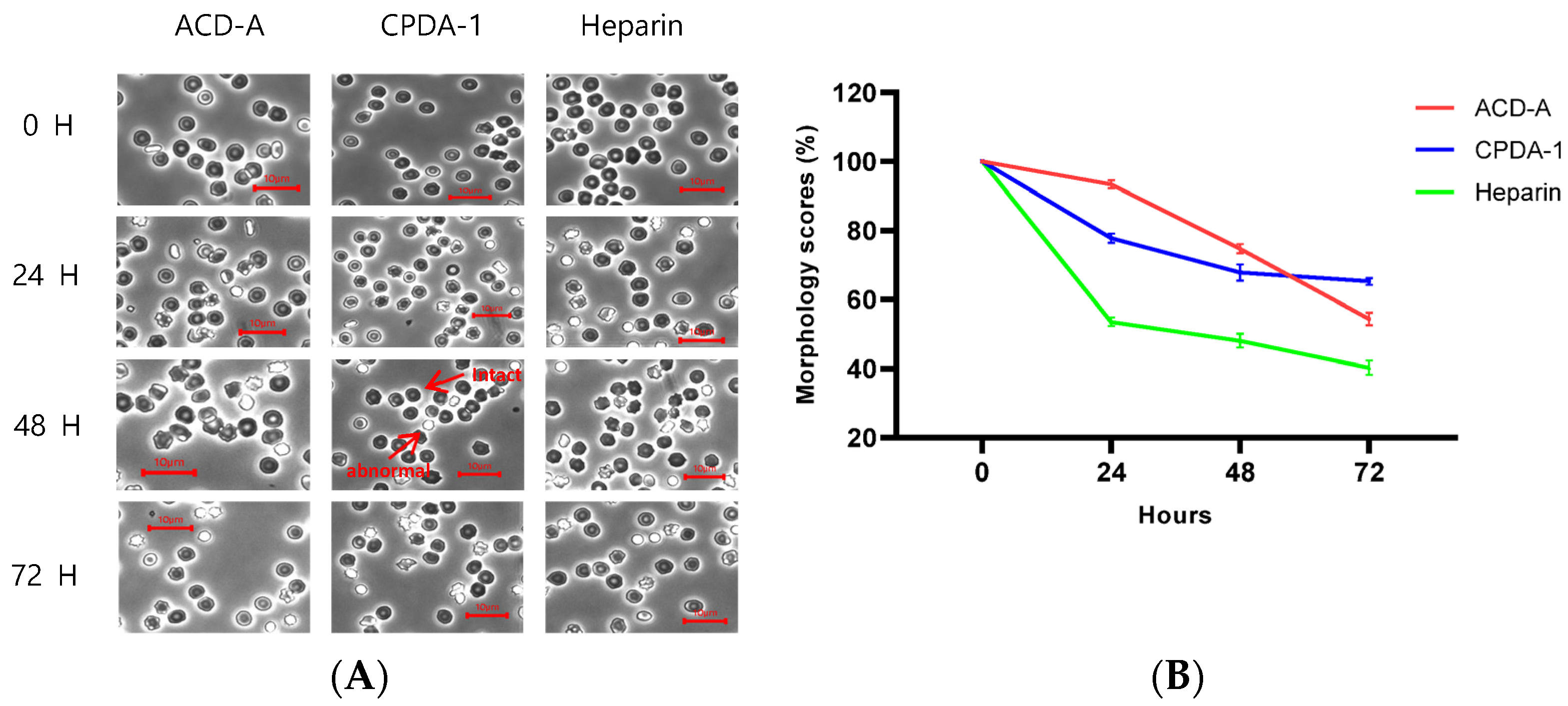
3.2. Morphology Score of Red Blood Cells in Rabbit
3.3. Morphology Score of Red Blood Cells in Pig
3.4. Morphology Score of Red Blood Cells in Rhesus Macaque
3.5. Morphology Score of Red Blood Cells in Cynomolgus Macaque
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASTM F1841-19; Standard Practice for Assessment of Hemolysis in Continuous Flow Blood Pumps. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- ASTM F1830-19; Standard Practice for Collection and Preparation of Blood for Dynamic in vitro Evaluation of Hemolysis in Blood Pumps. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- von Petersdorff-Campen, K.; Daners, M.S. Hemolysis Testing In Vitro: A Review of Challenges and Potential Improvements. ASAIO J. 2022, 68, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Niu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Shear-Induced Hemolysis: Species Differences. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, S.; Uda, M. Effectiveness of a morphology score as an index of the storage condition of red blood cells. Jpn. J. Transfus. Cell Ther. 1986, 32, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.H.H.; Ki, K.K.; Zhang, M.; Asnicar, C.; Cho, H.J.; Ainola, C.; Bouquet, M.; Heinsar, S.; Pauls, J.P.; Li Bassi, G.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation-induced hemolysis: An in vitro study to appraise causative factors. Membranes 2021, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, M.; Ohkuma, S.; Ishii, A.; Nishizaki, T. Preparation of blood components with saline-adenine-glucose-phosphate-maltose quadruple-pack system. Transfusion 1985, 25, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gov, N.S.; Safran, S.A. Red blood cell membrane fluctuations and shape controlled by ATP-induced cytoskeletal defects. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 1859–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.Y.; Kim, W.B.; Kang, D.Y.; Oh, Y.C.; Cho, M.J. Study on Effectiveness of a Morphology Score as an Index of the Storage Condition of Red Blood Cells Preserved with ACD. Korean J. Hematol. 1988, 23, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vierordt, K. Neue methode der quantitativen mikroskopischen Analyse des Blutes. Arch. Physiol. Heilk. 1852, 26, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Vierordt, K. Zählungen der Blutkörperchen des Menschen. Arch. Physiol. Heilk. 1852, 26, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Lesesve, J.-F.; Salignac, S.; Alla, F.; Defente, M.; Benbih, M.; Bordigoni, P.; Lecompte, T. Comparative evaluation of schistocyte counting by an automated method and by microscopic determination. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deline, S.; Schatz, T.; Grove, K.; Howard, S.; Smith, M. Development of a Novel Positive Control for the Standard Test Method for the Platelet Leukocyte Assay: An In Vitro Hemocompatibility Assessment of Blood-Contacting Medical Devices. J. Med. Device 2016, 10, 020909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessis, M. Erythrocyte form and deformability for normal blood and some hereditary hemolytic anemias (author’s transl). Nouv. Rev. Française D’hématologie Blood Cells 1977, 18, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bessis, M.; Feo, C.; Jones, E. Quantitation of red cell deformability during progressive deoxygenation and oxygenation in sickling disorders (the use of an automated Ektacytometer). Blood Cells 1982, 8, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Putter, J.S.; Seghatchian, J. Cumulative erythrocyte damage in blood storage and relevance to massive transfusions: Selective insights into serial morphological and biochemical findings. Blood Transfus. 2017, 15, 348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calzavara, P.; de Angeli, S.; Nieri, A.; Furlan, C.; Bolzonella, R.; da Porto, A. Alterations in erythrocyte morphology induced by blood pumps. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1993, 16, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, T.J.; Branton, D. Visualization of the protein associations in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6153–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Burgess, J.; Mizukami, H.; Ostafin, A. Sample Preparation and Imaging of Erythrocyte Cytoskeleton with the Atomic Force Microscopy. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 38, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, L.; Jin, H.; Feng, S.; Yu, Y. Quantification of the erythrocyte deformability using atomic force microscopy: Correlation study of the erythrocyte deformability with atomic force micros-copy and hemorheology. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2009, 43, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delves, P.J.; Roitt, I.M. Encyclopedia of Immunology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bessis, M. Erythrocytic series. In Blood Smears Reinterpreted; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; pp. 25–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, C.; Russell, W.J. When does blood haemolyse?: A temperature study. BJA Br. J. Anaesth. 1974, 46, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golański, J.; Pietrucha, T.; Baj, Z.; Greger, J.; Watala, C. Molecular insights into the anticoagulant-induced spontaneous activation of platelets in whole blood-various anticoagulants are not equal. Thromb. Res. 1996, 83, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.; Eom, J.; Kim, T. Effectiveness of Erythrocyte Morphology Observation as an Indicator for the Selection and Qualification of Blood in a Mechanically Induced Hemolysis Test. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-4; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 4: Selection of Tests for Interactions with Blood. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Arlington, TX, USA, 2017.

| Day of Storage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 H | 24 H | 48 H | 72 H | ||
| ACD-A | Rabbit | 5.50 | 4.29 | 3.54 | 2.43 |
| Porcine | 0.86 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| Rhesus | 3.55 | 3.34 | 2.66 | 1.94 | |
| Cynomolgus | 4.51 | 3.97 | 3.95 | 3.89 | |
| CPDA-1 | Rabbit | 4.93 | 4.64 | 4.61 | 4.53 |
| Porcine | 0.80 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.05 | |
| Rhesus | 3.07 | 2.37 | 2.13 | 2.00 | |
| Cynomolgus | 6.58 | 4.42 | 4.37 | 4.34 | |
| Heparin | Rabbit | 4.46 | 3.55 | 2.86 | 2.40 |
| Porcine | 0.86 | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.06 | |
| Rhesus | 4.46 | 2.42 | 2.14 | 1.81 | |
| Cynomolgus | 4.06 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 3.23 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, T. Performance Study of Anticoagulants and Animal Blood for Establishment of In Vitro Blood Circulation Loop System. LabMed 2025, 2, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020007
Kim J, Kim T. Performance Study of Anticoagulants and Animal Blood for Establishment of In Vitro Blood Circulation Loop System. LabMed. 2025; 2(2):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeonghwa, and Taewon Kim. 2025. "Performance Study of Anticoagulants and Animal Blood for Establishment of In Vitro Blood Circulation Loop System" LabMed 2, no. 2: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020007
APA StyleKim, J., & Kim, T. (2025). Performance Study of Anticoagulants and Animal Blood for Establishment of In Vitro Blood Circulation Loop System. LabMed, 2(2), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2020007







