Abstract
This review recalls some ISO 15189:2022 requirements for the management of examination results and emerging alternatives to internal quality control (IQC) in relation to Italian Society of Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine (SIPMeL) Recommendation Q19. We observed phenomena of contrasting “metrological”, or rather “tracealogic”, and “statistical” approaches. SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 enhances IQC with a moving average based on ISO 15189, which enables the use of the moving average of patient sample results (MA). In the veterinary field, the procedure of QC with repeat testing on patient samples (RPT-QC) has met with some success. The “Bayesian approach” of IQC makes use of the distinction between a priori probability, evidential probability (data) and a posteriori probability (IQC rules). SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 strictly adheres to the ISO 15189:2022 document. SIPMeL Q19 calls for abandoning the 1–2 s rule, using appropriate computer tools, not only control charts, and trying to reduce false positives to very low frequencies. Alternatives to IQC using patient results and the Bayesian approach are compatible with ISO 15189 and SIPMeL Q19. In contrast, the alternative using material designed for traceability with assigned values, is not compatible with the ISO standard.
1. ISO 15189 and Internal Quality Control on Examination Results (IQC)
This review recalls some ISO 15189:2022 [1] requirements for the management of examination results and emerging alternatives to internal quality control in relation to SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 [2].
ISO/TC212 WG1 “Quality and competence in the medical laboratory” worked on the revision of ISO 15189 for a long time, from October 2018 to December 2022, which is unusual in ISO tradition. The new ISO 15189 is the result of innovations requested by the ISO committee for conformity assessment (CASCO) leadership and choices made by WG1 itself [3], elaborated on in the intensive preparation work, with the outcomes of some compromises that had to be made [4].
Chapter 7 of ISO 15189:2022 (Processes) includes subchapter 7.3 Examination Processes with clauses 7.3.1 General, 7.3.2 Verification of Examination Methods, 7.3.3 Validation of Examination Methods, 7.3.4 Assessment of Measurement Uncertainty, 7.3.5 Biological Reference Intervals and Clinical Decision Limits, 7.3.6 Documentation of Examination Procedures, and 7.3.7 Ensuring Validity of Examination Results.
Clause 7.3.7 calls for a procedure to monitor the validity of results, detect trends and changes, and apply statistical techniques, with monitoring being planned and reviewed periodically. Laboratories should remember that the same procedure in the new standard takes on a dual use: the monitoring of results alongside the estimation of measurement uncertainty (MU), making use of ISO/TS 20914 guidance [5]. SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 picked up on this and developed the operational consequences [6].
The International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC) with its Task Force on Global Lab Quality (TF-GLQ) group has also produced Recommendations on Internal Quality Control [7]. Unfortunately, the IFCC Recommendations deviate significantly from ISO 15189 requirements and also contain discrepancies with the scientific literature on the subject [8], eliciting criticism from several authors [9], so we believe they are not useful for medical laboratories.
2. Alternatives to IQC: Calibration Materials?
We have observed phenomena of contrasting “metrological”, or rather “tracealogic”, and “statistical” approaches. The traceability of examination methods is a cardinal factor for the quality assurance of results [10]. It makes use of two fundamental ISO documents: ISO 17511 [11] for a general case and ISO 21151 [12] for the case of methods without reference to the international system of units.
Traceability has been proposed to modify IQC procedures, using certified reference materials, i.e., with assigned values, with the functions of calibration verification and the acceptance/rejection of analytical runs, collected as “IQC Component I”, leading to “IQC Component II”, which uses third-party, switchable control materials with concentrations at clinical decision limits, the control of measurement system variability (lot-to-lot variations, measurement drifts, etc.), the provision of data for the calculation of measurement uncertainty, and the satisfaction of allowable performance specifications [13].
This proposal has been countered by very well-founded criticisms: the cost of quality control, the use of material designed for determining trueness and not for monitoring, the violation of quality control principles, and the lack of fundamentals for establishing acceptability intervals, accounting for uncertainty [14,15].
Traceability by calibration and quality control with measurement uncertainty are two very distinct fields: the former makes use of CLSI EP15 (Verification of Precision and Estimation of Bias) [16], CLSI EP32 (Metrological Traceability) [17], ISO 15189 point 6.5 (Equipment calibration and metrological traceability), ISO 17511 (metrological traceability), ISO 21151 (harmonization traceability). The second, on the other hand, is based on CLSI C24 [18] and addresses the control of measurement system variability (lot-to-lot variations, measurement drifts, etc.), uses third-party control materials, with concentrations at clinical decision limits and calculated acceptability intervals, provides data for the calculation of measurement uncertainty and to meet allowable performance specifications, and allows acceptance/rejection decisions of result runs.
3. Alternatives to IQC: Patients’ Results
SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 improves IQC with a moving average based on ISO 15189, which enables the use of the moving average of patient sample results (MA), explaining that the documented methods refer to the MA of patient results, not QC materials. The main advantage of IQC with an MA is that it is continuous and thus offers the possibility of immediately (or at least more quickly) detecting examination problems, especially in the intervals between IQC measurements with materials.
However, calculating an MA can be labor-intensive and requires one to carefully fine-tune and optimize alarm settings [19,20,21,22]. The use of an MA has been well described with real-world experiences [23], as has the use of an exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) [24,25,26]. Original and interesting but requiring significant computer resources, this approach does not average patient results but differences between consecutive results [27,28].
The principle of averaging patient results has been known for many years and is used in many computer systems [7]. General-purpose spreadsheets or programs such as Matlab, as well as patented systems, have also proved useful for analyzing data. Despite this, it is seldom used in laboratories for various reasons studied by researchers. But the subject has undergone many evolutions. There are those who offer free computer programs [23]. The mention of commercially offered tools is present in many articles.
4. Alternatives to IQC: Repeated Examinations
SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 reports how, in the veterinary field, the procedure of QC with repeat testing on patient samples (RPT-QC) has met with some success [29,30,31,32]. Flatland and Freeman’s protocol, initially tried on blood counts, involves the day-after-day storage of a sample and a measurement of the sample from the day before. The control result is the difference between repeated measurements, on which the same statistical QC rules can be applied, starting, for example, from 1–3 s.
5. Alternatives to IQC: The “Bayesian” Approach
We saw the so-called “Bayesian approach” of IQC in an early 2015 article on coagulation examinations [33], which was applied recently [34]. The proposal has something in common with the “traceological” scheme described above, but with fewer flaws and more advantages.
An examination method, in the traditional way, entails the development, validation, verification, and initiation of IQC (phase I) and then moves on to IQC monitoring (phase II). It is not a matter of using the algebraic formula of Bayes’ theorem but of making use of the distinction between a priori probability, evidential probability (data) and a posteriori probability (IQC rules).
In practice, the initiation of IQC (phase I) contains the “a priori” probability and the monitoring of IQC (phase II) contains the “a posteriori” probability (Figure 1). Bayesian tools use the manufacturer’s available prior information along with the available data stream to derive posterior estimates between series [34].
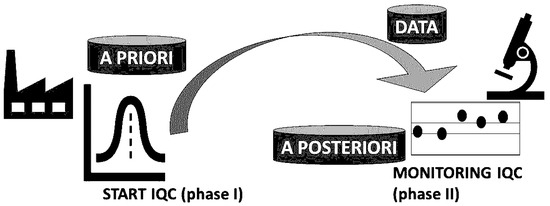
Figure 1.
The initiation and monitoring of IQC (the Bayesian approach). “A priori” derived from the manufacturer, and “data or probative” and “a posteriori” derived from the laboratory. Drawn based on [33]. The arrow represents the life of an examination method.
The principle of close collaboration between the IVD manufacturer and laboratory was also included and enhanced by SIPMeL Recommendation Q19 in relation to ISO document 15198 [35,36,37], but this has now unfortunately been proposed for withdrawal from ISO standards.
6. SIPMeL Q19 Recommendations for IQC According to ISO 15189: Final Thoughts
Data on the implementation in laboratories of ISO requirements on IQC are contradictory. For example, a survey conducted by UK NEQAS in 2024 suggested that all laboratories complied with the requirements, but only 127 out of 1200 participants responded to the questionnaire, thus meaning that the results were insignificant [38].
The objective of this review is to highlight the compatibility of different solutions with ISO 15189 requirements, not to assess their advantages and disadvantages, which would require a different kind of study. When a laboratory seeks accreditation, there is no obligation to adopt a particular solution. The one adopted by the laboratory, however, must be adequate to meet the ISO standard. Advantages and disadvantages depend greatly on the conditions of the individual laboratory.
SIPMeL recommendations [2] strictly adhere to ISO 15189:2022 documents as follows. (7.3.7.2 a) There are mandatory IQC procedures for the continuous monitoring of results, based on specified criteria, of expected quality relevant to clinical decision making. (7.3.7.2 b) IQC materials should be selected based on their similarity to patient samples regarding stability, matrix, behavior, and concentration levels close to clinical decision limits across the entire range of the examination method.
(7.3.7.2 c) If necessary, the material should be replaced by patient results, e.g., with a moving average or percentage of samples with results below or above thresholds, a comparison of patient results with an alternative validated procedure with the calibration of the same or higher order (ISO 17511), and the repetition of retained patient samples. (7.3.7.2 g) IQC must prevent the release of patient results if it does not meet the acceptability criteria, and samples must be re-examined after error correction (see 7.5), including those examined since the last successful IQC event.
(7.3.7.2 d) IQC should be performed with a frequency based on the stability and robustness of the examination method and the risk of harm to the patient. (7.3.7.2 e) Trends and variations should be identified and statistical techniques applied.
(7.3.7.2 f) IQC data should be reviewed at regular intervals. SIPMeL Q19 develops these requirements by adding reference to CLSI C24 for Sigma metrics, highlights the use of IQC for measurement uncertainty, and for Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) services, it references only CLSI POCT07 [39], POCT08 [40], and POCT14 [41]. It additionally warns that materials used in the “pass/fail” mode do not comply with IQC ISO 15189 requirements, which call for monitoring, asks for justifications of alternative procedures, highlights the need for quantitative measurements for qualitative end results and metrics for IQC generated by the process itself (as in the case of Next-Generation Sequencing, NGS), and proposes monitoring, even for nominal qualitative or ordinal numerical results.
At the very least, SIPMeL Q19 calls for abandoning the 1–2 s rule, using appropriate computer tools and only control charts, and trying to reduce false positives to very low frequencies, a few events per day, to allow an in-depth investigation of the detected phenomena without significantly disrupting the operational flow of diagnostic activity.
The alternatives to IQC using patient results and the Bayesian approach are compatible with ISO 15189 and SIPMeL Q19. In contrast, the alternative using material designed for tracking, with assigned values, is not compatible with ISO 15189 and SIPMeL Q19 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Alternatives to IQC, ISO 15189 and SIPMeL Q19 conformity.
Practical examples from the real world can be found in the literature contributions cited, such as in the recent example of hematology examinations [42,43]. This article merely judges the compatibility of alternatives with ISO 15189 requirements.
This concise review does not exhaust all alternatives to IQC but points out only those more recently brought to the attention of laboratories in the literature or in promotional or educational events (courses, webinars, and the like). It does not consider the possibility of using estimators such as the median or percentage of high or low results, peer comparison, the use of individual sample data, such as serum indices, clot detection, bubbles, kinetics analysis, or electronic signals, or individual delta checks or calculations on results such as the urea/creatinine ratio or anion gap. Regarding the use of so-called “artificial intelligence”, one waits to see its possibilities in this field.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created.
Acknowledgments
From the presentation: “The IQC: Metrologists and “Westgardians”, applying the ISO standard”. Updating Course: The Internal Quality Control (IQC): a daily tool for reliability of test results in Laboratory Medicine 9 April 2025, Ancona (Italy), Domus Stella Maris. SIPMeL Q19 Recommendations were produced by the SIPMeL National Commission on Quality and Accreditation, the SIPMeL Informatics Study Group, and the SIPMeL Study Group on Health Care Management.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| SIPMeL | Italian Society of Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine |
| IQC | Internal Quality Control |
| MA | Moving Average |
| RPT-QC | Quality Control with Repeat Testing on Patient Samples |
| CASCO | ISO Committee for Conformity Assessment |
| MU | Measurement Uncertainty |
| IFCC | International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine |
| TF-GLQ | Task Force on Global Lab Quality |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| EWMA | Exponentially Weighted Moving Average |
| POCT | Point-of-Care Testing |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
References
- ISO 15189:2022; Medical Laboratories—Requirements for Quality and Competence. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Q19 Recommendations for ISO 15189 Accreditation of Medical Laboratory: Examination Processes, Validity of Examination Results. 3 April 2024. Document Approved by the National Council on 27 February 2024. Available online: https://www.sipmel.it/it/lineeguida/approvate/121264 (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Linko, S.; Boursier, G.; Bernabeu-Andreu, F.; Dzneladze, N.; Vanstapel, F.; Brguljan, P.; Tosheska-Trajkovska, K.; Mehay, H.; Panteghini, M.; Brugnoni, D.; et al. EN ISO 15189 revision: EFLM Committee Accreditation and ISO/CEN standards (C: A/ISO) analysis and general remarks on the changes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025, 63, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradella, M. New ISO standards for medical biology laboratories, prescriptions and deviations. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2022, 80, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 20914:2019; Medical Laboratories—Practical Guidance for the Estimation of Measurement Uncertainty. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Pradella, M. Le raccomandazioni SIPMeL per l’accreditamento ISO del monitoraggio di validità dei risultati degli esami CQI per ISO 15189. Riv. Ital. Med. Lab. 2024, 20, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoli, J.M.; Vassault, A.; Carobene, A.; Liaudet, A.P.; Blasutig, I.M.; Dabla, P.K.; Lin, J.; Thomas, A.; Tesser Poloni, J.A.; Meng, Q.H.; et al. Ensuring internal quality control practices in medical Laboratories: IFCC recommendations for practical applications based on ISO 15189:2022. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 571, 120240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradella, M. Divergences between IFCC recommendations for Internal Quality Control and ISO standards. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 120334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çubukçu, H.C.; Thelen, M.; Plebani, M.; Panteghini, M. IFCC recommendations for internal quality control practice: A missed opportunity. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteghini, M. An improved implementation of metrological traceability concepts is needed to benefit from standardization of laboratory results. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2025, 63, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17511:2020; In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices—Requirements for Establishing Metrological Traceability of Values Assigned to Calibrators, Trueness Control Materials and Human Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO 21151:2020; In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices—Requirements for International Harmonisation Protocols Establishing Metrological Traceability of Values Assigned to Calibrators and Human Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Braga, F.; Pasqualetti, S.; Aloisio, E.; Panteghini, M. The internal quality control in the traceability era. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westgard, J.; Bayat, H.; Westgard, S. How to evaluate fixed clinical QC limits vs. riskbased SQC strategies. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, e199–e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradella, M. Controllo di qualità interno: Statistica avversaria della metrologia? Riv. Ital. Med. Lab. 2021, 17, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI EP15:2014; User Verification of Precision and Estimation of Bias. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2014.
- CLSI EP32 ED2:2024; Metrological Traceability in Laboratory Medicine. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2024.
- CLSI C24:2016; Statistical Quality Control for Quantitative Measurement Procedures: Principles and Definitions. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2016.
- van Andel, E.; Henricks, L.M.; Giliams, A.P.M.; Noordervliet, R.M.; Mensink, W.J.; Filippo, D.; van Rossum, H.H.; Cobbaert, C.M.; Gillis, J.M.E.P.; Schenk, P.W.; et al. Moving average quality control of routine chemistry and hematology parameters—A toolbox for implementation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossum, H.H.; van den Broek, D. Design and implementation of quality control plans that integrate moving average and internal quality control: Incorporating the best of both worlds. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, H.H. Technical quality assurance and quality control for medical laboratories: A review and proposal of a new concept to obtain integrated and validated QA/QC plans. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022, 59, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembrowski, G.S. Use of patient data for quality control. Clin. Lab. Med. 1986, 6, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çubukçu, H.C. QC Constellation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2024, 62, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, P.K.; Yeh, A.B. Exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) control charts for monitoring an analytical process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çubukçu, H.C. The weighting factor of exponentially weighted moving average chart. Turk. J. Biochem. 2020, 45, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, D.I.; Çubukçu, H.C. Optimization of patient based real-time quality control based on the Youden index. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 534, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembrowski, G.S.; Xu, Q.; Cervinski, M.A. Average of Patient Deltas: Patient-Based Quality Control Utilizing the Mean Within-Patient Analyte Variation. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bietenbeck, A.; Cervinski, M.A.; Katayev, A.; Loh, T.P.; van Rossum, H.H.; Badrick, T. Understanding Patient-Based Real-Time Quality Control Using Simulation Modeling. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatland, B.; Freeman, K.P. Repeat patient testing quality control (RPT-QC): Background and theory. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 53 (Suppl. 1), 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westgard, J.O. Basic QC Practices, 4th ed.; Training in Statistical Quality Control for Medical Laboratories; Westgard QC: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, S.; Graham, P.A.; Freeman, K.P. Repeat patient testing-quality control with canine samples shows promise as an alternative to commercial quality control material for a network of four Sysmex XT-2000iV hematology analyzers. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 53 (Suppl. 1), 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westgard, S.; Daly, S.; Freeman, K.; Flatlan, B. Repeat Patient QC: A new approach for patient-based control. Webinar, 14 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiamyrtzis, P.; Sobas, F.; Négrier, C. Use of prior manufacturer specifications with Bayesian logic eludes preliminary phase issues in quality control: An example in a hemostasis laboratory. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousselme, E.; Meijer, P.; Sobas, F.; Tsiamyrtzis, P. Complementarity between Bayesian Internal Quality Control results management and External Quality Assessment bivariate z-score analysis: Application to a concrete case study. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2025, 82, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15198:2004; Clinical Laboratory Medicine—In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices—Validation of User Quality Control Procedures by the Manufacturer. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Pradella, M. Produttore di diagnostici e laboratorio medico alleati per il controllo di qualità dei risultati: Ritardi e novità. Riv. Ital. Med. Lab. 2020, 16, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradella, M. Alliance of IVD manufacturer and medical laboratory for quality control of results. Adv. Lab. Med. 2021, 2, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly-Stitt, C.; Jennings, I.; Kitchen, S.; Walker, I.D. Internal Quality Control in Hemostasis Assays. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 50, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI POCT07:2010; Quality Management: Approaches to Reducing Errors at the Point of Care. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2010.
- CLSI POCT08:2010; Quality Practices in Noninstrumented Point-of-Care Testing: An Instructional Manual and Resources for Health Care Workers. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2010.
- CLSI POCT14:2020; Point-of-Care Coagulation Testing and Anticoagulation Monitoring. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2010.
- van Rossum, H.H.; Giannoli, J.-M. and Badrick, T. Patient Moving Average for Continuous Real-Time QC; Real-World Application Illustrated. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2025, 47, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembrowski, G. Whither Hematology Moving Averages? Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2025, 47, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).