Molecular Characterization of MDR and XDR Clinical Strains from a Tertiary Care Center in North India by Whole Genome Sequence Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Place of Study and Ethical Consideration
2.2. Sample Processing and Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Antimicrobial Sensitivity and Supplementary Testing
2.4. AMR Phenotype
2.5. Clinical History
2.6. Molecular Characterization
3. Results
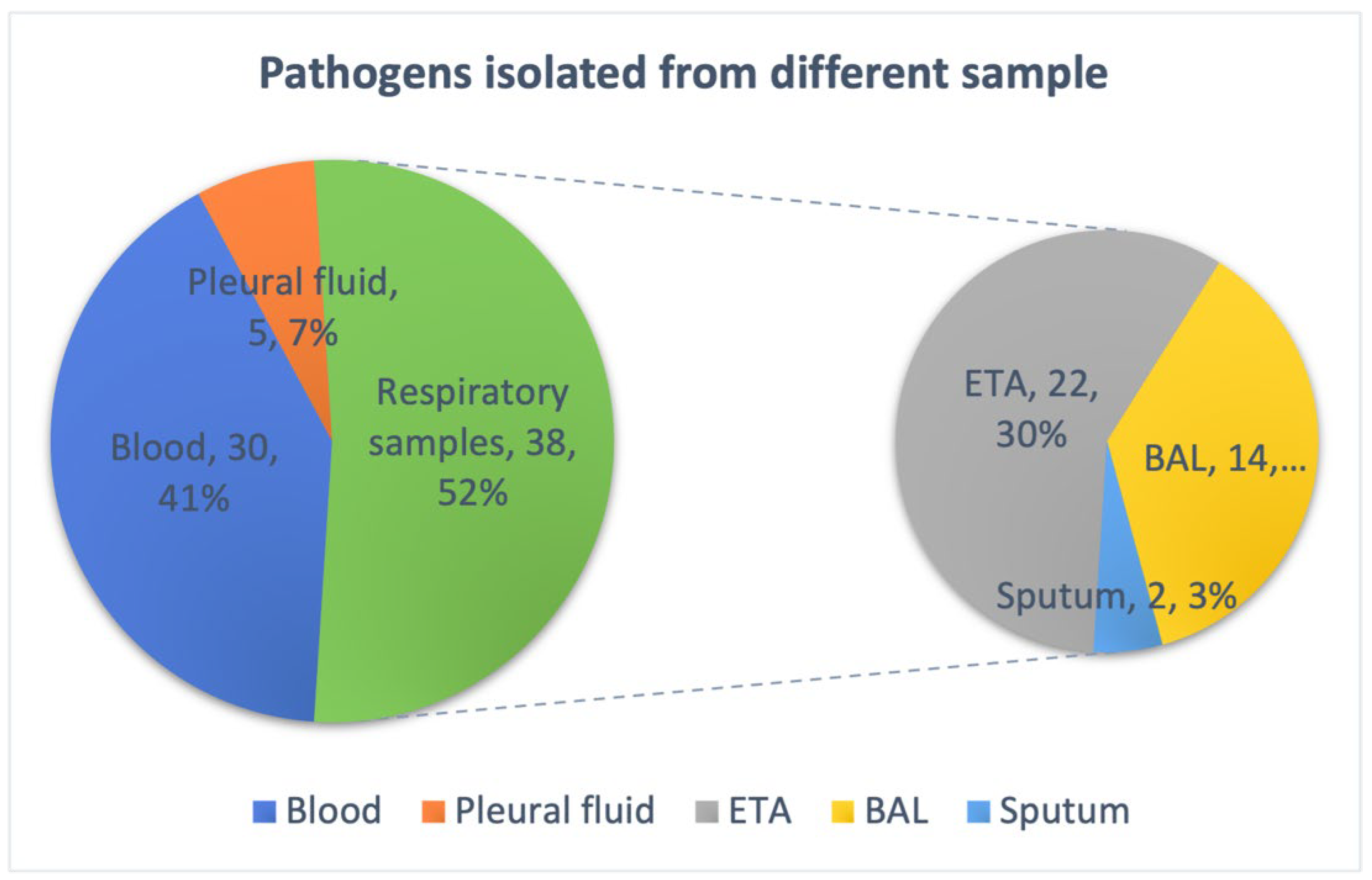
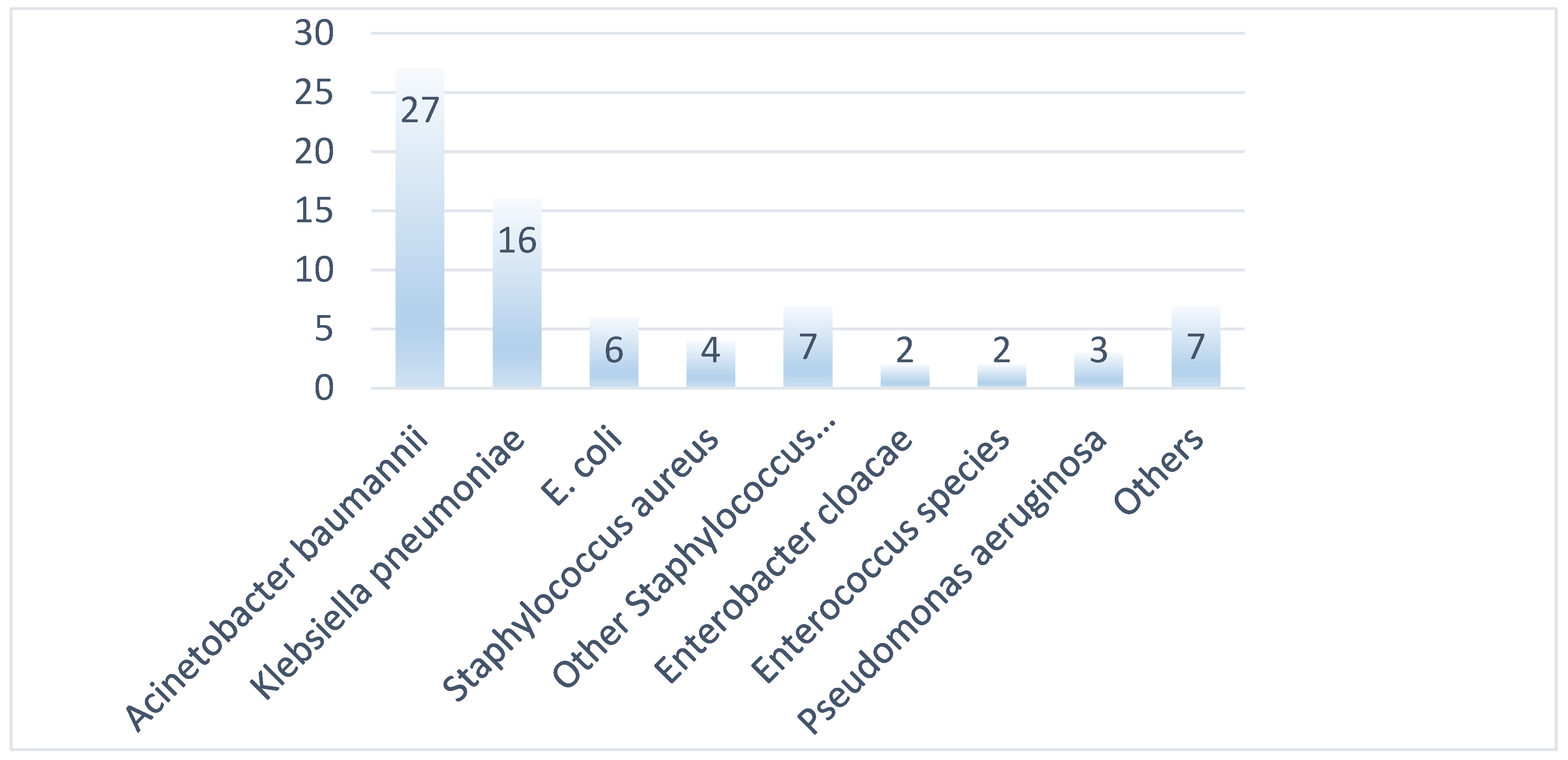
3.1. Bacterial Isolates and Phenotypic Characterization
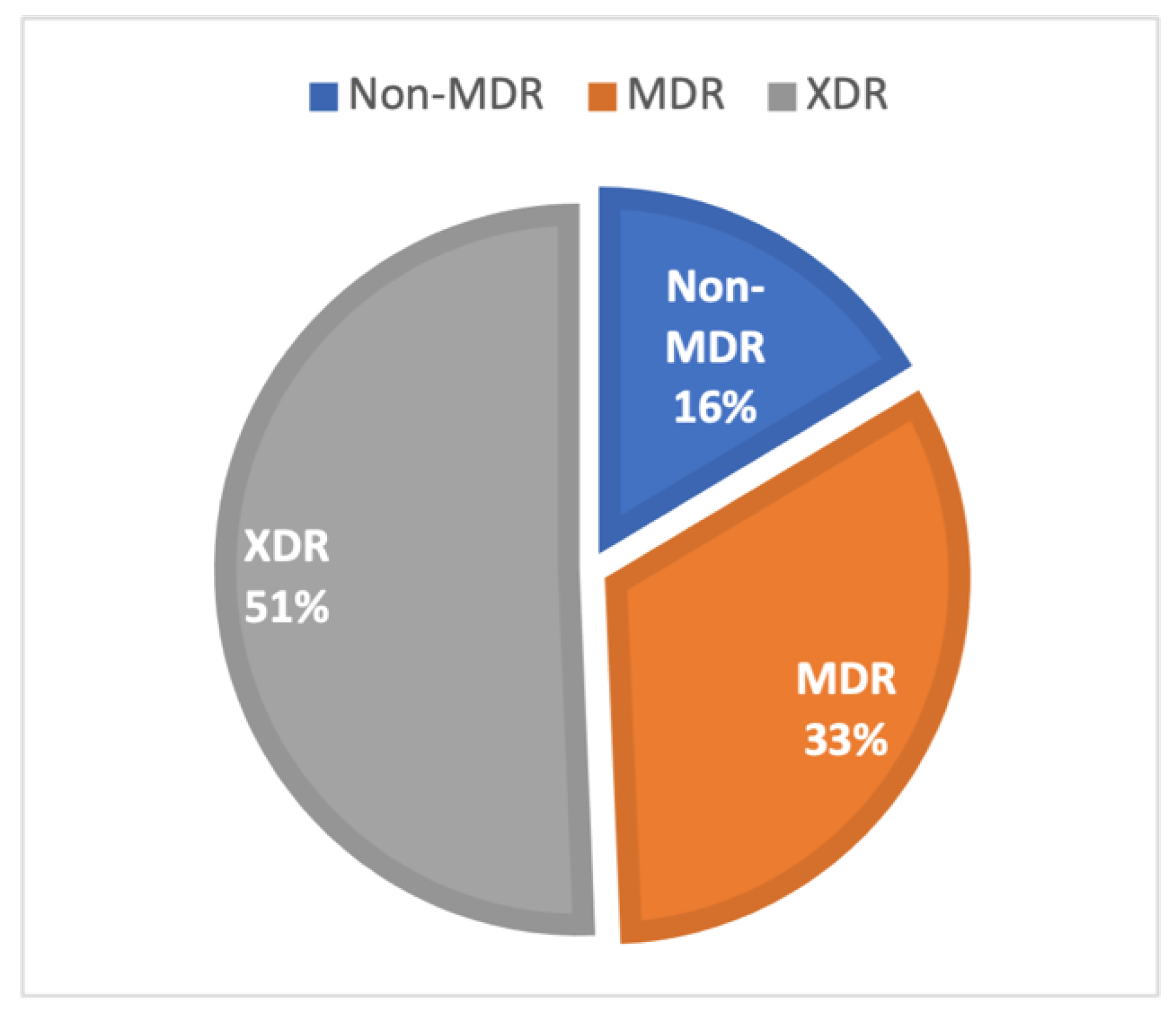
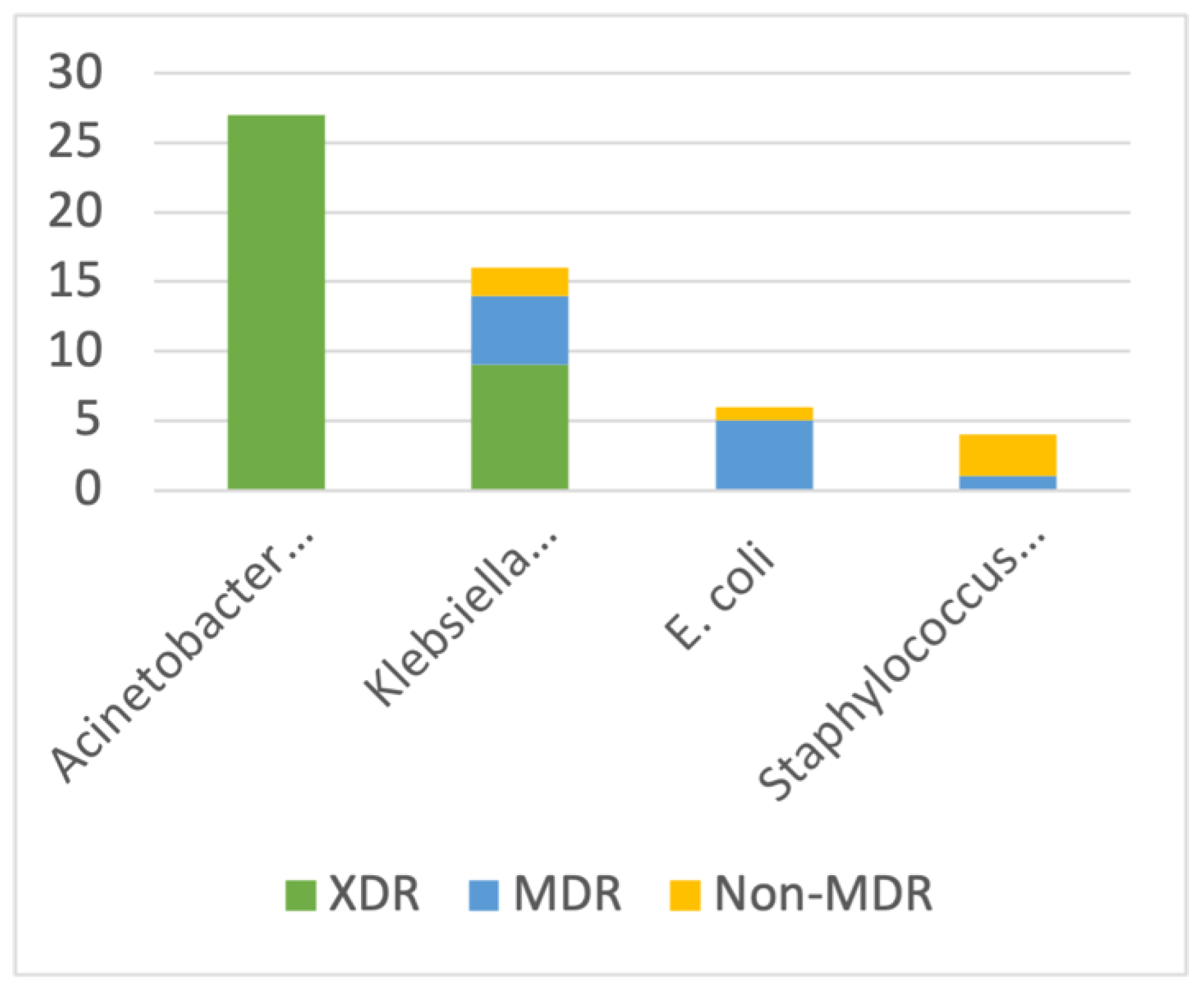
3.2. AMR Phenotypes
3.3. Clinical Data of Isolates with Molecular Characterization
3.4. Molecular Analysis
3.4.1. Klebsiella Pneumoniae
3.4.2. Acinetobacter baumannii
3.4.3. Escherichia coli
3.4.4. Staphylococcus aureus
3.4.5. Enterococcus faecalis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaynes, R.; Edwards, J.R. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samia, N.I.; Robicsek, A.; Heesterbeek, H.; Peterson, L.R. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus nosocomial infection has a distinct epidemiological position and acts as a marker for overall hospital-acquired infection trends. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System: Manual for Early Implementation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/188783 (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Spellberg, B.; Srinivasan, A.; Chambers, H.F. New Societal Approaches to Empowering Antibiotic Stewardship. JAMA 2016, 315, 1229–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alividza, V.; Mariano, V.; Ahmad, R.; Charani, E.; Rawson, T.M.; Holmes, A.H.; Castro-Sánchez, E. Investigating the impact of poverty on colonization and infection with drug-resistant organisms in humans: A systematic review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasovský, D.; Littmann, J.; Zorzet, A.; Cars, O. Antimicrobial resistance-a threat to the world’s sustainable development. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 121, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIHR Global Health Research Unit on Genomic Surveillance of AMR. Whole-genome sequencing as part of national and international surveillance programmes for antimicrobial resistance: A roadmap. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e002244. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S., II. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; M100Ed33; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A. GHRU (Genomic Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance) Retrospective 1 Bioinformatics Methods. 2020. Available online: https://protocols.io/view/ghru-genomic-surveillance-of-antimicrobial-resista-bpn6mmhe (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.; Mather, A.E.; Sánchez-Busó, L.; Page, A.J.; Parkhill, J.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. ARIBA: Rapid antimicrobial resistance genotyping directly from sequencing reads. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Coombs, G.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C.; Akpaka, P.; Borg, M.; Chow, H.; Ip, M.; Jatzwauk, L.; Jonas, D.; et al. A field guide to pandemic, epidemic and sporadic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Assignment of Staphylococcus aureus isolates to clonal complexes based on microarray analysis and pattern recognition. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares Pacheco, J.A.; Bernardini, A.; Garcia-Leon, G.; Corona, F.; Sanchez, M.B.; Martinez, J.L. The intrinsic resistome of bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, e00103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, A.; Oliver, A.; González-Diego, P.; Baquero, F.; Pérez-Díaz, J.C.; Ros, P.; Cobo, J.; Palacios, M.; Lasheras, D.; Cantón, R. Outbreak of a multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in an intensive care unit: Antibiotic use as risk factor for colonization and infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, W.R.; Munn, V.P.; Highsmith, A.K.; Culver, D.H.; Hughes, J.M. The epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Control 1985, 6, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, C.; Mathur, P.; Venkatesan, M.; Pragasam, A.K.; Anandan, S.; Khurana, S.; Veeraraghavan, B. Rapidly disseminating blaOXA-232 carrying Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to ST231 in India: Multiple and varied mobile genetic elements. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Sahoo, R.K.; Dixit, S.; Behera, D.U.; Subudhi, E. NDM-5-carrying Klebsiella pneumoniae ST437 belonging to high-risk clonal complex (CC11) from an urban river in eastern India. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Genetic Context, Treatment Options, and Detection Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Lam, M.M.C.; Judd, L.M.; van Vinh Chau, N.; Dance, D.A.B.; Ip, M.; Karkey, A.; Ling, C.L.; Miliya, T.; et al. Genomic surveillance for hypervirulence and multi-drug resistance in invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae from South and Southeast Asia. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follador, R.; Heinz, E.; Wyres, K.L.; Ellington, M.J.; Kowarik, M.; Holt, K.E.; Thomson, N.R. The diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae surface polysaccharides. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraraghavan, B.; Shankar, C.; Karunasree, S.; Kumari, S.; Ravi, R.; Ralph, R. Carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from bloodstream infection: Indian experience. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandan, S.; Damodaran, S.; Gopi, R.; Bakthavatchalam, Y.D.; Veeraraghavan, B. Rapid Screening for Carbapenem Resistant Organisms: Current Results and Future Approaches. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, DM01–DM03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Shamanna, V.; Nagaraj, G.; Sravani, D.; Gupta, P.; Omar, B.J.; Chakraborty, D.; Ravikumar, K.L. Molecular characterisation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates: Preliminary experience from a tertiary care teaching hospital in the Himalayas. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 116, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Reuter, S.; Harris, S.R.; Glasner, C.; Feltwell, T.; Argimon, S.; Abudahab, K.; Goater, R.; Giani, T.; Errico, G.; et al. Epidemic of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Europe is driven by nosocomial spread. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, S.Y.; Bernal, J.F.; Montilla-Escudero, E.; Arévalo, S.A.; Prada, D.A.; Valencia, M.F.; Moreno, J.; Hidalgo, A.M.; García-Vega, Á.S.; Abrudan, M.; et al. Complexity of Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in Colombia Urges the Reinforcement of Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Surveillance Programs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, S290–S299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, M.S.; O’Connor, C.; Miller, V.L. Yersiniabactin Is a Virulence Factor for Klebsiella pneumoniae during Pulmonary Infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, O.G.; Treat, L.P.; Teelucksingh, T.; Clarke, B.R.; Miner, T.A.; Whitfield, C.; Walker, K.A.; Miller, V.L. Hypermucoviscosity Regulator RmpD Interacts with Wzc and Controls Capsular Polysaccharide Chain Length. mBio 2023, 14, e0080023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, M.N.L.; de Sales, R.O.; da Silva, K.E.; Maciel, W.G.; Simionatto, S. Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreaks: A global problem in healthcare settings. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkasaby, N.M.; El Sayed Zaki, M. Molecular Study of Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates for Metallo-β-Lactamases and Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamases Genes in Intensive Care Unit, Mansoura University Hospital, Egypt. Int. J. Microbiol. 2017, 2017, e3925868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Dolma, K.G.; Khandelwal, B.; Goyal, R.K.; Mitsuwan, W.; Pereira, M.d.L.G.; Klangbud, W.K.; Gupta, M.; Wilairatana, P.; Siyadatpanah, A.; et al. Acinetobacter baumannii in suspected bacterial infections: Association between multidrug resistance, virulence genes, & biofilm production. Indian J. Med. Res. 2023, 158, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Linde, J.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, T.N.M.; Sprague, L.D.; Pletz, M.W.; Neubauer, H. WGS-Based Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Vietnam and Molecular Characterization of Antimicrobial Determinants and MLST in Southeast Asia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidian, M.; Nigro, S.J. Emergence, molecular mechanisms and global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Mehdinejadiani, K.; Gholizadeh, P.; Nasiri, M.J.; Mohtavinejad, N.; Dadashi, M.; Karimaei, S.; Safari, H.; Azimi, T. Global prevalence of colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.A.; Amyes, S.G.B. OXA β-Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Peters, B.M.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Shirliff, M.E. Staphylococcal chromosomal cassettes mec (SCCmec): A mobile genetic element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 101, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, K.; Katayama, Y.; Yuzawa, H.; Ito, T. Molecular genetics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 292, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaber, J.; Penadés, J.R.; Ingmer, H. Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Shamanna, V.; Nagaraj, G.; Sravani, D.; Gupta, P.; Omar, B.J.; Singh, A.; Rani, D.; Ravikumar, K.L. An insight into whole genome sequencing data of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus circulating in a teaching hospital in North India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 44, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satta, G.; Ling, C.L.; Cunningham, E.S.; McHugh, T.D.; Hopkins, S. Utility and limitations of Spa-typing in understanding the epidemiology of staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia isolates in a single University Hospital. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrudan, M.I.; Shamanna, V.; Prasanna, A.; Underwood, A.; Argimón, S.; Nagaraj, G.; Di Gregorio, S.; Govindan, V.; Vasanth, A.; Dharmavaram, S.; et al. Novel multidrug-resistant sublineages of Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex 22 discovered in India. mSphere 2023, 8, e00185-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armin, S.; Fallah, F.; Karimi, A.; Rashidan, M.; Shirdust, M.; Azimi, L. Genotyping, antimicrobial resistance and virulence factor gene profiles of vancomycin resistance Enterococcus faecalis isolated from blood culture. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.R.; Tedim, A.P.; Francia, M.V.; Jensen, L.B.; Novais, C.; Peixe, L.; Sánchez-Valenzuela, A.; Sundsfjord, A.; Hegstad, K.; Werner, G.; et al. Multilevel population genetic analysis of vanA and vanB Enterococcus faecium causing nosocomial outbreaks in 27 countries (1986–2012). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3351–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gram-Negative Bacilli | Susceptibility Rates %(n) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Isolates | Ceftriaxone | Ceftazidime | Amoxicillin Clavulanate | Gentamicin | Ciprofloxacin | Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | Cefepime | Piperacillin Tazobactam | Cefoperazone Sulbactam | Amikacin | Meropenem | Imipenem | Tigecycline | Colistin | |
| Acinetobacter baumannii complex | 27 | - | - | - | 3.7 (1) | 0 (0) | 19.2 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 7.4 (2) | 96.3 (26) |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 16 | 12.5 (2) | - | 12.5 (2) | 18.8 (3) | 0 (0) | 18.8 (3) | 12.5 (2) | 12.5 (2) | 12.5 (2) | 18.8 (3) | 12.5 (2) | 0 (0) | 18.8 (3) | 87.5 (14) |
| Escherichia coli # | 6 | 0 | - | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa # | 3 | - | 2 | - | 3 | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 |
| Citrobacter species # | 2 | 0 | - | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | - | 2 |
| Enterobacter cloacae complex # | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 |
| Gram-Positive Cocci | Susceptibility Rates (n) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates (n) | Penicillin | Oxacillin | Cefoxitin | Gentamicin | High-Level Gentamicin | Ciprofloxacin | Levofloxacin | Tetracycline | Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | Erythromycin | Clindamycin | Vancomycin | Teicoplanin | Linezolid | Tigecycline | Daptomycin | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| CONS (coagulase negative staphylococcus) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 6 | - | 7 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | - |
| Enterococcus species | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | |
| Organism | Sequence Type | Sample | Age | Sex | History: Diagnosis | Chief Complaint | Fever | TLC | Antibiotic History | Intubated | Outome | ICU Length of Stay (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABA | 2 | BAL | 2.5 Y | M | Resp Failure, Shock | Fast Breathing, Abnormal Movement | Yes | 16,500 | TAXIM/AK; MRP/AK | NO | Expired | 3 |
| ABA | 2 | ETA | 18 Y | F | T2DM, Diabetic Ketoacidosis | No | 18,000 | MRP, PIT | YES | Expired | 7 | |
| ABA | 2 | Blood | ||||||||||
| ABA | 2 | ETA | 18 Y | F | TBM | Unconscious | No | 16,600 | PIT | YES | Expired | 6 |
| ABA | 2 | ETA | 28 Y | M | ARDS, Broncho Pneumonia | SOB, Fever | Yes | 12,000 | PIT, MOXIFLOX, MRP, LZ | YES | Expired | 12 |
| ABA | 2 | ETA | 56 Y | F | Pneumonia; Post-Op Ileal Perforation | SOB, Infiltration on CXR | Yes | 12,000 | IMP-CL, METRON, MOXI | YES | Expired | 15 |
| ABA | 2 | ETA | 80 Y | M | Pneumonia; Ischemic CVA | RT Side Paralyzed, Pleural Effusion | No | 16,000 | PIT | YES | Expired | 16 |
| ECO | Novel | Blood | 23 Y | F | Sepsis, DIC | Fever | Yes | 4700 | MRP, PIT | YES | Expired | - |
| ECO | 53 | Blood | 69 Y | M | Dengue, Ascites, Splenomegaly | Fever, Pain Abd | Yes | 20,000 | PIT | NO | Expired | - |
| ENT | 946 | Blood | 2 m | M | BPN, Anaemia; Cysticercosis | Cough, SOB | Yes | 14,000 | AK; MRP, VANCO | YES | Expired | 4 |
| KPN | 437 | Blood | D7 | F | Bronchiolitis, EOS | Fever | Yes | 29,000 | AK, MRP | NO | Expired | 3 |
| KPN | 437 | Blood | 10 m | F | TOF with Cyanotic Spell, Pneumonia | Fever, SOB, B/L Infiltrate, Thrombocytopenia | Yes | 15,000 | CTR, MRP, VANCO | YES | Expired | 4 |
| KPN | 231 | BAL | 1 Y | M | Rt Pneumonia; F/U/C ARM (Stoma Closure) | Fever, SOB | Yes | 18,000 | MRP, METRO, TGC, FLUCON | NO | Expired | 23 |
| KPN | 437 | BAL | 11 m | M | Resp Distress | Yes | 22,000 | NO | Expired | 2 | ||
| KPN | 16 | BAL | 4 m | M | K/C/O Down’s, AV-Defect; BPN | Resp Distress | Yes | 19,500 | MRP, VANCO | YES | Expired | 7 |
| KPN | 15 | Blood | 72 Y | F | Post-Op TKR, K/C/O Syst HTN | No | 36,700 | MRP | YES | LAMA | 7 | |
| KPN | 985 | Blood | 28 Y | M | Sepsis, Obstructive Hydrocephalus, UTI | Fever, Unconsciousness | Yes | 25,000 | CAZ, MRP, VANCO | YES | Improved | 5 |
| KPN | 147 | ETA | 63 Y | F | ARDS, Shock | Altered Sensorium | Yes | 7000 | PIT | YES | Expired | 8 |
| KPN | 437 | Blood | 48 Y | F | Post-Op 4th Ventricle Meningioma | Hydrocephalus | No | 9000 | MRP/VANCO; CIS/AK | YES | Expired | 10 |
| KPN | 437 | ETA | ||||||||||
| SAU | 22 | Blood | 42 Y | F | Sepsis | Fever, Alt Senso, Hypotension | Yes | 8500 | MRP, PIT | NO | Improved | - |
| SAU | 22 | Blood | 50 Y | M | CAD/NSTEMI/AS | Fever, Chest Pain | Yes | 60,000 | AMC, PIT, Cefpodoxime | NO | Improved | - |
| ST | ISOLATES | Virulence Genes | Capsular Diversity | AMR Genes | Plasmids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yersiniabactin | Colibactin | Aerobactin | Salmochelin | RmpADC | rmpA2 | K_locus | O_locus | AGly_acquired | Col_acquired | Fcyn_acquired | Flq_acquired | Gly_acquired | MLS_acquired | Phe_acquired | Rif_acquired | Sul_acquired | Tet_acquired | Tgc_acquired | Tmt_acquired | Bla_acquired | Bla_ESBL | Bla_Carb_acquired | Bla_chr | Omp_mutations | Col_mutations | Flq_mutations | |||
| ST437 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | KL36 (4), KL52 (1) | O4 (4), OL101 (1) | rmtB (4), aph3-Ia (1) | - | - | qnrS1 (1) | - | ermB (4); mphA (4) | - | arr-2 (1) | sul1 (4) | - | - | dfrA30 (3), dfrA12 (1) | TEM-1D (4) | CTX-M-15 (5) | NDM-5 (4); OXA-48 (2); OXA-181 (2) | SHV-11 (5) | OmpK36GD (5) | PmrB (1) | GyrA-83I (5); GyrA-87N (2); ParC-80I (5) | Col(pHAD28) (5); IncFII (5); Col440II (4); Col440I (3), |
| ST15 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | KL112 (2) | O1/O2v1 (2) | aac(6′)-Ib; aadA2; rmtB; rmtF | - | - | qnrB1 (2) | - | ermB; mphA (2) | - | arr-2 (1) | sul1 (2) | - | - | dfrA12 (2) | TEM-1D (2) | CTX-M-15 (2) | NDM-5; OXA-232 (2) | SHV-28 (2) | OmpK35-17%; OmpK36TD | - | GyrA-83F; GyrA-87A; ParC-80I | Col(pHAD28) (2); IncFII (2); Col440I (2); Col440II (2); ColKP3; ColRNAI; IncFIB(pKPHS1); IncFII(pKP91) |
| ST147 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | KL51 | O1/O2v2 | aac(6′)-Ib; aadA3; rmtF | - | - | qnrB1 | - | mphA | - | arr-2 | sul1 | - | - | dfrA12 | - | CTX-M-15 - | NDM-5; OXA-181 | SHV-11 | OmpK35-76%; OmpK36TD | - | GyrA-83I; ParC-80I | Col(pHAD28); ColpVC; IncFIB(K); IncFII |
| ST16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | KL81 | OL101 | aac(3)-IIa; aac(6′)-Ib-cr; aadA2; rmtB; strA; strB | - | - | qnrB1; qnrS1 | - | ermB; mphA | CatB4 | - | sul1; sul2 | tet(A) | - | dfrA12; dfrA14 | OXA-1; TEM-1D | CTX-M-15 - | NDM-5; OXA-181 | SHV-1 | OmpK35-6%; OmpK36TD | - | GyrA-83F; GyrA-87N; ParC-84K | Col(pHAD28); IncX3; IncFIA |
| ST231 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | KL51 | O1/O2v2 | aac(6′)-Ib; aadA2; rmtF | - | - | - | - | ermB; mphA | catA1 | arr-2 | sul1 | - | - | dfrA12 | TEM-1D | CTX-M-15 - | OXA-232 | SHV-1 | OmpK35-30%; OmpK36TD | - | GyrA-83I; ParC-80I | Col(pHAD28); IncFIB(pQil); ColKP3; IncFII(K); IncFIA |
| ST985 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | KL39 | O1/O2v2 | aac(3)-IId; aph(3′)-VI; rmtB; rmtC | - | - | qnrB1 | - | mphA | - | - | sul1 | - | - | - | FONA-5 | SFO-1 - | NDM-1 | SHV-187 | - | - | - | IncFII; IncFIB(pQil); IncFII(K) IncHI1B(pNDM-MAR); repB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Oman Medical Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tayyaba, U.; Khan, S.W.; Sultan, A.; Khan, F.; Akhtar, A.; Nagaraj, G.; Ahmed, S.; Bhattacharya, B. Molecular Characterization of MDR and XDR Clinical Strains from a Tertiary Care Center in North India by Whole Genome Sequence Analysis. J. Oman Med. Assoc. 2024, 1, 29-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/joma1010005
Tayyaba U, Khan SW, Sultan A, Khan F, Akhtar A, Nagaraj G, Ahmed S, Bhattacharya B. Molecular Characterization of MDR and XDR Clinical Strains from a Tertiary Care Center in North India by Whole Genome Sequence Analysis. Journal of the Oman Medical Association. 2024; 1(1):29-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/joma1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleTayyaba, Uzma, Shariq Wadood Khan, Asfia Sultan, Fatima Khan, Anees Akhtar, Geetha Nagaraj, Shariq Ahmed, and Bhaswati Bhattacharya. 2024. "Molecular Characterization of MDR and XDR Clinical Strains from a Tertiary Care Center in North India by Whole Genome Sequence Analysis" Journal of the Oman Medical Association 1, no. 1: 29-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/joma1010005
APA StyleTayyaba, U., Khan, S. W., Sultan, A., Khan, F., Akhtar, A., Nagaraj, G., Ahmed, S., & Bhattacharya, B. (2024). Molecular Characterization of MDR and XDR Clinical Strains from a Tertiary Care Center in North India by Whole Genome Sequence Analysis. Journal of the Oman Medical Association, 1(1), 29-47. https://doi.org/10.3390/joma1010005






