Abstract
Background: Infants are at risk of cerebral hypoperfusion from low blood pressure during anesthesia. We conducted a retrospective observational study to determine the patient and perioperative factors associated with low systolic blood pressure (SBP) in healthy infants. Methods: We obtained perioperative data of 266 infants aged 0–6 months who underwent inguinal hernia repair between January 2015 and March 2019 at our institution. SBP was analyzed during two phases: the preparation phase (20 min before procedure start until incision) and the surgical phase (15 to 35 min after procedure start). Low SBP was defined as a value lower than two standard deviations below the 50th percentile for a phase- and weight-specific reference value. Results: Low SBP was observed in 11% (29/265) and 5% (13/259) of patients during the preparation and surgical phases, respectively. Neuromuscular blockade use was associated with normal SBP in both phases (regression coefficient β = 6.15 and p = 0.002, regression coefficient β = 6.52 and p < 0.001, respectively). SBP was more strongly associated with weight than with age (ratio of adjusted standardized regression coefficient = 2.0 in both phases). After controlling for covariates, patients given neuromuscular blockade had significantly fewer low SBP measurements during the preparation phase (regression coefficient β = −1.99 and p < 0.001). Conclusions: With respect to patient factors, in healthy infants under general anesthesia, weight was more strongly associated with SBP than age. A neuromuscular blocking agent administered during anesthesia induction was associated with fewer low SBP measurements in the preparation phase.
1. Introduction
Infants have proportionally greater decreases in blood pressure under general anesthesia compared with older children [1]. Reduced infant cerebral blood flow velocity has been found during post induction periods of low blood pressure [2]. There is concern that limited cerebral autoregulatory reserve in infants could lead to decreased cerebral perfusion pressure when blood pressure is low [3,4]. In severe cases, infants who undergo sustained low blood pressure can develop seizures, encephalopathy, and profound developmental delays [5]. General anesthesia (GA) in infants causes higher rates of intraoperative hypotension than spinal anesthesia, and younger infants (under 6 months of age) who undergo general anesthesia have the highest risk of cerebral hypoperfusion during periods of intraoperative hypotension [2,6].
Potentially modifiable anesthetic factors associated with low blood pressure in this population remain an area of ongoing investigation. Thus, to address this knowledge gap, we conducted a retrospective observational study of low blood pressure in infants undergoing general anesthesia for inguinal hernia surgery. We selected inguinal hernia repair surgery to optimize clinical relevance and generalizability as this is a very common surgical procedure that is performed in a generally uniform, otherwise healthy population of infants. Inguinal hernia repair patients experience minimal blood and evaporative water loss. Low blood pressure was defined using published reference values for healthy infants under general anesthesia according to weight and surgical stage [7].
The primary aim of our study was to determine patient and anesthetic factors associated with low systolic blood pressure in infants under general anesthesia. Because younger, smaller infants seem more vulnerable to low blood pressure under anesthesia, we hypothesized that lower age and weight would be associated with lower blood pressure under anesthesia. Some anesthesiologists will eschew neuromuscular blocking agents in favor of higher propofol doses for intubation; thus, we also hypothesized that the administration of propofol and avoidance of neuromuscular blocking agents would be associated with low blood pressure.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was reviewed by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and granted an exemption. The requirement for written informed consent was waived by the IRB. This manuscript adheres to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines [8].
We conducted a retrospective observational study of American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status (ASA PS) 1 and 2 patients under 6 months of age who underwent inguinal hernia repair from 25 January 2015 until 1 March 2019 at a single quaternary pediatric hospital. Inclusion criteria were an age of less than 6 months, ASA PS 1 and 2, and patients who had an elective hernia repair under general anesthesia with perioperative vital signs recorded. Exclusion criteria were ASA PS “E” cases, any hernia repair that was combined with another procedure, patients who received a spinal anesthetic, and patients who received desflurane.
Non-invasive blood pressure values were collected every 3 min during general anesthesia. At our institution, blood pressure cuffs are generally placed on the upper arm. The cuff size is selected so that the edge of the cuff falls within the range of markings on the other side of the cuff and the width does not extend over a joint. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) values for each patient were analyzed during two phases: (1) the preparation phase, defined as the 20-min period leading up to the start of the procedure, and (2) the surgical phase, defined as the 20-min period occurring between 15 to 35 min after procedure start. An occurrence of low SBP was defined as a value below the 50th percentile minus two standard deviations from previously published phase- and weight-specific reference values [7] (Table S1). The number of low SBP occurrences during each of the two 20-min phases were analyzed. Perioperative medications included propofol, opioids (fentanyl, morphine, and remifentanil), caudal epidural local anesthetics (ropivacaine and bupivacaine), and neuromuscular blocking medication (vecuronium and cisatracurium). Covariates included positive end expiratory pressure and exhaled sevoflurane concentration. SBP data filtering and validation were performed. Filtering identified and excluded from analysis any blood pressure artifact values that were blank, zero, negative, or greater than 200 mmHg.
Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis plan was developed prior to data analysis. Descriptive statistics were used to present characteristics of the patient cohort: categorical and numeric variables were described using count with percentage and median with interquartile range, respectively. A correlation matrix was developed to examine the relationships between key numeric variables: (1) Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated, (2) histograms with probability density curves were made, and (3) scatterplots were drawn with smooth curves and correlation ellipses. The smooth curves with 95% confidence intervals were fitted using the LOESS regression algorithm, and correlation ellipses were drawn around the mean with the axis length reflecting one standard deviation of the x and y variables.
A multiple linear regression model was built to assess the adjusted associations between SBP and risk factors. The selection of covariates into the model was based on a conceptual causal model and preliminary data analysis. The key assumptions of linear regression were evaluated with no obvious violation, including linearity, multivariate normality, homoscedasticity, no autocorrelation, and little multicollinearity. The regression coefficients (β) and standard errors (SE) were reported. The effect of weight and age on the SBP was compared by standardizing β using z-score transformation. When analyzing the number of low SBP occurrences as a count outcome variable, zero-inflated negative binomial regression analysis was performed to address the over-dispersion issue, that is, a high proportion of patients have zero occurrence of low SBP, and then to assess whether increased occurrences of low SBP were associated with any possible risk factors. All analyses were performed using R 3.4.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was used as the criterion for statistical significance.
3. Results
Of 266 eligible study patients, 265 (99.6%) had systolic blood pressure (SBP) values during the preparation phase, while 259 (97.4%) had SBP values during the surgical phase (Figure 1, study enrollment flow diagram). The patient characteristics by perioperative phases and SBP are presented in Table 1. The median age was 77 days (interquartile range (IQR): 60 to 100 days) and the median gestational age was 37 weeks (IQR: 32–39 weeks). Most patients were ASA PS 2 (72.9%) and were general surgery patients (87.6%). Endotracheal tubes were placed in all but one patient whose airway was managed with a supraglottic airway. During the preparation phase, 29 (10.9%) of the 265 patients had low SBP; during the surgical phase, 13 (5.0%) of the 259 patients had low SBP.
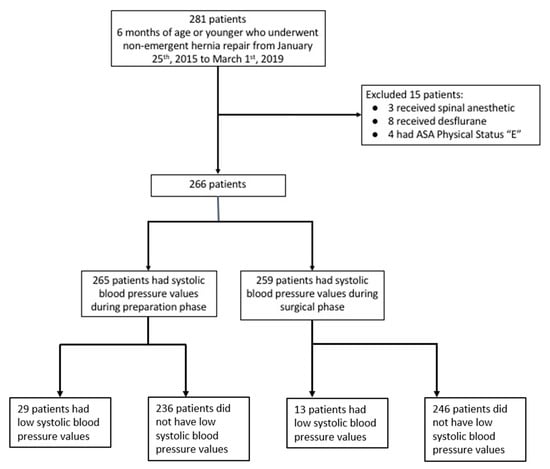
Figure 1.
Study enrollment flow diagram. Low systolic blood pressure was defined according to age-adjusted blood pressure reference values [7].

Table 1.
Characteristics of the patients by systolic blood pressure status during the preparation and surgical phases.
3.1. Risk Factors Associated with Occurrences of Low SBP
During the preparation phase, 236 patients had normal SBP while 14 patients had one occurrence of low SBP, 10 had two occurrences of low SBP, three had three occurrences of low SBP, and two had four occurrences of low SBP. During the surgical phase, 246 patients had normal SBP while three had one occurrence of low SBP, four had two occurrences of low SBP, two had three occurrences of low SBP, and four had four or more occurrences of low SBP. After adjusting for age, sevoflurane, propofol, and neuromuscular blockade, patients on the urologic surgery service tended to have a greater number of low SBP measurements compared with those cared for by the general surgery service during both the preparation and surgical phases: the difference in the logarithm of expected occurrences of low SBP was 1.14 (p = 0.025) and 2.71 (p = 0.010). Patients given muscle relaxant had significantly fewer occurrences of low SBP during the preparation phase (β = −1.99 and p < 0.001). Increased age was associated with fewer low SBP measurements during the surgical phase (β = −0.05 and p = 0.001). The corresponding results are displayed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Adjusted associations between risk factors and low SBP readings during the preparation and surgical phases.
3.2. Relationship of SBP to Neuromuscular Blockade, Propofol, and Anesthetic Technique
Neuromuscular blockade was used in 72.2 percent of patients. Patients who received neuromuscular blockade were more likely to have normal blood pressure in both preparation and surgical phases (Table 3, preparation phase, β = 6.15, p = 0.002; surgical phase, β = 6.52, p < 0.001).

Table 3.
Adjusted associations between risk factors and systolic blood pressure (as a continuous variable) during the preparation and surgical phases.
Propofol was given to 41.7% of patients. Use of propofol was not associated with the number of low SBP measurements in either phase. There was an association between propofol use and higher SBP during the surgical phase when SBP was analyzed as a continuous variable (Table 3, β = 3.24, p = 0.031).
Caudal anesthesia was used in 61.3% of patients. There was no association between caudal anesthesia and low SBP (preparation phase, p = 0.271; surgical phase, p = 0.270).
3.3. Relationship of SBP to Age and Weight
SBP values during the preparation and surgical phases were positively correlated with both age and weight. As shown in Figure 2, there were clear upward trends between weight and SBP during both perioperative phases. The strength of the correlation was moderate and statistically significant (correlation coefficient, r = 0.37 for SBP of preparation phase and r = 0.40 for SBP of surgical phase, both p < 0.001). Comparably, the correlation between age and SBP was slightly weaker in both phases but remained statistically significant (r = 0.32 for SBP of preparation phase and r = 0.36 for SBP of surgical phase, both p < 0.001).
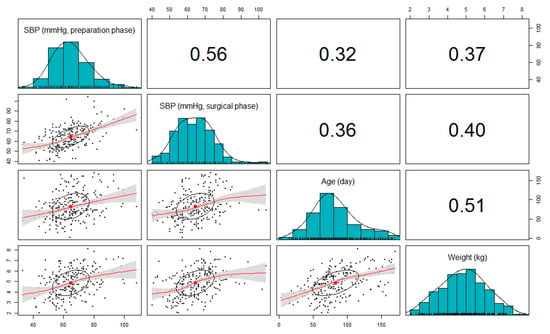
Figure 2.
A matrix of correlation coefficients, histograms, and scatterplots among systolic blood pressure (SBP), age, and weight. Red line calculated using locally estimated scatterplot smoothing (LOESS) curve fitting; gray shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval of the curve; the ellipses represent one standard deviation of the x and y variables for each scatterplot.
The effects of age and weight on the perioperative SBP were further illustrated in the multiple linear regression analysis controlling for possible confounders (Table 3). After adjustment for sex, race/ethnicity, ASA PS, surgical service, sevoflurane, propofol, and neuromuscular blocking agents, each kilogram increase in weight, on average, was significantly associated with a 3.7 mmHg increase in SBP during the preparation phase and a 3.4 mmHg increase during the surgical phase (both p < 0.001). In other words, SBP fell by 3.7 and 3.4 mmHg per kilogram weight decrease during the preparation and surgical phases, respectively. Age was also significantly associated with SBP. SBP decreased by 0.07 mmHg with each day decrease in age during both preparation and surgical phases (p = 0.008 and p = 0.004, respectively); this can be equivalently interpreted that SBP decreased by 2.1 mmHg with each 30-day decrease in age.
While both weight and age were significantly associated with SBP, weight had a stronger association with SBP with a larger standardized regression coefficient (β). During the preparation phase, the association of weight with SBP was almost two times greater than that of age (standardized β: 4.53 vs. 2.29; ratio of standardized β = 1.98). During the surgical phase, weight continued to have a stronger association with SBP when compared with age (standardized β: 4.08 vs. 2.20, ratio of standardized β = 1.85).
4. Discussion
Our study’s primary aim was to determine patient and anesthetic factors associated with low blood pressure in infants under general anesthesia and produced two main findings. First, increasing age was negatively associated with low SBP during the surgical phase, and SBP was linearly associated with patient age and weight, with weight having a stronger correlation than age. Second, use of neuromuscular blockade was associated with fewer occurrences of low SBP during the time period after intubation and prior to the start of the surgical procedure. Use of a neuromuscular blocking agent was associated with fewer low SBP measurements in the preparation phase. Neuromuscular blockade use may result in lower doses of anesthetic agents being given at induction of anesthesia to facilitate intubation. Most induction agents decrease blood pressure; thus, this possible sparing effect from neuromuscular blockade may result in higher SBP.
We observed lower rates of low blood pressure than previously reported by most other studies of blood pressure in infants under anesthesia. We attribute this observation to our definition of low blood pressure; one study using a similar definition of low blood pressure found comparable rates of low blood pressure in anesthetized children [9]. Earlier studies defined low blood pressure as a decrease from a baseline SBP value or an absolute mean arterial pressure (MAP) value. Multiple studies have used absolute MAP less than 35 mmHg in this age group, since cerebral metabolic oxygen reserve was found to decrease in this range [10]. However, at least half of infants under 6 months of age experience MAP values less than 35 mmHg during general anesthesia [11,12,13]. Conversely, a definition of low blood pressure based on a relative change from an awake baseline blood pressure suffers from difficulty obtaining accurate blood pressure values prior to induction, particularly since agitated patients may have falsely elevated blood pressure [14]. Although the definition of low blood pressure in our study differed from most previous studies, we observed similarly that low blood pressure was associated with decreased age and weight, with weight having a stronger effect than age. These findings align with prior work that found associations between blood pressure and both weight and age [5,11,15].
There was an association between propofol use and higher SBP during the surgical phase when SBP was analyzed as a continuous variable. This observation highlights the importance of biological and clinical plausibility as well as correlation versus causation in any retrospective study. Propofol administration in the surgical phase likely occurred in the context of deepening a “light” anesthetic; thus, one might speculate that a higher SBP was then returned closer to baseline after propofol administration, rather than the expectation of low SBP after propofol is given. In contrast, we did not find an association between propofol use and the number of low SBP measurements during either phase when low blood pressure was analyzed as a dichotomous variable. Use of propofol and sevoflurane during induction was a risk factor for pre-incision low blood pressure in a study of pediatric patients who were 1 to 17 years old [16]. Propofol use was not associated with low blood pressure in a recent study by Pasma et al., but that study had a low rate of propofol use and included older children undergoing a variety of procedures [9]. Use of a neuromuscular blocking agent (atracurium) in the same study was infrequent and not associated with changes in blood pressure [9]. Studies of propofol use in older children for sedated imaging studies found that SBP decreased after propofol [17,18]. Conversely, a study of induction propofol boluses found no change in SBP in the setting of pretreatment with atropine [19]. Two studies analyzing propofol induction dosages found that SBP decreased after propofol induction, but this decrease was not dose dependent [20,21].
We did not observe an association between low SBP and the use of either caudal epidural local anesthetic or opioids. In the general anesthesia or awake-regional anesthesia in infancy (GAS) study, a higher incidence of hypotension was seen in patients receiving general anesthesia compared with spinal anesthesia for inguinal herniorrhaphy. Many patients in the general anesthesia arm of the GAS study received caudal epidural local anesthetic; caudal anesthesia was not analyzed separately as a factor influencing blood pressure [11].
The avoidance of low blood pressure in infants is a worthwhile goal to limit the potential for hypoperfusion of the brain and other organs [4,12]. Depth of anesthesia monitoring with devices such as near infrared spectroscopy and processed electroencephalogram monitors has become increasingly prevalent in pediatric anesthesia to optimize anesthetic delivery and decrease the incidence of overly deep anesthesia [22,23,24]. Infants especially are subject to isoelectric encephalography during anesthesia for surgery [25]. Our study findings suggest that using a neuromuscular blocking agent rather than relying on higher doses of propofol for intubation may reduce the likelihood of low blood pressure in this patient population. This association between anesthetic management and isoelectric events in infants undergoing general anesthesia remains an area for current and future research.
Our study focused on infants’ blood pressure rather than heart rate to complement the research that has been conducted on this topic since the study by McCann et al. that implicated intraoperative hypotension rather than heart rate as a cause for postoperative infantile encephalopathy [5,9,10,11,12,13]. However, infants from birth to 6 months experience rapid changes in standard SBP values, and since the stroke volume of an infant’s heart does not vary significantly, heart rate is generally considered more important than blood pressure [26]. This interplay between heart rate, blood pressure, and cerebral autoregulation remains an important area for future research [4].
Our study had several limitations. First, a retrospective observational study can only describe associations and cannot establish causation between anesthetic agents and low blood pressure. Second, we analyzed categories of medications rather than dosages because of the prohibitively complex heterogeneity in administered drugs, the timing of drug administration, and patients’ weights and ages. Thus, while the observed association between neuromuscular blockade and SBP might be attributed to reduced administration of induction agents, we were unable to analyze induction medication dosages. Third, artifactual SBP readings could have been included in the analysis. While we identified and excluded certain vital sign artifacts based on our filtering criteria, artifacts could have remained that impacted our findings. Blood pressure was measured noninvasively per our standard approach in healthy infants undergoing herniorrhaphy. A study of non-invasive and arterial line blood pressure readings found that noninvasive monitors were accurate during normotension, but were more likely to be falsely normal when the infant was hypotensive [27]. This type of error might have contributed to an underestimation of the incidence of low blood pressure in our study. Fourth, while the study population included prematurely born infants, we did not consider this as a variable in our analysis. Fifth, given the margin of error of non-invasive blood pressure measurement in infants, small differences in SBP may have limited clinical relevance. Sixth, while fasting times have been associated with low blood pressure [28], we were unable to include this factor as a variable because of missing data. Seventh, we selected a definition of low blood pressure that was based on normograms published with multicenter data [7]. However, defining clinically relevant hypotension in infants remains a challenge and an area of active research and debate [29,30]. The use of different definitions of low SBP could certainly produce different findings, and this challenge highlights the importance of applying existing and new technologies to explore hypotension in infants [31]. Eighth, at our institution, the anesthetic management for inguinal hernia repairs consists nearly exclusively of the medication groups that we included in our analysis. The use of vasopressors or other medications with hemodynamic effects is extremely rare. Researchers at other institutions may observe different rates of hypotension and associations with medications based on their local practices. Ninth, due to complex heterogeneity in dosing and timing of propofol and other medications in this retrospective analysis of real-world clinical data, we focused our analysis on simplified medication groups rather than granular medication administration dose and time data. This also precluded the granular analysis of propofol and muscle relaxant dosing. This remains an ongoing challenge with retrospective analyses of electronic health record data that can primarily be addressed by prospective randomized trials. Tenth, the number of events is relatively small and this could have affected the multivariable model. Eleventh, fluid data have been notoriously unreliable in our institution based on our experience of analyzing it and trying to incorporate it into analyses for other studies, only to abandon it for poor quality [15]. Thus, we did not include fluid administration in this study. Twelfth, we did not perform analysis of whether having hypotension in the preparation phase exposed patients to greater risk of low SBP in the surgical phase. This is clearly an important factor for future study. Lastly, benzodiazepines are not routinely administered in patients in this study population—in fact, only one patient received a benzodiazepine, and this patient already met another exclusion criterion. Thus, we did not include benzodiazepines in our analysis. Despite these limitations, the strengths of our study include the use of a population-derived definition of blood pressure, the uniform nature of the surgical procedure, and a healthy patient population. These factors allowed us to analyze the anesthetic management approach for associations with low SBP that are generalizable to clinicians who manage these patients in a similar fashion.
In conclusion, younger age and lower weight were associated linearly with lower SBP in healthy infants under general anesthesia, and a neuromuscular blocking agent administered during induction of anesthesia was associated with fewer occurrences of low SBP in the preparation phase. The greater hemodynamic stability in the neuromuscular blocking agent group may not be due to the use of these agents, but to the avoidance of high doses of propofol. Future implications of this study include informing quality improvement initiatives of nonmodifiable and potentially modifiable factors to reduce the incidence of low blood pressure in infants during inguinal hernia repair as well. Future studies should explore the optimal induction approach to minimize low blood pressure in infants undergoing general anesthesia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/anesthres1020009/s1, Table S1: Systolic non-invasive blood pressure during preparation and surgical phases in relation to age, adapted from de Graaff et al.
Author Contributions
All authors meet the requirements for authorship: Conceptualization, A.F.S., O.N. and P.A.S.; methodology, A.F.S., O.N., L.W. and P.A.S.; formal analysis, O.N. and L.W.; resources, P.A.S. and F.R.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.S., O.N. and L.W.; writing—review and editing, A.F.S., O.N., L.W., J.A.B., I.Y., A.P., P.A.S. and F.R.T.; supervision, A.F.S., P.A.S. and F.R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
IRB number 18-015823—Study was submitted to the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia IRB and granted an exemption.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data generated during the study are the property of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and are unavailable due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sottas, C.E.; Cumin, D.; Anderson, B.J. Blood pressure and heart rates in neonates and preschool children: An analysis from 10 years of electronic recording. Pediatr. Anesth. 2016, 26, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhondali, O.; Mahr, A.; Simonin-Lansiaux, S.; De Queiroz, M.; Rhzioual-Berrada, K.; Combet, S.; Cejka, J.; Chassard, D. Impact of sevoflurane anesthesia on cerebral blood flow in children younger than 2 years. Pediatr. Anesth. 2013, 23, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.J.; Da Costa, C.S.; Austin, T.; Brady, K.M.; Czosnyka, M.; Lee, J.K. Neonatal cerebrovascular autoregulation. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.E.; Lee, J.K.; Inder, T. Beyond Anesthesia Toxicity: Anesthetic Considerations to Lessen the Risk of Neonatal Neurological Injury. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.E.; Schouten, A.; Dobija, N.; Munoz, C.; Stephenson, L.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Kalkman, C.; Hickey, P.R.; de Vries, L.S.; Tasker, R.C. Infantile Postoperative Encephalopathy: Perioperative Factors as a Cause for Concern. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e751–e757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.J.; Disma, N.; De Graaff, J.C.E.; Withington, D.; Dorris, L.; Bell, G.; Stargatt, R.; Bellinger, D.C.; Schuster, T.; Arnup, S.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years of age after general anaesthesia and awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): An international multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, J.C.; Pasma, W.; Van Buuren, S.; Duijghuisen, J.J.; Nafiu, O.O.; Kheterpal, S.; Van Klei, W.A. Reference values for noninvasive blood pressure in children during anesthesia: A multicentered retrospective observational cohort study. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Re-porting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasma, W.; Peelen, L.M.; Van Den Broek, S.; Van Buuren, S.; Van Klei, W.A.; De Graaff, J.C. Patient and anesthesia characteristics of children with low pre-incision blood pressure: A retrospective observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 64, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhondali, O.; Pouyau, A.; Mahr, A.; Juhel, S.; De Queiroz, M.; Rhzioual-Berrada, K.; Mathews, S.; Chassard, D. Sevoflurane anesthesia and brain perfusion. Pediatr. Anesth. 2014, 25, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.E.; Withington, D.E.; Arnup, S.J.; Davidson, A.J.; Disma, N.; Frawley, G.; Morton, N.S.; Bell, G.; Hunt, R.W.; Bellinger, D.C.; et al. Differences in Blood Pressure in Infants After General Anesthesia Compared to Awake Regional Anesthesia (GAS Study—A Prospective Randomized Trial). Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrecht, V.A.; Skowno, J.; Marchesini, V.; Ding, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ward, C.G.; Yu, G.; Liu, H.; Schurink, B.; Vutskits, L.; et al. An International, Multicenter, Observational Study of Cerebral Oxygenation during Infant and Neonatal Anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görges, M.; West, N.C.; Karlsdóttir, E.; Ansermino, J.M.; Cassidy, M.; Lauder, G.R. Developing an objective method for analyzing vital signs changes in neonates during general anesthesia. Pediatr. Anesth. 2016, 26, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Koning, L.; Scoones, G.P. Defining hypotension in anesthetized infants by individual awake blood pressure values: A prospective observational study. Pediatr. Anesth. 2017, 27, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpao, A.F.; Ahumada, L.M.; Gálvez, J.A.; Bonafide, C.P.; Wartman, E.C.; England, W.R.; Lingappan, A.M.; Kilbaugh, T.J.; Jawad, A.F.; Rehman, M.A. The timing and prevalence of intraoperative hypotension in infants undergoing laparoscopic pyloromyotomy at a tertiary pediatric hospital. Pediatr. Anesth. 2016, 27, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiu, O.O.; Kheterpal, S.; Morris, M.; Reynolds, P.I.; Malviya, S.; Tremper, K.K. Incidence and risk factors for preincision hypotension in a noncardiac pediatric surgical population. Pediatr. Anesth. 2009, 19, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart, C.R.; Parrish, M.; Rosen, K.L.; Dettorre, M.D.; Ceneviva, G.D.; Lucking, S.E.; Thomas, N.J. Safety and efficacy of sedation with propofol for transoesophageal echocardiography in children in an outpatient setting. Cardiol. Young 2006, 16, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.A.; Shayevitz, J.R.; Patel, V. Deep sedation with propofol for children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging of the brain: Experience from a pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 4, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.E.; Song, I.K.; Lee, J.H.; Hur, M.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.S. Pulse transit time shows vascular changes caused by propofol in children. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2015, 29, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, S.M.; Aun, C.S.T. Haemodynamic effects of propofol in children. Anaesthesia 1991, 46, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, J.; Houle, T.T.; Matthews, B.T.; Houck, J.; Burrows, F.A. Propofol for tracheal intubation in children anesthetized with sevoflurane: A dose–response study. Pediatr. Anesth. 2009, 19, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, Z.; Robino, C.; Rufini, P.; Cumbo, S.; Cavallini, S.; Gobbi, L.; Brocchi, A.; Serio, P.; Romagnoli, S. Monitoring anesthesia depth with patient state index during pediatric surgery. Pediatr. Anesth. 2023, 33, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, I.; Xu, T.; Kurth, C.D. Using Electroencephalography (EEG) to Guide Propofol and Sevoflurane Dosing in Pediatric Anes-thesia. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguh, S.J.; Iyer, R.S.; Yuan, I.; Missett, R.; Guris, R.J.D.; Johnson, G.; Babus, L.W.; Massa, C.B.; McClung-Pasqualino, H.; Garcia-Marcinkiewicz, A.G.; et al. Implementation of an electroencephalogram-guided propofol anesthesia practice in a large academic pediatric hospital: A quality improvement project. Pediatr. Anesth. 2024, 34, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, I.; Xu, T.; Skowno, J.; Zhang, B.; Davidson, A.; Von Ungern-Sternberg, B.S.; Sommerfield, D.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. BRAIN Collaborative Investigators. Isoe-lectric Electroencephalography in Infants and Toddlers during Anesthesia for Surgery: An International Observational Study. Anesthesiology 2022, 137, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, N.; Winberg, P.; Selldén, H. Changes in stroke volume cause change in cardiac output in neonates and infants when mean airway pressure is altered. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1999, 43, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidert, A.S.; Tholl, M.; Huttle, T.K.; Baerasconi, P.; Peraud, A.; Briegel, J. Accuracy of oscillometric noninvasive blood pressure compared with intra-arterial blood pressure in infants and small children during neurosurgical procedures: An observational study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 36, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpao, A.F.; Wu, L.; Nelson, O.; Gálvez, J.A.; Tan, J.M.; Wasey, J.O.; Muhly, W.T.; Tsui, F.C.; Masino, A.J.; Stricker, P.A. Preoperative Fluid Fasting Times and Postinduction Low Blood Pressure in Children: A Retrospective Analysis. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutskits, L.; Skowno, J. Perioperative Hypotension in Infants: Insights From the GAS Study. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ing, C.; DeStephano, D.; Hu, T.; Reighard, C.; Lackraj, D.; Geneslaw, A.S.; Miles, C.H.; Kim, M. Intraoperative Blood Pressure and Long-Term Neurodevelopmental Function in Children Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2022, 135, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vik, S.D.; Torp, H.; Jarmund, A.H.; Kiss, G.; Follestad, T.; Støen, R.; Nyrnes, S.A. Continuous monitoring of cerebral blood flow during general anaesthesia in infants. BJA Open 2023, 6, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).