Abstract
The Mediterranean Diet (MD) has emerged as a comprehensive model for promoting human health and environmental sustainability. This review proposes reconceptualization of the traditional MD pyramid, highlighting its functional food components and their relevance to modern health challenges. Rooted in a rich cultural and gastronomic heritage, the MD extends beyond nutritional adequacy. It offers substantial nutraceutical benefits due to its high content of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols, carotenoids, omega-3 fatty acids, and phytosterols. These compounds contribute to the prevention and management of chronic non-communicable diseases through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Simultaneously, the MD aligns with sustainable food system principles: it is predominantly plant-based; it promotes seasonal and local food sourcing; and it supports minimal food waste. In addition, this dietary pattern has been associated with a significantly lower ecological footprint compared to Western diets, thus supporting broader environmental goals. Ultimately, the MD stands as a scientifically grounded, culturally embedded, and ecologically viable approach to foster both individual and planetary wellbeing (One Health concept).
1. Food: More than Nutrients
The provision of energy and essential nutrients is fundamental to the survival of all living organisms. In humans, these critical elements are acquired through dietary intake. The early ancestors of Homo sapiens undertook extensive journeys to gather berries, hunt, or fish as their primary source of food [1]. Over time, humans began to engage in agriculture and animal husbandry, rather than relying solely on foraging for food [1,2]. This major shift marked the end of the nomadic lifestyle and facilitated the establishment of small settlements, which gradually expanded into complex societies and urban centres [2].
As civilisations evolved, the role of food went beyond its primary function of nourishment. It became a cultural and social phenomenon, deeply connected with human history and traditions [3,4,5]. The act of eating was transformed into a sensory experience, eventually giving rise to the early conceptualisation of gastronomy [3,4,5]. Culinary practices of different regions evolved based on locally available ingredients, climatic conditions, and historical influences, leading to the development of diverse gastronomic traditions [5,6]. Thus, beyond its biological importance, food promotes social cohesion, with meals serving as central events for family gatherings and communal interactions. The cultural significance of food is further emphasised by its role in festivals, religious rituals, and national identities [5,6]. In Portugal, although there is no official total number, it is possible to identify at least 30 distinct gastronomic events held throughout the year of 2024, ranging from regional festivals to major national celebrations. Regional differentiation in culinary habits has given rise to distinct dietary patterns, influencing both local and global food chains and economies [7,8]. Nevertheless, traditional dietary patterns have changed significantly, giving way to more processed foods, mass production systems, and greater reliance on industrialised food chains.
Food can contribute to maintaining health and preventing diseases [8,9,10]. Specific dietary interventions have been associated with weight management, metabolic regulation, and a reduced incidence of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases [8,9,10]. The exploration of functional foods and personalised nutrition became a focus in scientific research, highlighting the potential of dietary modifications to improve overall health and longevity [11,12]. This literature review was conducted to revise the traditional Mediterranean Diet (MD) model by integrating scientific evidence on its functional food components, with the aim of addressing current public health challenges and promoting environmentally sustainable dietary practices. Importantly, the MD conveys a social framework that actively promotes physical health, environmental sustainability and social well-being [13,14].
2. Dietary Choices and Sustainability
As illustrated in Figure 1A, millions of tonnes of food are wasted each year, representing one of the most significant global challenges. Food waste refers to losses before the consumer level, including post-harvest, storage, transport, and processing. This rising trend is increasing due to a combination of inefficient production practices and population growth [15,16], and is driven by multiple factors, including economic conditions, cultural attitudes, and dietary habits [17,18,19].
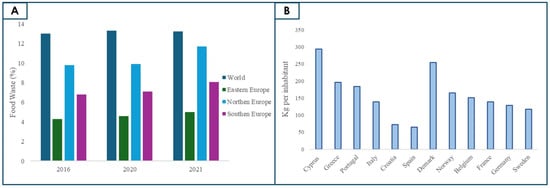
Figure 1.
(A). Food waste per capita (%) in 2016, 2020, and 2021 across selected regions. (B). Food waste (kg per capita) in selected European countries in 2022. Extracted from Eurostat using the latest available data [20].
Globally, circa 13% of food is lost before retail, with the average loss in Europe being ≈131 kg per person [20]. According to Eurostat, and for 2022, Cyprus stands out as the European country with the highest per capita food waste (approximately 295 kg per person), followed by Denmark and Greece. These results are particularly noteworthy in the European context, especially considering that some of these countries belong to the Mediterranean region, traditionally associated with more sustainable food practices. Portugal ranks fourth, with approximately 186 kg per person, indicating a concerning level of food waste, above the European average [20]. This position suggests that, despite the cultural appreciation of food and the Mediterranean diet (MD), significant challenges remain in the efficient management of food throughout the supply chain. In contrast, countries such as Spain and Croatia report significantly lower levels of per capita food waste, below 80 kg. Overall, Figure 1 highlights that even among countries with similar food traditions (such as Mediterranean region nations), there is considerable disparity in waste levels. This underscores the importance of effective public policies, food education, and technological innovation to mitigate this environmental and socio-economical issue. Food waste leads to unnecessary use of natural resources and increases the ecological footprint of the agri-food sector. Food production remains one of the most significant contributors to environmental pollution, mainly due to the extensive release of greenhouse gases and the substantial consumption of water and energy resources [20,21,22]. Moreover, large-scale production relies heavily on agrochemicals, such as pesticides and synthetic fertilisers, which not only degrade soil quality but also contaminate aquatic ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and the disruption of aquatic food chains [21,22]. In addition, food export and distribution require energy for transport, refrigeration, and packaging, increasing fossil fuel use and emissions [23]. Inefficient logistics and inadequate storage conditions can also result in significant food losses before products even reach consumers [24,25].
Tackling food waste and its environmental impact requires urgent and sustainable action across the entire food system, from harvesting and production to distribution and consumption [15,16]. Environmentally friendly agricultural methods, such as precision farming, help optimise crop yields while reducing water, fertiliser, and pesticide use. Regenerative agriculture restores soil health and promotes biodiversity, making food systems more resilient [26,27,28]. Applying circular economy principles, such as converting food waste into compost or bioenergy, reduces landfill use and pollution. Technological solutions like smart packaging extend shelf life by monitoring food freshness, while valorising food by-products (such as fruit peels or spent grains) creates new functional ingredients [15,16,17,18,19,20]. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being used to optimise supply chains, improving inventory and reducing spoilage. Public education, sustainable eating habits, and encouraging local food consumption further contribute to reducing environmental impacts [29,30]. Effective policies that support sustainable farming, efficient food distribution, and responsible consumer behaviour are essential to achieving long-term reductions in food waste and pollution at a global level [31].
Mediterranean Diet: A Model for Eco-Friendly Nutrition
A notable dimension of the MD’s sustainability is its association with reduced food waste. Closely aligned with modern zero waste principles, the MD favours the consumption of minimal processed foods that require fewer resources and encourages the reuse of leftovers for several ends [18]. Growing evidence suggests that the MD has a significantly lower environmental footprint than other dietary patterns, namely in greenhouse gas emissions and water footprint [17,18,19]. A key strength of the MD is its inherent emphasis on seasonal, locally grown foods, which reduces energy use for production, storage, and transportation, supports local economies, and may encourage sustainable agricultural practices [18,19]. By promoting diverse, plant-based foods cultivated with environmentally friendly techniques, the MD also contributes to biodiversity conservation and aligns dietary habits with ecological rhythms, fostering greater environmental awareness [17,18,19]. This practice not only improves the nutritional profile of the diet by ensuring a rotation of fresh produce but also aligns with agroecological principles. The seasonal characteristic and local preferences contribute to the significant heterogeneity observed in dietary habits across Mediterranean countries, and even between different regions within the same country. Such heterogeneity reflects the adaptability of the MD to local environments, resources, and cultural practices, while still maintaining a common set of shared values and principles [17,18,19,20].
As global food systems face increasing environmental pressures, adopting the principles of the MD could play a crucial role in promoting both human and planetary health. In this way, dietary choices can also play a crucial role in tackling food waste while supporting environmental sustainability.
3. Diet as a Major Factor in Healthier Living
Typically, weight loss is a primary motivation for adopting a particular eating plan [3]. However, research has highlighted that diets go beyond weight management and provide additional health benefits through the intake of bioactive compounds present in certain foods. Thus, a well-structured and nutritionally balanced diet can improve quality of life by reducing the risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and promoting physiological well-being [32].
NCDs are chronic conditions not transmitted through infectious agents and are typically linked to modifiable behavioural risk factors such as poor diet, physical inactivity, and tobacco use [32]. These diseases include, but are not limited to, cardiovascular disease (CVD), certain types of cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and type 2 diabetes mellitus [32,33]. Collectively, they account for the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. NCDs are responsible for approximately 41 million deaths annually, equating to over 70% of total global mortality [32,33,34,35] and strongly impacting the healthcare burden [32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. The integration of dietary strategies as a preventive tool is increasingly recognised in public health policies and clinical practice guidelines worldwide. Adherence to dietary patterns such as the MD or the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet has been shown to reduce the incidence of coronary heart disease, stroke, and metabolic syndrome [36]. Globally, about 34% of men and 32% of women live with high blood pressure [39]. Many doctors recommend dietary changes to manage high blood pressure, a condition that raises the risk of stroke and heart attack. For example, bananas are rich in potassium-a mineral that helps control blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium and reducing vascular resistance [40]. Similarly, watermelon, which contains citrulline, an amino acid that promotes the endogenous production of nitric oxide, improves endothelial function by increasing arterial flexibility, thereby reducing elevated blood pressure levels [40,41]. Other functional foods, such as garlic, dark chocolate, and leafy vegetables, have been shown to have similar blood pressure-lowering effects via different biochemical mechanisms [42,43].
There are numerous reviews addressing the health impacts of various dietary patterns, particularly their roles in lipid regulation, glycaemic control, and immunomodulation in the context of NCDs managing. Detailed revisions are available (e.g., [44,45]), one key aspect of adapted diets aimed for disease prevention and health promotion being the high proportion of plant-based foods. Table 1, summarizes major plant-based diets, highlighting characteristic features and primary health outcomes [21,44,45].

Table 1.
Common plant-based dietary patterns and its associated health benefits.
The regular consumption of plant-based foods potentially allows for the consumption of bioactive compounds, with minimally processed foods typically retaining the highest levels of these compounds. Bioactive compounds are naturally occurring chemical substances, primarily phytochemicals that are not essential for basic human nutrition yet may exert significant health-promoting effects [45,46]. Due to their pharmacologically relevant properties, such compounds are often referred to as nutraceuticals-a term derived from the combination of “nutrient” and “pharmaceutical” [46]. Possible mechanisms modulated at the molecular level by bioactive compounds are related with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55].
Healthier living also integrates socio-cultural dimensions and the emphasis on psychosocial well-being is one distinguishing feature of MD that is highlighted in the MD pyramid. Lifestyle elements, including regular physical activity, adequate hydration and social and cultural practices related to food preparation and consumption are central to the MD [56,57,58,59]. For instance, shared meals are not only moments of nourishment but also opportunities for social connection, fostering community bonds and emotional support. The intergenerational transmission of culinary knowledge, and taste, preserve traditional recipes and customs, reinforcing cultural identity and continuity [57,58]. This is reflected in the MD pyramid, designed 30 years ago and specifically designed for adults aged 18 to 65 years. The pyramid incorporating lifestyle practices adapted to the realities of modern life while providing a visual structure to convey basic options, such as which foods to eat more or less frequently and recommended portion sizes for different food groups [60,61,62]. Due to its flexible nature, MD accommodates individual preferences, cultural contexts and regional food availability, which can facilitate its adoption [57,58]. By accommodating variations in food types and preparation methods, without departing from the core principles of plant-based eating, moderate portions and seasonal variety, the adoption of the MD can foster the sustainability of ecosystems, including agroecosystems, while improving the health of people and communities. Together, these features position the MD as a dietary and lifestyle model that inherently supports the One Health approach goal.
4. Mediterranean Diet Health Benefits
The health benefits associated with the MD were systematically recognised since 1960, mainly through comparative epidemiological studies [56,57,58]. The evidence of lower incidence of CVD and increased life expectancy among Mediterranean populations was largely due to the traditional dietary practices [56,57,58,59,60,61,62]. Detailed reviews on the historical and nutritional aspects of the MD are available (e.g., [63,64]), both highlighting features as plant-based, nutrient-dense and rich in healthy fats, fibre, micronutrients and antioxidants. Extensive epidemiological and clinical evidence links adherence to the MD with lower mortality risk and reduced incidence of major cardiovascular events [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73], as summarized in Figure 2.
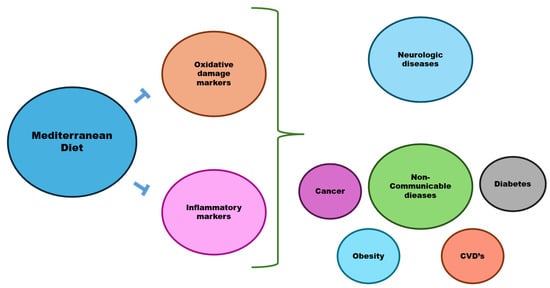
Figure 2.
The Mediterranean diet is associated with reductions in oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers, which, when increased, are associated with non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), diabetes, obesity, cancer and neurological disorders. Based on [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73].
It is important to highlight that studies on the effects of diet on individual health present certain limitations. The primary challenge lies in the necessity of working with human volunteers, which inherently raises both ethical and organisational issues. Furthermore, establishing clear cause-and-effect relationships is often compromised by external factors such as pre-existing medical conditions or the use of medication and the real adherence to the diet.
Families of Compounds with Bioactive Potential Associated with the Mediterranean Diet
The MD contains a rich spectrum of bioactive compounds that collectively influence key physiological pathways involved in the prevention of chronic diseases. Detailed revision on the typical classes of compounds found in MD mainly comprise polyphenols, carotenoids, phytosterols, omega-3s, dietary fibers and organosulfur compounds [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. It should be stressed that beneficial effects are strengthened by their synergistic activity. Traditional preparation techniques (such as slow cooking, use of fresh herbs, and combining foods to optimize nutrient absorption) further potentiate the health-promoting properties of the diet. This synergy reflects the MD’s foundational principle of food as both nourishment and medicine, where the interaction between ingredients contributes to outcomes greater than the sum of individual components.
Polyphenols represent one of the most significant classes of bioactive compounds in the MD, with high concentrations found in extra virgin olive oil, red wine, fruits, vegetables, legumes and herbs. Among these, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, mainly found in olives and olive oil, have demonstrated powerful antioxidant properties. They induce the expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase [74]. Resveratrol, abundant in red wine, contributes to cellular homeostasis by modulating pathways involved in mitochondrial biogenesis and energy metabolism [75]. It also downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines through reducing systemic inflammation, a major risk factor for cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Other polyphenols, including flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol, exert anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic effects by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and reducing the expression of cellular adhesion molecules [83].
Alongside polyphenols, dietary fibre provides the key ingredients for the prebiotic properties of the MD. During fermentation of soluble fibres, colonic microbiota produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These compounds exert multiple systemic effects. SCFAs modulate immune responses through G-protein-coupled receptors, improve insulin sensitivity, maintain intestinal barrier integrity and exert anti-inflammatory and anti-tumorigenic effects [76]. Butyrate, in particular, functions as a histone deacetylase inhibitor, influencing gene expression and contributing to the regulation of inflammatory pathways [77].
Another prominent group of MD bioactive compounds are carotenoids, lipid-soluble pigments responsible for the vibrant colours of many fruits and vegetables. Lycopene, highly concentrated in tomatoes, that unlike many others is particularly bioavailable when cooked, has potent singlet oxygen-scavenging properties. It has been associated with reduced risk of prostate cancer and cardiovascular disease through the modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers [84]. β-carotene, found in carrots and pumpkins, acts as a precursor to vitamin A and supports immune function and epithelial integrity. Lutein and zeaxanthin contribute to ocular health by protecting the retina from light-induced oxidative damage [78].
Phytosterols, including β-sitosterol and campesterol, are naturally occurring plant sterols structurally like cholesterol. Found in legumes, nuts and seeds, these compounds competitively inhibit cholesterol absorption in the intestinal lumen, resulting in reduced plasma LDL-cholesterol levels [79]. In addition to their hypocholesterolaemia effect, phytosterols may also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties by influencing immune cell activity and suppressing the synthesis of inflammatory mediators.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid from oily fish such as sardines and mackerel, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid. They promote the biosynthesis of specialised pro-resolvers, which actively contribute to the resolution of inflammation [78]. Docosahexaenoic acid also plays a key role in neuronal membrane fluidity, synaptogenesis and neuroprotection. It is associated with improved cognitive performance and reduced risk of neurodegenerative disorders [80].
Organic sulphur compounds, found in allium vegetables such as garlic and onions, provide additional bioactive complexity to the MD. Allicin, diallyl disulphide and S-allyl cysteine, among others, have demonstrated antioxidant, antimicrobial and cardioprotective properties [81].
Additional key component of the MD are fermented dairy products like yogurt and cheese. Casein, the main protein in dairy milk, is digested slowly, leading to a sustained release of amino acids that supports prolonged muscle protein synthesis and reduces muscle breakdown [85]. Additionally, casein-derived bioactive peptides exhibit antihypertensive, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties, contributing to cardiometabolic health [85].
To facilitate the adoption of the MD principles, the classical MD pyramid (Figure 3A) is presented in a different perspective, focusing on its bioactive compounds (Figure 3B).
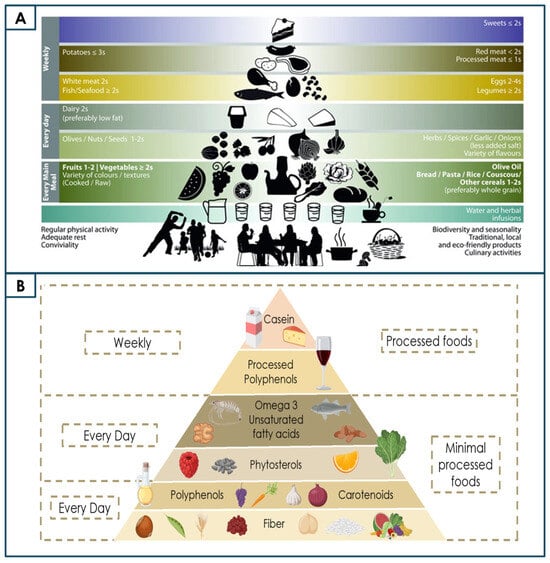
Figure 3.
(A). Classical Mediterranean Diet pyramid (adapted from [60]). (B). Proposed bioactive pyramid for the Mediterranean Diet, highlighting the main families of bioactive compounds. Panel B was created using BioRender.com.
The first Mediterranean Diet Pyramid was officially introduced in 1993 through a collaboration between the Harvard School of Public Health, the World Health Organization, and the Oldways Preservation & Exchange Trust. Similarly to the original pyramid, which provides a visual structure to convey basic options of how much and how often, the functional pyramid presented herein (Figure 3B) focuses on the principal bioactive compounds characteristic of MD foods. This approach structured foods hierarchically based on both their intake frequency and the functional relevance and bioactivity of their components. It is important to note that lifestyle elements traditionally associated with the MD (such as water consumption and physical activity, Figure 3A) were intentionally excluded, given that this model aims to exclusively represent the bioactive dimension of the diet. The pyramid clearly differentiates between processed and non-processed foods, visually reinforcing the MD’s alignment with a minimally processed, whole-foods approach. It also illustrates the plant-based nature of the diet, with the foundational layer composed primarily of plant-derived foods rich in fibre, polyphenols, carotenoids, and phytosterols. These naturally occurring compounds are found in whole foods characteristic of the MD, as well as in other sources. Collectively, they contribute to the diet’s health benefits via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms and through the modulation of the gut microbiota [32,76].
An important clarification is that the bioactive compound itself does not determine consumption frequency; rather, it is the food matrix in which the compound is present that guides its position in the hierarchy. For instance, although polyphenols are found throughout the pyramid, their intake varies according to food type and processing. This nuance reflects real-world dietary patterns within Mediterranean populations. Furthermore, some foods can be potentially allergenic (e.g., peanuts, lupins). While these legumes can contribute with valuable bioactives, such as resveratrol or flavonoids, their consumption must be individualised and assessed in the context of tolerance and dietary restrictions.
From a broader perspective, this functional pyramid provides a novel, bioactivity-focused view of the MD, highlighting the role of minimally processed, plant-based foods in promoting health. By aligning food hierarchy with bioactive content and real-world dietary patterns, it offers a practical tool for nutrition guidance and education [12].
5. Conclusions
The MD stands out as a dietary model that goes beyond its nutritional value, serving simultaneously as a tool for public health promotion and an example of environmental sustainability. A new pyramid illustrating MD’s richness in bioactive compounds with nutraceutical properties is provided. It positions the MD as a key strategy for preventing of chronic NCDs, namely through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Furthermore, by prioritizing local, seasonal, and minimally processed plant-based foods, it encourages sustainable agricultural practices. This approach can potentially reduce food waste, thereby lowering the environmental footprint of the food system. The MD is more than just a dietary pattern; it is cultural and social heritage with the potential to positively impact both human and planetary health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.C.-C. and F.C.; investigation, E.C.-C., F.C. and J.M.G.C.F.d.A.; writing—original draft preparation, E.C.-C. and F.C.; writing—review and editing, all authors; funding acquisition, G.P.C. and C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the project DM4You-“Potencial da Dieta Mediterrânica no aumento da qualidade de vida:+ saúde + sustentabilidade” by Agenda de Inovação para a Agricultura 20|30 «Terra Futura», PRR-C05-i03-I-000152 LA1.3. and PRR-C05-i03-I-000152LA1.4. and by FCT–Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., within the scope of the project UIDP/04378/2020 (DOI: 10.54499/UIDP/04378/2020) and UIDB/04378/2020 (DOI: 10.54499/UIDB/04378/2020) from the Unit of Applied Biomolecular Sciences-UCIBIO and the project LA/P/0140/2020 (DOI: 10.54499/LA/P/0140/2020) from the Associated Laboratory Institute for Health and Bioeconomy-i4HB.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| NCDs | Non-communicable Diseases |
| CVDs | Cardiovascular Diseases |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
References
- Andrews, P.; Johnson, R.J. Evolutionary basis for the human diet: Consequences for human health. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tattersall, I. Becoming modern Homo sapiens. Evol. Educ. Outreach 2009, 2, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, P.J.; Antonelli, M. Conceptual models of food choice: Influential factors related to foods, individual differences, and society. Foods 2020, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symons, M. Simmel’s gastronomic sociology: An overlooked essay. Food Foodways 1994, 5, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, J.A.; O’Mahony, G.B. Gastronomy: A phenomenon of cultural expressionism and an aesthetic for living. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2001, 20, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvache-Franco, M.; Orden-Mejía, M.; Carvache-Franco, W.; Zambrano-Conforme, D.; Carvache Franco, O. Attributes of the service that influence and predict satisfaction in typical gastronomy. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 24, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Gregory, P.J. Climate change and sustainable food production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2013, 72, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J. Role of gastronomy and new technologies in shaping healthy diets. In Gastronomy and Food Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, J.; Santich, B. A question of balance: Nutrition, health and gastronomy. Appetite 1997, 28, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, E.K. Nutraceutical-definition and introduction. AAPS Pharm. Sci. 2003, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaicu, P.A.; Untea, A.E.; Varzaru, I.; Saracila, M.; Oancea, A.G. Designing nutrition for health—Incorporating dietary by-products into poultry feeds to create functional foods with insights into health benefits, risks, bioactive compounds, food component functionality and safety regulations. Foods 2023, 12, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.P.; Costa-Camilo, E.; Duarte, I. Advancing health and sustainability: A holistic approach to food production and dietary habits. Foods 2024, 13, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.G.; Purcell, S.A.; Gold, S.L.; Christiansen, V.; D’Aloisio, L.D.; Raman, M.; Haskey, N. From Evidence to Practice: A Narrative Framework for Integrating the Mediterranean Diet into Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management. Nutrients 2025, 17, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Bryan, J.; Hodgson, J.; Murphy, K. Definition of the Mediterranean diet: A literature review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresán, U.; Cvijanovic, I.; Chevance, G. You Can Help Fight Climate Change With Your Food Choices. Front. Young Minds. 2023, 11, 1004636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, J.; De Witt, A.; Aiking, H. Help the climate, change your diet: A cross-sectional study on how to involve consumers in a transition to a low-carbon society. Appetite 2016, 98, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, C.; Haynes, R.; Oreszczyn, T.; Garrod, G. Seasonal diets: A sustainable approach to food systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Vasilopoulou, E.; Georga, K.; Soukara, S.; Dilis, V. Sustainable food consumption: A Mediterranean diet example. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Food Waste by Sector (env_wasfw). European Commission. 2024. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/env_wasfw/default/map?lang=en (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Costa-Camilo, E. Setting up the LC-MS/MS Approach for Plasma Proteomics in the DM4You Project. Instituto Superior Técnico. 2024. Available online: https://scholar.tecnico.ulisboa.pt/records/s_aDgpxSd2aeM6GCCGd-nZIDZDu1JIKieaA9 (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Parizad, S.; Bera, S. The effect of organic farming on water reusability, sustainable ecosystem, and food toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 71665–71676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Jia, N.; Lenzen, M.; Malik, A.; Wei, L.; Jin, Y.; Raubenheimer, D. Global food-miles account for nearly 20% of total food-systems emissions. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesterházy, Á.; Oláh, J.; Popp, J. Losses in the grain supply chain: Causes and solutions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Sánchez, M.V.; Torero, M.; Vos, R. Reducing food loss and waste: Five challenges for policy and research. Food Policy 2021, 98, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacka, K. Sustainable chemistry in adaptive agriculture: A review. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 46, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Zheng, L. Why is it necessary to integrate circular economy practices for agri-food sustainability from a global perspective? Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 600–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.L.; Kim, H.; Pan, S.Y.; Tseng, P.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Chiang, P.C. Implementation of green chemistry principles in circular economy system towards sustainable development goals: Challenges and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyberg, K.L.; Tonjes, D.J. Drivers of food waste and their implications for sustainable policy development. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 106, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moggi, S.; Bonomi, S.; Ricciardi, F. Against food waste: CSR for the social and environmental impact through a network-based organizational model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, K.; Ekardt, F.; Sund, L.; Roos, P. Potentials and limitations of subsidies in sustainability governance: The example of agriculture. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Ju, Z.; Zhou, P.K. A gut dysbiotic microbiota-based hypothesis of human-to-human transmission of non-communicable diseases. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, C.; Stein, E. The global burden of multiple chronic conditions: A narrative review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 12, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Scheepens, A. Vascular action of polyphenols. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.H. Health-promoting components of fruits and vegetables in the diet. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 384S–392S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts. New Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S. Eating a balanced diet: A healthy life through a balanced diet in the age of longevity. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 27, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budreviciute, A.; Damiati, S.; Sabir, D.K.; Onder, K.; Schuller-Goetzburg, P.; Plakys, G.; Katileviciute, A.; Khoja, S.; Kodzius, R. Management and prevention strategies for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and their risk factors. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 574111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Riley, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Bennett, J.E.; Solomon, B.; Singleton, R.K.; et al. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddy, F.J.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Feletou, M. Role of potassium in regulating blood flow and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R546–R552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Mahdavi, R.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Maleki, V.; Karamzad, N.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. Potential roles of Citrulline and watermelon extract on metabolic and inflammatory variables in diabetes mellitus, current evidence and future directions: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, K.; Frank, O.R.; Stocks, N.P.; Fakler, P.; Sullivan, T. Effect of garlic on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2008, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Lippi, C.; Croce, G.; Valeri, L.; Pasqualetti, P.; Desideri, G.; Blumberg, J.B.; Ferri, C. Cocoa reduces blood pressure and insulin resistance and improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in hypertensives. Hypertension 2005, 46, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.; Bowman, S.A.; Spence, S.; Freedman, M.; King, J. Popular diets: Correlation to health, nutrition, and obesity. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.E.; Nguyen, M.; Malik, V.S. Association between adherence to plant-based dietary patterns and obesity risk: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 47, 1115–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliu, P.; Santini, A.; Novellino, E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: Bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; DELLA-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jideani, A.I.; Silungwe, H.; Takalani, T.; Omolola, A.O.; Udeh, H.O.; Anyasi, T.A. Antioxidant-rich natural fruit and vegetable products and human health. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly) phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Hagen, T.M. Nutritional strategies for healthy cardiovascular aging: From oxidative stress to chronic inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Bosco, N.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Capuron, L.; Delzenne, N.; Doré; J; Visioli, F. Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A review of its effects on human health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gordon, G.B. A strategy for cancer prevention: Stimulation of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Camilo, E.; Rovisco, B.; Duarte, I.; Pinheiro, C.; Carvalho, G.P. Future-Proof a Mediterranean Soup. In International Conference on Water Energy Food and Sustainability; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, P. Breve história do conceito de dieta Mediterrânica numa perspetiva de saúde. Rev. Factores Risco 2014, 57, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Tomaino, L.; Dernini, S.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Ngo de la Cruz, J.; Bach-Faig, A.; Donini, L.M.; Medina, F.-X.; Belahsen, R.; et al. Updating the mediterranean diet pyramid towards sustainability: Focus on environmental concerns. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditano-Vázquez, P.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Galeano-Valle, F.; Pérez-Caballero, A.I.; Demelo-Rodríguez, P.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Katsiki, N.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Alvarez-Sala-Walther, L.A. The fluid aspect of the Mediterranean diet in the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: The role of polyphenol content in moderate consumption of wine and olive oil. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W. Mediterranean dietary pyramid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naska, A.; Trichopoulou, A. Back to the future: The Mediterranean diet paradigm. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B.; Drescher, G.; Trichopoulou, A.; Willett, W.C.; Martínez-González, M.A. Three Decades of the Mediterranean Diet Pyramid: A Narrative Review of Its History, Evolution, and Advances. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 122, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A. Mediterranean diet as intangible heritage of humanity: 10 years on. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakırhan, H.; Özkaya, V.; Pehlivan, M. Mediterranean diet is associated with better gastrointestinal health and quality of life, and less nutrient deficiency in children/adolescents with disabilities. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1243513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Di Bella, G.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Impact of Mediterranean diet on chronic non-communicable diseases and longevity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H. Protective mechanisms of the Mediterranean diet in obesity and type 2 diabetes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, R.; Sacanella, E.; Estruch, R. The immune protective effect of the Mediterranean diet against chronic low-grade inflammatory diseases. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Immune Endocr. Metab. Disord.) 2014, 14, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean diet: Science and practice. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.Á.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ros, E.; Covas, M.I.; Fiol, M.; Wärnberg, J.; Arós, F.; Ruíz-Gutiérrez, V.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; et al. Cohort profile: Design and methods of the PREDIMED study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K.; La Sala, L.; Pujadas, G.; De Nigris, V.; Testa, R.; Bucciarelli, L.; Rondinelli, M.; Genovese, S. The protective effect of the Mediterranean diet on endothelial resistance to GLP-1 in type 2 diabetes: A preliminary report. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccio, M.; Iacoviello, L.; de Gaetano, G.; Moli-Sani Investigators. The Mediterranean diet: The reasons for a success. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Masulli, M.; Calabrese, I.; Rivellese, A.A.; Bonora, E.; Signorini, S.; Perriello, G.; Squatrito, S.; Buzzetti, R.; Sartore, G.; et al. Impact of a Mediterranean dietary pattern and its components on cardiovascular risk factors, glucose control, and body weight in people with type 2 diabetes: A real-life study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Aiello, A.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.; Accardi, G.; Burgos-Ramos, E.; Silva, P. Olive oil components as novel antioxidants in neuroblastoma treatment: Exploring the therapeutic potential of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. Nutrients 2024, 16, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, M.R.; Nabavi, S.F.; Manayi, A.; Daglia, M.; Hajheydari, Z.; Nabavi, S.M. Resveratrol and the mitochondria: From triggering the intrinsic apoptotic pathway to inducing mitochondrial biogenesis, a mechanistic view. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, M.D.; Quiroga, J.; López, R.; Hidalgo, M.A.; Burgos, R.A. Participation of short-chain fatty acids and their receptors in gut inflammation and colon cancer. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 662739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mthembu, S.X.; Muller, C.J.; Dludla, P.V.; Madoroba, E.; Kappo, A.P.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E. Rooibos flavonoids, aspalathin, isoorientin, and orientin ameliorate antimycin A-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by improving mitochondrial bioenergetics in cultured skeletal muscle cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanaida, M.; Mykhailenko, O.; Lysiuk, R.; Hudz, N.; Balwierz, R.; Shulhai, A.; Shapovalova, N.; Shanaida, V.; Bjørklund, G. Carotenoids for Antiaging: Nutraceutical, Pharmaceutical, and Cosmeceutical Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetti, T.; Masciangelo, S.; Bicchiega, V.; Bertoli, E.; Ferretti, G. Phytosterols, phytostanols and their esters: From natural to functional foods. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 4, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Juárez, A.; Pérez-Carrillo, E.; Arredondo-Espinoza, E.U.; Islas, J.F.; Benítez-Chao, D.F.; Escamilla-García, E. Nutraceuticals and their contribution to preventing noncommunicable diseases. Foods 2023, 12, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.; Afonso, C.; Bandarra, N.M. Dietary DHA and health: Cognitive function ageing. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Hossain, R.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Islam, M.T.; Atolani, O.; Adeyemi, O.S.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Natural antioxidants from some fruits, seeds, foods, natural products, and associated health benefits: An update. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, P.L.; Chen, J.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of different drugs/agents with antioxidant property on endothelial expression of adhesion molecules. Cardiovasc. Haematol. Disord. Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord.) 2006, 6, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Dai, H.; Zhang, L. ERK5-regulated RERG expression promotes cancer progression in prostatic carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.Y.; Dar, T.A.; Singh, L.R. Casein proteins: Structural and functional aspects. In Milk Proteins—From Structure to Biological Properties and Health Aspects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).