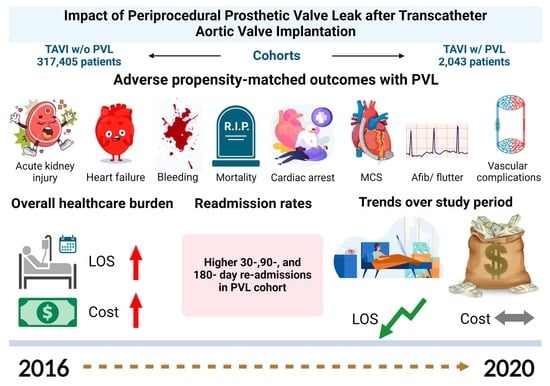
The Impact of Periprocedural Prosthetic Valve Leak After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.1.1. Baseline Characteristics
2.1.2. Study Outcomes
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Statistical Analyses
3.2.1. Outcomes After Univariate and Multivariate Regression Analysis of TAVI with PVL
3.2.2. Outcomes of Unmatched and Propensity-Matched Cohorts of TAVI with PVL
3.2.3. Outcomes After Propensity Matching and Multivariate Regression of TAVI with Mechanical Complications
3.2.4. Resource Utilization of TAVI Cohort with and Without PVL and Mechanical Complications
3.2.5. Readmission Analysis on the Propensity-Matched TAVI Cohorts with and Without PVL
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHRQ | Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality [10] |
| AHF | Acute heart failure |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| aOR | Adjusted odds ratio |
| CABG | Coronary artery bypass graft |
| CCR | Cost–charge ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DRG | Diagnosis-related group |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| HCUP | Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project [10] |
| HR HTN | Hazard ratio Hypertension |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification [11,12] |
| ICD-10-PCS | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System [14] |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| MCAR | Missing completely at random [16] |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| MNAR | Missing not at random |
| MCS | Mechanical circulatory support |
| NRD | Nationwide Readmissions Database [10] |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| PCI | Percutaneous coronary intervention |
| PSM | Propensity score matching |
| PVL | Prosthetic valve leak |
| SCA | Sudden cardiac arrest |
| TAVI | Transcatheter aortic valvular implantation |
| uOR | Unadjusted odds ratio |
| VIF | Variance inflation factor |
References
- Kawsara, A.; Sulaiman, S.; Linderbaum, J.; Coffey, S.R.; Alqahtani, F.; Nkomo, V.T.; Crestanello, J.A.; Alkhouli, M. Temporal Trends in Resource Use, Cost, and Outcomes of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in the United States. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.H.L.; Zaid, S.; Kleiman, N.S.; Goel, S.S.; Fukuhara, S.; Marin-Cuartas, M.; Kiefer, P.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; De Backer, O.; Søndergaard, L.; et al. Explant vs Redo-TAVR After Transcatheter Valve Failure: Mid-Term Outcomes From the EXPLANTORREDO-TAVR International Registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2023, 16, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belle, E.; Juthier, F.; Susen, S.; Vincentelli, A.; Iung, B.; Dallongeville, J.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Laskar, M.; Leprince, P.; Lievre, M.; et al. Postprocedural Aortic Regurgitation in Balloon-Expandable and Self-Expandable Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Procedures. Circulation 2014, 129, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá, M.P.; Jacquemyn, X.; Van den Eynde, J.; Tasoudis, P.; Erten, O.; Sicouri, S.; Macedo, F.Y.; Pasala, T.; Kaple, R.; Weymann, A.; et al. Impact of Paravalvular Leak on Outcomes After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Meta-Analysis of Kaplan-Meier-derived Individual Patient Data. Struct. Heart 2023, 7, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, W.J.; Xiang, M.; Selzer, R.H.; Hodis, H.N. Serial quantitative coronary angiography and coronary events. Am. Heart J. 2000, 139, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, T.G.; Reardon, M.J.; Popma, J.J.; Deeb, G.M.; Yakubov, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kleiman, N.S.; Chetcuti, S.; Hermiller, J.B.; Heiser, J.; et al. 5-Year Outcomes of Self-Expanding Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in High-Risk Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, M.P.B.O.; Simonato, M.; Van den Eynde, J.; Cavalcanti, L.R.P.; Roever, L.; Bisleri, G.; Dokollari, A.; Dvir, D.; Zhigalov, K.; Ruhparwar, A.; et al. Asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis, bicuspid aortic valves and moderate aortic stenosis in heart failure: New indications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 31, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, R.R.; Thourani, V.H.; Mack, M.J.; Kodali, S.K.; Kapadia, S.; Webb, J.G.; Yoon, S.-H.; Trento, A.; Svensson, L.G.; Herrmann, H.C.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of Transcatheter or Surgical Aortic-Valve Replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, M.P.B.O.; Simonato, M.; Van den Eynde, J.; Cavalcanti, L.R.P.; Alsagheir, A.; Tzani, A.; Fovino, L.N.; Kampaktsis, P.N.; Gallo, M.; Laforgia, P.L.; et al. Balloon versus self-expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation for bicuspid aortic valve stenosis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, E746–E757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA. Available online: https://www.ahrq.gov/data/hcup/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- ICD10Data.com. Available online: https://www.icd10data.com (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Cartwright, D.J. ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Codes: What? Why? How? Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, A.E.; Khan, F.L.; Singh, T.G.; Valluri, S.R.; Puzniak, L.A.; McLaughlin, J.M. Proportion of patients in the United States who fill their Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir prescriptions. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2024, 13, 2035–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2025 ICD-10-PCS|CMS. Available online: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coding-billing/icd-10-codes#CodeFiles (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Charlson, M.E.; Carrozzino, D.; Guidi, J.; Patierno, C. Charlson Comorbidity Index: A Critical Review of Clinimetric Properties. Psychother Psychosom 2022, 91, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutenburg, H.; Little, R.J.A.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical analysis with missing data. Stat. Pap. 1991, 32, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Image and Illustration Software|BioRender. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Laakso, T.; Laine, M.; Moriyama, N.; Dahlbacka, S.; Airaksinen, J.; Virtanen, M.; Husso, A.; Tauriainen, T.; Niemelä, M.; Mäkikallio, T.; et al. Impact of paravalvular regurgitation on the mid-term outcome after transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2020, 58, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, S.; Pibarot, P.; Douglas, P.S.; Williams, M.; Xu, K.; Thourani, V.; Rihal, C.S.; Zajarias, A.; Doshi, D.; Davidson, M.; et al. Paravalvular regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement with the Edwards sapien valve in the PARTNER trial: Characterizing patients and impact on outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Briasoulis, A.; Telila, T.; Afonso, L.; Grines, C.L.; Takagi, H. Does mild paravalvular regurgitation post transcatheter aortic valve implantation affect survival? A meta-analysis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 91, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popma, J.J.; Adams, D.H.; Reardon, M.J.; Yakubov, S.J.; Kleiman, N.S.; Heimansohn, D.; Hermiller, J.; Hughes, G.C.; Harrison, J.K.; Coselli, J.; et al. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Using a Self-Expanding Bioprosthesis in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis at Extreme Risk for Surgery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Umemoto, T. Impact of paravalvular aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation on survival. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibarot, P.; Hahn, R.T.; Weissman, N.J.; Arsenault, M.; Beaudoin, J.; Bernier, M.; Dahou, A.; Khalique, O.K.; Asch, F.M.; Toubal, O.; et al. Association of Paravalvular Regurgitation With 1-Year Outcomes After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With the SAPIEN 3 Valve. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azraai, M.; Gao, L.; Ajani, A.E. Cost-Effectiveness of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Intervention (TAVI) Compared to Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (SAVR) in Low- to Intermediate-Surgical-Risk Patients. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2020, 21, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, Y.-J.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.S.; Chang, M.; Han, J.-K.; Yang, H.-M.; Park, K.W.; Kang, H.-J.; Koo, B.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Optimal Oversizing Index Depending on Valve Type and Leakage-Proof Function for Preventing Paravalvular Leakage after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.R.; Nishimura, R.A.; Grover, F.L.; Brindis, R.G.; Carroll, J.D.; Edwards, F.H.; Peterson, E.D.; Rumsfeld, J.S.; Shahian, D.M.; Thourani, V.H.; et al. Annual Outcomes With Transcatheter Valve Therapy: From the STS/ACC TVT Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliger, C.; Eiros, R.; Isasti, G.; Einhorn, B.; Jelnin, V.; Cohen, H.; Kronzon, I.; Perk, G.; Fontana, G.P.; Ruiz, C.E. Review of surgical prosthetic paravalvular leaks: Diagnosis and catheter-based closure. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deharo, P.; Leroux, L.; Theron, A.; Ferrara, J.; Vaillier, A.; Jaussaud, N.; Porto, A.; Morera, P.; Gariboldi, V.; Iung, B.; et al. Long-Term Prognosis Value of Paravalvular Leak and Patient–Prosthesis Mismatch following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: Insight from the France-TAVI Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pais, J.; Lopez-Otero, D.; Garcia-Touchard, A.; Coronel, B.I.; Muiños, P.J.A.; Mendioroz, X.C.; Pérez-Poza, M.; Garcia, Ó.O.; Peredo, C.G.M.; Flores, C.A.; et al. Impact of significant paravalvular leaks after transcatheter aortic valve implantation on anaemia and mortality. Heart 2021, 107, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagar, A.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shah, J.P.; Sihag, V.; et al. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcome of Paravalvular Leak after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2020, 2020, 8249497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoechlin, S.; Hein, M.; Brennemann, T.; Eichenlaub, M.; Schulz, U.; Jander, N.; Neumann, F.J. 5-Year outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Focus on paravalvular leakage assessed by echocardiography and hemodynamic parameters. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 99, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, M.P.; Van den Eynde, J.; Jacquemyn, X.; Tasoudis, P.; Erten, O.; Dokollari, A.; Torregrossa, G.; Sicouri, S.; Ramlawi, B. Late outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in bicuspid versus tricuspid valves: Meta-analysis of reconstructed time-to-event data. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 33, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Liu, X.M.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, H.J.; Xu, L.; Xia, K.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhong, J.C.; Chen, M.L.; et al. Comparisons of different new-generation transcatheter aortic valve implantation devices for patients with severe aortic stenosis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 2414–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, A.S.; Redwood, S.R.; Allen, C.J.; Hurrell, H.; Chehab, O.; Rajani, R.; Prendergast, B.; Patterson, T. A 20-year journey in transcatheter aortic valve implantation: Evolution to current eminence. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 971762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Study Variables | ICD-10-CM Code |
|---|---|
| Acute kidney injury | N170, N171, N172, N178, N179, N1 |
| Alcohol use | “F101, F1010, F1011, F1012, F10120, F10121, F10129, F1014, F1015, F10150, F10151, F10159, F1018, F10180, F10181, F10182, F10188, F1019, F102, F1020, F1021, F1022, F10220, F10221, F10229, F1023, F10230, F10231, F10232, F10239, F1024, F1025, F10250, F10251, F10259, F1026, F1027, F1028, F10280, F10281, F10282, F10288, F1029, F10920, F10921, F10929, F1094, F1095, F10950, F10951, F10959, F1096, F1097, F1098, F10980, F10981, F10982, F10988, F1099” [14] * |
| Anemia | D50, D51, D52, D53, D55, D56, D57, D58, D59, D60, D61, D62, D63, D64, D46.0, D46.1, D46.2, D46.4, O99.0 |
| Aortic valve replacement/repair | 02RF07, 02RF08, 02RF0K, 02RF0J, 02RF47, 02RF48, 02RF4J, 02RF4K, 02QF0Z, 02QF4Z, 02UF07, 02UF08, 02UF0J, 02UF0K, 02UF47, 02UF48, 02UF4J, 02UF4K |
| Atrial fibrillation/flutter | I48 family |
| Breakdown of prosthetic heart valve | T8201XA, T8201XD, T8201XS |
| Cardiogenic shock | R570 |
| Chronic kidney disease stage ≥3 | N183, N184, N185, E082, E132, I12, I13 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | J449 |
| Coronary artery disease | “I2510, I25111, I25118, I25119, I252, I253, I254, I2541, I2542, I255, I256, I257, I2570, I25700, I25701, I25708, I25709, I2571, I25710, I25711, I25718, I25719, I2572, I25720, I25721, I25728, I25729, I2573, I25730, I25731, I25738, I25739, I2575, I25750, I25751, I25758, I25759, I2576, I25760, I25761, I25768, I25769, I2579, I25790, I25791, I25798, I25799, I258, I2581, I25810, I25811, I25812, I2582, I2583, I2584, I2589, I259” [14] * |
| Diabetes mellitus | E08-E13 family |
| Displacement of prosthetic heart valve | T8202XA, T8202XD, T8202XS |
| End stage renal disease | N186, Z992, Z4931, Z4901 |
| Heart failure | I50, I501, I502, I5020, I5021, I5022, I5023, I503, I5030, I5031, I5032, I5033, I504, I5040, I5041, I5042, I5043, I508, I5081, I50810, I50811, I50812, I50813, I50814, I5082, I5083, I5084, I5089, I509 |
| History of stroke | I69.3, Z86.73 |
| Hypertension | I10, I1150, I1151, I1152, I1158, I1159 |
| Mechanical circulatory support | 5A02110, 5A02210, 5A0211D, 02HA3RZ, 5A02116, 5A0221D, 5A1522F, 5A1522G, 5A1522H, 5A15A2F, 5A15A2G, 5A15A2H |
| Mitral stenosis | Non-rheumatic (I342); Rheumatic (I050, I052) |
| Mitral valve replacement/repair | 02RG07, 02RG08, 02RG0J, 02RG0K, 02RG47, 02RG48, 02RG4J, 02RG4K, 02QG0Z, 02QG4Z,02UG07, 02UG08, 02UG0J, 02UG0K, 02UG47, 02UG48, 02UG4J, 02UG4K |
| Obesity | E66, Z683, Z684, R939, Z6854, 09921 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | G47.33 |
| Other non-specific valve complications | T8209XA, T8209XD, T8209XS |
| Peripheral vascular disease | E08.5, E09.5, E10.5, E11.5, E13.5, I73, T82.856, Z98.62, Z95.820, I25.2, I25.83 |
| Prior coronary artery bypass graft | Z951 |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 1252 |
| Prior percutaneous coronary intervention | Z955 |
| Postprocedural bleeding | I97418, I9742, I97618, I97620, I97638, I97631, I97621, I9742, I97418, I97411, I97611, I97410, I97610, I97630, I97410 |
| Prosthetic valve leak | T8203XA, T8203XD, T8203XS |
| Pulmonary valve replacement/repair | 02RH07, 02RH08, 02RH0J, 02RH0K, 02RH47, 02RH48, 02RH4J, 02RH4K, 02QH0Z, 02QH4Z, 02UH07, 02UH08, 02UH0J, 02UH0K, 02UH47, 02UH48, 02UH4J, 02UH4K |
| Smoker | F17, Z87.891 |
| Transcatheter aortic valve implantation | 02RF37, 02RF37H, 02RF37Z, 02RF38, 02RF38H, 02RF38Z, 02RF3J, 02RF3JH, 02RF3JZ, 02RF3K, 02RF3KH, 02RF3KZ, 02RF4, 02RF47, 02RF47Z, 02RF48, 02RF48Z, 02RF4J, 02RF4JZ, 02RF4K, 02RF4KZ |
| Transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement | 02RH37H, 02RH37Z, 02RH38H, 02RH38Z, 02RH3JH, 02RH3JZ, 02RH3KH, 02RH3KZ |
| Tricuspid valve replacement/repair | 02RJ07, 02RJ08, 02RJ0J, 02RJ0K, 02RJ47, 02RJ480, 02RJ4J, 02RJ4K, 02QJ0Z, 02QJ4Z, 02UJ07, 02UJ08, 02UJ0J, 02UJ0K, 02UJ47, 02UJ48, 02UJ4J, 02UJ4K |
| Vascular complications | S15, S25, S35, S55, S65, S75, S85, T817, T8183XA, T8183XS, I770, I97621, I97630, I97631, I97638 |
| Outcomes | Definition |
|---|---|
| Acute kidney injury | Any acute kidney injury in TAVI patients during the hospital stay |
| Cardiogenic shock | Shock resulting from primary failure of the heart in its pumping function, as in myocardial infarction, severe cardiomyopathy, mechanical obstruction, or compression of the heart |
| Cost of hospitalization | The total adjusted amount that hospitals billed for their services for the duration of hospitalization |
| Length of stay (LOS) | The entire length of stay the patient spent in the hospital during the admission |
| Mechanical circulatory support | Any type of circulatory support with a balloon pump, impeller pump, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), or external heart assist system utilization during the index hospitalization |
| Mortality | All causes of death, including cardiovascular causes such as sudden cardiac death, death due to acute myocardial infarction, heart failure or cardiogenic shock, and non-cardiovascular causes |
| Postprocedural bleeding | Any major bleeding or hematoma during or after the procedure |
| Prosthetic valve leak | Leakage of prosthetic valve post-TAVI identified during the index hospitalization |
| Resource utilization | Calculated utilizing length of stay, inflation-adjusted total cost of the index hospitalization, including any reintervention or intensive care stays during index hospitalization. Subsequently, similar methodology was utilized to determine cost of hospitalization for readmission at 30, 90, and 180 days. |
| Valve complications | Valve breakdown, embolization, or other non-specified complications post-TAVI identified during the index hospitalization |
| Vascular complications | Any vascular injury as a complication of the procedure during the hospitalization post-TAVI |
| Variables Included in Multiple Regression |
|---|
| Age |
| Chronic kidney disease stage > 3 |
| Chronic heart failure |
| Chronic pulmonary disease |
| Coronary artery disease |
| COVID-19 |
| Deficiency anemia |
| Diabetes mellitus |
| End stage renal disease |
| Elective/non-elective admission |
| Family history of coronary artery disease |
| Gender |
| Hemodialysis |
| Hospital bed size |
| Hospital location and teaching status |
| Hospital region |
| Hyperlipidemia |
| Hypertension |
| Hypothyroidism |
| Obesity |
| Obstructive sleep apnea |
| Payer |
| Prior cerebral vascular accident |
| Prior coronary artery bypass graft |
| Prior myocardial infarction |
| Prior percutaneous coronary intervention |
| Pulmonary circulation disorder |
| Pulmonary hypertension |
| Rehab transfer |
| Resident |
| Weekend admission |
| Weight loss |
| TAVI Without PVL n = 317,405 | TAVI with PVL n = 2043 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median + interquartile range) | |||
| 80 (12) | 79 (13) | <0.01 | |
| Indicator of sex | |||
| Male | 176,444 (55.6%) | 1353.10 (66.2%) | <0.001 |
| Female | 140,960 (44.4%) | 690.60 (33.8%) | |
| Insurance type | |||
| Medicare | 284,526 (89.7%) | 1793.80 (87.9%) | 0.502 |
| Medicaid | 3820 (1.2%) | 39 (1.9%) | |
| Private insurance | 21,250 (6.7%) | 159.30 (7.8%) | |
| Self-pay | 1060 (0.3%) | 10.3 (<1%) | |
| Other | 6326 (2.%) | 39.30 (1.9%) | |
| Type of admission | |||
| Non-elective | 54,989.7 (17.4%) | 544.40 (26.6%) | <0.001 |
| Elective | 261,786.1 (82.6%) | 1499.30 (73.4%) | |
| Bed size of the hospital | |||
| Small | 15,728.5 (5.%) | 47 (2.3%) | 0.058 |
| Medium | 69,442 (21.9%) | 490.90 (24.%) | |
| Large | 232,234 (73.2%) | 1505.80 (73.7%) | |
| Teaching status of urban hospitals | |||
| Metropolitan non-teaching | 33,621.10 (10.6%) | 190.80 (9.3%) | 0.539 |
| Metropolitan teaching | 280,698.80 (88.4%) | 1828.90 (89.5%) | |
| Non-metropolitan hospital | 3084.70 (1.00%%) | 24 (1.2%) | |
| Hospital urban–rural designation | |||
| Large metropolitan areas with at least 1 million residents | 187,116.60 (59.%) | 1392.70 (68.1%) | <0.001 |
| Small metropolitan areas with less than 1 million residents | 127,203.20 (40.1%) | 627 (30.7%) | |
| Micropolitan areas | 3017.20 (1%) | 21.2 (1%) | |
| Admission day of the week | |||
| Mon–Fri | 306,417.20 (96.5%) | 1944.10 (95.1%) | 0.101 |
| Sat–Sun | 10,985.40 (3.5%) | 99.6 (4.9%) | |
| Transfer flag indicating combination of discharges involving same-day events | |||
| Not a transfer or other same-day stay | 304,517.80 (95.90%) | 1888.10 (92.40%) | <0.001 |
| Transfer involving two discharges from different hospitals | 6723.10 (2.10%) | 94.1 (4.60%) | |
| Same-day stay involving two discharges from different hospitals | 2743 (0.90%) | 28.8 (1.40%) | |
| Same-day stay involving two discharges at the same hospitals | 2314.30 (0.70%) | 17.4 (0.90%) | |
| Same-day stay involving three or more discharges at the same or different hospitals | 1106.50 (0.30%) | 15.3 (0.70%) | |
| Median household income national quartile for patient ZIP code | |||
| 0–25th percentile | 65,064.90 (20.70%) | 372.6 (18.50%) | 0.039 |
| 26th to 50th percentile | 87,288.20 (27.80%) | 549.3 (27.20%) | |
| 51st to 75th percentile | 85,584.10 (27.30%) | 512.9 (25.40%) | |
| 76th to 100th percentile | 75,669.10 (24.10%) | 582.1 (28.90%) | |
| Control/ownership of hospital | |||
| Public | 25,225.50 (7.90%) | 198.8 (9.70%) | 0.124 |
| Private non-profit | 262,429.40 (82.70%) | 1695.80 (83.0%) | |
| Private for profit | 29,749.80 (9.40%) | 149.1 (7.30%) | |
| A combined record involving rehab transfer | |||
| Not a combined record or a combined record not involving rehabilitation, evaluation, or other aftercare | 314,871 (99.20%) | 2011.70 (98.40%) | 0.017 |
| Combined record involving transfer to rehabilitation, evaluation, or other aftercare | 2533.6 (<1%) | 32 (1.60%) | |
| All patient refined diagnosis-related group: risk of mortality subclass | |||
| Minor likelihood of dying | 36,806.10 (11.60%) | 105.2 (5.10%) | <0.001 |
| Moderate likelihood of dying | 144,320.60 (45.50%) | 588.2 (28.80%) | |
| Major likelihood of dying | 108,728.60 (34.30%) | 967.8 (47.40%) | |
| Extreme likelihood of dying | 27,544.90 (8.70%) | 382.4 (18.70%) | |
| All patient refined diagnosis-related group: severity of illness subclass | |||
| Minor loss of function (includes cases with no comorbidity or complications) | 34,115 (10.70%) | 62.6 (3.10%) | <0.001 |
| Moderate loss of function | 77,171.20 (24.30%) | 255.9 (12.50%) | |
| Major loss of function | 50,937.5 (16.0%) | 577.9 (28.30%) | |
| Extreme loss of function | 155,176.40 (48.90%) | 1147.4 (56.10%) | |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Anemia | 16,369.70 (5.2%) | 132.10 (6.5%) | 0.128 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 120,701.90 (38.%) | 657.4 (32.2%) | 0.001 |
| Heart failure | 229,229.10 (72.2%) | 1620.10 (79.3%) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 232,502.90 (73.3%) | 1423.10 (69.6%) | 0.046 |
| Hypertension | 214,716.90 (67.6%) | 1473.10 (72.1%) | 0.018 |
| Hypothyroid | 59,188.40 (18.6%) | 375.90 (18.4%) | 0.891 |
| Liver disease | 4787.50 (1.5%) | 29.8 (1.5%) | 0.912 |
| Obesity | 65,920 (20.8%) | 364.80 (17.9%) | 0.064 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | 46,637.70 (14.7%) | 270.1 (13.2%) | 0.252 |
| Pneumonia | 4430.40 (1.4%) | 64.60 (3.2%) | <0.001 |
| Prior coronary artery bypass graft | 50,275.30 (15.8%) | 444 (21.7%) | <0.001 |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 37,917.70 (11.9%) | 258.60 (12.7%) | 0.566 |
| Prior percutaneous coronary intervention | 61,625.30 (19.4%) | 372.7 (18.2%) | 0.541 |
| Pulmonary disease | 65,411.20 (20.6%) | 410.60 (20.1%) | 0.719 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 36,927 (11.6%) | 257(12.6%) | 0.428 |
| Right ventricular failure | 1335 (0.4%) | 33 (1.6%) | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 113,184.40 (35.7%) | 706.60 (34.6%) | 0.569 |
| In-Hospital Outcomes | Univariate Regression Analysis | Multivariate Regression Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| uOR | 95% CI | p-Value | aOR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Acute congestive heart failure | 1.50 | 1.28–1.7 | <0.001 | 1.40 | 1.19–1.66 | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury | 2.54 | 2.0–3.2 | <0.001 | 2.42 | 1.82–3.18 | <0.001 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1.74 | 1.17–2.59 | <0.001 | 1.45 | 0.94–2.23 | 0.089 |
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 1.35 | 1.17–1.56 | <0.001 | 1.36 | 1.18–1.57 | <0.001 |
| Cardiac tamponade | 2.91 | 1.24–6.83 | 0.014 | 2.95 | 1.22–7.09 | 0.016 |
| Cardiogenic shock | 4.2 | 3.0–5.8 | <0.001 | 3.4 | 2.38–4.89 | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality | 2.52 | 1.6–3.97 | <0.001 | 2.16 | 1.35–3.45 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical circulatory support | 3.81 | 2.16–6.73 | <0.001 | 2.94 | 1.58–5.47 | <0.001 |
| Post procedural bleeding | 1.79 | 1.20–2.66 | <0.001 | 1.70 | 1.14–2.55 | <0.001 |
| Vascular complications | 1.81 | 1.24–2.64 | <0.001 | 1.76 | 1.20–2.57 | <0.001 |
| Outcomes | Crude Outcomes | Propensity-Matched Outcomes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI Without PVL n = 317,405 | TAVI with PVL n = 2043 | p-Value | TAVI Without PVL n = 1147 | TAVI with PVL n = 1147 | p-Value | |
| Acute congestive heart failure | 129,153 (40.7%) | 1036 (50.7%) | <0.001 | 472 (41.1%) | 569 (49.6%) | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury | 31,027 (9.8%) | 442 (21.6%) | <0.001 | 135 (11.7%) | 234 (20.4%) | <0.001 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 6732 (2.1%) | 74 (3.6%) | 0.005 | 35 (3.05%) | 39 (3.4%) | 0.636 |
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 122,011 (38.4%) | 937 (45.9%) | <0.001 | 443 (38.6%) | 514 (44.8%) | 0.003 |
| Cardiogenic shock | 6561 (2.1%) | 167 (8.2%) | <0.001 | 29 (2.5%) | 86 (7.5%) | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality | 2823(1.3%) | 66 (3.3%) | <0.001 | 12 (1.05%) | 35 (3.05%) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical circulatory support | 2823 (0.89%) | 67 (3.3%) | <0.001 | 20 (1.7%) | 30 (2.6%) | 0.153 |
| Postprocedure bleeding | 6246(2.0%) | 71 (3.5%) | 0.004 | 17 (1.48%) | 41 (3.57%) | <0.001 |
| Sudden cardiac arrest | 27,651 (8.7%) | 312 (15.3%) | <0.001 | 98 (8.5%) | 176 (15.34%) | <0.001 |
| Vascular complications | 7800 (2.5%) | 89 (4.4%) | 0.002 | 18 (1.57%) | 47 (4.1%) | <0.001 |
| Outcomes | Propensity-Matched Cohort | Adjusted Odds Ratios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Mechanical Complications n = 1414 | With Mechanical Complications n = 1414 | p-Value | aOR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| n (%) | n (%) | |||||
| Acute congestive heart failure | 623 (44.03) | 881 (62.26) | <0.001 | 2.25 | 1.94–2.63 | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury | 168 (11.87) | 326 (23.04) | <0.001 | 2.58 | 2.15–3.08 | <0.001 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 36 (2.54) | 67 (4.73) | 0.002 | 1.98 | 1.40–2.80 | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 536 (37.88) | 628 (44.38) | <0.001 | 1.34 | 1.17–1.54 | <0.001 |
| Cardiogenic shock | 51 (3.60) | 125 (8.83) | <0.001 | 3.3 | 2.53–4.31 | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality | 19 (1.34) | 65 (4.60) | <0.001 | 3.64 | 2.57–5.16 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical circulatory support | 21 (1.48) | 57 (4.03) | <0.001 | 3.35 | 2.39–4.71 | <0.001 |
| Postprocedure bleeding | 22 (1.55) | 43 (3.04) | 0.008 | 1.67 | 1.12–2.50 | 0.011 |
| Sudden cardiac arrest | 114 (8.06) | 184 (13) | <0.001 | 1.60 | 1.34–1.91 | <0.001 |
| Vascular complications | 30 (2.12) | 62 (4.38) | 0.001 | 2.03 | 1.50–2.74 | <0.001 |
| Resource Utilization | Without PVL | With PVL | p-Value | Without Mechanical Complications | With Mechanical Complications | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |||
| LOS in Days | 2 (3) | 3 (6) | <0.001 | 2 (3) | 3 (7) | <0.001 |
| Adjusted Total Charge | 176,354 (129,426) | 219,953 (169,018) | <0.001 | 176,392 (129,328) | 204,511 (166,063) | <0.001 |
| Total Cost | 45,339 (23,547) | 54,751 (35,037) | <0.001 | 45,341 (23,559) | 50,986 (29,661) | <0.001 |
| Year | Total Cost Yearly Trend | Length of Stay Yearly Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | |
| Median | Median | Median | Median | |
| 2016 | 50,801 (65,675–39,179) | 60,297 (77,712–48,221) | 3 (6–2) | 5 (10–3) |
| 2017 | 47,131 (60,930–36,913) | 55,562 (73,557–42,004) | 2 (5–2) | 3 (8–2) |
| 2018 | 45,224 (58,590–35,538) | 51,891 (74,054–37,348) | 2 (4–1) | 3 (7–2) |
| 2019 | 43,533 (57,087–34,081) | 51,525 (72,424–39,066) | 2 (3–1) | 3 (9–2) |
| 2020 | 46,199 (61,312–35,942) | 57,763 (80,647–42,591) | 1 (3–1) | 2 (7–1) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | 0.2802 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Readmission Rates in Propensity-Matched Cohorts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30-day Readmissions | Without PVL | With PVL | p-value |
| n = 1016 | n = 1016 | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Readmits | 122 (12) | 155 (15.2) | 0.023 |
| 90-day Readmissions | Without PVL | With PVL | p-value |
| n = 812 | n = 812 | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Readmits | 162 (19.9) | 198 (24.4) | <0.01 |
| 180-day Readmissions | Without PVL | With PVL | p-value |
| n = 521 | n = 521 | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Readmits | 129 (24.8) | 181 (34.7) | <0.01 |
| 30-Day Readmission Causes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICD-10 Code | ICD-10 Diagnosis | Count | Percentages (%) |
| I350 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis | 22,637.1 | 75.9 |
| I352 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis with insufficiency | 1928.768 | 6.5 |
| I080 | Rheumatic disorders of both mitral and aortic valves | 1479.659 | 5.0 |
| I083 | Combined rheumatic disorders of mitral, aortic and tricuspid valves | 1041.29 | 3.5 |
| T82857A | Stenosis of other cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 684.0428 | 2.3 |
| Q231 | Congenital insufficiency of aortic valve | 249.5053 | 0.8 |
| I130 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | 226.9943 | 0.8 |
| I082 | Rheumatic disorders of both aortic and tricuspid valves | 162.404 | 0.5 |
| I214 | Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction | 122.5465 | 0.4 |
| I351 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) insufficiency | 120.8068 | 0.4 |
| T82897A | Other specified complication of cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 100.2057 | 0.3 |
| I110 | Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure | 91.08601 | 0.3 |
| I060 | Rheumatic aortic stenosis | 62.9384 | 0.2 |
| I132 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease | 50.7093 | 0.2 |
| T82228A | Other mechanical complication of biological heart valve graft, initial encounter | 35.81099 | 0.1 |
| I5043 | Acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 34.5458 | 0.1 |
| I5033 | Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 32.08654 | 0.1 |
| T8209XA | Other mechanical complication of heart valve prosthesis, initial encounter | 30.77705 | 0.1 |
| T8203XA | Leakage of heart valve prosthesis, initial encounter | 29.33904 | 0.1 |
| A419 | Sepsis, unspecified organism | 23.98208 | 0.1 |
| 90-Day Readmission Causes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICD-10 Code | ICD-10 Diagnosis | Count | Percentage (%) |
| I350 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis | 34,014.22 | 73.9 |
| I352 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis with insufficiency | 3044.265 | 6.6 |
| I080 | Rheumatic disorders of both mitral and aortic valves | 2297.723 | 5.0 |
| I083 | Combined rheumatic disorders of mitral, aortic and tricuspid valves | 1570.149 | 3.4 |
| T82857A | Stenosis of other cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 1249.885 | 2.7 |
| I130 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | 466.6844 | 1.0 |
| Q231 | Congenital insufficiency of aortic valve | 359.0492 | 0.8 |
| I082 | Rheumatic disorders of both aortic and tricuspid valves | 284.2048 | 0.6 |
| I214 | Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction | 228.4911 | 0.5 |
| T82897A | Other specified complication of cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 199.5951 | 0.4 |
| I351 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) insufficiency | 197.9469 | 0.4 |
| I110 | Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure | 159.5987 | 0.3 |
| I060 | Rheumatic aortic stenosis | 111.0938 | 0.2 |
| I132 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease | 95.46474 | 0.2 |
| I5043 | Acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 73.09896 | 0.2 |
| T8209XA | Other mechanical complication of heart valve prosthesis, initial encounter | 72.47526 | 0.2 |
| T82228A | Other mechanical complication of biological heart valve graft, initial encounter | 61.68306 | 0.1 |
| A419 | Sepsis, unspecified organism | 60.80909 | 0.1 |
| I5023 | Acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure | 58.33688 | 0.1 |
| I5033 | Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 55.18985 | 0.1 |
| 180-Day Readmission Causes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICD-10 Code | ICD-10 Diagnosis | Count | Percentage (%) |
| I350 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis | 30,957.7 | 74.0 |
| I352 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) stenosis with insufficiency | 2810.865 | 6.7 |
| I080 | Rheumatic disorders of both mitral and aortic valves | 2003.486 | 4.8 |
| I083 | Combined rheumatic disorders of mitral, aortic and tricuspid valves | 1408.717 | 3.4 |
| T82857A | Stenosis of other cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 1169.29 | 2.8 |
| I130 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | 404.2754 | 1.0 |
| Q231 | Congenital insufficiency of aortic valve | 309.6377 | 0.7 |
| I082 | Rheumatic disorders of both aortic and tricuspid valves | 265.4324 | 0.6 |
| I214 | Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction | 225.5222 | 0.5 |
| I351 | Nonrheumatic aortic (valve) insufficiency | 198.491 | 0.5 |
| T82897A | Other specified complication of cardiac prosthetic devices, implants and grafts, initial encounter | 183.0957 | 0.4 |
| I110 | Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure | 150.0879 | 0.4 |
| I132 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease | 95.45225 | 0.2 |
| I060 | Rheumatic aortic stenosis | 86.65321 | 0.2 |
| T8209XA | Other mechanical complication of heart valve prosthesis, initial encounter | 68.50824 | 0.2 |
| I5043 | Acute on chronic combined systolic (congestive) and diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 65.36945 | 0.2 |
| T82228A | Other mechanical complication of biological heart valve graft, initial encounter | 60.17539 | 0.1 |
| I5033 | Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure | 59.84858 | 0.1 |
| A419 | Sepsis, unspecified organism | 52.57824 | 0.1 |
| I5023 | Acute on chronic systolic (congestive) heart failure | 50.53654 | 0.1 |
| Year | Inflation-Adjusted Total Cost Yearly Trend | Length of Stay Yearly Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| 2016 | 53,401 (67,520–41,147) | 49,921 (60,191–41,112) | 4 (7–2) | 4 (5–3) |
| 2017 | 47,748 (61,654–37,354) | 55,562 (65,246–44,192) | 3 (6–2) | 4 (10–2) |
| 2018 | 46,527 (61,220–36,564) | 50,024 (74,784–37,255) | 3 (5–2) | 5 (9–2) |
| 2019 | 45,238 (58,813–35,143) | 47,385 (78,422–36,637) | 2 (5–1) | 3 (6–2) |
| 2020 | 48,440 (63,441–36,669) | 65,430 (83,920–41,659) | 2 (4–1) | 3.5 (6.5–1.5) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | 0.7116 | <0.001 | 0.3014 |
| Year | Inflation-Adjusted Total Cost Yearly Trend | Length of Stay Yearly Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| 2016 | 54,167 (70,107–41,343) | 60,191 (103,561–39,737) | 4 (8–2) | 4 (18–3) |
| 2017 | 49,084 (65,183–37,838) | 55,562 (67,671–44,192) | 3 (7–2) | 4 (10–2) |
| 2018 | 47,800 (63,195–36,930) | 60,550 (80,142–38,036) | 3 (7–2) | 6 (15–2) |
| 2019 | 45,856 (60,878–35,179) | 51,897 (93,976–39,799) | 2 (6–1) | 4 (12–2) |
| 2020 | 49,239 (65,833–37,084) | 63,054 (87,055–45,033 | 2 (5–1) | 3 (9–2) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | 0.8631 | <0.001 | 0.0997 |
| Year | Inflation-Adjusted Total Cost Yearly Trend | Length of Stay Yearly Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | TAVI Without PVL | TAVI with PVL | |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |
| 2016 | 53,806 (69,992–41,117) | 67,034 (102,446–47,702) | 4 (8–2) | 4.5 (18–3) |
| 2017 | 48,770 (64,507–37,141) | 59,523 (75,619–44,420) | 3 (7–2) | 4 (11–2) |
| 2018 | 47,665 (62,790–36,927) | 62,097 (94,344–41,768) | 3 (6–2) | 6 (15–3) |
| 2019 | 45,384 (60,386–35,006) | 50,899 (86,077–38,923) | 2 (6–1) | 4 (12–2) |
| 2020 | 48,717 (64,272–37,101) | 55,352 (83,162–37,752) | 2 (5–1) | 3 (9–1) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | 0.1581 | 0.0554 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Duhan, S.; Alsaeed, T.; Atti, L.; Farooq, F.; Keisham, B.; Berry, R.; Sattar, Y.; Munir, A.; Brar, V.; et al. The Impact of Periprocedural Prosthetic Valve Leak After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Complications 2025, 2, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/complications2020009
Ali S, Duhan S, Alsaeed T, Atti L, Farooq F, Keisham B, Berry R, Sattar Y, Munir A, Brar V, et al. The Impact of Periprocedural Prosthetic Valve Leak After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Complications. 2025; 2(2):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/complications2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Shafaqat, Sanchit Duhan, Thannon Alsaeed, Lalitsiri Atti, Faryal Farooq, Bijeta Keisham, Ryan Berry, Yasar Sattar, Ahmad Munir, Vijaywant Brar, and et al. 2025. "The Impact of Periprocedural Prosthetic Valve Leak After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation" Complications 2, no. 2: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/complications2020009
APA StyleAli, S., Duhan, S., Alsaeed, T., Atti, L., Farooq, F., Keisham, B., Berry, R., Sattar, Y., Munir, A., Brar, V., Helmy, T. A., Alraies, M. C., & Brašić, J. R. (2025). The Impact of Periprocedural Prosthetic Valve Leak After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation. Complications, 2(2), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/complications2020009