Statistical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Consumer Drone Photogrammetry at a Romanesque Church in Eastern Bavaria (Germany)
Abstract
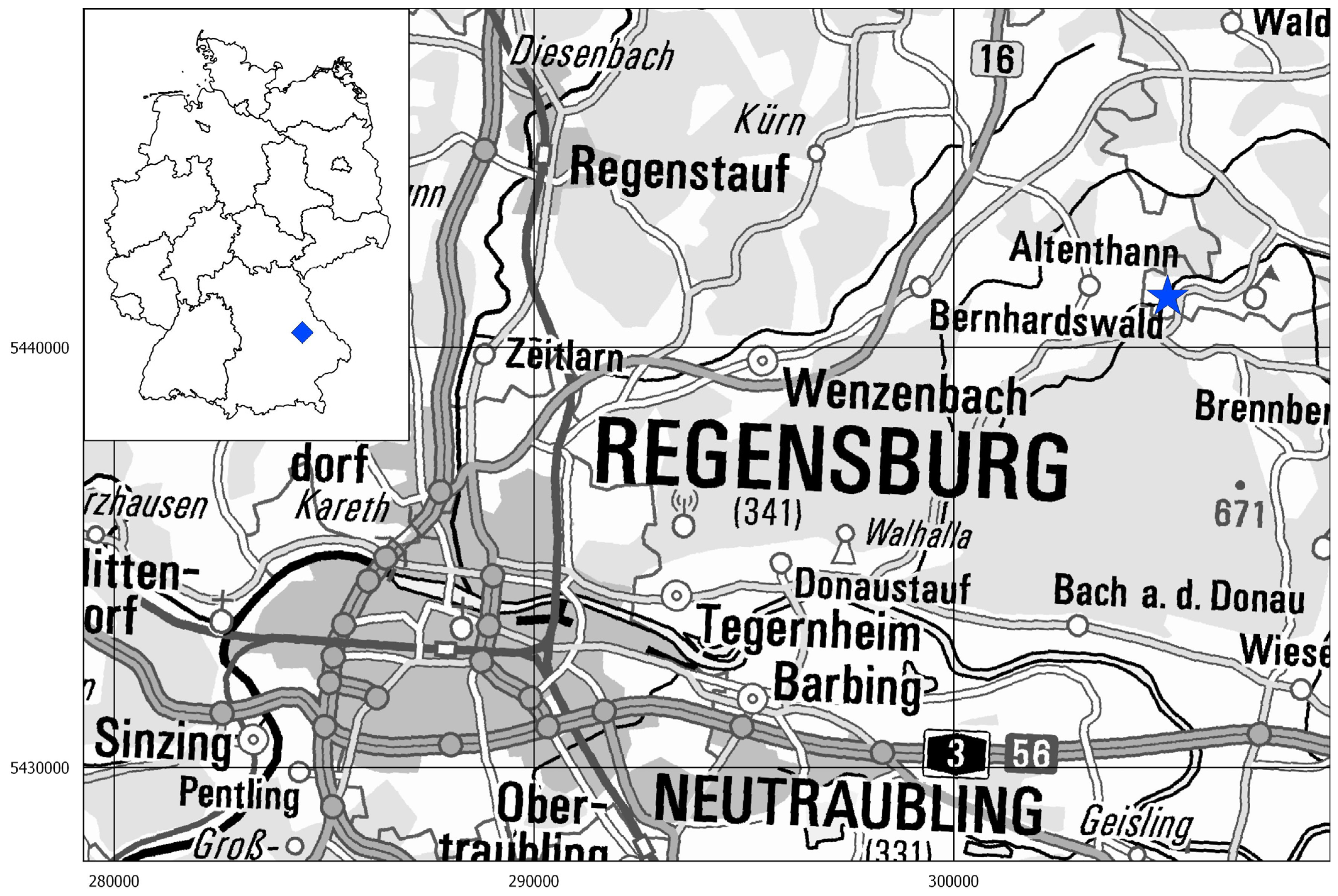
1. Introduction
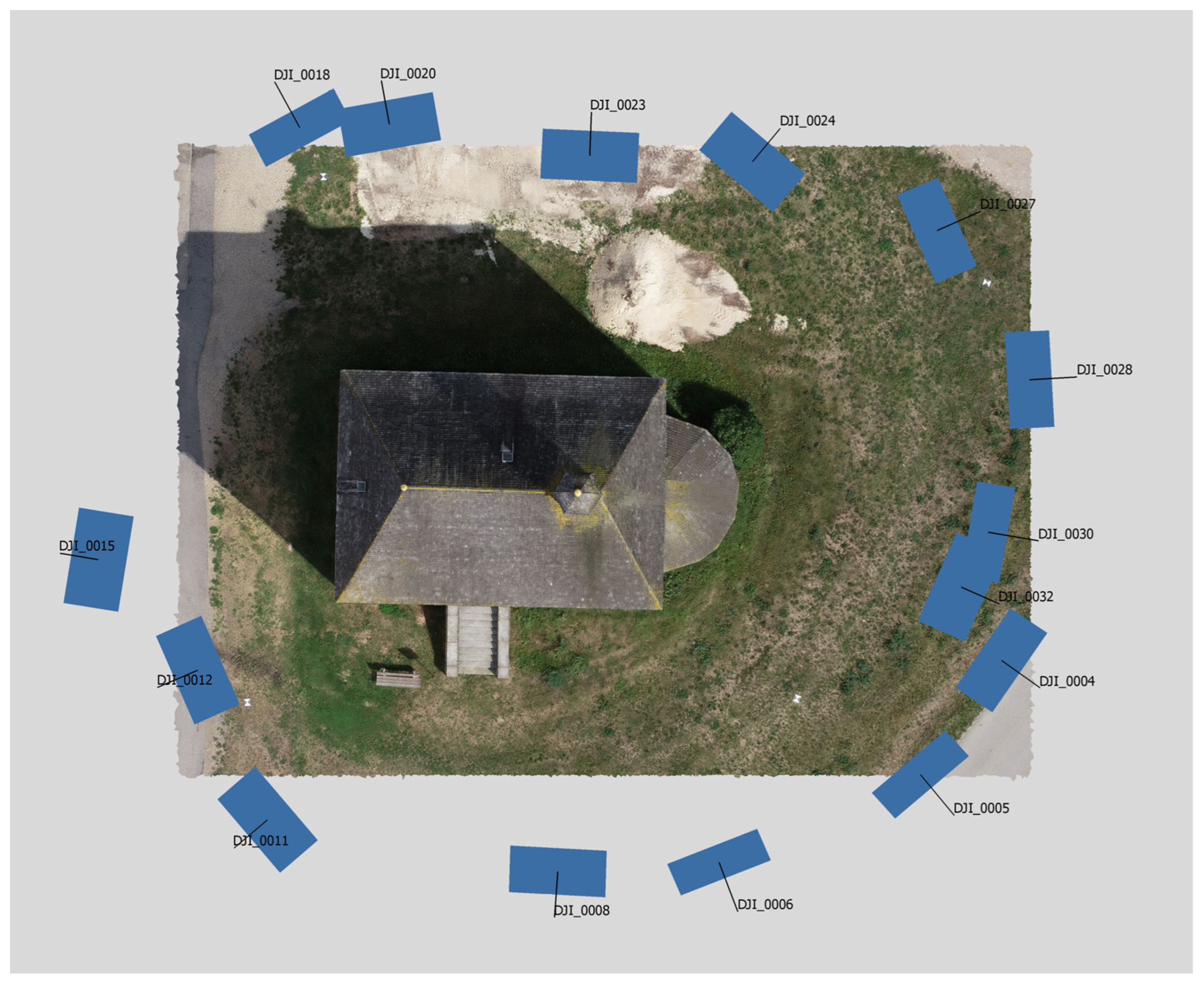
2. Materials and Methods
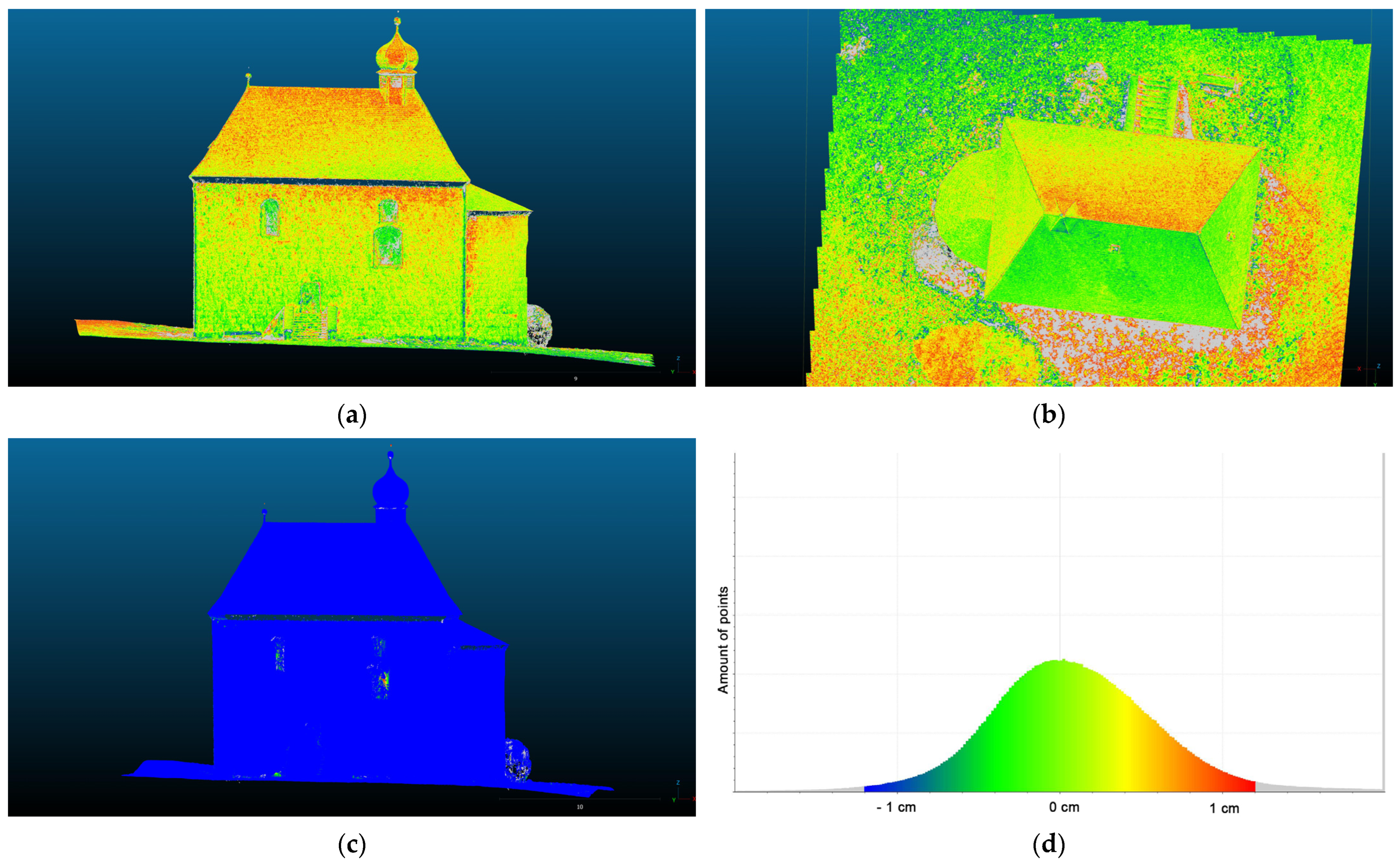
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Pang, Q. 3D Data Acquisition by Terrestrial Laser Scanning for Protection of Historical Buildings. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 21–25 September 2007; pp. 5971–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yastikli, N. Documentation of cultural heritage using digital photogrammetry and laser scanning. J. Cult. Herit. 2007, 8, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gussone, M.; Heister, H.; Liebl, W.; Oberhollenzer, I.; Sack, D.; Shash, H. Laserscanning als Grundlage für Bauforschung und Schadenskartierung in Resafa/Syrien—Objektive Dokumentation oder/und Analyse der Konstruktion?/! In Von Handaufmaß bis High-Tech III: 3D in der Historischen Bauforschung; Heine, K., Rheidt, K., Riedel, A., Eds.; WBG Philipp von Zabern: Mainz, Germany, 2011; pp. 201–210. ISBN 978-3-8053-4332-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kwoczyńska, B.; Piech, I.; Śledź, J.; Litwin, U.; Obirek, P. The Use of Terrestrial Laser Scanning in Surveying Historic Buildings. In Proceedings of the 2016 Baltic Geodetic Congress (BGC Geomatics), Gdansk, Poland, 2–4 June 2016; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drap, P.; Merad, D.; Boï, J.-M.; Seinturie, J.; Peloso, D.; Reidinger, C.; Vannini, G.; Nucciotti, M.; Pruno, E. Photogrammetry for Medieval Archaeology: A Way to Represent and Analyse Stratigraphy. In Proceedings of the 2012 18th International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, Milan, Italy, 2–5 September 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, A.; Schultzén, J.; Wikström, A. Reconstructing the spatial layout of the church of St. Lawrence, Sigtuna, Sweden using ground-penetrating radar and photogrammetry. In Archaeological Prospection, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, Vienna, Austria, 29 May–2 June 2013; Neubauer, W., Trinks, I., Salisbury, R.B., Einwögerer, C., Eds.; Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Archaeological Prospection and Virtual Archaeology, Austrian Academy of Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2013; pp. 74–76. ISBN 978-3-7001-7459-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stal, C.; Lonneville, B.; Nuttens, T.; De Maeyer, P.; De Wulf, A. Highly Detailed 3D Modelling of Mayan Cultural Heritage Using an UAV. In Proceedings of the FIG Congress “Engaging the Challenges—Enhancing the Relevance”, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 16–21 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karachaliou, E.; Georgiou, E.; Psaltis, D.; Stylianidis, E. UAV for Mapping Historic Buildings: From 3D Modelling to BIM. ISPRS Arch. 2019, XLII-2/W9, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carricondo, P.; Carvajal-Ramírez, F.; Yero-Paneque, L.; Agüera-Vega, F. Combination of nadiral and oblique UAV photogrammetry and HBIM for the virtual reconstruction of cultural heritage. Case study of Cortijo del Fraile in Níjar, Almería (Spain). Build. Res. Inf. 2019, 48, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, M.; Gonçalves, L.M.S.; Gonçalves, G.; Francisco, C.; Puente, I.; Providência, P.; Gaspar, F.; Rodrigues, H. A Building Information Modeling Approach to Integrate Geomatic Data for the Documentation and Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, D.; Alicandro, M.; Massimi, V. UAV photogrammetry in the post-earthquake scenario: Case studies in L’Aquila. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risks 2017, 8, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, C.; Gorrasi, M.; Izzo, F.; Langella, A.; Limongiello, M.; Mercurio, M.; Musmeci, D.; Santoriello, A.; Grifa, C. Damage Diagnosis of Ponte Rotto, a Roman Bridge Along the Ancient Appia. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 11, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, S.; Colica, E.; Galone, L.; Persico, R.; Venuti, V.; Caridi, F.; Foti, S.; Cantarella, C. Proximity Remote Sensing: Preliminary Results at The Batia Church (Tortorici, Sicily). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2204, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, R. Mapping a UNESCO World-Heritage Site in 3D: Drone photogrammetry of a Rococo church in southern Bavaria. ISAP News 2019, 58, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Knepper, T.; Sidiropolou, D.; Dietzsch, J.; Fielauf, M.; Krekeler, A. Hochauflösendes Laserscanning und Fotogrammetrie als Grundlage der Restaurierungs- und Objektplanung in der Denkmalpflege. In Bildgebende Verfahren—Trends und Fallbeispiele zur Zerstörungsfreien Untersuchung und Erhaltung von Kulturerbe—Arbeitshefte des Brandenburgischen Landesamtes für Denkmalpflege und Archäologischen Landesmuseum, 1st ed.; Brandenburgisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege und Archäologisches Landesmuseum, Ed.; Hendrik Bäßler: Berlin, Germany, 2021; Volume 61, pp. 162–174. ISBN 978-3-945880-90-6. [Google Scholar]
- Linck, R. Hoch hinaus im Allgäu: Drohnenfotogrammetrie der Burgruinen Eisenberg und Hohenfreyberg. Das Archäologische Jahr Bayern 2020, 2021, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Karataş, L.; Alptekin, A.; Yakar, M. Detection and documentation of stone material deterioration in historical masonry structures using UAV photogrammetry: A case study of Mersin Aba Mausoleum. Adv. UAV 2022, 2, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Manajitprasert, S.; Tripathi, N.K.; Arunplod, S. Three-Dimensional (3D) Modeling of Cultural Heritage Site Using UAV Imagery: A Case Study of the Pagodas in Wat Maha That, Thailand. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. Using Drones and 3D Modeling to Survey Tibetan Architectural Heritage: A Case Study with the Multi-Door Stupa. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhmann, T.; Chizhova, M.; Gorkovchuk, D. Fusion of UAV and Terrestrial Photogrammetry with Laser Scanning for 3D Reconstruction of Historic Churches in Georgia. Drones 2020, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalagli, N.; Gioffrè, M.; Grassi, S.; Gusella, V.; Pepi, C.; Volpi, G.M. On the accuracy of UAV photogrammetric survey for the evaluation of historic masonry structural damages. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2020, 29, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt—Naturräumliche Gliederung Bayerns. Available online: https://www.lfu.bayern.de/natur/naturraeume/doc/haupteinheiten_naturraum.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Hager, G. Die Kunstdenkmäler des Königreichs Bayern—Oberpfalz & Regensburg Bd. I: Bezirksamt Roding; Verlag von R. Oldenbourg: München, Germany, 1905; pp. 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, B. Burgenbau in der Südöstlichen Oberpfalz vom Frühmittelalter bis zur Frühen Neuzeit. Arbeiten zur Archäologie Süddeutschlands; Verlag Dr. Faustus: Büchenbach, Germany, 2003; Volume 16, pp. 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Robl, W. Burggraf Heinrich III. von Regensburg und sein Erbe: Die romanischen Schutzkirchen in Altbayern. 2017. Available online: http://schutzkirchen.robl.de/schutzkirchen.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Weininger, H. Die alte Kirche zu Schönfeld in der Oberpfalz. Westermanns Illus. Dtsch. Monatshefte 1860, 49, 376–378. [Google Scholar]
- Grund- und Aufriss von Sankt Ägidius. Hersenedis, 18 September 2008, CC-License. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Aegidius_Plan.jpg (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- DJI P 4 RTK. Available online: https://www.dji.com/de/phantom-4-rtk/info (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- DJI Enterprise. Zenmuse P1. Technische Daten. Available online: https://www.dji.com/de/zenmuse-p1/specs (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Enterprise. Zenmuse P1. FAQ. Available online: https://www.dji.com/de/zenmuse-p1/faq (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- CloudCompare. Available online: https://www.danielgm.net/cc/ (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- EASA Pro. Drones & Air Mobility. Available online: https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/domains/civil-drones (accessed on 9 February 2023).




| DJI P4RTK | DJI M300 with P1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor size | 13.1 × 8.8 mm | 35.9 × 24 mm |
| Effective pixels | 20 Megapixel | 45 Megapixel |
| Focal length * | 24 mm | 35 mm |
| Camera mode | Automatic | Shutter priority |
| Flight altitude | 40 m | 50 m |
| Image overlap | 85% | 85% |
| Number of images | 90 | 304 |
| Ground sampling distance | 9 mm | 6 mm |
| DJI P4RTK | Zenmuse P1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Amount of points | 5,381,000 | 11,160,000 |
| Point density | 6138/m2 | 12,694/m2 |
| DJI P4RTK | DJI M300 with P1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Δx | 1.1 cm | 0.7 cm |
| Δy | 1.3 cm | 1.4 cm |
| Δz | 0.2 cm | 0.4 cm |
| Δ3D | 1.7 cm | 0.8 cm |
| Minimum | −1.3 cm |
| Maximum | 9.3 cm |
| Mean | 0.4 cm |
| Median | 0.4 cm |
| Standard deviation | 0.8 cm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linck, R.; Stele, A.; Schimmer, C. Statistical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Consumer Drone Photogrammetry at a Romanesque Church in Eastern Bavaria (Germany). NDT 2024, 2, 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt2020005
Linck R, Stele A, Schimmer C. Statistical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Consumer Drone Photogrammetry at a Romanesque Church in Eastern Bavaria (Germany). NDT. 2024; 2(2):76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt2020005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinck, Roland, Andreas Stele, and Christoph Schimmer. 2024. "Statistical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Consumer Drone Photogrammetry at a Romanesque Church in Eastern Bavaria (Germany)" NDT 2, no. 2: 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt2020005
APA StyleLinck, R., Stele, A., & Schimmer, C. (2024). Statistical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Consumer Drone Photogrammetry at a Romanesque Church in Eastern Bavaria (Germany). NDT, 2(2), 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ndt2020005






