Abstract
Cardiovascular disease in gout is a central issue, but the underlying mechanisms linking the two are unclear. The existence of monosodium (MSU) crystal deposition directly inflaming vessel walls has been recurrently suggested and challenged since the 1950s and is again a matter of active debate since recent studies using dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) suggested a higher prevalence of plaques considered to be containing MSU crystals in patients with gout. The objective of this review is to critically cover the evidence gathered on MSU crystal deposition in the cardiovascular system. In patients affected with gout, histological evidence of MSU crystals in arteries lacks a biochemical characterization supporting the observation in polarized light microscopy, while current knowledge on vascular lesions identified in DECT as containing MSU crystals suggests that they may be only artifacts, including in cadaveric and phantom studies. In individuals without gout, MSU crystal deposition in vessel walls have not been demonstrated, despite higher urate local plaque concentrations and increased xanthine oxidase activity. Gout is associated with increased arterial calcification and atherosclerosis, both being potential confounders of suspected MSU crystal deposition for the analysis of DECT scans and histopathology, respectively. In summary, the reality of the presence of MSU crystals in vascular plaques has not been demonstrated so far, and needs further investigation as it represents a potential outcome for cardiovascular complications of gout.
1. Introduction
Beyond the excruciating joint pain it causes, the main issue with gout is its high association with comorbidities including cardiovascular diseases (CVD), which may explain the higher mortality associated with the disease [1]. Particularly, patients with gout exhibit a higher risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke. The causal mechanisms explaining this relationship between gout and CVD have not been clearly untangled [2]. To date, two main mechanisms are suspected to be involved. The first one is an indirect effect of systemic monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition in joints and peri-articular tissues, which causes chronic and often subclinical inflammation, such as what has been observed in auto-immune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) and in atherosclerosis in general [3]. The extent of the MSU crystal deposition in joints and peri-articular tissues has been shown to be associated with cardiovascular comorbidities cross-sectionally in a study using dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) [4]. Evidence has demonstrated an independent relationship between the extents of MSU crystal deposition in joints and around and of atheroma, particularly in carotid arteries [5,6,7]. In longitudinal studies, the extent of MSU crystal burden in joints and peri-articular tissues has been shown to be associated with CV events and mortality both in tophaceous gout in a clinical cohort and in an imaging cohort for using DECT [4,8,9]. The second hypothesis is far more debated and suggests a potential implication of MSU crystal deposits inside vessels. Theoretically, urate can crystalize anywhere, and have been found beyond joints and their surroundings [10,11]. Urate formation is mediated by xanthine oxidase activity, which has been found to be high in atheroma plaques [2] where a higher urate level could in theory lead to a local urate crystallization process. Such vascular crystal deposition could generate local inflammation, lead to an endoluminal obstruction such as the one occurring in atheroma, and cause cardiovascular events. While this hypothesis had been sporadically suggested since the 1950s [12], a renewed interest has recently crystalized with the first study using DECT, which identified coronary plaques compatible with MSU crystal deposits [13], which have been debated since. The reality of such MSU crystal-containing plaques and their involvement in CV outcomes could have critical implications in management, as they could become an important therapeutic objective in gout. It is therefore crucial to determine if these MSU crystal deposits in vessels truly exist, and if they do, how to detect and quantify them.
The objective of this review is to critically cover the evidence gathered on MSU crystal deposition in the CV system.
2. Evidence of MSU Crystals in Vessels of Patients with Gout
2.1. Histological Evidence
Together with other organs, the CV system has been explored for potential MSU crystal deposition as early as the 1950s, and had already been at the time a source of controversy [14]. Case series from autopsies of individuals with gout had led to the identification of crystal deposits in polarized light microscopy on the intima with cellular reactions involving vessel walls as deep as the adventitia [12]. The urate nature of such crystals was quickly challenged in another case series from 11 autopsies from patients with gout, in whom visceral MSU crystal deposits could be found in several organs, but not inside vessels [14]. The authors from this study argued that prior reports may have mistaken cholesterol crystals for MSU crystals, as they can share common features of morphology but also have a negative birefringence in polarized light microscopy [14]. In synovial fluids or suspected tophi, identifying needle-shaped, negatively birefringent crystals among other co-existing crystals that are essentially made of calcium (particularly calcium pyrophosphate that has a different morphology and positive birefringence) is indeed the gold standard for the diagnosis of gout [1,15]. However, tissue itself may exhibit some birefringence, making the search for potential crystals more difficult (e.g., in the cartilage), and most importantly, other crystals may frequently be present, particularly cholesterol crystals in vessels. The lone observation of negatively birefringent crystals in such tissues using polarized light microscopy is therefore not sufficient to qualify as MSU-crystal proof, and requires additional methods of chemical characterization [16]. Furthermore, the inflammatory response to MSU crystals mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome is not specific, as the same pathway is known to be activated by cholesterol crystals in atheroma plaques [2,17,18]. The histopathological evidence of leukocyte infiltrate in vessel walls near crystals cannot ascertain their nature.
New cadaver studies were performed very recently. Dalbeth et al. reported a study of six cadaveric donors with a known history of gout (including two subjects with crystal-proven tophi), which examined the crystal deposition of the aorta and the proximal few centimeters of the brachiocephalic, common carotids, and subclavian arteries [19]. The methods were different as the analyses were not performed on tissue sections of vessel walls, but on the aspirated fluid after the injection of 100 µL of phosphate-buffered saline into the vessel wall at ten standardized sites across each sample, and analyzed by polarizing light microscopy. Microscopic analysis demonstrated plate-like negatively birefringent cholesterol crystals from vascular tissue from five of the six subjects in three sites on average per donor. Of note, a single negatively birefringent needle-shaped crystal was observed from one of the 60 standardized sites analyzed, while numerous negatively birefringent needle-shaped crystals were present in aspirates from tophaceous joint tissue.
The only convincing evidence of MSU crystal deposition in the cardiovascular system of patients with gout is on cardiac valves. A case report from an older patient with a long-lasting history of gout reported crystal deposits in a resected aortic valve, and the presence of MSU crystals was chemically ascertained with X-ray diffraction [20]. Overall, nine studies of MSU crystal deposition on cardiac valves in tophaceous patients were reported, with various levels of evidence of the true nature of the crystals, but overall, the concept of valvular micro-tophi is convincing [10].
2.2. Imaging Evidence: The Debate on the Evidence Gathered with DECT
The discussion on the potential existence of arterial MSU crystal deposition was renewed by the publication of DECT scans of coronary arteries and the aorta from patients with gout and controls by Klauser et al. [13] (Figure 1). The study included 59 patients with gout who were compared to 47 controls. Using the post-processing software in ‘gout mode’, vascular plaques were coded by the machine as containing MSU crystals in the aorta more commonly among patients with gout (n = 51 [86.4%]) compared with controls (n = 7 [14.9%]) (χ2 = 17.68, p < 0.001), as well as in coronary arteries (n = 19 [32.2%] vs. n = 2 [4.3%]) (χ2 = 8.97, p = 0.003), respectively. Another important finding was that the coronary calcium scores (i.e., the extent of calcified plaques) was significantly higher in patients with gout than in controls, suggesting that there may be a relationship between calcified plaques and MSU-coded plaques. The same team performed other studies with similar methodologies, including analyses using crystal-containing phantoms providing the same results, which were also found in a small study by another team using the same methodology [21,22]. Methodological issues were raised in response to the publication of the first study, but at least the question was opened [23].
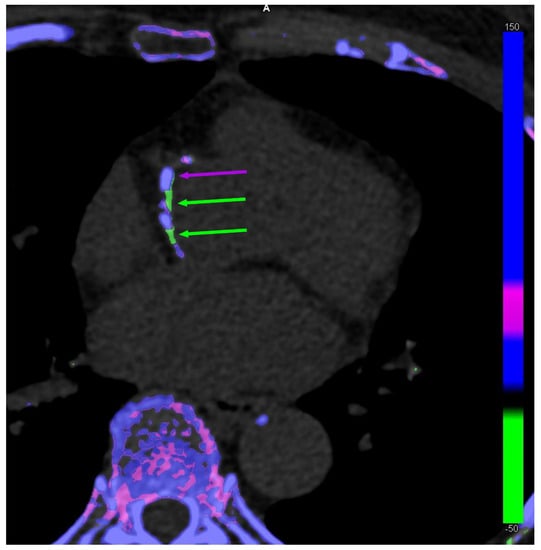
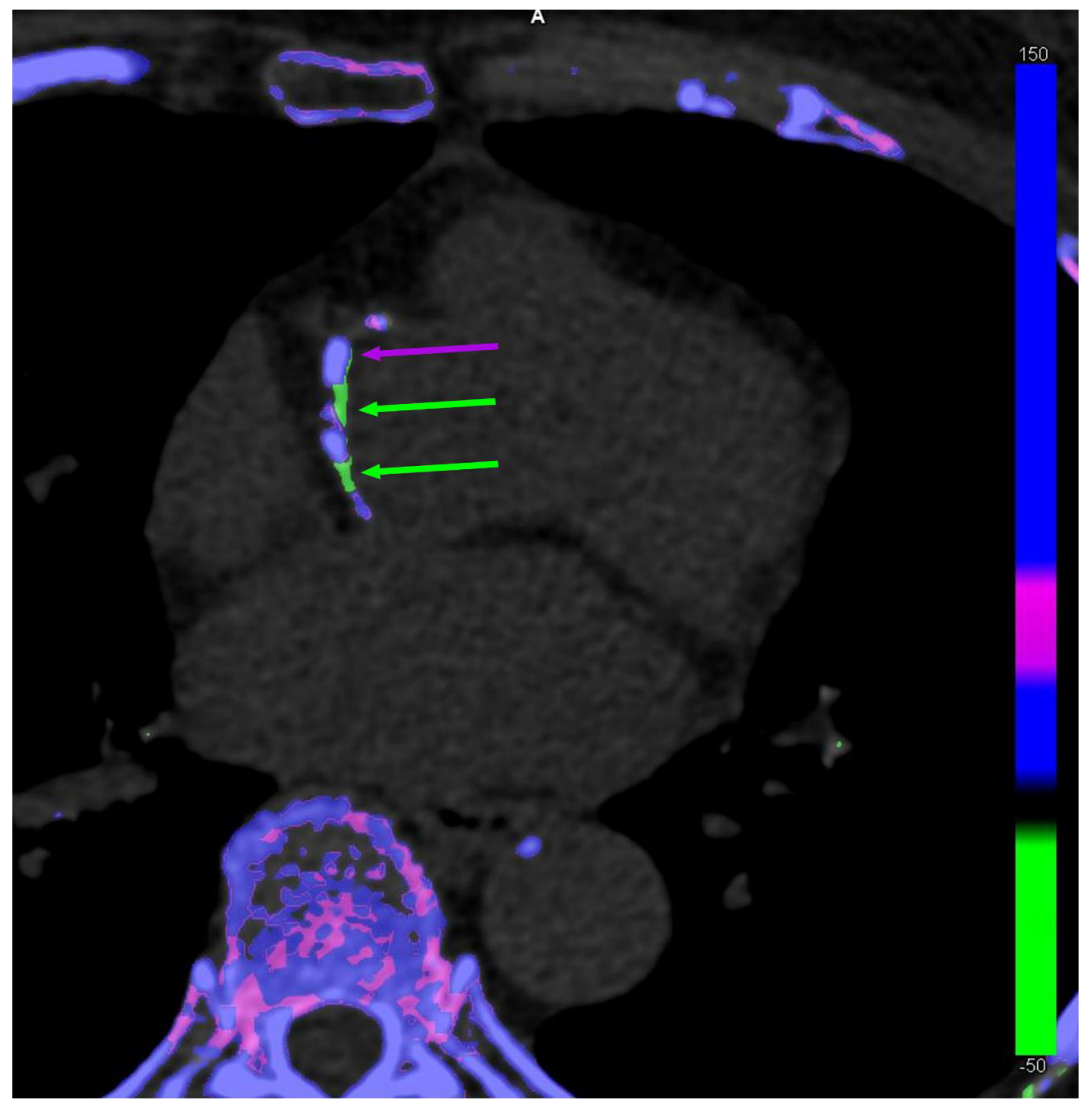
Figure 1.
Dual-energy computed tomography of co-existing monosodium urate (MSU) crystal-coded (green arrows) and calcium-coded (purple arrows) coronary plaques in a 63-year-old female patient without gout.
The VASCURATE study from our team focused on popliteal artery plaques from knee DECT scans of 126 patients with gout and 26 controls [24]. The main finding of the study was that the prevalence of DECT-based vascular MSU-coded plaques was comparable in patients with gout (24.6%) and controls (23.1%; p = 0.87). In addition, the presence of such MSU-coded plaques was strongly associated with coexisting arterial calcifications (p < 0.001), but not with soft-tissue MSU deposits. Moreover, 17 patients had follow-up DECT scans during urate-lowering treatment, and vascular MSU-coded plaques remained stable despite effective ULT (p = 0.64), which decreased both serum urate levels and soft-tissue MSU volumes (p < 0.001). A single MSU-coded plaque disappeared during follow-up to be eventually coded as being calcified.
In the cadaver study (n = 6) performed by Dalbeth et al., DECT scanning of the aorta and proximal section of large arteries showed calcification in all samples, but no evidence of MSU crystal deposition [19] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of the evidence of vascular monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition in patients with gout.
Data from a pegloticase trial, that included sequential DECT scans and even TEP-scans in ten patients before and after treatment with pegloticase, were recently presented at the 2022 American College of Rheumatology Convergence meeting [25]. The total volume of DECT-based MSU-coded plaques did not significantly decrease over time, while the authors reported a statistically significant decrease in SUV mean (p = 0.0003) and SUV max (p = 0.0090) across all arteries studied after treatment with pegloticase. Such results would suggest that inflammation in the arterial wall is reduced after massive MSU crystal debulking, unrelated to any evolution of what is considered to be composed of MSU crystals by DECT.
3. Evidence of MSU Crystals in Vessels of Patients without Gout
3.1. Histological Evidence
The first DECT study of coronary arteries and the aorta also included a cadaver study of six individuals without any knowledge of their medical history [13] (Table 2). Gross anatomical sections of vessels with MSU-coded lesions in DECT were analyzed by polarized light microscopy. No sections negative for MSU-coded lesions in DECT were analyzed. A total of 7/8 vessel biopsies from three cadavers with positive DECTs demonstrated the presence of strongly negatively birefringent needle-shaped crystals considered by the authors to be compatible with MSU crystals, but no attempt to obtain a biochemical characterization of these crystals was made to ascertain this assumption. Authors acknowledged how difficult crystal observation with polarized light microscopy is on tissue slices, and that typical MSU crystals were essentially found in the prostates that were also examined. The local cellular inflammatory infiltrate also varied from one site of crystal deposition to the other.
Another study focused on coronary arteries from 55 explanted hearts from patients requiring heart transplants, whose medical history were unknown but were expected to have a history of gout in around 40% of cases [26]. Among these explanted hearts, six (10.9%) contained a coronary artery with birefringent crystals, although no attempt was made to characterize these crystals other than through their morphological presentation on polarized light microscopy.
3.2. Biochemical Characterization of Urate Presence in Atherosclerotic Plaques
Several studies including participants unaffected with gout provided some analyses of urate presence and xanthine oxidase activity in vessel walls. A study including 23 non-gout patients ‘donating’ samples from carotid endarterectomies and 10 cadaver controls was performed to examine the presence of ‘uric acid’ in its soluble form (and therefore should be referred to as ‘urate’ [27]) and xanthine oxidase in atherosclerotic plaques [28]. Of note, none of the patients had serum urate above 8.0 mg/dL. The samples were incubated and homogenized in distilled water or uricase to achieve peak extinction. The ‘uric acid’ concentration was measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in the endarterectomy specimens and in the control carotid samples from cadavers. The comparison showed that urate concentration was, on average, almost six-fold higher in patients than in cadaver controls (who were surprisingly much younger than patients). Xanthine oxidase was labeled with a polyclonal, monospecific commercial rabbit anti-xanthine oxidase antibody, which showed that control carotid arteries stained positive for xanthine oxidase, but the staining was less than that of carotid plaque from endarterectomy specimens. Immunohistochemical staining with custom-made MSU crystal antibodies stained around what the authors identified as cholesterol clefts, questioning the actual specificity of these antibodies for MSU crystals. Overall, this study showed that there is some xanthine oxidase activity in artery walls, which may vary with atherosclerosis and is associated with a higher urate concentration, but did not provide proof that this higher urate concentration eventually translates into crystallization.
Another study involving ‘uric acid’ (and not urate [27]) measurements in atherosclerotic plaques involving samples from carotid endarterectomies was recently published [29]. The presence of ‘uric acid’ was assessed using Gomori methenamine silver staining as well as anti-uric acid immunohistochemical staining and was quantified using an enzymatic colorimetric assay. These measurements were performed in 32 patients who were either classified as symptomatic, defined as patients who experienced an ipsilateral cerebrovascular ischemic event, or asymptomatic. A significantly higher number of plaques from symptomatic patients were positively stained with Gomori silver compared with those from asymptomatic patients (20 [86.9%] versus 2 [22.2%]; p = 0.001; power = 0.97), and also with immunochemistry staining (16 [69.5%] versus 1 [11.1%]; p = 0.004; power = 0.92), which also translated into a higher quantity of ‘uric acid’ found in symptomatic carotid plaques. Of note, local urate plaque concentration was correlated with serum urate levels. No urate in its crystal form was reported in the study.
It is very probable that in atherosclerosis, increased endothelial xanthine oxidase activity explains the higher local urate concentration, but most of all the higher production of reactive oxygen species in particular, who are involved in plaque inflammation and destabilization, as well as endothelial dysfunction [30].
3.3. Vascular DECT Scans in Patients without Gout
A single study was performed using DECT exclusively in a group of patients without gout. The study included 44 participants with asymptomatic hyperuricemia—a metabolic syndrome—about to undergo, among other techniques, neck DECT scans to examine for the presence of urate deposits in carotid arteries [31]. None had urate deposits in the carotid arteries detected by DECT (Table 2).


Table 2.
Summary of the evidence of vascular monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition in individuals without gout.
Table 2.
Summary of the evidence of vascular monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition in individuals without gout.
| Study | Year | Subjects | Studied Arteries | MSU Crystal Present in Vessels | Technique of Crystal Identification | Urate Plaque Concentration | Xanthine Oxidase Activity | Chemical Characterization of MSU Crystals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klauser A.S. et al. [13] | 2019 | 6 cadaveric donors | Coronary and Aorta | Yes | Polarized light microscopy and Dual-energy CT | - | - | No |
| Park J.J. et al. [26] | 2014 | 55 explanted hearts | Coronary | Yes | Polarized light microscopy | - | - | No |
| Patetsios P. et al. [28] | 2001 | 23 endarterectomy samples vs. 10 cadaveric donors | Carotid | Yes | Polarized light microscopy and staining | Increased | Increased | Yes (questionable specificity) |
| Nardi V. et al. [29] | 2022 | 32 endarterectomy samples | Carotid | Unreported | - | Increased | Increased | - |
| Kim S.C. et al. [31] | 2018 | 44 patients | Carotid | No | Dual-energy CT | - | - | - |
4. If DECT-Based MSU-Coded Plaques in Vessels Are Not Made of MSU Crystals, What Are They?
Most of the debate on the existence of MSU crystal deposition in vessel walls depends on the interpretation of MSU-coded plaques by DECT scans. To provide insight in that discussion, an understanding of how DECT post-processing software ends up coding the presence of MSU crystals is required. By definition, with the difference of conventional single-energy CT, in DECT scans, each voxel contains the information resulting from the combined attenuations of two energy beams (one at low and one at high energy). The combinations of these two attenuations expressed in Hounsfield units (HU) provides some information of the biochemical composition of the given voxel [32]. Basically, every voxel with low density in both attenuations will be identified as soft tissue; all voxels with higher densities with a slight difference in attenuation between low and high energy resulting in an intermediate position between dense soft tissues and calcium will be considered to be MSU; and tissue with high density and a higher attenuation at low energy compared to high energy will be coded as containing calcium as it suggests a higher effective Z (Zeff) number of the voxel due to a significant photoelectric effect of the tissue (Figure 2). Today, the main concern when interpreting DECT scans depends on where to set the cut-off value discriminating calcium-containing and MSU-containing deposits to eliminate false positives [33,34], and more stringent post-processing settings make MSU-coded deposits disappear [35,36]. In the VASCURATE study, MSU-coded plaques exhibited a higher Zeff than that of tophi [24]. Taken together, the data suggest that it is therefore very likely that these MSU-coded plaques could be either early/low-concentration calcified plaques (or fibrous plaques), which are known to exhibit higher Zeff values than MSU deposits [24,37]. This hypothesis is supported by the phantom study presented with the VASCURATE study results and other recent studies, which showed that low-concentration calcium crystal deposition could be incorrectly color-coded as MSU when using default DECT post-processing settings [24,34,38]. Furthermore, all studies concurred to show a high association between the presence of DECT-based MSU-coded plaques and the degree of vascular calcifications [13,22,24]. In the VASCURATE study, the potential association between vascular MSU-coded plaques and the soft-tissue MSU crystal volume disappeared after adjusting the log-linear model for calcification severity scores (β1 coefficient: 0.03 [IQR: −1.07–1.11]), thus suggesting that this association was mediated by the one linking the MSU crystal soft tissue volume and vascular calcifications. This is consistent with the findings that silent MSU crystal deposition even in asymptomatic hyperuricemia is associated with increased coronary calcifications when compared to hyperuricemic participants without crystal deposition and normouricemic individuals [39].
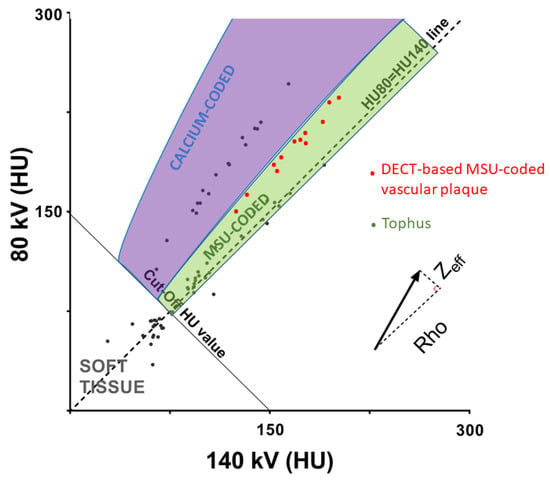
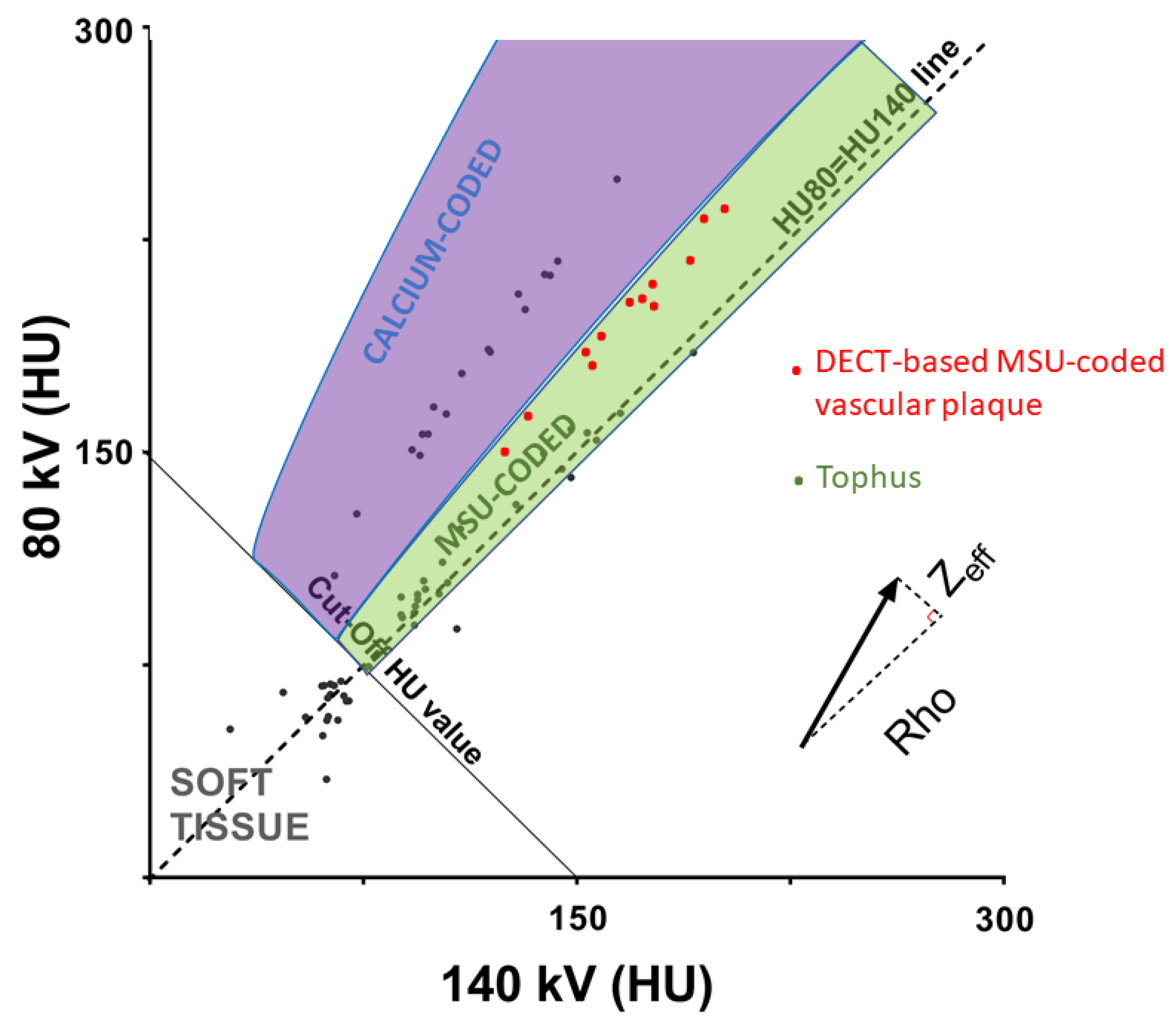
Figure 2.
Discrimination of calcium-containing structures and monosodium urate (MSU)-coded structures with DECT scans using combined effects of volumetric mass density (Rho) and effective atomic number (Zeff) on CT numbers at 80 and 140 kV. The slope of each material is correlated with its Zeff and photoelectric effect. The slope of DECT-MSU-coded plaques is steeper and closer to that of calcium-coded voxels, compared to tophi. HU: Hounsfield unit.
5. Conclusions
The attempts to demonstrate the reality of MSU crystal deposition in vessels is so far unconvincing, and increased vascular inflammation in gout is probably not directly induced by the local presence of MSU crystals. Direct analysis of arterial tissue using characterization methods such as Raman spectroscopy to ascertain the chemical composition of observed crystals needs to be carried out in individuals with gout, to discriminate between MSU and cholesterol crystals, particularly in patients with heavy periarticular MSU crystal burdens. Other studies using DECT on the coronary arteries and the aorta with stringent post-processing settings and attempts to provide a non-invasive biochemical characterization of the DECT-based MSU-coded plaques are under way and should enlighten the debate. This debate needs to be settled, as depleting these crystals from the vessels would certainly be an interesting therapeutic target to improve cardiovascular outcomes in gout.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, T.P.; writing—review and editing, J.-F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
T.P. received research grants on DECT studies from Horizon Pharmaceuticals. J.-F.B. has no disclosures.
References
- Pascart, T.; Liote, F. Gout: State of the art after a decade of developments. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrès, M. Gout and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms, Risk Estimations, and the Impact of Therapies. Gout Urate Cryst. Depos. Dis. 2023, 1, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Pradhan, A.D.; Glynn, R.J.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Nissen, S.E.; PROMINENT, REDUCE-IT, and STRENGTH Investigators. Inflammation and cholesterol as predictors of cardiovascular events among patients receiving statin therapy: A collaborative analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet 2023, 401, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascart, T.; Ramon, A.; Ottaviani, S.; Legrand, J.; Ducoulombier, V.; Houvenagel, E.; Norberciak, L.; Richette, P.; Becce, F.; Ornetti, P.; et al. Association of Specific Comorbidities with Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition in Urate-Lowering Therapy-Naive Gout Patients: A Cross-Sectional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, M.; Bernal, J.A.; Sivera, F.; Quilis, N.; Carmona, L.; Vela, P.; Pascual, E. Cardiovascular risk of patients with gout seen at rheumatology clinics following a structured assessment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig, I.; Martinez-Sanchis, A.; Andres, M. Sonographic Tophi and Inflammation Are Associated with Carotid Atheroma Plaques in Gout. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 795984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.B.; Rollefstad, S.; Semb, A.G.; Jensen, G.; Karoliussen, L.F.; Terslev, L.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Kvien, T.K.; Uhlig, T. Urate crystal deposition is associated with inflammatory markers and carotid artery pathology in patients with intercritical gout: Results from the NOR-Gout study. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty-Ane, A.; Norberciak, L.; Andres, M.; Houvenagel, E.; Ducoulombier, V.; Legrand, J.; Budzik, J.-F.; Pascart, T. Crystal deposition measured with Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: Association with mortality and cardiovascular risks in gout. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 4855–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ruiz, F.; Martinez-Indart, L.; Carmona, L.; Herrero-Beites, A.M.; Pijoan, J.I.; Krishnan, E. Tophaceous gout and high level of hyperuricaemia are both associated with increased risk of mortality in patients with gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Johnson, R.J.; Marder, B.; LaMoreaux, B.; Kumar, A. Systemic Urate Deposition: An Unrecognized Complication of Gout? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Masood, S.; Furlanetto, D.M.; Nicolaou, S. Urate Crystals; Beyond Joints. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 649505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traut, E.F.; Knight, A.A.; Szanto, P.B.; Passerelli, E.W. Specific vascular changes in gout. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1954, 156, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauser, A.S.; Halpern, E.J.; Strobl, S.; Gruber, J.; Feuchtner, G.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G.; Stofferin, H.; Jaschke, W. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Detection of Cardiovascular Monosodium Urate Deposits in Patients with Gout. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.H.; Lichtenstein, L.; Scott, H.W. Pathologic changes in gout; Survey of eleven necropsied cases. Am. J. Pathol. 1956, 32, 871–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neogi, T.; Jansen, T.L.; Dalbeth, N.; Fransen, J.; Schumacher, H.R.; Berendsen, D.; Brown, M.; Choi, H.; Edwards, N.L.; Janssens, H.J.E.M.; et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, T.; Iordache, A.M.; Nicolae, G.; Iordache, S.M.; Baciu, C.; Marinescu, S.; Rizac, R.I.; Militaru, M. Identification of Uric Acid Crystals Accumulation in Human and Animal Tissues Using Combined Morphological and Raman Spectroscopy Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duewell, P.; Kono, H.; Rayner, K.J.; Sirois, C.M.; Vladimer, G.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Abela, G.S.; Franchi, L.; Nunez, G.; Schnurr, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010, 464, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, A.R.; Westerterp, M. Inflammasomes, neutrophil extracellular traps, and cholesterol. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Alhilali, M.; Riordan, P.; Narang, R.; Chhana, A.; McGlashan, S.; Doyle, A.; Andres, M. Vascular deposition of monosodium urate crystals in gout: Analysis of cadaveric tissue by dual-energy computed tomography and compensated polarizing light microscopy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawoski, J.M.; Balogh, K.; Landis, W.J. Aortic valvular tophus: Identification by X-ray diffraction of urate and calcium phosphates. J. Clin. Pathol. 1985, 38, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazani, S.H.; Chi, W.-W.; Pyzik, R.; Chang, H.; Jacobi, A.; O’Donnell, T.; Fayad, Z.A.; Ali, Y.; Mani, V. Quantification of uric acid in vasculature of patients with gout using dual-energy computed tomography. World J. Radiol. 2020, 12, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuchtner, G.M.; Plank, F.; Beyer, C.; Schwabl, C.; Held, J.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G.; Gruber, J.; Widmann, G.; Klauser, A.S. Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition in Coronary Artery Plaque by 128-Slice Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Phantom and In Vivo Study. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2021, 45, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becce, F.; Ghoshhajra, B.; Choi, H.K. Identification of Cardiovascular Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition in Patients with Gout Using Dual-Energy Computed Tomography. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascart, T.; Carpentier, P.; Choi, H.K.; Norberciak, L.; Ducoulombier, V.; Luraschi, H.; Houvenagel, E.; Legrand, J.; Verclytte, S.; Becce, F.; et al. Identification and characterization of peripheral vascular color-coded DECT lesions in gout and non-gout patients: The VASCURATE study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, I.M.V.; Pyzik, R.; Kaufman, A.; Chi, W.; Bagiella, E.; Robson, P.; Ali, Y. Assessing Urate Deposition and Inflammation in the Vasculature of Gout Patients Using Dual Energy Computed Tomography and Positron Emission Tomography Pre and Post Pegloticase—A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 3592–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.J.; Roudier, M.P.; Soman, D.; Mokadam, N.A.; Simkin, P.A. Prevalence of birefringent crystals in cardiac and prostatic tissues, an observational study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursill, D.; Taylor, W.J.; Terkeltaub, R.; Kuwabara, M.; Merriman, T.R.; Grainger, R.; Pineda, C.; Louthrenoo, W.; Edwards, N.L.; Andres, M.; et al. Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal-Associated Disease Network Consensus Statement Regarding Labels and Definitions for Disease Elements in Gout. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patetsios, P.; Song, M.; Shutze, W.P.; Pappas, C.; Rodino, W.; Ramirez, J.A.; Panetta, T.F. Identification of uric acid and xanthine oxidase in atherosclerotic plaque. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, V.; Franchi, F.; Prasad, M.; Fatica, E.M.; Alexander, M.P.; Bois, M.C.; Lam, J.; Singh, R.J.; Meyer, F.B.; Lanzino, G.; et al. Uric Acid Expression in Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque and Serum Uric Acid Are Associated with Cerebrovascular Events. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine oxidoreductase: A leading actor in cardiovascular disease drama. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Di Carli, M.F.; Garg, R.K.; Vanni, K.; Wang, P.; Wohlfahrt, A.; Yu, Z.; Lu, F.; Campos, A.; Bibbo, C.F.; et al. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia and coronary flow reserve in patients with metabolic syndrome. BMC Rheumatol. 2018, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascart, T.; Budzik, J.F. Dual-energy computed tomography in crystalline arthritis: Knowns and unknowns. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.H.; Yoo, W.H.; Song, Y.S.; Byon, J.H.; Pak, J.; Choi, Y. Not All Green Is Tophi: The Importance of Optimizing Minimum Attenuation and Using a Tin Filter to Minimize Clumpy Artifacts on Foot and Ankle Dual-Energy CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, S.N.; Muller, F.C.; Ostergaard, M.; Slot, O.; Moller, J.M.; Borgesen, H.F.; Gosvig, K.K.; Terslev, L. Dual-energy CT in gout patients: Do all colour-coded lesions actually represent monosodium urate crystals? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprover, M.; Mechlin, M.; Fields, T.; Oh, C.; Becce, F.; Pillinger, M.H. Monosodium urate deposition in the lumbosacral spine of patients with gout compared with non-gout controls: A dual-energy CT study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 56, 152064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen, F.M.; Doyle, A.J.; Reeves, Q.; Gamble, G.D.; Dalbeth, N. DECT urate deposits: Now you see them, now you don’t. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Ito, H.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Kubo, Y.; Matsui, K.; Tanaka, I.; Fukui, R.; Omori, H.; Nakaoka, T.; Sakura, H.; et al. Clinical application of effective atomic number for classifying non-calcified coronary plaques by dual-energy computed tomography. Atherosclerosis 2017, 261, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossing, A.; Muller, F.C.; Becce, F.; Stamp, L.; Bliddal, H.; Boesen, M. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Detection and Characterization of Monosodium Urate, Calcium Pyrophosphate, and Hydroxyapatite: A Phantom Study on Diagnostic Performance. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, M.; Quintanilla, M.-A.; Sivera, F.; Sanchez-Paya, J.; Pascual, E.; Vela, P.; Ruiz-Nodar, J.-M. Silent Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposits Are Associated with Severe Coronary Calcification in Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia: An Exploratory Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).