Influence of Tissue Curvature on the Absolute Quantification in Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
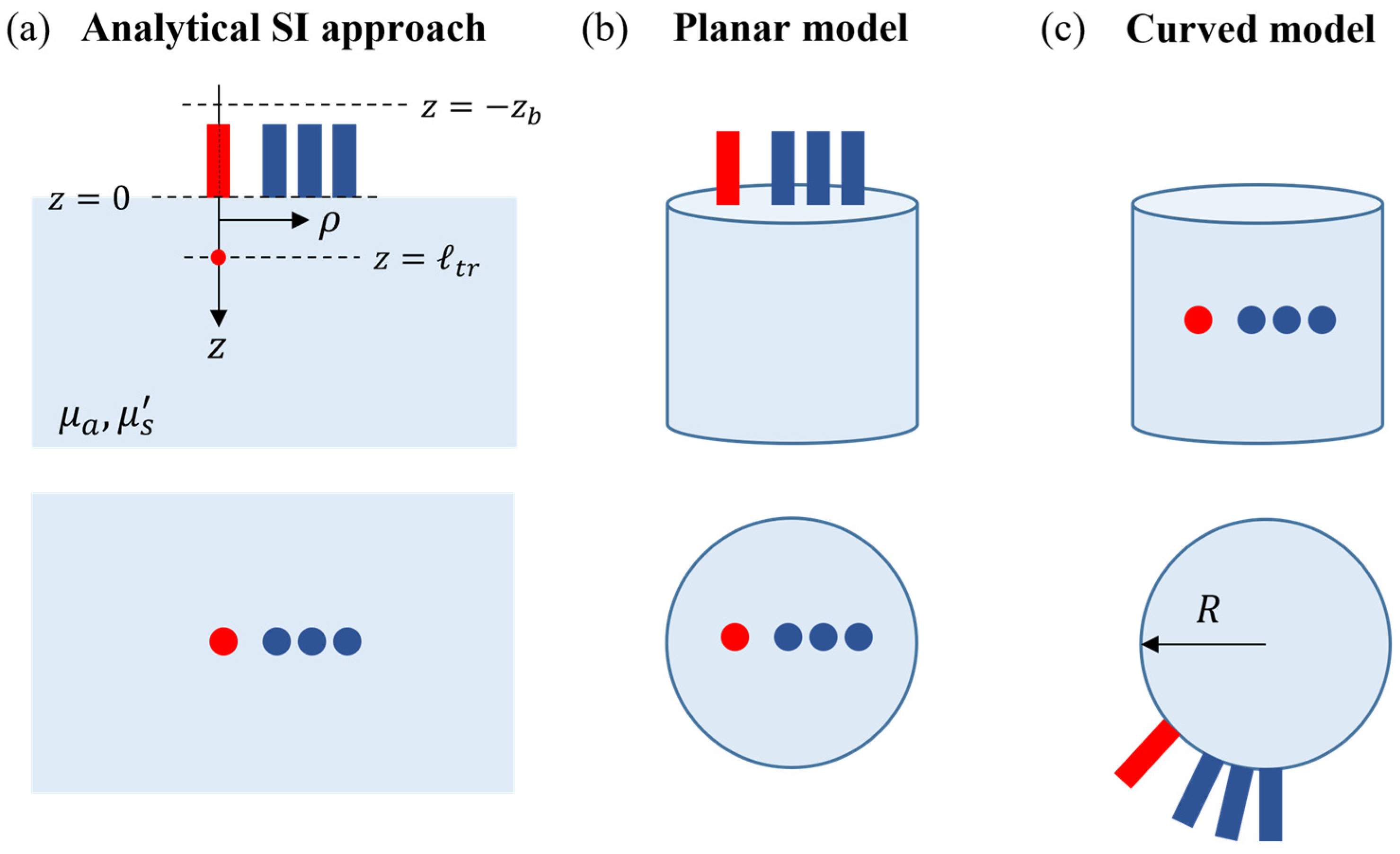
2.1. Forward Models for Parameter Estimation
2.1.1. Analytical Semi-Infinite Model
2.1.2. Numerical Models
2.2. Validation Datasets
2.2.1. Numerical Simulations in Mimicking Phantoms
2.2.2. Phantom Measurements
2.2.3. Numerical Simulations on a Realistic Head
2.3. Human Brain Dataset
3. Results
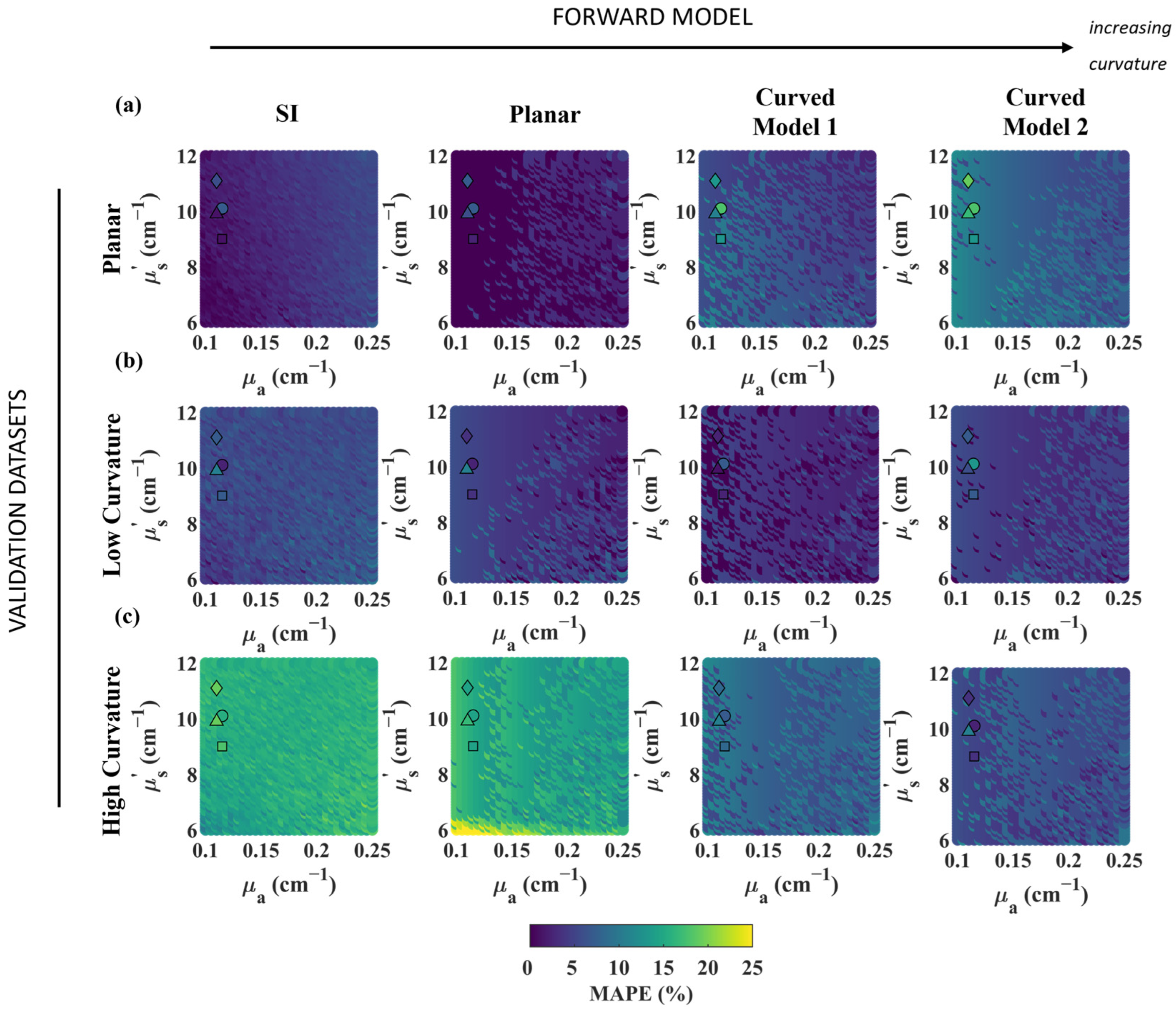
3.1. Effect of Curvature on Phantoms
3.2. Model Validation in Head Simulations
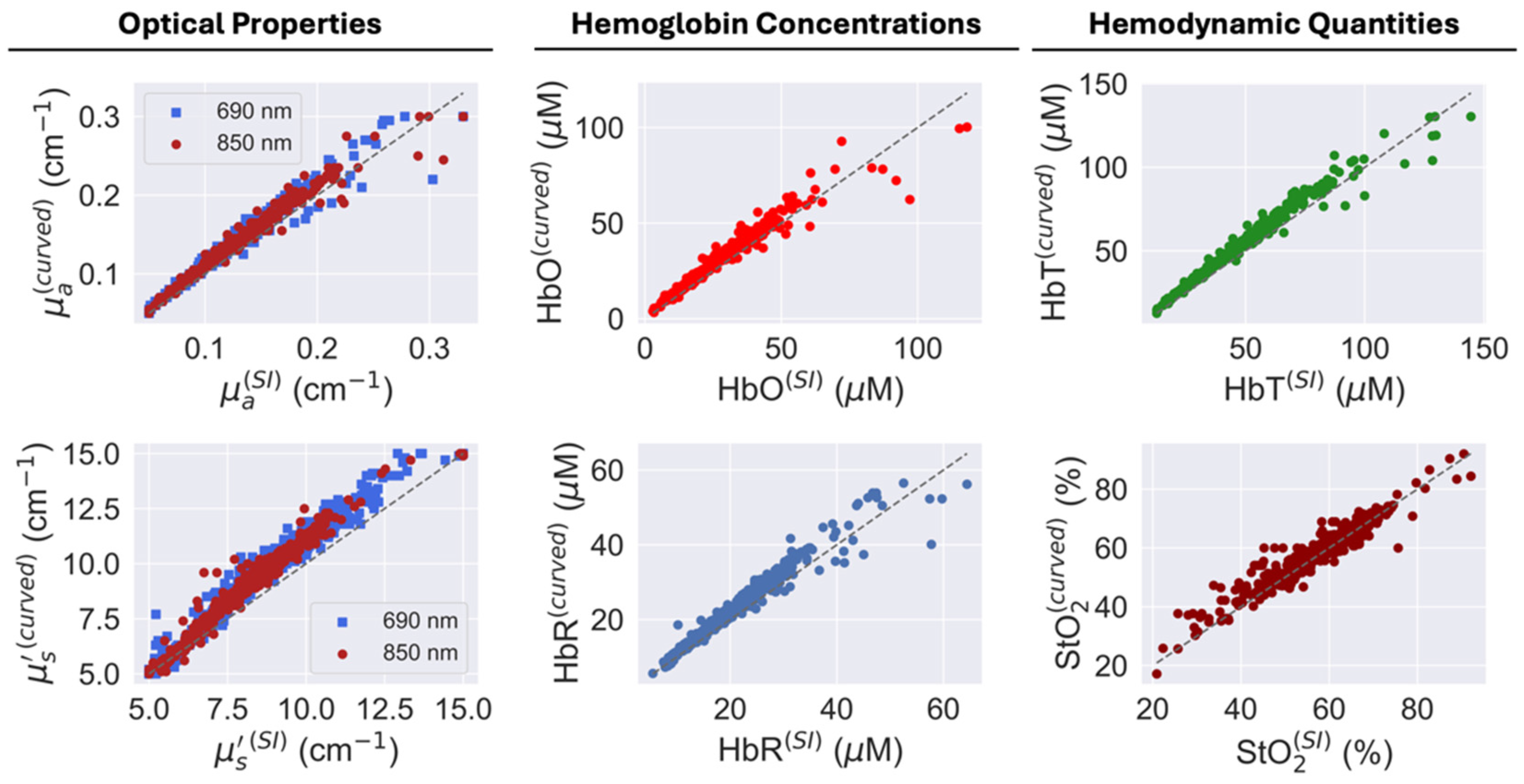
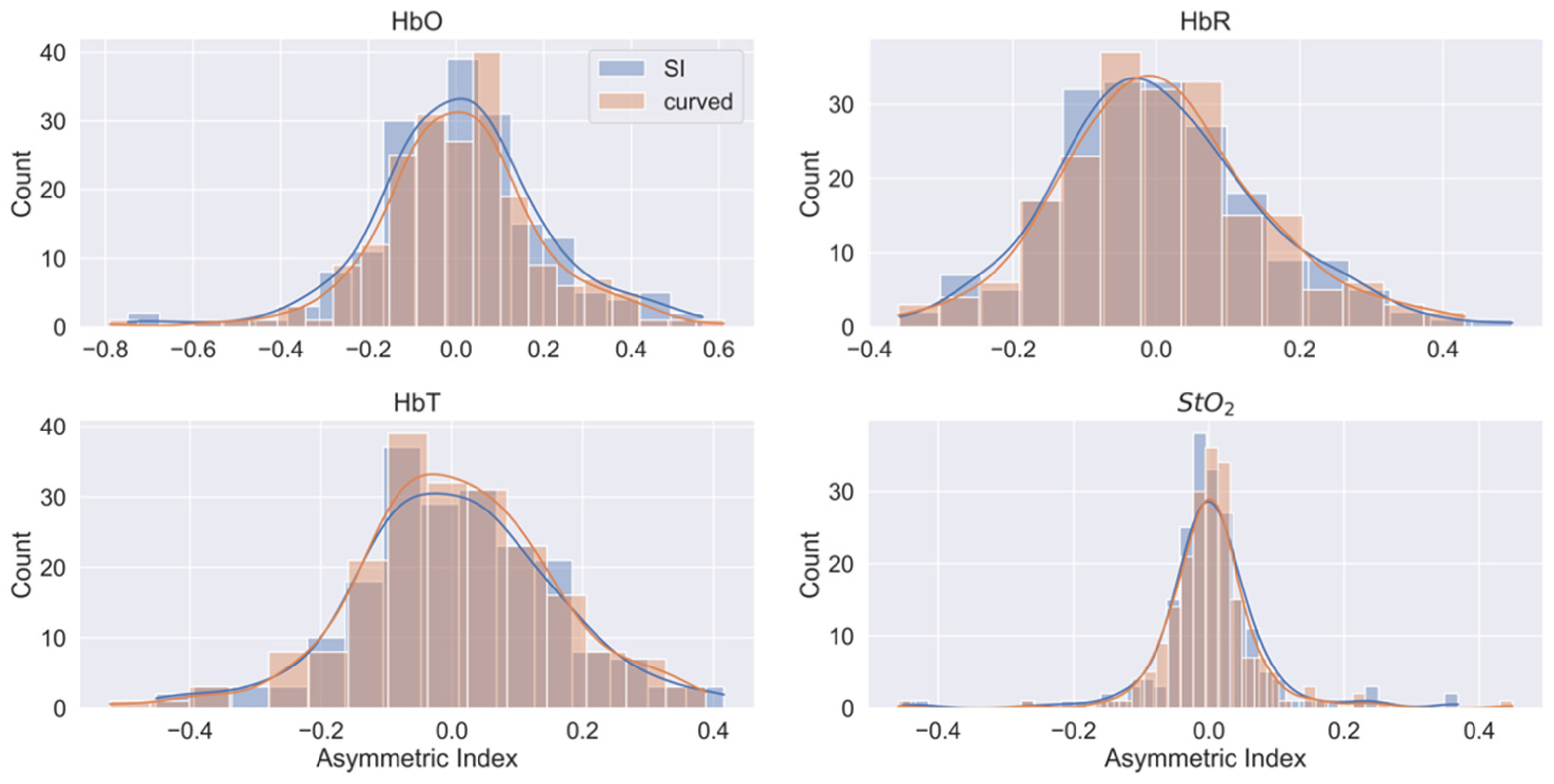
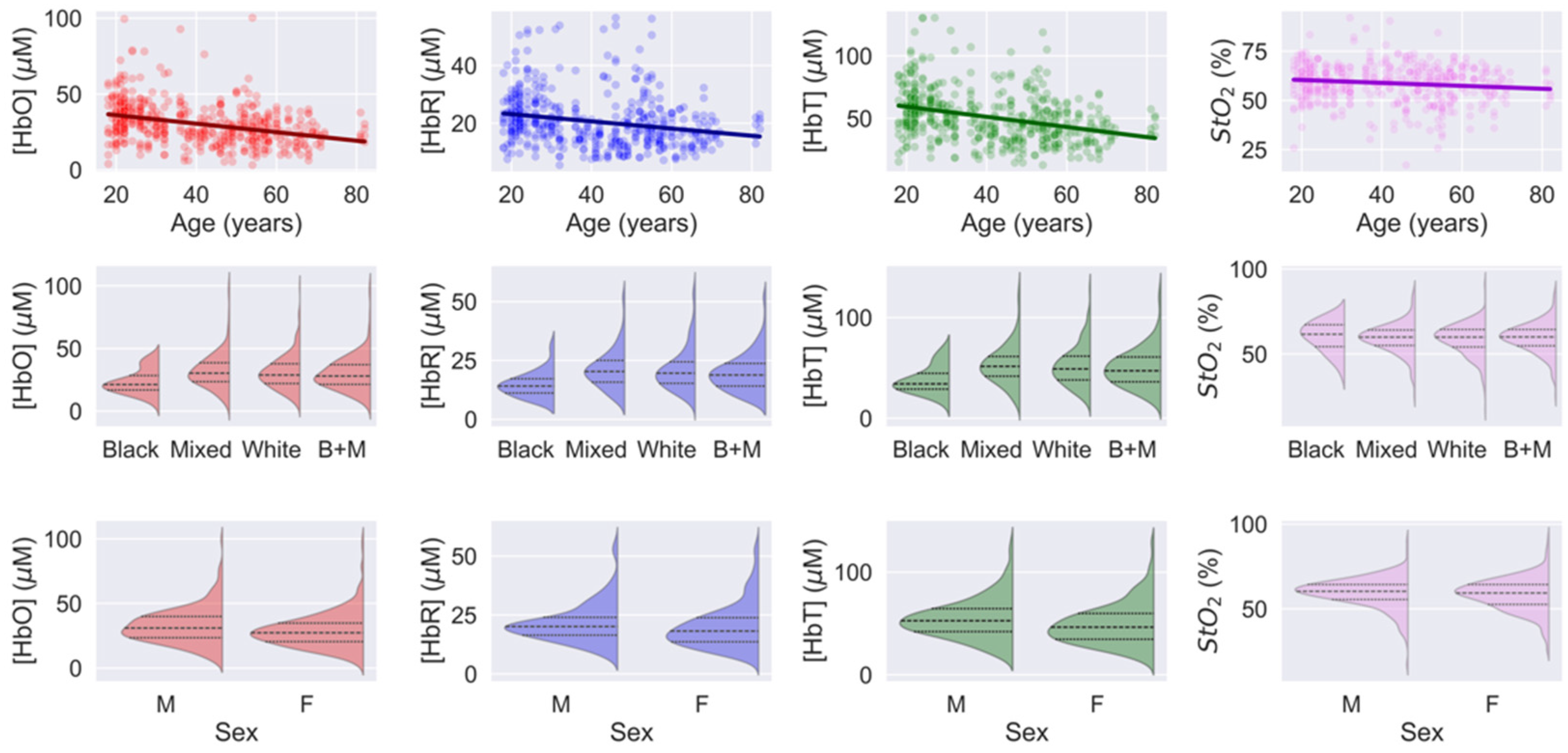
3.3. Human Head Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Effects of Curvature on Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy

References
- Fantini, S.; Sassaroli, A. Frequency-Domain Techniques for Cerebral and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B.; Cope, M.; Gratton, E.; Ramanujam, N.; Tromberg, B. Phase measurement of light absorption and scatter in human tissue. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1998, 69, 3457–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.K.; Xia, Y.J.; Uchitel, J.; Collins-jones, L.; Yang, S.F.; Loureiro, R.; Cooper, R.J.; Zhao, H.B. Review of recent advances in frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy technologies Invited. Biomed. Opt. Express 2023, 14, 3234–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Noval, S.R.; Cayuela, A.; Arellano-Orden, V.; Marin-Caballos, A.; Padilla, V.; Ferrandiz-Millon, C.; Corcia, Y.; Garcia-Alfaro, C.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Murillo-Cabezas, F. Invasive and noninvasive assessment of cerebral oxygenation in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forti, R.M.; Katsurayama, M.; Menko, J.; Valler, L.; Quiroga, A.; Falcao, A.L.E.; Li, L.; Mesquita, R.C. Real-Time Non-invasive Assessment of Cerebral Hemodynamics with Diffuse Optical Spectroscopies in a Neuro Intensive Care Unit: An Observational Case Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokose, N.; Sakatani, K.; Murata, Y.; Awano, T.; Igarashi, T.; Nakamura, S.; Hoshino, T.; Katayama, Y. Bedside Monitoring of Cerebral Blood Oxygenation and Hemodynamics after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Quantitative Time-Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. World Neurosurg. 2010, 73, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournoyer, A.; Iseppon, M.; Chauny, J.M.; Denault, A.; Cossette, S.; Notebaert, E. Near-infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring During Cardiac Arrest: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2016, 23, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arridge, S.R.; Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. The Theoretical Basis for the Determination of Optical Pathlengths in Tissue—Temporal and Frequency-Analysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 1531–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, S.; Franceschini, M.A.; Gratton, E. Semi-Infinite-Geometry Boundary-Problem for Light Migration in Highly Scattering Media—A Frequency-Domain Study in the Diffusion-Approximation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 1994, 11, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durduran, T.; Choe, R.; Baker, W.B.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse optics for tissue monitoring and tomography. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2010, 73, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liemert, A.; Kienle, A. Light diffusion in a turbid cylinder. II. Layered case. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 9266–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripoll, J.; Ntziachristos, V.; Culver, J.P.; Pattanayak, D.N.; Yodh, A.G.; Nieto-Vesperinas, M. Recovery of optical parameters in multiple-layered diffusive media: Theory and experiments. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A-Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2001, 18, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Farrell, T.J.; Patterson, M.S. Accuracy of the diffusion approximation in determining the optical properties of a two-layer turbid medium. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 7401–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielscher, A.H.; Liu, H.L.; Chance, B.; Tittel, F.K.; Jacques, S.L. Time-resolved photon emission from layered turbid media. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, R.M.; Martins, G.G.; Baker, W.B.; Mesquita, R.C. Optimizing a two-layer method for hybrid diffuse correlation spectroscopy and frequency-domain diffuse optical spectroscopy cerebral measurements in adults. Neurophotonics 2023, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, L.; Desjardins, M.; Jehanne-Lacasse, J.; Bherer, L.; Lesage, F. Investigation of diffuse correlation spectroscopy in multi-layered media including the human head. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 15514–15530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallacoglu, B.; Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Optical Characterization of Two-Layered Turbid Media for Non-Invasive, Absolute Oximetry in Cerebral and Extracerebral Tissue. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienle, A.; Glanzmann, T.; Wagnieres, G.; van den Bergh, H. Investigation of two-layered turbid media with time-resolved reflectance. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 6852–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienle, A.; Patterson, M.S.; Dognitz, N.; Bays, R.; Wagnieres, G.; van den Bergh, H. Noninvasive determination of the optical properties of two-layered turbid media. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, D.A.; Dale, A.M.; Franceschini, M.A. Diffuse optical imaging of brain activation: Approaches to optimizing image sensitivity, resolution, and accuracy. Neuroimage 2004, 23, S275–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Huang, K.X.; Zhang, M.H.; Uddin, K.M.S.; Zhu, Q. Effect and correction of optode coupling errors in breast imaging using diffuse optical tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Tan, Z.J. Effects of tissue surface curvature and incident light angle on diffuse correlation spectroscopy. J. Mod. Opt. 2019, 66, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassaroli, A.; Martelli, F.; Zaccanti, G.; Yamada, Y. Performance of fitting procedures in curved geometry for retrieval of the optical properties of tissue from time-resolved measurements. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, R. Boundary-Conditions for Diffusion of Light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A-Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 1995, 12, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, H.; Baker, W.B.; Blaney, G.; Boas, D.A.; Bortfeld, H.; Brady, K.; Brake, J.; Brigadoi, S.; Buckley, E.M.; Carp, S.A.; et al. Optical imaging and spectroscopy for the study of the human brain: Status report. Neurophotonics 2022, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, H.; Eames, M.E.; Yalavarthy, P.K.; Davis, S.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Carpenter, C.M.; Pogue, B.W.; Paulsen, K.D. Near infrared optical tomography using NIRFAST: Algorithm for numerical model and image reconstruction. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 2009, 25, 711–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermyn, M.; Ghadyani, H.; Mastanduno, M.A.; Turner, W.; Davis, S.C.; Dehghani, H.; Pogue, B.W. Fast segmentation and high-quality three-dimensional volume mesh creation from medical images for diffuse optical tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doulgerakis, M.; Eggebrecht, A.T.; Dehghani, H. High-density functional diffuse optical tomography based on frequency-domain measurements improves image quality and spatial resolution. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissila, I.; Noponen, T.; Kotilahti, K.; Katila, T.; Lipiainen, L.; Tarvainen, T.; Schweiger, M.; Arridge, S. Instrumentation and calibration methods for the multichannel measurement of phase and amplitude in optical tomography. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, R.M.; Katsurayama, M.; Valler, L.; Quiroga, A.; Simioni, L.; Menko, J.; Falcao, A.L.E.; Li, L.M.; Mesquita, R.C. Real-Time Monitoring of Neurocritical Patients with Diffuse Optical Spectroscopies. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 20, e61608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.P.; Yan, S.; Fang, Q. Improving model-based functional near-infrared spectroscopy analysis using mesh-based anatomical and light-transport models. Neurophotonics 2020, 7, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algina, J.; Keselman, H.J.; Penfield, R.D. An alternative to Cohen’s standardized mean difference effect size: A robust parameter and confidence interval in the two independent groups case. Psychol. Methods 2005, 10, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.G.; Mesquita, R.C. FD-DOS Data of Healthy Subjects During Rest. 2025. Available online: https://osf.io/fqksh/?view_only=5d3daa5b2f4b46048b42a444d940e65e (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Woodard, H.Q.; White, D.R. The Composition of Body-Tissues. Br. J. Radiol. 1986, 59, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Contini, D.; Re, R.; Spinelli, L.; Roveri, L.; Torricelli, A. Cerebral time domain-NIRS: Reproducibility analysis, optical properties, hemoglobin species and tissue oxygen saturation in a cohort of adult subjects. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4987–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmae, E.; Ouchi, Y.; Oda, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nobesawa, S.; Kanno, T.; Yoshikawa, E.; Futatsubashi, M.; Ueda, Y.; Okada, H.; et al. Cerebral hemodynamics evaluation by near-infrared time-resolved spectroscopy: Correlation with simultaneous positron emission tomography measurements. Neuroimage 2006, 29, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Buckley, E.M.; Licht, D.J.; Lynch, J.M.; Schwab, P.J.; Naim, M.Y.; Lavin, N.A.; Nicolson, S.C.; Montenegro, L.M.; Yodh, A.G.; et al. Cerebral oxygen metabolism in neonates with congenital heart disease quantified by MRI and optics. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Choe, R.; Shah, N.; Durduran, T.; Yu, G.Q.; Durkin, A.; Hsiang, D.; Mehta, R.; Butler, J.; Cerussi, A.; et al. Diffuse optical monitoring of blood flow and oxygenation in human breast cancer during early stages of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.R.; Balu, R.; Baker, W.B.; Guo, W.S.; He, L.; Diop, M.; Milej, D.; Kavuri, V.; Amendolia, O.; St Lawrence, K.; et al. Detection of Brain Hypoxia Based on Noninvasive Optical Monitoring of Cerebral Blood Flow with Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy. Neurocritical Care 2019, 30, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Zheng, C.; Brothers, R.; Buckley, E.M. Small separation frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy for the recovery of tissue optical properties at millimeter depths. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 5362–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, K.; Diop, M.; Lee, A.; Morrison, L.B.; Lee, T.Y.; St Lawrence, K. Assessment of a multi-layered diffuse correlation spectroscopy method for monitoring cerebral blood flow in adults. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3659–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milej, D.; Abdalmalak, A.; Rajaram, A.; St Lawrencea, K. Direct assessment of extracerebral signal contamination on optical measurements of cerebral blood flow, oxygenation, and metabolism. Neurophotonics 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.T.; Sathialingam, E.; Buckley, E.M. Accuracy of diffuse correlation spectroscopy measurements of cerebral blood flow when using a three-layer analytical model. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 7149–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.M.; Chan, S.T.; Mazumder, D.; Tamborini, D.; Stephens, K.A.; Deng, B.; Farzam, P.; Chu, J.Y.; Franceschini, M.A.; Qu, J.Z.; et al. Improved accuracy of cerebral blood flow quantification in the presence of systemic physiology cross-talk using multi-layer Monte Carlo modeling. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, R.; Hoffman, W.E.; Mueller, M.; Paisansathan, C.; Charbel, F. Age effects on brain oxygenation during hypercapnia. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallacoglu, B.; Sassaroli, A.; Wysocki, M.; Guerrero-Berroa, E.; Beeri, M.S.; Haroutunian, V.; Shaul, M.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Troen, A.M.; Fantini, S. Absolute measurement of cerebral optical coefficients, hemoglobin concentration and oxygen saturation in old and young adults with near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzel, K. Correlation Techniques in Dynamic Light-Scattering. Appl. Phys. B-Photophysics Laser Chem. 1987, 42, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sex | Skin Color | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Men | Women | White | Non-White (NW) | |
| Participants | 152 | 55 | 97 | 99 | 53 |
| Age [years] | 39 (17) | 39 (18) | 38 (17) | 37 (17) | 41 (17) |
| Comparison of the Estimated Parameters in FD-DOS Using Different Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical properties | ||||
| 690 nm | 850 nm | |||
| absorption (cm−1) | scattering (cm−1) | absorption (cm−1) | scattering (cm−1) | |
| Curved | 0.120 (0.116; 0.124) | 9.91 (9.72; 10.1) | 0.134 (0.130; 0.138) | 8.77 (8.61; 8.93) |
| SI | 0.110 (0.107; 0.114) | 8.92 (8.75; 9.08) | 0.123 (0.119; 0.127) | 8.00 (7.87; 8.14) |
| Physiological parameters | ||||
| [HbO] (molar) | [HbR] (molar) | [HbT] (molar) | StO2 (%) | |
| Curved | 30.5 (29.3; 31.6) | 20.7 (19.9; 21.4) | 51.1 (49.4; 52.8) | 58.9 (58.1; 59.7) |
| SI | 27.1 (25.9; 28.3) | 19.0 (18.3; 19.7) | 46.1 (44.4; 47.8) | 57.6 (56.8; 58.4) |
| Slope | Intercept | Pearson Correlation Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbO [M] | −0.28 (0.03) | 42 (5) | −0.35 (p < 10−5) |
| HbR [M] | −0.13 (0.02) | 26 (1) | −0.23 (p < 10−5) |
| HbT [M] | −0.41 (0.05) | 67 (2) | −0.34 (p < 10−5) |
| StO2 [%] | −0.08 (0.02) | 62 (1) | −0.14 (p = 0.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, G.G.; Forti, R.M.; Mesquita, R.C. Influence of Tissue Curvature on the Absolute Quantification in Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. J. 2025, 3, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/spectroscj3020014
Martins GG, Forti RM, Mesquita RC. Influence of Tissue Curvature on the Absolute Quantification in Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy. Spectroscopy Journal. 2025; 3(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/spectroscj3020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Giovani G., Rodrigo M. Forti, and Rickson C. Mesquita. 2025. "Influence of Tissue Curvature on the Absolute Quantification in Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy" Spectroscopy Journal 3, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/spectroscj3020014
APA StyleMartins, G. G., Forti, R. M., & Mesquita, R. C. (2025). Influence of Tissue Curvature on the Absolute Quantification in Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy. Spectroscopy Journal, 3(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/spectroscj3020014







