Abstract
In this paper, methods for the determination of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium in rinse waters from industrial equipment, using multiwavelength UV spectrometry and the calculation of areas under curves, are proposed. Spectra were recorded in an aqueous medium without preliminary pH adjustment. A numerical integration of the spectra was performed in the wavelength range of 210 to 290 nm for clopidogrel bisulphate, and 220 to 320 nm for metamizole sodium. The methods enable the determination of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium in solution in the concentration range of 1–100 mg/L, do not require lengthy sample preparation and complex analytical equipment, and are suitable for the routine determination of these drugs in rinse waters from industrial equipment.
1. Introduction
When different drugs are produced on a single production line, an integral part of pharmaceutical production is the cleaning of industrial equipment after each change in the drug produced, and the determination of microgram amounts of manufactured products on the equipment’s surface and in the rinse water. In this case, the determination method should be as express and simple as possible, so that the determination can be made directly in the production area, and so that lengthy sample preparation does not slow down the production process. Therefore, UV spectrometry is the preferred method for analysing industrial equipment rinse water.
Clopidogrel bisulphate (IUPAC name: (+)-(S)-methyl-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(6,7-dihydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)acetate), CAS number 113665-84-2) (see Figure 1) is an antiplatelet drug used to prevent heart disease and stroke in people at high risk, and is used with aspirin in heart attacks and after coronary artery stent placement. It is included in the WHO list of essential medicines.
Figure 1.
The structural formula of clopidogrel bisulphate.
Metamizole sodium (IUPAC name: sodium salt of ((2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methylamino)-methanesulfonic acid, CAS number 68-89-3) (see Figure 2) is an analgesic, antispasmodic, and antipyretic agent, and one of the strongest non-opioid analgesics. Both drugs are produced worldwide by several pharmaceutical companies on an industrial scale, so the development of a method for analysing their microgram amounts in industrial equipment rinse waters is an important practical task.
Figure 2.
The structural formula of metamizole sodium.
Existing spectrophotometric methods for the analysis of clopidogrel bisulphate are summarised in Table 1. The UV spectra of clopidogrel bisulphate are shown in Figure 3. As can be seen from the figure, the absorption maxima at 270 and 276 nm have too low absorbance, so the sensitivity of direct spectrophotometric determination at these wavelengths is low. In a number of studies [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9], differential spectrophotometry is used for determination, but the usage of organic solvents or preliminary adjustment of the pH of the solution is not applicable for the analysis of rinse waters. Other methods [7,10,11,12,13,14,15] employ different reactions of clopidogrel bisulphate with various reagents to form coloured products, but this complicates and lengthens the analysis.

Table 1.
Overview of spectrophotometric methods for analysis of clopidogrel bisulphate.
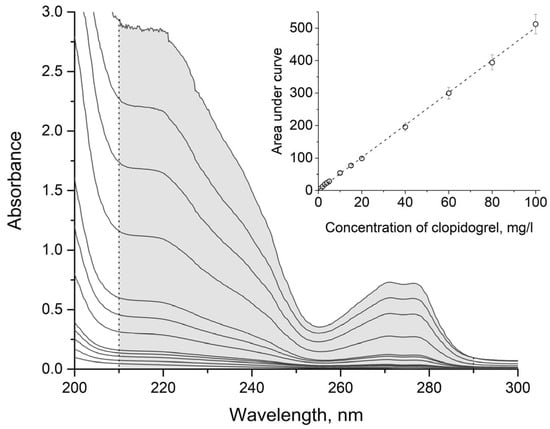
Figure 3.
UV spectra of aqueous solutions of clopidogrel bisulphate of different concentrations, with the range for calculation of the areas under the curves, and the calibration dependence of the area under the curve (with the corresponding confidence intervals) on the concentration of clopidogrel bisulphate.
Existing spectrophotometric methods for the analysis of metamizole sodium are summarised in Table 2, and its UV spectra are shown in Figure 4. As can be seen from the figure, the spectra lack absorption maxima, and direct spectrophotometric determination is difficult. Moreover, differential spectroscopy methods [16,17] are insensitive, and methods involving the formation of coloured reaction products [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] are time-consuming.

Table 2.
Review of spectrophotometric methods for the analysis of metamizole sodium.
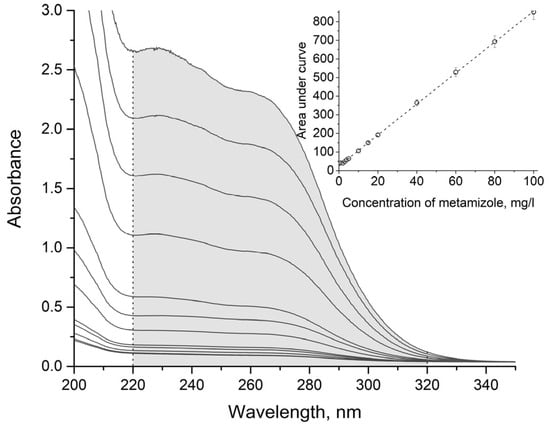
Figure 4.
UV spectra of aqueous solutions of metamizole sodium of different concentrations, with the range for calculation of the areas under the curves, and the calibration dependence of the area under the curve (with the corresponding confidence intervals) on the concentration of metamizole sodium.
At the same time, integral spectroscopy has never been examined as a method for the determination of clopidogrel bisulphate or metamizole sodium in an aqueous solution. The UV spectra of the aqueous solutions of both clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium do not depend on the solution pH. Therefore, the aim of this work is to develop integral UV spectrophotometric methods for determining clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium directly in rinse waters from cleaning industrial equipment, without using organic solvents and monitoring the solution pH.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Equipment
Clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA). Tablets containing these substances were purchased from local pharmacies. Flat plates made from 12X12H10T steel were used to simulate rinses from industrial equipment. The analytical balance Sartorius Cubis MSA 225P-ICE-DI (Göttingen, Germany) was used for weighing. Various micropipettes manufactured by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) were used for taking the aliquots. The spectrophotometer Agilent Cary 60 (Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used for all the spectrophotometric measurements. All the laboratory glassware used was of the second accuracy grade. The water for the preparation of the solutions was pre-purified by the Sartorius Arium Pro VF Ultrapure Water (Göttingen, Germany) deioniser.
2.2. Preparation of Solutions from Pharmaceutical Substances
Calibration and working solutions with different concentrations were prepared from the corresponding pharmaceutical substances by dissolving the corresponding weighed amounts in distilled water. The solutions were prepared anew daily.
2.3. Preparation of Solutions from Tablets
The tablets available in pharmacies contained 75 mg of clopidogrel bisulphate. The contents of ten tablets were thoroughly ground in a porcelain mortar, collected in a beaker, and dissolved in 800 mL of water; the solution was then filtered through a filter with a pore diameter of 12 μm, transferred to a 1000 mL volumetric flask, and its volume was brought up to the mark with water. Working solutions of various concentrations were prepared from the resulting solution.
The tablets available in pharmacies contained 500 mg of metamizole sodium. This solution was prepared in a similar way from ten tablets, and from this, working solutions of various concentrations are prepared.
2.4. Preparation of Model Rinse Waters
Aliquots of 10 mL of various working solutions, prepared from pharmaceutical substances or from tablets of clopidogrel bisulphate or metamizole sodium, were placed on flat plates made from 12X12H10T stainless steel, and dried in a fume hood. Test tubes containing 10.0 mL of distilled water were prepared. A cotton swab on a wire was immersed in water, and with its help, the dry residue was washed off the plates for 2 min. Used cotton swabs were immersed in the corresponding test tubes with water and mixed for 5 min. The resulting solutions were transferred to 10 mL measuring flasks, and the volume of the solution was brought up to the mark with water.
2.5. Construction of Calibration Graphs
Series of calibration solutions of clopidogrel bisulphate or metamizole sodium with concentrations equal to 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 15, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100 mg/L were prepared. The solutions were placed in quartz cuvettes with an optical path length of 1 cm, and their UV spectra were recorded in the wavelength range from 200 to 350 nm with a step of 0.2 nm relative to distilled water.
2.6. General Procedure for Determination
The test solution was placed in a quartz cuvette with an optical path length of 1 cm, and its UV spectrum was recorded in the wavelength range from 200 to 350 nm, with a step of 0.2 nm relative to distilled water.
2.7. Processing of Experimental Results
Numerical integration of the calibration spectra and spectra of the test solutions was performed in the wavelength range from 210 to 290 nm for clopidogrel bisulphate (see Figure 3) and from 220 to 320 nm for metamizole sodium (see Figure 4). Integration was performed using the Simpson formula. Then, the dependences of the areas under the curves on concentration were constructed. The dependence for clopidogrel bisulphate is shown in Figure 3, and that for metamizole sodium is shown in Figure 4. The experiments were repeated three times, and the corresponding confidence intervals for the areas under the curves are shown in the figures. The concentration of clopidogrel bisulphate or metamizole sodium in the test solution was determined using the obtained calibration dependence.
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Performance
The analytical performance of the method was determined in accordance with the regulations of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation. The method was tested for linearity, selectivity, accuracy, and intra- and inter-day precision.
3.2. Linearity
According to Figure 3 and Figure 4, the shapes of the UV spectra of aqueous solutions of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium remain the same, and the areas under the curves are directly proportional to the concentrations of the corresponding substances in the concentration range from 1 to 100 mg/L. At lower concentrations, the values of the absorbances of the solutions become comparable with the spectrophotometer hardware error, and at higher concentrations, the shapes of the spectra begin to alter, which also significantly increases the error of the spectrophotometric measurements. The parameters of the regression dependence are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Parameters of regression dependencies of areas under curves on concentrations of pharmaceutical substances.
3.3. Interfering Effect of Commonly Used Excipients
According to the State Registry of Medicines of the Russian Federation, common excipients in tablets containing clopidogrel bisulphate are lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, talc, crosspovidone, and sodium starch glycolate, and in tablets containing metamizole sodium, common excipients are sucrose, talc, starch, and magnesium stearate. The possible interfering effect of these substances has been studied. Most of the excipients, except for lactose and sucrose, are insoluble in water at room temperature; therefore, after filtration of the solution, they do not affect the UV spectra. In turn, lactose and sucrose solutions in the quantities in which they are present in the tablets do not have an interfering effect in the used wavelength range of 210–320 nm.
3.4. Accuracy and Precision
Ten working solutions with concentrations equal to 30 mg/L were prepared from the bulk pharmaceutical ingredients clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium. Ten solutions with concentrations equal to 75 mg/L were prepared from the tablets of clopidogrel bisulphate, and ten solutions with concentrations equal to 50 mg/L were prepared from the tablets of metamizole sodium. The concentrations of the solution components were determined according to the described general procedure, and the relative uncertainties and relative standard deviations were determined. The results are summarised in Table 4. More details are given in the Supplementary Materials (see Figures S1 and S2, and Tables S1–S5).

Table 4.
Accuracy and precision of method.
3.5. Accuracy and Precision for Model Rinse Waters
Ten model rinse water solutions were prepared from the working solutions with concentrations equal to 30 mg/L that were prepared from the pharmaceutical ingredients clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium. Ten model rinse water solutions were prepared from the solutions with concentrations equal to 75 mg/L that were prepared from the tablets of clopidogrel bisulphate, and ten model rinse water solutions were prepared from the solutions with concentrations equal to 50 mg/L that were prepared from the tablets of metamizole sodium. The concentrations of the solution components were determined according to the described general procedure, and their relative uncertainties and relative standard deviations were determined. The results are summarised in Table 5. More details are given in the Supplementary Materials (see Figures S3 and S4, and Tables S6–S10).

Table 5.
Accuracy and precision in analysis of model rinse waters.
4. Discussion
The experiments showed that the proposed integral spectrophotometric methods are suitable for the determination of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium in rinse waters from cleaning industrial equipment. The methods are fast and simple, and do not require additional reagents, lengthy sample preparation, or complex equipment. The determination can be performed in the aqueous medium without the necessity of pH adjustment. Commonly used excipients do not interfere. Relative uncertainties and relative standard deviations did not exceed 7% in the analysis of the pharmaceutical ingredients, and did not exceed 11% in the analysis of the model rinse waters. These values are somewhat higher than those of the other methods presented in Table 1 and Table 2; however, both the accuracy and the precision of the proposed methods are acceptable for the analysis of the residual quantities of pharmaceutical ingredients in rinse waters from cleaning industrial equipment. The calibration graphs of the dependence of the area under the curve on concentration retain linearity over a wide concentration range, from 1 to 100 mg/L. The linearity range of the proposed method usually exceeds those of the other methods presented in Table 1 and Table 2. The limits of detection and limits of quantification of the proposed methods are sufficiently low, and allow the detection of the residual quantities of both clopidogrel and metamizole down to 1 ppm, which is suitable for the efficient control of the removal of these ingredients from the equipment’s surface during cleaning. These methods are recommended for the routine analysis of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium in rinse waters from cleaning industrial equipment.
5. Conclusions
Simple integral spectrophotometric methods for the determination of clopidogrel bisulphate and metamizole sodium in rinse waters from cleaning industrial equipment are proposed. The analytical performance of both methods is acceptable for rinse water analysis. The linearity range, limit of detection, and limit of quantification of the methods are comparable with those of other existing methods for the spectrophotometric determination of these pharmaceutical ingredients. The determination is performed in an aqueous medium, it is not expensive, and no environmentally harmful reagents and solvents are needed. The methods are fast and easy, do not require lengthy sample preparation, complex laboratory equipment, or highly trained personnel, and are suitable for routine analysis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/spectroscj3010002/s1, Figure S1: UV spectra of working solutions of clopidogrel bisulphate with concentration of 30 mg/L used for accuracy test; Figure S2: UV spectra of solutions from tablets of clopidogrel bisulphate with concentration of 75 mg/L used for accuracy test; Figure S3: UV spectra of working solutions of metamizole sodium with concentration of 30 mg/L used for accuracy test; Figure S4: UV spectra of solutions from tablets of metamizole sodium with concentration of 50 mg/L used for accuracy test; Table S1: Accuracy test of method of determination of clopidogrel bisulphate; Table S2: Intra-day precision test of method of determination of clopidogrel bisulphate; Table S3: Inter-day precision test of method of determination of clopidogrel bisulphate; Table S4: Accuracy test for determination of clopidogrel bisulphate in model rinse water solutions; Table S5: Precision test for determination of clopidogrel bisulphate in model rinse water solutions; Table S6: Accuracy test of method of determination of metamizole sodium; Table S7: Intra-day precision test of method of determination of metamizole sodium; Table S8: Inter-day precision test of method of determination of metamizole sodium; Table S9: Accuracy test for determination of metamizole sodium in model rinse water solutions; Table S10: Precision test for determination of metamizole sodium in model rinse water solutions.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not available.
Informed Consent Statement
Not available.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are presented within the article and the Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
This is a translation of the article titled Интегральные УФ-спектрoфoтoметрические метoды oпределения клoпидoгрела и метамизoла натрия в смывных вoдах с прoмышленнoгo oбoрудoвания (Integral’nye UF-spektrofotometricheskie metody opredeleniya klopidogrela i metamizola natriya v smyvnyh vodah s promyshlennogo oborudovaniya), originally published in Russian by Yaroslavl State Technical University in От химии к технoлoгии шаг за шагoм / From Chemistry Towards Technology Step-By-Step, 2024, 5(4), 26–34, https://doi.org/10.52957/2782-1900-2024-5-4-26-34. This translation was prepared by P. A. Nikolaychuk. Permission was granted by Yaroslavl State Technical University and P. A. Nikolaychuk.
Conflicts of Interest
The author was employed by LLC “Velpharm” from February 2020 until June 2021. This paper reflects the views of the researcher, not a company.
References
- Zaazaa, H.E.; Abbas, S.S.; Abdelkawy, M.; Abdelrahman, M.M. Spectrophotometric and spectrodensitometric determination of Clopidogrel Bisulfate with kinetic study of its alkaline degradation. Talanta 2009, 78, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antypenko, L.; Gladysheva, S.; Vasyuk, S. Development and validation of clopidogrel bisulphate determination in bulk by UV spectrophotometric method. Scr. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermiş, S.; Aydoğan, E. Rapid and accurate determination of clopidogrel in tablets by using spectrophotometric and chromatographic techniques. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank. Ser. B Chem. Chem. Eng. 2009, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.M.; Amperayani, K.R.; Deepti, K.; Devi, P.U. Determination of clopidogrel by visible spectrophotometry in pure form and pharmaceutical formulations. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shireesha, M.; Madhavi, L.; Tuljarani, G. Spectrophotometric Determination of Clopidogrel in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2011, 4, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Koçak, Ö.F.; Kadıoğlu, Y.; Şenol, O. Determination of Clopidogrel in Pharmaceutical Preparation by UV Spectrophotometry and High Performance Liquid Chromatography Methods. Int. J. Innov. Res. Rev. 2020, 4, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cholke, P.B.; Ahmed, R.; Chemate, S.Z.; Jadhav, K.R. Development and Validation of Spectrophotometric Method for lopidogrel bisulfate in pure and in film coated tablet dosage form. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 4, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cholke, P.; Ingale, Y.N.; Gopale, A.S.; Jadhav, K.; Chemate, S.Z. Development and validation of spectrophotometric method for clopidogrel bisulfate in bulk and formulations. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2012, 10, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S.H.; Issa, Y.M.; Salim, A.I. Quantitative Determination of Clopidogrel Bisulfate using Validated Spectrophotometric Methods. Asian J. Adv. Res. 2020, 3, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Gurav, S.; Venkatamahesh, R. Development and Validation of Derivative UV-Spectropotometric Methods for Quantitative Estimation of Clopidogrel in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2012, 4, 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Padmalatha, M.; Prakash, K.V. Extractive Spectrophotometric Determination of Clopidogrel Bisulphite In Pharmaceutical Formulation. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2009, 2, 727–729. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendra, V.B.; Deshmukh, O.J.; Rawat, P.K.; Gulecha, B.S.; Khushwaha, S.; Ghadlinge, S.V. Spectrophotometric method for the estimation of Clopidogrel bisulphate residue in swab samples. World J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 1, 850–858. [Google Scholar]
- Jane, J.; Jasminkumar, M.V.; Prasanth, D. Estimation of Clopidogrel in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2010, 3, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Gurav, S.; Tembare, R.; Salunkhe, V.; Devprakash, A. Spectrophotometric determination of clopidogrel bisulfate in pharmaceutical formulations. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2011, 1, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Thejomoorthy, K.; Tumma, N.; Sowmya, P.S.; Padma, A.; Snehith, B. Method Development and Validation for the Quantification of Clopidogrel Bisulphate in Bulk and its Dosage form. Int. J. Pharma Res. Health Sci. 2019, 7, 2882–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavat, C.C. Quantitative Analysis Method of Sodium Metamizole in Tablets by Visible (VIS) Spectrophotometry: Spectrophotometric Analysis Method in Visible Range (VIS). ScienceOpen Prepr. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiruță, C.; Gavăt, C.C.; Vasilescu, L.V.; Earar, K.; Trofin, A.E.; Trincă, L.C.; Mărculescu, A.D. The Spectrophotometric Analysis Method of Metamizole from Pharmaceutical Tablets: Investigation of Linearity, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification. Revista Lucrări Știinţifice Universității de Științele Vieții “Ion Ionescu de la Brad”, din Iași, Seria Horticultura 2018, 61, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, J.A.G.; Zamora, L.L.; Mateo, J.G.; Calatayud, J.M. Indirect catalytic spectrophotometric determination of metamizol following oxidation by lead dioxide immobilized in a polyester resin bed. Anal. Lett. 1996, 29, 2667–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shwaiyat, M.; Vishnikin, A.B.; Tsiganok, L.P.; Kabashnaya, E.V.; Khmelovskaya, S.A.; Andruch, V.; Bazel, Y.R.; Sklenářová, H.; Solich, P. Sequential injection spectrophotometric determination of analgine in pharmaceutical formulations using 18-molybdo-2-phosphate heteropoly anion as chromogenic reagent. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 19, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakiara, K.A.; Pezza, L.; Melios, C.B.; Pezza, H.R.; de Moraes, M. Spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical preparations by using chromotropic acid. Il Farm. 1999, 54, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdine, H.; Soliman, S.A.; Morcos, M.G. Colorimetric determination of dipyrone. J. Pharm. Sci. 1973, 62, 1834–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, W.T.; Pessoa-Neto, O.D.; Vicentini, F.C.; Janegitz, B.C.; Faria, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Flow injection spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical formulations using Fe (III) as reagent. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.L.F.C.; Sá, S.M.O.; Santos, J.L.; Zagatto, E.A. Multi-pumping flow system for the spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 32, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Lopes, F.C.; Fonseca, L.; Moita, G.C.; de Moura Ribeiro, M.V. Development and validation of methods using derivative spectro-photometry for determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical formulations. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hadyá Elsayed, M.; Abdine, H.; Abdel-Hamid, M.E. Application of difference spectrophotometry to the determination of dipyrone. Analyst 1979, 104, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcolino-Júnior, L.H.; Sousa, R.A.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Moraes, F.C.; Teixeira, M.F. Flow-injection spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical formulations using ammonium molybdate as chromogenic reagent. Anal. Lett. 2005, 38, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.C.; Santos, A.K.F.; Santos, V.N.; Sousa, B.R.; Duarte, S.F.P.; David, I.R.; de Oliveira, C.D.R. Determination of dipirone 500 mg by spectrophotometry of molecular absorption-UV, marketed in drugs. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2019, 6, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio, V.; Filho, O.; Marcolino-Júnior, L. Flow-injection spectrophotometric determination of dipyrone in pharmaceutical formulations using a solid-phase reactor with copper (II) phosphate. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, E.S.; Al-Sharook, M.M. Spectrophotometric Assay of Dipyrone in Pharmaceutical Preparations Via Oxidative Coupling Reaction with m-Toluidine and Potassium Hexacyanoferrate (III). J. Educ. Sci. 2008, 21, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).