Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer and Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. BTK in Cancer
2.1. Role of BTK in Hematological Malignancies
2.2. BTK in Solid Tumors
3. The Role of BTK in TME Modulation
4. BTK Impact on Tumor Angiogenesis
5. Tumoricidal Effects of BTK Inhibition
5.1. Ibrutinib
5.2. Acalabrutinib
5.3. Zanubrutinib
6. Resistance to BTK Inhibition and Challenges
6.1. Tumor-Intrinsic Mechanisms of Resistance
6.2. Extrinsic Mechanisms of Resistance
6.3. BTK Degraders
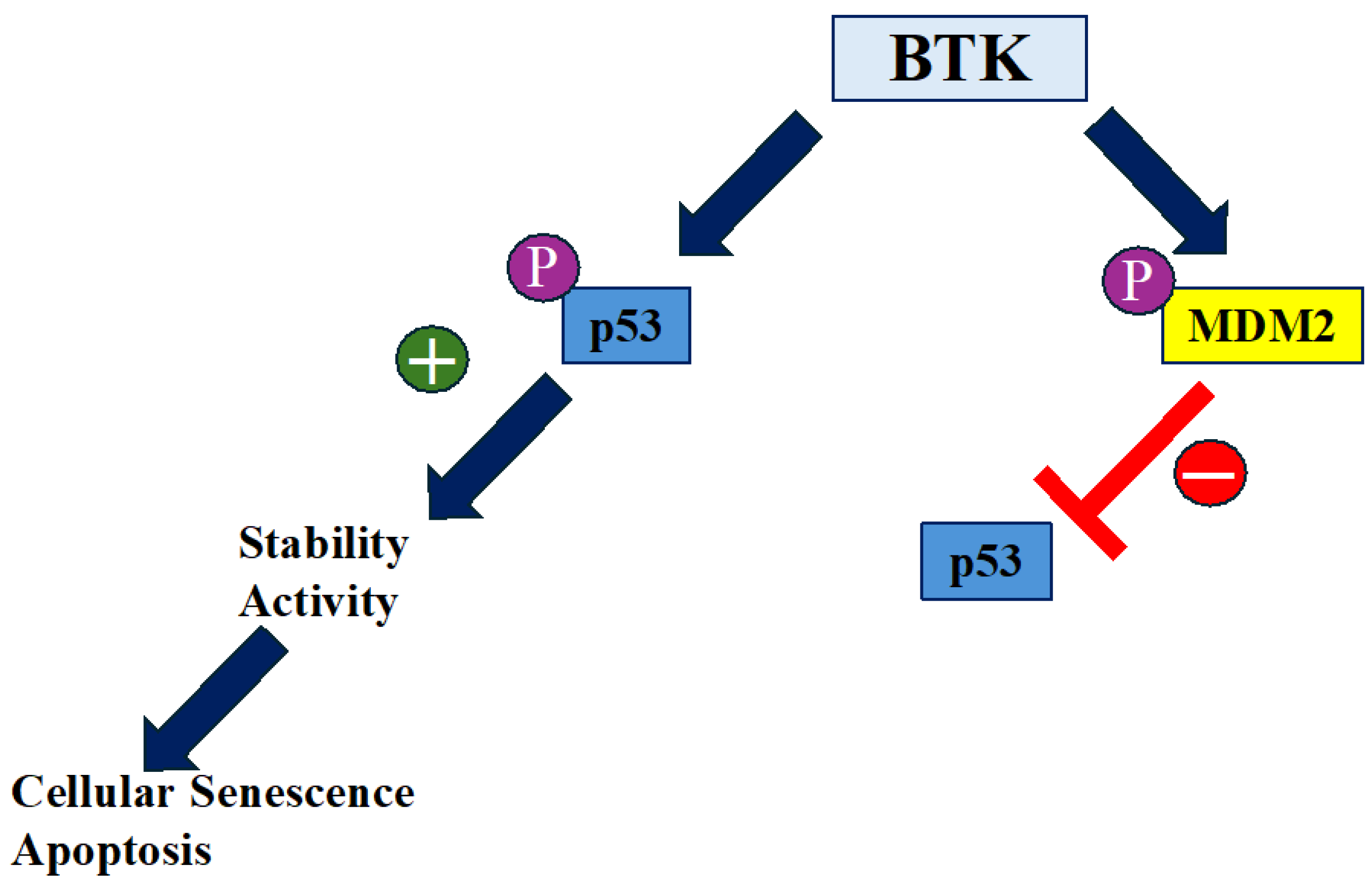
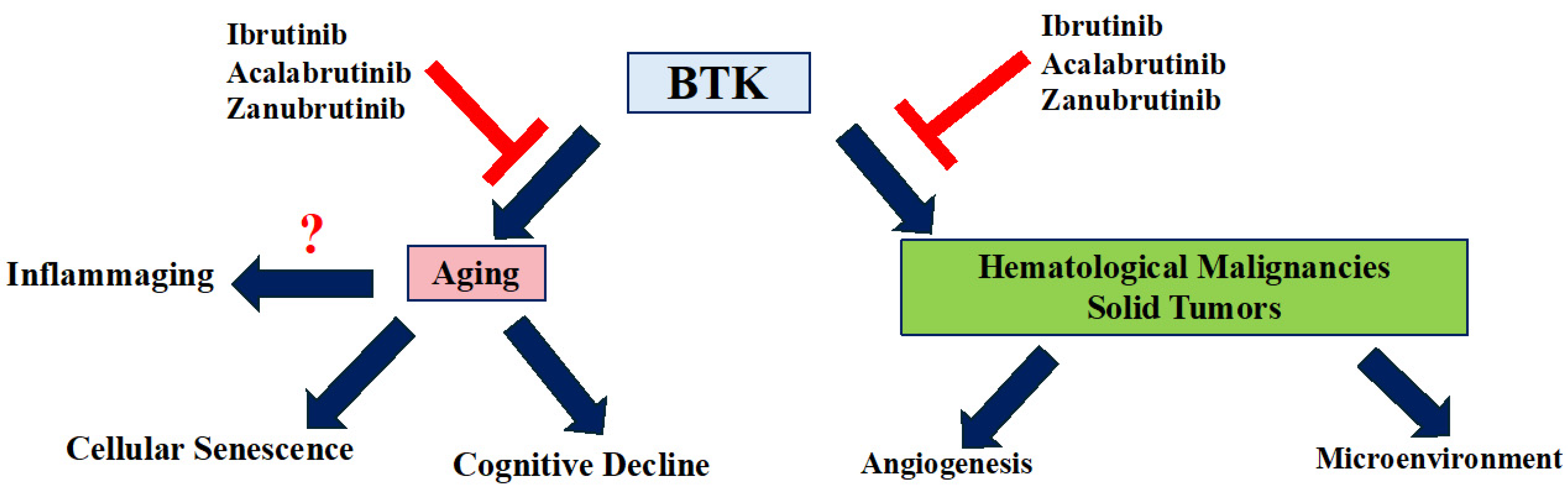
7. The Role of BTK in Aging
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rada, M.; Barlev, N.; Macip, S. BTK modulates p73 activity to induce apoptosis independently of p53. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, M.M. Characterisation of Novel Post-Translational Modulators of p53. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rada, M.; Barlev, N.; Macip, S. BTK: A two-faced effector in cancer and tumour suppression. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, M.; Qusairy, Z.; Macip, S. Relevance of the Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) as a target for COVID-19 therapy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckun, F.M.; Venkatachalam, T. Targeting Solid Tumors With BTK Inhibitors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 650414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.; Chong, G.; Hawkes, E. Novel Indications for Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors, beyond Hematological Malignancies. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell development. Dev. Immunol. 2001, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, D.; Wang, E.S.; Morrow, S.; Leahy, C.; Faust, T.; Nowak, R.P.; Donovan, K.A.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Fischer, E.S. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase degradation as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Blood 2019, 133, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papin, A.; Tessoulin, B.; Bellanger, C.; Moreau, A.; Le Bris, Y.; Maisonneuve, H.; Moreau, P.; Touzeau, C.; Amiot, M.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C. CSF1R and BTK inhibitions as novel strategies to disrupt the dialog between mantle cell lymphoma and macrophages. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bibikova, E.; Ayres, M.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Gandhi, V. Comparison of acalabrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3734–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Champlin, R.E.; Wang, M.L. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in B-cell malignancies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 97, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.; O’Brien, S. Acalabrutinib and its use in treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wong, J.; Sevinsky, C.J.; Kokabee, L.; Khan, F.; Sun, Y.; Conklin, D.S. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Prevent Therapeutic Escape in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Mullick Chowdhury, S.; Hart, A.; Sircar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Nath, U.K.; Mamgain, M.; Singhal, N.K.; Sehgal, L.; Jain, N. Ibrutinib Resistance Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies for B-Cell Lymphomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpenyong-Akiba, A.E.; Poblocka, M.; Althubiti, M.; Rada, M.; Jurk, D.; Germano, S.; Kocsis-Fodor, G.; Shi, Y.; Canales, J.J.; Macip, S. Amelioration of age-related brain function decline by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibition. Aging 2020, 19, e13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althubiti, M.; Rada, M.; Samuel, J.; Escorsa, J.M.; Najeeb, H.; Lee, K.-G.; Lam, K.-P.; Jones, G.D.D.; Barlev, N.A.; Macip, S. BTK modulates p53 activity to enhance apoptotic and senescent responses. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5405–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechle, J.J.; Chen, N.; Makhijani, P.; Winer, S.; Furman, D.; Winer, D.A. Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol. Metab. 2023, 74, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, G.M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a signaling pathway in immune-mediated diseases: From molecular mechanisms to leading treatments. Adv. Rheumatol. 2024, 64, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, M.I.; Catalan-Dibene, J.; Zlotnik, A. B cells responses and cytokine production are regulated by their immune microenvironment. Cytokine 2015, 74, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.; Lopez-Herrera, G.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Lindvall, J.M.; Berglöf, A.; Edvard Smith, C.I.; Vargas, L. Defective Toll-like receptor 9-mediated cytokine production in B cells from Bruton’s tyrosine kinase-deficient mice. Immunology 2008, 123, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profitós-Pelejà, N.; Santos, J.C.; Marín-Niebla, A.; Roué, G.; Ribeiro, M.L. Regulation of B-Cell Receptor Signaling and Its Therapeutic Relevance in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.; Xanthopoulos, C.; Kostareli, E. The role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in the immune system and disease. Immunology 2021, 164, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouhssine, S.; Maher, N.; Matti, B.F.; Alwan, A.F.; Gaidano, G. Targeting BTK in B Cell Malignancies: From Mode of Action to Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, M.; Mulder, T.A.; Österborg, A. BTK Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Biological Activity and Immune Effects. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, K.; Puła, B. A Review of Resistance Mechanisms to Bruton’s Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhoda, S.; Vistarop, A.; Wang, Y.L. Resistance to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Rule, S.; Martin, P.; Goy, A.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.S. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu, A.; Lei, H.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. BTK inhibitors in the treatment of hematological malignancies and inflammatory diseases: Mechanisms and clinical studies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Jung, J.; Victor, E.; Arceo, J.; Gokhale, S.; Xie, P. Clinical Trials of the BTK Inhibitors Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib in Human Diseases Beyond B Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Doubek, M.; Ferrant, E.; Diels, J.; Andersone, L.; Wilbertz, S.; Healy, N.C.; Neumayr, L.; van Sanden, S. Overall survival of patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib in the first line compared to second-line ibrutinib after chemotherapy/chemoimmunotherapy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2024, 40, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Owen, C.; Robak, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Burger, J.A.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Dearden, C.; Grosicki, S. Up to 8-year follow-up from RESONATE-2: First-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Owen, C.; Robak, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Burger, J.A.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Dearden, C.; Grosicki, S.; et al. CLL-076 Final Analysis of the RESONATE-2 Study: Up to 10 Years of Follow-Up of First-Line Ibrutinib Treatment in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024, 24, S342–S343. [Google Scholar]
- Kittai, A.S.; Allan, J.N.; James, D.; Bridge, H.; Miranda, M.; Yong, A.S.M.; Fam, F.; Roos, J.; Shetty, V.; Skarbnik, A.; et al. An indirect comparison of acalabrutinib with and without obinutuzumab vs zanubrutinib in treatment-naive CLL. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.; Thompson, P.A. BTK inhibitors in CLL: Second-generation drugs and beyond. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; Jurczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Zanubrutinib or Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassilli, E.; Cerrito, M.G.; Bonomo, S.; Giovannoni, R.; Conconi, D.; Lavitrano, M. p65BTK Is a Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Solid Tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 690365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kokabee, L.; Kokabee, M.; Conklin, D.S. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and Its Isoforms in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 668996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Nallanthighal, S.; Cha, J.; Ryan, K.; Sage, J.; Eldred, C.; Ullo, M.; Orsulic, S.; Cheon, D.J. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) mediate collagen type XI alpha 1-driven cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4809–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, M.; Cha, J.; Sage, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Orsulic, S.; Cheon, D.J. COL11A1 confers cisplatin resistance through fatty acid oxidation in ovarian cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallanthighal, S.; Rada, M.; Heiserman, J.P.; Cha, J.; Sage, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Hu, Y.; Korgaonkar, C.; Hanos, C.T.; et al. Inhibition of collagen XI alpha 1-induced fatty acid oxidation triggers apoptotic cell death in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Yu, B.; Choe, H.C.; Ding, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of drug resistance in ovarian cancer from 2013 to 2022. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1173863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, L.; Cirillo, G.; Riva, G.; Romano, G.; Giussani, C.; Cialdella, A.; Todisco, A.; Virtuoso, A.; Cerrito, M.G.; Bentivegna, A.; et al. Specific Expression of a New Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Isoform (p65BTK) in the Glioblastoma Gemistocytic Histotype. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucha, M.A.; Wu, A.T.H.; Lee, W.-H.; Wang, L.-S.; Lin, W.-W.; Yuan, C.-C.; Yeh, C.-T. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor ibrutinib suppresses stem-like traits in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13255–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklener, K.; Michalski, A.; Żak, K.; Piwoński, M.; Mańdziuk, S. Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions. Cells 2022, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, J.M.; Fink, D.; Imesch, P. Ibrutinib Could Suppress CA-125 in Ovarian Cancer: A Hypothesis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassilli, E.; Pisano, F.; Cialdella, A.; Bonomo, S.; Missaglia, C.; Cerrito, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Ianzano, L.; Narloch, R.; D’Amato, F.; et al. A novel oncogenic BTK isoform is overexpressed in colon cancers and required for RAS-mediated transformation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4368–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.; Gerratana, L.; Buonadonna, A.; Garattini, S.K.; Perin, T.; Grassilli, E.; Miolo, G.; Cerrito, M.G.; Belluco, C.; Bertola, G. Role of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in Stage III Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Meng, C.; Yang, D.; Qian, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, Y. Recent development of BTK-based dual inhibitors in the treatment of cancers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 233, 114232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, F.; Vaira, V.; Cortinovis, D.; Bonomo, S.; Goedmakers, J.; Brena, F.; Cialdella, A.; Ianzano, L.; Forno, I.; Cerrito, M.G.; et al. p65BTK is a novel potential actionable target in KRAS-mutated/EGFR-wild type lung adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassilli, E.; Cerrito, M.G.; Lavitrano, M. BTK the new kid on the (oncology) block? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 944538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, L.; Xia, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, M. The impact of BTK knockdown on lung adenocarcinoma growth and immune response. Cancer Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzler, A.C.; Strobel, H.; Abou Kors, T.; Ezić, J.; Lesakova, K.; Pscheid, R.; Azoitei, N.; Sporleder, J.; Staufenberg, A.R.; Drees, R. BTK Isoforms p80 and p65 Are Expressed in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) and Involved in Tumor Progression. Cancers 2023, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kwak, M.; Kang, J.; Cesaire, M.; Tang, K.; Robey, R.W.; Frye, W.J.; Karim, B.; Butcher, D.; Lizak, M.J.; et al. Ibrutinib disrupts blood-tumor barrier integrity and prolongs survival in rodent glioma model. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2024, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Niu, M.; Shan, Q.Q.; Zhou, T.; Tu, Y.; Xie, P.; Hua, L.; Yu, R.; Liu, X. High expression of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is required for EGFR-induced NF-κB activation and predicts poor prognosis in human glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messex, J.K.; Liou, G.-Y. Targeting BTK Signaling in the Microenvironment of Solid Tumors as a Feasible Cancer Therapy Option. Cancers 2021, 13, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, L.; Benner, B.; Carson, W.E. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: An emerging targeted therapy in myeloid cells within the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, B.; Scarberry, L.; Stiff, A.; Duggan, M.C.; Good, L.; Lapurga, G.; Butchar, J.P.; Tridandapani, S.; Carson, W.E. Evidence for interaction of the NLRP3 inflammasome and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in tumor-associated macrophages: Implications for myeloid cell production of interleukin-1beta. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, 1659704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, R.Y.; Zagrodnik, J.L.; Carew, S.J.; Moore, C.S. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Decreases Inflammation and Differentially Impacts Phagocytosis and Cellular Metabolism in Mouse- and Human-derived Myeloid Cells. Immunohorizons 2024, 8, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedquist, K.; Hartkamp, L.; Radstake, T. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in chronic inflammation: From pathophysiology to therapy. Int. J. Interferon Cytokine Mediat. Res. 2015, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiff, A.; Trikha, P.; Wesolowski, R.; Kendra, K.; Hsu, V.; Uppati, S.; McMichael, E.; Duggan, M.; Campbell, A.; Keller, K. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Express Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and Can Be Depleted in Tumor-Bearing Hosts by Ibrutinib Treatment. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, X.-P.; Luoreng, Z.-M.; Yang, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, Y.; Wei, D.-W. miR-223: An Effective Regulator of Immune Cell Differentiation and Inflammation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2308–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Lazaris, A.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Mayer, T.Z.; Metrakos, P. Tumor microenvironment conditions that favor vessel co-option in colorectal cancer liver metastases: A theoretical model. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 71, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, T.Z.; Kim, D.H.; Rada, M.; Petrillo, S.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Role of innate immune cells in the development of vessel co-opting CRC liver metastases. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, Y.; Tang, F.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Immunosuppressive cells in cancer: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, A.J.; Kaneda, M.M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Nguyen, A.V.; Affara, N.I.; Ruffell, B.; Gorjestani, S.; Liudahl, S.M.; Truitt, M.; Olson, P.; et al. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase–Dependent Immune Cell Cross-talk Drives Pancreas Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, M.; Reynolds, A.R.; Lazaris, A.; Seidah, N.; Metrakos, P. Inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin-like kexin type 9 (PCSK9) potentiates anti-angiogenic therapy in colorectal cancer liver metastases. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Tsamchoe, M.; Petrillo, S.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Angiopoietin-1 Upregulates Cancer Cell Motility in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases through Actin-Related Protein 2/3. Cancers 2022, 14, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Krzywon, L.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Kim, D.; Petrillo, S.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Vitamin D supplementation improves the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Petrillo, S.; Tabariès, S.; Siegel, P.; Reynolds, A.R.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Runt related transcription factor-1 plays a central role in vessel co-option of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Krzywon, L.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Petrillo, S.; Reynolds, A.R.; Lazaris, A.; Seidah, N.; Metrakos, P. High levels of serum cholesterol positively correlate with the risk of the development of vessel co-opting tumours in colorectal cancer liver metastases. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Tsamchoe, M.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Bloom, J.; Petrillo, S.; Kim, D.H.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Cancer cells induce hepatocytes apoptosis in co-opted colorectal cancer liver metastatic lesions. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.S.; Lazaris, A.; Rada, M.; Petrillo, S.K.; Huck, L.; Hussain, S.; Ouladan, S.; Gao, Z.-H.; Gregorieff, A.; Essalmani, R.; et al. Angiopoietin1 Deficiency in Hepatocytes Affects the Growth of Colorectal Cancer Liver. Cancers 2020, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Sui, L.; Yu, J. Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varikuti, S.; Singh, B.; Volpedo, G.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Jha, B.K.; Saljoughian, N.; Viana, A.G.; Verma, C.; Hamza, O.; Halsey, G.; et al. Ibrutinib treatment inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing conversion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells to dendritic cells. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozkiewicz, D.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Kwiatkowska, I.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (BTKIs): Review of Preclinical Studies and Evaluation of Clinical Trials. Molecules 2023, 28, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, A.; Carracedo Uribe, C.; Martinez, D.; Rehman, T.; Silva Rondon, C.; Sandoval-Sus, J. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Recent Updates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estupiñán, H.Y.; Berglöf, A.; Zain, R.; Smith, C.I.E. Comparative Analysis of BTK Inhibitors and Mechanisms Underlying Adverse Effects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.D.; Pacholczyk, R.; Shi, H.; Berrong, Z.J.; Zakharia, Y.; Greco, A.; Chang, C.-S.S.; Eathiraj, S.; Kennedy, E.; Cash, T.; et al. Inhibition of the BTK-IDO-mTOR axis promotes differentiation of monocyte-lineage dendritic cells and enhances anti-tumor T cell immunity. Immunity 2021, 54, 2354–2371.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gokhale, S.; Jung, J.; Spirollari, E.; Tsai, J.; Arceo, J.; Wu, B.W.; Victor, E.; Xie, P. Multifaceted Immunomodulatory Effects of the BTK Inhibitors Ibrutinib and Acalabrutinib on Different Immune Cell Subsets—Beyond B Lymphocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 727531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Wierda, W.G. Acalabrutinib: A Selective Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 668162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Series, J.; Garcia, C.; Levade, M.; Viaud, J.; Sie, P.; Ysebaert, L.; Payrastre, B. Differences and similarities in the effects of ibrutinib and acalabrutinib on platelet functions. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, J.; Reneau, J.; Devata, S.; Wilcox, R.A.; Kaminski, M.S.; Mercer, J.; Carty, S.; Phillips, T.J. Evaluating Acalabrutinib In The Treatment Of Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Design, Development, And Place In Therapy. OncoTargets and Therapy 2019, 12, 8003–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyed, M.; Lueff, S.; Borbely, J.; Illes, A. Acalabrutinib and its use in the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, S.E.M.; Montraveta, A.; Niemann, C.U.; Mora-Jensen, H.; Gulrajani, M.; Krantz, F.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.L.; McClanahan, F.; Harrington, B.K.; et al. The Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor Acalabrutinib Demonstrates Potent On-Target Effects and Efficacy in Two Mouse Models of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.S.; Muñoz, J.L.; Seymour, J.F.; Opat, S. Zanubrutinib: Past, present, and future. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Washer, A.; Robak, T. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies: Current status and future directions. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhebany, N.; Pan, C.; Holovac, E.; Do, B.; McBride, A. Zanubrutinib in Mantle Cell Lymphoma Management: A Comprehensive Review. Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2023, 13, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Gao, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; et al. Zanubrutinib ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulating macrophage polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T.; et al. Zanubrutinib Ameliorates Cardiac Fibrosis and Inflammation Induced by Chronic Sympathetic Activation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, M.; End, P.; Cabanski, M.; Schuhler, C.; Jakab, A.; Kistowska, M.; Kinhikar, A.; Maiolica, A.; Sinn, A.; Fuhr, R.; et al. Remibrutinib (LOU064): A selective potent oral BTK inhibitor with promising clinical safety and pharmacodynamics in a randomized phase I trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, M.D.; Reeves, D.J. Pirtobrutinib: A New and Distinctive Treatment Option for B-Cell Malignancies. Ann. Pharmacother. 2024, 58, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaratne, V.; Sondhi, A.K.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Taylor, J. New means and challenges in the targeting of BTK. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in malignant tumors: Molecular mechanisms and future perspective. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bödör, C.; Kotmayer, L.; László, T.; Takács, F.; Barna, G.; Kiss, R.; Sebestyén, E.; Nagy, T.; Hegyi, L.L.; Mikala, G.; et al. Screening and monitoring of the BTKC481S mutation in a real-world cohort of patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia during ibrutinib therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyach, J.A.; Jones, D.; Jurczak, W.; Robak, T.; Illés, Á.; Kater, A.P.; Ghia, P.; Byrd, J.C.; Seymour, J.F.; Long, S.; et al. Mutational profile in previously treated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression on acalabrutinib or ibrutinib. Blood 2024, 144, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Mi, X.; Thompson, M.C.; Montoya, S.; Notti, R.Q.; Afaghani, J.; Durham, B.H.; Penson, A.; Witkowski, M.T.; Lu, S.X.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Noncovalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampson, B.L.; Brown, J.R. Are BTK and PLCG2 mutations necessary and sufficient for ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia? Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondrisova, L.; Mraz, M. Genetic and Non-Genetic Mechanisms of Resistance to BCR Signaling Inhibitors in B Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 591577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Kapelanski-Lamoureux, A.; Zlotnik, O.; Petrillo, S.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. Disruption of integrin alpha-5/beta-1-dependent transforming growth factor beta-1 signaling pathway attenuates vessel co-option in colorectal cancer liver metastases. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, M.; Krzywon, L.; Petrillo, S.; Lazaris, A.; Metrakos, P. A Retrospective Study on the Role of Metformin in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Manstein, V.; Yang, C.M.; Richter, D.; Delis, N.; Vafaizadeh, V.; Groner, B. Resistance of Cancer Cells to Targeted Therapies Through the Activation of Compensating Signaling Loops. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2013, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernot, S.; Evrard, S.; Khatib, A.-M. The Give-and-Take Interaction Between the Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Cells Regulating Tumor Progression and Repression. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 850856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Barroso, J.; Munaretto, A.; Rouquié, N.; Mougel, A.; Chassan, M.; Gadat, S.; Dewingle, O.; Poincloux, R.; Cadot, S.; Ysebaert, L.; et al. Lymphocyte migration and retention properties affected by ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2023, 109, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, U.D.; Zhang, K.; Teutsch, M.; Sen, R.; Wortis, H.H. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Links the B Cell Receptor to Nuclear Factor κb Activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rip, J.; de Bruijn, M.J.W.; Appelman, M.K.; Singh, S.P.; Hendriks, R.W.; Corneth, O.B.J. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Drives Btk-Mediated Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyach, J.A.; Smucker, K.; Smith, L.L.; Lozanski, A.; Zhong, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Lucas, D.; Williams, K.; Zhao, W.; Rassenti, L.; et al. Prolonged lymphocytosis during ibrutinib therapy is associated with distinct molecular characteristics and does not indicate a suboptimal response to therapy. Blood 2014, 123, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, B.; Kang, N.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ding, N.; et al. PROTAC for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase degradation alleviates inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Omer, Z.; Collins, G.P.; Forconi, F.; Danilov, A.; Byrd, J.C.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Searle, E.; Alencar, A.J.; Ma, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Degrader NX-5948 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Updated Results from an Ongoing Phase 1a/b Study. Blood 2024, 144, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvaris, R.T.; Brennan, J.; Lewis, K.L. BTK Is the Target That Keeps on Giving: A Review of BTK-Degrader Drug Development, Clinical Data, and Future Directions in CLL. Cancers 2025, 17, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, A.; O’Loghlen, A. Cellular Senescence and Ageing: Mechanisms and Interventions. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 866718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic Inflammation (Inflammaging) and Its Potential Contribution to Age-Associated Diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qusairy, Z.; Rada, M. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer and Aging. Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020010
Qusairy Z, Rada M. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer and Aging. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2025; 3(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleQusairy, Zahraa, and Miran Rada. 2025. "Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer and Aging" Kinases and Phosphatases 3, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020010
APA StyleQusairy, Z., & Rada, M. (2025). Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer and Aging. Kinases and Phosphatases, 3(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3020010






