Abstract
The diagnosis and treatment of lymphoid neoplasms have undergone a progressively positive change in the last three decades, with accelerated progress in the previous decade due to the advent of genomics in cancer diagnosis. Significantly, there has been an increasing emphasis on integrating molecular genetics with clinical, morphologic, immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic evaluation for diagnosis. As we consider moving forward with further advances in the genomics era, it is first helpful to understand our current state of knowledge and how we achieved it in the challenging and complex field of lymphoid neoplasms, which comprise very heterogeneous neoplastic diseases in children and adults, including clinically acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALLs) arising from precursor lymphoid cells and clinically indolent and aggressive lymphomas arising from mature lymphoid cells. This work aims to provide an overview of the historical evolution and the current state of knowledge to anyone interested in the field of lymphoid neoplasms, including students, physicians, and researchers. Therefore, I have discussed this complex topic in three review manuscripts, designated Parts 1–3. In Part 1, I explain the basis of the diagnostic classification of lymphoid neoplasms and its evolution up to the current fifth edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms and the crucial importance of diagnostic tumor classifications in achieving and advancing patient care and precision medicine. In the second and third manuscripts, I discuss current diagnostic considerations for B-ALL and T-ALL (Part 2) and common indolent and aggressive mature leukemias/lymphomas (Part 3), including significant updates in the WHO 2022 classification, newly described entities and concepts, including genetic predisposition to ALLs and lymphomas, and throughout emphasizing the essential integration of molecular genetics with clinical, morphologic (pathologic), immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic evaluation, as is required for precise diagnosis of the type of lymphoma/leukemia in any patient.
1. Introduction
Lymphomas are neoplasms of lymphoid tissues and may arise at any lymph node or extranodal site in the human body. If the neoplastic lymphoid cells involve the circulating blood, the disease comprises leukemia and may be called leukemia/lymphoma. For more than 150 years, lymphoma diagnosis has required morphologic (visual) examination of blood cells or a tissue biopsy obtained from the enlarged lymph node or tissue mass, complemented by immunophenotypic evaluation in the last four decades and cytogenetic analysis for definitive diagnosis in selected types of lymphoma.
In 1674, Leeuwenhoek invented the microscope and described red blood cells, and a century later, in 1774, Hewson described the lymphocytes after Lieutaud described the white blood cells in 1749 [1]. In the next century, in November 1845, Rudolph Virchow, a demonstrator of anatomy in Berlin, Germany, described the first case of what is now understood to be chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) six weeks after David Craigie, a physician at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, and John Hughes Bennett, a clinician, and pathologist at the same institution in Edinburgh, described the first two patients with chronic myeloid leukemia [1,2]. In the same century, Thomas Hodgkin described Hodgkin’s disease in 1832 in at least one among seven patients described post-mortem [3,4], with the credit given to Hodgkin in 1865 by Samuel Wilks, who studied similar patients with the diagnoses of tuberculosis, syphilis, and neoplastic disease (leukemia or lymphoma) [4]. Subsequently, in 1898 and 1902, the characteristic large, nucleolated neoplastic cells in Hodgkin’s disease were independently described by Sternberg and Reed by histologic examination of tissue sections in Hodgkin’s disease, which to this day form the diagnostic criteria for classic Hodgkin lymphoma in the presence of the required background polymorphous inflammatory cells. Follicular lymphoma (FL), a non-Hodgkin lymphoma arising from germinal center B cells, was next described in 1925 and 1927 by Brill and Symmers, respectively. Burkitt lymphoma was described as a tumor of the jaws in 38 patients in Africa by Dennis Burkitt in 1958 [5] and was found to be associated with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in 1964 [6]. Characteristic cytogenetic abnormalities involving the 8q24 chromosomal locus were discovered in Burkitt lymphoma in the late 1970s [7,8,9], which were most often used for confirming the specific diagnosis.
Since then, in the last five decades, very significant advances have occurred in our understanding of the pathology and molecular genetics of lymphoid neoplasms due to the work of countless individuals. This work aims to provide an overview of the historical evolution and the current state of knowledge to anyone interested in the field of lymphoid neoplasms, including students, physicians, and researchers. In addition, before moving forward with further advances, it is first helpful to understand how we achieved our current state of knowledge in the challenging and complex field of lymphoid neoplasms. These neoplasms comprise very heterogeneous neoplastic diseases in children, adolescents, and adults of all ages. These diseases include clinically acute lymphoblastic leukemias/lymphomas (ALLs) arising from precursor lymphoid cells and clinically indolent and aggressive lymphomas arising from mature lymphoid cells. Therefore, I have discussed this complex topic in three review manuscripts. The first review provides a historical overview of lymphoma classifications and the principles of the diagnostic classification of lymphoid neoplasms. It includes sections on B- and T-cell development in the bone marrow and the thymus, respectively, germinal center components of the lymphoid follicle, the origin of ALLs and mature B-cell neoplasms, clonality analysis in lymphoid neoplasms, and the crucial role of the diagnostic World Health Organization (WHO) classification in achieving and advancing precision medicine. The second review focuses on ALLs, including inherited predisposition to ALLs, as we understand these diseases today, in 2023. The third review on mature lymphoid neoplasms of B, T, or natural killer (NK) cell lineage is focused on common indolent and aggressive mature leukemias/lymphomas in the pediatric and adult age groups, a few rare lymphomas, updates in the 5th edition WHO classification, newly described lymphomas, and new concepts, including lymphomas of immune-privileged sites, T follicular helper (TFH) cell lymphomas, in situ mantle cell neoplasia, and inherited predisposition to lymphoid neoplasms, with particular emphasis throughout on the integration of molecular genetics with clinical, morphologic, immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic evaluation, as is currently required for precise diagnosis of the specific type of lymphoma in any patient.
2. Historical Overview of Lymphoma Classifications
Lymphomas are often broadly classified as Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas, possibly due to the initial description of Hodgkin’s disease described almost two centuries (190 years) ago. Therefore, all lymphomas other than Hodgkin lymphoma are termed non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The latter comprise a diverse group of lymphoid neoplasms arising from lymphoid cells at different stages of differentiation, including precursor and mature lymphoid cells, representing (precursor) acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALLs) and several types of mature B, T, or natural killer (NK) lymphoid neoplasms, respectively. In contrast, Hodgkin lymphomas are classified as either classic Hodgkin lymphoma or nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Both types of Hodgkin lymphomas arise from mature B cells. Interestingly, Hodgkin’s disease was termed Hodgkin lymphoma only 22 years ago in 2001, after the neoplastic cells in Hodgkin lymphoma were shown to be clonally derived from B cells in 1994 [10,11]. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the variable-diversity-junctional (VDJ) region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) genes in microdissected neoplastic cells showed IGH-rearranged B-lineage neoplastic cells in Hodgkin’s disease [10,11], with defective immunoglobulin transcription in the IGH-rearranged neoplastic B cells in classic Hodgkin lymphoma [12].
The classification of lymphoid neoplasms has a rich history, beginning in the mid-20th century, described up to the present day in a recent publication [13]. The most widely used early effort in the USA was the Rappaport classification, proposed in 1956. This classification scheme was based on histologic features, i.e., the lymphoma growth pattern as either nodular or diffuse, separating the neoplasms as nodular or diffuse lymphomas, respectively. The Rappaport classification included Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The latter included the following four types of lymphomas [14]:
(1) Lymphocytic type, well-differentiated
(2) Lymphoblastic type, poorly differentiated
(3) Mixed type (lymphocytic and reticulum cell), and
(4) Reticulum cell type
In 1966, Lukes and Butler proposed the following six subtypes of Hodgkin’s disease: (1) lymphocytic and/or histiocytic (L&H) nodular; (2) Lymphocytic and/or histiocytic (L&H) diffuse; (3) Nodular sclerosis; (4) Mixed; (5) Diffuse fibrosis; and (6) Reticular [15]. This proposal by Lukes and Butler [15] was modified as the widely used Rye classification of Hodgkin’s disease. The Rye classification defined the following nomenclature for all subtypes of Hodgkin’s disease:
(1) The lymphohistiocytic (L&H) diffuse and nodular subtypes were combined to form lymphocytic predominance (L&H) Hodgkin’s disease;
(2) Nodular sclerosis
(3) Mixed cellularity
(4) Lymphocyte depletion: this subtype was formed by combining the diffuse fibrosis and reticular subtypes in the earlier proposal by Lukes and Butler [16].
The landmark discoveries of different B- and T-lineage lymphocytes in 1965 [17,18], reviewed in [19], led to incorporating B- and T-cell lineages in lymphoma classifications. In 1974, Lukes and Collins in the USA classified non-Hodgkin lymphomas based on two features: (1) the immunologic cell-of-origin, classifying lymphomas as undefined cell type, B-cell type, T-cell type, histiocytic, and unclassifiable; and (2) the cytology of lymphoma cells, including small and large cleaved and non-cleaved cells [20]. At the same time, in 1974, the Kiel classification was introduced in Europe, which classified lymphomas as low or high grade based on the cytologic features, not clinical features [21]. The Kiel classification was updated in 1988 to include B- and T-lineage types of lymphoma, with the previous low- and high-grade types based on cytology [22].
Several other classifications were used at that time, which led to the United States National Cancer Institute (NCI) sponsoring a landmark study of six major classifications in use before 1982. These classifications included those proposed by Rappaport, Lukes and Collins, Dorfman, the World Health Organization (WHO), British National Lymphoma Investigation, and the Kiel classification. This NCI study led to The Working Formulation of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas for Clinical Usage in 1982 [23], which grouped lymphomas as low grade, intermediate grade, and high grade, with miscellaneous types. Although developed for clinical use, the Working Formulation was widely used by clinicians and pathologists in the U.S.A.
In 1994, the International Lymphoma Study Group of nineteen expert pathologists, based primarily in the USA and Europe with one expert from Asia, developed the Revised European American Lymphoma (REAL) classification. This group described lymphoma entities based on clinical, morphologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic features that pathologists could recognize [24]. The REAL classification included precursor and mature (or peripheral) types of B- and T- or Natural Killer (NK)-cell-derived non-Hodgkin lymphomas (at least 23, including eleven mature B and ten mature T or NK subtypes) and five subtypes of Hodgkin’s disease, including provisional entities [24].
After the REAL classification was proposed, 1403 cases of non-Hodgkin lymphomas from eight international sites were studied in the Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Classification Project in 1997 [25]. These study cases included 30.6% diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) and 45% small B-cell lymphomas as the most frequent lymphoma subtypes. The small B-cell lymphomas comprised 22% follicular lymphoma (FL), 7.6% marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MZL) of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues, 6.7% small B-lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), 6% mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), 1.8% nodal MZL, 1.2% lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma, and <1% splenic MZL. The other B-cell lymphomas included 2.4% primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, <1% Burkitt lymphoma, and 2.1% high-grade B-cell Burkitt-like lymphoma. The T-cell lymphomas comprised 7% peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), 2.4% anaplastic large T/null-cell lymphoma, 1.7% precursor T-lymphoblastic lymphoma, and <1% mycosis fungoides, as percentages of all cases.
Significantly, the Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Classification Project showed that most subtypes of lymphomas, as classified by the REAL classification criteria, could be diagnosed by hematopathologists. The study also validated the clinical usefulness of the diagnostic distinction between the lymphoma subtypes. The study showed the following 5-year overall survival rates in patients with the following types of lymphomas:
(1) >70% (the best prognosis) for FL, MZL of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues, and anaplastic large T/null-cell lymphoma;
(2) 50–70% for nodal MZL, SLL, and lymphoplasmacytoid lymphoma;
(3) 30–50% for DLBCL, mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and high-grade Burkitt-like B-cell lymphoma; and
(4) Less than 30% (the worst prognosis) for MCL and PTCL [25].
3. Normal B- and T-Lymphocyte Development, the Lymphoid Follicle Germinal Center, and the Basis for Lymphoma Classification
Antigen expression during hematopoiesis is the basis for interpreting immunophenotypic profiles of various types of leukemias. Hematopoiesis begins in the fetal yolk sac in the third embryonic week and the liver and placenta in the eighth embryonic week. Subsequently, this process occurs in the thymus and bone marrow, wherein hematopoietic stem cells committed to lymphoid lineage give rise to progenitors of T (thymus-derived) and B (bursa or bone-marrow-derived) lymphocytes [26]. The developmental stages of B and T precursor lymphoid cells in the bone marrow and thymus are used to identify neoplastic cells and diagnose B and T lymphoblastic leukemias, respectively. The antigen expression in these developmental stages was determined by flow cytometric immunophenotypic (FCI) analyses, as depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Of note, the presence or absence of IGH or T-cell receptor gene rearrangements cannot be used to determine the B or T lymphoid lineage of the leukemic cells in ALL.
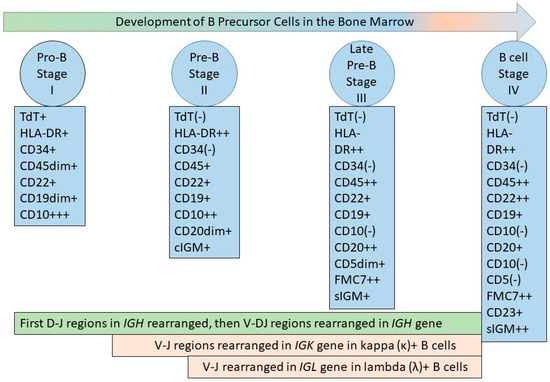
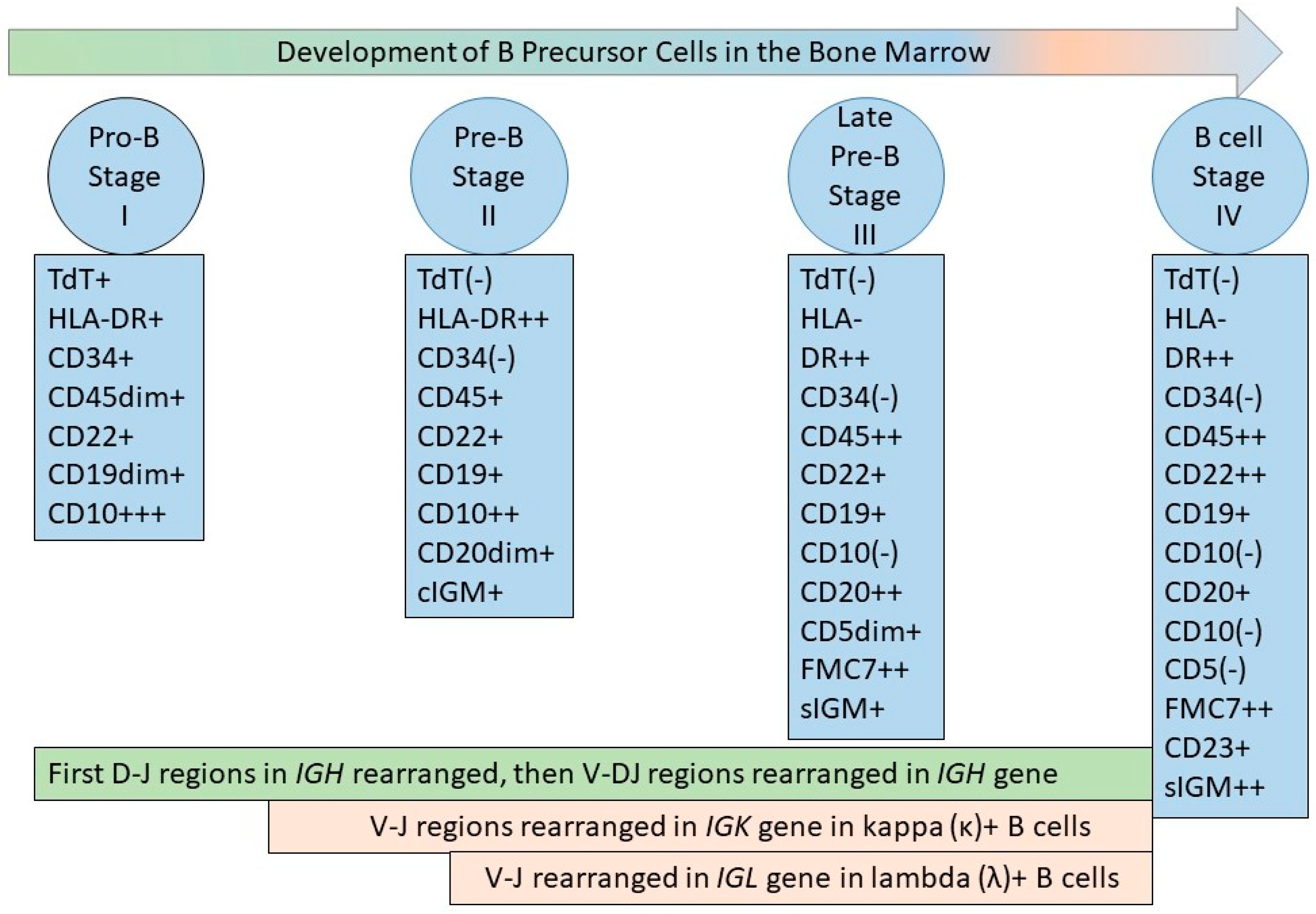
Figure 1.
B-cell development in the bone marrow. The figure depicts the developing B-cell stages recognized by flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI), termed stage I, II, III, and IV [27,28], or pro-B cells, pre-B cells, and late pre-B cells, which lead to mature naïve B cells. The antigen expression on precursor B cells is synchronous with the VDJ gene rearrangement process in IGH, and VJ gene rearrangement in IGK and IGL, as depicted [29]. The most immature bone marrow cells are positive for surface CD34 and HLA-DR, both of which are expressed in multiple lineages. The earliest B-lineage precursor cells are positive for CD19, CD34, and HLA-DR, with intense expression of nuclear terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and cell surface CD10 antigen. In the next stage (stage II), CD34 and nuclear TdT are lost; there is decreased expression of CD10 and increased expression of CD19, which shows stable intensity after the initial increase at the beginning of stage II; there is a continuous increase in CD20 expression until the third stage, and CD45 is expressed. Cytoplasmic immunoglobulin M (IgM) can be detected in Stage II, but the presence of surface IgM is characteristic of Stage III. In addition, stage III is characterized by stable CD19 expression, increased expression of CD20 (from the previous stage) and CD45, a decrease in CD10 intensity (until there is a complete loss of CD10 by the end of stage III), and the appearance of FMC7 expression. CD5 appears transiently during stage III. Stage IV is characterized by the loss of CD10 and the expression of CD19, CD20, CD23, CD45, FMC7, surface IgM, and surface kappa or lambda light chain immunoglobulins. CD22 is present throughout all stages of a B-lineage precursor cell and increases in intensity at stage IV [27,28].
Figure 1.
B-cell development in the bone marrow. The figure depicts the developing B-cell stages recognized by flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI), termed stage I, II, III, and IV [27,28], or pro-B cells, pre-B cells, and late pre-B cells, which lead to mature naïve B cells. The antigen expression on precursor B cells is synchronous with the VDJ gene rearrangement process in IGH, and VJ gene rearrangement in IGK and IGL, as depicted [29]. The most immature bone marrow cells are positive for surface CD34 and HLA-DR, both of which are expressed in multiple lineages. The earliest B-lineage precursor cells are positive for CD19, CD34, and HLA-DR, with intense expression of nuclear terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and cell surface CD10 antigen. In the next stage (stage II), CD34 and nuclear TdT are lost; there is decreased expression of CD10 and increased expression of CD19, which shows stable intensity after the initial increase at the beginning of stage II; there is a continuous increase in CD20 expression until the third stage, and CD45 is expressed. Cytoplasmic immunoglobulin M (IgM) can be detected in Stage II, but the presence of surface IgM is characteristic of Stage III. In addition, stage III is characterized by stable CD19 expression, increased expression of CD20 (from the previous stage) and CD45, a decrease in CD10 intensity (until there is a complete loss of CD10 by the end of stage III), and the appearance of FMC7 expression. CD5 appears transiently during stage III. Stage IV is characterized by the loss of CD10 and the expression of CD19, CD20, CD23, CD45, FMC7, surface IgM, and surface kappa or lambda light chain immunoglobulins. CD22 is present throughout all stages of a B-lineage precursor cell and increases in intensity at stage IV [27,28].
B-lymphocyte development is controlled by several transcription factors, including Ikaros, E2A, early B-cell factor (Ebf1), Pax5, lymphoid enhancer factor (Lef1), and bcl11a (Evi9). Pax5 is required for initiating and maintaining B-cell commitment and is present throughout the B-cell stages from the pro-B-cell to the mature B-cell. Pax5 is downregulated in plasma cells. In the absence of Pax5, B-cell development is arrested at the early pro-B-cell stage [30].
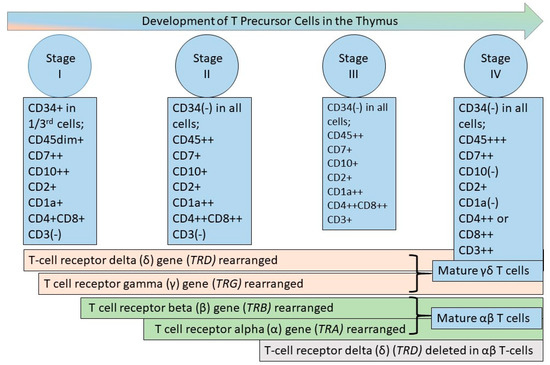
Figure 2.
T-cell development in the thymus. T-cell development occurs in the thymus from bone marrow-derived progenitors. The figure depicts the T-lineage-committed precursor cell stages recognized by flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI), initially described in 1992 [28,31]. As depicted in the figure, synchronous T-cell receptor gene rearrangement occurs first in TRD, followed by TRG for γδ T-cells and in TRB and TRA for αβ T-cells [32]. The earliest stage (Stage I) T-lineage precursors express CD7 and CD10 in the absence of CD3 and with increasing expression of CD1a. CD34 is expressed very early and decreases during stage 1, while CD1a expression increases. Stages II and III are immunophenotypically similar, with Stage II cells larger than Stage III cells. These cell stages II and III are characterized by co-expressed CD4 and CD8, increasing expression of CD3, a decrease in CD10 and CD7, albeit with continued expression throughout Stage III, and increased CD1a, which is expressed throughout Stage III. In Stage IV, CD1a decreases until it is no longer expressed, CD7 expression increases, and CD4 and CD8 are no longer co-expressed. CD45 increases in intensity throughout the development stages, with the lowest intensity in Stage 1 and the highest intensity in Stage IV [28,31].
Figure 2.
T-cell development in the thymus. T-cell development occurs in the thymus from bone marrow-derived progenitors. The figure depicts the T-lineage-committed precursor cell stages recognized by flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI), initially described in 1992 [28,31]. As depicted in the figure, synchronous T-cell receptor gene rearrangement occurs first in TRD, followed by TRG for γδ T-cells and in TRB and TRA for αβ T-cells [32]. The earliest stage (Stage I) T-lineage precursors express CD7 and CD10 in the absence of CD3 and with increasing expression of CD1a. CD34 is expressed very early and decreases during stage 1, while CD1a expression increases. Stages II and III are immunophenotypically similar, with Stage II cells larger than Stage III cells. These cell stages II and III are characterized by co-expressed CD4 and CD8, increasing expression of CD3, a decrease in CD10 and CD7, albeit with continued expression throughout Stage III, and increased CD1a, which is expressed throughout Stage III. In Stage IV, CD1a decreases until it is no longer expressed, CD7 expression increases, and CD4 and CD8 are no longer co-expressed. CD45 increases in intensity throughout the development stages, with the lowest intensity in Stage 1 and the highest intensity in Stage IV [28,31].
In contrast with ALL, the classification of mature lymphoid neoplasms is based on the stages of antigen-dependent B-lymphocyte differentiation, with other factors such as neoplastic cell size by morphologic evaluation, tumor location, and the clinical mode of presentation also considered in the classification.
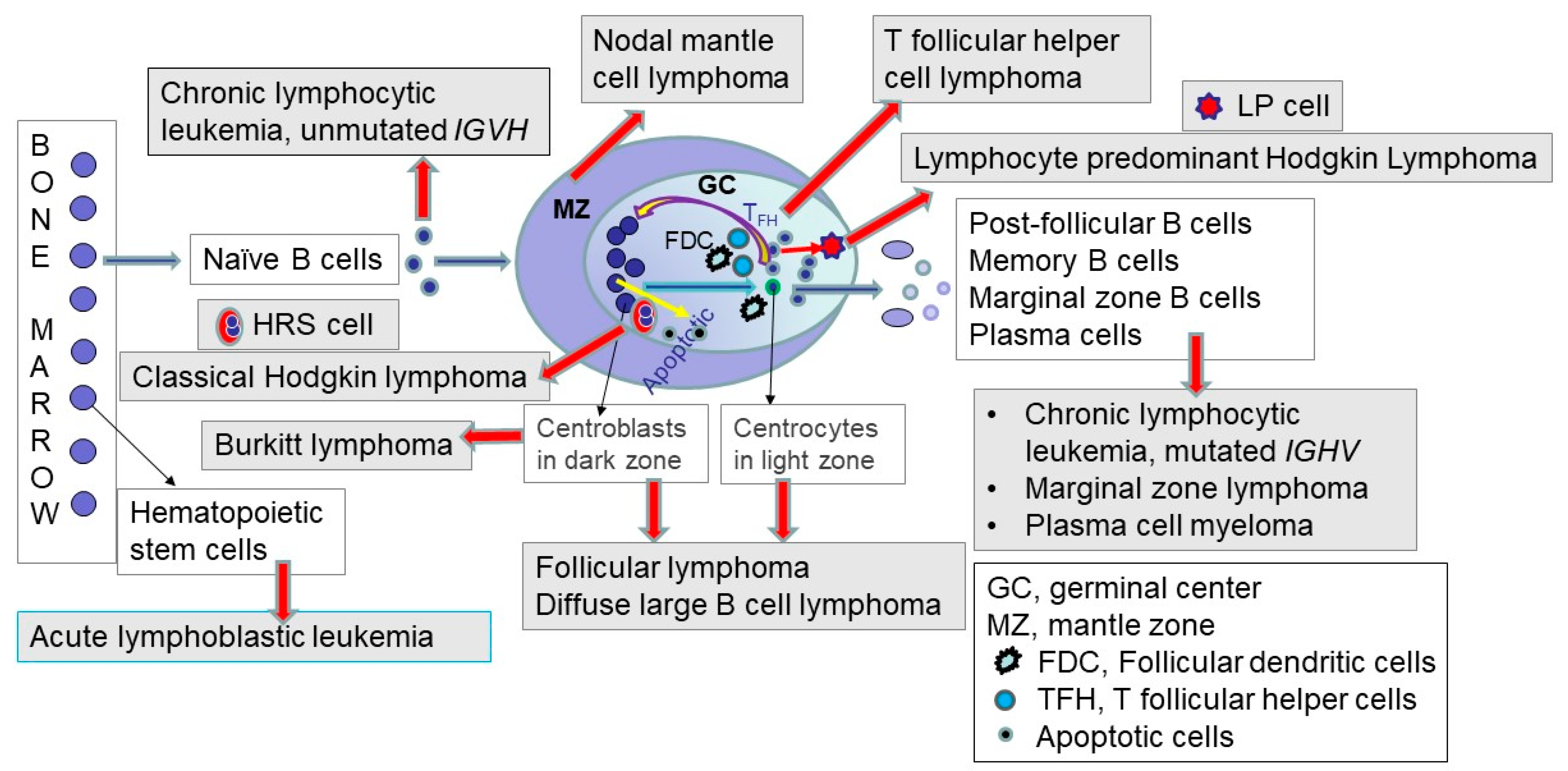
Precursor B-lineage cells in the bone marrow develop into mature B cells, which have rearranged IGH genes, as described above. Mature B-cell neoplasms represent clonal proliferations of mature B lymphocytes that mimic normal stages of B-cell differentiation [13]. The concept and process are depicted and briefly described in Figure 3; the interested reader is referred to excellent in-depth reviews [33,34,35].
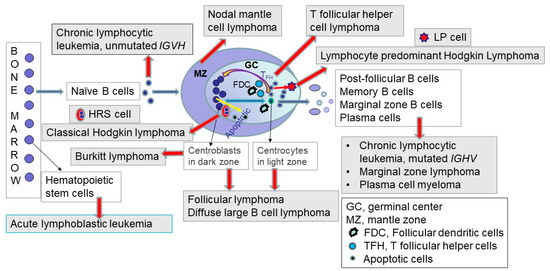
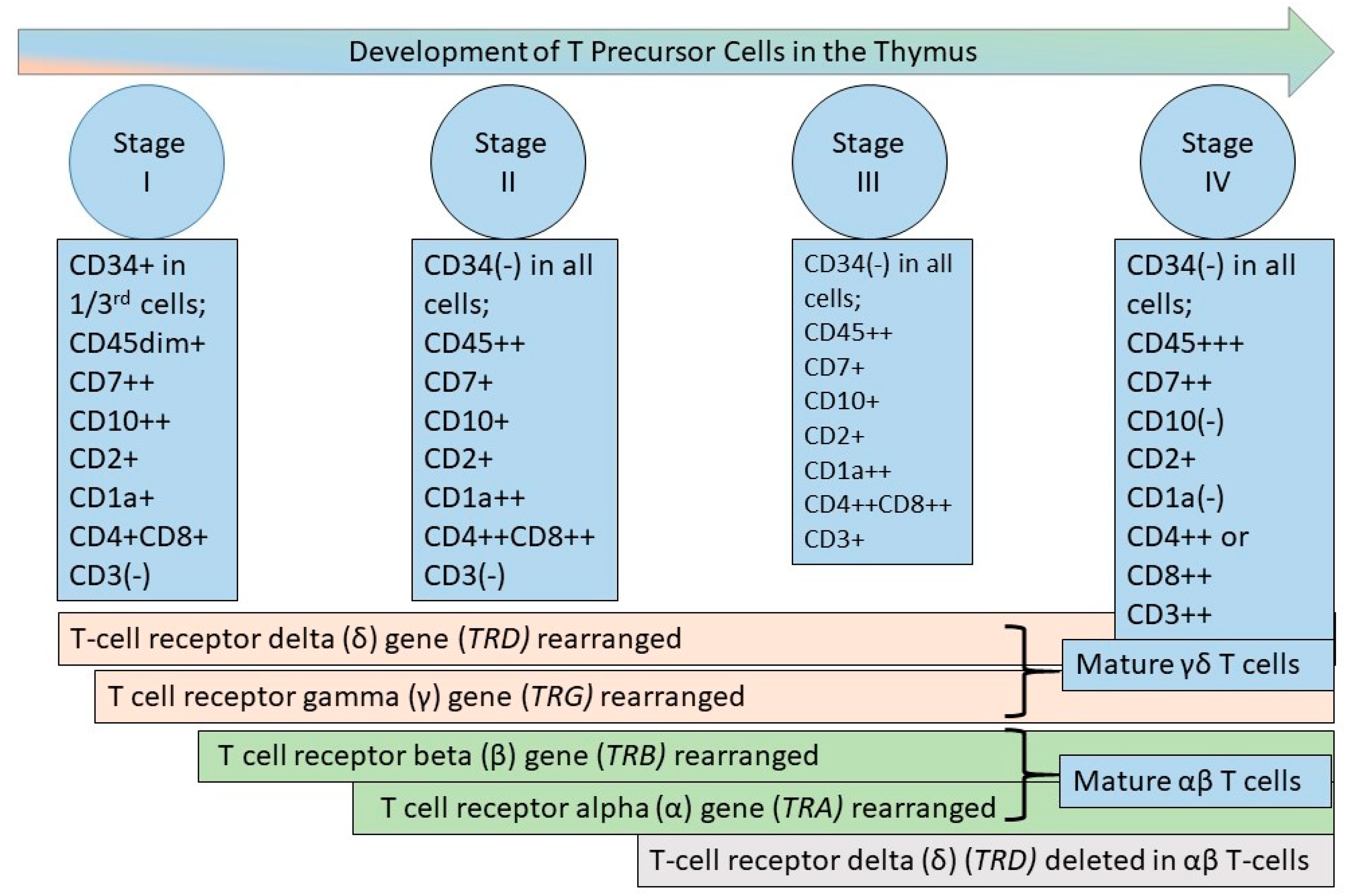
Figure 3.
Germinal center and the origin of mature lymphoid neoplasms in relation to the origin of acute lymphoblastic leukemias. The left side of the figure depicts acute lymphoblastic leukemia, which represents a precursor lymphoid neoplasm arising from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in the bone marrow. Precursor cells arising from the HSCs develop into mature B and T lymphoid cells, as described and depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 2. In the periphery, when naïve mature B cells encounter antigen, they enter the lymphoid follicle, and a follicular germinal center is formed. The germinal center (also termed follicular center) includes a dark zone comprised of proliferating centroblasts and a light zone consisting of centrocytes with an underlying network of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), and admixed T-follicular helper (TFH) cells and macrophages containing fragments of apoptotic cells. The follicular or germinal center B-cells undergo somatic hypermutation of the IGH gene variable region. This somatic hypermutation process either decreases or increases the affinity of the B-cell for antigen. If the affinity decreases, this process leads to cell death. In contrast, if the affinity increases for antigens, this germinal center process leads to cell survival, differentiation, and renewed proliferation. Follicular lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas arise from the follicle center (germinal center) B-cells. The post-follicular B cells include memory B-cells, marginal zone B-cells, and plasma cells, which are the normal cell counterparts for marginal zone lymphoma and plasma cell myeloma. Also depicted in the figure are the neoplastic Hodgkin–Reed–Sternberg (HRS) cells in classic Hodgkin lymphoma, which arise from pre-apoptotic B-cells. The neoplastic lymphocyte-predominant (LP) cells (also termed L&H cells) in lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma are transformed from centrocytes, as depicted [13]. The red arrows represent malignant transformation to the neoplasms shown in grey-shaded boxes. The filled (non-red-colored) arrows depict normal processes, with the blue-green arrows showing the path of naïve B-cell through the germinal center and exit as post-follicular B-cells. The yellow arrows depict the normal germinal center processes of apoptosis (on the left) and cell survival and renewed proliferation (right side of the figure), as described above. The three black line arrows indicate the types of normal cells, depicted in white rectangles in the figure.
4. Clonality Evaluation in Lymphoid Neoplasms
Diagnosing a benign versus malignant neoplasm in any case of lymphoid proliferation is critical. In B-cell proliferations, kappa, and lambda light chain immunoglobulin evaluation via FCI or immunohistochemistry stains may help to determine the presence of a light-chain-restricted B-cell population. In T-cell proliferations, molecular methods have been the primary methods of evaluating clonality. The natural process of antigen receptor gene rearrangement ensures immense diversity in B and T lymphocytes, enabling an immune response to millions of antigens [36]. Therefore, normal, benign lymphoid tissues usually show a polyclonal population when examined by IGH or TCR gene rearrangement assays. In contrast, malignant lymphoid neoplasms usually show a clonal proliferation of lymphoid cells that share the same genetically rearranged sequence, which serves as a molecular signature or “fingerprint” of that lymphoid neoplasm in any individual patient.
Historically, such evaluation has been used to distinguish between benign and malignant lymphoid proliferations, keeping in mind that the presence of a clonal population does not equate with malignancy. The earliest methods used since the early 1980s included Southern blot hybridization for IGH [37] and TCR genes [38]. Subsequently, fragment-length polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assays were developed to detect monoclonal and polyclonal B and T lymphoid populations in clinical specimens; amplified DNA from monoclonal populations of lymphoid cells showed homogeneous fragment lengths seen as a band on electrophoresis in contrast with a broad smear in polyclonal populations [39,40]. Guidelines for clonality evaluation by PCR-based assays were developed by the European BIOMED-2 consortium from 2003 to 2012 and have been used since then in many clinical laboratories [41,42,43].
In 2012, deep sequencing of IGH and TCR genes was shown to be a sensitive method for detecting minimal residual disease (MRD) in ALL [44]. Subsequently, next-generation sequencing (NGS) showed greater clinical utility than PCR for clonality evaluation in benign, atypical, and definite hematolymphoid neoplasms, including peripheral blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid tissues; see illustrated NGS findings for 28 clinical cases in the cited reference [45]. Of note, since PCR-based assays were the primary types of assays used for clonality evaluation in hematolymphoid tissues in most clinical laboratories in the last three decades until at least 2019–2020, the defining criteria for clonality in hematolymphoid neoplasms in the WHO classification editions described in the following sections have been based primarily on PCR-based assays.
5. The World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Hematolymphoid Tumors: The Third, Fourth, and Revised Fourth Editions
In 2001, the WHO classification of hematolymphoid neoplasms was introduced under the auspices of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [46]. Based on the REAL classification principles, the third edition WHO “blue book” described the following eleven major categories of neoplasms of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: chronic myeloproliferative diseases, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases, myelodysplastic syndromes, acute myeloid leukemia, precursor B- and T-cell neoplasms, mature B-cell neoplasms, mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms, Hodgkin lymphoma (name changed from Hodgkin’s disease); and three new categories: immunodeficiency-associated lymphoproliferative disorders, histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms, and mastocytosis [46]. This review is focused on the diagnosis and classification of ALL and lymphomas, included in four of the above eleven major categories.
While these four categories have not substantially changed in the successive classifications, the types of diseases included in these categories and the defining criteria of many of these lymphoid neoplasms have changed with subsequent classification updates due to the increasing evolution of knowledge. For instance, a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma diagnosis in the year 2000 could have included several other specific types of lymphomas now recognized in 2023. Similarly, the classification of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma has changed, with increasingly recognized specific entities. The defining criteria for chronic lymphocytic leukemia have changed over the years. Another example is follicular lymphoma, where grading the lymphoma was introduced a long time ago when we did not have current knowledge, and the criteria for grading these lymphomas have changed with classification updates. For any researcher retrieving cases of any lymphoma entity from a time point when a different version of the classification was in effect, an overview of that classification at that time is essential for the researcher to understand, since this would help to harmonize the cases or patients being studied for the researcher’s work. Even for clinical practitioners in the field, knowing when a patient’s diagnosis was made can help the practitioner to better understand the patient’s disease and appropriately manage the patient. Therefore, an overview of the major classifications used since 1994 is provided in tabular form. For the earlier widely used lymphoma classifications, the reader is referred to a recent publication [13].
Table 1 compares the WHO 2001-defined lymphoid neoplasms in the four major categories mentioned above with the previous REAL 1994 classification.

Table 1.
WHO 2001 classification of lymphoid neoplasms compared with the REAL 1994 classification.
As shown in Table 1, there were changes in terminology, provisional entities upgraded to definite entities, and new and deleted entities. Significantly, the WHO 2001 classification began to incorporate genetics in defining specific neoplasms. This change occurred in acute leukemias, with recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities recognized in acute myeloid leukemia and B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Based on the recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities, subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia were recognized by the WHO 2001 classification, not shown in this table. In mature lymphoid neoplasms, the previously termed B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the REAL classification was termed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by the WHO 2001 classification.
The WHO classification was updated in 2008 to the fourth edition [47], with subsequent summary publications for myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemias [48] and mature lymphoid neoplasms [49]. The summary publications for the revised fourth edition for myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemias [50] and mature lymphoid neoplasms [51] were published in 2016, followed by the revised fourth edition WHO blue book in 2017 [52]. The four lymphoid neoplasm categories remained the same in 2008 and 2017. Still, many changes in the subtypes of lymphoid neoplasms were recognized in these updates, with many additional subtypes introduced and a few nomenclature changes, as shown in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 2.
WHO 2008 types of precursor lymphoid neoplasms compared with WHO 2017 classification.

Table 3.
Comparison of the types of mature B-cell neoplasms in WHO 2001, 2008, and 2017 classifications [46,47,52].

Table 4.
Comparison of the types of T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms and Hodgkin lymphoma in WHO 2001, 2008, and 2017 classifications [46,47,52].
As shown in Table 2, the WHO 2008 classification recognized specific subtypes of B-ALL with numerical or structural chromosomal abnormalities diagnosed by standard cytogenetic techniques, including chromosome banding (or karyotypic) analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization. If a specific cytogenetic abnormality was not identified, the diagnosis was B-ALL, not otherwise specified. The WHO 2017 classification introduced two important provisional subtypes of B-ALL and one provisional subtype of T-ALL. These genetic subtypes of ALL are discussed in Part 2 of the three reviews.
6. The Fifth Edition WHO 2022 and the International Consensus Classifications
The WHO classification in 2001 was jointly developed by the American Society of Hematopathology and the European Society of Hematopathology after convening a formal Clinical Advisory Committee (CAC) meeting in which questions related to the classification were discussed to obtain a consensus [53]. Similar CAC meetings were held in 2007 and 2014 before the fourth and revised fourth editions of the WHO classification were published in 2008 and 2017, respectively. The WHO classification is updated, and books are published for all types of cancer in various editions, as recently described [13].
For the fifth-edition of WHO classification blue books, which began publishing in 2019, the IARC appointed a standing board of experts with expert members for each tumor site-specific book. For the fifth edition hematolymphoid classification (WHO-HAEM5), CAC meetings were no longer allowed by the IARC governance, which followed the same process for hematolymphoid neoplasms as for updating the books for the other types of cancers [54,55]. This situation led to the development of a parallel International Consensus Classification (ICC) after a CAC meeting was held separately from the WHO 2022 classification group [56,57]. Of note, authors in both classifications were members of the same hematopathology societies in the USA and Europe. They read the same published literature that formed the evidence base for classifications, and clinicians were included in the WHO 2022 group. In June 2022, summary papers were published for the WHO fifth edition [58,59] and the ICC [60,61].
The WHO classification is now also published online, which is offered as a beta version before the book is printed [62]. The beta version of the 5th edition WHO classification of hematolymphoid tumors was released in August 2022. This updated fifth edition includes several very desirable features, including essential and desirable diagnostic criteria for each defined neoplasm, numerous color figures for all types of tests necessary for diagnosis, concepts explained in figures, easily accessible references, and the addition of a benign lymphoid proliferations section that may arise in the differential diagnosis of B- and T-cell neoplasms, all written by several hundred (>400) authors worldwide [62].
7. The Crucial Role of Diagnostic Tumor Classifications for Precision Medicine
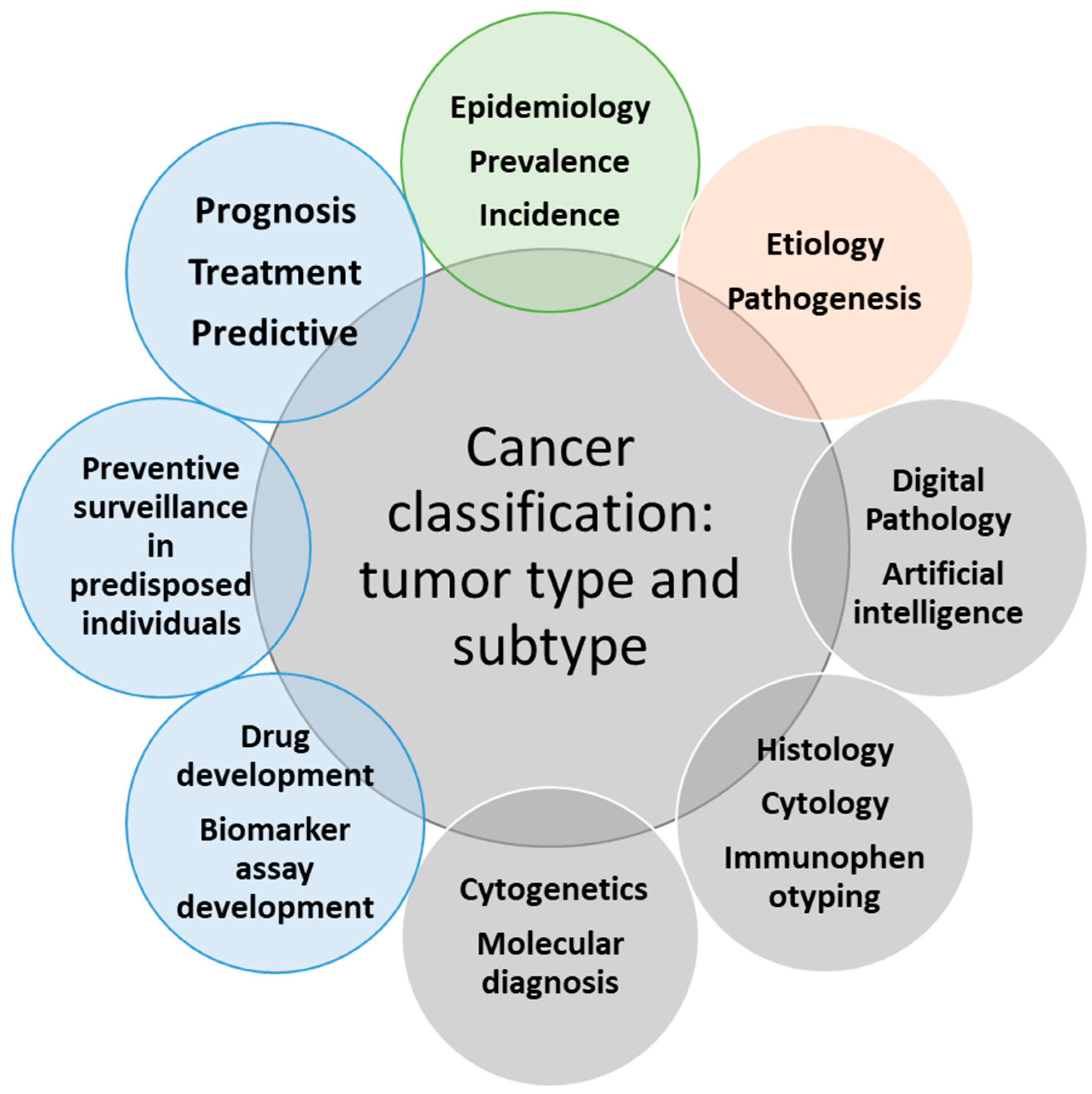
Figure 4, adapted from a concurrent publication, highlights the crucial role of the WHO classification in providing appropriate patient care and advancing precision medicine in the current genomics era for patients with cancer [13]. As previously mentioned, the WHO classification is used worldwide for all types of tumors, including hematolymphoid neoplasms. The hematolymphoid tumor book represents one of 14 volumes in the 5th edition WHO classification.
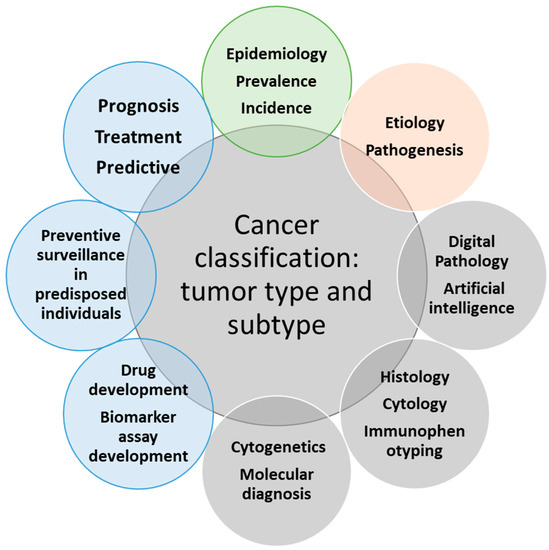
Figure 4.
This figure depicts the relationships of cancer classification (or the types and subtypes of tumors) with various inputs and outputs from any particular tumor type or subtype, which are critical for implementing appropriate patient care and precision medicine in cancer. The inputs are represented by four circles, including the three grey circles for the modalities that lead to the diagnostic cancer classification and the beige circle, which represents research into etiology and pathogenesis, feeding into refining tumor classification. The outputs are represented by the remaining four outer circles in the figure, including the three blue circles with a direct effect on the clinical outcomes of cancer patients and the impact on the epidemiology statistics of tumors, including incidence and prevalence of tumor types (figure modified from cited reference [13] with the permission obtained from Nova Science Publishers, Inc.).
As the figure shows, using the diagnostic criteria as written in the classification leads to establishing the tumor type and subtype, and this precise diagnosis is required to determine the prognosis, treat the patient, and predict response to therapy. The diagnosis also leads to preventive surveillance in specific clinical situations, including in individuals predisposed to cancer due to genetic tumor syndromes. Distinct molecular genetic subtypes based on evidence-based, comprehensive biologic features of the disease also lead to drug development and biomarker assay development. In addition, changing the diagnostic criteria of tumor types or the terminology linked to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes affects the epidemiologic information about various tumors [13].
Therefore, these three reviews on lymphoid neoplasms are focused on the diagnosis and classification of ALL and lymphomas arising from mature B and T lymphocytes, integrating the advances in molecular pathology and genetics with the traditional methods of diagnosis since these advances are the primary reasons for the significant updates in the diagnostic classification, especially in ALL. Lymphomas and lymphoid proliferations include numerous diseases in children and adults, all of which cannot be covered in this work. In this work, I have elected to discuss the most common clinically indolent and aggressive lymphomas/leukemias in children and adults; a few rare lymphomas; newly described entities; and newer concepts, such as lymphomas in immune-privileged sites, T follicular helper (TFH) cell lymphomas, in situ mantle cell neoplasia and, wherever possible, inherited genetic predisposition to lymphoid neoplasms.
8. Additional Discussion Points for the Fifth Edition of the WHO 2022 Classification of Hematolymphoid Tumors (WHO-HAEM5)
Tumor classification is increasingly moving ahead with genetic features with the recognition that advanced techniques may not yet be available in many institutions and countries. The WHO classification is evidence-based and, like any other classification, is based on the evidence available at that point in time when it was finalized. The fifth edition WHO classification no longer recognizes “provisional” entities and follows a hierarchical structure [62].
The names of the types and subtypes of various neoplastic entities with genetic features no longer include the complete cytogenetic nomenclature of the genetic abnormality in the name of the neoplastic disease, but WHO-HAEM5 continues to recognize the importance of cytogenetics throughout the classification, as clarified by the editors of the WHO classification in a recent communication [63]. In this same context, WHO-HAEM5 has adopted the recommendations of the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) to use the term “fusion” in genetic abnormalities even if the term does not always represent the actual biological mechanism, such as enhancer hijacking or chimeric gene fusion, underlying the fusion [63,64].
9. Conclusions and Future Questions
The enormous progress in the diagnosis and classification of lymphoid neoplasms in the last three decades is based on the work of countless individuals. ALL and lymphomas, the disease focus of this three-part review, have been diagnosed primarily by visual morphologic evaluation of peripheral blood, bone marrow, and biopsied tissues in cases of lymphomas, in conjunction with clinical history and supplemented by traditional immunophenotyping, cytogenetics, and molecular genetics methods. The significant strides in the diagnostic classification of ALL and lymphomas in the last decade based on genomic advances are reflected in the current classifications and discussed in Parts 2 and 3 of this three-part review.
Looking back much further to almost two centuries ago, the most significant milestones that likely changed the course of the history of medicine occurred when the prevailing wisdom was questioned; for example, when Craigie, Bennett, and Virchow questioned and disagreed with inflammation as the answer for the patients they served and examined with leukemia. Notably, the first recognition of neoplastic diseases occurred due to collaboration, exemplified by Craigie, Bennett, and Virchow. In the genomic era of 2023, when knowledge of medicine is much more excellent than two centuries ago, there is real potential for even more significant possibilities for patient-centered medicine, including early diagnosis, effective treatments, monitoring therapies, and preventing and even curing patients with malignant neoplasms. The complete human genome sequence is known, and whole genome sequencing is used for patient care in genetics and cancer, not just research, in some parts of the world; for interested readers, a recent review described how this hugely challenging and unprecedented task was achieved by countless dedicated individuals worldwide [65]. Also, the enormous advances in technology have enabled us to use other novel methods apart from the traditional techniques for the care of patients and research in hematolymphoid neoplasms. The reader is referred to publications discussing novel applications and measurable disease detection by flow cytometry [66] and the possibilities and challenges to be overcome in using liquid biopsies [67], digital pathology [68,69], computational pathology [70], and artificial intelligence in pathology [68,69,70,71,72], including by FCI [73,74] and whole slide digital imaging of histologic tissue sections in diagnosing lymphomas [75,76].
Questions for the future include: (1) Are there other ways to better diagnose and classify these neoplasms, including by “molecular fingerprinting” mentioned above, which is used for monitoring treatment in some patients with lymphoid neoplasms? (2) Can we avoid having to perform invasive biopsies on patients, particularly when a tissue biopsy may be difficult to obtain, by using newer methods such as non-invasive liquid biopsies and artificial intelligence to diagnose these neoplasms? (3) Can we diagnose with computational pathology, which includes digital pathology and other data, and artificial intelligence tools that the human eye and traditional methods cannot yet diagnose? Answers to these and other questions with worldwide collaboration, incorporating and moving forward from the current state of knowledge described in the following two parts of this review, will hopefully achieve the ultimate common goals for patients with hematolymphoid neoplasms.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Kansal, R. Toward Integrated Genomic Diagnosis in Routine Diagnostic Pathology by the World Health Organization Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 1, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piller, G. Leukaemia—A brief historical review from ancient times to 1950. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 112, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin. On some morbid appearances of the absorbent glands and spleen. Med. Chir. Trans. 1832, 17, 68–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, H. Remarks on the presentation of microscopical preparations made from some of the original tissue described by Thomas Hodgkin, 1832. Ann. Med. Hist. 1926, 8, 370–374. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33944510/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [PubMed]
- Burkitt, D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br. J. Surg. 1958, 46, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Henle, G.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Morphological and biological studies on a virus in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 1965, 121, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, L.; Haglund, U.; Nilsson, K.; Klein, G. Characteristic chromosomal abnormalities in biopsies and lymphoid-cell lines from patients with Burkitt and non-Burkitt lymphomas. Int. J. Cancer 1976, 17, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Bernheim, A.; Weh, H.J.; Flandrin, G.; Daniel, M.T.; Brouet, J.C.; Colbert, N. A new translocation in Burkitt’s tumor cells. Hum. Genet. 1979, 53, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, I.; Hiraki, S.; Kimura, I.; Miyamoto, K.; Sato, J. 2/8 translocation in a Japanese Burkitt’s lymphoma. Experientia 1979, 35, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küppers, R.; Rajewsky, K.; Zhao, M.; Simons, G.; Laumann, R.; Fischer, R.; Hansmann, M.L. Hodgkin disease: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells picked from histological sections show clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and appear to be derived from B cells at various stages of development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, J.; Hummel, M.; Zemlin, M.; Kalvelage, B.; Stein, H. Hodgkin’s disease with a B-cell phenotype often shows a VDJ rearrangement and somatic mutations in the VH genes. Blood 1994, 84, 708–715. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8043859/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marafioti, T.; Hummel, M.; Foss, H.D.; Laumen, H.; Korbjuhn, P.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Lammert, H.; Demel, G.; Theil, J.; Wirth, T.; et al. Hodgkin and reed-sternberg cells represent an expansion of a single clone originating from a germinal center B-cell with functional immunoglobulin gene rearrangements but defective immunoglobulin transcription. Blood 2000, 95, 1443–1450. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10666223/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansal, R. (Ed.) The World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors with Emphasis on the Classification of Hematolymphoid Neoplasms. In Precision Medicine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 315–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, E.B.; Rappaport, H.; Winter, W.J. Follicular lymphoma; a re-evaluation of its position in the scheme of malignant lymphoma, based on a survey of 253 cases. Cancer 1956, 9, 792–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, R.J.; Butler, J.J. The pathology and nomenclature of Hodgkin’s disease. Cancer. Res. 1966, 26, 1066–1081. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/26/6_Part_1/1063/476140/The-Pathology-and-Nomenclature-of-Hodgkin-s (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Lukes, R.J.; Craver, L.F.; Hall, T.C.; Rappaport, H.; Ruben, P. Report of the Nomenclature Committee. Cancer Res. 1966, 26, 1311. Available online: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/26/6_Part_1/1311/476364/Report-of-the-Nomenclature-Committee (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Cooper, M.D.; Peterson, R.D.; Good, R.A. Delineation of the thymic and bursal lymphoid systems in the chicken. Nature 1965, 205, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.D.; Perey, D.Y.; McKneally, M.F.; Gabrielsen, A.E.; Sutherland, D.E.; Good, R.A. A mammalian equivalent of the avian bursa of Fabricius. Lancet 1966, 1, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.D. The early history of B cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, R.J.; Collins, R.D. Immunologic characterization of human malignant lymphomas. Cancer 1974, 34 (Suppl. S4), 1488–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.H.; Farrer-Brown, G.; Henry, K.; Jelliffe, A.M.; Gerard-Marchant, R.; Hamlin, I.; Lennert, K.; Rilke, F.; Stansfeld, A.G.; Van Unnik, J.A.M. Classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Lancet 1974, 304, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfeld, A.G.; Diebold, J.; Noel, H.; Kapanci, Y.; Rilke, F.; Kelényi, G.; Sundstrom, C.; Lennert, K.; van Unnik, J.A.; Mioduszewska, O.; et al. Updated Kiel classification for lymphomas. Lancet 1988, 1, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Pathologic Classification Project. National Cancer Institute sponsored study of classifications of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: Summary and description of a working formulation for clinical usage. Cancer 1982, 49, 2112–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Banks, P.M.; Chan, J.K.; Cleary, M.L.; Delsol, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Falini, B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84, 1361–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1997, 89, 3909–3918. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9166827/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, C.; Nishimoto, N.; Gartland, G.L.; Billips, L.G.; Burrows, P.D.; Kubagawa, H.; Cooper, M.D. B cells are generated throughout life in humans. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 866–872. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8543844/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Loken, M.R.; Shah, V.O.; Dattilio, K.L.; Civin, C.I. Flow cytometric analysis of human bone marrow. II. Normal B lymphocyte development. Blood 1987, 70, 1316–1324. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3117132/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Loken, M.R.; Wells, D.A. Normal antigen expression in hematopoiesis. In Immunophenotyping; Stewart, C.C., Nicholson, J.K.A., Eds.; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 133–160. [Google Scholar]
- van Zelm, M.C.; van der Burg, M.; de Ridder, D.; Barendregt, B.H.; de Haas, E.F.; Reinders, M.J.; Lankester, A.C.; Révész, T.; Staal, F.J.; van Dongen, J.J. Ig gene rearrangement steps are initiated in early human precursor B cell subsets and correlate with specific transcription factor expression. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5912–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, S.L.; Kee, B.L. The transcriptional regulation of B cell lineage commitment. Immunity 2007, 26, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terstappen, L.W.; Huang, S.; Picker, L.J. Flow cytometric assessment of human T-cell differentiation in thymus and bone marrow. Blood 1992, 79, 666–677. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1370641/ (accessed on 10 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Dik, W.A.; Pike-Overzet, K.; Weerkamp, F.; de Ridder, D.; de Haas, E.F.; Baert, M.R.; van der Spek, P.; Koster, E.E.; Reinders, M.J.; van Dongen, J.J.; et al. New insights on human T cell development by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene expression profiling. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, I.C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Linterman, M.A.; Yu, D.; MacLennan, I.C. Follicular Helper T Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 335–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonegawa, S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 1983, 302, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Cossman, J.; Bakhshi, A.; Jaffe, E.S.; Waldmann, T.A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Immunoglobulin-gene rearrangements as unique clonal markers in human lymphoid neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertness, V.; Kirsch, I.; Hollis, G.; Johnson, B.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. T-cell receptor gene rearrangements as clinical markers of human T-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, K.J.; Brisco, M.J.; Story, C.J.; Morley, A.A. Monoclonality in B-lymphoproliferative disorders detected at the DNA level. Blood 1990, 75, 2220–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, K.J.; Brisco, M.J.; Wan, J.H.; Neoh, S.; Grist, S.; Morley, A.A. Gene rearrangement in B- and T-lymphoproliferative disease detected by the polymerase chain reaction. Blood 1991, 78, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.J.; Langerak, A.W.; Brüggemann, M.; Evans, P.A.; Hummel, M.; Lavender, F.L.; Delabesse, E.; Davi, F.; Schuuring, E.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003, 17, 2257–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Krieken, J.H.; Langerak, A.W.; Macintyre, E.A.; Kneba, M.; Hodges, E.; Sanz, R.G.; Morgan, G.J.; Parreira, A.; Molina, T.J.; Cabeçadas, J.; et al. Improved reliability of lymphoma diagnostics via PCR-based clonality testing: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2007, 21, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerak, A.W.; Groenen, P.J.; Brüggemann, M.; Beldjord, K.; Bellan, C.; Bonello, L.; Boone, E.; Carter, G.I.; Catherwood, M.; Davi, F.; et al. EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faham, M.; Zheng, J.; Moorhead, M.; Carlton, V.E.; Stow, P.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Pui, C.H.; Campana, D. Deep-sequencing approach for minimal residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 5173–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansal, R.; Grody, W.W.; Zhou, J.; Dong, L.; Li, X. The Value of T-Cell Receptor γ (TRG) Clonality Evaluation by Next-Generation Sequencing in Clinical Hematolymphoid Tissues. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 150, 193–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) World Health Organization Classification of Haematopoietic Tumours. In Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Bosman, F.T., Lakhani, S.R., Jaffe, E.S., Ohgaki, H., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Borowitz, M.J.; Porwit, A.; Harris, N.L.; Le Beau, M.M.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Tefferi, A.; et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important changes. Blood 2009, 114, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Bosman, F.T., Lakhani, S.R., Jaffe, E.S., Ohgaki, H., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Diebold, J.; Flandrin, G.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Vardiman, J.; Lister, T.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. The World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November, 1997. Ann. Oncol. 1999, 10, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, I.A. The WHO Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1701–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumors. Frequently Asked Questions. Available online: https://whobluebooks.iarc.fr/about/faq/ (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Cazzola, M.; Sehn, L.H. Developing a classification of hematologic neoplasms in the era of precision medicine. Blood 2022, 140, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S. Advances in the Classification of Myeloid and Lymphoid Neoplasms. Virchows. Arch. 2023, 482, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Hematolymphoid tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours Series, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022; Volume 11, Available online: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/home (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Siebert, R.; Schuh, A.; Ott, G.; Cree, I.A.; Du, M.Q.; Ferry, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Naresh, K.N.; Solary, E.; Khoury, J.D. Response to the Comments from the Groupe Francophone de Cytogénétique Hématologique (GFCH) on the 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumors. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruford, E.A.; Antonescu, C.R.; Carroll, A.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.; Cree, I.A.; Cross, N.C.P.; Dalgleish, R.; Gale, R.P.; Harrison, C.J.; Hastings, R.J.; et al. HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) recommendations for the designation of gene fusions. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3040–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, R. (Ed.) An Introduction to Genomics and Precision Medicine. In Precision Medicine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.W.; Wallace, P.; Maguire, O.; Minderman, H. Flow Cytometry for Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Neoplasms. In Precision Medicine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Kansal, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 417–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.K.; Kuss, B.; Talaulikar, D. Liquid Biopsy in Blood Cancer. In Precision Medicine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Kansal, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 473–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Yagi, Y. Digital Pathology and Precision Medicine. In Precision Medicine: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Kansal, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 519–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, R.; Coupland, S.E. Software-assisted decision support in digital histopathology. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.; Pantanowitz, L.; Aeffner, F.; Zarella, M.D.; van der Laak, J.; Bui, M.M.; Vemuri, V.N.; Parwani, A.V.; Gibbs, J.; Agosto-Arroyo, E.; et al. Computational pathology definitions, best practices, and recommendations for regulatory guidance: A white paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. 2019, 249, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Levenson, R.; Pantanowitz, L. Artificial Intelligence in Pathology. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Abel, J.T.; Balis, U.G.J.; McClintock, D.S.; Pantanowitz, L. Challenges in the Development, Deployment, and Regulation of Artificial Intelligence in Anatomic Pathology. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, S.W. On Its Way to Primetime: Artificial Intelligence in Flow Cytometry Diagnostics. Cytometry A 2020, 97, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Mallesh, N.; Höllein, A.; Schabath, R.; Haferlach, C.; Haferlach, T.; Elsner, F.; Lüling, H.; Krawitz, P.; Kern, W. Hematologist-Level Classification of Mature B-Cell Neoplasm Using Deep Learning on Multiparameter Flow Cytometry Data. Cytometry A 2020, 97, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, H.; Sato, K.; Kabeya, Y.; Yonezawa, S.; Nakano, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ozawa, I.; Higo, S.; Yanagida, E.; Yamada, K.; et al. Deep learning shows the capability of high-level computer-aided diagnosis in malignant lymphoma. Lab Investig. 2020, 100, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrykh, C.; Abreu, A.; Amara, N.; Siegfried, A.; Maisongrosse, V.; Frenois, F.X.; Martin, L.; Rossi, C.; Laurent, C.; Brousset, P. Accurate diagnosis of lymphoma on whole-slide histopathology images using deep learning. NPJ Digit Med. 2020, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).