Cognitive Impairment Screening in Multiple Sclerosis Using CoGeval: Clinical and Functional Predictors in a Mexican Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection: Demographics and Clinical Variables
2.4. Cognitive Screening
2.5. Functional Measures
2.6. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence and Severity of Cognitive Impairment
3.3. Bivariate Relationships with Cognitive Status
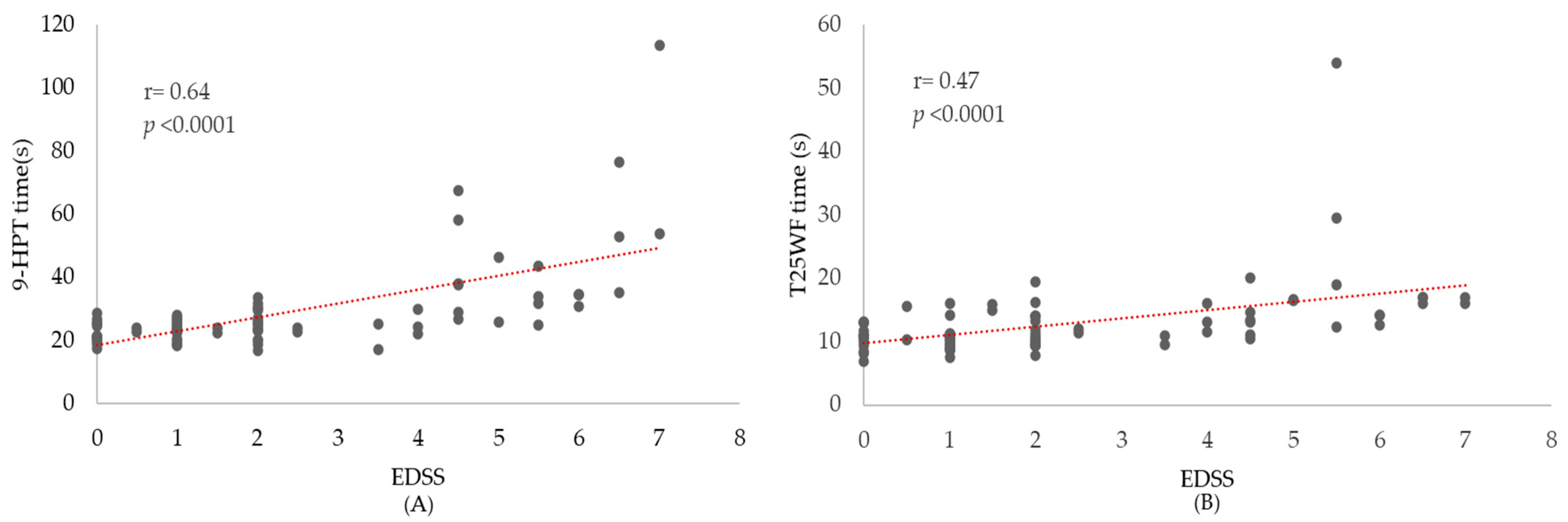
3.4. Disability Strata and Functional Performance
3.5. Multivariable Model
3.6. Exploratory Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Screening Tool and Clinical Implications
4.2. Pathophysiological Considerations
4.3. MRI Assessment
4.4. Treatment of Cognitive Impairment
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| EDSS | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| CogEval | Cognitive Evaluation |
| 9-HPT | 9-Hole Peg Test |
| T25FW | Timed 25-Foot Walk |
| MSFC | Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite |
| MSOAC | Multiple Sclerosis Outcomes Assessment Consortium |
| BICAMS | Brief International Cognitive Assessment for MS |
| SDMT | Symbol Digit Modalities Test |
| NfL | Neurofilament light chain |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| CI | Cognitive impairment |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CIS | Clinically isolated syndrome |
| RRMS | Relapsing–remitting MS |
| SPMS | Secondary progressive MS |
| PPMS | Primary progressive MS |
| PST | Processing speed test |
References
- Haki, M.; Al-Biati, H.A.; Al-Tameemi, Z.S.; Ali, I.S.; Al-Hussaniy, H.A. Review of multiple sclerosis: Epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Medicine 2024, 103, e37297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.; Sandroff, B. Treatment and management of cognitive dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Bar-Or, A.; Piehl, F.; Preziosa, P.; Solari, A.; Vukusic, S.; Rocca, A.M. Multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Razavi, S.; Nikzad, E. Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Diagnoses and Cell-Based Therapy. Cell J. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovic, D.; Valsasina, P.; Rocca, M.A.; Stromillo, M.; Gallo, A.; Enzinger, C.; Hulst, H.; Rovira, A.; Muhlert, N.; De Stefano, N.; et al. Hippocampal and Deep Gray Matter Nuclei Atrophy Is Relevant for Explaining Cognitive Impairment in MS: A Multicenter Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Talebi, M.; Naseri, A.; Zafarani, F. Predominant domains and associated demographic and clinical characteristics in multiple sclerosis-related cognitive impairment in mildly disabled patients. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, J.; Langdon, D.; Dhakal, B.; Benedict, R.H.B. An Update on New Approaches to Cognitive Assessment in Multiple Sclerosis. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechenberger, S.; Helmlinger, B.; Tinauer, C.; Jauk, E.; Ropele, S.; Heschl, B.; Wurth, S.; Damulina, A.; Eppinger, S.; Demjaha, R.; et al. Evaluation of a self-administered iPad®-based processing speed assessment for people with multiple sclerosis in a clinical routine setting. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 3268–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Losinski, G.; Mourany, L.; Schindler, D.; Mamone, B.; Reece, C.; Kemeny, D.; Narayanan, S.; Miller, D.M.; Bethoux, F.; et al. Processing speed test: Validation of a self-administered, iPad®-based tool for screening cognitive dysfunction in a clinic setting. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feys, P.; Lamers, I.; Francis, G.; Benedict, R.; Phillips, G.; LaRocca, N.; Hudson, L.D.; Rudick, R.; Multiple Sclerosis Outcome Assessments Consortium. The Nine-Hole Peg Test as a manual dexterity performance measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; Cohen, J.A.; Benedict, R.H.B.; Phillips, G.; LaRocca, N.; Hudson, L.D.; Rudick, R.; Multiple Sclerosis Outcome Assessments Consortium. Validity of the Timed 25-Foot Walk as an ambulatory performance outcome measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.W.; Repovic, P.; Mostert, J.; Bowen, J.D.; Comtois, J.; Strijbis, E.; Uitdehaag, B.; Cutter, G. The nine hole peg test as an outcome measure in progressive MS trials. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 69, 104433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaravalloti, N.D.; DeLuca, J. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, D.W.; Amato, M.P.; Boringa, J.; Brochet, B.; Foley, F.; Fredrikson, S.; Hämäläinen, P.; Hartung, H.-P.; Krupp, L.; Penner, I.; et al. Recommendations for a brief international cognitive assessment for Multiple Sclerosis (BICAMS). Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, M.; Magliozzi, R.; Ciccarelli, O.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Reynolds, R.; Martin, R. Exploring the origins of grey matter damage in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineen, R.A.; Vilisaar, J.; Hlinka, J.; Bradshaw, C.M.; Morgan, P.S.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Auer, D.P. Disconnection as a mechanism for cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2009, 132, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaro, C.; Grange, E.; Di Giovanni, R.; Cattaneo, D.; Bertoni, R.; Prosperini, L.; Uccelli, M.M.; Malrengo, D. Nine Hole Peg Test asymmetry in refining upper limb assessment in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 45, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learmonth, Y.C.; Motl, R.W.; Sandroff, B.M.; Pula, J.H.; Cadavid, D. Validation of patient determined disease steps (PDDS) scale scores in persons with multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, M.; Rinaldi, F.; Grossi, P.; Gallo, P. Cortical pathology and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Tur, C.; Eshaghi, A.; Doshi, A.; Chan, D.; Binks, S.; Wellington, H.; Heslegrave, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Chataway, J. Serum neurofilament light and MRI predictors of cognitive decline in patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: Analysis from the MS-STAT randomised controlled trial. Mult. Scler. J. 2022, 28, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, C.; Fernandes, A. Linking Cognitive Impairment to Neuroinflammation in Multiple Sclerosis using neuroimaging tools. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 47, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, F.; Datta, S.; Garcia, N.; Rozario, N.L.; Perez, F.; Cutter, G.; Narayana, P.A.; Wolinsky, J.S. Intracortical lesions by 3T magnetic resonance imaging and correlation with cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 17, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, K.A.; Eijlers, A.J.; Douw, L.; Uitdehaag, B.M.; Barkhof, F.; Geurts, J.J.; Schoonheim, M.M. Increased connectivity of hub networks and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2017, 88, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, K.A.; van Geest, Q.; Eijlers, A.; Geurts, J.; Schoonheim, M.; Hulst, H. Is impaired information processing speed a matter of structural or functional damage in MS? Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 20, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalincik, T.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Sobisek, L.; Jokubaitis, V.; Spelman, T.; Horakova, D.; Havrdova, E.; Trojano, M.; Izquierdo, G.; Lugaresi, A.; et al. Towards personalized therapy for multiple sclerosis: Prediction of individual treatment response. Brain 2017, 140, 2426–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmeyer, N.C.; Bürkner, P.C.; Wiendl, H.; Ruck, T.; Hartung, H.-P.; Holling, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Johnen, A. Disease-modifying treatments and cognition in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 94, e2373–e2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Goverover, Y.; Genova, H.M.; DeLuca, J. Cognitive efficacy of pharmacologic treatments in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 599–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampit, A.; Heine, J.; Finke, C.; Barnett, M.H.; Valenzuela, M.; Wolf, A.; Leung, I.H.K.; Hill, N.T.M. Computerized cognitive training in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2019, 33, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messinis, L.; Nasios, G.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Zampakis, P.; Malefaki, S.; Ntoskou, K.; Nousia, A.; Bakirtzis, C.; Grigoriadis, N.; Gourzis, P.; et al. Efficacy of a computer-assisted cognitive rehabilitation intervention in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 5919841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, L.E.; Yang, J.; Shaw, M.T.; Sherman, K.; Haider, L.; Xu, J.; Krupp, L.B. Cognitive function in multiple sclerosis improves with telerehabilitation: Results from a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics (n = 81) | |
|---|---|
| Age | 35.7 ± 9.9 |
| Female | 50 (61.7%) |
| Male | 31 (38.3%) |
| Phenotype RRMS | 81 (100%) |
| Disease duration, years, median (IQR) | 4.0 (3.0–8.0) |
| EDSS, median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) |
| 9-HPT(s) median (IQR) | 25.0 (22.3–29.7) |
| T25FW(s) median (IQR) | 11.1 (10.0–14.0) |
| Variable | Normal (n = 41) | Impaired (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDSS mean | 1.0 [0.0–2.0] | 4.0 [2.0–5.5] | <0.001 |
| 9-HPT mean | 22.96 [20.06–24.70] | 29.87 [25.21–35.71] | <0.001 |
| T25FW mean | 10.50 [9.32–11.85] | 12.70 [10.74–14.19] | 0.0058 |
| Female (%) | 26 (63.4%) | 24 (60.0%) | 0.930 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández Salomón, L.F.; Mejía Chávez, J.A.; Sánchez Galván, D.M.S.; Zapata Mercado, L.E. Cognitive Impairment Screening in Multiple Sclerosis Using CoGeval: Clinical and Functional Predictors in a Mexican Cohort. Sclerosis 2025, 3, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3040039
Hernández Salomón LF, Mejía Chávez JA, Sánchez Galván DMS, Zapata Mercado LE. Cognitive Impairment Screening in Multiple Sclerosis Using CoGeval: Clinical and Functional Predictors in a Mexican Cohort. Sclerosis. 2025; 3(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández Salomón, Luis F., José A. Mejía Chávez, Diana M. S. Sánchez Galván, and Luis E. Zapata Mercado. 2025. "Cognitive Impairment Screening in Multiple Sclerosis Using CoGeval: Clinical and Functional Predictors in a Mexican Cohort" Sclerosis 3, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3040039
APA StyleHernández Salomón, L. F., Mejía Chávez, J. A., Sánchez Galván, D. M. S., & Zapata Mercado, L. E. (2025). Cognitive Impairment Screening in Multiple Sclerosis Using CoGeval: Clinical and Functional Predictors in a Mexican Cohort. Sclerosis, 3(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3040039






