Abstract
Background: Readmission within 30 days of discharge for heart failure (HF) has become a challenging public health issue. Predicting the risk of 30-day readmission may assist clinicians in making individualized treatment plans for HF patients. Methods: A total of 2254 patients were enrolled in this study. The risk predictors associated with 30-day readmission were selected using the least absolute shrinkage and the selection operator regression model. The performance of the nomogram was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, Hosmer–Lemeshow (HL) test, and decision curve analysis (DCA). Results: The 30-day all-cause readmission rate was 7.1%. Thirteen clinical parameters were identified as the risk predictors, including age, cystatin C, albumin, red cell distribution width coefficient variation, neutrophils, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T, myoglobin, sex, dyslipidaemia, left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, and atrial fibrillation. The nomogram showed good discrimination, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.653 (95% confidence interval: 0.608–0.698) and good calibration results (HL test p = 0.328). The DCA showed that the nomogram would have good clinical utility. Conclusions: This predictive model based on clinical data makes it simple for clinicians to assess the 30-day HF readmission risk.
1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that causes multiple related symptoms, such as dyspnea, fatigue, and peripheral or pulmonary edema, affecting the life quality of the patients [1]. While the medical equipment and techniques for treating HF have improved greatly in recent decades, hospitalization due to HF remains an increasingly serious problem worldwide [2]. The length of hospitalization of HF patients is often prolonged, and in many cases the patients will be readmitted to the hospital within a short time. Importantly, HF and its 30-day readmission rate have been a primary focus for reducing medical care costs [3]. Several prediction systems have been developed to identify high-risk patients for short-term readmission among the general medical population. However, they cannot be widely implemented for HF patients due to their poor consistency and practical performance [4,5,6]. While many indicators that are significantly associated with HF prognosis have been identified, few studies have used them to establish a prognosis-prediction model. Indeed, in the Chinese population, the prediction of 30-day HF readmission only applies to elderly patients aged ≥65 years [7]. The emerging evidence suggests that the 30-day readmission rates for HF differ greatly in different hospitals and periods, potentially related to disease management [3,8]. Therefore, prediction models based on data from different countries and hospitals of different grades are not necessarily universally applicable. Consequently, there is an urgent need for novel predictive models for 30-day HF readmission in the Chinese hospitalized population.
Cardiovascular risk factors affect the HF all-cause death and readmission. Most HF patients suffer from one or more comorbidities, including metabolic syndromes, which are critical for disease progression and may exacerbate the HF treatment outcome. Non-cardiovascular comorbidities such as diabetes and chronic kidney disease are considered independent prognostic factors in HF patients, and their numbers can predict all-cause hospitalization and even short-term mortality [9,10]. Neurohumoral activation is also very important for HF diagnosis and prognosis, especially brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and its precursor (NT-proBNP) [11]. In addition, blood cells, inflammatory and immune indicators, electrolytes, metabolites, and myocardial injury also contribute to HF prognosis [12,13,14,15]. In this study, we develop a predictive model of early readmission for HF patients based on clinical baseline data. To facilitate the operation of clinicians to predict the disease outcomes in advance, we screened out independent risk factors and developed a multi-factor predictive model that can effectively judge the early HF readmission.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
We selected patients hospitalized for HF between January 2019 and December 2020 at the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (Zhanjiang, China). All the patients had to meet the following criteria: (1) HF diagnosed according to the 2018 guideline for HF diagnosis and treatment in China [16]; (2) aged ≥18 years; (3) received HF treatment during admission. Cases that died during the index admission or lost during follow-up were excluded. This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, and consent was obtained from all participants. After excluding drug-related contraindications, all the selected patients received therapy for underlying diseases and triggers. In addition, the HF patients with preserved and mid-range left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were given β-blockers to maintain heart rhythm at 50–70 beats/min, and those comorbided with sodium and water retention were given diuretics and aldosterone receptor antagonists (spironolactone). According to the individual patient situation, we used ivabradine, AECI/ARB, or ARNI to control blood pressure at 90–140 mmHg and used SGLT-2i to treat patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition to the above treatments, patients with reduced LVEF were treated with cardiotonic drugs such as digoxin and Qili Qiangxin capsules. The clinical baseline data and treatment methods were listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics and 30-day readmission of the patients with HF.
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
Clinical characteristics (age, sex, and smoking), laboratory findings [including glucose (Glu), potassium (K), sodium (Na), serum creatinine (Scr), serum uric acid (SUA), cystatin C (CysC), albumin (ALB), red cell distribution width (RDW) coefficient variation (CV), hemoglobin (HGB), neutrophils (NE), lymphocytes (LY), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT), myoglobin (MYO), left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVEDD), and LVEF], and comorbidities (diabetes, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, stable coronary heart disease, acute coronary syndrome, atrial fibrillation, and chronic kidney disease) of their first examinations were obtained from electronic medical records (Table 1). The primary outcome of this study was all-cause readmission within the first 30 days after discharge. The patients were followed up for 30 days after discharge by telephone and their conditions were further confirmed in the hospital system.
2.3. Predictor Selection
Potential prognostic factors associated with the outcome were screened out using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method. The minimum criterion for 10-fold cross-validation in the LASSO model was used to determine the optimal penalty coefficient (λ), and the variable factor of a non-zero coefficient was defined as a risk predictor. Subsequently, a regression model was established using the binary logistic regression model.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The continuous variables are reported as means ± standard deviations for parameters with normal distributions or medians and interquartile ranges for non-normal distributions. The categorical variables are reported as frequencies and percentages. Continuous variables were divided into categorical variables for analyses according to clinical routine cut-offs. The glmnet package in R was used to identify factors associated with 30-day readmission via LASSO regression. The selected predictors were incorporated into the binary logistic regression model to construct a predictive model. Then, a 30-day readmission risk-predictive nomogram model was constructed regarding discrimination and calibration. Finally, the calibration and discriminative abilities of the model were quantified using the Hosmer–Lemeshow (HL) test and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and the clinical applicability of the model was evaluated using a decision curve analysis (DCA).
All analyses were performed using the Stata v.15.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA) and R v.4.0.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). All results with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of the Patients
The clinical baseline data for all 2254 patients included in this study are listed in Table 1. Their median age was 71.54 ± 12.36 years, and 1324 (58.74%) were male. Their 30-day all-cause readmission rate was 7.1%.
3.2. Risk Predictors for the Model
We screened the prediction variables from the baseline indicators and excluded variables with no clinical significance. The results of the LASSO analysis showed that several non-zero coefficients, including age, CysC, ALB, RDW-CV, NE, NT-proBNP, hs-cTnT, MYO, sex, dyslipidaemia, LVEDD, LVEF, and atrial fibrillation, were associated with 30-day readmission when the optimal λ was 0.037 (Figure 1). Therefore, these factors were subsequently selected as predictors and included in the prediction model.
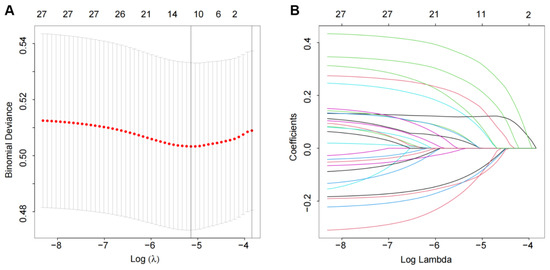
Figure 1.
Predictor selection using the LASSO logistic regression model: (A) the penalty coefficient (λ) selection in the LASSO model used 10-fold cross-validation via minimum criteria; (B) LASSO coefficient distribution for 27 variables and non-zero coefficients selected in the LASSO coefficient profiles.
3.3. Predictive Nomogram for 30-Day Readmission
A nomogram was developed for prediction of the 30-day readmission risk (Figure 2). Then, the prediction model was internally validated via a 10-fold cross-validation analysis. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.653 (95% confidence interval: 0.608–0.698; Figure 3), indicating that the nomogram has good identification capability.
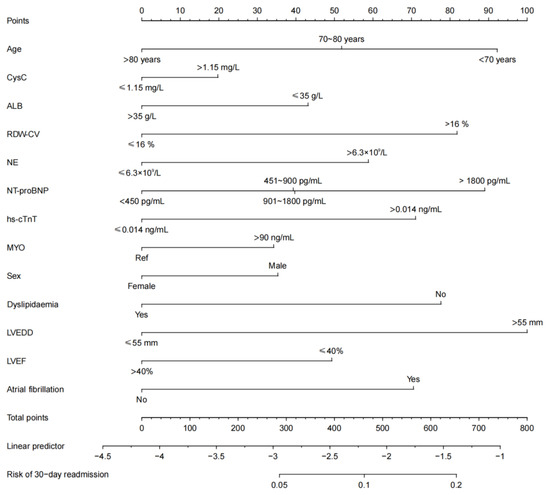
Figure 2.
The 30-day readmission risk prediction nomogram. Key: CysC, cystatin C; ALB, albumin; RDW-CV, red distribution width coefficient variation; NE, neutrophils; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; hs-cTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; MYO, myoglobin; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension.
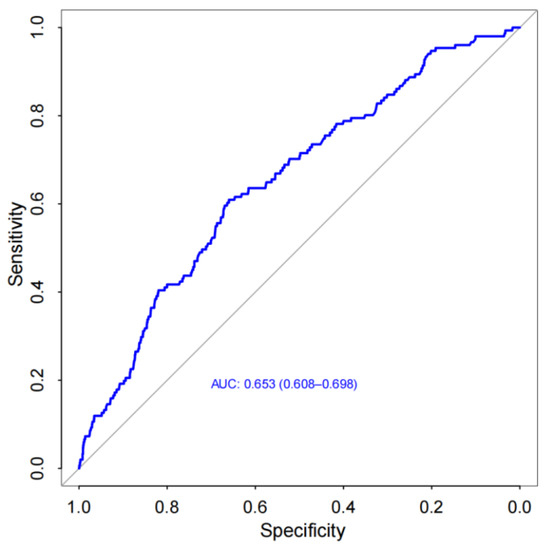
Figure 3.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the nomogram [area under the curve (AUC)=0.653, 95% confdence interval (CI): 0.608–0.698].
3.4. Performance of the Nomogram
The predictive accuracy and discriminative ability of the nomogram were assessed using a calibration curve. The HL test indicated good calibration (p = 0.328), and the calibration curves showed good agreement between the readmission risk and actual observation (Figure 4A). By comparing the net benefit of default strategies for treating all or no patients across different threshold probabilities, the DCA showed that the nomogram could be clinically useful (Figure 4B). Altogether, the predictive nomogram is appropriate for clinically predicting the 30-day readmission risk of HF patients.
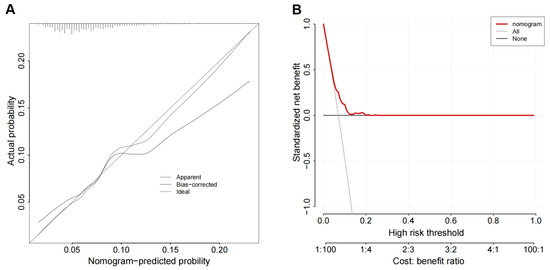
Figure 4.
Discrimination ability and calibration degree of the nomogram: (A) the Hosmer–Lemeshow (HL) test, showing good calibration; (B) the decision curve analysis (DCA), indicating clinical usefulness.
4. Discussion
The readmission rate within 30 days is an important quality control indicator for HF patients. According to the survey, most of the 30-day readmission cases of HF occurred within two weeks after discharge. Therefore, accurately predicting the 30-day readmission risk of HF patients will help formulate appropriate diagnosis and treatment plans and disease management guidelines. In this study, we developed an easy-to-use nomogram based on readily available clinical variables, ensuring the wide applicability of our predictive model. Our findings showed that the all-cause 30-day readmission rate of the 2254 selected HF patients was 7.1%. The 30-day readmission prediction model developed based on independent predictors selected by multivariate analysis showed good internal consistency. Overall, this prediction model can help to easily and quickly assessing a patient’s 30-day readmission risk, and may contribute to reducing the incidence of early readmission by adjusting the disease management plan.
A machine learning model was used to predict 30-day readmission in HF patients from seven major hospitals in the Boston Metro area and eastern Massachusetts [17]. However, it may be unsuitable for patients in other countries due to differences in disease management patterns and readmission rates. In addition, machine learning methods may be difficult for most clinicians as there are no equations used for calculating risk scores. Therefore, we used the LASSO method to develop a prediction model that will be easy for clinicians to evaluate the risk of 30-day HF readmission. Compared with an ordinary least squares estimation, LASSO can efficiently extract important variables and simplify the model when there are many candidate variables. In this study, the internal validation results showed that our nomogram based on the thirteen predictors selected by the LASSO method had good identification ability (Figure 1), although its AUC was slightly less than the machine learning model (Figure 3).
The clinical data used as the potential prognosticfactors included leading baseline indicators, laboratory test indexes, and comorbidities, which may affect the HF outcome. The results of the LASSO regression analysis showed that age, CysC, ALB, RDW-CV, NE, NT-proBNP, hs-cTnT, MYO, sex, dyslipidaemia, LVEDD, LVEF, and atrial fibrillation were independent predictors of 30-day readmission (Figure 2). It has been shown that age and sex affect the prognosis of HF comorbided with diabetes [18,19]. Serum ALB has been associated with myocardial fibrosis [20], poor pulsatile aortic hemodynamics, and prognosis of HF with preserved ejection fraction [21]. Similarly, RDW and its changes during hospitalization are associated with 30-day mortality, the hospital stay length, and 30-day all-cause readmission [22]. Anemia, particularly persistent and new-onset anemia and milder temporary anemia, are suggested to be harmful to HF patients [23]. Inflammatory markers have been confirmed to be associated with adverse outcomes in HF patients [24]. NT-ProBNP secreted by the ventricle with increased wall stress is a prognostic HF biomarker [25]. In addition, hs-cTnT and serum ALB are two independent HF prognostic factors in the DCTA scoring system [26]. LVEDD ≤ 55 mm is an independent prognostic factor for LVEF recovery after clinical HF treatment [27]. Therefore, we used these significant risk factors to develop a predictive model for 30-day HF readmission.
Ibrahim et al. found that both the HOSPITAL Score and LACE index have poor specificity in predicting 30-day HF readmission [4]. In contrast to a scoring system, a risk prediction model is not just a simple mathematical combination of dependent and independent variables [28]. It must also possess a good discrimination ability and a good calibration degree. Some clinical indexes have been identified as the risk factors associated with adverse prognosis of HF [29]; however, using these factors to developed mathematical models may be more beneficial for predicting HF prognosis. Thus, we developed a 30-day readmission model using routine clinical indexes associated with HF prognosis. The AUC of the nomogram suggested that the 30-day readmission model had good discrimination ability (Figure 3). Moreover, the HL test and DCA indicated that this model also had a good degree of calibration and clinical usefulness (Figure 4).
This study is not unique in using this method to predict HF readmission. Both traditional and machine learning methods have been used in developing readmission models for HF patients from different grades of hospitals in different countries [8,17,28,30,31,32,33]. Nevertheless, machine learning methods may be difficult for most clinicians as there are no equations used for calculating risk scores. While the AUCs of the machine learning models are slightly higher than this prediction model, it may be unsuitable for patients in other countries due to differences in disease management patterns and readmission rates. Indeed, there are large differences in HF readmission rates among different hospitals. Our data were collected from a large-scale teaching hospital, where the 30-day readmission rate of HF patients appeared lower than the average reported by most studies. Therefore, we must establish a suitable predictive model to evaluate the 30-day HF readmission risk. While the prediction model developed is relatively simple and useful, there remains room for improvement. In future studies, we will further develop novel biomarkers to predict HF prognosis.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we developed a novel nomogram for accurately predicting the risk of 30-day readmission for HF patients. The nomogram is easy to use and can assist clinicians in assessing the risk of 30-day HF readmission and making personalized treatment programs for HF patients. However, this study had several limitations. First, it was a retrospective observational study without external validation. In addition, we only focused on 30-day readmission without other endpoints such as 180-day readmission and death. Therefore, we plan to conduct a multicenterprospective cohort study on HF prognosis predictions.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.H. and L.S.; software, J.-B.H.; validation, Z.-K.H. and L.C.; formal analysis, J.-B.H. and L.C.; investigation, Z.-K.H. and C.-Z.Z.; datacuration, C.-Z.Z. and B.-Z.W.; writing-original draft preparation, J.-B.H. and L.C.;writing-review and editing, Y.H. and Z.-K.H.; supervision, L.S.; project administration, Y.H. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Zhanjiang Science and Technology Development Special Funding Competitive Allocation Project (2021A05058).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (approval No. PJ2021-108).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baman, J.R.; Ahmad, F.S. Heart failure. JAMA 2020, 324, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.; Bush, N. Heart failure: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, medical treatment guidelines, and nursing management. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 50, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldgrab, D.; Balakumaran, K.; Kim, M.J.; Tabtabai, S.R. Updates in heart failure 30-day readmission prevention. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Koester, C.; Al-Akchar, M.; Tandan, N.; Regmi, M.; Bhattarai, M.; Al-Bast, B.; Kulkarni, A.; Robinson, R. HOSPITAL Score, LACE Index and LACE+ Index as predictors of 30-day readmission in patients with heart failure. BMJ. Evid. Based Med. 2020, 25, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakar, S.; Zhang, W.; Kuo, Y.F.; Alghrouz, M.; Barbajelata, A.; Sharma, G. Validation of the readmission risk score in heart failure patients at a tertiary hospital. J. Card. Fail. 2015, 21, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, Q.; Negishi, K.; De Pasquale, C.G.; Hare, J.L.; Leung, D.; Stanton, T.; Marwick, T.H. Validation of predictive score of 30-Day hospital readmission or death in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 121, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahewala, S.; Arora, S.; Tripathi, B.; Panaich, S.; Kumar, V.; Patel, N.; Savani, S.; Dave, M.; Varma, Y.; Badheka, A.; et al. Heart failure: Same-hospital vs. different-hospital readmission outcomes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 278, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tao, L.; An, H.; Liu, G.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qin, L.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; et al. A novel nomogram to predict all-cause readmission or death risk in Chinese elderly patients with heart failure. ESC. Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolillo, S.; Scardovi, A.B.; Campodonico, J. Role of comorbidities in heart failure prognosis Part I: Anaemia, iron deficiency, diabetes, atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Agostoni, P.; Pezzuto, B.; Corra’, U.; Scrutinio, D.; La Gioia, R.; Raimondo, R.; Passantino, A.; Piepoli, M.F. Role of comorbidities in heart failure prognosis Part 2: Chronic kidney disease, elevated serum uric acid. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maries, L.; Manitiu, I. Diagnostic and prognostic values of B-type natriuretic peptides (BNP) and N-terminal fragment brain natriuretic peptides (NT-pro-BNP). Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2013, 24, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, L.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P. Inflammatory biomarkers and therapeutic targets in heart failure. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 2716–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costache, I.I.; Alexandrescu, D.M.; Cimpoeşu, D.; Petriş, O.R.; Petriş, A.O. Hyponatremia--risk factor in patients with chronic heart failure—Clinical, evolutive and therapeutic implications. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi. 2014, 118, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borghi, C.; Palazzuoli, A.; Landolfo, M.; Cosentino, E. Hyperuricemia: A novel old disorder-relationship and potential mechanisms in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 25, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Vasan, R.S. Novel markers for heart failure diagnosis and prognosis. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2005, 20, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heart Failure Group of Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Heart Failure Association of Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Cardiology. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure 2018. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2018, 46, 760–789. [Google Scholar]
- Golas, S.B.; Shibahara, T.; Agboola, S.; Otaki, H.; Sato, J.; Nakae, T.; Hisamitsu, T.; Kojima, G.; Felsted, J.; Kakarmath, S.; et al. A machine learning model to predict the risk of 30-day readmissions in patients with heart failure: A retrospective analysis of electronic medical records data. BMC. Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.M.; Pereira, J.; Ribeiro, A.; Amorim, M.; Silva, S.; Araújo, J.P.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Bettencourt, P.; Lourenço, P. Age affects the prognostic impact of diabetes in chronic heart failure. Acta. Diabetol. 2018, 55, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.C.K.; Chia, S.Y.; Sim, D.K.L.; Chai, P.; Loh, S.Y.; Shum, A.K.L.; Lee, S.S.G.; Lim, P.Z.Y.; Yap, J. Interaction of sex and diabetes in Asian patients with heart failure with mildly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2022, 51, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arques, S. Human serum albumin in cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenner, S.B.; Pillutla, R.; Yenigalla, S.; Gaddam, S.; Lee, J.; Obeid, M.J.; Ans, A.H.; Jehangir, Q.; Kim, J.; Zamani, P.; et al. Serum albumin is a marker of myocardial fibrosis, adverse pulsatile aortic hemodynamics, and prognosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlestein, J.B.; Lappe, D.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Budge, D.; May, H.T.; Bennett, S.T.; Bair, T.L.; Horne, B.D. Both initial red cell distribution width (RDW) and change in RDW during heart failure hospitalization are associated with length of hospital stay and 30-day outcomes. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-López, C.; Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Zamora, E.; Domingo, M.; Santesmases, J.; Troya, M.I.; Boldó, M.; Bayes-Genis, A. Hemoglobin kinetics and long-term prognosis in heart failure. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2016, 69, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, X. A nomogram based on systemic inflammation markers can predict adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2022, 42, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zile, M.R.; Claggett, B.L.; Prescott, M.F.; McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Rouleau, J.L.; Swedberg, K.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Shi, V.C.; et al. Prognostic implications of changes in N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.J.; Yang, Q.K.; Bi, L.D.; Li, J.; Tan, C.Y.; Miao, Z.L. Prognostic value of DCTA scoring system in heart failure. Herz 2021, 46, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chai, K.; Cheng, Y.L.; Zhu, W.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.F. Clinical characteristics of heart failure with recovered ejection fraction. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2021, 49, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Austin, P.C.; Ross, H.J.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Freitas, C.; Tomlinson, G.; Chicco, D.; Mahendiran, M.; Lawler, P.R.; Billia, F.; et al. Machine learning vs. conventional statistical models for predicting heart failure readmission and mortality. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whellan, D.J.; Ousdigian, K.T.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Pu, W.; Sarkar, S.; Porter, C.B.; Pavri, B.B.; O’Connor, C.M. Combined heart failure device diagnostics identify patients at higher risk of subsequent heart failure hospitalizations: Results from PARTNERS HF (Program to Access and Review Trending Information and Evaluate Correlation to Symptoms in Patients with Heart Failure) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, L.M.; Gavin, M.; Piatkowski, G.; Chang, J.D.; Mukamal, K.J. Derivation and validation of a 30-day heart failure readmission model. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Ren, J.; Tian, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Han, L.; Li, C.; Yan, J.; et al. A nomogram based on a patient-reported outcomes measure: Predicting the risk of readmission for patients with chronic heart failure. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzell, J.D.; Liang, L.; Schulte, P.J.; Yancy, C.W.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Hernandez, A.F.; Bhatt, D.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Laskey, W.K. Prediction of 30-Day All-Cause Readmissions in Patients Hospitalized for Heart Failure: Comparison of Machine Learning and Other Statistical Approaches. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, B.J.; Downing, N.S.; Bucholz, E.M.; Dharmarajan, K.; Manhapra, A.; Li, S.X.; Negahban, S.N.; Krumholz, H.M. Analysis of machine learning techniques for heart failure readmissions. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2016, 9, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).