Relating the Ramsay Quotient Model to the Classical D-Scoring Rule
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Item Response Modeling
2.1. Two-Parameter Logistic (2PL) Item Response Model
2.1.1. Rasch Model (1PL Model)
2.1.2. Implementation
2.2. Ramsay Quotient Model (RQM)
Implementation
3. Dimitrov’s D-Scoring Approach
3.1. Classical D-Scoring Method
3.2. Rational Function Model (RFM) as a Latent D-Scoring Model
4. Modified Ramsay Quotient Model and the Classical D-Scoring Rule
5. Numerical Examples
6. Discussion
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1PL | one-parameter logistic |
| 2PL | two-parameter logistic |
| CTT | classical test theory |
| EM | expectation maximization |
| IRF | item response function |
| IRT | item response theory |
| RFM | rational function model |
| RM | Rasch model |
| RQM | Ramsay quotient model |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Baker, F.B.; Kim, S.H. Item Response Theory: Parameter Estimation Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, W.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.R. Item response theory. In Educational Measurement; Brennan, R.L., Ed.; Praeger Publishers: Westport, CT, USA, 2006; pp. 111–154. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, D.M. An approach to scoring and equating tests with binary items: Piloting with large-scale assessments. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2016, 76, 954–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, D. D-scoring Method of Measurement: Classical and Latent Frameworks; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.M.; Atanasov, D.V. Latent D-scoring modeling: Estimation of item and person parameters. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2021, 81, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A. About the equivalence of the latent D-scoring model and the two-parameter logistic item response model. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Ying, Z. Item response theory – A statistical framework for educational and psychological measurement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.08604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, W.J. Unidimensional logistic response models. In Handbook of Item Response Theory, Volume 1: Models; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- San Martin, E. Identification of item response theory models. In Handbook of Item Response Theory, Volume 2: Statistical Tools; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, R.D.; Gibbons, R.D. Item Response Theory; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.G.; da Silva, J.M.N.; Bispo, L.G.M.; de Souza, D.S.F.; Serafim, R.S.; Torres, M.G.L.; Leite, W.K.d.S.; Vieira, E.M.d.A. Construction of a musculoskeletal discomfort scale for the lower limbs of workers: An analysis using the multigroup item response theory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmahl, C.; Greffrath, W.; Baumgärtner, U.; Schlereth, T.; Magerl, W.; Philipsen, A.; Lieb, K.; Bohus, M.; Treede, R.D. Differential nociceptive deficits in patients with borderline personality disorder and self-injurious behavior: Laser-evoked potentials, spatial discrimination of noxious stimuli, and pain ratings. Pain 2004, 110, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasch, G. Probabilistic Models for Some Intelligence and Attainment Tests; Danish Institute for Educational Research: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, A. Some latent trait models and their use in inferring an examinee’s ability. In Statistical Theories of Mental Test Scores; Lord, F.M., Novick, M.R., Eds.; MIT Press: Reading, MA, USA, 1968; pp. 397–479. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; von Davier, M. Fitting the Structured General Diagnostic Model to NAEP Data; (Research Report No. RR-08-28); Educational Testing Service: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkin, M. Expectation maximization algorithm and extensions. In Handbook of Item Response Theory, Vol. 2: Statistical Tools; van der Linden, W.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Chalmers, R.P. mirt: A multidimensional item response theory package for the R environment. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A. R Package Version 4.0-6; sirt: Supplementary Item Response Theory Models; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://github.com/alexanderrobitzsch/sirt (accessed on 12 August 2023).
- Ramsay, J.O. A comparison of three simple test theory models. Psychometrika 1989, 54, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maas, H.L.J.; Molenaar, D.; Maris, G.; Kievit, R.A.; Borsboom, D. Cognitive psychology meets psychometric theory: On the relation between process models for decision making and latent variable models for individual differences. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 118, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, D.; Tuerlinckx, F.; van der Maas, H.L.J. Fitting diffusion item response theory models for responses and response times using the R package diffIRT. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 66, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemker, B.T. To a or not to a: On the use of the total score. In Essays on Contemporary Psychometrics; van der Ark, L.A., Emons, W.H.M., Meijer, R.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.M. Modeling of item response functions under the D-scoring method. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2020, 80, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, N.D.; Glas, C.A.W. The one parameter logistic model. In Rasch Models. Foundations, Recent Developments, and Applications; Fischer, G.H., Molenaar, I.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzsch, A.; Kiefer, T.; Wu, M. R Package Version 4.1-4; TAM: Test Analysis Modules; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=TAM (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Mazza, A.; Punzo, A.; McGuire, B. KernSmoothIRT: An R package for kernel smoothing in item response theory. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 58, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.O.; Abrahamowicz, M. Binomial regression with monotone splines: A psychometric application. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.M. Marginal true-score measures and reliability for binary items as a function of their IRT parameters. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2003, 27, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.M.; Atanasov, D.V. Testing for differential item functioning under the D-scoring method. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2022, 82, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, D.M.; Atanasov, D.V. An approach to test equating under the latent D-scoring method. Meas. Interdiscip. Res. Persp. 2021, 19, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.C.T.; Dimitrov, D.M.; Al-Mashary, F. Developing multistage tests using D-scoring method. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2019, 79, 988–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, D.M. The response vector for mastery method of standard setting. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2022, 82, 719–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
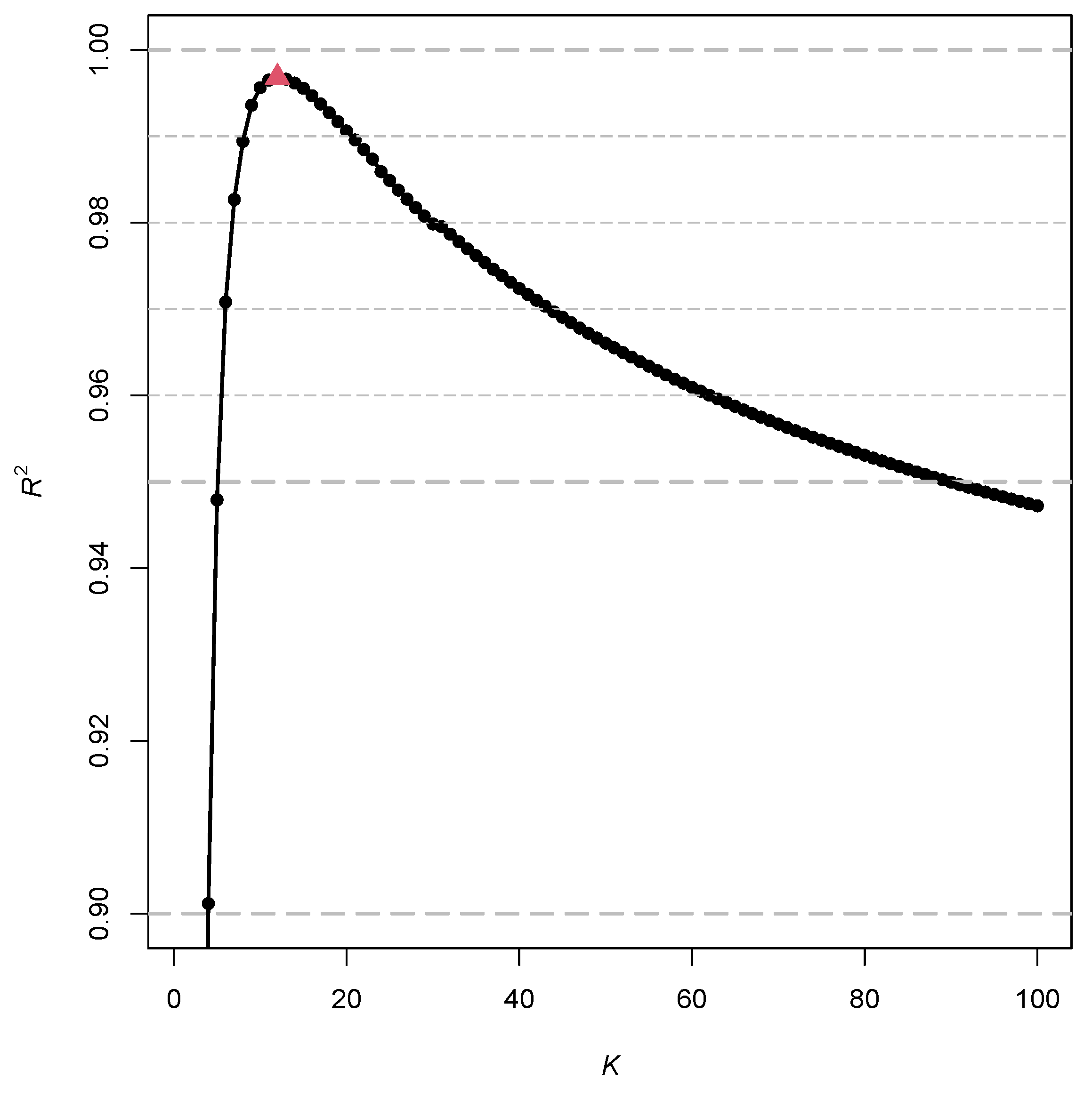
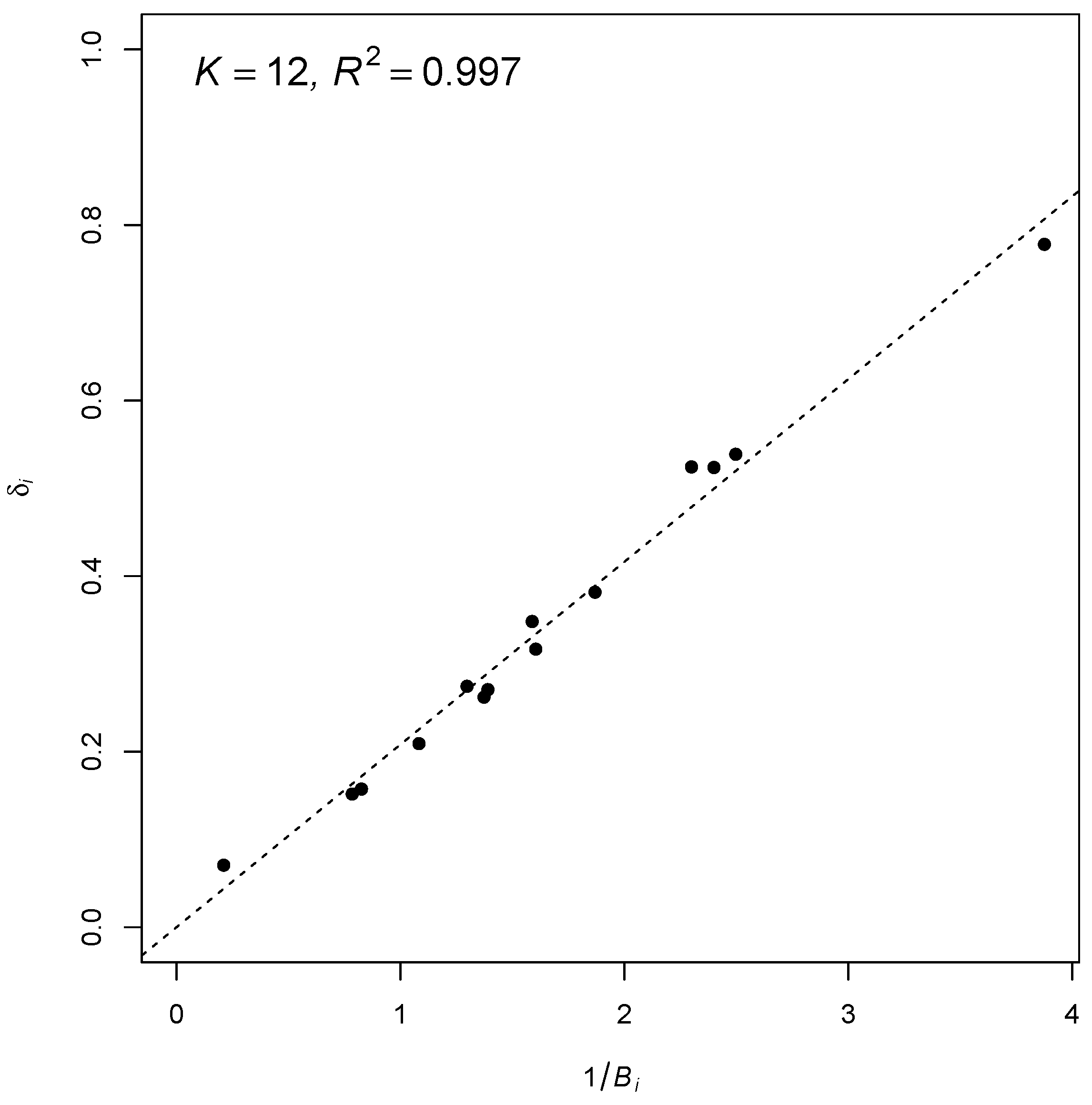
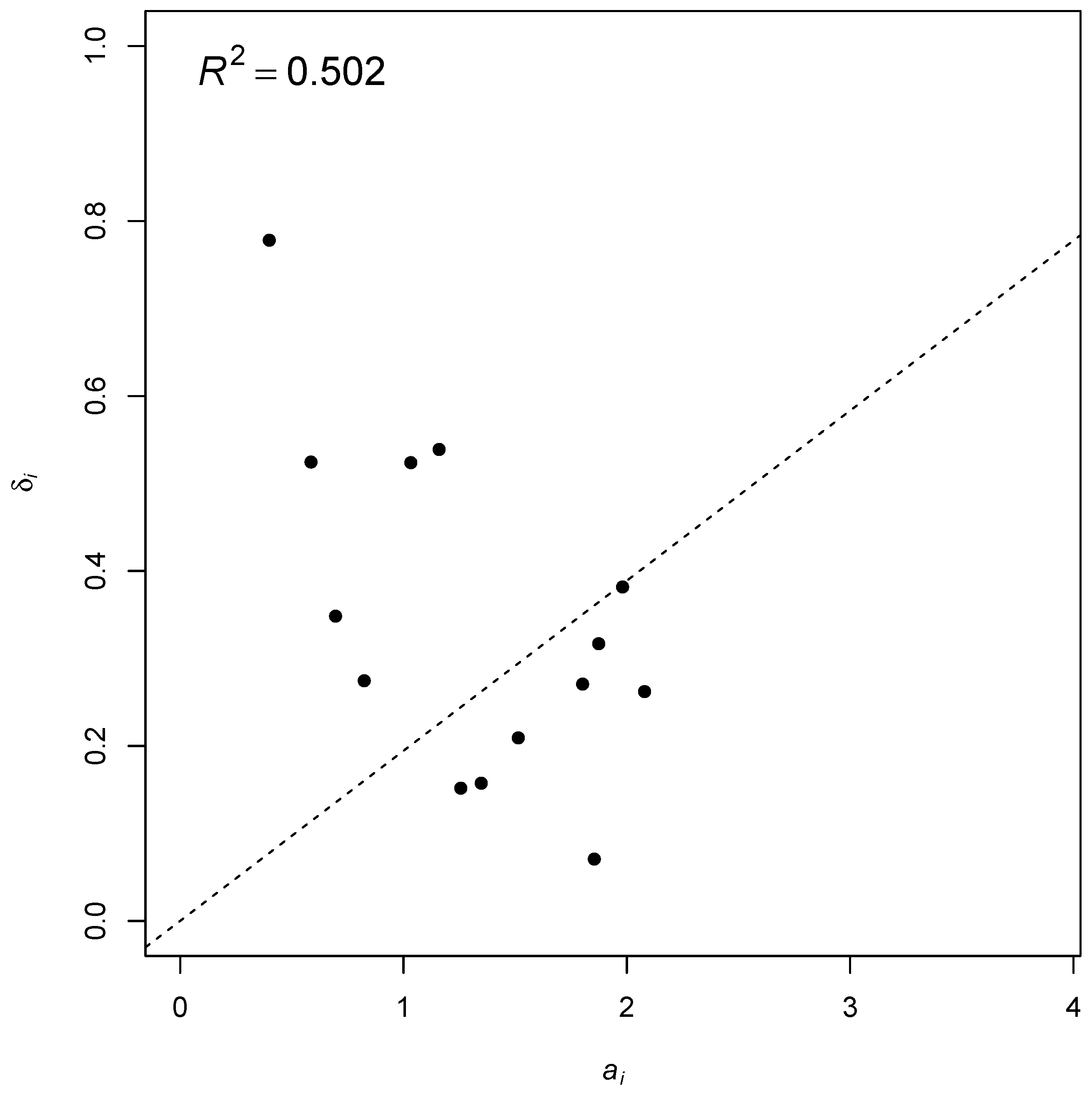
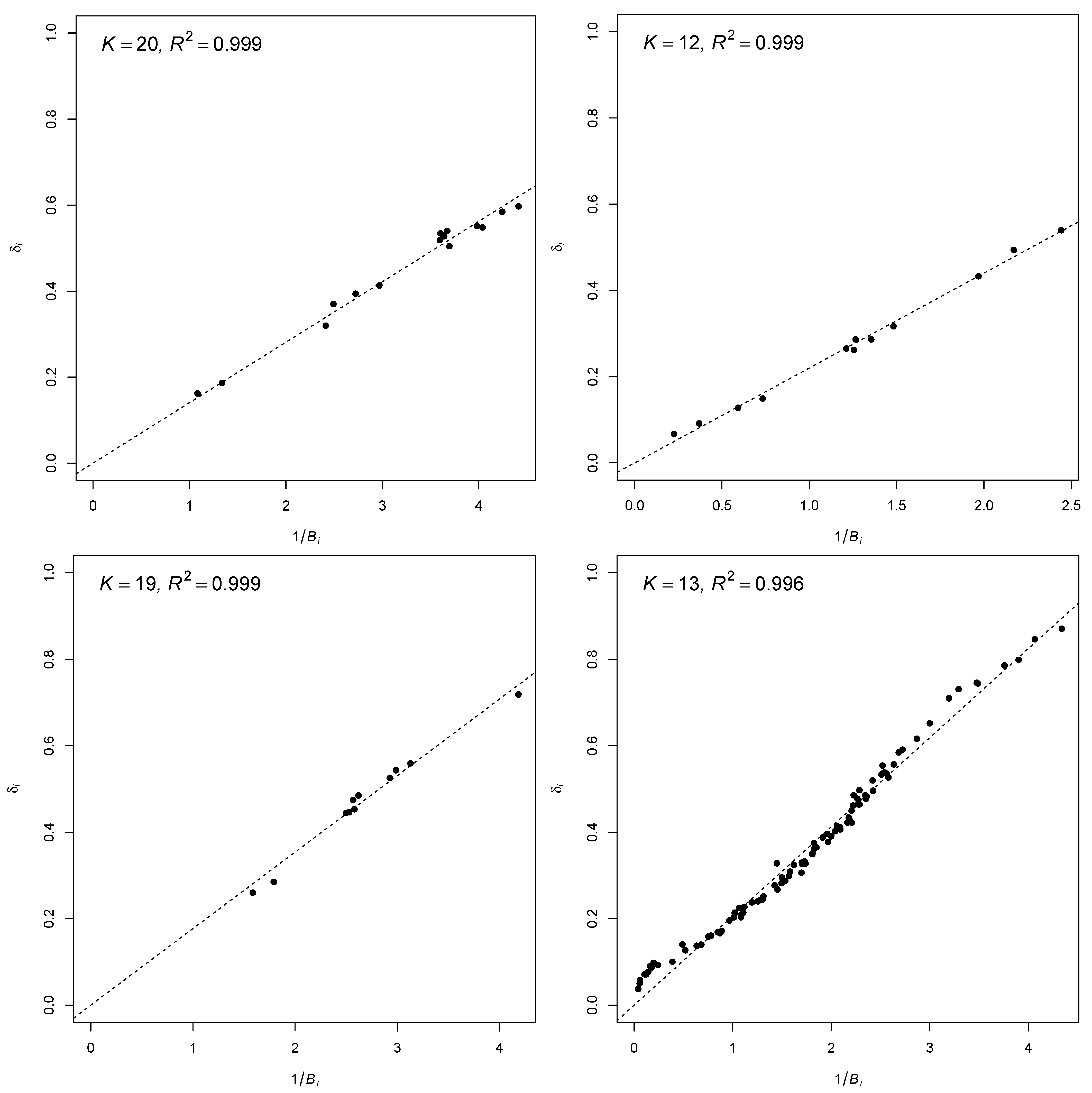
| CTT | RQM | 2PL | Normalized Weights | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | |||||||||||
| WV01 | 0.79 | 0.21 | −0.08 | 12 | 0.92 | 1.08 | 1.51 | −1.23 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 1.15 |
| WV02 | 0.65 | 0.35 | −0.46 | 12 | 0.63 | 1.59 | 0.70 | −1.00 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 0.53 |
| WV03 | 0.73 | 0.27 | −0.33 | 12 | 0.72 | 1.39 | 1.80 | −0.86 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 1.37 |
| WV04 | 0.74 | 0.26 | −0.32 | 12 | 0.73 | 1.37 | 2.08 | −0.85 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 1.58 |
| WV05 | 0.48 | 0.52 | −0.88 | 12 | 0.42 | 2.40 | 1.03 | 0.10 | 1.53 | 1.45 | 0.79 |
| WV06 | 0.68 | 0.32 | −0.47 | 12 | 0.62 | 1.60 | 1.87 | −0.66 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 1.43 |
| WV07 | 0.85 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 12 | 1.27 | 0.78 | 1.26 | −1.74 | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.96 |
| WV08 | 0.62 | 0.38 | −0.63 | 12 | 0.54 | 1.87 | 1.98 | −0.42 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 1.51 |
| WV09 | 0.93 | 0.07 | 1.56 | 12 | 4.74 | 0.21 | 1.85 | −2.02 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 1.41 |
| WV10 | 0.48 | 0.52 | −0.83 | 12 | 0.43 | 2.30 | 0.59 | 0.18 | 1.53 | 1.39 | 0.45 |
| WV11 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 12 | 1.21 | 0.83 | 1.35 | −1.63 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 1.03 |
| WV12 | 0.73 | 0.27 | −0.26 | 12 | 0.77 | 1.30 | 0.82 | −1.35 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.63 |
| WV13 | 0.46 | 0.54 | −0.92 | 12 | 0.40 | 2.50 | 1.16 | 0.16 | 1.57 | 1.51 | 0.88 |
| WV14 | 0.22 | 0.78 | −1.35 | 12 | 0.26 | 3.88 | 0.40 | 3.25 | 2.27 | 2.35 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robitzsch, A. Relating the Ramsay Quotient Model to the Classical D-Scoring Rule. Analytics 2023, 2, 824-835. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytics2040043
Robitzsch A. Relating the Ramsay Quotient Model to the Classical D-Scoring Rule. Analytics. 2023; 2(4):824-835. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytics2040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobitzsch, Alexander. 2023. "Relating the Ramsay Quotient Model to the Classical D-Scoring Rule" Analytics 2, no. 4: 824-835. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytics2040043
APA StyleRobitzsch, A. (2023). Relating the Ramsay Quotient Model to the Classical D-Scoring Rule. Analytics, 2(4), 824-835. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytics2040043






