A Real-Time Immersive Augmented Reality Interface for Large-Scale USD-Based Digital Twins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
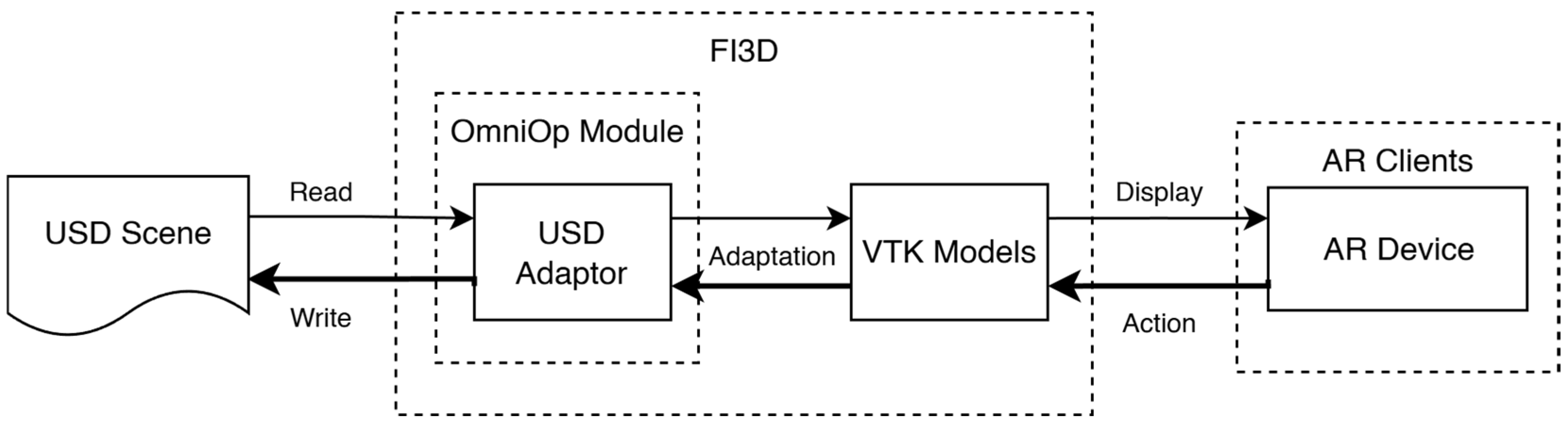
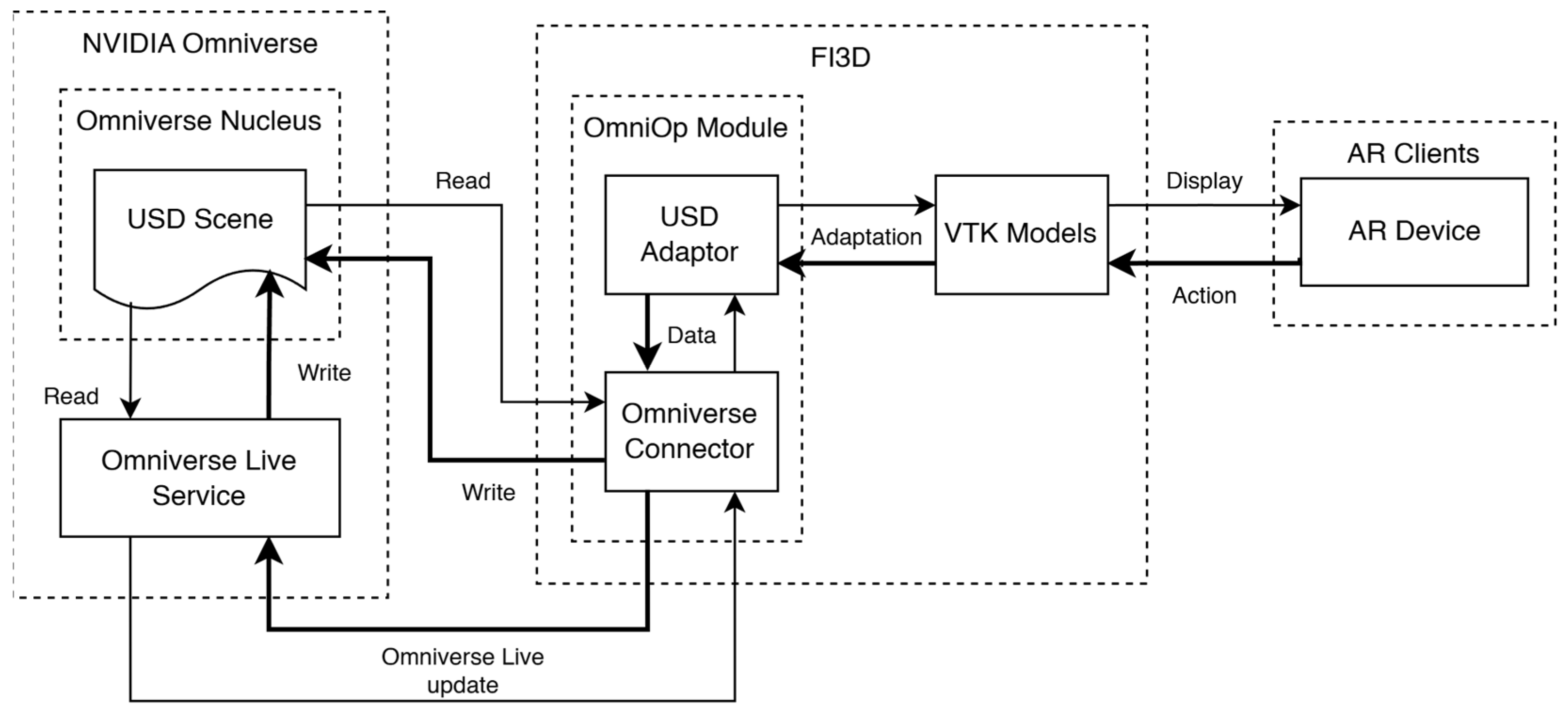
2.1. FI3D-USD Adaptor
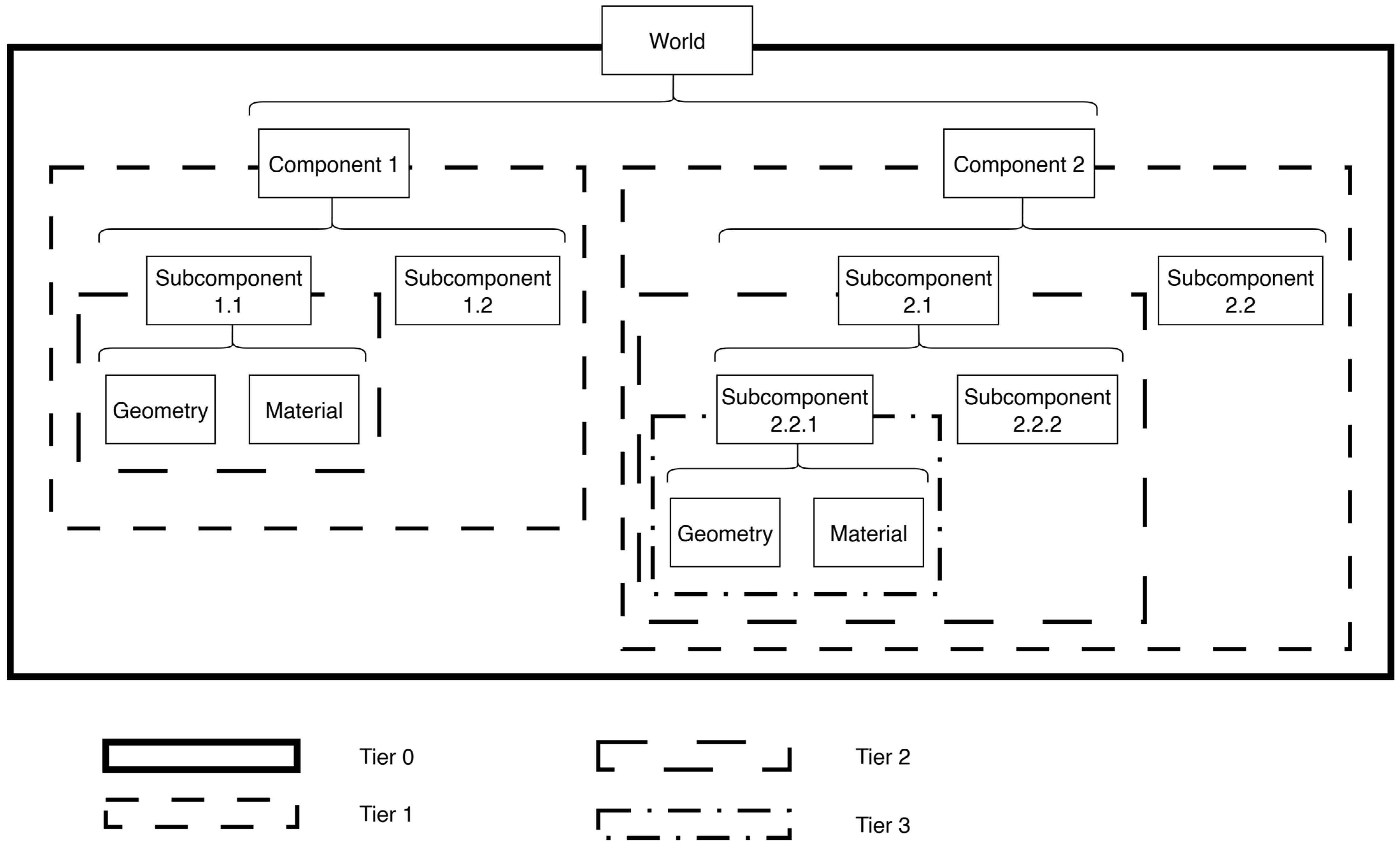
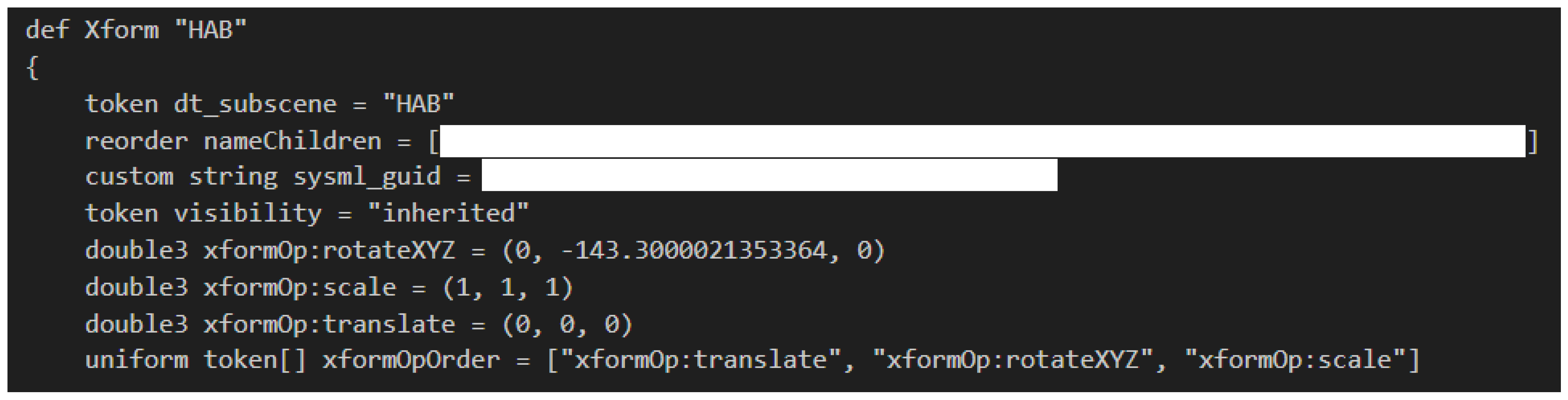
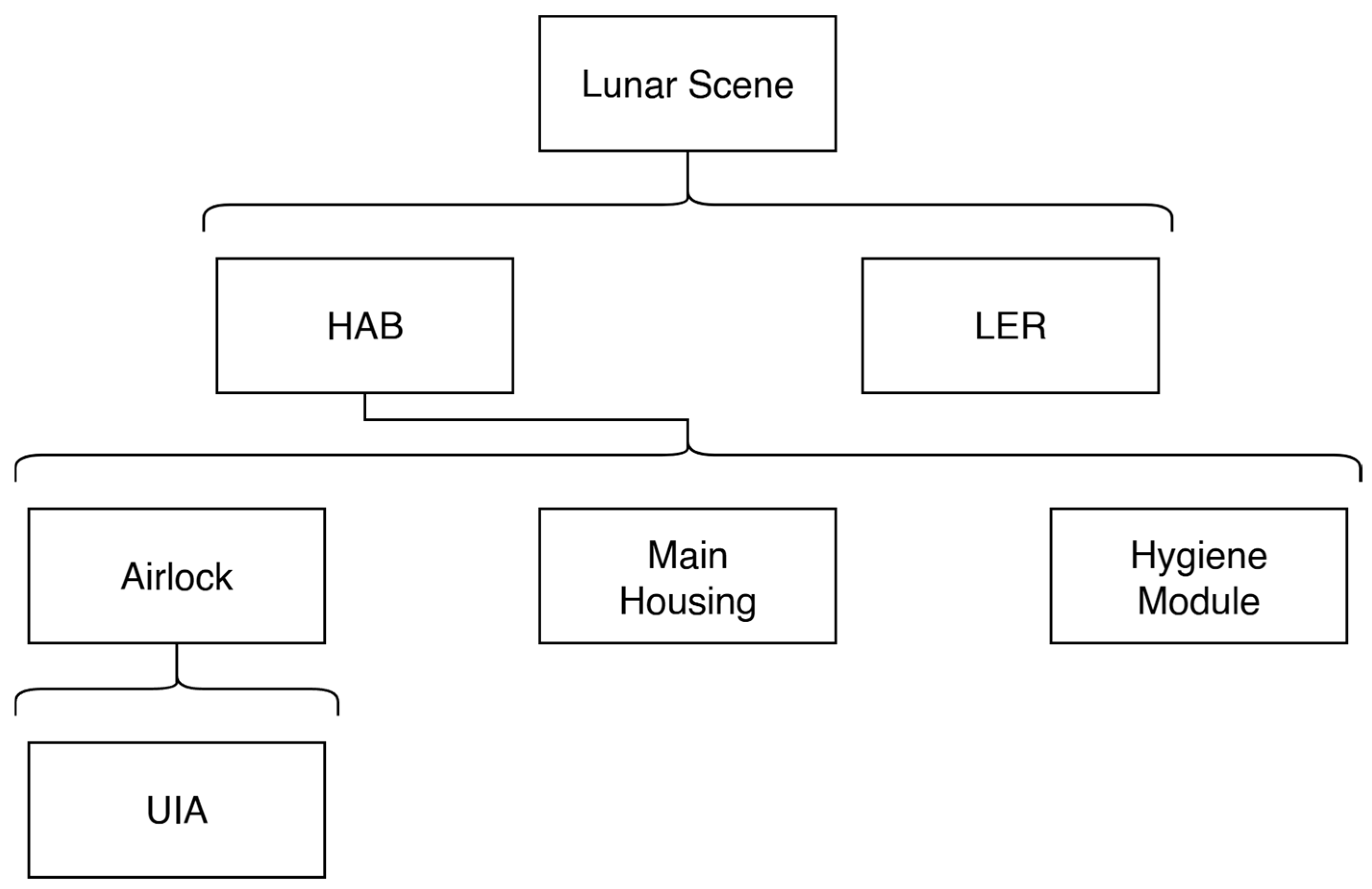
2.2. Subscene Extraction
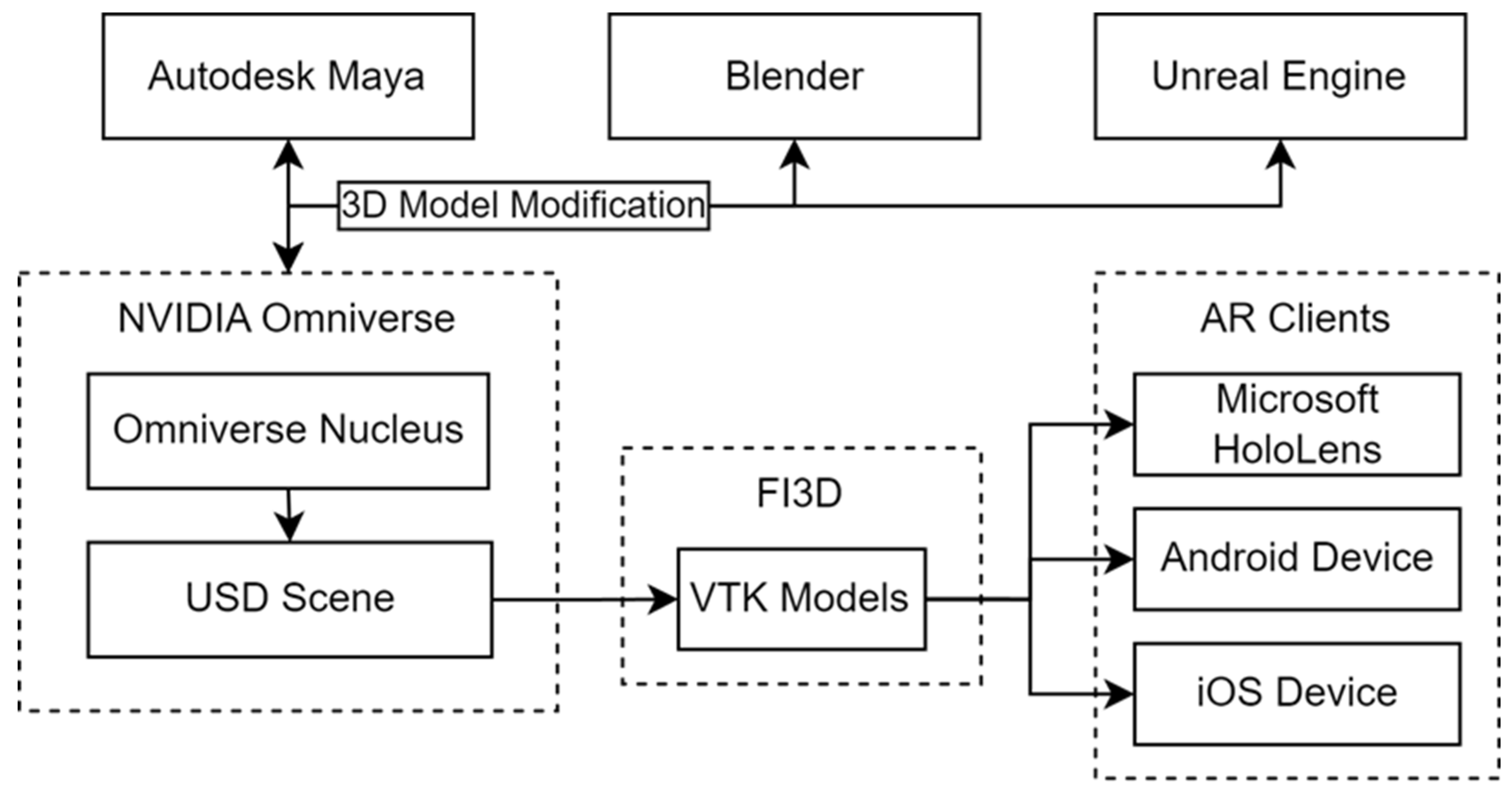
2.3. FI3D-NVIDIA Omniverse Connector
2.3.1. Accessing USD Files on Omniverse Nucleus Server
2.3.2. Omniverse Live
3. Results
3.1. AR Visualization
3.2. Subscene Navigation
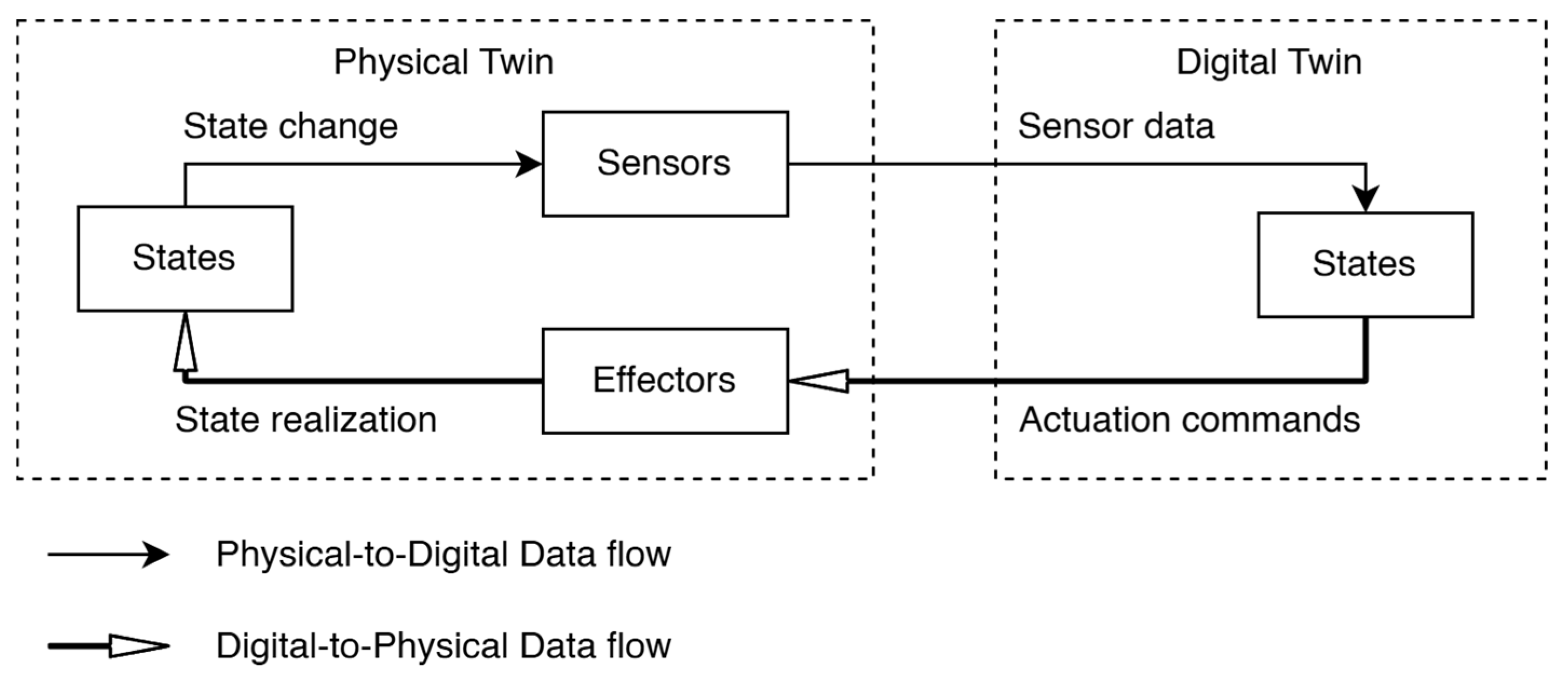
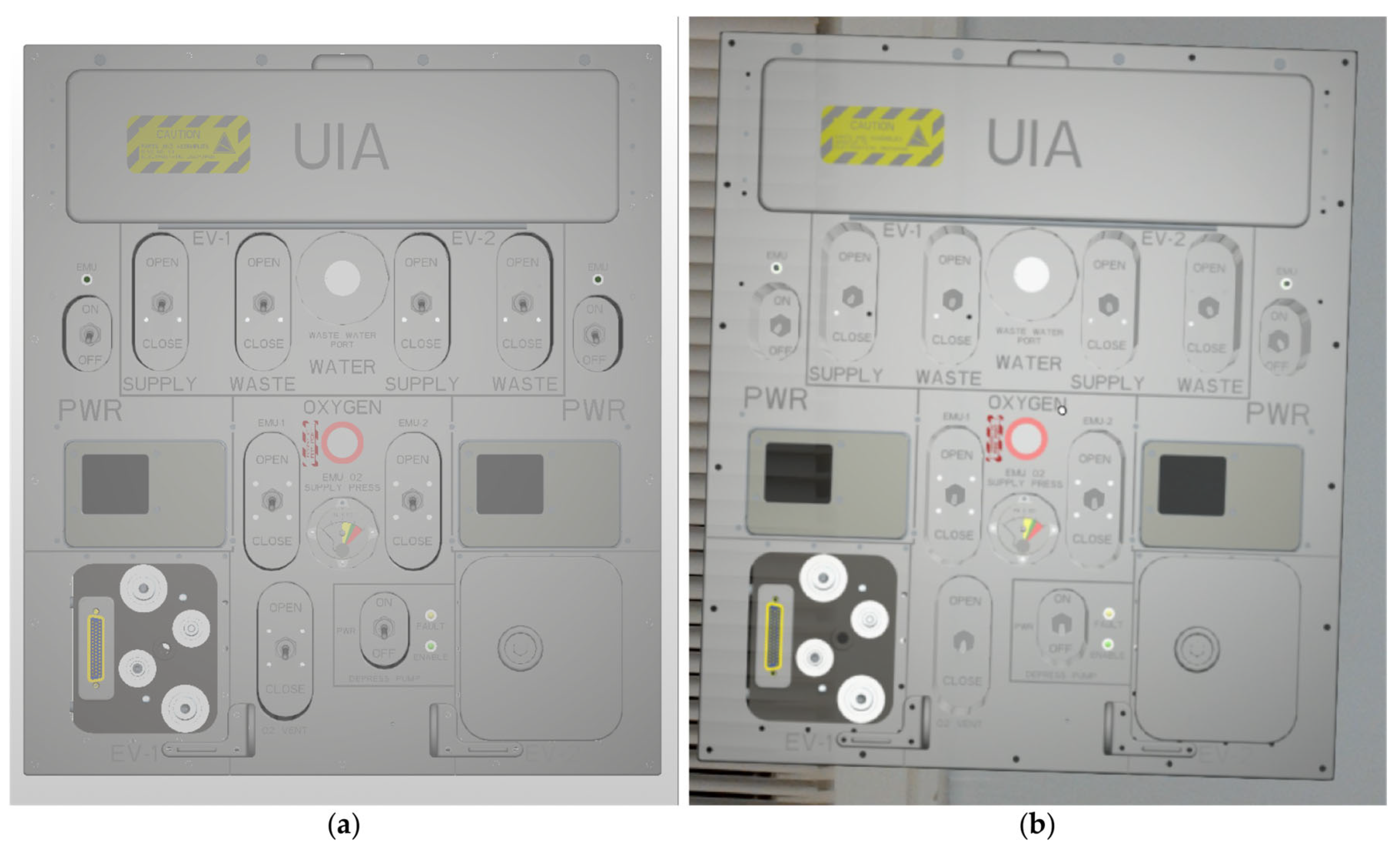
3.3. Physical-Digital Twin Pipeline
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velazco-Garcia, J.D.; Navkar, N.V.; Balakrishnan, S.; Younes, G.; Abi-Nahed, J.; Al-Rumaihi, K.; Darweesh, A.; Elakkad, M.S.M.; Al-Ansari, A.; Christoforou, E.G.; et al. Evaluation of How Users Interface with Holographic Augmented Reality Surgical Scenes: Interactive Planning MR-Guided Prostate Biopsies. Robot. Comput. Surg. 2021, 17, e2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Mojica, C.M.; Velazco-Garcia, J.D.; Pappas, E.P.; Birbilis, T.A.; Becker, A.; Leiss, E.L.; Webb, A.; Seimenis, I.; Tsekos, N.V. A Holographic Augmented Reality Interface for Visualizing of MRI Data and Planning of Neurosurgical Procedures. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, C.M.M.; Garcia, J.D.V.; Navkar, N.V.; Balakrishnan, S.; Abinahed, J.; Ansari, W.E.; Al-Rumaihi, K.; Darweesh, A.; Al-Ansari, A.; Gharib, M.; et al. A Prototype Holographic Augmented Reality Interface for Image-Guided Prostate Cancer Interventions. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine, Granada, Spain, 20–21 September 2018; Eurographics Association: Goslar, Germany, 2018; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capecchi, I.; Bernetti, I.; Borghini, T.; Caporali, A. CaldanAugmenty—Augmented Reality and Serious Game App for Urban Cultural Heritage Learning. In Proceedings of the Extended Reality: International Conference, XR Salento 2023, Lecce, Italy, 6–9 September 2023; pp. 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A.; Pulijala, Y. The Application of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkaria, U. BMW to build factories faster virtually: Nvidia’s Omniverse cuts costs, increases flexibility. Automotive News 2023, 98, 3. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/2864615448/ABF598FC6D82418DPQ/1 (accessed on 13 September 2025).
- Garg, S.; Sinha, P.; Singh, A. Overview of Augmented Reality and Its Trends in Agriculture Industry. In IOT with Smart Systems; Senjyu, T., Mahalle, P., Perumal, T., Joshi, A., Eds.; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; Volume 251, pp. 627–636. ISBN 978-981-16-3944-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroushaki, T.; Lam, M.; Chen, W.; Dodds, L.; Eid, A.; Adib, F. Exploiting Synergies between Augmented Reality and RFIDs for Item Localization and Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–15 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegele, D.; Di Staso, U.; Piovano, M.; Marcher, C.; Matt, D.T. State of the Art of Non-vision-Based Localization Technologies for AR in Facility Management. In Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Computer Graphics; De Paolis, L.T., Bourdot, P., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12242, pp. 255–272. ISBN 978-3-030-58464-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribà-Gelonch, M.; Liang, S.; Van Schalkwyk, P.; Fisk, I.; Long, N.V.D.; Hessel, V. Digital Twins in Agriculture: Orchestration and Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10737–10752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.J.C.; Mishra, A.; Xu, G.; Garcia, J.D.V.; Tsekos, N.V. Mixed Reality Holographic Models for the Interactive and Synergetic Exploration of Space Structures in Architectural Design and Education. In Shell and Spatial Structures; Gabriele, S., Manuello Bertetto, A., Marmo, F., Micheletti, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 437, pp. 540–548. ISBN 978-3-031-44327-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Mosca, N.; Di Summa, M. Augmented and Virtual Reality for Improving Safety in Railway Infrastructure Monitoring and Maintenance. Sensors 2025, 25, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannis, H. How AR Is Redefining Retail in the Pandemic. Available online: https://hbr.org/2020/10/how-ar-is-redefining-retail-in-the-pandemic (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Boland, M. Does AR Really Reduce eCommerce Returns? Available online: https://arinsider.co/2021/09/28/does-ar-really-reduce-ecommerce-returns-2/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Maio, R.; Santos, A.; Marques, B.; Ferreira, C.; Almeida, D.; Ramalho, P.; Batista, J.; Dias, P.; Santos, B.S. Pervasive Augmented Reality to Support Logistics Operators in Industrial Scenarios: A Shop Floor User Study on Kit Assembly. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 1631–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-García, S.; Otero-Agra, M.; Fernández-Méndez, F.; Herrera-Pedroviejo, E.; Darné, M.; Barcala-Furelos, R.; Rodríguez-Núñez, A. Augmented Reality Training in Basic Life Support with the Help of Smart Glasses. A pilot study. Resusc. Plus 2023, 14, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ma, C.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Xu, T.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Feasibility of Augmented Reality Using Dental Arch-Based Registration Applied to Navigation in Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis: A Phantom Experiment. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liamruk, P.; Onwong, N.; Amornrat, K.; Arayapipatkul, A.; Sipiyaruk, K. Development and Evaluation of an Augmented Reality Serious Game to Enhance 21st Century Skills in Cultural Tourism. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carulli, M.; Generosi, A.; Bordegoni, M.; Mengoni, M. Design of XR Applications for Museums, Including Technology Maximising Visitors’ Experience. In Advances on Mechanics, Design Engineering and Manufacturing IV; Gerbino, S., Lanzotti, A., Martorelli, M., Mirálbes Buil, R., Rizzi, C., Roucoules, L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1460–1470. ISBN 978-3-031-15927-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuno, K.; Kusunoki, F.; Inagaki, S.; Mizoguchi, H. Talkative Museum: Augmented Reality Interactive Museum Guide System Towards Collaborative Child-Parent-Specimen Interaction. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual ACM Interaction Design and Children Conference, Delft, The Netherlands, 17–20 June 2024; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, V.; Guidazzoli, A.; Bellavia, G.; De Luca, D.; Liguori, M.C.; Delli Ponti, F.; Farroni, F.; Chiavarini, B. Il Piccolo Masaccio e le Terre Nuove. Creativity and Computer Graphics for Museum Edutainment. In Electronic Imaging & the Visual Arts. EVA 2018 Florence; Cappellini, V., Ed.; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italy, 2018; pp. 166–172. ISBN 978-88-6453-706-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.G.; Admakin, O.; Lerner, H.; Mangano, C. Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality for Guided Implant Surgery Planning: A Proof of Concept. J. Dent. 2023, 133, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, F.; Van Aerschot, F.; Frantz, T.; Verhellen, A.; Barbé, K.; Jansen, B.; Vandemeulebroucke, J.; Duerinck, J.; Scheerlinck, T. Augmented Reality Guidance Improves Accuracy of Orthopedic Drilling Procedures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCloskey, K.; Turlip, R.; Ahmad, H.S.; Ghenbot, Y.G.; Chauhan, D.; Yoon, J.W. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2023, 173, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-R.; Wang, M.-L.; Liu, K.-C.; Hu, M.-H.; Lee, P.-Y. Real-time Advanced Spinal Surgery via Visible Patient Model and Augmented Reality System. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazco-Garcia, J.D.; Navkar, N.V.; Balakrishnan, S.; Abinahed, J.; Al-Ansari, A.; Younes, G.; Darweesh, A.; Al-Rumaihi, K.; Christoforou, E.G.; Leiss, E.L.; et al. Preliminary Evaluation of Robotic Transrectal Biopsy System on an Interventional Planning Software. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Athens, Greece, 28–30 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; De Benedetto, E.; De Paolis, L.; D’Errico, G.; Donato, N.; Duraccio, L. Performance and Usability Evaluation of an Extended Reality Platform to Monitor Patient’s Health during Surgical Procedures. Sensors 2022, 22, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, M.; Ghanimeh, J.; Otayek, J.; Ghoul, A.; Bizdikian, A.-J.; El Abiad, R. Augmented Reality and Shoulder Replacement: A State-of-the-Art Review Article. JSES Rev. Rep. Tech. 2023, 3, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Sueyoshi, T. Development of Holoeyes Holographic Image-Guided Surgery and Telemedicine System: Clinical Benefits of Extended Reality (Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality), The Metaverse, and Artificial Intelligence in Surgery with a Systematic Review. MRAJ 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W. Enhancing Lower-Limb Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review of Augmented Reality Environment. J Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ong, S.K.; Nee, A.Y.C. Hand Rehabilitation Based on Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering & Assistive Technology—ICREATE ’09, Singapore, 22–26 April 2019; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, P.; Sukralia, S.; Alam, B.; Shaikh, S.; Farrukh, S.; Ali, S.; Ojha, R. Augmented Reality-based Training versus Standard Training in Improvement of Balance, Mobility and Fall Risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 4026–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Gama, A.E.F.; Chaves, T.M.; Figueiredo, L.S.; Baltar, A.; Meng, M.; Navab, N.; Teichrieb, V.; Fallavollita, P. MirrARbilitation: A Clinically-related Gesture Recognition Interactive Tool for an AR Rehabilitation System. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 135, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.L.; Le, T.H.; Lim, J.M.; Hwang, C.H.; Koo, K. Effectiveness of Augmented Reality in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Q.; Du, D.; Wei, X.-Y.; Tong, R.K.-Y. Augmented Reality for Stroke Rehabilitation during COVID-19. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.U.; Ali, Y.; Khan, F.; Al-antari, M.A. A Comprehensive Study on Unraveling the Advances of Immersive Technologies (VR/AR/MR/XR) in the Healthcare Sector during the COVID-19: Challenges and Solutions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak-Marcincin, J.; Barna, J.; Janak, M.; Novakova-Marcincinova, L. Augmented Reality Aided Manufacturing. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2013, 25, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.J.; Pai, Y.S.; Chang, S.-W.; Yap, K.S. Development of an Augmented Reality-Based G-Code Generator in a Virtual CNC Milling Simulation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. (IJCSE) 2016, 5, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Angelino, A.; Martorelli, M.; Tarallo, A.; Cosenza, C.; Papa, S.; Monteleone, A.; Lanzotti, A. An Augmented Reality Framework for Remote Factory Acceptance Test: An Industrial Case Study. In Advances on Mechanics, Design Engineering and Manufacturing IV; Gerbino, S., Lanzotti, A., Martorelli, M., Mirálbes Buil, R., Rizzi, C., Roucoules, L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 768–779. ISBN 978-3-031-15927-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, A.; Cheng, L.; Netland, T. Augmented Reality for Industrial Quality Inspection: An Experiment Assessing Task Performance and Human Factors. Comput. Ind. 2023, 151, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menk, C.; Jundt, E.; Koch, R. Visualisation Techniques for Using Spatial Augmented Reality in the Design Process of a Car. Comput. Graph. Forum 2011, 30, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, L.; Santi, G.; Donnici, G.; Leon-Cardenas, C.; Ferretti, P.; Liverani, A.; Neri, M. An Innovative Ford Sedan with Enhanced Stylistic Design Engineering (SDE) via Augmented Reality and Additive Manufacturing. Designs 2021, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.T.; Albajez, J.A.; Santolaria, J.; Yagüe-Fabra, J.A. Study of Augmented Reality Based Manufacturing for Further Integration of Quality Control 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, G. Wearable Biosensor Smart Glasses Based on Augmented Reality and Eye Tracking. Sensors 2024, 24, 6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.Q.; Neeli, H.; Tsekos, N.V.; Velazco-Garcia, J.D. Immersion into 3D Biomedical Data Via Holographic AR Interfaces Based on the Universal Scene Description (USD) Standard. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Dayton, OH, USA, 4–6 December 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeli, H.; Tran, K.Q.; Velazco-Garcia, J.D.; Tsekos, N.V. A Multiuser, Multisite, and Platform-Independent On-the-Cloud Framework for Interactive Immersion in Holographic XR. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M.; Vickers, J. Digital Twin: Mitigating Unpredictable, Undesirable Emergent Behavior in Complex Systems. In Transdisciplinary Perspectives on Complex Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 85–113. ISBN 978-3-319-38754-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Ferreira, A.E.; Lozoya-Santos, J.d.J.; Vargas-Martınez, A.; Mendoza, R.R.; Morales-Menendez, R. Digital Twin Applications: A Review. In Proceedings of the Memorias del Congreso Nacional de Control Automático, Puebla, México, 23–25 October 2019; Volume 2, pp. 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Verdouw, C.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Beulens, A.; Wolfert, S. Digital Twins in Smart Farming. Agric. Syst. 2021, 189, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z. Digital Twin Based Definition (DTBD) Modeling Technology for Product Life Cycle Management and Optimization. In Flexible Automation and Intelligent Manufacturing: The Human-Data-Technology Nexus; Kim, K.-Y., Monplaisir, L., Rickli, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 573–583. ISBN 978-3-031-17628-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botín-Sanabria, D.M.; Mihaita, A.-S.; Peimbert-García, R.E.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.A.; Ramírez-Mendoza, R.A.; Lozoya-Santos, J.D.J. Digital Twin Technology Challenges and Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallagst, K.; Pauly, J.; Stumpf, M. Conceptualising Smart Cities in the Japanese Planning Culture. In KEEP ON PLANNING FOR THE REAL WORLD. Climate Change Calls for Nature-Based Solutions and Smart Technologies. Proceedings of the REAL CORP 2024, 29th International Conference on Urban Development, Regional Planning and Information Society, Mannheim, Germany, 15–17 April 2024; CORP–Competence Center of Urban and Regional Planning: Graz, Austria, 2024; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Savian, C.; Burns, A.; Cooper, C. Digital Twins for the Built Environment: An Introduction to the Opportunities, Benefits, Challenges and Risks; Institution of Engineering and Technology: Hertfordshire, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.theiet.org/media/8762/digital-twins-for-the-built-environment.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Geyer, M. BMW Group Starts Global Rollout of NVIDIA Omniverse; NVIDIA Blog: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/bmw-group-nvidia-omniverse/ (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Kazuhiko, I.; Atsush, Y. Building a Common Smart City Platform Utilizing FIWARE (Case Study of Takamatsu City). NEC Tech. J. 2018, 13, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Goldenits, G.; Mallinger, K.; Raubitzek, S.; Neubauer, T. Current Applications and Potential Future Directions of Reinforcement Learning-Based Digital Twins in Agriculture. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.; DeLise, F.; Kim, T.-Y. SIGGRAPH 2019: NVIDIA Omniverse: An Open, USD Based Collaboration Platform for Constructing and Simulating Virtual Worlds. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/siggraph/2019/video/sig921 (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Johnston, K. NVIDIA Omniverse Opens Portals to Vast Worlds of OpenUSD. Available online: https://nvidianews.nvidia.com/news/nvidia-omniverse-opens-portals-to-vast-worlds-of-openusd (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Byrne, C. Bentley Systems Brings Infrastructure Digital Twins to NVIDIA Omniverse | Bentley Systems, Incorporated. Available online: https://investors.bentley.com/news-releases/news-release-details/bentley-systems-brings-infrastructure-digital-twins-nvidia (accessed on 13 September 2025).
- Autodesk Inc. Maya Creative Help | Supported File Formats | Autodesk. Available online: https://help.autodesk.com/view/MAYACRE/ENU/?guid=GUID-3A6190CA-E296-4A10-9287-5AEE156DBA9D (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Unity Technologies. Unity—Manual: Model File Formats. Available online: https://docs.unity3d.com/6000.3/Documentation/Manual/3D-formats.html (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Blender Documentation Team. Importing & Exporting Files—Blender Manual. Available online: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/2.93/files/import_export.html (accessed on 15 August 2025).
- Library of Congress. STL (STereoLithography) File Format, Binary. Available online: https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000505.shtml (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Pixar Animation Studios. USD Frequently Asked Questions—Universal Scene Description 25.08 Documentation. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/usdfaq.html (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Van Gelder, D. Real-time Graphics in Pixar Film Production. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Real-Time Live! Anaheim, CA, USA, 24–28 July 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixar Animation Studios. Introduction to USD. Available online: https://openusd.org/docs/ (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Autodesk Inc. Universal Scene Description | OpenUSD | Autodesk. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/universal-scene-description (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. OmniUsdResolver Details—Omniverse USD Resolver 1.42.3 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/kit/docs/usd_resolver/latest/docs/resolver-details.html (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. USD Connections Overview—Omniverse Connect. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/connect/latest/index.html (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Blevins, A.; Murray, M. Zero to USD in 80 Days. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2018 Talks, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–16 August 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walt Disney Animation Studios. Walt Disney Animation Studios—Moana Island Scene. Available online: https://disneyanimation.com/resources/moana-island-scene/ (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Vavilala, V. Light pruning on Toy Story 4. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2019 Talks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 28 July–1 August 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, N.; Johnston, K. Pixar, Adobe, Apple, Autodesk, and NVIDIA Form Alliance for OpenUSD to Drive Open Standards for 3D Content. Available online: https://nvidianews.nvidia.com/news/aousd-to-drive-open-standards-for-3d-content (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Xu, B.; Gao, F.; Yu, C.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. OmniDrones: An Efficient and Flexible Platform for Reinforcement Learning in Drone Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G. NVIDIA Blog: CloudXR Platform on AWS; NVIDIA Blog: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA Corporation. FAQ—NVIDIA CloudXR SDK Documentation. Available online: https://docs.nvidia.com/cloudxr-sdk/support/faq.html (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Oun, A.; Hagerdorn, N.; Scheideger, C.; Cheng, X. Mobile Devices or Head-Mounted Displays: A Comparative Review and Analysis of Augmented Reality in Healthcare. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21825–21839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazco-Garcia, J.D.; Shah, D.J.; Leiss, E.L.; Tsekos, N.V. A Modular and Scalable Computational Framework for Interactive Immersion into Imaging Data with a Holographic Augmented Reality Interface. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 198, 105779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Luo, X. Digital Twin for 3D Interactive Building Operations: Integrating BIM, IoT-enabled Building Automation Systems, AI, and Mixed Reality. Autom. Constr. 2025, 176, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, V.K.; Küper, M.A.; Menger, M.M.; Herath, S.C.; Histing, T.; Audretsch, C.K. Augmented Reality in Pelvic Surgery: Using an AR-headset as Intraoperative Radiation-free Navigation Tool. Int. J. CARS 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Xie, W.; Peng, X.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Ren, J. Large-Scale Spatial Data Visualization Method Based on Augmented Reality. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2024, 6, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixar Animation Studios. USD Terms and Concepts—Universal Scene Description 25.02 Documentation. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/glossary.html (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Prim—Omniverse USD. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/usd/latest/learn-openusd/terms/prim.html (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdPrim Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_usd_prim.html (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdGeomMesh Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_usd_geom_mesh.html (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdStage Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_usd_stage.html (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdGeomXformable Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_usd_geom_xformable.html (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: GfMatrix4d Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_gf_matrix4d.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdGeom: USD Geometry Schema. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/usd_geom_page_front.html (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- VTK. VTK: vtkTransform Class Reference. Available online: https://vtk.org/doc/nightly/html/classvtkTransform.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Pixar Animation Studios. Universal Scene Description: UsdShadeMaterial Class Reference. Available online: https://openusd.org/release/api/class_usd_shade_material.html (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Omniverse Client Library—Omniverse Client Library 2.47.1 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/kit/docs/client_library/latest/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Omniverse Connect SDK—Omniverse Connect SDK 1.0.0 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/kit/docs/connect-sdk/latest/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Omniverse Drive (Beta)—Omniverse Utilities. Available online: https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/ (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. NVIDIA Omniverse Live Overview|Omniverse 2020|NVIDIA On-Demand. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/omniverse2020-om1572/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Nucleus Overview—Omniverse Nucleus. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/nucleus/latest/index.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Omniverse USD Resolver—Omniverse USD Resolver 1.42.3 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/kit/docs/usd_resolver/latest/index.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Legacy Tools for Omniverse Launcher | NVIDIA Developer. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/omniverse/legacy-tools (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- NVIDIA Corporation. Residential Lobby—Omniverse USD. Available online: https://docs.omniverse.nvidia.com/usd/latest/usd_content_samples/res_lobby.html (accessed on 19 August 2025).






| Feature | USD | STL | OBJ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open source | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Texture, material properties | Supported | Not supported | Supported |
| Non-destructive authoring | Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| Real-time collaboration | Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| USD | VTK |
|---|---|
| Points (VtVec3fArray) | Points (vtkFloatArray) |
| Faces | Cells |
| Face vertices | Cell vertices |
| Face vertex counts (VtIntArray) | Cell vertex offsets (vtkTypeInt32Array) |
| Face vertex index array (VtIntArray) | Cell connectivity array (vtkTypeInt32Array) |
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| UsdPrim | Principal container of other types of scene description; providing API for accessing and creating all of the contained kinds of scene description [84] |
| UsdGeomMesh | Encodes a mesh with optional subdivision properties and features [85] |
| UsdStage | Outermost container for scene description [86] |
| UsdGeomXformable | Base class for all transformable prims [87] |
| Rotation Type | USD | VTK |
|---|---|---|
| X | Supported (degree) | Supported (radian) |
| Y | Supported (degree) | Supported (radian) |
| Z | Supported (degree) | Supported (radian) |
| XYZ | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| XZY | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| YZX | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| YXZ | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| ZXY | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| ZYX | Supported (degree) | Not supported |
| Component/Dependency | Description |
|---|---|
| NVIDIA Omniverse Client Library | Library for Omniverse Clients to communicate with Omniverse servers [92] |
| NVIDIA Omniverse Connector SDK | Development kit for building an Omniverse Connector [93] |
| NVIDIA Omniverse Drive | Application mapping folders from Nucleus Servers to local folders [94] |
| NVIDIA Omniverse Live | Service for real-time, non-destructive collaboration on the same content from various applications [95] |
| NVIDIA Omniverse Nucleus server | Database and collaboration engine of Omniverse [96] |
| NVIDIA Omniverse USD Resolver Library | Plugin for working with files on Omniverse servers [97] |
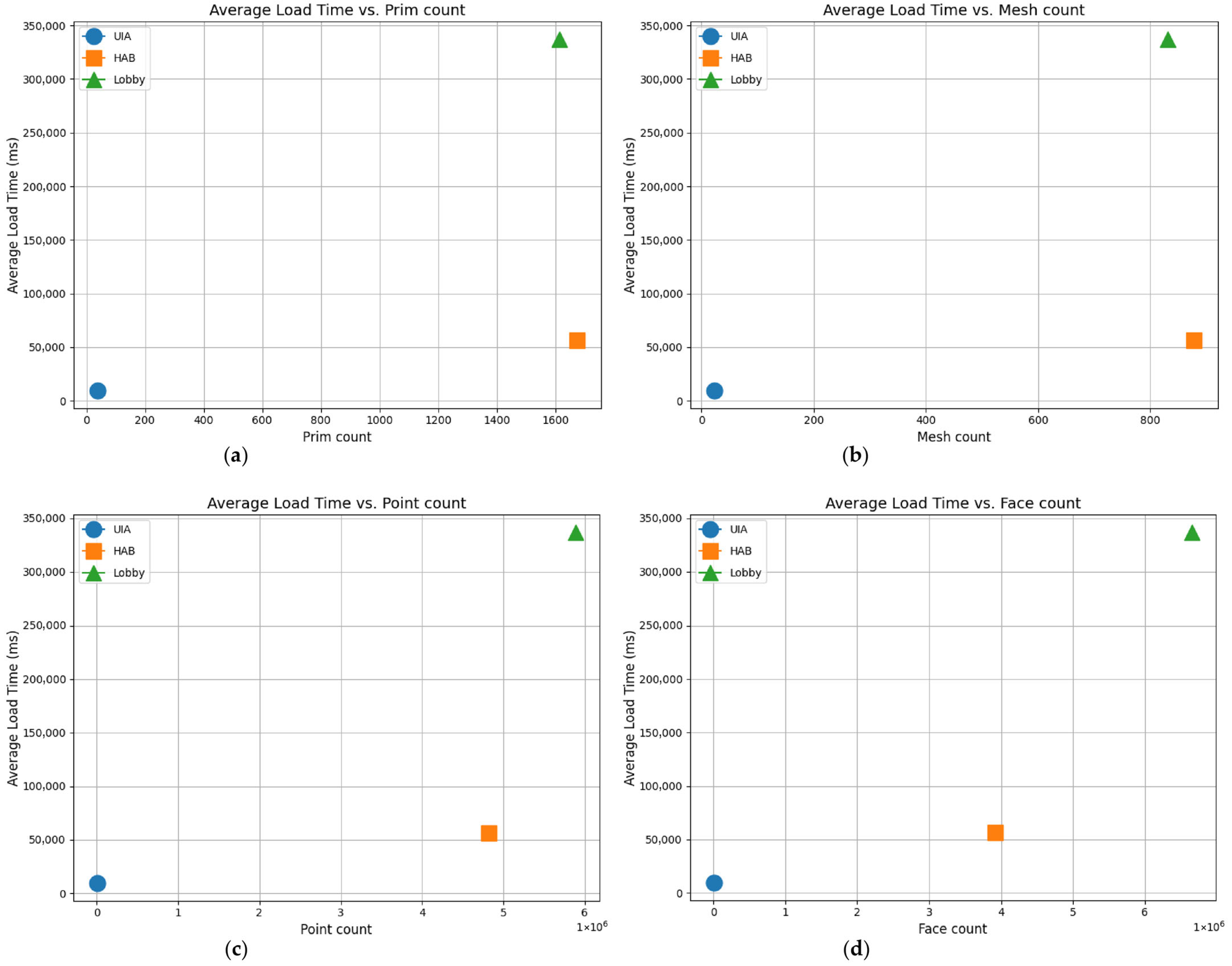
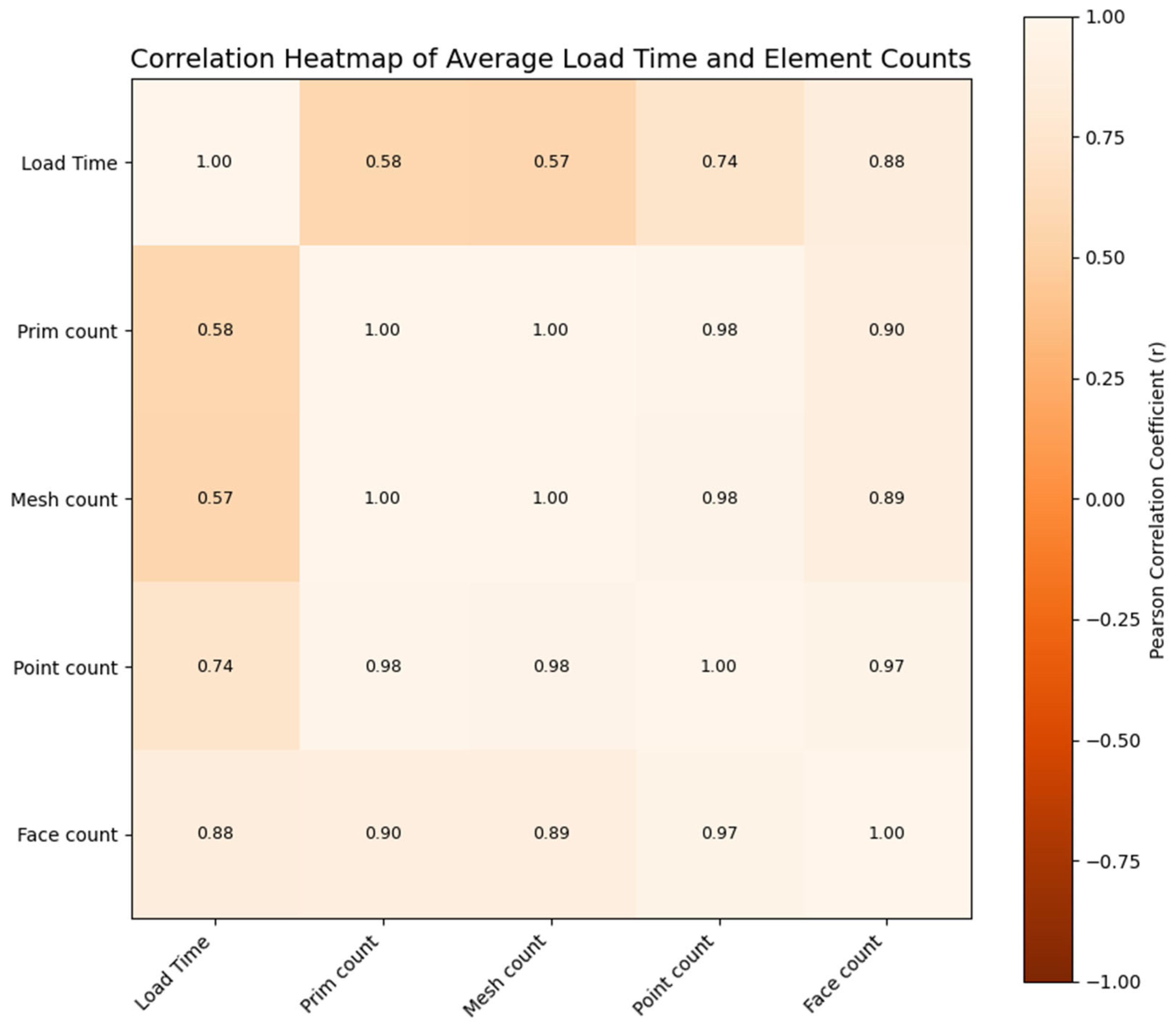
| Model | Prim Count | Mesh Count | Point Count | Face Count | Native USD/ Converted USD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
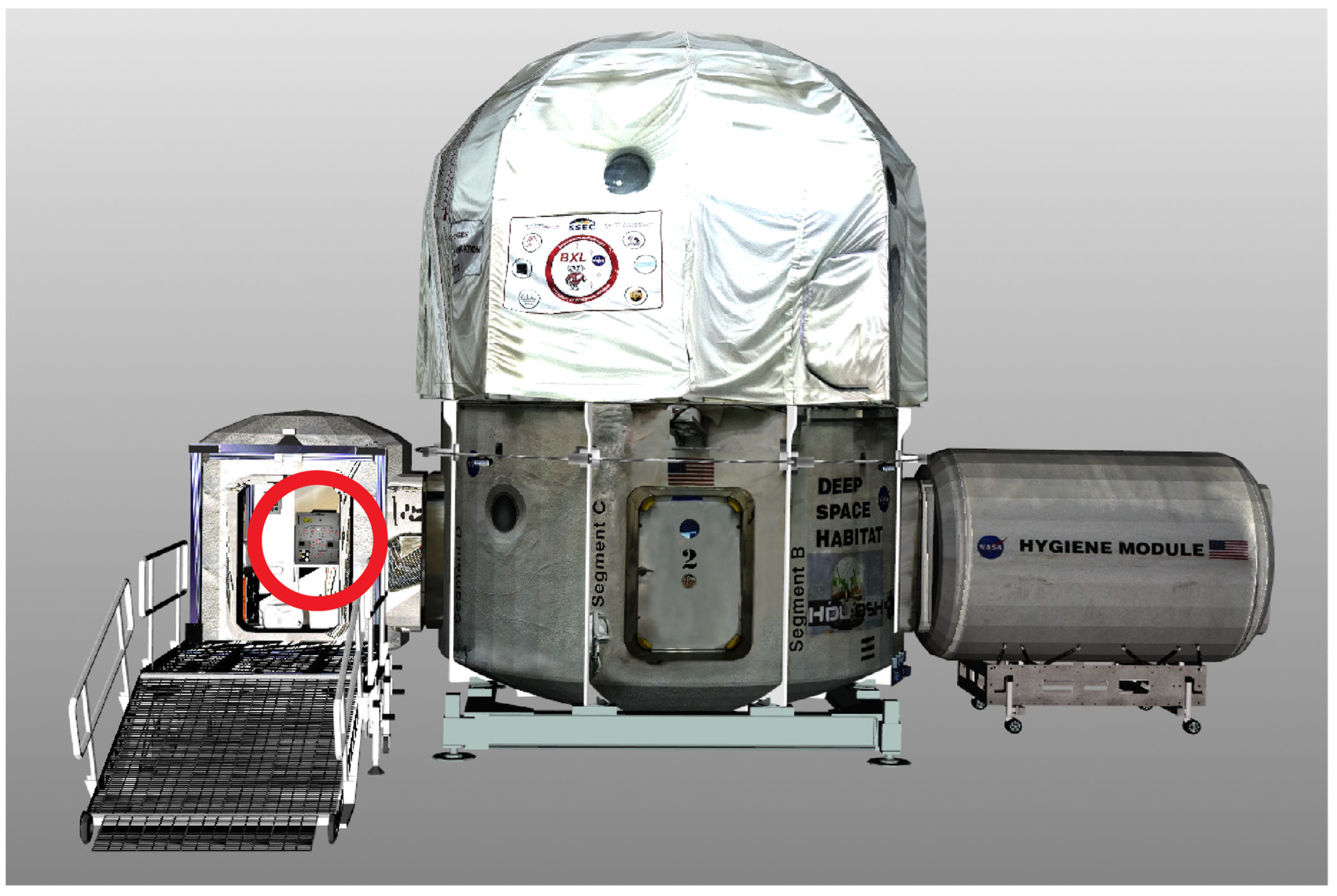
| Umbilical Interface Assembly (UIA) | 38 | 23 | 5306 | 5708 | Native USD |
| Lunar Habitat Complex (HAB) | 1674 | 878 | 4,821,107 | 3,918,260 | Native USD |
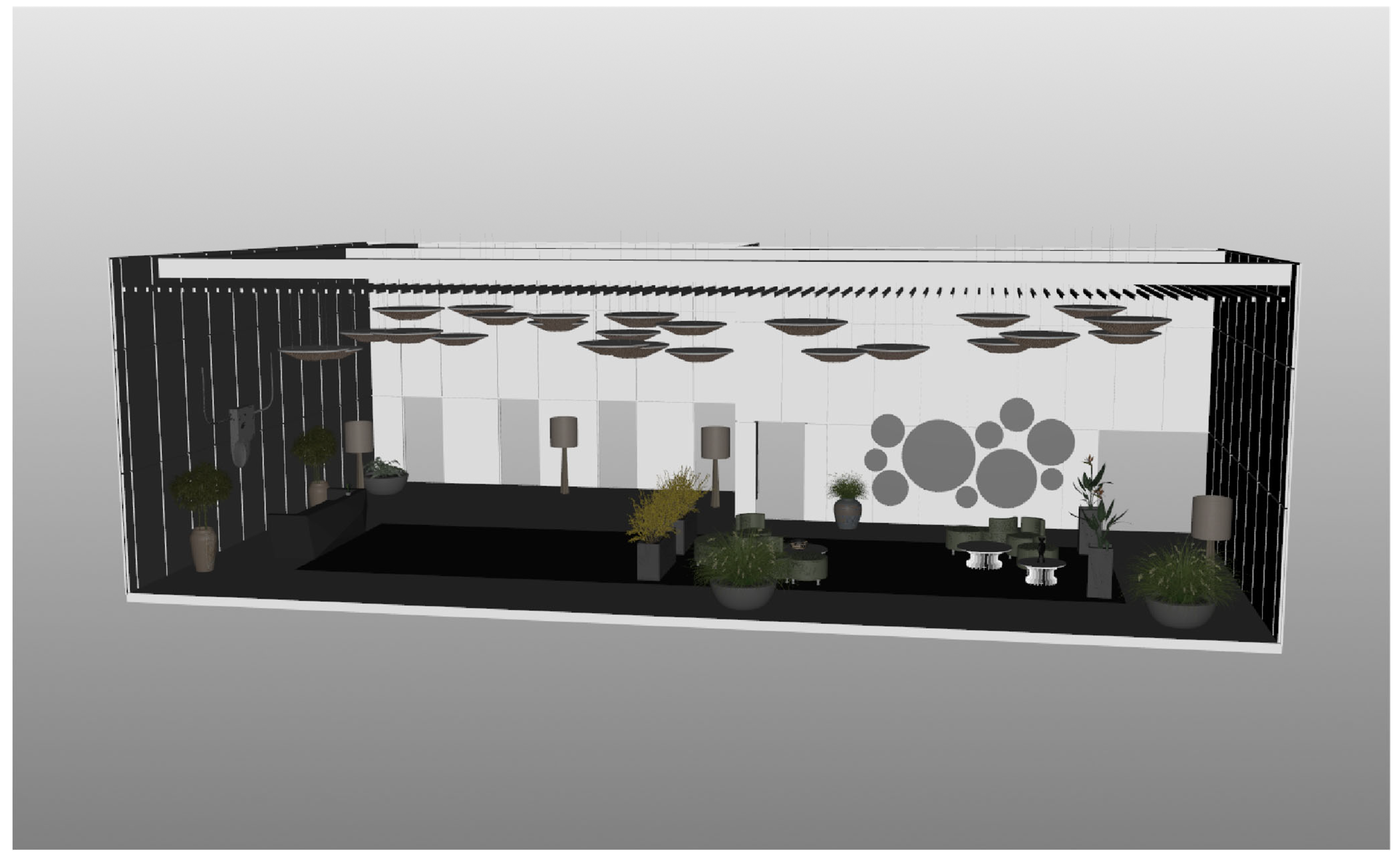
| Residential Lobby | 1613 | 832 | 5,889,594 | 6,656,299 | Native USD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, K.Q.; Leiss, E.L.; Tsekos, N.V.; Velazco-Garcia, J.D. A Real-Time Immersive Augmented Reality Interface for Large-Scale USD-Based Digital Twins. Virtual Worlds 2025, 4, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds4040050
Tran KQ, Leiss EL, Tsekos NV, Velazco-Garcia JD. A Real-Time Immersive Augmented Reality Interface for Large-Scale USD-Based Digital Twins. Virtual Worlds. 2025; 4(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds4040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Khang Quang, Ernst L. Leiss, Nikolaos V. Tsekos, and Jose Daniel Velazco-Garcia. 2025. "A Real-Time Immersive Augmented Reality Interface for Large-Scale USD-Based Digital Twins" Virtual Worlds 4, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds4040050
APA StyleTran, K. Q., Leiss, E. L., Tsekos, N. V., & Velazco-Garcia, J. D. (2025). A Real-Time Immersive Augmented Reality Interface for Large-Scale USD-Based Digital Twins. Virtual Worlds, 4(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds4040050






