Navigating the Healthcare Metaverse: Immersive Technologies and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Immersive Technologies—A Spectrum of Realistic Possibilities
3. Application Trends of Immersive Technologies in Healthcare
3.1. VR for Rehabilitation
3.2. XR Telehealth
3.3. Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET)
3.4. VR in Oncology
3.5. XR-Based Surgery
3.6. AR-Based Digital Operations
3.7. XR in Healthcare Education
4. From XR to the Metaverse
- Augmented reality (AR): this technology involves the overlaying of virtual objects onto the physical world, thereby enhancing the user’s environment (e.g., Pokémon Go).
- Lifelogging: this involves the capturing, storing and sharing of users’ daily activities and experiences (e.g., Facebook, Instagram, Fitbit).
- Mirror worlds: these are digital reflections of the real world that also incorporate external environmental data (e.g., Google Maps, Zoom).
- Virtual worlds: this is the VR technology that we are familiar with, whereby users explore virtual environments and interact with virtual objects through avatars, often using VR headsets.
5. Opportunities of the Metaverse in Healthcare
6. Generative AI + Metaverse: To Infinity and Beyond
7. Considerations When Designing and Developing Healthcare Innovations Using Immersive Technologies
8. Readiness and Sustainability of Immersive Technologies in Healthcare
9. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skarbez, R.; Smith, M.; Whitton, M.C. Revisiting Milgram and Kishino’s reality-virtuality continuum. Front. Virtual Real. 2021, 2, 647997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Lo, H.Y.; Lichliter, R.; Wallin, K.; Elegores, G.; Jacobson, S.; Doughty, C. Twelve tips for creating an escape room activity for medical education. Med. Teach. 2022, 44, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.Y.; Koh, D.W.H.; Lee, V.S.J.; Wong, L.L. Use of virtual reality in the supportive care management of paediatric patients with cancer. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.-N.; Le, C.V.; Tromp, J.G.; Nguyen, G.N. Emerging Technologies for Health and Medicine: Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Robotics, Industry 4.0; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Milgram, P.; Kishino, F. A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE Trans. Inform. Syst. 1997, E77-D, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Nextech3D.ai. What Are the Different Types of Augmented Reality? 2022. Available online: https://www.nextechar.com/blog/what-are-the-different-types-of-augmented-reality (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Ikea. IKEA Place App Launched to Help People Virtually Place Furniture at Home. 2017. Available online: https://www.ikea.com/global/en/newsroom/innovation/ikea-launches-ikea-place-a-new-app-that-allows-people-to-virtually-place-furniture-in-their-home-170912/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Palma, G.; Perry, S.; Cignoni, P. Augmented virtuality using touch-sensitive 3D-printed objects. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVT Simulation. Augmented Virtuality—What Is it? 2021. Available online: https://www.avtsim.com/augmented-virtuality-what-is-it/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Spacey, J. Augmented Reality vs Augmented Virtuality. Simplicable. 2016. Available online: https://simplicable.com/technology/augmented-reality-vs-augmented-virtuality (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Lukacs, M.J.; Salim, S.; Katchabaw, M.J.; Yeung, E.; Walton, D.M. Virtual reality in physical rehabilitation: A narrative review and critical reflection. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2022, 27, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokgoz, P.; Stampa, S.; Wahnert, D.; Vordemvenne, T.; Dockweiler, C. Virtual reality in the rehabilitation of patients with injuries and diseases of upper extremities. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massetti, T.; da Silva, T.D.; Crocetta, T.B.; Guarnieri, R.; de Freitas, B.L.; Bianchi Lopes, P.; Watson, S.; Tonks, J.; de Mello Monteiro, C.B. The clinical utility of virtual reality in neurorehabilitation: A systematic review. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2018, 10, 1179573518813541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, L.; van den Berg, M.; Lindley, R.I.; Crotty, M.; McCluskey, A.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Smith, S.T.; Schurr, K.; Howard, K.; Hackett, M.L.; et al. Digitally enabled aged care and neurological rehabilitation to enhance outcomes with Activity and MObility UsiNg Technology (AMOUNT) in Australia: A randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med 2020, 17, e1003029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin Okmen, B.; Dogan Aslan, M.; Nakipoglu Yuzer, G.F.; Ozgirgin, N. Effect of virtual reality therapy on functional development in children with cerebral palsy: A single-blind, prospective, randomized-controlled study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 65, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, D.; Vitali, A.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C. Medical assessment test of extrapersonal neglect using virtual reality: A preliminary study. In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference; The American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. DETC2020-22416, V009T09A064. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzoni, D.; Vitali, A.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C. Design of customized virtual reality serious games for the cognitive rehabilitation of retrograde amnesia after brain stroke. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2022, 22, 031009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.; Wilczewski, H.; Paige, S.R.; Soni, H.; Welch, B.M.; Bunnell, B.E. Extended reality for enhanced telehealth during and beyond COVID-19: Viewpoint. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e26520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovett, L. XRHealth Launches VR Telehealth Clinic. Mobi Health News. 2020. Available online: https://www.mobihealthnews.com/news/north-america/xrhealth-launches-vr-telehealth-clinic (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Emmelkamp, P.M.G.; Meyerbroker, K. Virtual reality therapy in mental health. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2021, 17, 495–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.; Park, J.H. Effects of virtual reality-based graded exposure therapy on PTSD symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buche, H.; Michel, A.; Blanc, N. Use of virtual reality in oncology: From the state of the art to an integrative model. Front. Virtual Real. 2022, 3, 894162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoorn, M.T.; Wulfse, M.; Van Doormaal, T.P.C.; Ruurda, J.P.; Van der Kaaij, N.P.; De Heer, L.M. Mixed reality in modern surgical and interventional practice: Narrative review of the literature. JMIR Serious Games 2023, 11, e41297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, V.; Khanduja, V. The impact of extended reality on surgery: A scoping review. Int. Orthop. 2023, 47, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, S.; Whitfield, B. How VR and AR Are Used in Surgery: 12 Examples. Built in. 2022. Available online: https://builtin.com/healthcare-technology/augmented-virtual-reality-surgery (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Augmedix. Augmedix Introduces New Services That Increase Clinician Productivity and Enhance the Clinician-Patient Relationship. Augmedix Press Releases. 2020. Available online: https://ir.augmedix.com/news-events/press-releases/detail/11/augmedix-introduces-new-services-that-increase-clinician (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Muoio, D. Augmedix’s Device-Based Remote Scribing System Announces $19M Series B. MobiHealthNews. 2019. Available online: https://www.mobihealthnews.com/news/north-america/augmedixs-device-based-remote-scribing-system-announces-19m-series-b (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Augmedix. Augmedix Launches Industry’s First Fully-Automated, GenAI-Powered, Medical Documentation Product for Emergency Departments. Augmedix Press Releases. 2024. Available online: https://ir.augmedix.com/news-events/press-releases/detail/107/augmedix-launches-industrys-first-fully-automated (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Woodun, C. Augmedix: Using Generative AI to Document Medical Records. Seeking Alpha. 2023. Available online: https://seekingalpha.com/article/4638874-augmedix-using-generative-ai-document-medical-records (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Coiera, E.; Kocaballi, B.; Halamka, J.; Laranjo, L. The digital scribe. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesko, B. Augmented Reality in Healthcare: 9 Examples. The Medical Futurist. 2021. Available online: https://medicalfuturist.com/augmented-reality-in-healthcare-will-be-revolutionary/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Roswell, R.O.; Cogburn, C.D.; Tocco, J.; Martinez, J.; Bangeranye, C.; Bailenson, J.N.; Wright, M.; Mieres, J.H.; Smith, L. Cultivating empathy through virtual reality: Advancing conversations about racism, inequity, and climate in medicine. Acad. Med. 2020, 95, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Ducleroir, C.; Stollman, T.I.; Wood, E. Parkinson’s disease simulation in virtual reality for empathy training in medical education. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), Lisbon, Portugal, 27 March–1 April 2021; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland. RCSI Develops World’s First Virtual Reality Medical Training Simulator. RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences. 2016. Available online: https://www.rcsi.com/dublin/news-and-events/news/news-article/2016/07/rcsi-develops-worlds-first-virtual-reality-medical-training-simulator (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Mao, R.Q.; Lan, L.; Kay, J.; Lohre, R.; Ayeni, O.R.; Goel, D.P.; Sa, D. Immersive virtual reality for surgical training: A systematic review. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 268, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SingHealth Group. Where Healthcare Professionals Get Serious about Gamification. Singapore General Hospital. 2022. Available online: https://www.sgh.com.sg/news/tomorrows-medicine/where-healthcare-professionals-get-serious-about-gamification (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Tsang, W.Y.; Fan, P.; Raj, S.D.H.; Tan, Z.J.; Lee, I.Y.Y.; Boo, I.; Yap, K.Y.-L. Development of a three-dimensional (3D) virtual reality apprenticeship program (VRx) for training of medication safety practices. Int. J. Digit. Health 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case Western Reserve University. CWRU Achieves Global First in Mixed-Reality Education during COVID-19 Pandemic. The Daily. 2020. Available online: https://thedaily.case.edu/cwru-achieves-global-first-in-mixed-reality-education-during-covid-19-pandemic/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Microsoft News Center. Medical Education Goes Holographic with Mixed Reality from Microsoft. Microsoft. 2022. Available online: https://news.microsoft.com/en-sg/2022/01/11/medical-education-goes-holographic-with-mixed-reality-from-microsoft/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Velazco, C. Mark Zuckerberg Just Laid Out His Vision for the Metaverse. These Are the Five Things You Should Know. The Washington Post. 2021. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2021/10/28/facebook-meta-metaverse-explained/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Wiles, J. What Is a Metaverse? And Should You Be Buying in? Gartner. 2022. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/what-is-a-metaverse (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Kye, B.; Han, N.; Kim, E.; Park, Y.; Jo, S. Educational applications of metaverse: Possibilities and limitations. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrigna, L.; Musumeci, G. The Metaverse: A new challenge for the healthcare system: A scoping review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesko, B. The promise of the metaverse in cardiovascular health. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2647–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H. Training in lung cancer surgery through the metaverse, including extended reality, in the smart operating room of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Korea. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K. Learner perceptions of the potential of the metaverse for digital health education. In Proceedings of the Digital Health Summit, Sydney, Australia, 17–18 October 2022; Australasian Institute of Digital Health and eHealth New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 2022; p. 49. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/367167568_Learner_perceptions_of_the_potential_of_the_metaverse_for_digital_health_education (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Yap, K. Developing a digital health metacademy for continuing professional education. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2024, 310, 1536–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.B.; Tan, S.; Yap, K. The Saltomachy War—A metaverse escape room on the War Against Salt. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2024, 310, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Badal, A.; Jia, X.; Maltz, J.S.; Mueller, K.; Myers, K.J.; Niu, C.; Vannier, M.; Yan, P.; Yu, Z.; et al. Development of metaverse for intelligent healthcare. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Manocha, D. Sound Synthesis, Propagation, and Rendering, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Mihelj, M.; Novak, D.; Beguš, S. Virtual Reality Technology and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bergholz, M.; Ferle, M.; Weber, B.M. The benefits of haptic feedback in robot assisted surgery and their moderators: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Pickering, O.; Ellis, C.; Sabri, O.; Pucher, P. Impact of haptic feedback on surgical training outcomes: A randomised controlled trial of haptic versus non-haptic immersive virtual reality training. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 83, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.; Ng, C.L.; Han, J.; Tsang, W.Y.; Fan, P.; Raj, S.D.H. Immersive Training for Sterile Drug Preparation through Extended reality: Insights into the Virtual Aseptic Compounding (VAC) Programme. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382636915_Immersive_Training_for_Sterile_Drug_Preparation_through_Extended_Reality_Insights_into_the_Virtual_Aseptic_Compounding_VAC_Programme (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Chamola, V.; Bansal, G.; Das, T.K.; Hassija, V.; Reddy, N.S.S.; Wang, J.; Zeadally, S.; Hussain, A.; Yu, F.R.; Guizani, M.; et al. Beyond reality: The pivotal role of generative AI in the metaverse. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.06272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathan, C. Generative AI in the Metaverse. Psychology Today. 2023. Available online: https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/inventing-the-future/202306/generative-ai-in-the-metaverse (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Deloitte Insights. Deloitte: Younger Generations Have One Foot in the Metaverse via Gaming and Social Media. VentureBeat. 2023. Available online: https://venturebeat.com/games/deloitte-younger-generations-have-one-foot-in-the-metaverse-via-gaming-and-social-media/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Strange, A. Younger Generations Expect to Spend a Lot More Time in the Metaverse. World Economic Forum. 2022. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/08/metaverse-technology-virtual-future-people/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Pershikov, A. The Meta Generation Is Coming: How Will They Affect Our Future? Forbes. 2022. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2022/08/03/the-meta-generation-is-coming-how-will-they-affect-our-future/?sh=10da001b490d (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Rowan, D. Nielsen’s State of Play Report Reveals That Streaming Is the Future, but Consumers Are Currently Overwhelmed by Choice. Nielson. 2022. Available online: https://www.nielsen.com/news-center/2022/nielsens-state-of-play-report-reveals-that-streaming-is-the-future-but-consumers-are-currently-overwhelmed-by-choice/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Aiello, C.; Bai, J.; Schmidt, J.; Vilchynskyi, Y. Probing Reality and Myth in the Metaverse. McKinsey & Company. 2022. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/probing-reality-and-myth-in-the-metaverse (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Bestsennyy, O.; Gilbert, G.; Harris, A.; Rost, J. Telehealth: A Quarter-Trillion-Dollar Post-COVID-19 Reality? McKinsey & Company. 2021. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare/our-insights/telehealth-a-quarter-trillion-dollar-post-covid-19-reality (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Fernandez, R. Healthcare Turns to The Gaming Industry to Build Its Metaverse. Tech Republic. 2022. Available online: https://www.techrepublic.com/article/healthcare-turns-to-the-gaming-industry-to-build-its-metaverse/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Yap, K.Y.-L.; Ho, J.; Toh, P.S.T. Development of a Metaverse Art Gallery of Image Chronicles (MAGIC) for healthcare education: A digital health humanities approach to patients’ medication experiences. Information 2024, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Mac Blog. Virtual Reality—Advantages and Disadvantages. Medium. 2019. Available online: https://macbook.medium.com/virtual-reality-advantages-and-disadvantages-a86492f7f8e9 (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Oxford Medical Simulation. How Virtual Reality Creates a Safe Space for Learning. 2023. Available online: https://oxfordmedicalsimulation.com/how-virtual-reality-creates-a-safe-space-for-learning/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Swider, P. The Future of Healthcare and Patient Care in the Metaverse. Acceleration Economy. 2022. Available online: https://accelerationeconomy.com/metaverse/the-future-of-healthcare-patient-care-in-the-metaverse/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Ning, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Dhelim, S.; Farha, F.; Ding, J.; Daneshmand, M. A survey on metaverse: The state-of-the-art, technologies, applications, and challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09673. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, A. 10 Pros and Cons of Augmented Reality. Available online: https://honestproscons.com/pros-and-cons-of-augmented-reality/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Cheng, Z.A.; Greenwood, B.N.; Pavlou, P.A. Location-based mobile gaming and local depression trends: A study of Pokémon Go. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2022, 39, 68–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team DigitalDefynd. 20 Pros and Cons of Augmented Reality. 2024. Available online: https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/augmented-reality-pros-cons/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Neely, E.L. Augmented reality, augmented ethics: Who has the right to augment a particular physical space? Ethics Inf. Technol. 2019, 21, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaretta, A. Security and Privacy in Virtual Reality—A Literature Survey. 2024. Available online: https://arxiv.org/html/2205.00208v3 (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Alismail, A.; Altulaihan, E.; Rahman, M.M.H.; Sufian, A. A systematic literature review on cybersecurity threats of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). In Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems; Jacob, I.J., Kolandapalayam Shanmugam, S., Izonin, I., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 761–774. [Google Scholar]
- Tsavlis, T. The Metaverse Dilemma: Privacy Concerns in Virtual Worlds. Forbes. 2023. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2023/10/23/the-metaverse-dilemma-privacy-concerns-in-virtual-worlds/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Krishnan, A. Metaverse Privacy Concerns and How to Address Them. TechTarget. 2024. Available online: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/tip/Metaverse-privacy-concerns-and-how-to-address-them (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Cattaneo, A.; Vitali, A.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C. A sustainable approach to telerehabilitation in Europe: Patients are ready, but caregivers are essential. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2024, 313, 68–73. [Google Scholar]

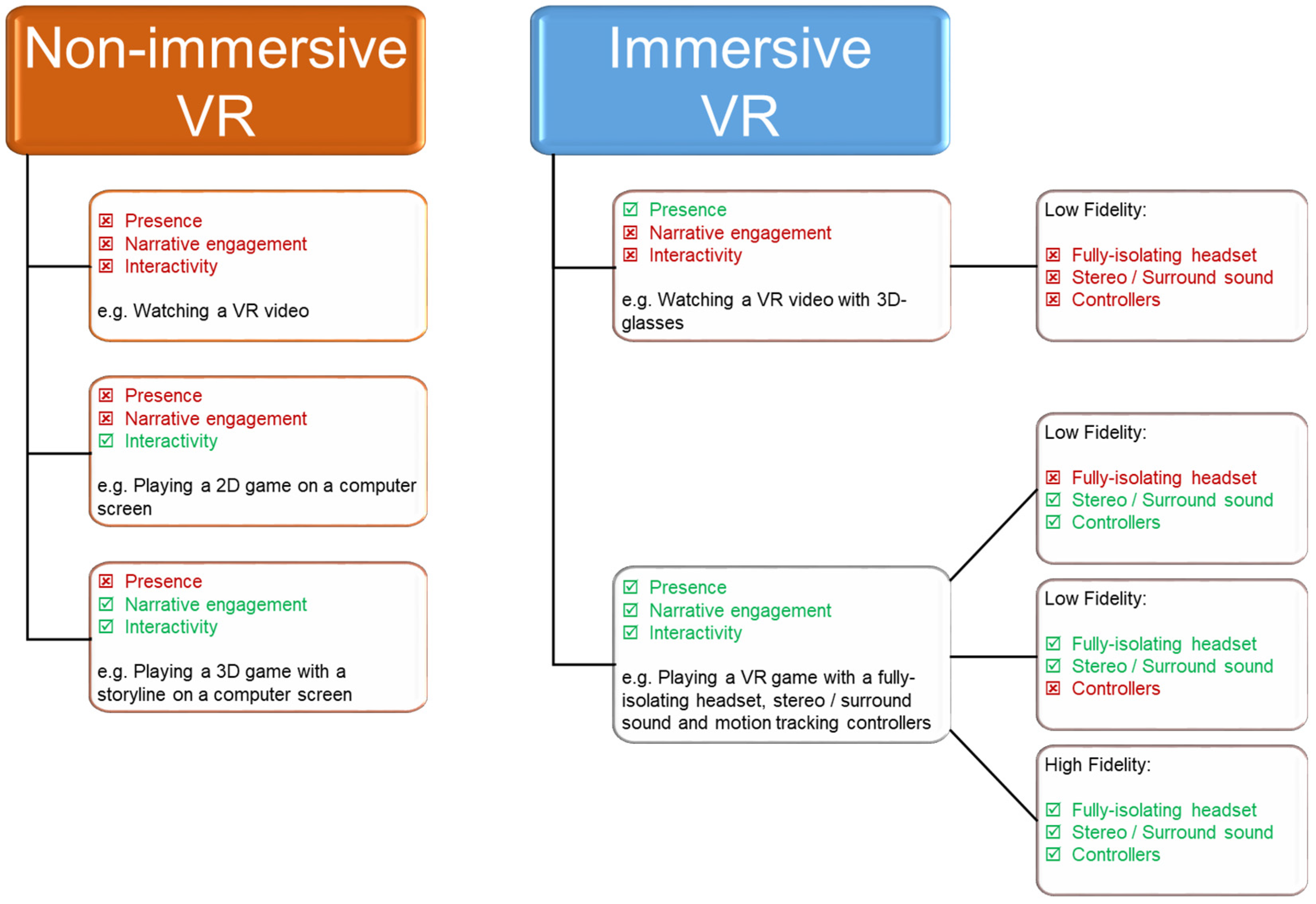
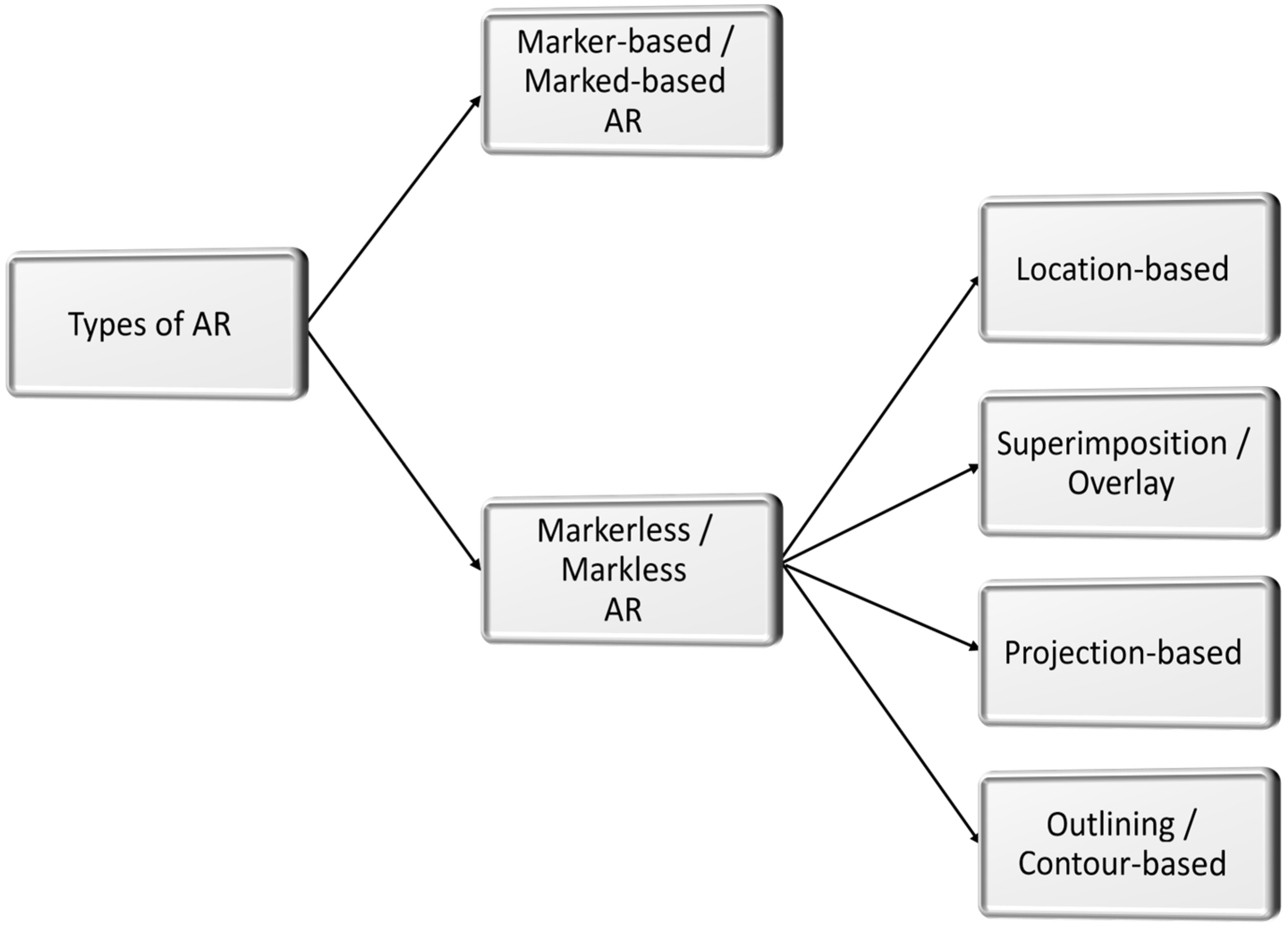
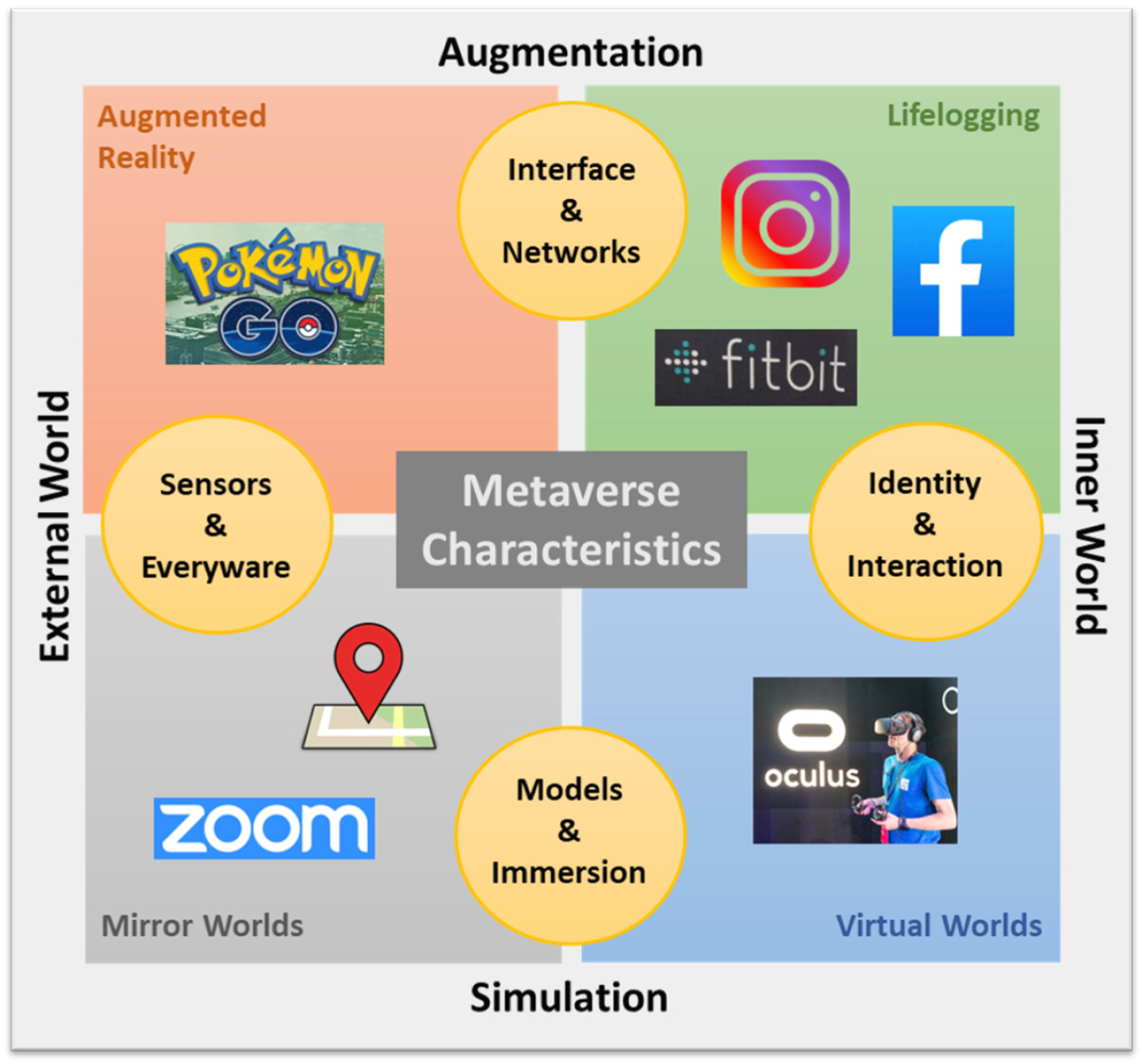
| Consideration Factors | Immersive Technologies Spanning the Reality-Virtuality Spectrum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reality (Physical World) | Augmented Reality (AR) | Augmented Virtuality (AV) | Virtual Reality (VR) | Mixed Reality (MR) | Metaverse | |
| Description | No digital augmentation. | Virtual objects overlaid in a physical environment. | Real-world objects in a virtual environment. | Fully immersive virtual environment, includes EVE and MVE. | A combined use of AR and VR in which virtual and physical objects and environments exist together and can interact with each other in real-time. | A combined virtual environment that is shared, and where the physical and virtual worlds are integrated and enhanced, covering the entire XR spectrum. |
| Technical requirements | None, except for physical tools and resources. | Examples include smartphones, iPads/tablets, or AR glasses/headset; with AR software. | VR setup with additional real-world object integration (e.g., haptic devices). | VR headset with or without controllers; may include haptic devices; requires powerful computing software. | MR headset, usually with sensors and integration software. | Advanced XR setups; users navigate virtual worlds; may involve cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. |
| Technical cost and scalability | Low cost; easily scalable. | Moderate cost to users; potentially scalable with devices that are widely available. | High cost; less scalable due to specialized equipment needs. | High cost; need for advanced hardware may limit scalability. | High cost; scalability depends on availability and compatibility of equipment and devices. | Very high cost; scalability depends on technological infrastructure and user adoption. |
| User experience | Users are familiar, no learning curve. | Device interfaces are usually familiar, generally easy to use. | High immersivity but can be disorienting to user. | Highly immersive, but some users may experience motion sickness. | Highly interactive and engaging, but users may need to adapt to the mixed environment. | Highly engaging and immersive, but can be overwhelming to users who are not familiar with immersive technologies. |
| Learning curve and adoption | No learning curve; universally understood. | Low to moderate learning curve; familiar interfaces but requires initial installation and setup. | High learning curve; requires familiarity with VR and physical interactions. | Steep learning curve due to specialized equipment, software and hardware. | Moderate to high learning curve; users may need to adapt to new ways of interacting with the mixed environment. | Steep learning curve due to the complexity of the metaverse environment and its applications. |
| Advantages | Completely realistic, no technological barriers. | Enhances real-world tasks with additional virtual information; generally accessible. | High level of immersivity with real-world relevance. | High to full immersivity experienced in a controlled environment; can be used for creating high fidelity, vivid, authentic and life-like scenarios and/or complex scenarios; improves patient safety as it allows learners to commit mistakes in a safe space, yet without experiencing negative consequences that may happen in clinical practices. | Versatile in applications as it combines the best aspects of AR and VR. | Advanced and comprehensive integration of virtual and physical worlds; vast potential for various applications when combined with other advanced technologies. |
| Disadvantages | Limited digital enhancements and interactivity, bound by physical space. | High costs of development and implementation; Limited immersivity depending on device capability; may lead to safety risks if users are distracted. | High cost, complex setup, may cause motion sickness in users. | High cost, complex setup, lack of face-to-face interaction; may cause motion sickness, disorientation or discomfort in users. | High cost, complex setup, may cause disorientation in users. | Still in early development; high costs of metaverse technologies may impede healthcare adoption; challenges with compatibility, interoperability and computational power of metaverse healthcare technologies. |
| Privacy concerns | Privacy concerns are related to the use of the physical space and/or data from wearable sensors. | Privacy concerns are in relation to capturing and usage of data (e.g., photos) in public places. | Privacy concerns are around the data and simulated environments; physical safety concerns during use. | Privacy and security concerns are around the collected data, especially within MVE scenarios. | Privacy and security concerns are around the collected data, potential safety issues during interactions with both the virtual and real-world environments. | Significant ethical and cyberprivacy concerns surrounding digital identities, virtual properties, data privacy and digital rights. |
| Future trends and potential | Limited to physical interactions. However, advancements in wearable sensors can potentially augment physical parameters. | Advancements in AR technologies may enable more seamless integration with daily activities. | Integration with real-world objects provides potential for more realistic simulations. | Highly immersive and realistic; potential for users to have full-body VR experiences; VR equipment may become more accessible in future. | Advancements in wearable technologies and sensors have the potential to make MR more seamless and integrated with user tasks and activities. | Evolving rapidly with uptake by various brands, societies and organizations; potential for large-scale adoptions through events in virtual worlds, integration with other advanced technologies, and adoption of virtual economies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yap, K.Y.-L. Navigating the Healthcare Metaverse: Immersive Technologies and Future Perspectives. Virtual Worlds 2024, 3, 368-383. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds3030020
Yap KY-L. Navigating the Healthcare Metaverse: Immersive Technologies and Future Perspectives. Virtual Worlds. 2024; 3(3):368-383. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds3030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleYap, Kevin Yi-Lwern. 2024. "Navigating the Healthcare Metaverse: Immersive Technologies and Future Perspectives" Virtual Worlds 3, no. 3: 368-383. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds3030020
APA StyleYap, K. Y.-L. (2024). Navigating the Healthcare Metaverse: Immersive Technologies and Future Perspectives. Virtual Worlds, 3(3), 368-383. https://doi.org/10.3390/virtualworlds3030020





