Abstract
(1) Background: 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is an illicit drug that is sold as ecstasy. We aimed to develop a voltammetric method based on a chemically modified electrode (CME) to analyze MDMA. (2) Methods: The CME was evaluated with respect to the percentage of modifier, pre-concentration time, electroanalytical parameters, and selectivity. Then, the performance of the new voltammetric method was compared to the performance of color tests and chromatographic analyses (GC-MS and UPLC-MS) during the analysis of 11 seized ecstasy batches. (3) Results: The modifier percentage (v/v) of 1.5% provided the best CME. The electroanalytical parameters were in a linear range from 4.06 to 25.42 µmol L−1, SD = 0.018 µA, m = 84.0 × 103 µA L mol−1, r = 0.999, LD = 0.64 µmol L−1, and LQ = 2.17 µmol L−1. The CME was selective for MDMA. The MDMA concentration in the analyzed ecstasy lots ranged from 0 (without MDMA) to 63% (w/w). The voltammetric method developed for quantifying MDMA in ecstasy lots proved feasible and accurate (with a relative percentage error of ≤ ±13.2%). (4) Conclusions: The CME developed herein showed greater sensitivity (m) and lower LD and LQ for quantifying MDMA traces, paving the way for the use of voltammetric methods during forensic investigations.
1. Introduction
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is the psychoactive component of ecstasy. It was in 1912 that the German chemist Anton Köllisch described MDMA synthesis for the first time in reports owned by the pharmaceutical company Merck [1]. At that time, the drug was an unimportant precursor of the synthesis of homeostatic compounds [1]. In 1927, working at Merck, the scientist Max Oberlin studied the pharmacological effects of MDMA on animals [1]. Almost five decades later, the scientists Alexander T. Shulgin and David Nichols published the first article on the psychopharmacological effects of MDMA on humans [2]. Then, between the 1970s and 1990s, Alexander T. Shulgin and collaborators published other papers about the chemistry, kinetics, dosage, and psychotropic effects of MDMA [2,3]. Now, three decades later, MDMA is illegally sold as tablets, powder, or liquid [4,5]. Like other recreational drugs, the tablets of MDMA are marketed in different shapes, colors, and logos.
MDMA is an entactogen psychotropic drug that acts on the central nervous system (CNS), releasing the neurotransmitters serotonin (5-HT), noradrenaline, and dopamine [6,7]. It elicits effects on the emotional state, like the feeling of love and empathy [7]. The molecule also causes hallucinogenic (mescaline-like) and stimulant (amphetamine-like) effects [8]. However, MDMA promotes acute untoward effects such as hyperthermia, dry mouth, and agitation [9]. In addition, illicit psychostimulants including MDMA have been associated with morphological changes in the CNS and increased risk of developing Parkinson’s disease [9,10].
Synthetic drugs currently correspond to a notable share of the illicit drug market. Because ecstasy use is associated with recreational purposes [9,11], it is generally consumed by young people [5,11]. For example, in 2021, over three-quarters of ecstasy users in the European Union were aged between 15 and 34 years [11]. A study carried out in 35 European countries and published in 2019 found that about 100,000 high school students and about 2.3% of young people aged 15−16 had already used ecstasy at least once, making this drug the second most consumed in this population group [12]. This fact raises concerns and has become a public health issue to be dealt with.
The Scientific Working Group for the Analysis of Seized Drugs (SWGDRUG) classifies drug analysis techniques into three categories, called A, B, and C [13]. Category A techniques include the most selective ones, such as mass spectrometry, and provide structural information about molecules [13]. Category B techniques have intermediate selectivity and provide physical/chemical information but no structural information about molecules; examples of these techniques are liquid and gas chromatography [13]. Category C techniques, like color tests, are poorly selective, but they provide general information or information about a group of molecules [13].
When it comes to identifying drugs, the SWGDRUG recommends employing a Category A technique followed by a technique belonging to another category (A, B, or C). When a Category A technique cannot be applied, the use of two Category B techniques and one Category C technique is advocated [13]. Voltammetric techniques are not classified in the SWGDRUG list, so they can only be used as a preliminary identification technique (Category C). Nevertheless, when sensors are employed, voltammetric techniques display good selectivity and can be classified as a Category A or B technique.
In voltammetric techniques, the working electrode surface, the modifier concentration, and the modifier deposition mode are fundamental parameters when constructing CMEs. The number of studies involving chemically modified electrodes (CMEs) applied in forensic voltammetric analysis has increased [14]. Indeed, CMEs combined with voltammetric techniques offer advantages including high sensitivity and precision, possible miniaturization and automation, and portability [14].
Color tests are used for qualitative MDMA detection [15,16,17]. More specifically, these tests are applied for initial screening. Examples of color tests to detect amphetamines, methamphetamines, and derivatives include the Marquis test [15,16,17], Simon’s Test [15,16,17], Simon’s test with acetone [15,17], sulfuric acid test [15,17], and Vitali-Morin’s Reagent test [15].
The literature has reported the use of instrumental techniques for MDMA analysis in forensic samples, e.g., chromatographic techniques with several detectors (liquid chromatography–diode array detector [18] and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry [19], for instance), the use of capillary electrophoresis–tandem mass spectrometry [20], and voltammetric techniques [21,22,23,24], among others.
This work aims to develop and to optimize a cyclic voltammetric method that employs a glassy carbon electrode chemically modified with a sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene fluoropolymer for MDMA analysis. The developed method will be used to determine MDMA in seized samples and will be compared to color tests, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
The standard of methanolic (±)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine solution (1.0 mg mL−1) was purchased from Cerilliant® (Round Rock, TX, USA).
KCl (analytical grade) was acquired from Cinética® (Jandira, SP, Brazil) and used as the support electrolyte during voltammetric analyses. The electrochemical system consisted of the reference electrode (Ag/AgCl filled with 3.0 mol L−1 KCl), the working electrode (glassy carbon with a diameter of 2.0 mm) purchased from Metrohm® (Herisau, Switzerland), and the platinum spiral auxiliary electrode, manufactured in our laboratory.
To produce the CME, a sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene fluoropolymer copolymer (Nafion® 117), acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), was employed.
For voltammetric analyses, the potentiostat PGSTAT 128 N obtained from Metrohm® (Herisau, Switzerland) was coupled to a computer purchased from Dell (Round Rock, TX, USA) operating with the software GPES version 4.9.007 purchased from Autolab® (Kanaalweg, Utrecht, The Netherlands).
To evaluate the CME selectivity, anhydrous caffeine standard (analytical grade) was obtained from Synth (Diadema, SP, Brazil); theobromine (purity index ≥ 99%), lidocaine (purity index ≥ 98%), and procaine hydrochloride (purity index ≥ 99%) standards were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA); the standard methanolic (±)-methamphetamine (1.0 mg mL−1) solution was acquired from LGC Standards (Teddington, Middlesex, UK); and cocaine hydrochloride (purity index ≥ 99%) standard was obtained by purifying seized cocaine samples [25] obtained through a partnership with the Laboratory of Toxicological Analysis of the Technical-Scientific Police of Ribeirão Preto (São Paulo, Brazil).
Eleven samples of ecstasy lots seized by the police were provided by the Laboratory of Toxicological Analysis of the Technical-Scientific Police of Ribeirão Preto (São Paulo, Brazil) through a previously established partnership (Figure S1). An ultrasound bath 97403-960 purchased from VWR (Missouri, TX, USA), an analytical scale AB204 purchased from Mettler Toledo (Barueri, SP, Brazil), and a vortex model vortamix acquired from Argos (Milton Keynes, United Kingdom) were employed in the sample preparation step.
For color tests, 37% (v/v) formaldehyde (A.C.S. reagent) was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), glacial acetic acid (spectroscopic grade) was purchased from Vetec Química Fina Ltda (Duque de Caxias, RJ, Brazil), sulfuric acid (A.C.S. reagent) was acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), sodium nitroprusside (analytical grade) was acquired from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), acetaldehyde (GC grade) was bought from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), sodium carbonate (analytical grade) was acquired from Carlo Erba Reagents GmbH (Denzlinger, Emmendingen, Germany), and acetone (spectroscopic grade) was purchased from Vetec Química Fina Ltda (Duque de Caxias, RJ, Brazil).
For gas chromatography analyses, the gas chromatograph (GC-MS) was acquired from the Shimadzu Corporation (Kyoto, Japan) and coupled to an AOC-20i auto-injector with an electron ionization source operating at 70 eV purchased from the Shimadzu Corporation (Kyoto, Japan). The column Rtx®-5 (30 m × 0.25 mm; 0.25 µm) acquired from Restek (Centre County, PA, USA) was used for chromatographic separation.
For liquid chromatography analyses, the methanol (HPLC grade) was obtained from Chromasolv® (Seelze, Germany), and ammonium acetate (analytical grade) was acquired from Neon Comercial LTDA (Suzano, SP, Brazil). Ultrapure water was obtained from a Direct-Q3 UV system acquired from Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA). The solvents were used to prepare the mobile phases. Modified PTFE filters (0.45 µm) obtained from Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA) were used to filter the mobile phase.
For UPLC-MS analyses, the ultra-high performance liquid chromatography ACQUITY UPLC H-Class system was acquired from Waters® (Milford, MA, USA). The system was coupled to the mass spectrometer detector Xevo TQ-S bought from Waters® (Milford, MA, USA). For chromatographic separation, the column C4 BEH (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 µm) was acquired from Waters® (Milford, MA, USA). The centrifuge HIMAC CF 15D2 was acquired from Hitachi (Tokyo, Japan) and used in the sample preparation step.
The software Origin 2022b (Academic) was acquired from the OriginLab Corporation (Northampton, MA, USA) and used for data processing.
2.2. Voltammetry
2.2.1. CME Production
Sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene fluoropolymer copolymer solutions were prepared at 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0% (v/v) in methanol. The glassy carbon electrode surface was modified with the solvent evaporation method: 2.5 µL of the solution was pipetted, and it was dropped over the active area of the working electrode. The process was carried out at a fixed temperature of (25 ± 1) °C to standardize solvent evaporation. After 1 h, the polymeric film was dry, and the solvent evaporation procedure was repeated. After another hour, the resulting CME was ready for use.
2.2.2. CME Performance
CMEs (n = 4, polymer solution 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0% v/v) were prepared; designated CME 0.5, CME 1.0, CME 1.5, and CME 2.0, respectively; and assessed with cyclic voltammetry. The procedure for measuring CME performance can be found in the Supplementary Material.
2.2.3. Pre-Concentration Time Evaluation
CME 1.5 was assessed to verify the voltammetric response with or without pre-concentration. The procedure for determining pre-concentration time can be found in the Supplementary Material.
2.2.4. Evaluation of Electroanalytical Parameters
After the optimized working conditions for the CME were established, electroanalytical studies were carried out to establish the analytical curve parameters. Analysis was performed with cyclic voltammetry, using a 5 mL conventional electrochemical cell containing 3 mL of 0.1 mol L−1 KCl support electrolyte in methanol/water 1:24 (v/v). CME 1.5, Ag/AgCl (3 mol L−1 KCl), and platinum spiral were used as the working electrode, reference electrode, and auxiliary electrode, respectively. The experimental conditions were potential ranging from 0.80 to 1.30 V (1.30 to 0.80 V), scan speed of 100 mV s−1, and potential of 0.80 V for a pre-concentration time of 60 s. The standard (±)MDMA solutions (n = 3) were prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 KCl support electrolyte in methanol/water 1:24 (v/v) medium at concentrations of 5.64, 7.96, 12.45, 14.62, 16.74, 20.85, 22.84, and 25.42 µmol L−1. The analytical curve equation was obtained on the basis of the following equation:
were m is the angular coefficient and n is the linear coefficient of the analytical curve. From the analytical curve, the correlation coefficient, the limit of detection (LD), and the limit of quantification (LQ) were calculated by using Equations (2) and (3), respectively, where SD corresponds to the standard deviation of the linear coefficient of the analytical curve, and m is the amperometric sensitivity, corresponding to the angular coefficient of the analytical curve.
Ip (µA) = m (CMDMA; µmol L−1 ) + n
LD = (3 × SD)/m
LQ = (10 × SD)/m
2.2.5. Selectivity of the Developed CME
Considering that other drugs might be present in ecstasy tablets [19], caffeine, theobromine, procaine, lidocaine, cocaine, and methamphetamine standards were prepared at 2.0 mg mL−1 in methanol to simulate a simple sample preparation step for real ecstasy samples. Note: this study was carried out at a fixed standard concentration to observe the analytical method selectivity. In this step, the solubility of the analytical standards in methanolic medium was not considered. CME 1.5 had its selectivity assessed by using the established method described in Section 2.2.4.
2.2.6. Analysis of Seized Ecstasy Lots
In an ultrasound bath, seized tablets were solubilized at 400 µg mL−1 in methanol for 5 min [26]. The external standardization method was used to quantify MDMA in ecstasy tablets (n = 3). The quantification method is described in Section 2.2.4.
2.3. Color Tests
The Marquis Test, Simon’s test, Simon’s test with acetone, and sulfuric acid test were performed according to the United Nations recommendations [17]. Each ecstasy lot was macerated in a mortar, and 1.0 mg was weighed and added to a 1.50 mL tube. A 0.1 mg mL−1 (±)MDMA reference solution in methanol was used as a positive control. For each test, 100 µL of reagent was added to each tube, and the samples were shaken in a vortex for 1 min. Colorimetric variation of the samples was evaluated right after the reagent was added (0 h) and after 48 h. The expected results are described below:
- Marquis: positive when the final color is between black and dark brown.
- Sulfuric acid: positive when the final color is black.
- Simon’s reagent: positive when the final color is between black and dark brown.
- Simon’s reagent with acetone: positive when the final color is reddish.
2.4. Chromatographic Analyses
Each ecstasy sample was macerated in a mortar, and 6.0 mg was weighed and added to glassy tubes (n = 3). Afterwards, 10.00 mL of methanol was added to each tube, and the samples were subjected to ultrasound bath for one minute; the tablet concentration in the solution was 600 µg mL−1. After that, the samples were centrifuged at 3000× g for 5 min. The supernatant was collected for use in chromatographic analysis.
2.4.1. Gas Chromatography (GC-MS)
The ecstasy samples (600 µg mL−1, prepared as Section 2.4) were analyzed using GC-MS under chromatographic conditions of an injection volume of 1.0 µL (splitless mode), injection temperature of 220 °C, column oven temperature ramp of 40 °C (5 min hold) up to 150 °C at 10 °C/minute up to 300 °C at 5 °C min−1. Helium was employed as a carrier gas under constant pressure. The time retention and mass spectra were compared with the standard (±)MDMA solution in methanol (100 µg mL−1). The spectral libraries Wiley 7 and Nist 62 where were used to confirm the presence of MDMA or other drugs. Correspondence between mass spectra greater than 99% was considered.
2.4.2. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC-MS)
Ecstasy samples (600 µg mL−1, prepared as Section 2.4) were analyzed using UPLC-MS under the following chromatographic conditions: mobile phase in the isocratic mode, 93% ultrapure water + 0.1% ammonium acetate (w/v) and 7% methanol + 0.1% ammonium acetate (w/v); with a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1; 5 µL loop; and Z-spray ionization source. The standard (±)MDMA solution in methanol was used to prepare the analytical curves at concentrations ranging from 37.5 to 600.0 ng mL−1 (n = 3). The external standardization method (n = 3) was used for quantifying MDMA in ecstasy tablets. The percent relative error between the chromatographic and voltammetric results was calculated by assuming the chromatography results as a reference (100%).
3. Results
3.1. Voltammetry
3.1.1. CME Performance
Under the experimental conditions, the potential range of the glassy carbon electrode without modification was up to 1.20 V; thereafter, the current increased progressively during voltammetry. The use of a CME allowed for a slightly larger potential window to be used, up to 1.30 V (Figure 1a).
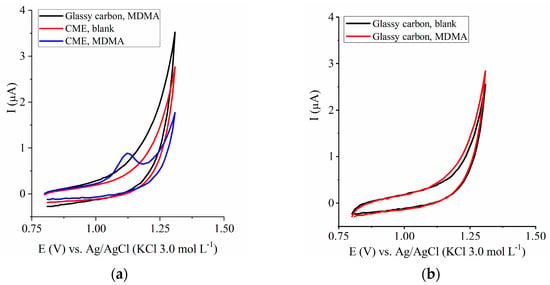
Figure 1.
Voltammetric response obtained by employing the working electrodes of (a) glassy carbon in supporting electrolyte containing MDMA compared to the CME electrode (polymer 1.5% (v/v)) in blank support electrolyte or the medium containing MDMA and (b) glassy carbon in blank support electrolyte or the medium containing MDMA. The MDMA content in the supporting electrolyte is 7.96 µmol L−1.
The CME showed more sensibility in comparison to the glassy carbon electrode, as observed by the presence of an MDMA peak in the medium containing 7.96 µmol L−1 (Figure 1a,b).
In the voltammograms recorded in the presence of CME (Figure 1a), an anodic peak emerged at ~1.1 V, due to irreversible MDMA oxidation (Figure 2).
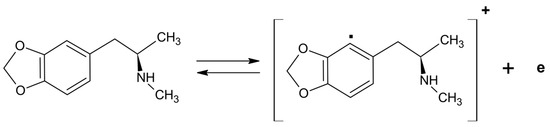
Figure 2.
Simplified mechanism for MDMA oxidation in aqueous medium [25,26].
The CME 0.5, CME 1.0, CME 1.5, and CME 2.0 showed differences in analyte response (Figure 3, Table 1). The CME 0.5 resulted in a greater dispersion of peak current data (RSD Ip = 19.2%). The CME 2.0 showed a noisier peak signal and a higher peak potential (~1.19 V) when compared to the other CMEs. The CME 1.0 and CME 1.5 exposed acceptable RSD Ep and RSD Ip (<15%), and they showed lower oxidation Ep for MDMA. On the basis of these observations, we applied statistical analysis to compare the best electrodes, CME 1.0 and CME 1.5, where F = 0.360, and the Test-T (assuming both groups have the same variance, α = 0.05), where p = 0.006.
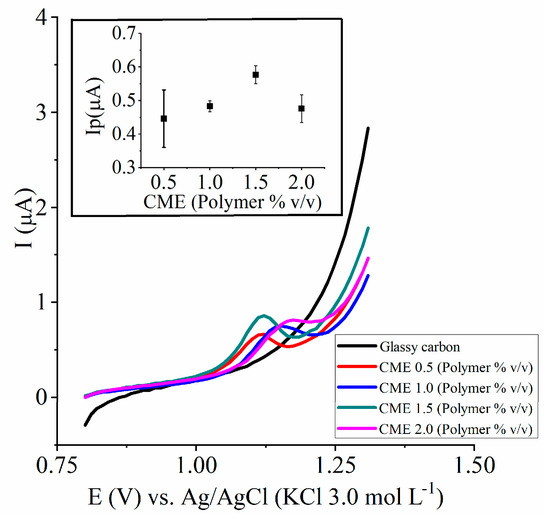
Figure 3.
Study of the CME response for MDMA detection with cyclic voltammetry. Graph of peak current vs. different CMEs (n = 4). MDMA concentration in the support electrolyte = 7.96 µmol L−1. Note: For didactic purposes, we removed the response generated in the range from 1.30 V to 0.80 V and only represent the potential range from 0.80 V to 1.30 V.

Table 1.
Study of the anodic peak current (Ip) and peak potential (Ep) of chemically modified electrodes with cyclic voltammetry *.
3.1.2. Pre-Concentration Time Evaluation
In this study, which employed 20 sequential cycles during cyclic voltammetry analysis, we tested the pre-concentration before the first cycle only and before all the cycles. In the former case, the electrode system provided a more intense current during the first cycle, whereas the response for the analyte decreased in the subsequent cycles (Figure S2a). In the latter case, the voltammetric response was constant (Figure S2b). During pre-concentration time evaluation (Figure S3a), a “plateau” was reached after 480 s (Figure S3b), with 72% higher Ip compared to the Ip observed after 5 s (Figure S3c). The pre-concentration times of 60 and 600 s improved the Ip by 16% and 76%, respectively (Figure S3c).
3.1.3. Evaluation of Electroanalytical Parameters
We assessed CME 1.5 under the optimized conditions to obtain the analytical curve (Figure 4a,b) and to analyze real samples with the external standardization method. In the work range, the Ip was proportional to the MDMA concentration in the bulk, so weighting was not necessary. The analytical curve showed a correlation coefficient of 0.999, and the corresponding equation was Ip = 0.0840CMDMA + 0.1838. The limit of detection was 0.64 µmol L−1, and the limit of quantification was 2.17 µmol L−1. Table 2 shows the literature data and the results obtained with the CME.
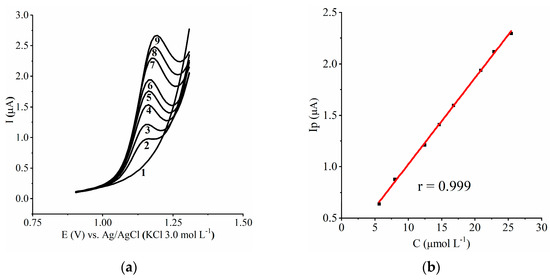
Figure 4.
Electroanalytical results: (a) voltamograms of the analytical curve: 1—Blank, 2—5.64 µmol L−1 MDMA, 3—7.96 µmol L−1 MDMA, 4—12.45 µmol L−1 MDMA, 5—14.62 µmol L−1 MDMA, 6—16.74 µmol L−1 MDMA, 7—20.85 µmol L−1 MDMA, 8—22.84 µmol L−1 MDMA, and 9—25.42 µmol L−1 MDMA; (b) analytical curve.

Table 2.
Comparison with literature data and analytical results obtained by employing CME 1.5.
3.1.4. Selectivity of the Developed CME
The analyzed drugs did not provide an Ep close to 1.1 V, so there was no risk of false-positive results for MDMA detection (Figure 5a). Procaine gave an anodic peak at 0.95 V (Figure 5a). When we tested procaine and MDMA together (Figure 5b), the MDMA peak shifted from ~1.1 V to 1.19 V, so procaine did not interfere in the MDMA analysis, and these two drugs could be detected separately even if both of them are present in the same matrix (Figure 5b). Also, when we compared the pre-concentration times of 60 and 180 s, the procaine Ep remained constant (there was only a decrease in the contribution of capacitive current); additionally, the MDMA Ep increased because, as expected (see Section 3.1.2), there is a pre-concentration of MDMA on the electrode’s surface.
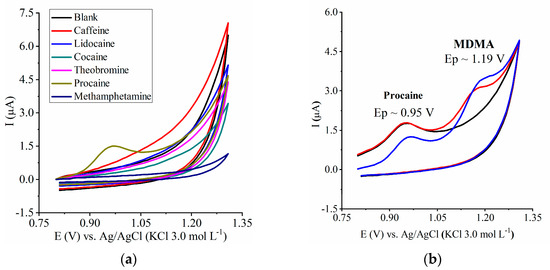
Figure 5.
Evaluation of the CME selectivity: (a) cyclic voltammetry of the blank (support electrolyte only), caffeine, lidocaine, cocaine, theobromine, procaine, and methamphetamine at 7.66 µg mL−1 in KCl support electrolyte (0.1 mol L−1) in MeOH/H2O, 1:24 (v/v); (b) voltammograms of procaine and MDMA: (-----) procaine (7.66 µg mL−1), pre-concentration time of 60 s; (-----) procaine (7.66 µg mL−1) + MDMA (1.53 µg mL−1), pre-concentration time of 60 s, and (-----) procaine (7.66 µg mL−1) + MDMA (1.53 µg mL−1), pre-concentration time of 180 s.
3.2. Color Tests
In all the tests, we verified false-positive or false-negative results (Table 3) in at least one of the studied batches. Among the eleven batches seized as ecstasy, right after the reagents were added (at 0 h), the Marquis and sulfuric acid tests provided one false-positive and one false-negative result, Simon’s test gave five false-negative results, and Simon’s test with acetone provided four false-negative results.

Table 3.
Color test results for ecstasy batches.
Because we obtained several false-negative results, we decided to wait 48 h to verify the coloration after this reaction time (Figure S4) to observe interesting changes in the results of Simon’s test (from four false-negative to one false-positive result) and Simon’s test with acetone (from five false-negative to three false-negative results).
The MDMA standard (positive control, 0.1 mg mL−1 MDMA) did not show the expected color in the Marquis and sulfuric acid tests, resulting in false-negative results.
3.3. Chromatographic Studies
Among the eleven batches analyzed herein, two did not contain MDMA (one featured fenproporex and the other contained caffeine), and one contained a mixture of MDMA and caffeine (Table 4).

Table 4.
Evaluation of the tablets seized as ecstasy: active ingredient (GC-MS), quantification with liquid chromatography (UPLC-MS), quantification with cyclic voltammetry (CV), and comparison between the instrumental techniques.
By using UPLC-MS, we obtained the analytical curve to quantify MDMA at concentrations ranging from 37.5 to 600.0 ng mL−1. The analytical curve had a correlation coefficient of 0.998, and the equation was Area = 6.178 × 106 CMDMA + 8.268 × 107. Table 4 shows the quantification of ecstasy batches with cyclic voltammetry and chromatography.
4. Discussion
4.1. Voltammetry
4.1.1. CME Performance
The increase in the potential window toward a more positive potential range favored MDMA analysis given that the MDMA anodic peak emerges at potential values greater than 1.0 V (Figure 1a) [26]. The electric potential is higher when the glassy carbon electrode is used without modification.
In addition, the CME containing the perfluorinated ionomer was more sensitive to the molecule of interest (Figure 1a), so we were able to detect lower MDMA concentrations compared to the glassy carbon electrode without modification (Figure 1a,b).
The anodic peak observed in MDMA detection (Figure 1a) is due to the oxidation of the aromatic nucleus of the molecule, which was followed by the reaction of the resulting radical cation (Figure 2) [26].
The polymer concentration on the electrode’s surface impacted the analyte response (Figure 3 and Table 1). CME 0.5 showed highly dispersed Ip data, as indicated by RSD Ip > 15%. The CME 2.0 showed a noisier peak signal and higher Ep (~1.19 V) when compared to the other CMEs, which could interfere in MDMA detection. On the basis of these observations, the 0.5 and 2.0 CMEs were not adequate for this analysis.
The CMEs 1.0 and 1.5 showed acceptable deviations in RSD Ip and RSD Ep, remaining less than 15%. After applying the F test, we observed that the groups had supposedly equal variances. We employed the T test assuming that both groups had the same variance, which demonstrated that the CMEs were significantly different.
4.1.2. Pre-Concentration Time Evaluation
The pre-concentration step is carried out before quantitative analysis so that the electroactive species can accumulate on the electrode’s surface. Thus, the time and the applied potential (or the open circuit, without potential being applied) must be controlled.
The behavior described in Section 3.1.2 (Figure S2a,b) suggested that the process was governed by the adsorption of the electroactive species on the CME surface. Hence, it was necessary to apply a pre-concentration time before each cycle, first to guarantee the equilibrium of the double electrical layer between the electrode and the medium and then for the adsorption of the analyte on the surface of the work electrode to occur.
Because these studies aimed to achieve fast analysis, we decided to adopt the pre-concentration time of 60 s, which provided fast responses and improved analyte detection (Figure S3). Nevertheless, if the need to analyze samples containing lower MDMA concentrations, which is the case with biological samples, should arise, a longer pre-concentration time, such as 480 s, should be applied to concentrate a greater amount of the target drug on the electrode’s surface and consequently improve the sensitivity of the method.
4.1.3. Evaluation of Electroanalytical Parameters
The electroanalytical evaluation of CME 1.5 in the concentration range of 5.64−25.42 µmol L−1 presented a good correlation coefficient (>0.99), with it being possible to quantify MDMA in seized tablets.
Garrido et al. evaluated MDMA quantification in a conventional system containing a glassy carbon working electrode and phosphate buffer support electrolyte (pH 7) with square wave voltammetry [26]. In turn, Cumba et al. evaluated MDMA quantification in a system containing a screen-printed graphite electrode and phosphate buffer electrolyte support (pH 7) with differential pulse voltammetry [24]. Here, we observed (Table 2) better sensitivity (when compared to Garrido et al.) and lower LD and LQ values for MDMA (when compared to both Garrido et al. and Cumba et al.), so the method developed by us constitutes a new alternative for MDMA analysis.
4.1.4. Selectivity of the Developed CME
Tablets sold as ecstasy may contain a mixture of psychoactive or non-psychoactive drugs (adulterants) [19,27]. Thus, we performed voltammetric analyses in the presence of other drugs to evaluate the electrochemical detector selectivity (Figure 5a) given that other compounds present in ecstasy tablets could give rise to peaks at the same Ep as MDMA or close to the MDMA Ep.
Note that the analysis of selectivity was carried out at the concentration of 7.66 µg mL−1 in the supporting electrolyte for each drug and it did not show an anodic peak near to the MDMA anodic peak; thus, the developed CME was selective for MDMA detection, demonstrating its promising use as a voltammetric detector in real ecstasy samples.
In the subsequent study, the selectivity can be observed with other concentrations to observe false-positive or false-negative responses.
Procaine was the only species that presented an anodic peak at 0.95 V. However, MDMA can be detected without prejudice in the analysis, with it being possible to detect both species when they were present in the same matrix (Figure 5b).
Also, the pre-concentration times of 60 s and 180 s were compared in MDMA and procaine analyses. It was observed that the peak potential for procaine remained constant (there was only a decrease in the contribution of the capacitive current that occurred for the pre-concentration time of 180 s).
Additionally, it was possible to observe an increase in Ep values for MDMA, with it being demonstrated that these species presented different electrochemical behavior on the CME surface (as previously mentioned, MDMA adsorbed on the CME surface).
Considering the studies carried out with the CME, mainly the selectivity tests, we still cannot say that it acts as a sensor (which is much more specific and has a good level of selectivity), so we have classified the developed voltammetric method as a preliminary identification technique (Category C).
4.2. Color Tests
Color tests are usually simple and fast, and they are widely employed to screen amphetamine-like compounds [16]. Here, we used color tests for this purpose. However, color tests do not indicate the exact compounds the sample contains and may not be reliable, providing false-positive/-negative results due to factors such as drug content in the tablets, tablet purity, emergence of new psychoactive substances in the market, and the poor specificity of these tests [16,28]. Thus, here we followed the SWGDRUG classification [13] and analyzed the seized samples with color tests (Marquis, sulfuric acid, Simon’s reagent, Simon’s reagent with acetone), classified as Category C, and compared the results with the qualitative results we obtained with gas chromatography and the results we obtained with the voltammetric method developed herein.
Because Category A techniques have the highest level of selectivity, we employed the GC-MS qualitative results to infer whether the results of the color tests were adequate (as will be discussed in Section 4.3).
Simon’s test is widely used to detect secondary amines, including MDMA [16]. In turn, the Marquis test has become an interesting complementary test that distinguishes amphetamines and their ring-substituted analogues [16].
Simon and Simon + acetone tests were more impacted by the color of the dye in the ecstasy tablets, which affected the results of the analyses; when additional time was applied to this reaction, we reduced the number of false results in the color tests.
Moreover, the amount of MDMA in the samples was important for the colorimetric visualization of the tests. The MDMA standard (0.1 mg mL−1) resulted in false-negative results, which led us to conclude that these tests were less sensitive than Simon’s test and Simon’s test with acetone.
4.3. Chromatographic Studies
According to the SWGDRUG classification, spectroscopic techniques are classified as Category A, while chromatographic techniques are classified as Category B [13]. We employed GC-MS and UPLC-MS to detect and to quantify MDMA and to detect other drugs that could be present in ecstasy tablets. Then, we compared the results obtained by using the chromatographic techniques and the developed voltammetric method.
Among the eleven seized batches, two licit drugs were found: caffeine and fenproporex. Fenproporex and caffeine exert stimulant properties on the CNS and can be present in ecstasy tablets as adulterants or MDMA substituents [4,19]. Some studies in Brazil have already reported an expressive number of seized ecstasy tablets containing only caffeine or a mixture of MDMA and caffeine [4,19]. Souza Júnior and co-authors reported that, from 2011 to 2017, 47.6% of the tablets seized as MDMA in Santa Catarina (a Brazilian state) actually contained a mixture of MDMA and caffeine, and 21.3% of the tablets contained a mixture of MDMA, caffeine, and another drug [4].
The batches varied significantly in terms of the amount of MDMA (from ~28% w/w to ~61% w/w) (Table 4). Batches 7 and 9 (~24% w/w) and batches 8 and 11 (~28% w/w) had similar MDMA concentrations, which could suggest that they had the same origin.
Croft and co-workers found that tablets seized as ecstasy in Queensland (Australia) from 2017 to 2020 contained MDMA contents varying between 0.4% w/w and 45.7% w/w [27]. Togni and co-workers found that samples seized as ecstasy in São Paulo (Brazil) contained 12–125 mg of MDMA/tablet [19]. From 2012 to 2021 in European drug checking services, Vrolijk and co-workers found that ecstasy tablets had a widely varied mass of MDMA [29]. Ecstasy can present a varied amount of MDMA across countries, and adulterants can also vary.
We emphasize the need to discuss the use/abuse of ecstasy due to its toxicological aspects, especially when it is sold with other adulterants or when the MDMA concentration in the tablet is high. This is because its use can damage and pose risks to users’ health.
4.4. Comparison between Voltammetric and Chromatographic Analyses
The relative error between the chromatographic and cyclic voltammetry analyses performed herein was less than ±15%, indicating that the cyclic voltammetry proved to be feasible and accurate. Therefore, the developed voltammetric method can help to detect MDMA quantitatively even when adulterants are present in the sample of forensic interest, but other instrumental techniques must be used in combination with voltammetry for quantitative purposes.
5. Conclusions
CMEs are valuable for forensic analysis given that they improve detector selectivity or sensitivity. A considerable cost–benefit ratio is observed for this technique; it requires less analysis time and cheaper equipment in comparison to that employed in chromatographic techniques, for example. According to the experimental results, CME 1.5 was the one that presented the best electrochemical response for MDMA detection. This electrode was able to detect and to quantify MDMA traces at lower MDMA concentrations compared to the literature. This demonstrated its potential application in forensic samples.
The selectivity studies conducted for the developed CME indicated that the other tested analytes did not generate an anodic peak in the MDMA detection region, so the CME proved a promising voltammetric MDMA detector in ecstasy samples.
When we performed qualitative and quantitative analyses on 11 seized ecstasy batches supplied by the technical-scientific police, the MDMA concentration in the samples ranged from 0 (did not contain MDMA) to ~61% w/w. Thus, developing methods to detect MDMA is of great value to help to control the illegal sale of this drug more effectively.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/psychoactives2040023/s1, Figure S1: Seized ecstasy samples; Figure S2: Pre-concentration time study: Cyclic voltammetry employing CME 1.5 (Polymer % (v/v) (a) 20 consecutive cycles: 1—Blank: Pre-concentration time of 60 s, 2—1st cycle. Bulk with MDMA: Pre-concentration time of 60 s, 3—2nd to 20th cycle. Bulk with MDMA: without pre-concentration time; (b) 20 non-consecutive cycles: 1st to 20th cycle. Bulk with MDMA: Pre-concentration time of 60 s; Figure S3: Evaluation of pre-concentration time: (a) Voltammograms recorded with different pre-concentration time (5−600 s); (b) Graph of the peak current as a function of pre-concentration time; (c) Table of the peak current and the in-crease in the peak current, in percentage, compared to the pre-concentration time of 5 s; Figure S4: Colorimetric results of the Marquis test, sulfuric acid test, Simon’s test, and Simon’s test with acetone. From 0 to 48 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation, M.C.T.; resources and visualization, A.J.I.; supervision and writing—review and editing, M.F.d.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are thankful to CAPES (CAPES, PROCAD-SPCF—File number process 88887.613955/2021-00), FAPESP (File number 2022/12189-0), and CNPq (File number 302742/2022-0) for financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors are willing to share information about the experimental part, according to demand.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Cynthia Maria de Campos Prado Manso, who revised and edited this full text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Freudenmann, R.W.; Öxler, F.; Bernschneider-Reif, S. The Origin of MDMA (Ecstasy) Revisited: The True Story Reconstructed from the Original Documents. Addiction 2006, 101, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzenhöfer, U.; Passie, T. Rediscovering MDMA (Ecstasy): The Role of the American Chemist Alexander T. Shulgin. Addiction 2010, 105, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulgin, A.T. The Background and Chemistry of MDMA. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1986, 18, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Júnior, J.L.; Silveira Filho, J.; Boff, B.S.; Nonemacher, K.; Rezin, K.Z.; Schroeder, S.D.; Ferrão, M.F.; Danielli, L.J. Seizures of Clandestinely Produced Tablets in Santa Catarina, Brazil: The Increase in NPS from 2011 to 2017. J. Forensic. Sci. 2020, 65, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Division for Treaty Affairs World Drug Report 2022; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 9789211483758. [Google Scholar]
- Sessa, B.; Higbed, L.; Nutt, D. A Review of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-Assisted Psychotherapy. Front Psychiatry 2019, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holze, F.; Vizeli, P.; Müller, F.; Ley, L.; Duerig, R.; Varghese, N.; Eckert, A.; Borgwardt, S.; Liechti, M.E. Distinct Acute Effects of LSD, MDMA, and d-Amphetamine in Healthy Subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalant, H. The pharmacology and toxicology of “ecstasy” (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ 2001, 165, 917–928. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, G.; Gołembiowska, K. Neurotoxicity of MDMA: Main Effects and Mechanisms. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, G.; Noyes, C.; Flavel, S.C.; Della Vedova, C.B.; Spyropoulos, P.; Chatterton, B.; Berg, D.; White, J.M. Illicit Stimulant Use Is Associated with Abnormal Substantia Nigra Morphology in Humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European Drug Report 2021: Trends and Developments; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2021; ISBN 9789294976345. [Google Scholar]
- ESPAD Group; EMCDDA Joint Publications. ESPAD Report 2019: Results from the European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs; ESPAD Group: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Working Group for the Analysis of Seized Drugs (SWGDRUG). Scientific Working Group for the Analysis of Seized Drugs (SWGDRUG) Recommendations, Version 8.1; United States Department of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Zeng, J.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, H. Perspective and Application of Modified Electrode Material Technology in Electrochemical Voltammetric Sensors for Analysis and Detection of Illicit Drugs. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 329, 112821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, K.-A.; Laudszum, M. Chemistry and Reaction Mechanisms of Rapid Tests for Drugs of Abuse and Precursors Chemicals; United Nations: Tubingen, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations; United Nations Office on Drugs. Recommended Methods for the Identification and Analysis of Amphetamine, Methamphetamine and Their Ring-Substituted Analogues in Seized Materials (Revised and Updated) Manual for Use by National Drug Testing Laboratories; United Nations: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Rapid Testing Methods of Drugs of Abuse: Manual Use Nacional Law Enforcement and Narcotics and Laboratory Personnel; United Nations International Drug Control Programme: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, L.O.; Ferreira, B.; Silva, G.R.; Ipólito, A.J.; de Oliveira, M.F. Validated Green Phenyl Reversed-Phase LC Method Using Ethanol to Determine MDMA in Seized Ecstasy Tablets. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togni, L.R.; Lanaro, R.; Resende, R.R.; Costa, J.L. The Variability of Ecstasy Tablets Composition in Brazil. J. Forensic. Sci. 2015, 60, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, C.L.; Angnes, L.; Porto, S.K.S.S.; Daniel, D. Determination of 3,4-MDMA in Ecstasy Tablets by CE-MS/MS Application Note; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murilo Alves, G.; Soares Castro, A.; McCord, B.R.; de Oliveira, M.F. MDMA Electrochemical Determination and Behavior at Carbon Screen-Printed Electrodes: Cheap Tools for Forensic Applications. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midori, J.; Katayama, T.; Oiye, N.; Fernanda, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Ipólito, A.J.; Fernando De Andrade, J.; Firmino De Oliveira, M. MDMA Electrochemical Determination in Aqueous Media Containing Illicit Drugs and Validation of a Voltammetric Methodology. Drug Anal. Res. 2020, 4, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Naomi Oiye, É.; Midori Toia Katayama, J.; Fernanda Muzetti Ribeiro, M.; Oka Duarte, L.; de Castro Baker Botelho, R.; José Ipólito, A.; Royston McCord, B.; Firmino de Oliveira, M. Voltammetric Detection of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in Saliva in Low Cost Systems. Forensic Chem. 2020, 20, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumba, L.R.; Smith, J.P.; Zuway, K.Y.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Do Carmo, D.R.; Banks, C.E. Forensic Electrochemistry: Simultaneous Voltammetric Detection of MDMA and Its Fatal Counterpart “Dr Death” (PMA). Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadini, M.C.; Balbino, M.A.; Eleoterio, I.C.; De Oliveira, L.S.; Dias, L.G.; Jean-François Demets, G.; De Oliveira, M.F. Developing Electrodes Chemically Modified with Cucurbit[6]Uril to Detect 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) by Voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, E.M.P.J.; Garrido, J.M.P.J.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Electrochemical Oxidation of Amphetamine-like Drugs and Application to Electroanalysis of Ecstasy in Human Serum. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 79, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, S.; Blakey, K.; McGowan, J. Assessment of MDMA Tablet and Capsule Dosages from Seizures in Queensland, Australia. Forensic Chem. 2022, 31, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunty, S.; Carmany, D.; Dhummakupt, E.S.; Manicke, N.E. Combining Presumptive Color Tests, Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive-Based Collection, and Paper Spray-Mass Spectrometry for Illicit Drug Detection Contents. Analyst 2023, 148, 3274–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrolijk, R.Q.; Measham, F.; Quesada, A.; Luf, A.; Schori, D.; Radley, S.; Acreman, D.; Smith, J.; Verdenik, M.; Martins, D.; et al. Size Matters: Comparing the MDMA Content and Weight of Ecstasy Tablets Submitted to European Drug Checking Services in 2012–2021. Drugs Habits Soc. Policy 2022, 23, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).