Recontextualizing Neuromyelitis Optica as a Systemic Condition: A Perspective
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
- Category I: Evidence from at least one properly randomized controlled trial.
- Category II-1: Evidence from well-designed controlled trials without randomization.
- Category II-2: Evidence from well-designed cohort or case–control analytic studies, preferably from more than one center or research group.
- Category II-3: Evidence from multiple time series with or without intervention, or dramatic results in uncontrolled experiments such as the results of the introduction of penicillin treatment in the 1940s.
- Category III: Opinions of respected authorities, based on clinical experience, descriptive studies and case reports, or reports of expert committees.
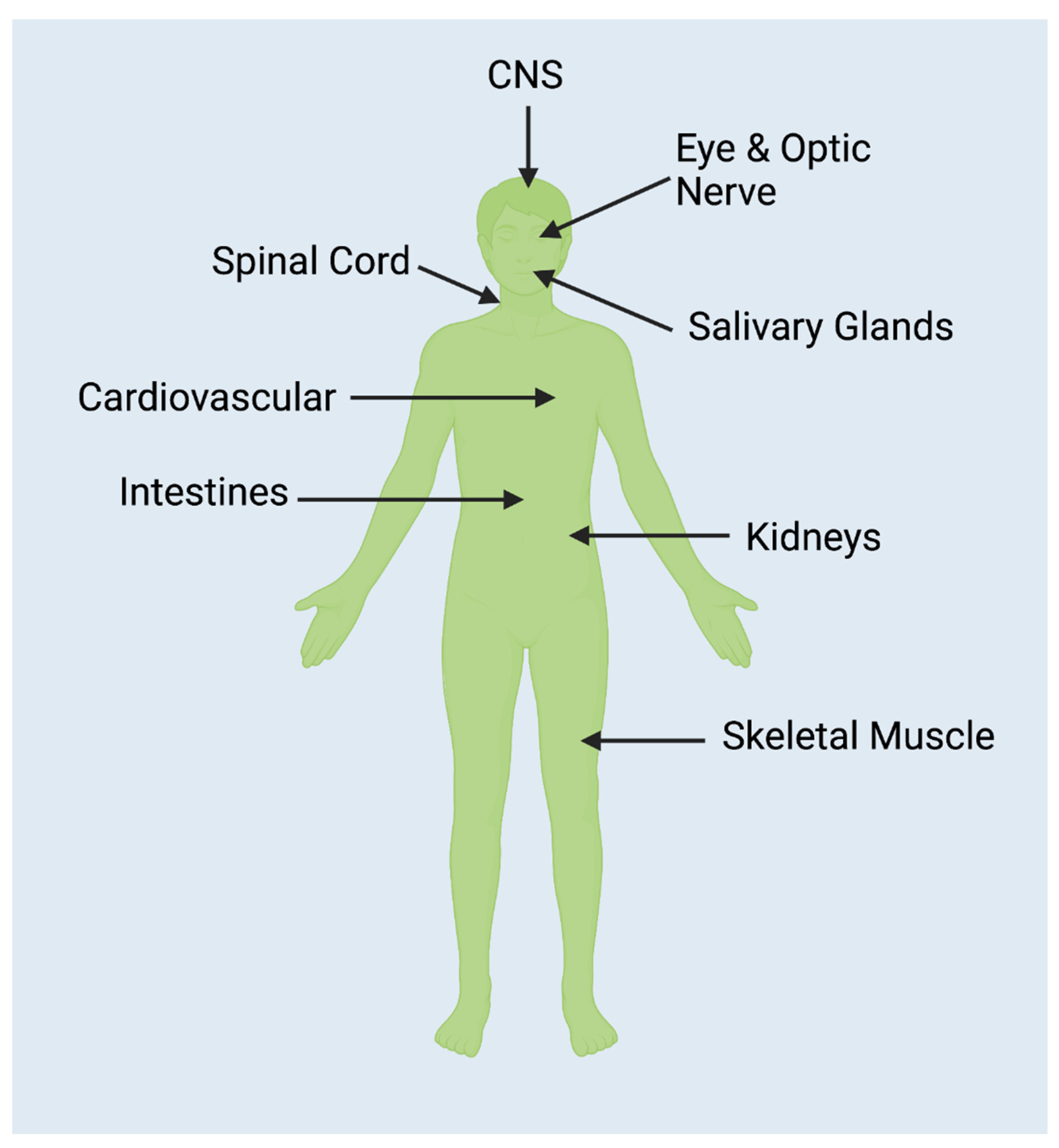
3. Results
3.1. CNS
3.2. Muscular
3.3. Cancer
3.4. Autoimmune
3.5. Other
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verkman, A. Aquaporins. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R52–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Salman, M.M.; Conner, M.T.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, A.C. Beyond water homeostasis: Diverse functional roles of mammalian aquaporins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A.S. Physiological roles of glycerol-transporting aquaporins: The aquaglyceroporins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippidis, A.S.; Carozza, R.B.; Rekate, H.L. Aquaporins in brain edema and neuropathological conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Rossi, A.; Crane, J.M. Live-cell imaging of aquaporin-4 supramolecular assembly and diffusion. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 504, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Binder, D.K.; Bloch, O.; Auguste, K.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Taylor, L.H.; Salman, M.M.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C. Identification and molecular mechanisms of the rapid tonicity-induced relocalization of the aquaporin 4 channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16873–16881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Brown, J.E.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, A.C.; Conner, M.T. Hypothermia increases aquaporin 4 (AQP4) plasma membrane abundance in human primary cortical astrocytes via a calcium/transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4)- and calmodulin-mediated mechanism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; Macdonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting aquaporin-4 subcellular localization to treat central nervous system edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin 4 and neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, J.Y.; Asgari, N.; Nakashima, I.; Broadley, S.A.; Leite, M.I.; Kissani, N.; Jacob, A.; Marignier, R.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Paul, F.; et al. Epidemiology of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and its prevalence and incidence worldwide. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Wildemann, B.; Paul, F. Neuromyelitis optica: Clinical features, immunopathogenesis and treatment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciappelloni, S.; Bouchet, D.; Dubourdieu, N.; Boué-Grabot, E.; Kellermayer, B.; Manso, C.; Marignier, R.; Oliet, S.H.; Tourdias, T.; Groc, L. Aquaporin-4 surface trafficking regulates astrocytic process motility and synaptic activity in health and autoimmune disease. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3860–3872.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, S.; Whittam, D.; Bhojak, M.; Chamberlain, J.; Noonan, C.; Jacob, A. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Clin. Med. 2019, 19, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; De Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Optic Neuritis. Mayo Clinic. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/optic-neuritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354953?utm_source=Google&utm_medium=abstract&utm_content=Optic-neuritis&utm_campaign=Knowledge-panel (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Transverse Myelitis Fact Sheet. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Available online: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/fact-sheets/transverse-myelitis-fact-sheet. (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Apetse, K.; Diatewa, J.E.; Tajeuna, J.J.D.; Dansou, Y.M.; Bakoudissa, R.; Waklatsi, K.P.; Kombate, D.; Assogba, K.; Balogou, A.A.K. Case report: An area postrema syndrome revealing a neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder associated with central nervous system tuberculosis in a young Togolese (black African) woman. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, H.; Witherick, J.; Wilkins, A. Diagnosis of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr1020103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Chojdak-Łukasiewicz, J.; Budrewicz, S.; Pokryszko-Dragan, A. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder treatment-current and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Yool, A.J.; Bill, R.M. Recent breakthroughs and future directions in drugging aquaporins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, N.J.; Salman, M.M.; Pushie, M.J.; Hou, H.; Meher, V.; Herlo, R.; Peeling, L.; Kelly, M.E. The effects of trifluoperazine on brain edema, aquaporin-4 expression and metabolic markers during the acute phase of stroke using photothrombotic mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Al-Obaidi, Z.; Kitchen, P.; Loreto, A.; Bill, R.M.; Wade-Martins, R. Advances in applying computer-aided drug design for neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldewachi, H.; Al-Zidan, R.N.; Conner, M.T.; Salman, M.M. High-throughput screening platforms in the discovery of novel drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wevers, N.R.; Kasi, D.G.; Gray, T.; Wilschut, K.J.; Smith, B.; van Vught, R.; Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Kanda, T.; Marsh, G.; et al. A perfused human blood-brain barrier on-a-chip for high-throughput assessment of barrier function and antibody transport. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Marsh, G.; Kusters, I.; Delincé, M.; Di Caprio, G.; Upadhyayula, S.; de Nola, G.; Hunt, R.; Ohashi, K.G.; Gray, T.; et al. Design and validation of a human brain endothelial microvessel-on-a-chip open microfluidic model enabling advanced optical imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 573775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekeridou, A.; Lennon, V.A. Aquaporin-4 autoimmunity. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, S.R.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Roemer, S.F.; Fryer, J.P.; Kryzer, T.J.; Lennon, V.A. Pathogenic potential of IgG binding to water channel extracellular domain in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2007, 69, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Paul, F.; Franciotta, D.; Waters, P.; Zipp, F.; Hohlfeld, R.; Vincent, A.; Wildemann, B. Mechanisms of disease: Aquaporin-4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2008, 4, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasi, A.N.; Mirmosayyeb, O.; Mohammadi, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Ghajarzadeh, M. The prevalence of cognitive impairment in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 49, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Kleerekooper, I.; Davagnanam, I.; Trip, S.A. Acute anosmia in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1958–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, O.; Girelli, E.; Harikrishnan, S. Neuromyelitis optica: An elusive cause of dysphagia. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, bcr-2018-227041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Miao, H.; Kwapong, W.R.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chen, W.; Tu, Y.; Liu, X. Alterations in the brain structure and functional connectivity in aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, L.N.; Zanaty, M.; Kirby, P.; Dlouhy, B.J. Acute hydrocephalus resulting from neuromyelitis optica: A case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillo-Contreras, J.L.; Ramírez-Lorca, R.; Villadiego, J.; Echevarría, M. Cellular distribution of brain aquaporins and their contribution to cerebrospinal fluid homeostasis and hydrocephalus. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Li, Y.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, G.; Chu, L. Myopathy associated with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi, S.; Doosti, R.; Shahmohammadi, A.; Azimi, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Fattahi, M.-R.; Moghadasi, A.N. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) associated with cancer: A systematic review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 56, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, M.; Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Hao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Cui, L.; Jiao, J. Reduced sarcolemmal aquaporin 4 expression can support the differential diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 339, 577121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Qin, C.; Bu, B.T.; Tian, D.S. Aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder subsequent to rhabdomyolysis: A case report and literature review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelibter, S.; Moiola, L.; Previtali, S.C.; Filippi, M. Neuromyelitis optica and myotonic dystrophy type 2: A rare association with diagnostic implications. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2744–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigeri, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Balena, R.; Nico, B.; Svelto, M. Aquaporins in skeletal muscle: Reassessment of the functional role of aquaporin-4. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 905–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibril, M.; Walters, R. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder as a paraneoplastic syndrome: A rare and challenging diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Lan, Y.-L.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. A bioinformatics analysis of the potential roles of aquaporin 4 in human brain tumors: An immune-related process. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 692175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgilio, E.; Vecchio, D.; Vercellino, M.; Naldi, P.; Tesser, F.; Cantello, R.; Cavalla, P.; Comi, C. Paraneoplastic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A case series. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 2519–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Hayashida, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Sasahara, Y.; Takaki, T.; Yatera, K. Paraneoplastic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder associated with malignant melanoma: A case report. Thorac. Cancer. 2021, 12, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jia, Z.; Qin, W.; Hu, W. Paraneoplastic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder associated with breast cancer. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1039–1044, Published 6 Jun 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, M.; Guo, Y.; Tselis, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Lisak, R.P. Paraneoplastic neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder associated with metastatic carcinoid expressing aquaporin-4. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, T.; Al-Sarawi, A.; Binfalah, M.; Dermime, S. Paraneoplastic Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Associated with Stomach Carcinoid Tumor. Hematology/Oncology and Stem Cell Therapy. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S165838761400048X?via%3Dihub (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Iorio, R.; Rindi, G.; Erra, C.; Damato, V.; Ferilli, M.; Sabatelli, M. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder as a paraneoplastic manifestation of lung adenocarcinoma expressing aquaporin-4. Mult. Scler. 2015, 21, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, T.; Ueno, T.; Suzuki, C.; Nunomura, J.; Igarashi, S.; Sato, T.; Tomiyama, M. Aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder associated with esophageal cancer. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 309, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi, S.; Doosti, R.; Shahmohammadi, A.; Mohammadianinejad, S.E.; Sahraian, M.A.; Azimi, A.R.; Harirchian, M.H.; Asgari, N.; Naser Moghadasi, A. Autoimmune diseases associated with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A literature review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 27, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangani, V.; Pokal, M.; Balla, M.; Merugu, G.P.; Adapa, S.; Naramala, S.; Konala, V.M. A case of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with coexisting systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2021, 11, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamvil, S.S.; Spencer, C.M.; Baranzini, S.E.; Cree, B.A.C. The gut microbiome in neuromyelitis optica. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Ruan, Y.; Qiu, W. Potential role of the gut microbiota in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: Implication for intervention. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 82, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.I.; Atarashi, K.; Manel, N.; Brodie, E.L.; Shima, T.; Karaoz, U.; Wei, D.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Santee, C.A.; Lynch, S.V.; et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell 2009, 139, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badihian, S.; Manouchehri, N.; Mirmosayyeb, O.; Ashtari, F.; Shaygannejad, V. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and menstruation. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 174, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, H.; Ueno, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Miyamoto, N.; Yamashiro, K.; Tanaka, R.; Yokoyama, K.; Hattori, N. Pontine hemorrhage accompanied by neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 330, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, K.; Waliszewska-Prosół, M.; Budrewicz, S.; Szewczyk, P.; Ejma, M. Severe course of neuromyelitis optica in a female patient with chronic C hepatitis. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2018, 52, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, M.; Mirmosayyeb, O.; Ebrahimi, N.; Bagherieh, S.; Afshari-Safavi, A.; Hosseinabadi, A.M.; Shaygannejad, V.; Asgari, N. COVID-19 susceptibility and outcomes among patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 57, 103359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleiser, C.; Wagner, A.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Wolburg, H.; Hirt, B.; Mack, A.F. Aquaporin-4 in astroglial cells in the CNS and supporting cells of sensory organs-a comparative perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.G.; Huang, J.; Fan, R.; Weng, R.H.; Shinohara, R.T.; Landis, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y. Urinalysis in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, L.; Huang, D.; Yau, V.; Yu, S. Pruritus in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders and multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 79, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
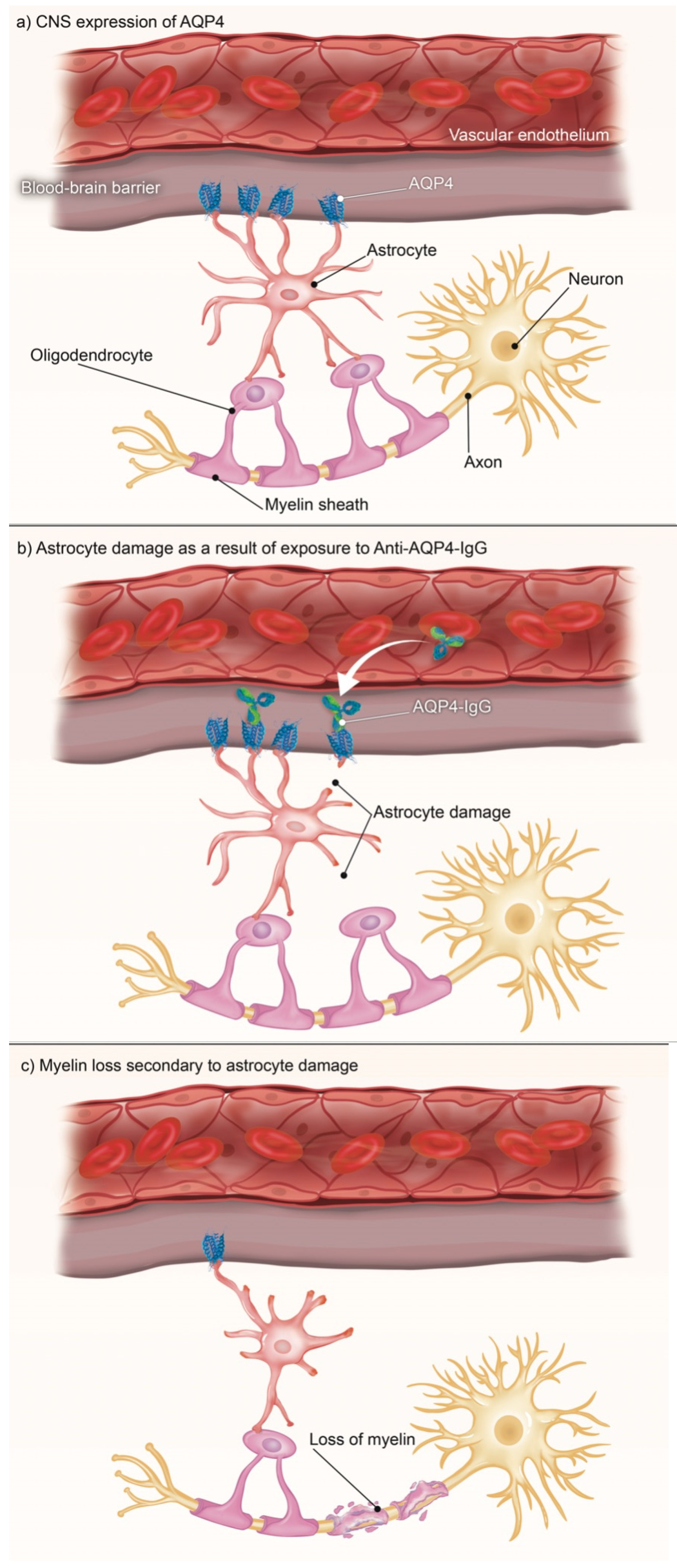
| NMOSD Diagnostic Criteria for Adult Patients [15]. | |
|---|---|
Diagnosis with AQP4-Abs:
| |
| Core Clinical Characteristic | Symptoms |
| Optic Neuritis | Ocular pain, blurred vision, vision disorder, inability to distinguish certain colors, and partial or complete loss of vision [16]. |
| Acute Myelitis | Lower back pain or sharp, shooting sensations that radiate down the legs or arms or around the torso, paresthesia [17]. |
| APS | Hiccups, nausea, and/or uncontrollable vomiting for several days in connection with an area postrema attack, a bulbar region, and an emetic reflex center [18]. |
| LETM | Contiguous inflammatory lesions of the spinal cord [19]. |
| Summary of Non-CNS Pathologies with a Connection to NMOSD |
|---|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Webber, P.; Landis, B.C.; Brooks, A.E. Recontextualizing Neuromyelitis Optica as a Systemic Condition: A Perspective. J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2023, 1, 61-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1020008
Webber P, Landis BC, Brooks AE. Recontextualizing Neuromyelitis Optica as a Systemic Condition: A Perspective. Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology. 2023; 1(2):61-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWebber, Parker, Brianna C. Landis, and Amanda E. Brooks. 2023. "Recontextualizing Neuromyelitis Optica as a Systemic Condition: A Perspective" Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology 1, no. 2: 61-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1020008
APA StyleWebber, P., Landis, B. C., & Brooks, A. E. (2023). Recontextualizing Neuromyelitis Optica as a Systemic Condition: A Perspective. Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology, 1(2), 61-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1020008







