Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans
Abstract
1. Introduction
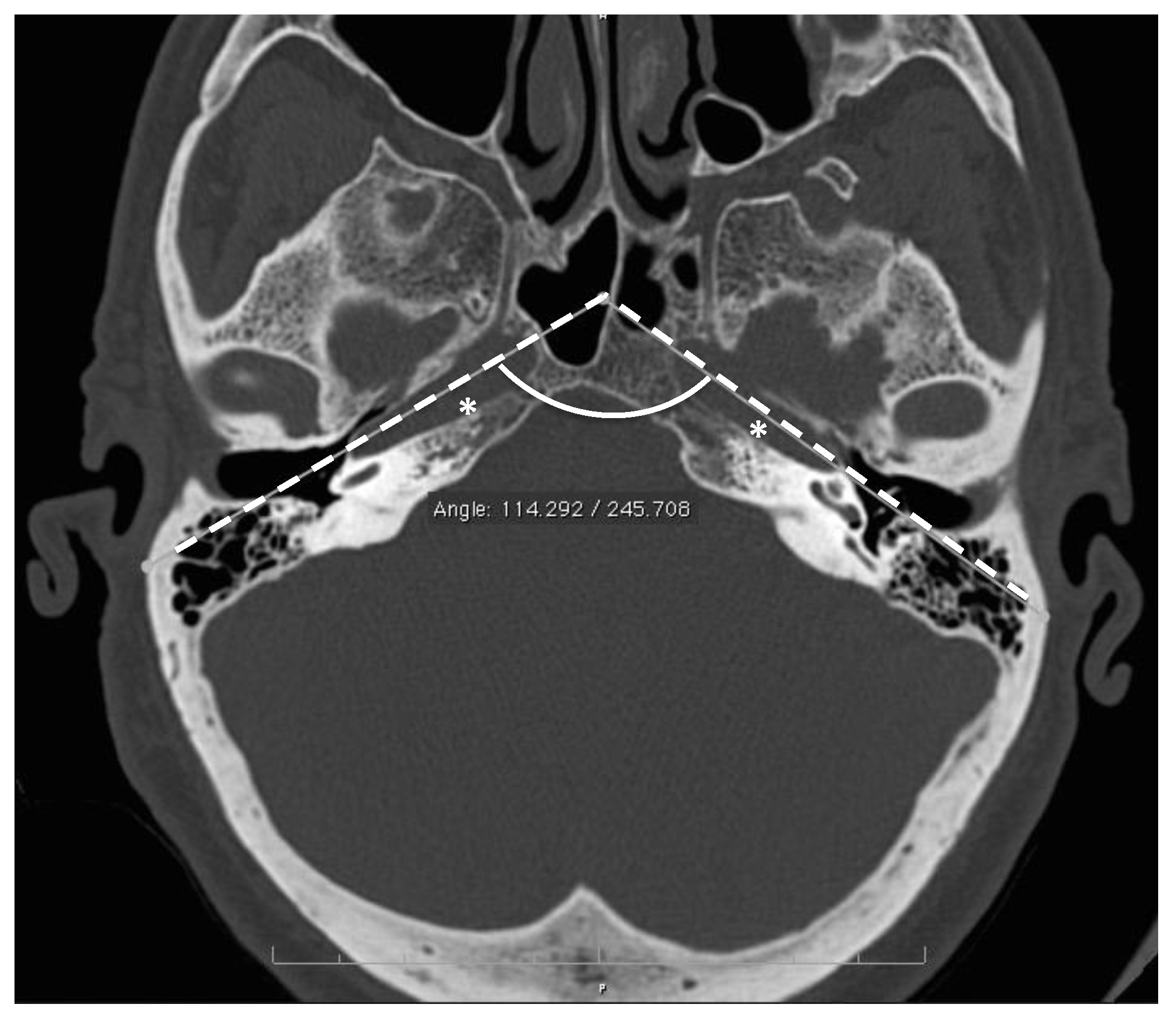
2. Materials and Methods
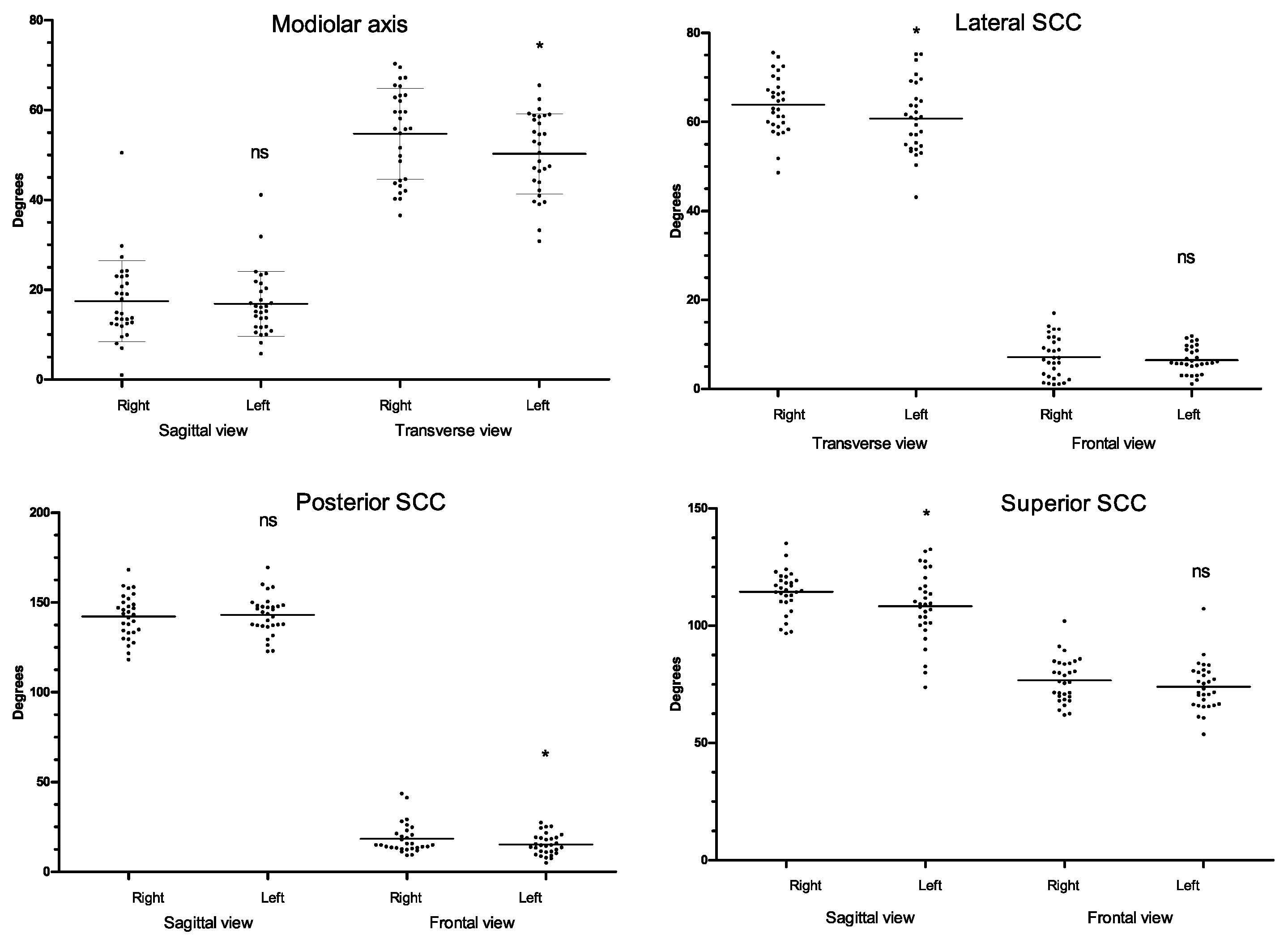
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson Chacko, L.; Schmidbauer, D.T.; Handschuh, S.; Reka, A.; Fritscher, K.D.; Raudaschl, P.; Saba, R.; Handler, M.; Schier, P.P.; Baumgarten, D.; et al. Analysis of Vestibular Labyrinthine Geometry and Variation in the Human Temporal Bone. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Santina, C.C.; Potyagaylo, V.; Migliaccio, A.A.; Minor, L.B.; Carey, J.P. Orientation of human semicircular canals measured by three-dimensional multiplanar CT reconstruction. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2005, 6, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanks, R.H.; Curthoys, I.S.; Markham, C.H. Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in man. Acta Otolaryngol. 1975, 8, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Andersen, H.; Liu, W.; Erixon, E.; Kinnefors, A.; Pfaller, K.; Schrott-Fischer, A.; Glueckert, R. Human cochlea: Anatomical characteristics and their relevance for cochlear implantation. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.; Suzuki, J.I.; Bender, M.B. Eye Movements from semicircular canal nerve stimulation in the cat. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1964, 73, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Blanks, R.H.; Markham, C.H. Semicircular canal functional anatomy in cat, guinea pig and man. Acta Otolaryngol. 1977, 83, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guigou, C.; Schein, A.; Trouilloud, P.; Lalande, A.; Hussain, R.; Grayeli, A.B. Curvilinear Multiplanar Reconstruction to Predict Useful Length and Diameter of Cochlear Lumen for Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e1207–e1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, M. The length of the organ of Corti in man. Am. J. Anat. 1938, 62, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, E.; Nauwelaers, T.; Lenarz, T.; Hamacher, V.; Kral, A. Variations in microanatomy of the human cochlea. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 3245–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietsch, M.; Schurzig, D.; Salcher, R.; Warnecke, A.; Erfurt, P.; Lenarz, T.; Kral, A. Variations in microanatomy of the human modiolus require individualized cochlear implantation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenova, K.; Stoyanov, S.; Karchev, T. Anatomic considerations for electrode implantation into the modiolus. Mediterr. J. Otol. 2007, 3, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Guigou, C.; Hussain, R.; Lalande, A.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Augmented Reality based Transmodiolar Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlebrooks, J.C.; Snyder, R.L. Intraneural stimulation for auditory prosthesis: Modiolar trunk and intracranial stimulation sites. Hear. Res. 2008, 242, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhy Afifi, W.F.; Guigou, C.; Mazalaigue, S.; Camuset, J.P.; Ricolfi, F.; Grayeli, A.B. Navigation-guided transmodiolar approach for auditory nerve implantation via the middle ear in humans. Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.D. The jugular bulb: Its anatomic and clinical considerations on contemporary otology. Laryngoscope 1977, 87, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao Trong, P.; Beynon, C.; Unterberg, A.; Schneider, T.; Jesser, J. Racial Differences in the Anatomy of the Posterior Fossa: Neurosurgical Considerations. World Neurosurg. 2018, 117, e571–e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roller, L.A.; Bruce, B.B.; Saindane, A.M. Demographic confounders in volumetric MRI analysis: Is the posterior fossa really small in the adult Chiari 1 malformation? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhide, A. Study of interpetrous angle in chronic otitis media cases. Indian J. Otolaryngol. 1983, 35, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, H. Topography of the human labyrinth in the temporal bone. Acra Anat. 1965, 60, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, M. Dimensional study of the vestibular apparatus. Laryngoscope 1967, 77, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
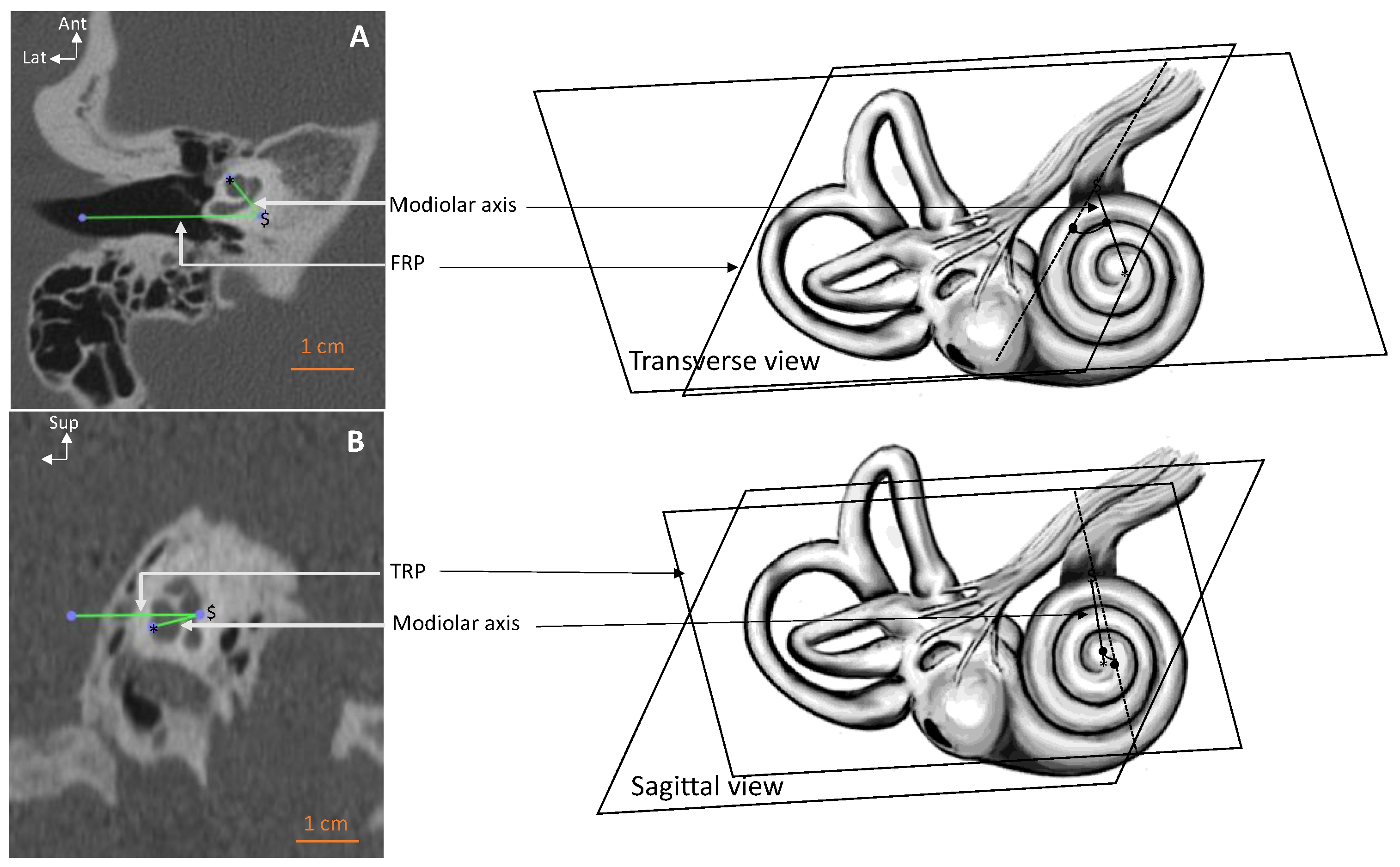
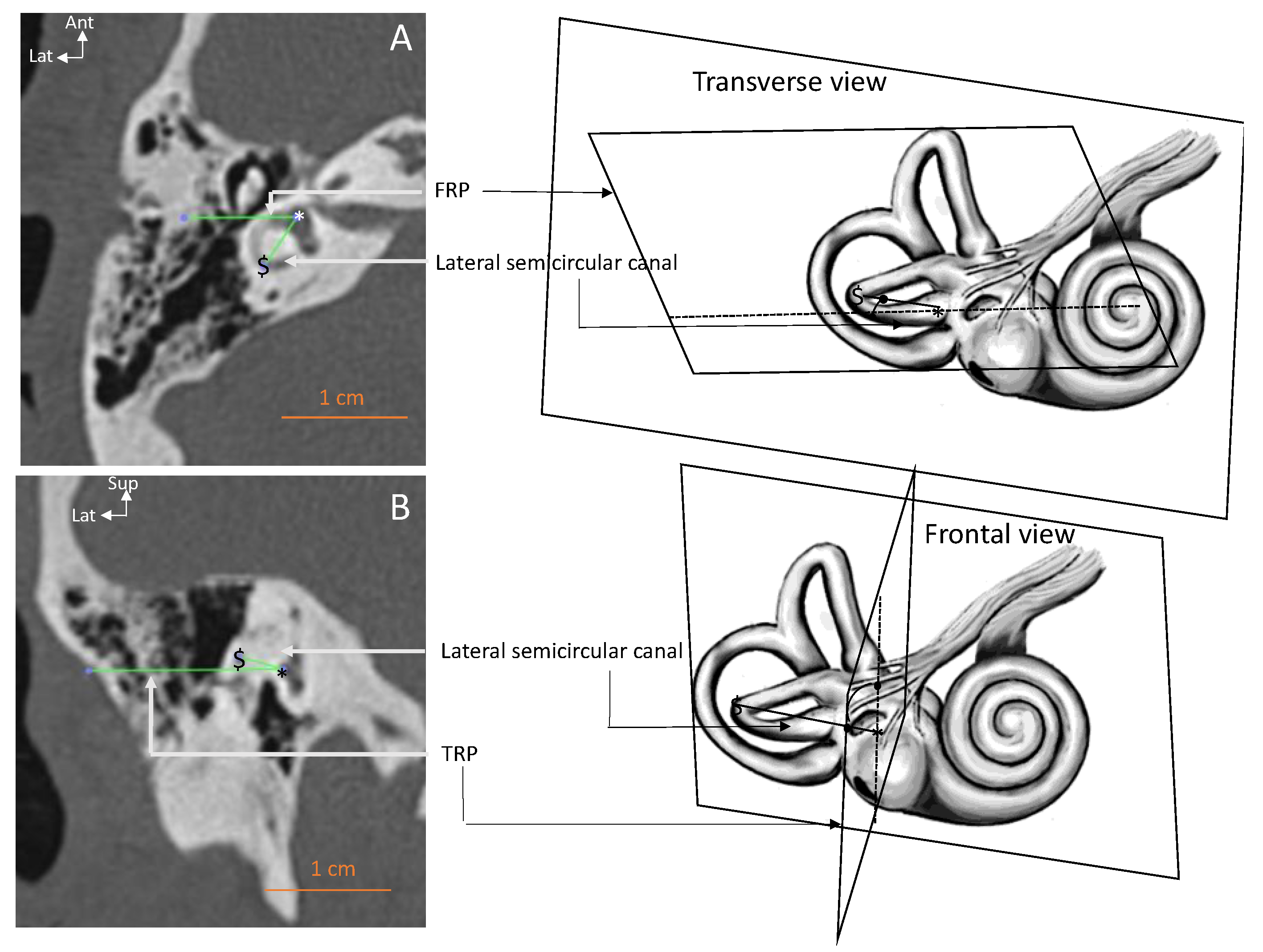
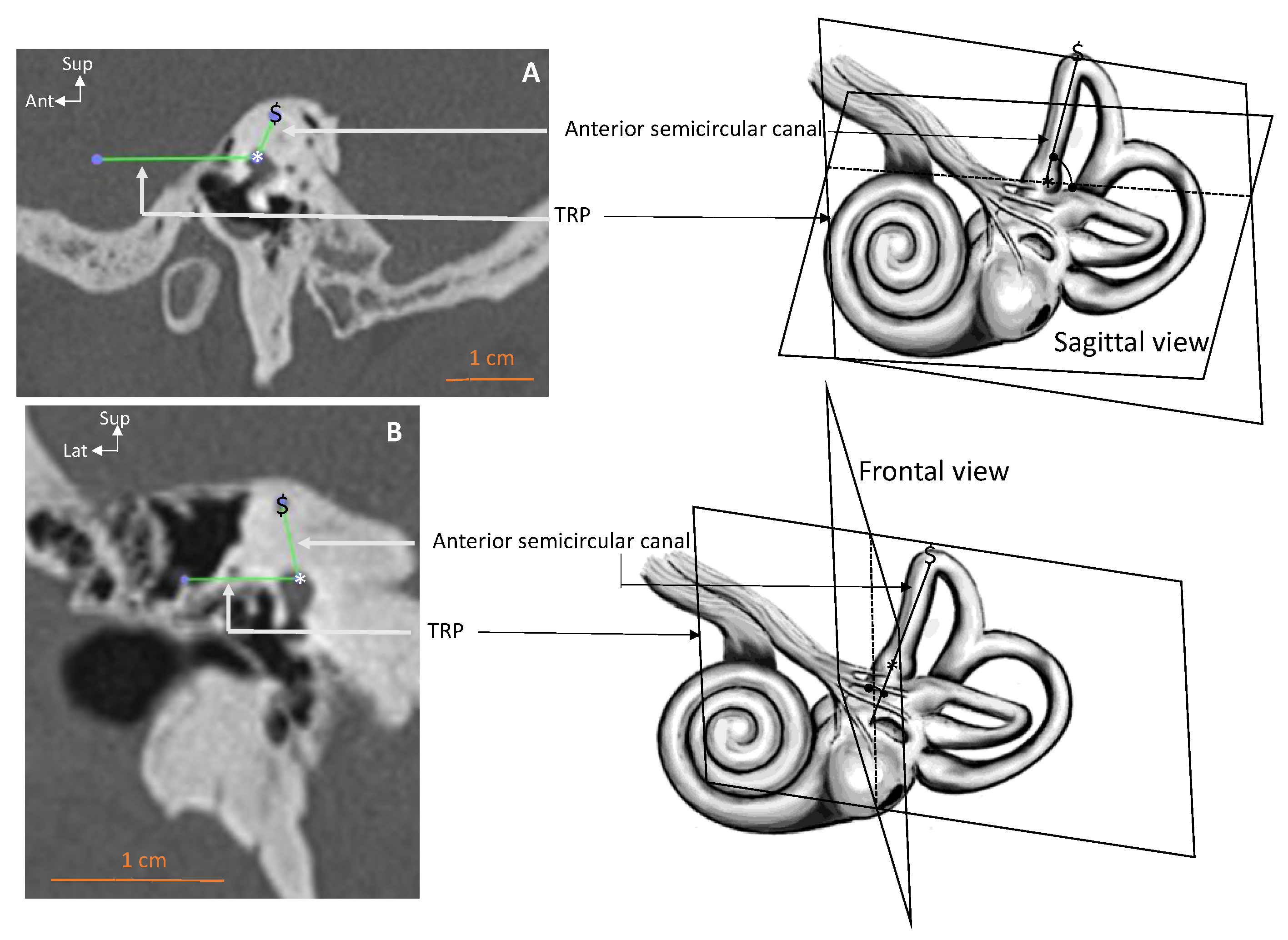
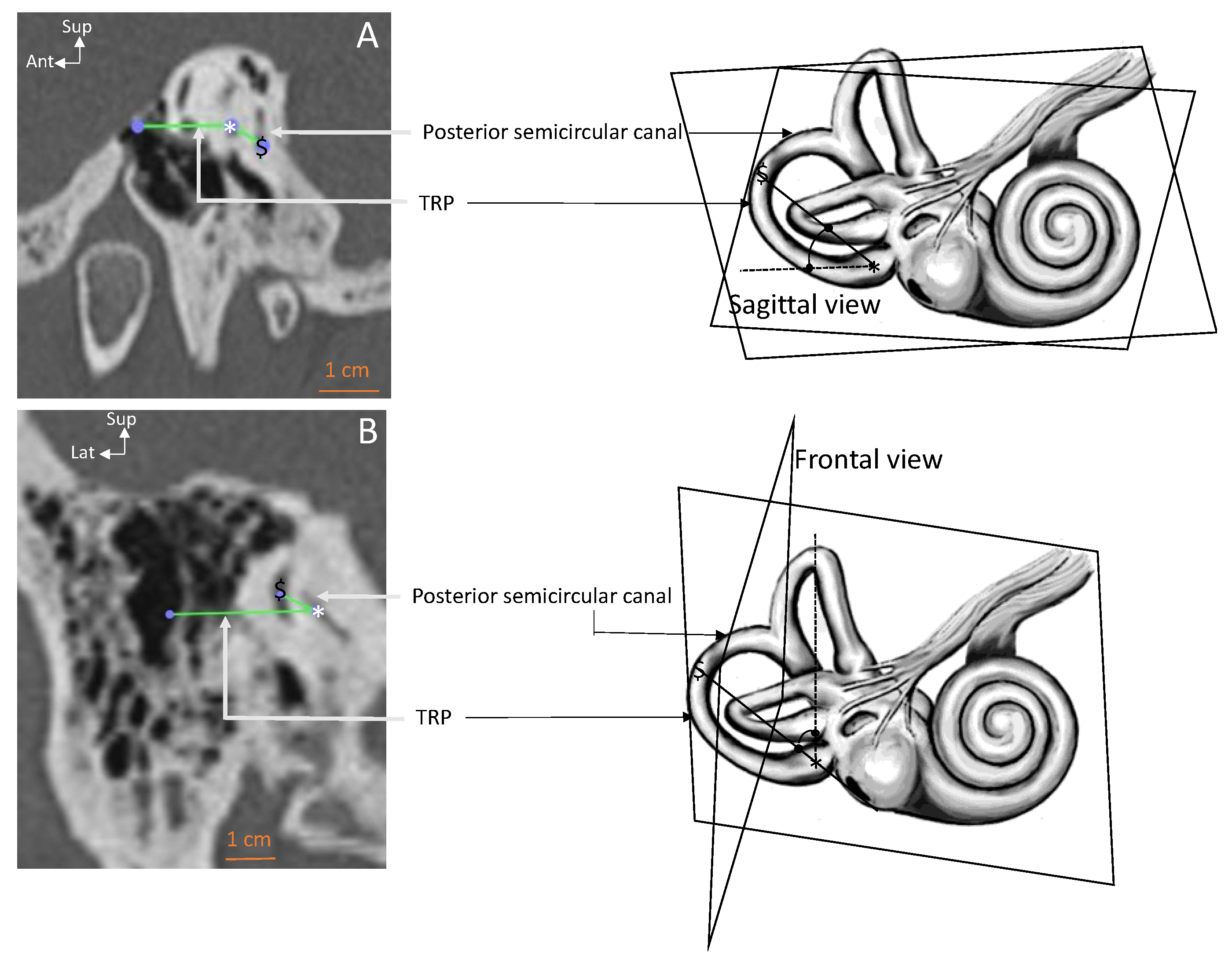
| Parameter–View | All Ears | Right Ears | Left Ears | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervestibular distance (cm) | 7.8 ± 0.38 [6.9–8.7] | - | - | 5 |
| Interpetrous angle (deg.) | 107 ± 3.7 [94–123] | - | - | 3 |
| Modiolus–transverse (deg.) | 52.5 ± 9.74 [30.8–70.3] | 54.7 ± 6.75 * | 50.3 ± 5.56 | 19 |
| Modiolus–sagittal (deg.) | 17.1 ± 8.09 [1–50.5] | 17.4 ± 5.77 | 16.8 ± 5.27 | 47 |
| Lateral SCC–transverse (deg.) | 62.3 ± 7.31 [43.1–75.6] | 63.9 ± 7.39 * | 60.8 ± 9.15 | 11.7 |
| Lateral SCC–frontal (deg.) | 6.8 ± 3.86 [1–17] | 7.1 ± 5.21 | 6.5 ± 2.01 | 57 |
| Posterior SCC–sagittal (deg.) | 142.6 ± 11.3 [118.2–169.4] | 142.2 ± 16.79 | 142.9 ± 10.25 | 8 |
| Posterior SCC–frontal (deg.) | 16.9 ± 7.34 [5–43.5] | 18.4 ± 14.93 * | 15.3 ± 8.64 | 43 |
| Superior SCC–frontal (deg.) | 75.3 ± 9.81 [53.7–107.2] | 76.7 ± 9.61 | 73.9 ± 6.79 | 13 |
| Superior SCC–sagittal (deg.) | 111.4 ± 12.53 [73.7–135.1] | 114.5 ± 7.74 * | 108.4 ± 17.88 | 11 |
| Parameter–Plane | Pearson’s r | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value (Fisher’s r to z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modiolus–Sagittal | 0.686 | 0.432–0.839 | <0.0001 |
| Modiolus–Transverse | 0.580 | 0.277–0.778 | 0.0006 |
| Lateral SCC–Frontal | 0.344 | −0.190–0.627 | 0.0625 |
| Lateral SCC–Transverse | 0.602 | 0.309–0.791 | 0.0003 |
| Posterior SCC–Frontal | 0.622 | 0.377–0.803 | 0.0002 |
| Posterior SCC–Sagittal | 0.694 | 0.446–0.844 | p < 0.0001 |
| Superior SCC–Frontal | 0.239 | −0.133–0.552 | 0.2 |
| Superior SCC–Sagittal | 0.536 | 0.218–0.751 | 0.0019 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guigou, C.; Hussain, R.; Lalande, A.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia 2023, 2, 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
Guigou C, Hussain R, Lalande A, Bozorg Grayeli A. Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia. 2023; 2(1):99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuigou, Caroline, Raabid Hussain, Alain Lalande, and Alexis Bozorg Grayeli. 2023. "Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans" Anatomia 2, no. 1: 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009
APA StyleGuigou, C., Hussain, R., Lalande, A., & Bozorg Grayeli, A. (2023). Anatomical Variations of Modiolus in Relation with Vestibular and Cranial Morphology on CT Scans. Anatomia, 2(1), 99-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia2010009







