GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis of Fecal Metabolome Stabilized Using an At-Home Stool Collection Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
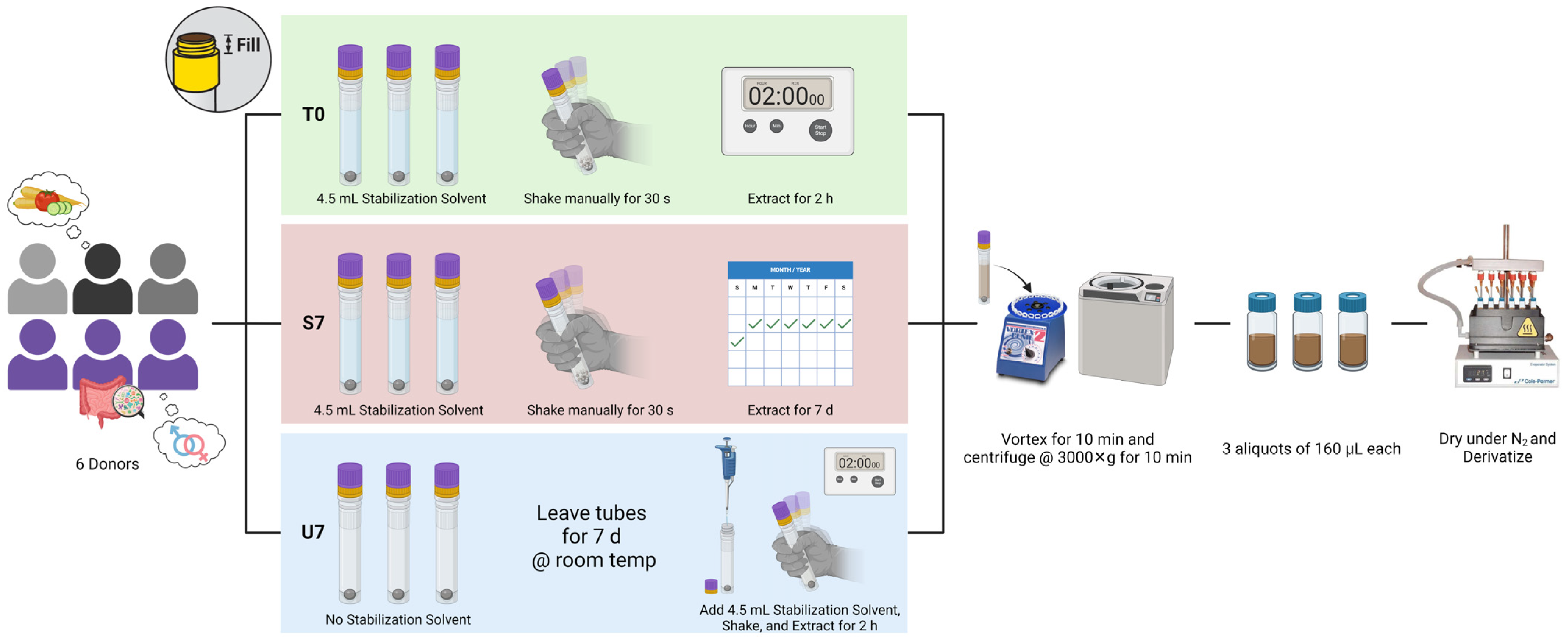
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Extraction and Stability Experiment
2.3. Derivatization
2.4. GC×GC-TOFMS Metabolomics
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. GC×GC-TOFMS Results
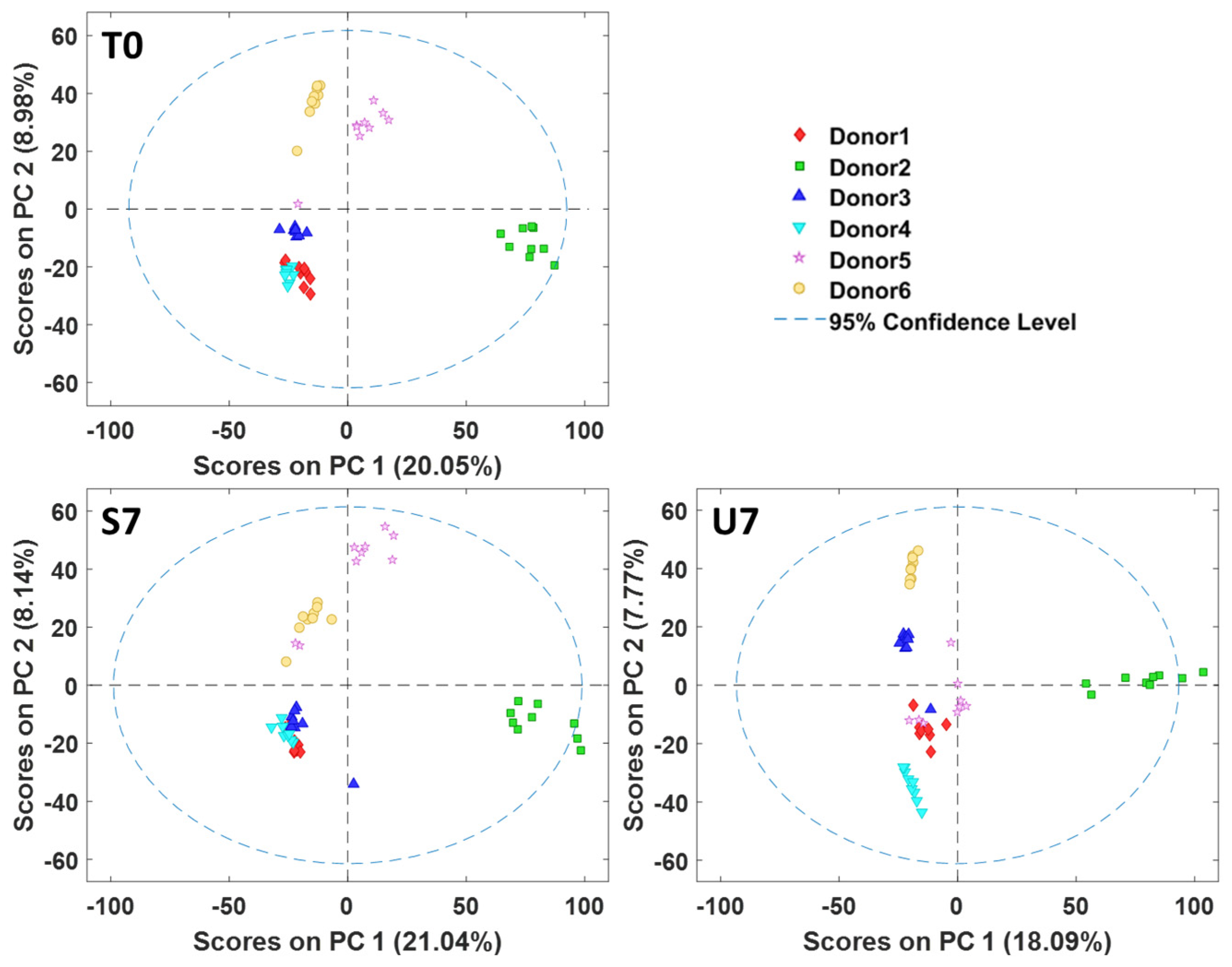
3.2. Principal Component Analysis
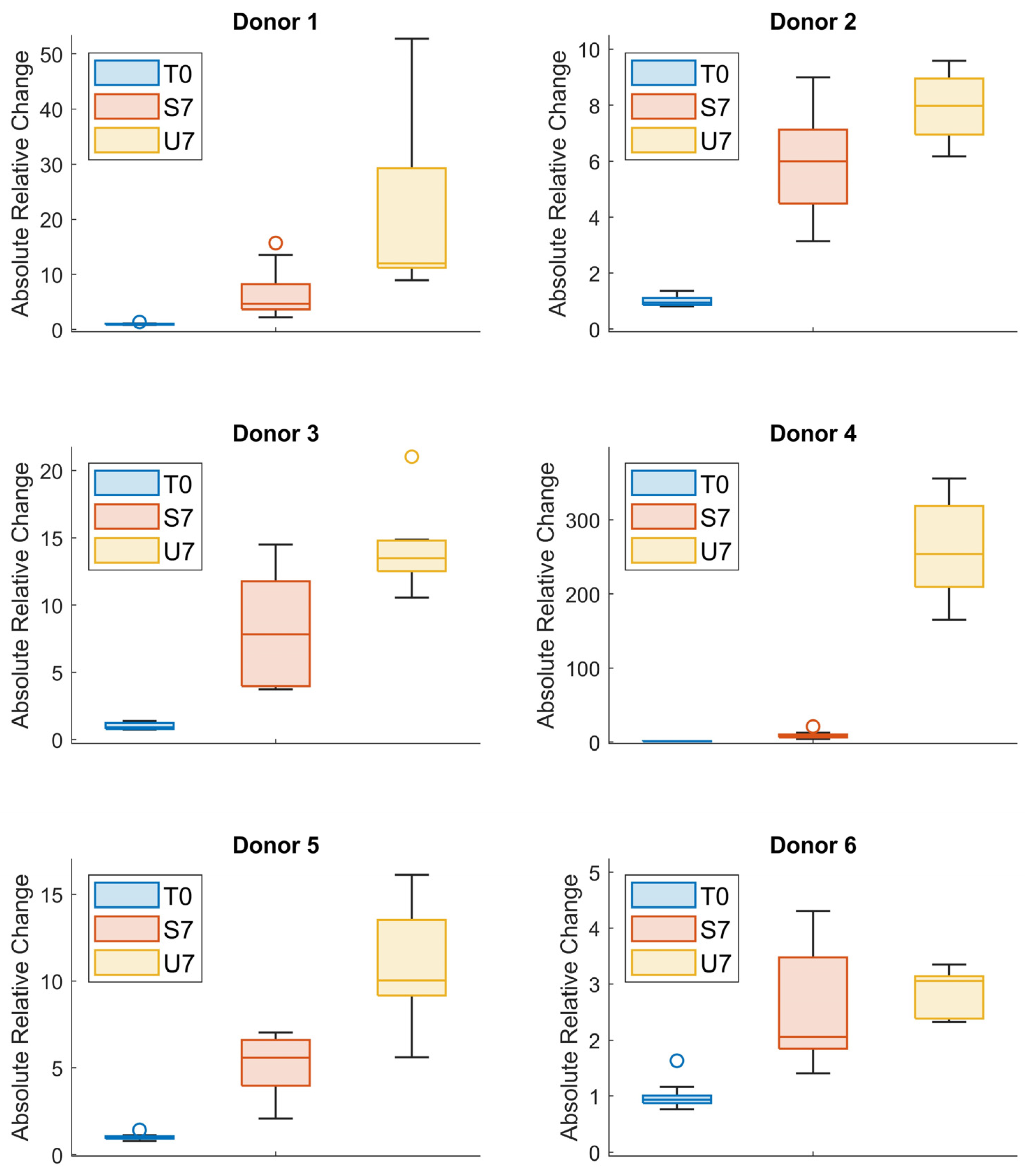
3.3. Absolute Value of the Relative Change
3.4. Considerations for Use in Research and Clinical Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—The link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebelhaus, R.T.; Biggs, L.; Murch, S.J.; Erland, L.A.E. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics to understand plant growth regulation and evolution in Wollemi pine (Wollemia nobilis). Botany 2023, 101, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, N.; Deng, L.; Slae, M.; Guo, A.C.; Sajed, T.; Huynh, H.; Wine, E.; Wishart, D.S. A review on human fecal metabolomics: Methods, applications and the human fecal metabolome database. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1030, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Rahimpour, E.; Soleymani, J.; Saei, A.A.; Jouyban, A. Breathomics: Review of Sample Collection and Analysis, Data Modeling and Clinical Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1461–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, V.L.; Hoover, E.; Wang, Y.; Zanetti, K.A. Pre-Analytical Factors that Affect Metabolite Stability in Human Urine, Plasma, and Serum: A Review. Metabolites 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochel, J.P.; Ward, J.L.; Blondel, T.; Kundu, D.; Merodio, M.M.; Zemirline, C.; Guillot, E.; Giebelhaus, R.T.; de la Mata, P.; Iennarella-Servantez, C.A.; et al. A Preclinical Model of Obesity-Independent Metabolic Syndrome for Studying the Effects of Novel Antidiabetic Therapy Beyond Glycemic Control. Research Square 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, V.; Poschet, G.; Schrotz-King, P.; Brenner, H. Evaluation of different stool extraction methods for metabolomics measurements in human faecal samples. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2021, 4, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, J.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Mullish, B.H.; Williams, H.R.T.; Thursz, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Li, J.V. Optimized Sample Handling Strategy for Metabolic Profiling of Human Feces. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4661–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, J.; Jackson, M.A.; Kastenmüller, G.; Mangino, M.; Long, T.; Telenti, A.; Mohney, R.P.; Small, K.S.; Bell, J.T.; Steves, C.J.; et al. The fecal metabolome as a functional readout of the gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-Z.; Chen, G.; Hong, Q.; Huang, S.; Smith, H.M.; Shah, R.D.; Scholz, M.; Ferguson, J.F. Multi-Omic Analysis of the Microbiome and Metabolome in Healthy Subjects Reveals Microbiome-Dependent Relationships Between Diet and Metabolites. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Xia, Y.; Qi, H.; Baker, P.N.; Zhang, H.; Han, T.-L. Evaluating different extraction solvents for GC-MS based metabolomic analysis of the fecal metabolome of adult and baby giant pandas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, K.T.; Nam, S.L.; Mata, A.P.D.L.; De Bruin, O.M.; Doukhanine, E.; Harynuk, J. Optimization of fecal sample homogenization for untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Levy, S.; Mohamed, M.; Abdelghani, A.; Evans, A.M.; Miller, L.A.D.; Mehta, L.; Moore, S.; Freinkman, E.; Hourigan, S.K. An ambient-temperature storage and stabilization device performs comparably to flash-frozen collection for stool metabolomics in infants. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzik, D.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Quality assurance procedures for mass spectrometry untargeted metabolomics. a review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.; Shi, J.; Yu, G.; Ma, B.; Ravel, J.; Goedert, J.J.; Sinha, R. Collection media and delayed freezing effects on microbial composition of human stool. Microbiome 2015, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.M.; Leong, L.E.; Rogers, G.B. Sample storage conditions significantly influence faecal microbiome profiles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftfield, E.; Vogtmann, E.; Sampson, J.N.; Moore, S.C.; Nelson, H.; Knight, R.; Chia, N.; Sinha, R. Comparison of Collection Methods for Fecal Samples for Discovery Metabolomics in Epidemiologic Studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Zhou, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Effect of storage conditions on the assessment of bacterial community structure in soil and human-associated samples: Influence of short-term storage conditions on microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 307, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Amir, A.; Metcalf, J.L.; Amato, K.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Humphrey, G.; Knight, R. Preservation Methods Differ in Fecal Microbiome Stability, Affecting Suitability for Field Studies. mSystems 2016, 1, e00021-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, I.M.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Siddle, J.P.; Klaenhammer, T.R.; Ringel, Y. Characterization of the Fecal Microbiota Using High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals a Stable Microbial Community during Storage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.-H.; Kuang, Y.-S.; He, J.-R.; Lu, J.-H.; Luo, B.-J.; Jiang, F.-J.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Papasian, C.J.; Xia, H.-M.; et al. Effect of short-term room temperature storage on the microbial community in infant fecal samples. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, J.; Cools-Portier, S.; Pavan, S.; Druesne, A.; Öhman, L.; Törnblom, H.; Simren, M.; Derrien, M. Effects of the long-term storage of human fecal microbiota samples collected in RNAlater. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.; Acero, M.M.; Doukhanine, E.V.; Iwasiow, R.M.; Hernandez, C.A.M. Device for Collecting, Transporting and Storing Biomolecules from a Biological Sample. U.S. Patent Application No. 15/310,698, 16 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Isokääntä, H.; Pinto da Silva, L.; Karu, N.; Kallonen, T.; Aatsinki, A.-K.; Hankemeier, T.; Schimmel, L.; Diaz, E.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Dorrestein, P.C.; et al. Comparative Metabolomics and Microbiome Analysis of Ethanol versus OMNImet/geneGUT Fecal Stabilization. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 8893–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins Keppler, E.A.; Jenkins, C.L.; Davis, T.J.; Bean, H.D. Advances in the application of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography in metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.L.; De La Mata, A.P.; Dias, R.P.; Harynuk, J.J. Towards Standardization of Data Normalization Strategies to Improve Urinary Metabolomics Studies by, GC×GC-TOFMS. Metabolites 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebelhaus, R.T.; de la Mata, A.P.; Harynuk, J.J. Region of interest selection for GC×GC–MS data using a pseudo fisher ratio moving window with connected components segmentation. J. Chromatogr. Open 2023, 4, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.L.; Tarazona Carrillo, K.S.; de la Mata, A.P.; Giebelhaus, R.T.; de Bruin, O.M.; Doukhanine, E.; Harynuk, J.J. Evaluation of solution chemistries for stabilizing feces in metabolomics studies using GC×GC-TOFMS. Metabolomics 2024. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.L.; Giebelhaus, R.T.; Tarazona Carrillo, K.S.; de la Mata, A.P.; Harynuk, J.J. Evaluation of normalization strategies for GC-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2024, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Spiegeleer, M.; De Graeve, M.; Huysman, S.; Vanderbeke, A.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Vanhaecke, L. Impact of storage conditions on the human stool metabolome and lipidome: Preserving the most accurate fingerprint. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1108, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giebelhaus, R.T.; Nguyen, G.; Schmidt, S.A.; Wang, S.; Mesfin, E.Y.; Nam, S.L.; de la Mata, A.P.; Harynuk, J.J. GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis of Fecal Metabolome Stabilized Using an At-Home Stool Collection Device. Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3, 348-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3030023
Giebelhaus RT, Nguyen G, Schmidt SA, Wang S, Mesfin EY, Nam SL, de la Mata AP, Harynuk JJ. GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis of Fecal Metabolome Stabilized Using an At-Home Stool Collection Device. Applied Biosciences. 2024; 3(3):348-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiebelhaus, Ryland T., Gwen Nguyen, Sheri A. Schmidt, Seoin Wang, Ewenet Y. Mesfin, Seo Lin Nam, A. Paulina de la Mata, and James J. Harynuk. 2024. "GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis of Fecal Metabolome Stabilized Using an At-Home Stool Collection Device" Applied Biosciences 3, no. 3: 348-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3030023
APA StyleGiebelhaus, R. T., Nguyen, G., Schmidt, S. A., Wang, S., Mesfin, E. Y., Nam, S. L., de la Mata, A. P., & Harynuk, J. J. (2024). GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis of Fecal Metabolome Stabilized Using an At-Home Stool Collection Device. Applied Biosciences, 3(3), 348-359. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3030023










