Abstract
Due to the aromatase enzyme’s involvement in estrogen biosynthesis, aromatase inhibitors have emerged as the preferred treatment for postmenopausal women with ER+ breast cancer. Using computational chemistry tools, we investigate how the human placental aromatase cytochrome P450 interacts with various phorbols with distinct chains at C-12, C-13, and C-20, as well as the well-known aromatase inhibitors anastrozole, exemestane, and letrozole. To identify phorbol-aromatase interactions, we performed a protein–ligand docking using the structures of our ligands and proteins using the Flare software (version 2.0, Cresset Software, Litlington, UK). These preliminary findings show that the phorbols considered (P-12,13-diAcPh, P-12,13-diiBu, P-12AcPh-13iBu, P-12Ang-13iBu, P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu and P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu) had the highest binding energies in comparison with the commercially available aromatase inhibitors (anastrozole, letrozole, exemestane) used in this study. A subset of the previously described binding residues of testosterone (TST), the endogenous ligand, were also found to be responsible for the phorbol diesters’ binding to the aromatase enzyme, as demonstrated by the findings. This further suggests that the phorbol diesters can bind efficiently to CYP19A1 and may be able to alter its activity because they had higher binding energies than the commercially available drugs.
1. Introduction
Cancer is a significant health challenge worldwide; its prevalence and mortality rate are rising rapidly [1]. Many women worldwide die from cancer-related causes, including breast cancer, the most common type of cancer diagnosed in women [1,2]. The Global Cancer Observatory 2020 factsheet states that breast cancer accounts for approximately 2.2 million new cases of cancer worldwide [3]. Breast cancer is a complex disease without a known cause, with genetic alteration being one of the significant risk factors [1]. The term “breast cancer” frequently refers to cancers that originate in breast tissue, typically in the milk duct lobules or their inner linings [4]. Multiple cell types are involved in the multistage process of breast cancer development [5]. The prevention of breast cancer remains a challenge, and it is also the second leading cause of women’s cancer-related deaths [5]. The early diagnosis of breast cancer is one of the prevention strategies [5]. Notwithstanding, one of the significant difficulties in the therapy of breast cancer is because of the heterogeneity of the disease [6].
Breast ductal hyperplasia is the starting point for breast tumors, which can progress into benign tumors or metastatic carcinomas after being repeatedly stimulated by a number of carcinogenic factors [5]. Breast cancer is generally diagnosed using a mammograph; another method of diagnosis is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [5]. Based on the presence or absence of molecular markers for estrogen, progesterone, and human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2), breast cancer is divided into three main categories [7]. Estrogen receptor alpha (ER), which is expressed in approximately 70% of invasive breast cancers, is one of the two primary molecular targets in the pathogenesis of breast cancer and the steroid hormone progesterone receptor (PR), which is also a biological marker for Erα signaling [7]. The transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase HER2, which is overexpressed in about 20% of breast cancers, is the other molecular target [7]. When systemic therapy is unavailable, HER2 has been linked to a poor prognosis [7]. HER2 does not participate in ligand binding; however, the activation of HER2 is through the homotypic or heterotypic interactions between the extracellular domain of HER2 and other epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-like receptors [6].
The enzyme human aromatase (HA) is encoded by the gene CYP19 (which can be found on chromosome 15q21.2) [2]. The enzyme (HA), which belongs to the cytochrome P450 family, is important in the process of converting androgens to estrogens [2,8,9]. The biosynthesis of estrogens is catalyzed by the aromatase enzyme. From C19 androgens (androstenedione and testosterone), it initiates the production of aromatic C18 estrogens (estrone and estradiol) [1,2]. The ovaries, as well as other extragonadal tissues such as the brain, liver, bone, vascular endothelial tissues, and the mesenchymal cells of the breast’s adipose tissue, contain the enzyme aromatase [1,2]. Estrogens are synthesized in several extra ovarian tissues, such as adipose tissues and bones, in postmenopausal women, whereas estrogens are synthesized in the ovarian granulosa and corpus luteum cells in premenopausal women [1]. An association between breast cancer and the expression levels of the gene CYP19A1 was previously described [1,10,11,12]. However, the relationship between expression levels and breast cancer survival and progression requires clarification [1]. Estrogens and their metabolites have been linked to breast cancer development in some studies [2,13,14]. Tamoxifen, a common hormonal therapy and selective estrogen receptor modulator, was regarded as the standard treatment for hormone-responsive breast cancer in premenopausal and postmenopausal women [2,15].
In postmenopausal women with estrogen-receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer, aromatase inhibitors are now the preferred treatment option [16,17,18]. Aromatase inhibitors work by inhibiting estrogens biosynthesis, thus preventing tumor development [16]. These drugs have been associated with better outcomes clinically, including decreased risks of all-cause and breast-cancer-related mortality, in comparison with tamoxifen [18]. There are two primary categories of aromatase inhibitors: (i) steroidal inhibitors (type 1 inhibitors) that bind covalently to the aromatase enzyme–substrate binding site; (ii) non-steroidal inhibitors (type 2 inhibitors) that bind noncovalently to the heme moiety of the aromatase and reversibly compete with the enzyme [19,20,21,22]. Several studies have synthesized new compounds as potential aromatase inhibitors [20,21,22]. The findings of these studies showed aromatase inhibitory activity in a sub-micromolar range [20,21,22]. It has been demonstrated previously that phorbol esters interact with protein kinase C [23,24,25]. The findings of a study investigating the effect of phorbol diesters and 12-Deoxy-16-hydroxyphorbol 13,16-Diesters showed that they affected adult mouse neurogenesis and induced transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα) release [26]. We herein used computational chemistry tools to examine the interaction between phorbols bearing chain variations at C-12, C-13 and C-20 and the known aromatase inhibitors anastrozole, exemestane and letrozole (Figure 1) and the human placental aromatase cytochrome P450 (PDB ID: 5JKW [27]).

Figure 1.
Schematic image of the chemical structures of the phorbol diesters used in the study. 1. P-12,13-diAcPh: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-9-(2-(cyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)acetoxy)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1,1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9-decahydro-9aH-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9a-yl 2-cyclohexylacetate. 2. P-12,13-diiBu: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1,1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9-decahydro-9aH-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulene-9,9a-diyl bis(2-methylpropanoate). 3. P-12AcPh-13iBu: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-9-(2-cyclohexylacetoxy)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1,1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9-decahydro-9aH-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9a-yl isobutyrate. 4. P-12Ang-13iBu: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-9a-(isobutyryloxy)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9,9a-decahydro-1H-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9-yl (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate. 5. P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-9-(2-(cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-yl)acetoxy)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1,1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9-decahydro-9aH-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9a-yl iso-butyrate. 6. P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu: (1aR,1bS,4aR,7aS,7bS,8R,9R,9aS)-3-(acetoxymethyl)-4a,7b-dihydroxy-9a-(isobutyryloxy)-1,1,6,8-tetramethyl-5-oxo-1a,1b,4,4a,5,7a,7b,8,9,9a-decahydro-1H-cyclopropa[3,4]benzo[1,2-e]azulen-9-yl (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate. 7. Anastrozole. 8. Letrozole. 9. Exemestane.
2. Materials and Methods
To identify phorbol–aromatase interactions, we performed a protein–ligand docking using the structures of our ligands and the human placental aromatase cytochrome P450 (CYP19A1). The structure 5JKW was selected because it was crystalized using the endogenous ligand Testosterone. The Flare software was used to prepare the protein and ligand structures (version 2.0, Cresset Software, Litlington, UK). The full preparation of the protein and ligand at a pH of 7.0 and active site size of 6.00 Å adds missing hydrogens to the protein(s) and cofactor(s), and also assigns the best ionization states to the protein residues. It maximizes hydrogen bonding and reduces steric interference by optimizing the spatial locations of polar hydrogen atoms. His, Asn, and Gln side chains are optimized for side chain orientation, and then residues with unresolved side chains are found and reconstructed. During the preparation step, the endogenous ligands testosterone and heme were extracted from the protein structure. The XED-accurate approach on Flare was then used to minimize the protein and ligands. The docking calculation was set to the “very accurate but slow” option (this option in the software is based on the genetic algorithm; it performs three independent docking runs to achieve the lowest possible calculated binding energy for the protein–ligand complex). The grid box was set by selecting all the amino acid residues present in the protein. The docking was validated by redocking the endogenous ligand testosterone and the heme into the binding pocket. The BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer, version 19.1, was used to visualize the poses with the highest binding energy (Dassault Systemes, San Diego, CA, USA). The PRODIGY web server was used to analyze the protein–ligand complexes’ binding affinities [28,29].
3. Results and Discussions
Table 1 shows the ligand binding energy upon docking into CYP19A1. Flare lead finder module ranked the ligand poses produced during the docking run [30,31]. The dG-score provides a free energy value of protein–ligand binding for any protein–ligand complex being investigated [30,31]. Presented in Table 1 are the results of the binding affinity analysis.

Table 1.
Table showing the binding energy of the compounds and binding affinities of the docked complexes.
The results in Table 1 showed that the phorbol diesters had higher binding energies than the commercially available aromatase inhibitors. The diester P-12,13-diAcPh had the highest binding energy value (−13.993 Kcal/mol) in comparison to the aromatase inhibitor Anastrozole with a binding energy of −7.301 Kcal/mol. The phorbol diesters having higher binding energies implies a more stable protein–ligand complex than the commercially available aromatase inhibitors. This was in line with the findings of Rampogu et al.; their results showed that the 81 compounds they looked at had interaction energies that were higher than those of known drug candidates [32]. The ligands evaluated in this study docked in the same binding pocket interacting with similar amino acid residues. This pose was validated by redocking the endogenous ligand testosterone. The binding pocket identified in this study is also consistent with the binding pocket identified in previous studies [32,33]. A previous study also showed that amino acid residues such as A307, V370, T310, F134, F221, W224, A306, S478, M374, D309, L372 and L477 play significant roles in the interaction of aromatase inhibitors and the aromatase enzyme [33,34,35,36].
An important pharmacodynamic endpoint in the drug discovery process is protein–ligand binding affinity [37]. In molecular docking and rational drug discovery, predicting protein–ligand binding affinity is crucial [38]. Binding affinity is a measure of the strength between binding drug molecule(s) and protein(s) [39]. In thermodynamic terms, the binding affinity of any complex is essential in determining whether or not a reaction will take place within a cell under certain conditions [40]. The PRODIGY-LIG webserver determines a complex’s binding affinity in Kcal/mol by utilizing atomic contacts between the protein and the ligand within a distance of 10.5 Å [28].The findings of the binding affinity analysis showed that the phorbol diesters (P-12,13-diAcPh, −13.7 Kcal/mol; P-12,13-diiBu, −11.5 Kcal/mol; P-12AcPh-13iBu, −12.9 Kcal/mol; P-12Ang-13iBu, −11.8 Kcal/mol; P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu, −13.0 Kcal/mol and P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu, −12.3 Kcal/mol) had higher binding affinities than the commercial inhibitors (Letrozole, −8.2 Kcal/mol; Anastrozole, −8.4 Kcal/mol and Exemestane, −10.3 Kcal/mol) studied. The binding affinity results shown in Table 1 demonstrates the thermodynamic feasibility of the docked complexes. The phorbols had the highest binding energies and binding affinities in comparison with the commercially available aromatase inhibitors (Table 1). The results in Table 1 suggest that P-12,13-diAcPh would bind strongly to the binding site of the human aromatase enzyme.
Most of the interactions observed in the P-12,13-diAcPh-5JKW complex were alkyl and pi-alkyl. The residues Arg 145, Ala 438 and Glu 302 formed hydrogen bonds with the ligand (Figure 2A). The majority of the residues present in the binding site were non-polar (Trp 141, Ile132, Ala 438, Ala 306, Val 370, and Phe 430). The residues Arg 435 and Arg 145 are polar and positively charged. The residue Arg 435 plays a significant role in heme binding in the active site of CYP19A1 [34]. The residues Glu 302 and Cys 437 are negatively charged and polar, respectively (Figure 2A). The residue Glu 302 is a highly conserved residue in the active site of CYP19A1; it plays a significant role in the inhibition of aromatase [35,36]. P-12,13-diiBu interacted with mostly non-polar residues except the residue Cys 437 (Figure 2B). Hydrogen bonds were formed between Cys 437, Ala 438, Ala 307, Gly 439, Ala 306 and Met 303; the rest of the residues formed alkyl and pi-alkyl interactions. The ligand P-12AcPh-13iBu interacted with the vast majority of non-polar residues. The residues His 480, Arg 115 and Cys 437 were the only polar residues interacting with this ligand (Figure 2C). Alkyl and pi-alkyl interactions were observed with most of the residues except Ala 438, Arg 115 and Phe 430 which formed hydrogen bonds with the ligand P-12AcPh-13iBu.
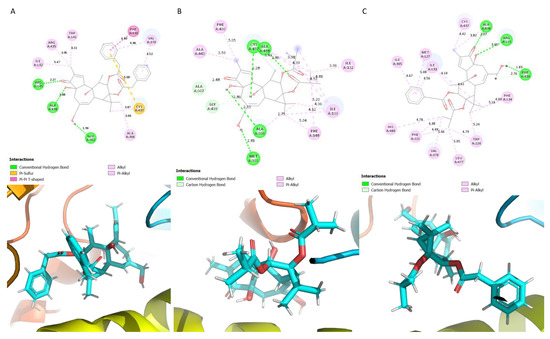
Figure 2.
Schematic showing the protein ligand interactions (A) P-12,13-diAcPh, (B) P-12,13-diiBu and (C) P-12AcPh-13iBu.
The ligands P-12Ang-13iBu, P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu and P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu interacted with non-polar residues, bar the residue Cys 437 which is polar (Figure 3). The ligand P-12Ang-13iBu formed a carbon–hydrogen interaction with the residues Ala 307 and Gly 439 (Figure 3A). Hydrogen bonds were also formed with Cys 437, Ala 438, Ala 306 and Met 303 (Figure 3A). Hydrogen bonds were formed with Ala 438, Cys 437 and Ala 306 and the phorbol diester P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu (Figure 3B). Ala 307 and Gly 439 formed carbon hydrogen interactions with the ligand; the rest of the interacting residues formed alkyl and pi-alkyl interactions (Figure 3B). Ala 307 and Gly 439 formed carbon hydrogen bonds with the ligand, Ala 438, Cys 437 and Ala 306 formed hydrogen bonds with the phorbol diester P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu (Figure 3C).
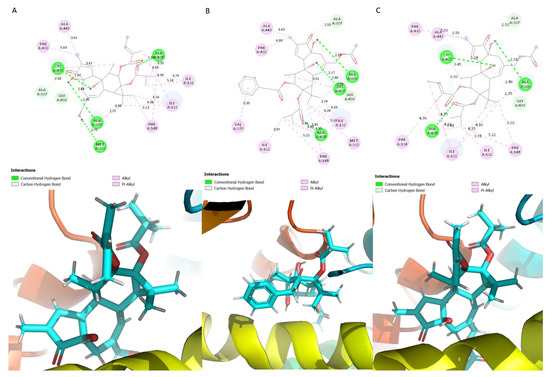
Figure 3.
Schematic showing the protein ligand interactions (A) P-12Ang-13iBu (B) P-20Ac-12AcPh-13iBu (C) P-20Ac-12Ang-13iBu.
The aromatase inhibitor anastrozole interacted with mostly non-polar residues with the exception of Tyr 220, Ser 478 and His 480, which were the only polar residues interacting with the ligand (Figure 4A). A carbon–hydrogen bond and pi-anion interaction was observed between the benzene ring of the ligand anastrozole and the amino acid residue Asp 309 (Figure 4A). Hydrogen bonds were formed between His 480 and Ser 478; the residues Trp 224 and Tyr 220 formed a pi–pi t-shaped interaction with the anastrozole (Figure 4A). Letrozole interacted with non-polar residues with the exception of Ser 314 (Figure 4B). Carbon–hydrogen bonds were formed with Thr 310 (a pi–pi t-shaped interaction was also formed) and Ser 314, and a Pi–sulphur interaction was formed with the ligand Letrozole (Figure 4B). Phe 430 formed an amide–pi stacked interaction with the ligand (Figure 4B). The ligand exemestane interacted with only five residues: Ile 133, Ala 438, Arg 145, Cys 437 and Ile 132 (Figure 4C). The residue Arg 145 formed a hydrogen bond with the ligand exemestane; the other interacting residues formed alkyl interactions with the ligand. The findings of this study are in line with those of a previous study regarding the residues that were identified [33].
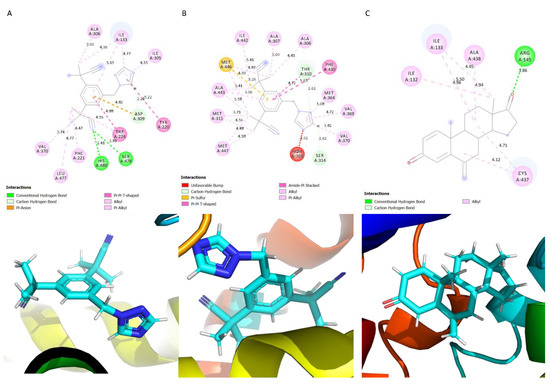
Figure 4.
Schematic showing the protein–ligand interactions. (A) Anastrozole, (B) Letrozole, (C) Exemestane.
The endogenous ligand testosterone interacted with the following residues: Met 374, Arg 115, Val 373, Val 370, Asp 309, Ala 306, Trp 224, Leu 477 and the heme molecule. The phorbol diesters also interacted with some of the of the amino acid residues (Ala 306, Val 370, Leu 477, Trp 224, Arg 115, Asp 309) that the endogenous ligand testosterone (TST) interacted with in the CYP19A1 binding site. This confirmed that a number of the previously described binding residues of TST (the endogenous ligand) interacted with the phorbol diesters and commercially available drugs (Letrozole, Exemestane, and Anastrozole) upon docking to the aromatase enzyme binding site [27]. The hydrophobic side chains Trp 224, Phe 221, Phe 134, Ile 133, Val 370, and Met 374 surrounded the ligand binding site, shaping the active site cleft to precisely match the TST structure [27]. In addition to the heme group cofactor, these residues are important for ligand binding [22,27].
4. Conclusions
The aromatic C18 estrogens (estrone and estradiol) are produced by the enzyme aromatase in the steroid biosynthesis pathway from C19 androgens. The inhibition of CYP19A1 activity could potentially lead to high androgen levels, which is usually linked to disorders such as ovarian cancer, infertility, and prostate cancer. Previous research has described the functions of protein kinase C (PKC) and phorbol diesters. Cytotoxic 4-phorbol esters were used to target cancerous tissues. The findings demonstrated that the phorbol prodrug effectively eliminated peptidase-positive and -negative cells and activated PKC [41]. Tsai et al. studied the activation of PKC by phorbol esters using platelet aggregation as a model. The results of the study by Tsai et al. showed that platelets are a useful model to study natural PKC activators [42]. The interactions between the aromatase and phorbol diesters have been investigated herein using molecular docking as a coarse-grained computational analytical technique. The findings of this computational study suggest that phorbol-CYP19A1 complexes can display higher binding energies than currently available drugs.
The residue Ala 438 formed hydrogen bond interactions with the phorbol diesters. However, no interaction was seen with the commercially available treatment options, except for the ligand exemestane, which formed an alkyl interaction with the residue. The phorbol diesters in this study formed alkyl interactions with the residue Phe 430, except P-12AcPh-13iBu, which resulted in a hydrogen bond interaction with the residue. A pi–pi T-shaped interaction was, however, observed with P-12,13-diAcPh and Letrozole. The reoccurrence of these residues would suggest that they play a role in binding of the phorbol diesters to CYP19A1. The results of the binding affinity analysis showed the ligand P-12,13-diAcPh had the highest binding affinity value (−13.7 Kcal/mol). This suggests a very strong binding between P-12,13-diAcPh and the human aromatase enzyme. The ligand P-12,13-diAcPh also had a higher binding energy (−13.993 Kcal/mol) from the docking calculation.
Analysis of the ligand binding pocket showed that the majority of the residues interacting with the ligands were all hydrophobic. This is because the highest region of conversation in cytochrome P450 enzymes is the binding pocket; this binding pocket contains the heme moiety and hydrophobic residues, which accommodate the heme group [43]. Anam et al. reported that the binding pocket of the aromatase enzyme needs to comprise primarily non-polar residues to facilitate the conversion of hydrophobic androstenedione to estrone [44]. In conclusion, our findings show that using a coarse-grained technique, the phorbol diesters were bound to the accurate binding pocket and may be able to potentially mediate the activity of CYP19A1. This is subject to further characterization using advanced methods such as molecular dynamics simulations, ligand binding assays and breast cancer cell lines to determine the mechanism of action of these phorbol diesters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B.W. and S.W.; methodology, P.B.W. and Z.A.; software, C.S.O.; validation, E.H., D.E. and B.B.; formal analysis, C.S.O.; investigation, C.S.O.; resources, P.B.W.; data curation, Z.A.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S.O.; writing—review and editing, P.B.W.; visualization, C.S.O.; supervision, E.H., S.W and P.B.W.; project administration, E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the nature of the datasets contained herein and their relative size.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barros-Oliveira, M.d.C.; Costa-Silva, D.R.; Dos Santos, A.R.; Pereira, R.O.; Soares-Júnior, J.M.; Silva, B.B.d. Influence of CYP19A1 gene expression levels in women with breast cancer: A systematic review of the literature. Clinics 2021, 76, e2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artigalás, O.; Vanni, T.; Hutz, M.H.; Ashton-Prolla, P.; Schwartz, I.V. Influence of CYP19A1 polymorphisms on the treatment of breast cancer with aromatase inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GLOBOCAN. Breast Cancer Fact Sheet. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Sharma, G.N.; Dave, R.; Sanadya, J.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, K.K. Various types and management of breast cancer: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.N.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.J.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Yao, P.P.; Zhu, H.P. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, J.; Baselga, J.; Pedersen, K.; Parra-Palau, J.L. p95HER2 and Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgrignani, J.; Cavalli, A.; Colombo, G.; Magistrato, A. Enzymatic and inhibition mechanism of human aromatase (CYP19A1) enzyme. A computational perspective from QM/MM and classical molecular dynamics simulations. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santen, R.J.; Brodie, H.; Simpson, E.R.; Siiteri, P.K.; Brodie, A. History of Aromatase: Saga of an Important Biological Mediator and Therapeutic Target. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 343–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Iyengar, N.M.; Zhou, X.K.; Gucalp, A.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Wang, H.; Giri, D.D.; Morrow, M.; Falcone, D.J.; Wendel, N.K.; et al. Menopause Is a Determinant of Breast Aromatase Expression and Its Associations With BMI, Inflammation, and Systemic Markers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüzüner, M.B.; Öztürk, T.; Eronat, A.P.; Seyhan, F.; Kısakesen, H.İ.; Calay, Z.; İlvan, Ş.; Turna, H.; Yılmaz-Aydoğan, H.; Bermek, H.; et al. Evaluation of Local CYP17A1 and CYP19A1 Expression Levels as Prognostic Factors in Postmenopausal Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Cases. Biochem. Genet. 2016, 54, 784–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesenhengst, A.; Pribitzer-Winner, T.; Miedl, H.; Pröstling, K.; Schreiber, M. Elevated Aromatase (CYP19A1) Expression Is Associated with a Poor Survival of Patients with Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Horm. Cancer 2018, 9, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, J.D. Endogenous estrogens as carcinogens through metabolic activation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2000, 27, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, E.; Frenkel, K.; Liehr, J.G.; Rogan, E.; Roy, D. Estrogens as endogenous genotoxic agents—DNA adducts and mutations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2000, 2000, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, E.B.C.T.C. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005, 365, 1687–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Augusto, T.V.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Teixeira, N.; Amaral, C. Acquired resistance to aromatase inhibitors: Where we stand! Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, R283–R301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistelli, M.; Della Mora, A.; Ballatore, Z.; Berardi, R. Aromatase Inhibitors in Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer: The State of the Art and Future Prospects. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, e168–e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrow-Khavar, F.; Filion, K.B.; Bouganim, N.; Suissa, S.; Azoulay, L. Aromatase Inhibitors and the Risk of Cardiovascular Outcomes in Women with Breast Cancer. Circulation 2020, 141, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar Çevik, U.; Sağlık, B.N.; Osmaniye, D.; Levent, S.; Kaya Çavuşoğlu, B.; Karaduman, A.B.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and docking study of benzimidazole–triazolothiadiazine hybrids as aromatase inhibitors. Archiv. Pharm. 2020, 353, e2000008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampietro, L.; Gallorini, M.; Gambacorta, N.; Ammazzalorso, A.; De Filippis, B.; Della Valle, A.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Maccallini, C.; Mollica, A.; Cataldi, A.; et al. Synthesis, structure-activity relationships and molecular docking studies of phenyldiazenyl sulfonamides as aromatase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingaew, R.; Mandi, P.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Synthesis, molecular docking, and QSAR study of sulfonamide-based indoles as aromatase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantacuzzi, M.; De Filippis, B.; Gallorini, M.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Giampietro, L.; Maccallini, C.; Aturki, Z.; Donati, E.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Shawky, E.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking study of indole aryl sulfonamides as aromatase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Staveness, D.; Ryckbosch, S.M.; Axtman, A.D.; Loy, B.A.; Barnes, A.B.; Pande, V.S.; Schaefer, J.; Wender, P.A.; Cegelski, L. REDOR NMR reveals multiple conformers for a protein kinase C ligand in a membrane environment. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ziemba, B.P.; Falke, J.J.; Voth, G.A. Interactions of protein kinase C-α C1A and C1B domains with membranes: A combined computational and experimental study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11757–11766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Rahman, G.M. C1 domains: Structure and ligand-binding properties. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 12108–12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzanad, A.; Gómez-Oliva, R.; Escobar-Montaño, F.; Díez-Salguero, M.; Geribaldi-Doldan, N.; Dominguez-Garcia, S.; Botubol-Ares, J.M.; Reyes, C.d.l.; Durán-Patrón, R.; Nunez-Abades, P. Phorbol Diesters and 12-Deoxy-16-hydroxyphorbol 13, 16-Diesters Induce TGFα Release and Adult Mouse Neurogenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6070–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Egbuta, C.; Lo, J. Testosterone complex and non-steroidal ligands of human aromatase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 181, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangone, A.; Schaarschmidt, J.; Koukos, P.; Geng, C.; Citro, N.; Trellet, M.E.; Xue, L.C.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J. Large-scale prediction of binding affinity in protein–small ligand complexes: The PRODIGY-LIG web server. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1585–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkcuoglu, Z.; Koukos, P.I.; Citro, N.; Trellet, M.E.; Rodrigues, J.; Moreira, I.S.; Roel-Touris, J.; Melquiond, A.S.J.; Geng, C.; Schaarschmidt, J. Performance of HADDOCK and a simple contact-based protein–ligand binding affinity predictor in the D3R Grand Challenge 2. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2018, 32, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroganov, O.V.; Novikov, F.N.; Stroylov, V.S.; Kulkov, V.; Chilov, G.G. Lead Finder: An Approach to Improve Accuracy of Protein−Ligand Docking, Binding Energy Estimation, and Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 2371–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, F.N.; Stroylov, V.S.; Zeifman, A.A.; Stroganov, O.V.; Kulkov, V.; Chilov, G.G. Lead Finder docking and virtual screening evaluation with Astex and DUD test sets. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampogu, S.; Son, M.; Park, C.; Kim, H.H.; Suh, J.K.; Lee, K.W. Sulfonanilide Derivatives in Identifying Novel Aromatase Inhibitors by Applying Docking, Virtual Screening, and MD Simulations Studies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvannang, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Prachayasittikul, V. Molecular Docking of Aromatase Inhibitors. Molecules 2011, 16, 3597–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, G.; Zhang, C.; Marcelli, A.G.; Gilardi, G. Molecular and Structural Evolution of Cytochrome P450 Aromatase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.C.; Chen, S. Molecular characterization of aromatase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.J.; Petrossian, K.; Chen, S. Structural and functional characterization of aromatase, estrogen receptor, and their genes in endocrine-responsive and -resistant breast cancer cells. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 161, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, C.; Gaieb, Z.; Amaro, R.E. An Analysis of Proteochemometric and Conformal Prediction Machine Learning Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity Models. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, J.M. Binding Affinity Analysis of Protein-Ligand Complexes. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Athens, Greece, 16–18 May 2008; pp. 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Prabaharan, M. 7-Characterization of tissue scaffolds drug release profiles. In Characterisation and Design of Tissue Scaffolds; Tomlins, P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Thorston, UK, 2016; pp. 149–168. [Google Scholar]
- Odoemelam, C.S.; Hunter, E.; Simms, J.; Ahmad, Z.; Chang, M.-W.; Percival, B.; Williams, I.H.; Molinari, M.; Kamerlin, S.C.; Wilson, P.B. In Silico Ligand Docking Approaches to Characterise the Binding of Known Allosteric Modulators to the Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor and Prediction of ADME/Tox Properties. Appl. Biosci. 2022, 1, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, I.; Zimmermann, T.; Heinonen, P.; Jäntti, M.H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Talman, V.; Franzyk, H.; Tuominen, R.K.; Christensen, S.B. Missing Selectivity of Targeted 4β-Phorbol Prodrugs Expected to be Potential Chemotherapeutics. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-Y.; Rédei, D.; Forgo, P.; Li, Y.; Vasas, A.; Hohmann, J.; Wu, C.-C. Isolation of Phorbol Esters from Euphorbia grandicornis and Evaluation of Protein Kinase C- and Human Platelet-Activating Effects of Euphorbiaceae Diterpenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2658–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Cruz, J.; da Costa, K.S.; de Carvalho, T.A.A.; de Alencar, N.A.N. Measuring the structural impact of mutations on cytochrome P450 21A2, the major steroid 21-hydroxylase related to congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Holien, J.K.; Tiwari, C.; Parker, M.W.; Rodgers, R.J.; Martin, L.L. Sequence comparisons of cytochrome P450 aromatases from Australian animals predict differences in enzymatic activity and/or efficiency†. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 102, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).