Molecular Patterns and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterization of Salmonella enterica Non-Typhoidal from Human, Food, and Environment Samples Isolated in Luanda, Angola
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Processing, Isolation, and Serovar Identification
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
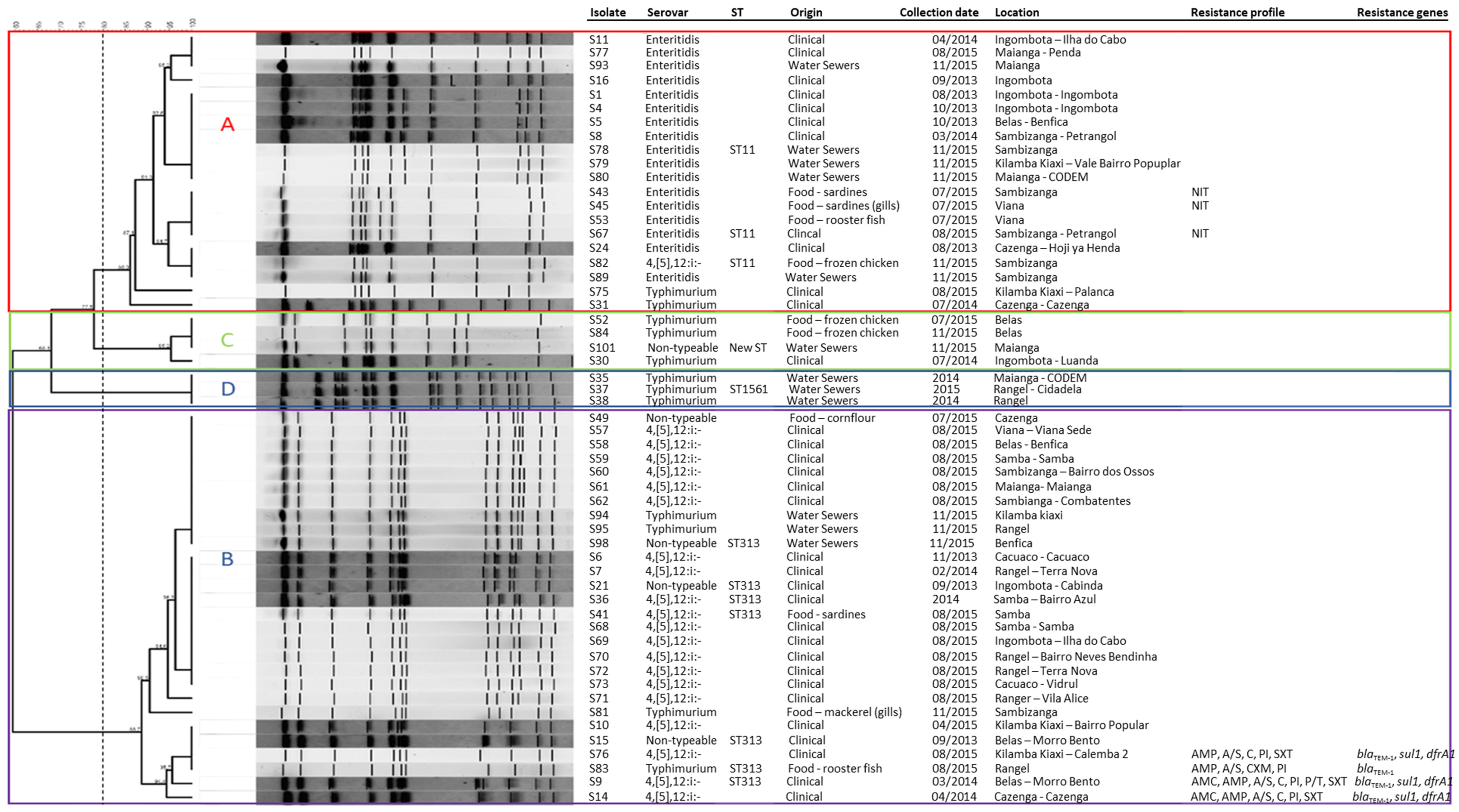
2.3. Clonal Relationship and MLST Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
4.2. Bacteria Isolation, Identification, and DNA Extraction
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
4.5. Typing and Subtyping Using Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) and Multilocus Sequence Type (MLST)
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ananchaipattana, C.; Hosotani, Y.; Kawasaki, S.; Pongsawat, S.; Mdlatiful, B.; Isobe, S.; Inatsu, Y. Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Retailed Foods in Thailand. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bado, I.; García-Fulgueiras, V.; Cordeiro, N.F.; Betancor, L.; Caiata, L.; Seija, V.; Robino, L.; Algorta, G.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Ayala, J.A.; et al. First Human Isolate of Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis Harboring Bla CTX-M-14in South America. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2132–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Kirchner, M.; Guerra, B.; Granier, S.A.; Lucarelli, C.; Porrero, M.C.; Jakubczak, A.; Threlfall, E.J.; Mevius, D.J. Multiresistant Salmonella enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:I:- In Europe: A New Pandemic Strain? Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallati, C.; Stephan, R.; Hächler, H.; Malorny, B.; Schroeter, A.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:I:- Clones Isolated from Human and Other Sources in Switzerland between 2007 and 2011. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadi, N. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella spp. In Raw Retail Frozen Imported Freshwater Fish to Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, B.; Vanaenrode, J.; Verbakel, J.Y.; Toelen, J.; Jacobs, J. Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Infections in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review on Antimicrobial Resistance and Treatment. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, J.R.; Kimball, A.M. The Global Diet: Trade and Novel Infections. Glob. Health 2005, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akullian, A.; Montgomery, J.M.; John-Stewart, G.; Miller, S.I.; Hayden, H.S.; Radey, M.C.; Hager, K.R.; Verani, J.R.; Ochieng, J.B.; Juma, J.; et al. Multi-Drug Resistant Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Associated with Invasive Disease in Western Kenya. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feasey, N.A.; Dougan, G.; Kingsley, R.A.; Heyderman, R.S.; Gordon, M.A. Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Disease: An Emerging and Neglected Tropical Disease in Africa. Lancet 2012, 379, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Campos, J.; Mourao, J.; Ribeiro, T.G.; Novais, C.; Peixe, L. High Occurrence and Unusual Serotype Diversity of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella in Non-Clinical Niches, Angola. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, E.; Tietze, E.; Helmuth, R.; Junker, E.; Blank, K.; Prager, R.; Rabsch, W.; Appel, B.; Fruth, A.; Malorny, B. Pork Contaminated with Salmonella Enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:I:-, An Emerging Health Risk for Humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4601–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossong, J.; Marques, P.; Ragimbeau, C.; Huberty-Krau, P.; Losch, S.; Meyer, G.; Moris, G.; Strottner, C.; Rabsch, W.; Schneider, F. Outbreaks of Monophasic Salmonella Enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:I:- in Luxembourg, 2006. Eurosurveillance 2007, 12, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricardo Dias Poultry and Products Annual. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/Report/DownloadReportByFileName?fileName=Poultry%20and%20Products%20Annual_Luanda_Angola_09-01-2021 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Moreno Switt, A.I.; Soyer, Y.; Warnick, L.D.; Wiedmann, M. Emergence, Distribution, and Molecular and Phenotypic Characteristics of Salmonella enterica Serotype 4,5,12:I:-. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, L.; Ramon, E.; Cortini, E.; Longo, A.; Dalla Pozza, M.C.; Lettini, A.A.; Dionisi, A.M.; Olsen, J.E.; Ricci, A. Molecular Characterization of Salmonella enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:I:- DT193 ASSuT Strains from Two Outbreaks in Italy. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, M.R.; Finley, R.; Allen, V.; Ang, L.; Bekal, S.; el Bailey, S.; Haldane, D.; Hoang, L.; Horsman, G.; Louie, M.; et al. Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serotype 4,[5],12:I:- Involving Human Cases in Canada: Results from the Canadian Integrated Program on Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS), 2003–10. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1982–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uche, I.V.; MacLennan, C.A.; Saul, A. A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Risk Factors and Case Fatality Rates of Invasive Nontyphoidal Salmonella (INTS) Disease in Africa (1966 to 2014). PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morpeth, S.C.; Ramadhani, H.O.; Crump, J.A. Invasive Non-Typhi Salmonella Disease in Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaw, A.K.; Nthaba, P.; Matle, I. Detection of Salmonella from Animal Sources in South Africa between 2007 and 2014. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2018, 89, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015. In WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization & Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) Progress Report 2004–2010; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Mandomando, I.; Bassat, Q.; Sigaúque, B.; Massora, S.; Quintó, L.; Ácacio, S.; Nhampossa, T.; Vubil, D.; Garrine, M.; Macete, E.; et al. Invasive Salmonella Infections Among Children From Rural Mozambique, 2001–2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, S339–S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Friis, C.; Zankari, E.; Svendsen, C.A.; Price, L.B.; Rahmani, M.; Herrero-Fresno, A.; Fashae, K.; Vandenberg, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Genomics of an Emerging Clone of Salmonella Serovar Typhimurium ST313 from Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2013, 7, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, R.A.; Msefula, C.L.; Thomson, N.R.; Kariuki, S.; Holt, K.E.; Gordon, M.A.; Harris, D.; Clarke, L.; Whitehead, S.; Sangal, V.; et al. Epidemic Multiple Drug Resistant Salmonella typhimurium Causing Invasive Disease in Sub-Saharan Africa Have a Distinct Genotype. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, P.M.; Owen, S.V.; Kaindama, L.; Rowe, W.P.M.; Lane, C.R.; Larkin, L.; Nair, S.; Jenkins, C.; de Pinna, E.M.; Feasey, N.A.; et al. Public Health Surveillance in the UK Revolutionises Our Understanding of the Invasive Salmonella typhimurium Epidemic in Africa. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Chang, W. Prevalence and Characteristics of Salmonella Isolated from Free-Range Chickens in Shandong Province, China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8183931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, S.; Ksibi, B.; Gharsallah, H.; Mnif, B.; Maalej, S.; Rhimi, F.; Hammami, A. Molecular Epidemiological Characteristics of Salmonella enterica Serovars Enteritidis, Typhimurium and Livingstone Strains Isolated in a Tunisian University Hospital. APMIS 2016, 124, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Mourão, J.; Machado, J.; Peixe, L. First Description of QnrS1-IncN Plasmid in a ST11 Salmonella enteritidis Clinical Isolate from Portugal. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 69, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, T.; Petridou, E.; Zdragas, A.; Mandilara, G.; Nair, S.; Peters, T.; Chattaway, M.; de Pinna, E.; Passiotou, M.; Vatopoulos, A. Comparative Study of All Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Strains Isolated from Food and Food Animals in Greece from 2008 to 2010 with Clinical Isolates. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Bae, I.K.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, H.K.; Ahn, J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, K. Occurrence of IncFII Plasmids Carrying the BlaCTX-M-15 Gene in Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Sequence Type 11 in Korea. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 71, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, R.; Tadayon, K.; Khaki, P.; Mosavari, N. Iranian Clonal Population of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis, Characterized by Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) Method. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2015, 7, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 6579. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs—Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp. 2002. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:6579:ed-4:v1:en (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Malorny, B.; Hoorfar, J.; Bunge, C.; Helmuth, R. Multicenter Validation of the Analytical Accuracy of Salmonella PCR: Towards an International Standard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars. In WHO Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella, 9th ed.; Institute Pasteur: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Koneman, E.W.; Allen, S.D.; Janda, W.M.; Schreeckenberger, P.C. Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, S.M.; Diallo, S.; Levy, H.; Livio, S.; Sow, S.O.; Tapia, M.; Fields, P.I.; Mikoleit, M.; Tamboura, B.; Kotloff, K.L.; et al. Identification by PCR of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars Associated with Invasive Infections among Febrile Patients in Mali. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific Opinion on Monitoring and Assessment of the Public Health Risk of “Salmonella typhimurium-like” Strains. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féria, C.; Machado, J.; Correia, J.D.; Gonçalves, J.; Gaastra, W. Virulence Genes and P Fimbriae PapA Subunit Diversity in Canine and Feline Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters Version 14.0. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_5.0_Breakpoint_Table_01.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781684400324. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomba, C.; Mendonça, N.; Costa, M.; Louro, D.; Baptista, B.; Ferreira, M.; Correia, J.D.; Caniça, M. Improved Multiplex PCR Method for the Rapid Detection of β-Lactamase Genes in Escherichia coli of Animal Origin. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 56, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Fagan, E.J.; Ellington, M.J. Multiplex PCR for Rapid Detection of Genes Encoding CTX-M Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, F.J.; Hanson, N.D. Detection of Plasmid-Mediated AmpC β-Lactamase Genes in Clinical Isolates by Using Multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, Y.; Briñas, L.; Domínguez, E.; Ruiz, J.; Zarazaga, M.; Vila, J.; Torres, C. Mechanisms of Resistance in Multiple-Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains of Human, Animal, and Food Origins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Rotimi, V.; Soussy, C.J.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Qnr Genes in ESBL-Producing Enterobacterial Isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Standard Operating Procedure for PulseNet PFGE of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Escherichia coli Non-O157 (STEC), Salmonella serotypes, Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri. Available online: https://www.pulsenetinternational.org/assets/PulseNet/uploads/pfge/PNL05_Ec-Sal-ShigPFGEprotocol.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- Carriço, J.A.; Pinto, F.R.; Simas, C.; Nunes, S.; Sousa, N.G.; Frazão, N.; de Lencastre, H.; Almeida, J.S. Assessment of Band-Based Similarity Coefficients for Automatic Type and Subtype Classification of Microbial Isolates Analyzed by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5483–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M. A Genomic Overview of the Population Structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achtman, M.; Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Tyne, W.; Parkhill, J.; Cormican, M.; Chiou, C.-S.; Torpdahl, M.; Litrup, E.; Prendergast, D.M.; et al. Genomic Diversity of Salmonella enterica—The UoWUCC 10K Genomes Project. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 5, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Salmonella Serovar | Isolates n (%) | Origin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical n | Food n | Environment n | ||
| Enteritidis | 17 (30.9) | 9 | 3 | 5 |
| 4,[5],12:i:- | 21(38.1) | 18 | 2 | 1 |
| Typhimurium | 12 (21.8) | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Non-typeable | 5 (9.0) | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 55 (100) | 32 | 10 | 13 |
| Sample ID | Sample Origin | Salmonella Serovar | Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotypes 1 and MIC Values (mg/L) | Resistance Genes Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S9 | Human feces | Enteritidis | AMP (>16), A/S (>16/8), PI (>64), C (>16), SXT (>4/76) | blaTEM-1-sul1-dfrIa |
| S14 | Human feces | 4,[5],12:i:- | AMP (>16), A/S (>16/8), PI (>64), C (>16), SXT (>4/76) | blaTEM-1-sul1-dfrIa |
| S76 | Human feces | 4,[5],12:i:- | AMP (>16), PI (>64), C (>16), SXT (>4/76) | blaTEM-1-sul1-dfrIa |
| S83 | Fish | Typhimurium | AMP (>16), A/S (>16/8), PI (>64) | blaTEM-1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francisco, M.; Belas, A.; Costa, S.S.; Menezes, J.; Ramos, J.; Couto, I.; Viveiros, M.; Pomba, C. Molecular Patterns and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterization of Salmonella enterica Non-Typhoidal from Human, Food, and Environment Samples Isolated in Luanda, Angola. Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 4, 259-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040022
Francisco M, Belas A, Costa SS, Menezes J, Ramos J, Couto I, Viveiros M, Pomba C. Molecular Patterns and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterization of Salmonella enterica Non-Typhoidal from Human, Food, and Environment Samples Isolated in Luanda, Angola. Zoonotic Diseases. 2024; 4(4):259-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040022
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancisco, Moisés, Adriana Belas, Sofia Santos Costa, Juliana Menezes, Jorge Ramos, Isabel Couto, Miguel Viveiros, and Constança Pomba. 2024. "Molecular Patterns and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterization of Salmonella enterica Non-Typhoidal from Human, Food, and Environment Samples Isolated in Luanda, Angola" Zoonotic Diseases 4, no. 4: 259-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040022
APA StyleFrancisco, M., Belas, A., Costa, S. S., Menezes, J., Ramos, J., Couto, I., Viveiros, M., & Pomba, C. (2024). Molecular Patterns and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterization of Salmonella enterica Non-Typhoidal from Human, Food, and Environment Samples Isolated in Luanda, Angola. Zoonotic Diseases, 4(4), 259-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040022








