Genomic Analysis of Novel Bacterial Species Corynebacterium ramonii ST344 Clone Strains Isolated from Human Skin Ulcer and Rescued Cats in Japan
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of C. ramonii from Samples
2.2. Whole-Genome C. ramonii and C. ulcerans Isolate Sequencing and Analysis
2.3. Complete Genome Sequence Determination
3. Results
3.1. C. ramonii Clinical Isolate KCU0303-001
3.2. C. ramonii and C. ulcerans Rescued Cat Isolates
3.3. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Clinical and Rescued Cat Strains
3.4. Structural Comparison of Complete Genome Sequences for C. ramonii ST344
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappenheimer, A.M., Jr.; Gill, D.M. Diphtheria. Science 1973, 182, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, R.; Stewart, F.C. Corynebacterium ulcerans: A pathogenic microorganism resembling Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1927, 12, 756–761. [Google Scholar]
- Lartigue, M.F.; Monnet, X.; Le Fleche, A.; Grimont, P.A.; Benet, J.J.; Durrbach, A.; Fabre, M.; Nordmann, P. Corynebacterium ulcerans in an immunocompromised patient with diphtheria and her dog. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsukawa, C.; Kawahara, R.; Inoue, K.; Ishii, A.; Yamagishi, H.; Kida, K.; Nishino, S.; Nagahama, S.; Komiya, T.; Iwaki, M.; et al. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans isolated from the domestic dog for the first time in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizuka, T.; Katsukawa, C.; Kuroda, M.; Shibayama, K.; Otsuji, K.; Saito, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Iwaki, M. Limitations of Ribotyping as Genotyping Method for Corynebacterium ulcerans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2457–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, Y.; Efstratiou, A.; Brennan, G.; Hallanan, S.; Leggett, B.; Leonard, F.C.; Markey, B.K.; Tuite, C.; Fry, N.K. Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans associated with upper respiratory infections in cats and dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 61, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, K.; Kikuchi, J.; Uchida, M.; Nemoto, M.; Kaji, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Suzuki, H.; Fukushima, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Iwaki, M.; et al. Transmission of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans infection with airway obstruction from cats to a human. Acute Med. Surg. 2021, 8, e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, A.; Herrera-Leon, S.; Dominguez, L.; Gavin, M.O.; Romero, B.; Piedra, X.B.A.; Calzada, C.S.; Uria Gonzalez, M.J.; Herrera-Leon, L.; Case Study Investigation Group. Zoonotic Transmission of Diphtheria from Domestic Animal Reservoir, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Museux, K.; Arcari, G.; Rodrigo, G.; Hennart, M.; Badell, E.; Toubiana, J.; Brisse, S. Corynebacteria of the diphtheriae Species Complex in Companion Animals: Clinical and Microbiological Characterization of 64 Cases from France. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0000623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostock, A.D.; Gilbert, F.R.; Lewis, D.; Smith, D.C. Corynebacterium ulcerans infection associated with untreated milk. J. Infect. 1984, 9, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, T.M.; Smith, A.; Cleverly, L.M.; Neave, F.K. Corynebacterium ulcerans infections in a dairy herd. Vet. Rec. 1967, 81, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hommez, J.; Devriese, L.A.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Riegel, P.; Butaye, P.; Haesebrouck, F. Identification of nonlipophilic corynebacteria isolated from dairy cows with mastitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendri, F.; Isgren, C.M.; Sinovich, M.; Richards-Rios, P.; Hopkins, K.L.; Russell, K.; Groves, N.; Litt, D.; Fry, N.K.; Timofte, D. Case Report: Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans Diphtheria-Like Infection in a Horse in the United Kingdom. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 650238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Peters, M.; Muhldorfer, K.; Braune, S.; Eisenberg, T.; Szentiks, C.A.; Rau, J.; Konrad, R.; Hormansdorfer, S.; et al. Tox-positive Corynebacterium ulcerans in hedgehogs, Germany. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.; Boyen, F.; Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Sing, A.; Berger, A.; Chiers, K.; Van Praet, S.; Verbanck, S.; Vervaeke, M.; et al. Widespread Disease in Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Caused by Toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2686–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunderson, S.C.; Nouioui, I.; Midwinter, A.C.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Young, M.J.; McInnes, K.M.; Watts, J.; Sangal, V. Phylogenomic Characterization of a Novel Corynebacterium Species Associated with Fatal Diphtheritic Stomatitis in Endangered Yellow-Eyed Penguins. mSystems 2021, 6, e0032021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, H.J.; Kleinhagauer, T.; Glaeser, S.P.; Spergser, J.; Kampfer, P.; Ruckert, C. Classification of three corynebacterial strains isolated from the Northern Bald Ibis (Geronticus eremita): Proposal of Corynebacterium choanae sp. nov., Corynebacterium pseudopelargi sp. nov., and Corynebacterium gerontici sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, R.P.; Cassiday, P.K.; Venezia, J.; Shen, Z.; Buckley, E.M.; Peters, Y.; Taylor, N.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Tondella, M.L.; Fox, J.G. Corynebacterium ulcerans in ferrets. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contzen, M.; Sting, R.; Blazey, B.; Rau, J. Corynebacterium ulcerans from diseased wild boars. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Kutzer, P.; Peters, M.; Sing, A.; Contzen, M.; Rau, J. Nontoxigenic tox-bearing Corynebacterium ulcerans infection among game animals, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Blazey, B.; Contzen, M.; Sting, R. [Corynebacterium ulcerans infection in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus)]. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2012, 125, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seto, Y.; Komiya, T.; Iwaki, M.; Kohda, T.; Mukamoto, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kozaki, S. Properties of corynephage attachment site and molecular epidemiology of Corynebacterium ulcerans isolated from humans and animals in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hifumi, T.; Ato, M.; Iwaki, M.; Senoh, M.; Hatanaka, A.; Nureki, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Hirose, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Corynebacterium ulcerans Infection, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel, D.M.; Margos, G.; Konrad, R.; Krebs, S.; Blum, H.; Sing, A. Next generation sequencing analysis of nine Corynebacterium ulcerans isolates reveals zoonotic transmission and a novel putative diphtheria toxin-encoding pathogenicity island. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, A.; Hogardt, M.; Bierschenk, S.; Heesemann, J. Detection of differences in the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of diphtheria toxin from Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans causing extrapharyngeal infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4848–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizuka, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Komiya, T.; Kenri, T.; Takeuchi, F.; Shibayama, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kuroda, M.; Iwaki, M. Corynebacterium ulcerans 0102 carries the gene encoding diphtheria toxin on a prophage different from the C. diphtheriae NCTC 13129 prophage. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, J.; Sekizuka, T.; Sakai, T.; Fujisawa, N.; Iwaki, M.; Kimura, M.; Kuroda, M. Complete Genome Sequence of Corynebacterium ulcerans Strain TSU-28, Harboring Two Diphtheria Toxin Genes, Isolated from a Patient with Diphtheria-Like Symptoms. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e0007223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crestani, C.; Arcari, G.; Landier, A.; Passet, V.; Garnier, D.; Bremont, S.; Armatys, N.; Carmi-Leroy, A.; Toubiana, J.; Badell, E.; et al. Corynebacterium ramonii sp. nov., a novel toxigenic member of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae species complex. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, H.; Popovic, T. Development of a direct PCR assay for detection of the diphtheria toxin gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Comparison between rpoB and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for molecular identification of 168 clinical isolates of Corynebacterium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1934–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, K.H.; Glushkevich, T.; Mazurova, I.K.; George, R.C.; Efstratiou, A. A modified Elek test for detection of toxigenic corynebacteria in the diagnostic laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, C.S.; Sesardic, D. In vitro assays for detection of diphtheria toxin. Toxicol. In Vitro 1994, 8, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitada, C.; Sekizuka, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Sakamoto, C.; Hashino, M.; Kuroda, M.; Takahashi, M. Comparative pathogenomic analysis reveals a highly tetanus toxin-producing clade of Clostridium tetani isolates in Japan. mSphere 2023, 8, e0036923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizawa, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y. DFAST: A flexible prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline for faster genome publication. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yamada, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Ogata, H. DiGAlign: Versatile and Interactive Visualization of Sequence Alignment for Comparative Genomics. Microbes Environ. 2024, 39, ME23061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, E.; Al-Dilaimi, A.; Papavasiliou, P.; Schneider, J.; Viehoever, P.; Burkovski, A.; Soares, S.C.; Almeida, S.S.; Dorella, F.A.; Miyoshi, A.; et al. Comparative analysis of two complete Corynebacterium ulcerans genomes and detection of candidate virulence factors. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badell, E.; Alharazi, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Almoayed, K.A.A.; Lefrancq, N.; Bouchez, V.; Guglielmini, J.; Hennart, M.; Carmi-Leroy, A.; Zidane, N.; et al. Ongoing diphtheria outbreak in Yemen: A cross-sectional and genomic epidemiology study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e386–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, K.; Hirai, Y. Comparative whole-genome analysis of diphtheria toxin-producing Corynebacterium ulcerans isolates from sheltered cats in Osaka, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 85, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, J.; Katsukawa, C.; Matsubayashi, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Furuya, M.; Tani, H.; Sasai, K. The detection of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans from cats with nasal inflammation in Japan. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2660–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsukawa, C.; Komiya, T.; Yamagishi, H.; Ishii, A.; Nishino, S.; Nagahama, S.; Iwaki, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Takahashi, M. Prevalence of Corynebacterium ulcerans in dogs in Osaka, Japan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Control and Management of Diphtheria in England. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/654944a9bdb7ef000d4af91c/diphtheria-guidelines-version19-November2023.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Diphtheria Nigeria. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2023-DON485 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
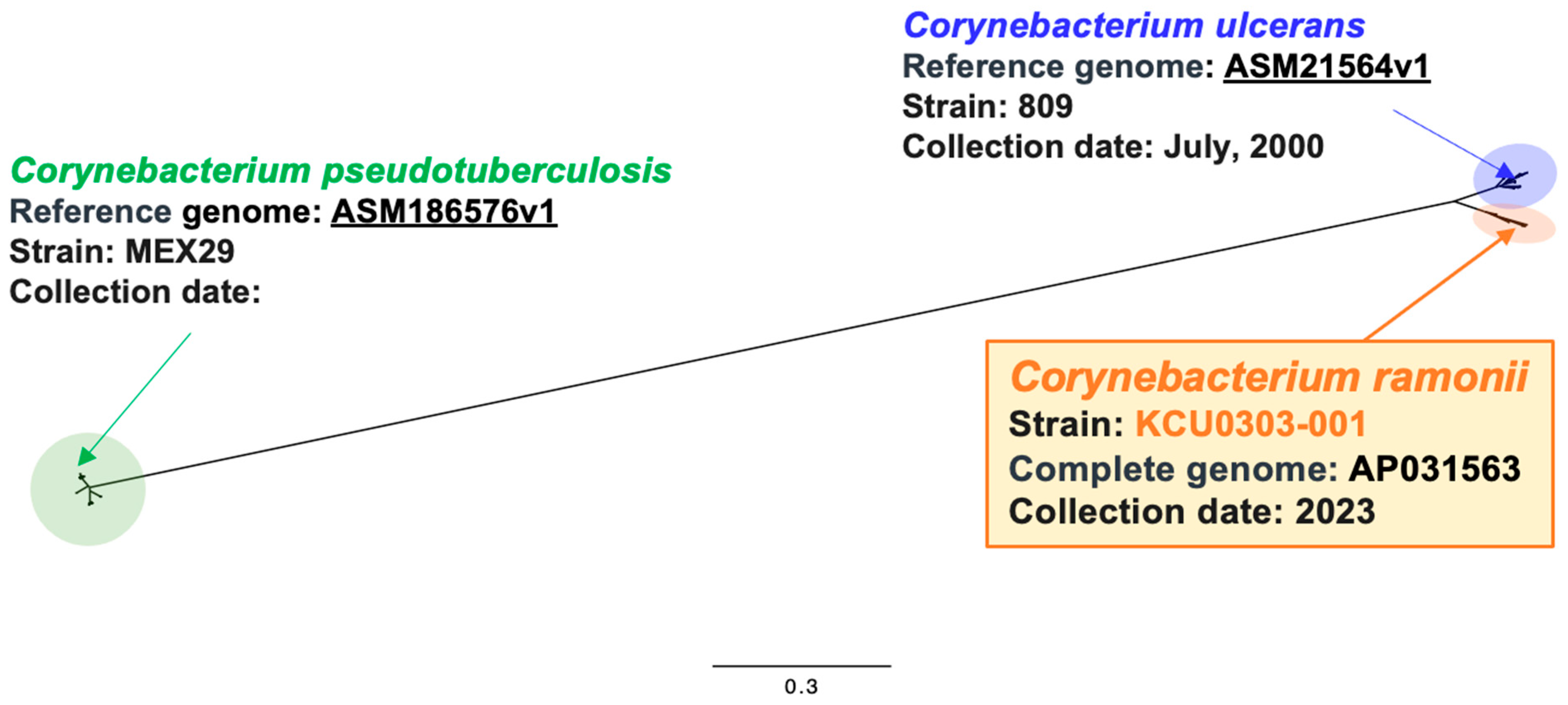

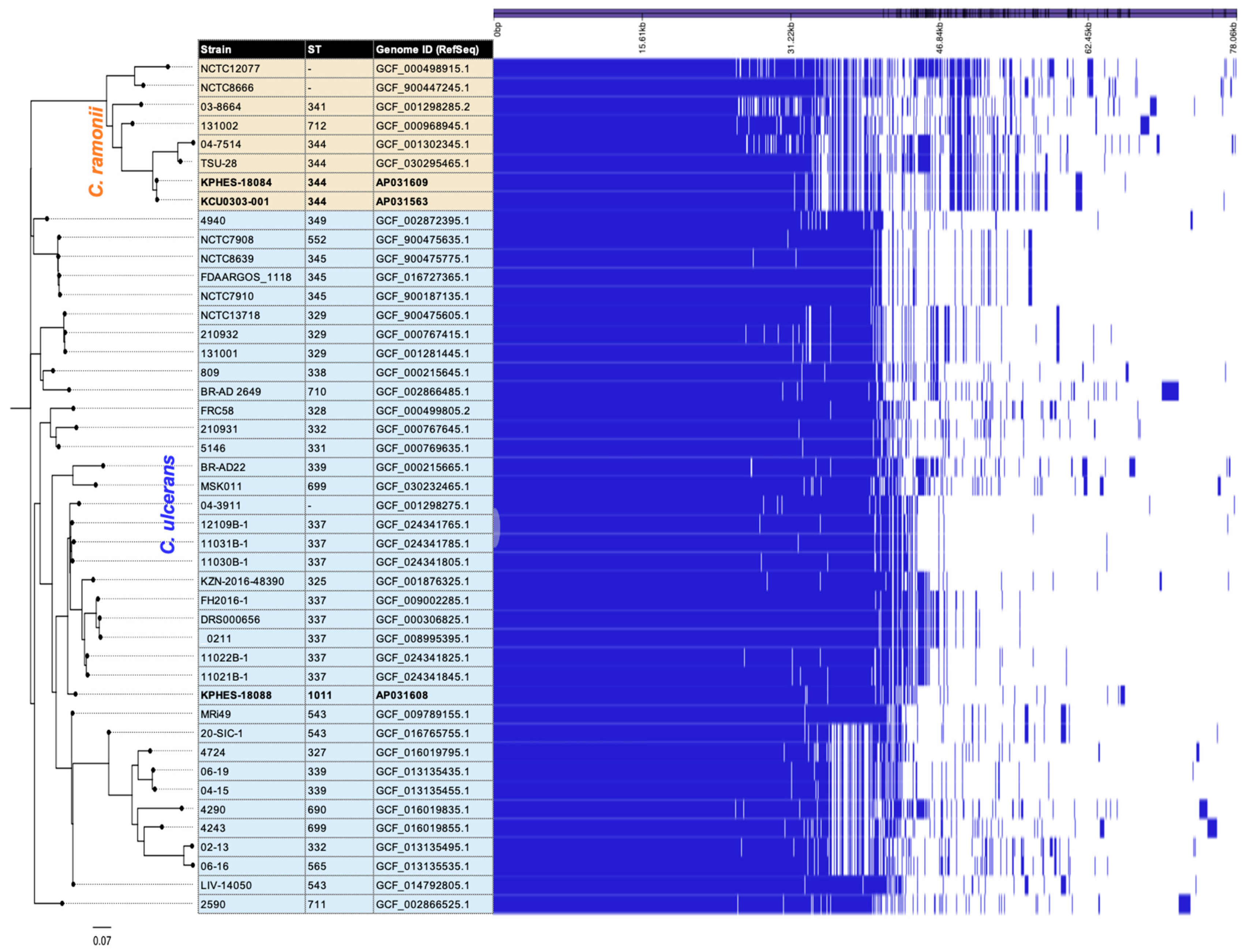
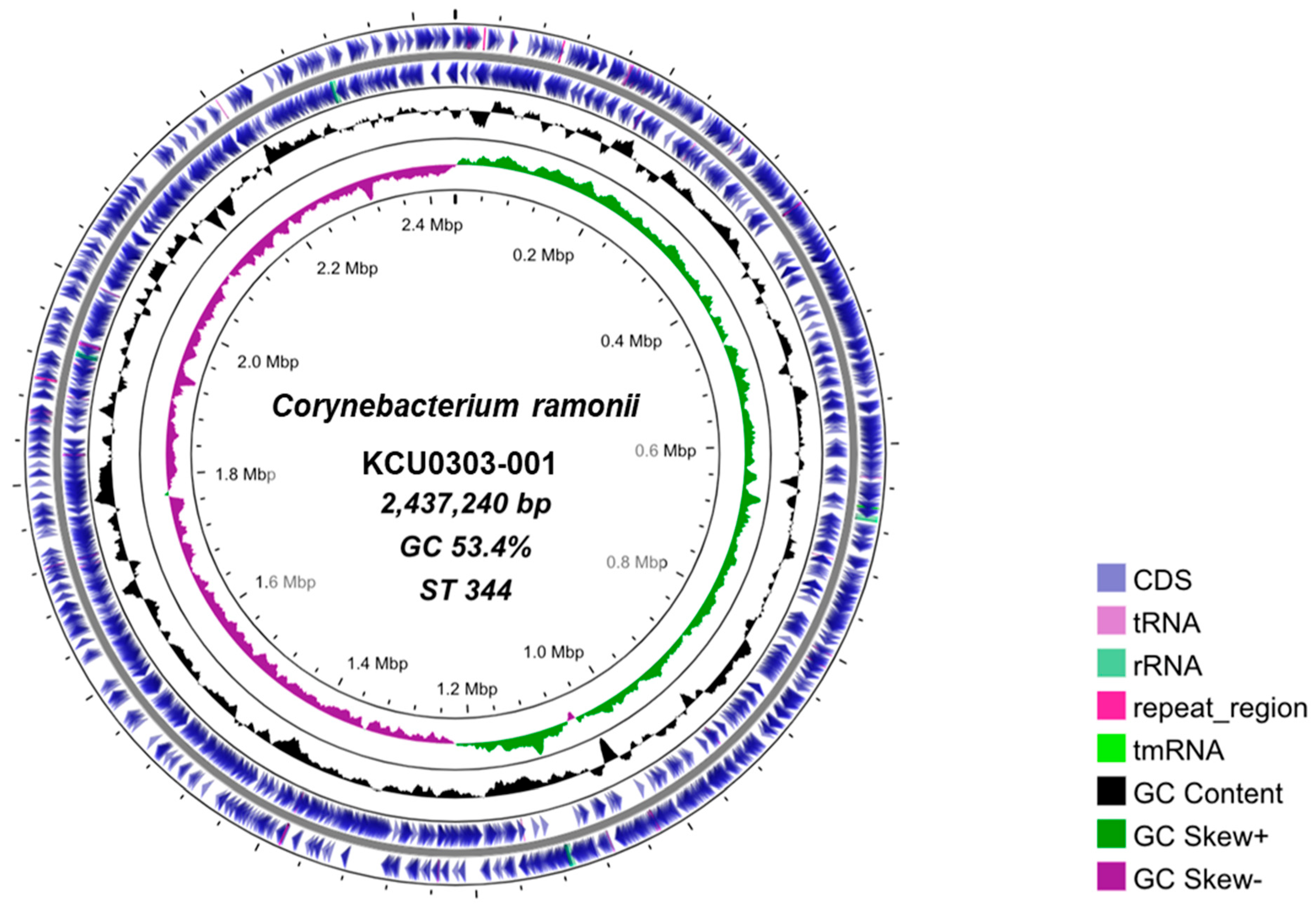

| Strain | Isolation Year | Source | API Coryne | rpoB * | DT-PCR † | Elek ‡ | Vero § | MLST || |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCU0303-001 | 2023 | Human | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | ND | ND | 344 |
| KPHES-18088 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 1011 |
| KPHES-18089 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 1011 |
| KPHES-18090 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 1011 |
| KPHES-18087 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 1011 |
| KPHES-18084 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 344 |
| KPHES-18091 | 2018 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 1011 |
| KPHES-19104 | 2019 | Cat | C. ulcerans | C. ulcerans | + | − | + | 337 |
| KCU0303-001 | KPHES-18084 | KPHES-18088 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Length (bp) | 2,437,240 | 2,438,574 | 2,490,749 |
| No. of Sequences | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| GC Content (%) | 53.4% | 53.4% | 53.3% |
| No. of CDSs | 2166 | 2167 | 2215 |
| No. of rRNA | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| No. of tRNA | 51 | 51 | 53 |
| Coding Ratio (%) | 88.3% | 88.3% | 88.3% |
| MLST | ST344 | ST344 | ST 1011 |
| GenBank ID | AP031563 | AP031609 | AP031608 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shitada, C.; Moriguchi, M.; Hayashi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Mori, M.; Tokuoka, E.; Yahiro, S.; Gejima, S.; Horiba, K.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Novel Bacterial Species Corynebacterium ramonii ST344 Clone Strains Isolated from Human Skin Ulcer and Rescued Cats in Japan. Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 4, 234-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040020
Shitada C, Moriguchi M, Hayashi H, Matsumoto K, Mori M, Tokuoka E, Yahiro S, Gejima S, Horiba K, Yamamoto T, et al. Genomic Analysis of Novel Bacterial Species Corynebacterium ramonii ST344 Clone Strains Isolated from Human Skin Ulcer and Rescued Cats in Japan. Zoonotic Diseases. 2024; 4(4):234-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleShitada, Chie, Mikoto Moriguchi, Hideyuki Hayashi, Kazutoshi Matsumoto, Misato Mori, Eisuke Tokuoka, Shunsuke Yahiro, Shouichirou Gejima, Kazuhiro Horiba, Takatoshi Yamamoto, and et al. 2024. "Genomic Analysis of Novel Bacterial Species Corynebacterium ramonii ST344 Clone Strains Isolated from Human Skin Ulcer and Rescued Cats in Japan" Zoonotic Diseases 4, no. 4: 234-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040020
APA StyleShitada, C., Moriguchi, M., Hayashi, H., Matsumoto, K., Mori, M., Tokuoka, E., Yahiro, S., Gejima, S., Horiba, K., Yamamoto, T., Takahashi, M., & Kuroda, M. (2024). Genomic Analysis of Novel Bacterial Species Corynebacterium ramonii ST344 Clone Strains Isolated from Human Skin Ulcer and Rescued Cats in Japan. Zoonotic Diseases, 4(4), 234-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4040020






