Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus velezensis from Lake Bogoria as a Potential Biocontrol of Fusarium solani in Phaseolus vulgaris L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Morphological Characteristics
2.2. Molecular Characterization
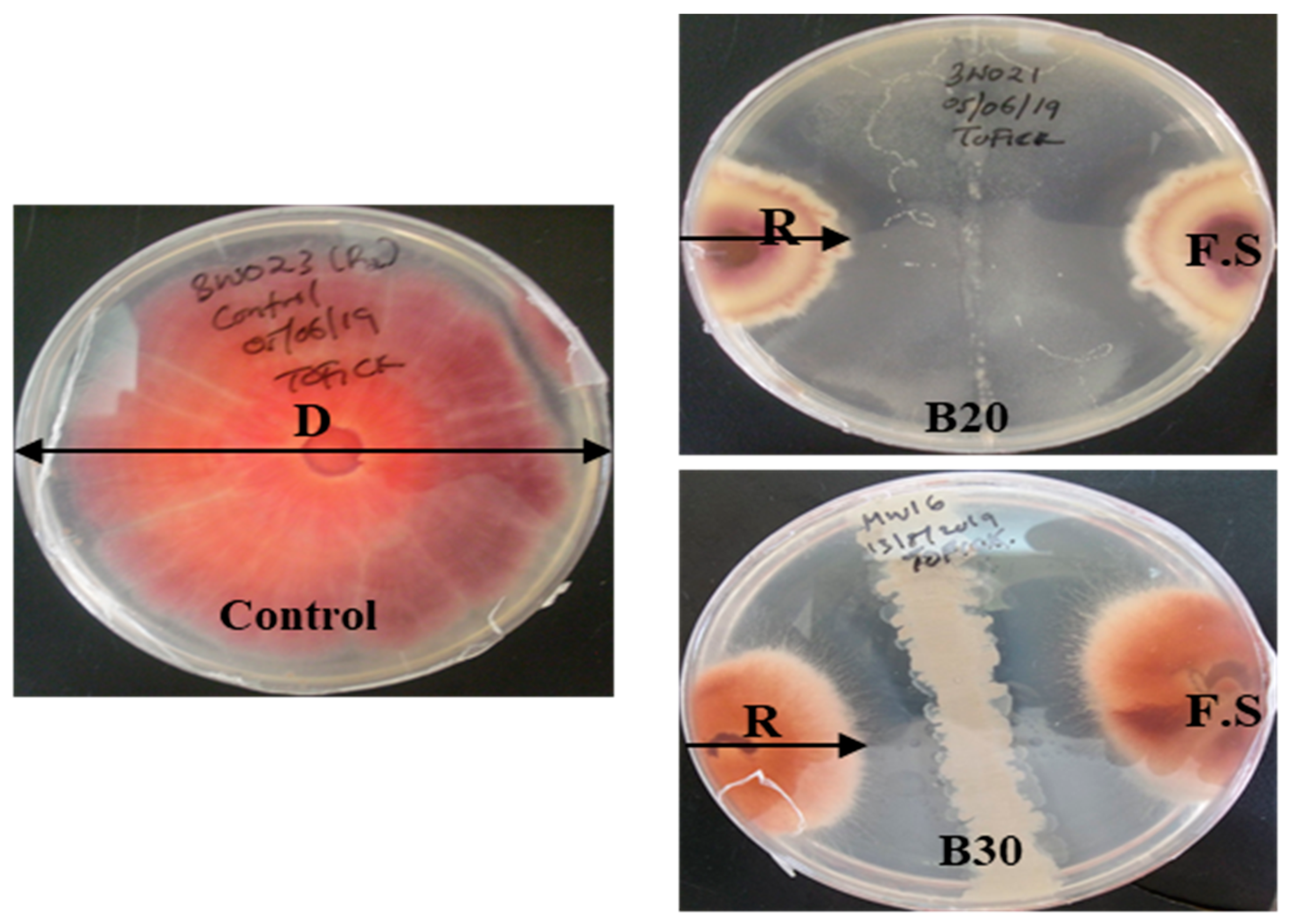
2.3. Evaluation of Bacillus velezensis against Fusarium solani
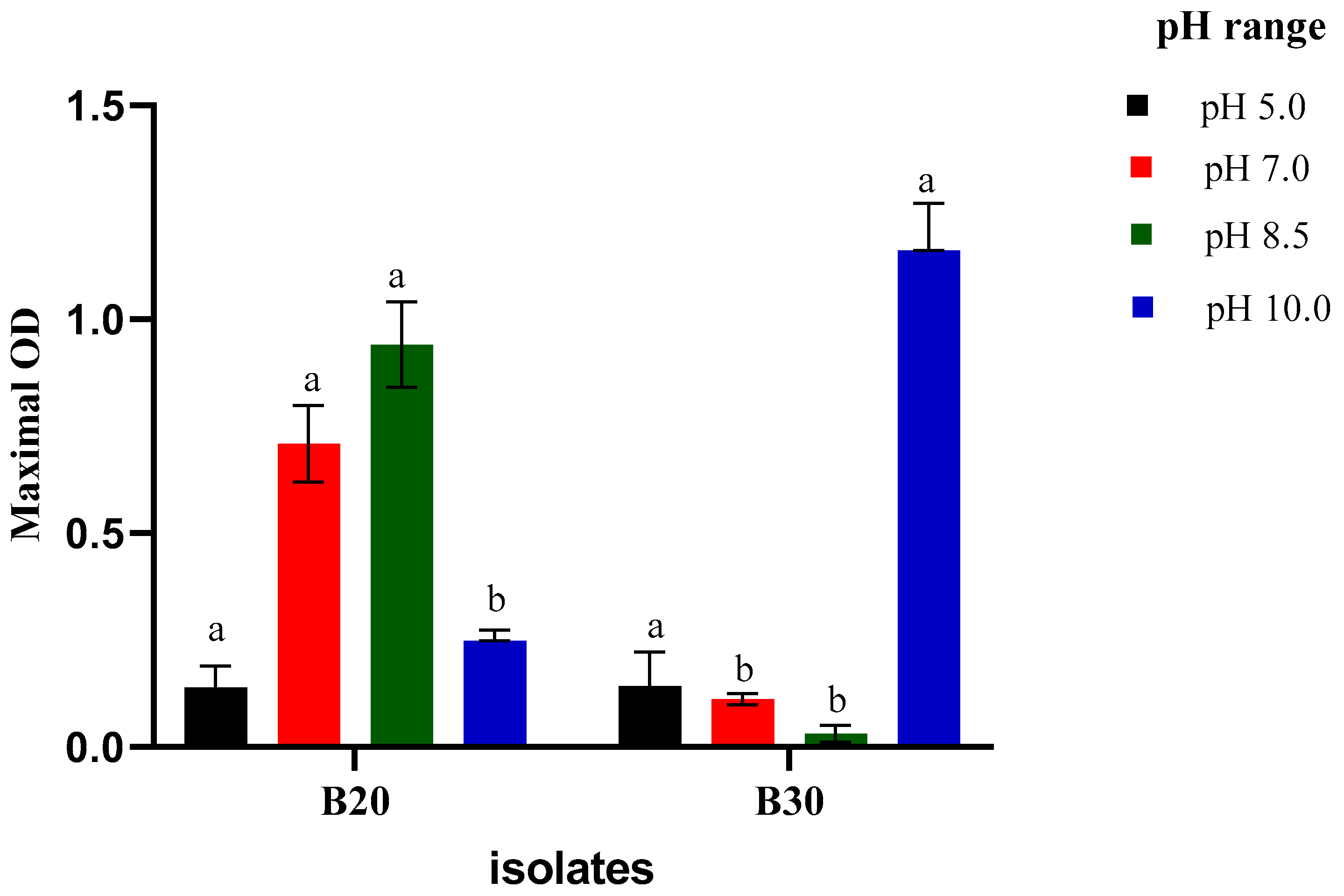
2.3.1. Growth at Different pH
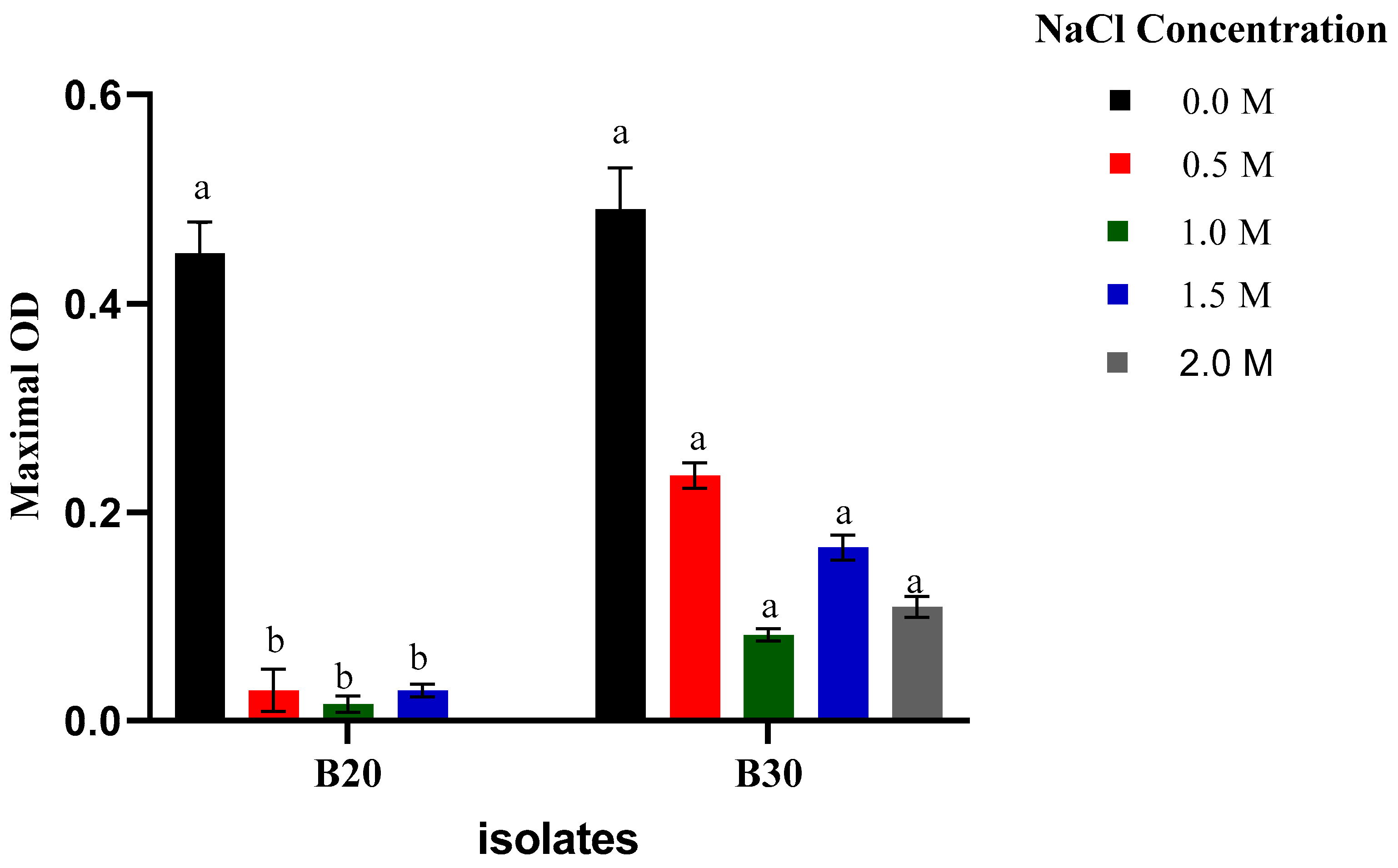
2.3.2. Growth at Different Salinity
2.3.3. Growth at Different Temperatures
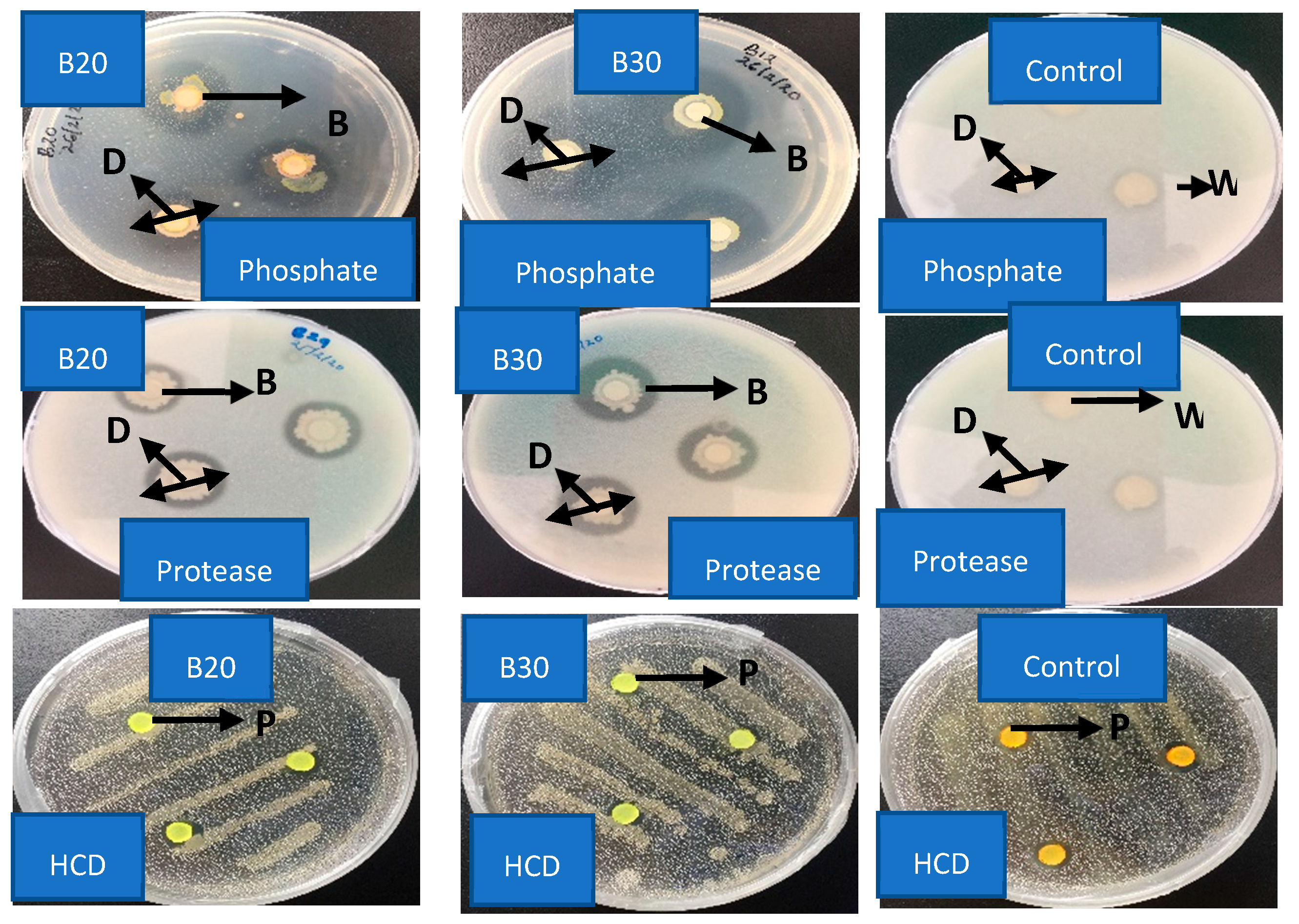
2.4. Enzymatic Bioassay of Isolate B20 and B30
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Site and Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation and Morphological Characterization of Lake Bogoria
4.3. Molecular Characterization
4.3.1. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.3.2. PCR Amplification of 16S rRNA Genes
4.3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Bioactive Isolates
4.4. Evaluation of Bacillus velezensis against Fusarium solani
4.5. Physiochemical Characterization
4.5.1. Growth at Different Sodium Chloride Concentrations
4.5.2. Growth at Various Temperatures
4.5.3. Effect of pH on the Growth of the Isolates
4.6. Enzymatic Characterization
4.6.1. Protease Activity
4.6.2. Chitinase Activity
4.6.3. Pectinase Activity
4.6.4. Hydrogen Cyanide (HCD) Production Ability
4.6.5. Phosphate Solubilization Ability
4.6.6. Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) Production Ability
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathna Priya, T.S.; Manickavasagan, A. Common Bean. In Pulses: Processing and Product Development; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 77–97. ISBN 9783030413767. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, B. Bean Production and Fusarium Root Rot in Diverse Soil Environments in Iran. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Cheon, W.; Park, J.; Kwon, H.-T.; Balaraju, K.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.J.; Jeon, Y. Characterization of Bacillus Velezensis AK-0 as a Biocontrol Agent against Apple Bitter Rot Caused by Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, H.; Júnior, T.J.P.; Vieira, R.F.; Lehner, M.S.; Lima, R.C.; Ponte, E.M. Del Seasonal Dynamics of Soil-Borne Inoculum and Severity of Fusarium Root Rot of Common Beans Affected by Sequential Planting of Legume or Cereal Crops. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2015, 40, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Takishita, Y.; Zhou, G.; Smith, D.L. Plant Associated Rhizobacteria for Biocontrol and Plant Growth Enhancement. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baazeem, A.; Almanea, A.; Manikandan, P.; Alorabi, M.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Abdel-Hadi, A. In Vitro Antibacterial, Antifungal, Nematocidal and Growth Promoting Activities of Trichoderma Hamatum FB10 and Its Secondary Metabolites. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, G.; Muleta, D. The Effect of Rhizobia Isolates Against Black Root Rot Disease of Faba Bean (Vicia Faba L) Caused by Fusarium Solani. Open Agric. J. 2018, 12, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JM, P.; CA, D.; MJ, B.; SN, C. Bacillus Velezensis RC 218 as a Biocontrol Agent to Reduce Fusarium Head Blight and Deoxynivalenol Accumulation: Genome Sequencing and Secondary Metabolite Cluster Profiles. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 192, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtegebriel, B.; Boydom, A. Biocontrol of Faba Bean Black Root Rot Caused by Fusarium solani Using Seed Dressing and Soil Application of Trichoderma harzianum. J. Biol. Control 2017, 30, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydi, R.; Abdallah, B.; Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H.; Nefzi, A.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Daami-Remadi, M. Endophytic Bacteria from Datura Stramonium for Fusarium Wilt Suppression and Tomato Growth Promotion. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 30–041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukare, A.; Paul, S.; Arambam, A. Isolation and Efficacy of Native Chitinolytic Rhizobacteria for Biocontrol Activities against Fusarium Wilt and Plant Growth Promotion in Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan L.). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Naderi, D. Anti-Fungal and Bio-Control Properties of Chitinolytic Bacteria against Safflower Fusarium Root Rot. J. Crop Prot. 2017, 2017, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbee, M.F.; Ali, M.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, B.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Baek, K. Bacillus Velezensis: A Valuable Member of Bioactive Molecules within Plant Microbiomes. Molecules 2019, 24, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Ho, M.T.; Weselowski, B.; McDowell, T.; Solomon, O.; Renaud, J.; Yuan, Z.-C. Characterization and Complete Genome Analysis of the Surfactin-Producing, Plant-Protecting Bacterium Bacillus Velezensis 9D-6. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, D.M.; Childress, R.B.; Harper, M.M.; Boar, R.R.; Hickley, P.; Mills, S.C.; Otieno, N.; Drane, T.; Vareschi, E.; Nasirwa, O.; et al. Aquatic Biodiversity and Saline Lakes: Lake Bogoria National Reserve, Kenya. Aquat. Biodivers. 2003, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambura, A.; Mwirichia, R.; Ngaira, J.; Boga, H. Isolation and Characterization of Bacterial Isolates from Lake Magadi. J. Trop. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torome*, T.K.; Matasyoh, L.G.; Orinda, G.; Gakuya, F. Isolation and Characterization of Antibiotic Producing Bacillus Species in Lake Bogoria, Kenya. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simasi, L. Isolation, Identification and Characterization of Alkalithermophiles from the Hot Springs of Lake Bogoria of the Kenyan Rift Valley. 2013. Available online: http://ir.jkuat.ac.ke/handle/123456789/954 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Duckworth, A.; Grant, W.; Jones, B.; Steenbergen, R. Van Phylogenetic Diversity of Soda Lake Alkaliphiles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1996, 19, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.; Grant, W.; Jones, B.; Meijer, D.; Márquez, M.; Ventosa, A. Halomonas Magadii Sp. Nov., a New Member of the Genus Halomonas, Isolated from a Soda Lake of the East African Rift Valley. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, K.; Knight, B.P.; Barbosa-Jefferson, V.L.; Lane, P.W.; Lilley, A.K.; Paton, G.I.; McGrath, S.P.; O’Flaherty, S.M.; Hirsch, P.R. Comparison of Methods to Investigate Microbial Populations in Soils under Different Agricultural Management. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 33, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil PH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The Diversity and Biogeography of Soil Bacterial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi-Zecchin, V.J.; Mógor, F.; Figueiredo, G.G.O. Strategies for Characterization of Agriculturally Important Bacteria. In Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity: Vol. 1: Research Perspectives; Springer: Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 1–21. ISBN 9788132226475. [Google Scholar]
- Mwirichia, R.; Muigai, A.; Tindall, B.; Boga, H.; Stackebrandt, E. Isolation and Characterisation of Bacteria from the Haloalkaline Lake Elmenteita, Kenya. Extremophiles 2010, 14, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shao, D.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Q.; Rajoka, M.; Yang, H.; Jin, M. Biological Activity of Lipopeptides from Bacillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5951–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamley, I.W. Lipopeptides: From Self-Assembly to Bioactivity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8574–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Fujita, R.; Kato, Y.; Asahara, M.; Yokota, A. Reclassification of Brevibacillus brevis Strains NCIMB 13288 and DSM 6472 (=NRRL NRS-887) as Aneurinibacillus danicus sp. Nov. and Brevibacillus limnophilus sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraszkiewicz, K.; Bernat, P.; Siewiera, P.; Moryl, M.; Paszt, L.S.; Trzciński, P.; Jałowiecki, Ł.; Płaza, G. Agricultural Potential of Rhizospheric Bacillus Subtilis Strains Exhibiting Varied Efficiency of Surfactin Production. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.H.; Liao, M.J.; Wang, H.K.; Zheng, M.Z.; Xu, J.J.; Guo, J.H. Bacillus Velezensis, a Potential and Efficient Biocontrol Agent in Control of Pepper Gray Mold Caused by Botrytis Cinerea. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdi, S.; Kadir, J.; Mohamed, M.T.M.; Vadamalai, G.; Akter, S. Isolation, Screening and Characterization of Effective Microbes with Potential for Biological Control of Fusarium Wilt of Rock Melon. World J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myo, E.M.; Liu, B.; Ma, J.; Shi, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, K.; Ge, B. Evaluation of Bacillus Velezensis NKG-2 for Bio-Control Activities against Fungal Diseases and Potential Plant Growth Promotion. Biol. Control 2019, 134, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, R.Y.; Horikoshi, K.; Grant, W.D. Extremophiles: Microbial Life in Extreme Environments. Bioscience 1999, 49, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- DeLong, E.; Pace, N. Environmental Diversity of Bacteria and Archaea. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krulwich, T.A.; Agus, R.; Schneier, M.; Guffanti, A.A. Buffering Capacity of Bacilli That Grow at Different PH Ranges. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 162, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Kawamura, Y.; Shida, O.; Yamagata, S.; Deguchi, T.; Ezaki, T. Bacillus Okuhidensis Sp. Nov., Isolated from the Okuhida Spa Area of Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, C.P.; Kumaresan, D.; Hunger, S.; Drake, H.L.; Murrell, J.C.; Shouche, Y.S. Microbiology of Lonar Lake and Other Soda Lakes. ISME J. 2012, 7, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoon, R.N. Lakes of the Gregory Rift Valley: Baringo, Bogoria, Nakuru, Elmenteita, Magadi, Manyara and Eyasi. In Geology of National Parks of Central/Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Kenya’s Lake Bogoria Is Feeding the Global Biotech Industry. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/how-kenyas-lake-bogoria-feeding-global-biotech-industry (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Bano, A.; Muqarab, R. Plant Defence Induced by PGPR against Spodoptera Litura in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Biol. 2017, 19, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernava, T.; Aschenbrenner, I.A.; Grube, M.; Liebminger, S.; Berg, G. A Novel Assay for the Detection of Bioactive Volatiles Evaluated by Screening of Lichen-Associated Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpatte, D.G.; Jhala, Y.K.; Shelat, H.N.; Vyas, R.V. Pseudomonas Fluorescens: A Promising Biocontrol Agent and PGPR for Sustainable Agriculture. In Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity: Vol. 1: Research Perspectives; Springer: Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 257–270. ISBN 9788132226475. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, S.; Sharma, S.; Saraf, M.; Buck, M.; Schumacher, J. Analysis of Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) Production in Klebsiella by LC-MS/MS and the Salkowski Method. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Alikhani, H.A.; Hosseini, H.M. Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) Production Trait, a Useful Screening to Select Endophytic and Rhizosphere Competent Bacteria for Rice Growth Promoting Agents. MethodsX 2015, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korir, H.; Mungai, N.W.; Thuita, M.; Hamba, Y.; Masso, C. Co-Inoculation Effect of Rhizobia and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria on Common Bean Growth in a Low Phosphorus Soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaramoorthy, S.; Raguchander, T.; Ragupathi, N.; Samiyappan, R. Combinatorial Effect of Endophytic and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria against Wilt Disease of Capsicum Annum L. Caused by Fusarium Solani. Biol. Control 2012, 60, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Sekhar, A.C.; Upreti, R.; Mujawar, M.M.; Pasha, S.S. Optimization of Single Plate-Serial Dilution Spotting (SP-SDS) with Sample Anchoring as an Assured Method for Bacterial and Yeast Cfu Enumeration and Single Colony Isolation from Diverse Samples. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waksman, S.A. A Method for Counting the Number of Fungi in the Soil. J. Bacteriol. 1922, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, D. Perfecting Your Spread Plate Technique. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 2011, 12, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullane, P. Research Guides: BIO 2410: Microbiology: Bacterial Colonial Morphology. Available online: https://guides.baker.edu/c.php?g=303096&p=2022446 (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Tripathi, N.; Sapra, A. Gram Staining; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, T.J. Use of the Gram Stain in Microbiology. Biotech. Histochem. 2001, 76, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 7.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, S.; Isar, J.; Saxena, R.K. A Modified Method for the Detection of Microbial Proteases on Agar Plates Using Tannic Acid. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijavec, T.; Lapanje, A. Hydrogen Cyanide in the Rhizosphere: Not Suppressing Plant Pathogens, but Rather Regulating Availability of Phosphate. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 0, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katznelson, H.; Bose, H. Metabolic Activity and Phosphate-Dissolving Capability of Bacterial Isolates from Wheat Roots, Rhizosphere, and Non-Rhizosphere Soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 1959, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Colony Morphology | Cell Morphology | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate | Form | Elevation | Margin | Size | Color | Surface | Shape | Gram Staining |
| B7 | Circular | Raised | Circular | Medium | Cream | Smooth | Streptococcus | Positive |
| B11 | Circular | Raised | Irregular | Small | White | Dull | Diplococcus | Positive |
| B12 | Circular | Flat | Circular | Small | Cream | Smooth | Coccus | Negative |
| B17 | Circular | Raised | Circular | Small | Teal | Smooth | Coccus | Negative |
| B19 | Irregular | Raised | Circular | Small | Blue | Smooth | Coccus | Negative |
| B20 | Penctiform | Flat | Wavy | Medium | Cream-white | Smooth | Coccus | Positive |
| B21 | Irregular | Flat | Lobate | Medium | Cream | Rough | Bacillus | Positive |
| B26 | Circular | Raised | Circular | Small | Cream | Smooth | Streptococcus | Positive |
| B29 | Irregular | Raised | Irregular | Medium | Cream-white | Smooth | Coccus | Positive |
| B30 | Irregular | Raised | Circular | Medium | Cream-white | Smooth | Streptobacillus | Positive |
| B32 | Irregular | Flat | Filamentous | Large | Cream | Dull | Streptococcus | Positive |
| B38 | Circular | Raised | Smooth | Medium | Cream-yellow | Smooth | Coccus | Positive |
| B39 | Circular | Raised | Smooth | Medium | Cream-white | Smooth | Bacillus | Positive |
| Lakes | Isolate Code | Mycelium Length (cm) | Inhibition Rate % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bogoria | Control | 8.4 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 |
| B20 | 6.03 ± 0.25 b | 28.17 | |
| B30 | 5.60 ± 0.20 c | 33.33 |
| Isolate Code | Protease | Pectinase | Phosphate | Chitinase | HCD | Indole-3-Acetic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | −ve | −ve |
| B20 | 1.23 ± 0.03 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.93 ± 0.03 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | −ve | +ve |
| B30 | 1.70 ± 0.06 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.40 ± 0.00 b | 1.37 ± 0.03 a | −ve | +ve |
| CV | 6.82 | 3.00 | 7.32 | |||
| LSD | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.07 | ||
| p> | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wekesa, T.B.; Wekesa, V.W.; Onguso, J.M.; Wafula, E.N.; Kavesu, N. Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus velezensis from Lake Bogoria as a Potential Biocontrol of Fusarium solani in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Bacteria 2022, 1, 279-293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1040021
Wekesa TB, Wekesa VW, Onguso JM, Wafula EN, Kavesu N. Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus velezensis from Lake Bogoria as a Potential Biocontrol of Fusarium solani in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Bacteria. 2022; 1(4):279-293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1040021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWekesa, Tofick B., Vitalis W. Wekesa, Justus M. Onguso, Eliud N. Wafula, and Ndinda Kavesu. 2022. "Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus velezensis from Lake Bogoria as a Potential Biocontrol of Fusarium solani in Phaseolus vulgaris L." Bacteria 1, no. 4: 279-293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1040021
APA StyleWekesa, T. B., Wekesa, V. W., Onguso, J. M., Wafula, E. N., & Kavesu, N. (2022). Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus velezensis from Lake Bogoria as a Potential Biocontrol of Fusarium solani in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Bacteria, 1(4), 279-293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1040021







