Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
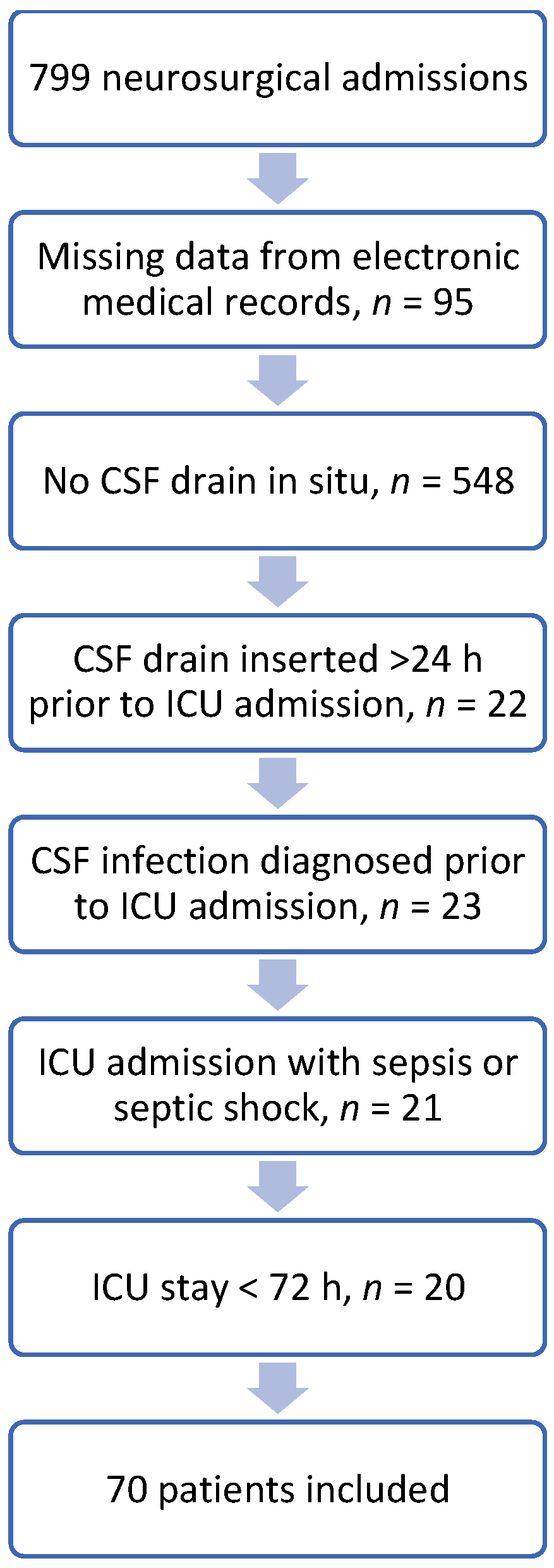
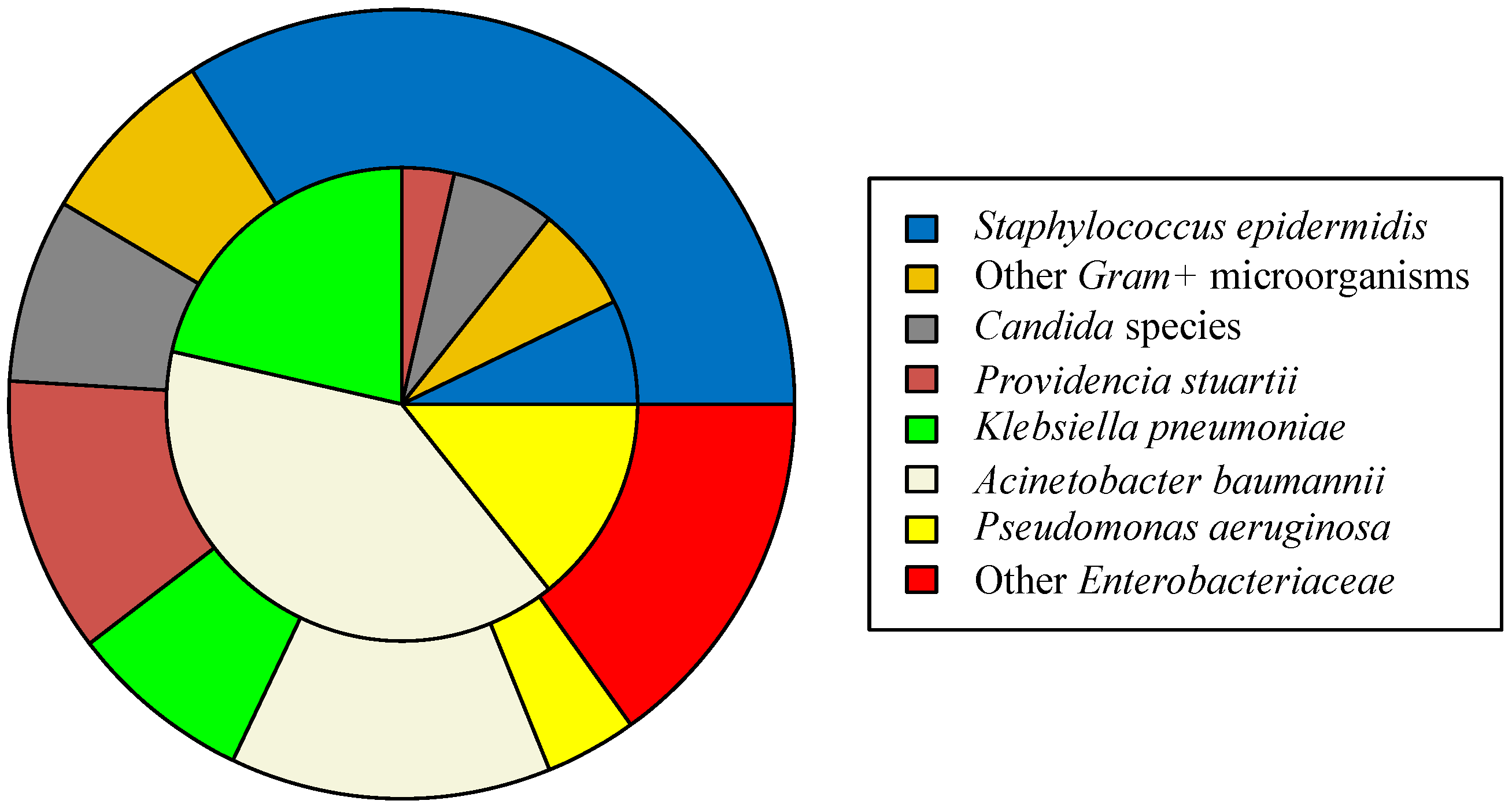
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van de Beek, D.; Drake, J.M.; Tunkel, A.R. Nosocomial Bacterial Meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tunkel, A.R.; Hasbun, R.; Bhimraj, A.; Byers, K.; Kaplan, S.L.; Scheld, W.M.; van de Beek, D.; Bleck, T.P.; Garton, H.J.L.; Zunt, J.R. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival Mechanisms of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mounier, R.; Lobo, D.; Cook, F.; Martin, M.; Attias, A.; Ait-Mamar, B.; Gabriel, I.; Bekaert, O.; Bardon, J.; Nebbad, B.; et al. From the Skin to the Brain: Pathophysiology of Colonization and Infection of External Ventricular Drain, a Prospective Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez, P.; Gordón, M.; Soriano, A.; Gil-Perotin, S.; Marti, V.; Gonzalez-Barbera, E.M.; Sanchez-Aguilar, M.T.; Simal, J.A.; Bonastre, J. Assessment of the in Vivo Formation of Biofilm on External Ventricular Drainages. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheithauer, S.; Bürgel, U.; Ryang, Y.M.; Haase, G.; Schiefer, J.; Koch, S.; Häfner, H.; Lemmen, S. Prospective Surveillance of Drain Associated Meningitis/Ventriculitis in a Neurosurgery and Neurological Intensive Care Unit. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enoch, D.A.; Summers, C.; Brown, N.M.; Moore, L.; Gillham, M.I.; Burnstein, R.M.; Thaxter, R.; Enoch, L.M.; Matta, B.; Sule, O. Investigation and Management of an Outbreak of Multidrug-Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii in Cambridge, UK. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 70, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citerio, G.; Signorini, L.; Bronco, A.; Vargiolu, A.; Rota, M.; Latronico, N. External Ventricular and Lumbar Drain Device Infections in Icu Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Italian Study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.M.; Hsu, J.F.; Lee, C.W.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.R.; Chiang, M.C.; Fu, R.H.; Tsai, M.H. Neurological Complications after Neonatal Bacteremia: The Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akturk, H.; Sutcu, M.; Somer, A.; Aydin, D.; Cihan, R.; Ozdemir, A.; Coban, A.; Ince, Z.; Citak, A.; Salman, N. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Colonization in Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care Units: Risk Factors for Progression to Infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williamson, R.A.; Phillips-Bute, B.G.; McDonagh, D.L.; Gray, M.C.; Zomorodi, A.R.; Olson, D.W.M.; Britz, G.W.; Laskowitz, D.T.; James, M.L. Predictors of Extraventricular Drain-Associated Bacterial Ventriculitis. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.B.; Moradiya, Y.; Shah, J.; Hanley, D.F.; Ziai, W.C. Incidence, Predictors, and Outcomes of Ventriculostomy-Associated Infections in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurocritical Care 2016, 24, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, L.J.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, Y.J.; Wang, S.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yen, H.C. Risk Factors Associated with Postcraniotomy Meningitis: A Retrospective Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, E.F.; Boszczowski, Í.; Freire, M.P.; Pinto, F.C.G.; Guimaraes, T.; Teixeira, M.J.; Costa, S.F. Impact of an Educational Intervention Implanted in a Neurological Intensive Care Unit on Rates of Infection Related to External Ventricular Drains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.A.; Leslie, G.D.; Dobb, G.J.; Roberts, B.; van Heerden, P.V. Decrease in Proven Ventriculitis by Reducing the Frequency of Cerebrospinal Fluid Sampling from Extraventricular Drains: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.R.; Vlachos, S.; Patel, S.; Innocent, S.; Tolias, C.; Barkas, K. Recurrent Sampling and Ventriculostomy-Associated Infections: A Case-Control Study. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hader, W.J.; Steinbok, P. The Value of Routine Cultures of the Cerebrospinal Fluid in Patients with External Ventricular Drains. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, M.; Lipman, J.; Shorr, A.; Shankar, A. A Meta-Analysis of Ventriculostomy-Associated Cerebrospinal Fluid Infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, K.; Rabino, G.; Feder, O.; Eghbaryeh, H.; Zayyad, H.; Sviri, G.; Benenson, R.; Paul, M. Risk Factors for Meningitis in Neurosurgical Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains: Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Nielsen, T.B.; Bonomo, R.A.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.; Spellberg, B. Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview of Acinetobacter Infections: A Century of Challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 409–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.Y.M.; Wong, H.T.; Pu, J.K.S.; Wong, W.K.; Wong, L.Y.W.; Lee, M.W.Y.; Yam, K.Y.; Lui, W.M.; Poon, W.S. Moving the Goalposts: A Comparison of Different Definitions for Primary External Ventricular Drain Infection and Its Risk Factors: A Multi-Center Study of 2575 Patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Wohoush, I.; Rivera, J.; Cairo, J.; Hachem, R.; Raad, I. Comparing Clinical and Microbiological Methods for the Diagnosis of True Bacteraemia among Patients with Multiple Blood Cultures Positive for Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Drai, D.; Elmer, G.; Kafkafi, N.; Golani, I. Controlling the False Discovery Rate in Behavior Genetics Research. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| CSF Infection Present n = 28 | CSF Infection Absent n = 42 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age 1 | 56 (44.75–70) | 52.5 (45.5–61.25) | 0.890 |
| Sex 2 | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 16 | 23 | |
| Female | 12 | 19 | |
| Reason for ICU admission 2 | 0.985 | ||
| Ischemic Stroke | 1 | 2 | |
| Intracranial Hemorrhage | 11 | 15 | |
| Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | 7 | 12 | |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | 3 | 3 | |
| Brain Tumor | 6 | 9 | |
| Foreign body type 2 | 0.349 | ||
| EVD | 21 | 36 | |
| LD | 7 | 6 | |
| Antibiomicrobial-impregnated catheters used 2 | 0.352 | ||
| Yes | 3 | 10 | |
| No | 20 | 32 | |
| Previously cultured pathogens in blood cultures 2 | 0.027 | ||
| Yes | 20 | 18 | |
| No | 8 | 24 | |
| Number of CSF samples sent before bacterial growth 1 | 3 (2–5) | 3.5 (2–5) | 0.473 |
| Foreign body days 1 | 14 (10.75–18) | 12 (7–18.25) | 0.214 |
| Length of ICU stay 1 | 31.5 (23.75–52) | 25.5 (9–33.25) | 0.037 |
| ICU outcome 2 | 0.039 | ||
| Survival | 14 | 32 | |
| Death | 14 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrettou, C.S.; Drosos, E.; Nepka, M.; Bouboulis, G.; Kalamatianos, T.; Liakopoulou, C.; Gkouvelos, G.; Kotanidou, A.; Stranjalis, G. Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study. Bacteria 2022, 1, 48-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1010005
Vrettou CS, Drosos E, Nepka M, Bouboulis G, Kalamatianos T, Liakopoulou C, Gkouvelos G, Kotanidou A, Stranjalis G. Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study. Bacteria. 2022; 1(1):48-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrettou, Charikleia S., Evangelos Drosos, Martha Nepka, George Bouboulis, Theodosis Kalamatianos, Christina Liakopoulou, Grigorios Gkouvelos, Anastasia Kotanidou, and George Stranjalis. 2022. "Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study" Bacteria 1, no. 1: 48-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1010005
APA StyleVrettou, C. S., Drosos, E., Nepka, M., Bouboulis, G., Kalamatianos, T., Liakopoulou, C., Gkouvelos, G., Kotanidou, A., & Stranjalis, G. (2022). Bacteremia Is a Risk Factor for Cerebrospinal Fluid Infection in Patients with Cerebrospinal Fluid Drains—A Retrospective Study. Bacteria, 1(1), 48-55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bacteria1010005








