Defined, Simplified, Scalable, and Clinically Compatible Hydrogel-Based Production of Human Brain Organoids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GelMA Synthesis
2.2. Preparation of GelMA Hydrogel Discs
2.3. Printing GelMA Hydrogel Multiwell Arrays
2.4. Rheometry
2.5. Human iPSC Culture
2.6. Human iPSC Differentiation and Generation of Brain Organoids
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Live Cell Labelling
2.11. Calcium Imaging
2.12. Multielectrode Array Electrophysiological Recordings
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of GelMA Hydrogels
3.2. iPSC Culture and Differentiation on GelMA Hydrogels
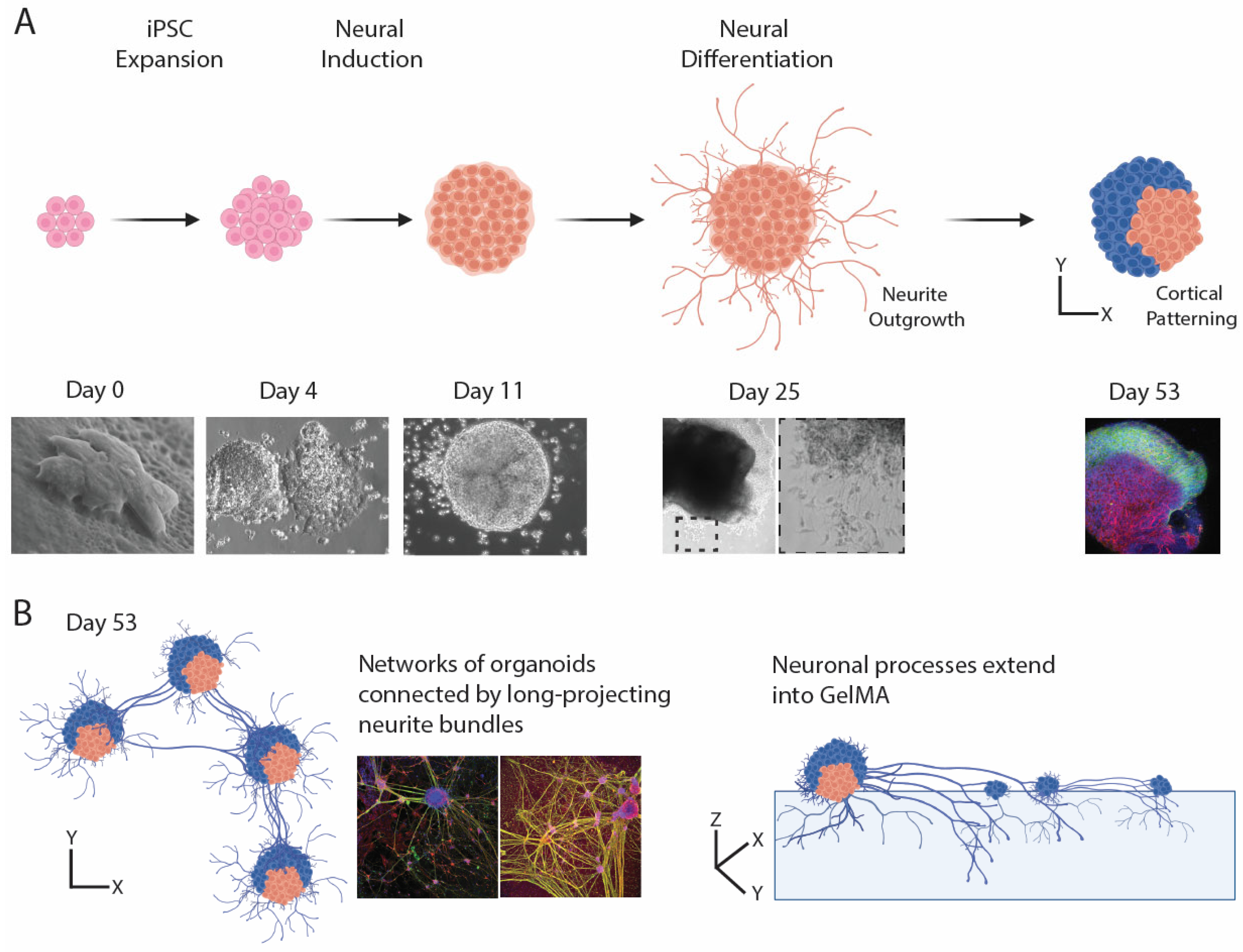
3.3. Generation of Brain Organoids
3.4. Brain Organoids Exhibit Cellular and Regional Heterogeneity
3.5. Recapitulation of Archetypal Brain Neuronal Network Activity
4. Discussion
5. Limitations, Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Generation of cerebral organoids from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aurand, E.R.; Lampe, K.J.; Bjugstad, K.B. Defining and designing polymers and hydrogels for neural tissue engineering. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 72, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, Z.; Solanki, A.; Hamilos, H.; Levy, O.; Wen, K.; Yin, Z.; Karp, J.M. Application of biomaterials to advance induced pluripotent stem cell research and therapy. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 987–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Q.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. 3D Bioprinting human induced pluripotent stem cell constructs for in situ cell proliferation and successive multi-lineage differentiation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Inokuma, M.S.; Denham, J.; Golds, K.; Kundu, P.; Gold, J.D.; Carpenter, M.K. Feeder-free growth of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.E.; Levenstein, M.E.; Jones, J.M.; Berggren, W.T.; Mitchen, E.R.; Frane, J.L.; Crandall, L.J.; Daigh, C.A.; Conard, K.R.; Piekarczyk, M.S.; et al. Derivation of human embryonic stem cells in defined conditions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykandriotis, E.; Arkudas, A.; Horch, R.E.; Kneser, U.; Mitchell, G. To matrigel or not to matrigel. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichol, J.W.; Koshy, S.T.; Bae, H.; Hwang, C.M.; Yamanlar, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, J.L.; Quigley, A.F.; Duchi, S.; O’Connell, C.D.; Crook, J.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Cook, M.; Kapsa, R.M.I. Three-dimensional neural cultures produce networks that mimic native brain activity. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, A.; Schaffer, D.V. Biophysical regulation of stem cell behavior within the niche. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2012, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keung, A.J.; Asuri, P.; Kumar, S.; Schaffer, D.V. Soft microenvironments promote the early neurogenic differentiation but not self-renewal of human pluripotent stem cells. Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Rengarajan, V.; Kjar, A.; Huang, Y. A matrigel-free method to generate matured human cerebral organoids using 3D-Printed microwell arrays. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simsa, R.; Rothenbucher, T.; Gurbuz, H.; Ghosheh, N.; Emneus, J.; Jenndahl, L.; Kaplan, D.; Bergh, N.; Serrano, A.M.; Fogelstrand, P. Brain organoid formation on decellularized porcine brain ECM hydrogels. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindborg, B.A.; Brekke, J.H.; Vegoe, A.L.; Ulrich, C.B.; Haider, K.T.; Subramaniam, S.; Venhuizen, S.L.; Eide, C.R.; Orchard, P.J.; Chen, W.; et al. Rapid induction of cerebral organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells using a chemically defined hydrogel and defined cell culture medium. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cullen, D.K.; Gordián-Vélez, W.J.; Struzyna, L.A.; Jgamadze, D.; Lim, J.; Wofford, K.L.; Browne, K.D.; Chen, H.I. Bundled three-dimensional human axon tracts derived from brain organoids. iScience 2019, 21, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagley, J.A.; Reumann, D.; Bian, S.; Lévi-Strauss, J.; Knoblich, J.A. Fused cerebral organoids model interactions between brain regions. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Nguyen, H.N.; Song, M.M.; Hadiono, C.; Ogden, S.C.; Hammack, C.; Yao, B.; Hamersky, G.R.; Jacob, F.; Zhong, C.; et al. Brain-region-specific organoids using mini-bioreactors for modeling ZIKV exposure. Cell 2016, 165, 1238–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, A.X.; Cukuroglu, E.; Tran, H.D.; Göke, J.; Tan, Z.Y.; Saw, T.Y.; Tan, C.-P.; Lokman, H.; et al. Midbrain-like organoids from human pluripotent stem cells contain functional dopaminergic and neuromelanin-producing neurons. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, J.; Pao, G.M.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Verma, I.M. Glioblastoma Model Using Human Cerebral Organoids. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krieger, T.G.; Tirier, S.M.; Park, J.; Jechow, K.; Eisemann, T.; Peterziel, H.; Angel, P.; Eils, R.; Conrad, C. Modeling glioblastoma invasion using human brain organoids and single-cell transcriptomics. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goranci-Buzhala, G.; Mariappan, A.; Gabriel, E.; Ramani, A.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Buccarelli, M.; D’Alessandris, Q.G.; Pallini, R.; Gopalakrishnan, J. Rapid and Efficient Invasion Assay of Glioblastoma in Human Brain Organoids. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Song, H.; Ming, G.L. Brain organoids: Advances, applications, and challenges. Development 2019, 146, dev166074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Higginbottom, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Bourke, J.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. Defined, Simplified, Scalable, and Clinically Compatible Hydrogel-Based Production of Human Brain Organoids. Organoids 2023, 2, 20-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2010002
Tomaskovic-Crook E, Higginbottom SL, Zhang B, Bourke J, Wallace GG, Crook JM. Defined, Simplified, Scalable, and Clinically Compatible Hydrogel-Based Production of Human Brain Organoids. Organoids. 2023; 2(1):20-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomaskovic-Crook, Eva, Sarah Liza Higginbottom, Binbin Zhang, Justin Bourke, Gordon George Wallace, and Jeremy Micah Crook. 2023. "Defined, Simplified, Scalable, and Clinically Compatible Hydrogel-Based Production of Human Brain Organoids" Organoids 2, no. 1: 20-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2010002
APA StyleTomaskovic-Crook, E., Higginbottom, S. L., Zhang, B., Bourke, J., Wallace, G. G., & Crook, J. M. (2023). Defined, Simplified, Scalable, and Clinically Compatible Hydrogel-Based Production of Human Brain Organoids. Organoids, 2(1), 20-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/organoids2010002










