Abstract
Monitoring Campylobacter and antimicrobial resistance is critical, as its presence in the food chain, particularly in poultry, represents a serious threat to public health. However, despite its significant impact, this bacterium remains largely underestimated and under-surveilled in many countries, including Morocco. The current study aims to understand the occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in different poultry production systems, highlighting the importance of continuously monitoring antimicrobial susceptibility in these bacteria. For this purpose, 300 poultry samples were collected from a slaughterhouse and 254 from traditional markets in the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region. The research on Campylobacter was performed according to the standard ISO10272-1(2017), and the confirmation of Campylobacter species was carried out using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Additionally, the disk diffusion method was employed to assess antimicrobial susceptibility, and conventional PCR was utilized to detect the presence of the tet(O) gene in tetracycline-resistant strains. Out of 554 samples collected, 159 (28.7%) tested positive for Campylobacter, of which 84% were identified as Campylobacter coli and 16% as Campylobacter jejuni. Moreover, the results revealed a notably higher detection of Campylobacter in traditional markets (41.33%) than in slaughterhouses (19.85%). Additionally, it was more prevalent in chicken samples (35.37%) than in turkey samples (22.02%). Campylobacter resistance to antimicrobials revealed a resistance rate of 99% to ciprofloxacin, 73% to ampicillin, 82% to tetracycline, 29% to erythromycin, and 0% to gentamicin, as well as to the association of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Among the strains with a phenotypic resistance profile to tetracycline, 80% carried the tet(O) gene. The results provide an overview of the current state of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter in Morocco. They underline the urgent need for the prudent use of antimicrobials and may encourage further research into the development of new antimicrobial agents. They also highlight the importance of raising awareness of the risk of carcass contamination
1. Introduction
Morocco’s poultry sector produces 655,000 tonnes of poultry meat and 5 billion eggs a year. It covers 100% of poultry meat and egg requirements [1]. This sector is regulated by Law 49-99, which imposes authorizations and veterinary controls on farms, slaughterhouses, and processing plants [2].
Campylobacteriosis ranks among the most commonly reported foodborne illnesses worldwide, posing significant public health concerns. Globally, C. jejuni and C. coli are responsible for approximately 98% of all human Campylobacter gastroenteritis cases [3]. The infection may result in severe extra-intestinal sequelae, especially acute neurological symptoms such as the Guillain-Barré syndrome and Miller-Fisher syndrome [4]. The cost of Campylobacteriosis to public health systems and in terms of lost productivity in the EU is estimated by the European Food Safety Authority at around 2.4 billion euros per year, with approximately 200,000 human cases per year infected with the most frequently reported foodborne Campylobacter in the European Union (EU) [5].
Although various transmission routes exist, poultry meat stands out as one of the main routes by which these pathogens are transmitted [6]. Recognizing its importance, it is imperative to implement an action plan for the surveillance of Campylobacter spp. and its antimicrobial resistance. This will enable a better understanding of the risks to public health and the implementation of more targeted and effective control measures.
Campylobacter infections in humans are generally self-limiting, but in cases where symptoms persist and in immunocompromised individuals, antimicrobials such as macrolides (erythromycin), fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin), and tetracycline are administered. Macrolides and fluoroquinolones are the first-line treatment measures when therapeutic intervention is required, while tetracycline serves as a choice in treating clinical Campylobacter infection [7]. The development of antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter species has serious implications for treating human infections [8]. Alarming studies show that there is a link between the uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents to prevent, control, and treat bacterial infections in animals and the emergence and spread of resistance, and even multi-resistance, in Campylobacter strains [9].
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that bacterial antimicrobial resistance is responsible for 700,000 deaths annually and warns that, without coordinated and effective actions, this phenomenon could lead to 10 million deaths per year by 2050 [10].
In light of these concerning trends, it becomes imperative to explore measures to mitigate the spread of Campylobacter infections and address antimicrobial resistance.
This study aimed to (i) assess the presence of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in various poultry samples collected from slaughterhouses and traditional markets in the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region in Morocco, (ii) detect the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in the isolated strains, and (iii) investigate the presence of the tet(O) gene in strains resistant to tetracycline.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
This study used post-mortem animal samples obtained exclusively from carcasses originally intended for human consumption, following Moroccan food safety law 28–07. As no live animals were involved, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) approval was not required. Samples were sourced from government-approved slaughterhouses and traditional markets. No animals were sacrificed for this research. To ensure data reliability and public health safeguards, sample collection and handling followed the internationally recognized ISO10272-1(2017) [11] protocols to prevent cross-contamination. This approach aligns with replacement principle of the 3Rs, promoting the ethical use of by-products from the food industry.
2.2. Study Area
This study was conducted in the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region, Morocco, which covers a total area of 17,570 km2, representing 2.5% of the country’s total area. The region is administratively divided into three prefectures (Rabat, Salé, and Skhirate-Témara) and four provinces (Khémisset, Kénitra, Sidi-Kacem, and Sidi-Slimane).
2.3. Sample Collection
A total of 554 non-frozen poultry samples were collected from the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region from September 2022 to October 2023. Of these, 300 samples (60 turkey caecum, 60 turkey neck skin, 30 turkey breast muscle, 60 chicken caecum, 60 chicken neck skin, and 30 chicken breast muscle) were obtained from a slaughterhouse in Temara, which supplies poultry meat to almost the entire Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region. The remaining 254 samples (51 turkey caecum, 46 turkey neck skin, 30 turkey breast muscle, 51 chicken caecum, 46 chicken neck skin, and 30 chicken breast muscle) were collected from five traditional markets. Regarding the age of the birds before slaughter, slaughterhouses operate under legal regulations, which set the minimum slaughter age at 18 days for broiler chickens and 100 days for turkeys according to decree from the Minister of Agriculture, Maritime Fisheries, Rural Development, and Water and Forests (n° 2986-17, dated 7 November 2017) concerning the approval and publication of a standard specification document related to the organic production of livestock animals and beekeeping products.
All samples were carefully placed in sterile bags to avoid cross-contamination and transported under cold conditions (4 °C) to the laboratory within two hours, where they were analyzed the same day.
2.4. Culture and Growth Conditions
The enrichment and isolation of Campylobacter was performed according to the standard ISO 10272-1 (2017). In brief, for samples such as muscle and neck skin, it was necessary to apply an enrichment step. A 10 g sample was homogenously mixed with 90 mL Preston Enrichment Broth Base (Biolife, Italiana, Milano-Italia), supplemented with Preston antimicrobic supplement (Biolife, Italiana, Milano-Italia) and containing 5% lysed horse blood. Homogenization was carried out in a stomacher for two minutes, and then an incubation period under microaerophilic conditions was performed at 41.5 °C for 24 h.
A loopful (10 µL) of the broth enrichment culture was streaked onto mCCDA (Biolife, Italiana, Milano-Italia) plates that were prepared by adding Bolton CCDA antimicrobic supplement (Biolife, Italiana, Milano-Italia) to mCCDA. These plates were then incubated under microaerophilic conditions at 41.5 °C for 48 h. After that, the suspicious colony was selected and inoculated onto Columbia Agar Base (Condalab, Madrid, Spain) with 5% lysed horse blood.
For caecum samples, a loopful (10 µL) from the interior of the caecum was directly streaked into mCCDA and then incubated under microaerophilic conditions at 41.5 °C for 48 h. The suspected colonies were selected and inoculated onto Columbia Agar Base containing 5% lysed horse blood and incubated at 41.5 °C.
2.5. Biochemical Identification
The pure suspected colonies, obtained from different samples, were analyzed for the following properties, according to the ISO 10272-1 (2017) standard:
2.5.1. Culture Characteristics
The strains studied were characterized based on their phenotypic properties, including Gram staining, morphology, motility, and growth requirements. Gram-staining confirmed their Gram-negativity, while microscopic observation revealed a curved bacillus morphology. The mobility of the strains was assessed to verify their tendril-like movement. In addition, dependence on a microaerophilic environment was analyzed to confirm their adaptation to specific growth conditions by incubating them aerobically at 25 °C.
2.5.2. Biochemical Reactions
Various enzymatic tests were carried out to assess oxidase and catalase activity, as well as the ability of the strains to hydrolyze hippurate and indoxyl acetate.
2.6. Confirmation of Campylobacter Species
The strains isolated were subcultured using an overnight culture, and one pure colony was spotted onto a one-use target (MBT Biotarget 96 MALDI Biotyper® IVD System, Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) and overlaid with 0.1 µL of matrix solution (a-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). The target plate was then inserted into a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer (MALDI Biotyper, MBT smart, Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). Peptidic spectra were compared with the Bruker MALDI Biotyper library (version 5627) and software (version 3.4) (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany).
2.7. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
The disk diffusion method was employed to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility, according to the international guideline recommendations of the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST, 2023) [12]. Six antimicrobials (Liofilchem, Scozia, Italy) were tested, including gentamicin (10 μg), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (20/10 μg), erythromycin (15 μg), tetracycline (30 μg), ampicillin (10 μg), and ciprofloxacin (5 μg). From a fresh culture, several colonies were transferred to reach a standard inoculum adjusted to 0.5 McFarland. On a dried plate of Mueller–Hinton agar (Biokar, Pantin, France) supplemented with 5% lysed horse blood and β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Acros organicsTM, Heysham Lancashire, UK), inoculation was performed by swabbing the surface, and the plate was allowed to dry. After that, antimicrobial disks were placed upon the plates and incubated at 42 °C for up to 48 h. The diameters of the inhibition zone around the disks were measured, and the results were interpreted according to the criteria provided by the EUCAST guidelines [12].
2.8. Detection of Tet(O) Gene by Conventional PCR
Campylobacter spp. strains showing phenotypic resistance to tetracycline were subjected to DNA extraction. Colonies were harvested, suspended in 200 μL of PBS, and incubated at 100 °C for 10 min. Cell suspensions were centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was collected and transferred to a new sterile tube.
A PCR mix (25 μL), consisting of 12.5 μL of PCR buffer (GoTaq®G2 Green Master Mix Metabion international AG, Planegg, Germany), and 1 μL (1 μL of the forward (Fw) primer and 1 μL of the reverse (Rv) primer) of tet(O) primers (20 μM) was mixed with 5 μL of previously extracted DNA and supplemented with 5.5 μL of nuclease-free water.
The conserved forward primer DMT1 and reverse primer DMT2 from Metabion international AG (Planegg, Germany) were used to generate a 559-bp tet(O) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Primers description used for the detection of tet(O).
The PCR cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. Campylobacter jejuni ATCC 33560 were used as a negative control.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
GraphPad Prism 10th Version software (GraphPad Software, LLC, San Diego, CA, USA) was used to analyze the data. Our data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). The two-way ANOVA repeated measures test was performed to compare values of various groups. A p-value < 0.05 indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
2.10. Quality Assurance
All the techniques outlined in this study are first tested using reference strain Campylobacter jejuni ATCC 33560 as a quality control strain for standard operational procedures.
3. Results
3.1. Strain Identification
The biochemical tests indicated that 133 isolates were Gram-negative, catalase and oxidase-positive, able to grow only in microaerophilic conditions at 41.5 °C, and able to hydrolyze indoxyl acetate. Additionally, 26 showed an ability to hydrolyze hippurate.
The results of the identification by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry were consistent with the biochemical tests, indicating 133 Campylobacter coli and 26 Campylobacter jejuni. The identification score ranged from 2.00 to 3.00, which represents identification with a high degree of confidence.
3.2. Occurrence of Campylobacter Species in Various Samples
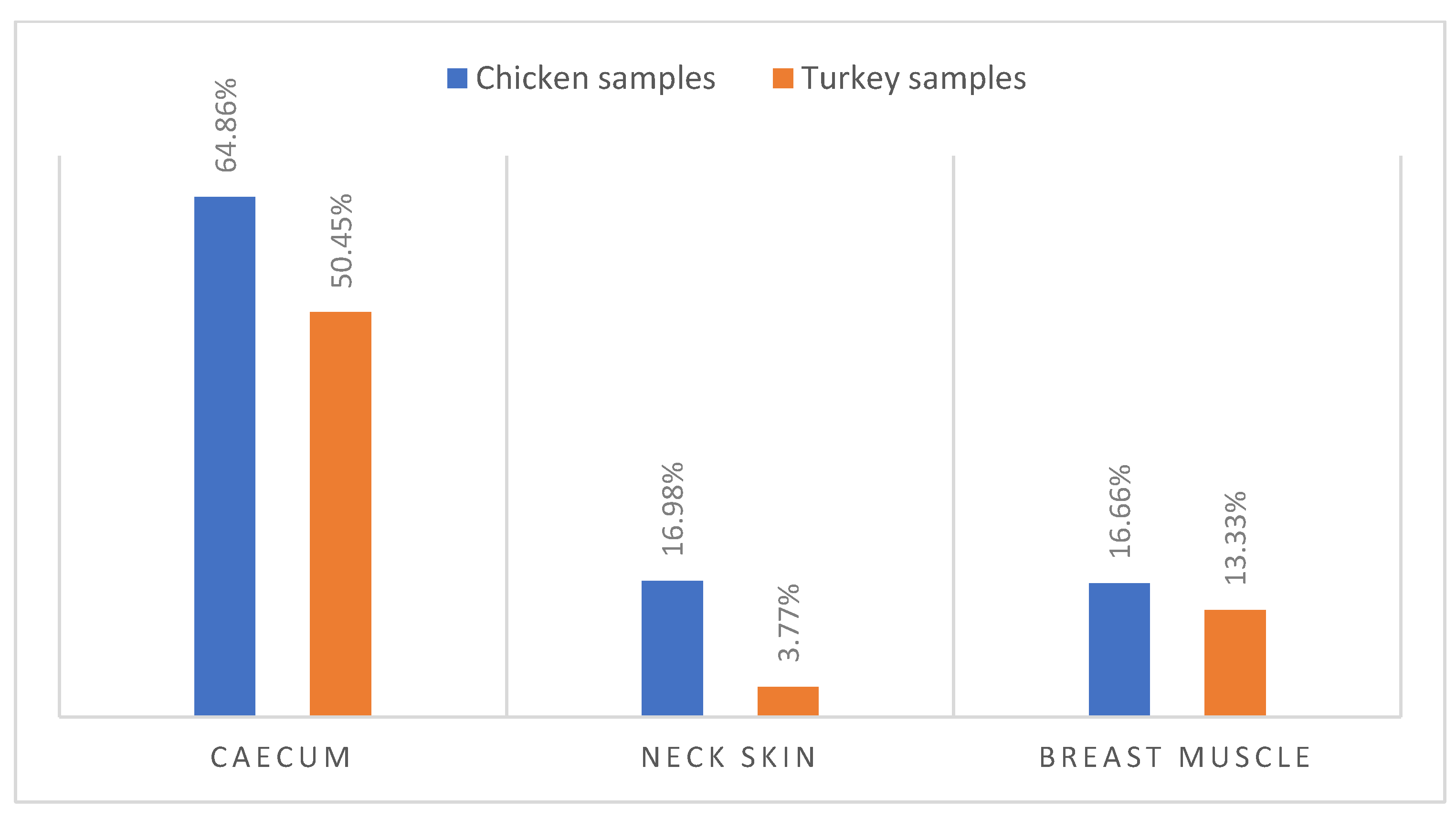
According to biochemical identification and MALDI-TOF confirmation, 159 (28.7%) Campylobacter isolates were recovered from 150 poultry samples, including 133 isolates of Campylobacter coli (89 isolates in chicken samples and 44 isolates in turkey samples) and 26 isolates of Campylobacter jejuni (9 isolates in chicken samples and 17 isolates in turkey samples). Notably, (57.65%) of caecum samples were colonized by Campylobacter, with a higher occurrence in chicken caecum (64.86%) compared to turkey caecum (50.45%) (Figure 1).
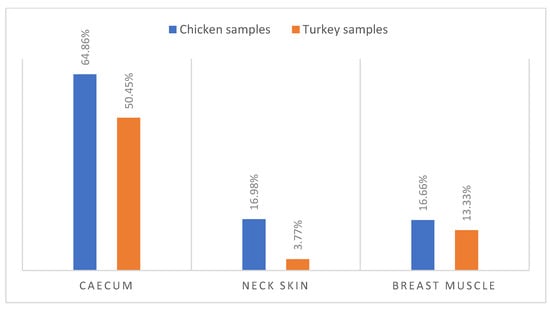
Figure 1.
Occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in Turkey and Chicken samples.
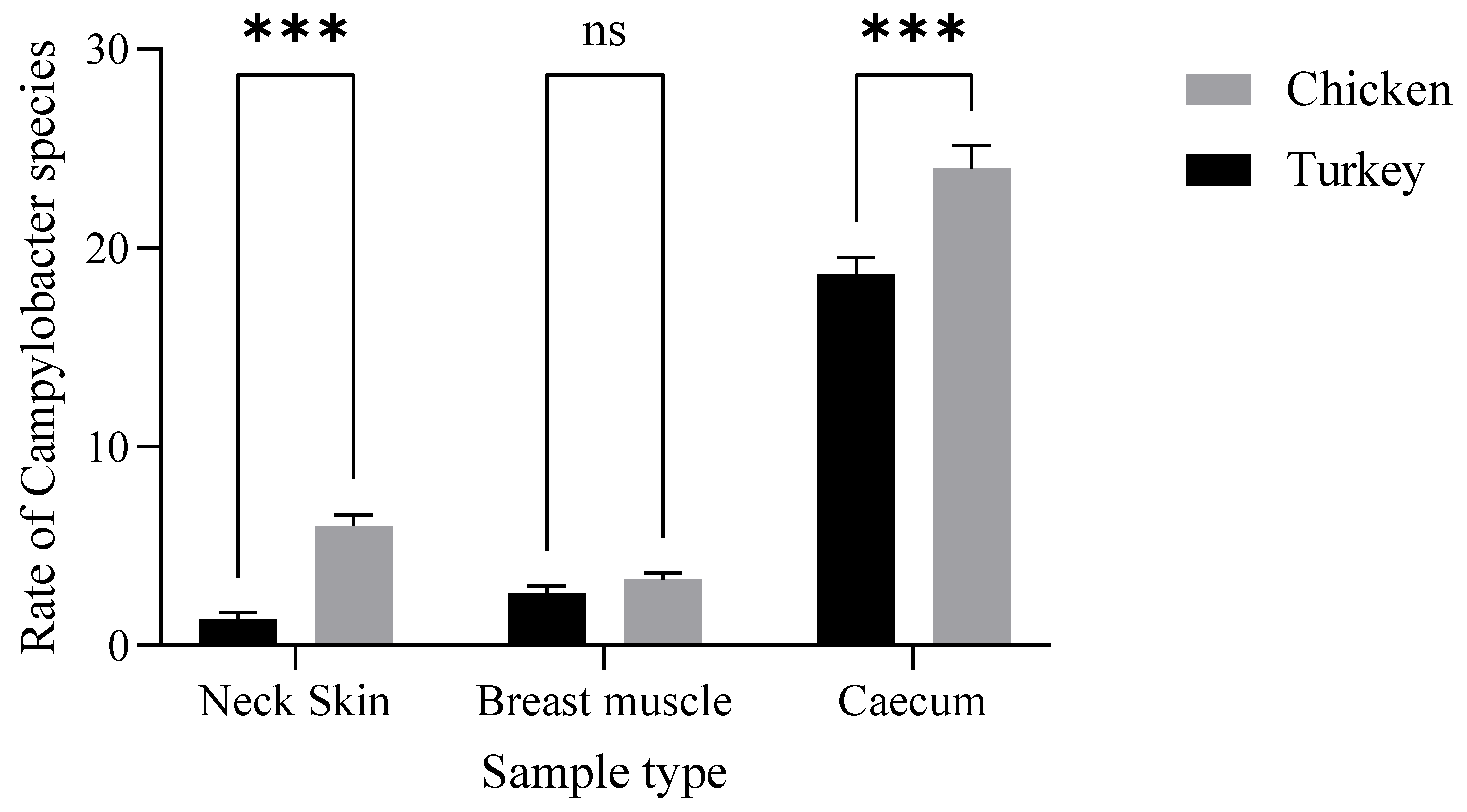
Additionally, chicken samples showed a higher contamination rate in neck skin (16.98%) and in muscle (16.66%) compared to turkey, which demonstrated contamination rates of 3.77% in neck skin and 13.33% in muscle (Figure 1). Furthermore, there were statistically significant variations (p ˂ 0.001) in the incidence of Campylobacter contamination between turkey and chicken samples (Figure 2).
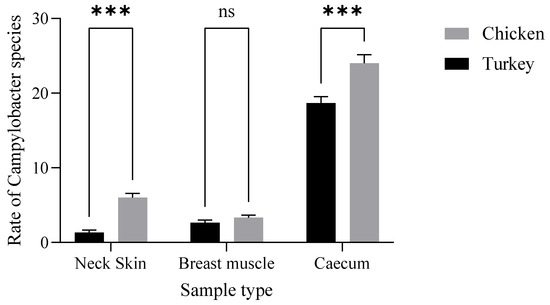
Figure 2.
Distribution of Campylobacter spp. in turkey and chicken samples. The results indicate that the poultry type (F (1.12) = 40.96, p < 0.0001) and their interaction (F (2.12) = 6.880, p = 0.0102) have a statistically significant effect (Neck Skin ***: p = 0.0004; Caecum ***: p= 0.0001).
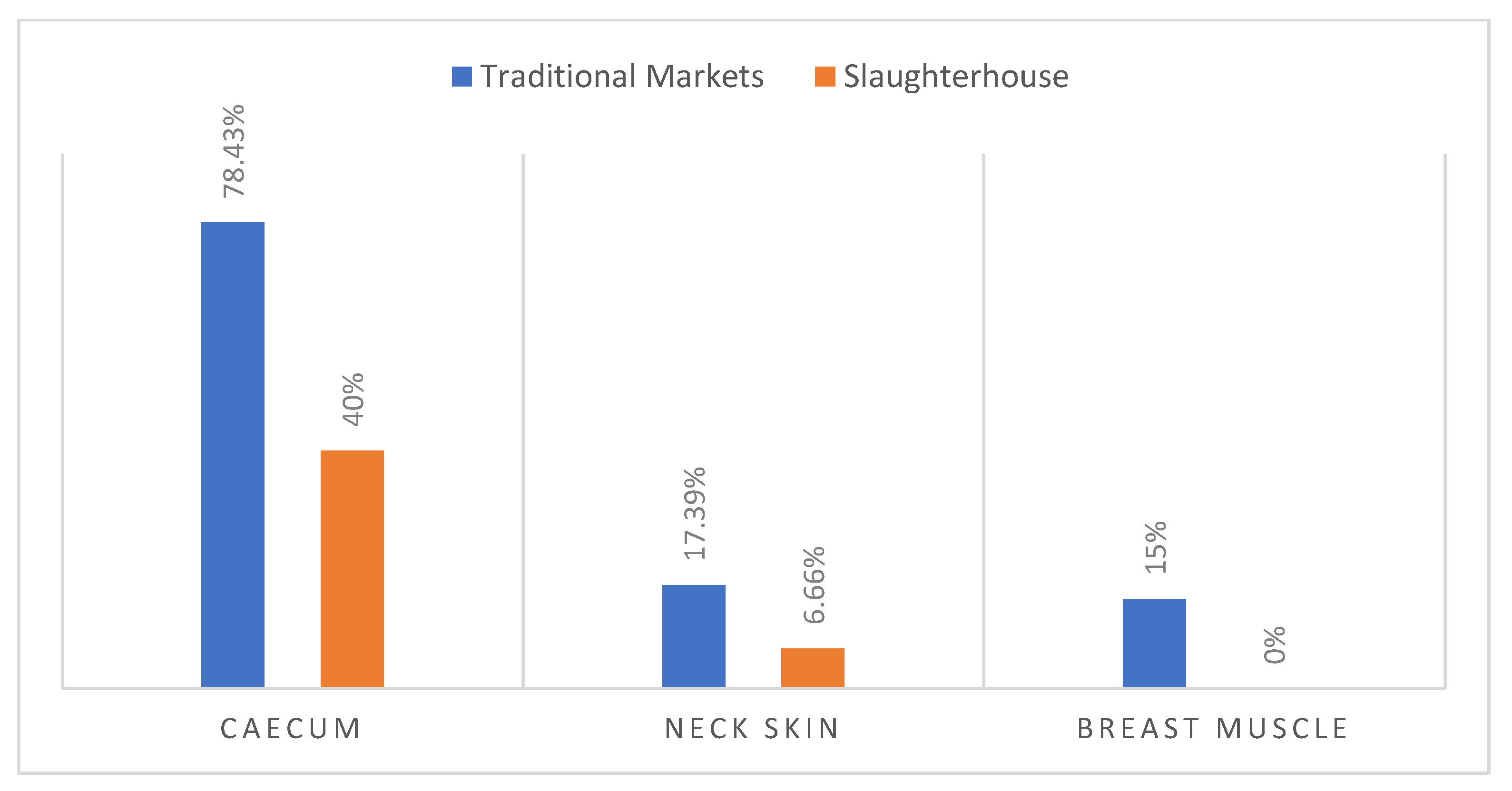
The Campylobacter rate observed in caecum samples coming from traditional markets (78.43%) was higher compared to caecum samples from slaughterhouses (40%) (Figure 3).
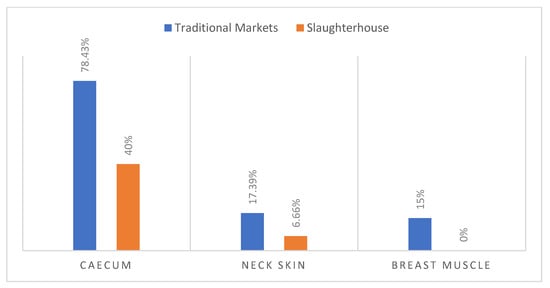
Figure 3.
Occurrence of Campylobacter in samples from slaughterhouse and from traditional market.
Regarding carcass contamination with Campylobacter, the slaughterhouse showed 6.66% of positive neck skin samples and 0% in muscle. However, 17.39% and 15% were revealed in the traditional market samples (Figure 3).
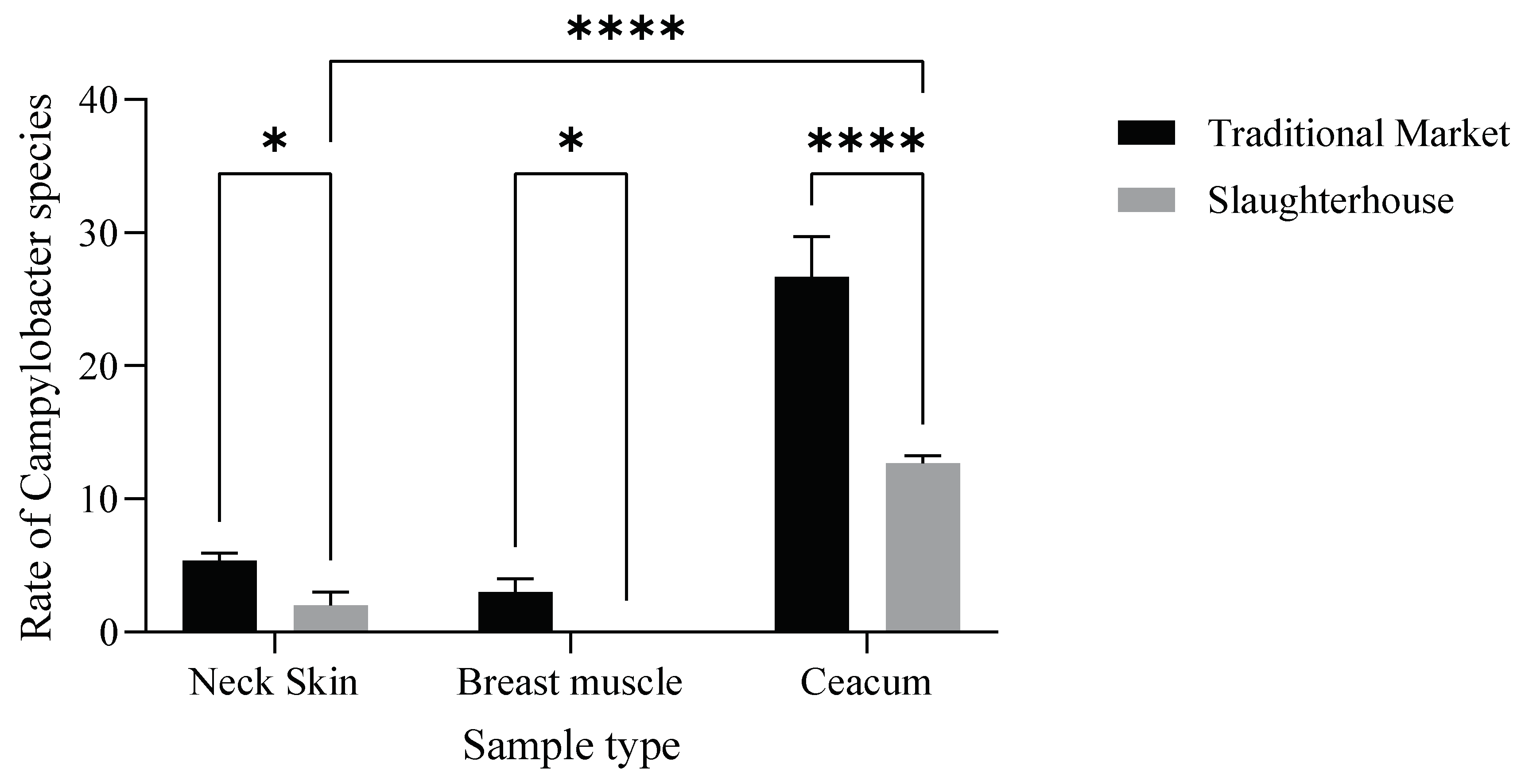
Moreover, the incidence of Campylobacter varied significantly (p < 0.001) (Figure 4) between slaughterhouses and traditional markets.
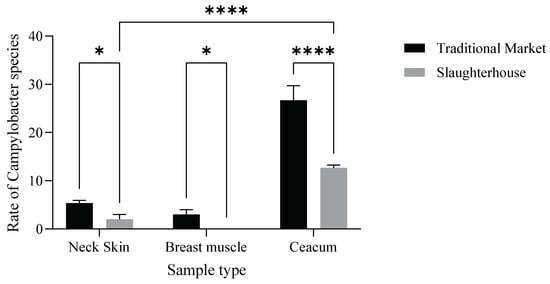
Figure 4.
Distribution of Campylobacter spp. in the samples from the slaughterhouses and traditional markets. The results indicate that the market type (F (1.12) = 103.4, p < 0.0001) and their interaction (F (2.12) = 29.36, p < 0.0001) have a statistically significant effect (Neck Skin *: p= 0,014; Breast Muscle *: p = 0.023; **** p < 0.0001).
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
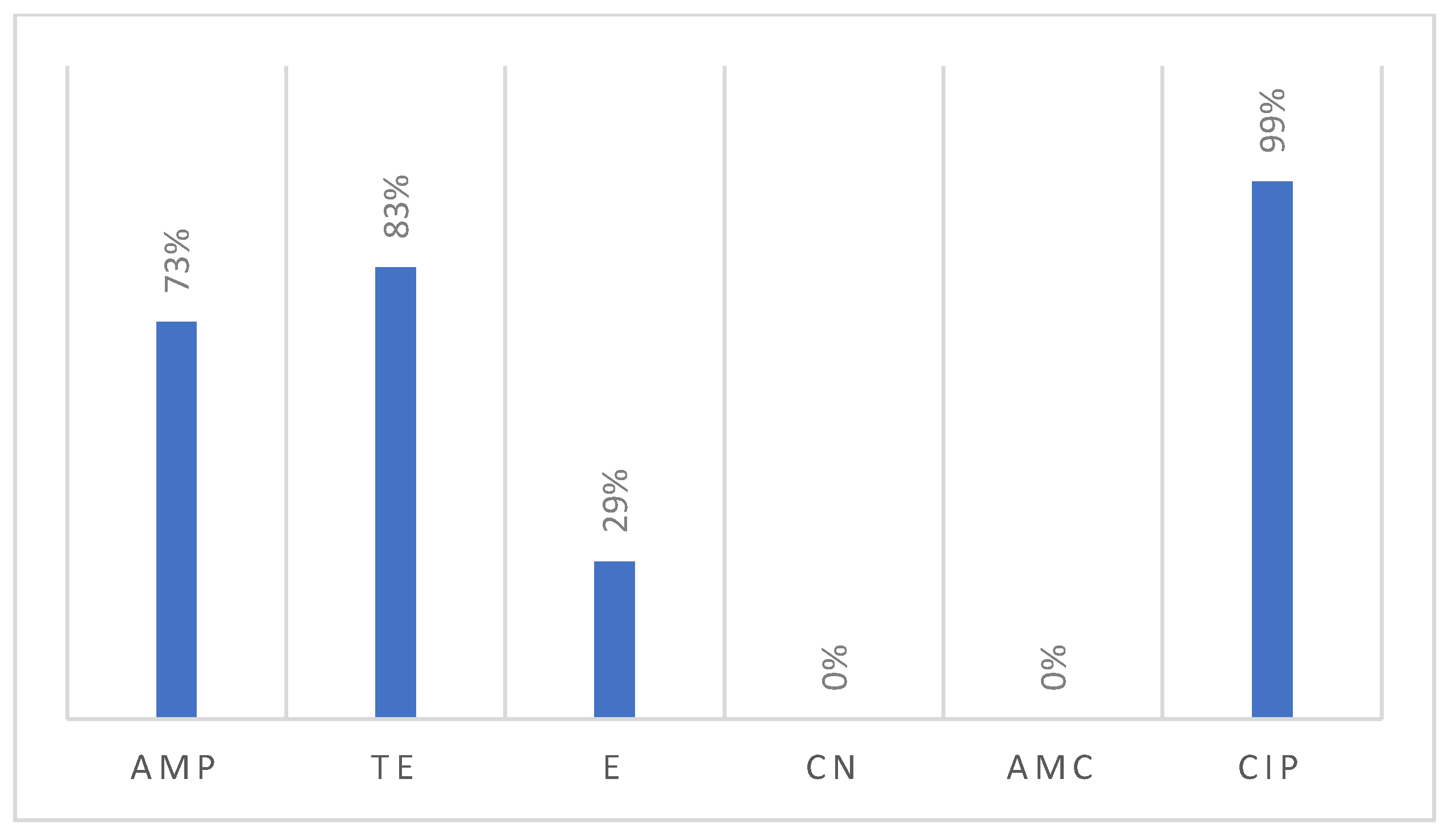
All 159 recovered Campylobacter isolates were tested for their susceptibility against six antimicrobials, revealing notable resistance patterns (Figure 5). Interestingly, nearly all the examined Campylobacter isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin (99%). Additionally, the majority of isolates were resistant to tetracycline (83%), followed by ampicillin (73%), and erythromycin (29%). Meanwhile, none of the tested isolates showed resistance against gentamicin (0%) or the association of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid (0%).
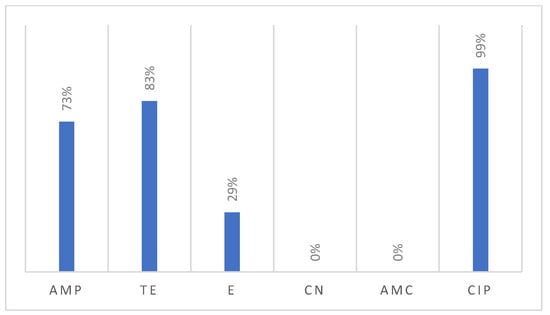
Figure 5.
Resistance profile of Campylobacter isolated from poultry samples.
The resistance profiles of both C. coli and C. jejuni are largely similar (Table 2). However, there are notable differences in resistance to specific antimicrobials. For instance, in the case of tetracycline, ampicillin, and erythromycin, C. jejuni exhibits a higher resistance prevalence (80.45%, 71.18%, 35.33%, respectively) compared to C. coli (96.15%, 61.53%, 19.23%, respectively).

Table 2.
Antimicrobial resistance pattern of C. coli and C. jejuni isolates in the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region.
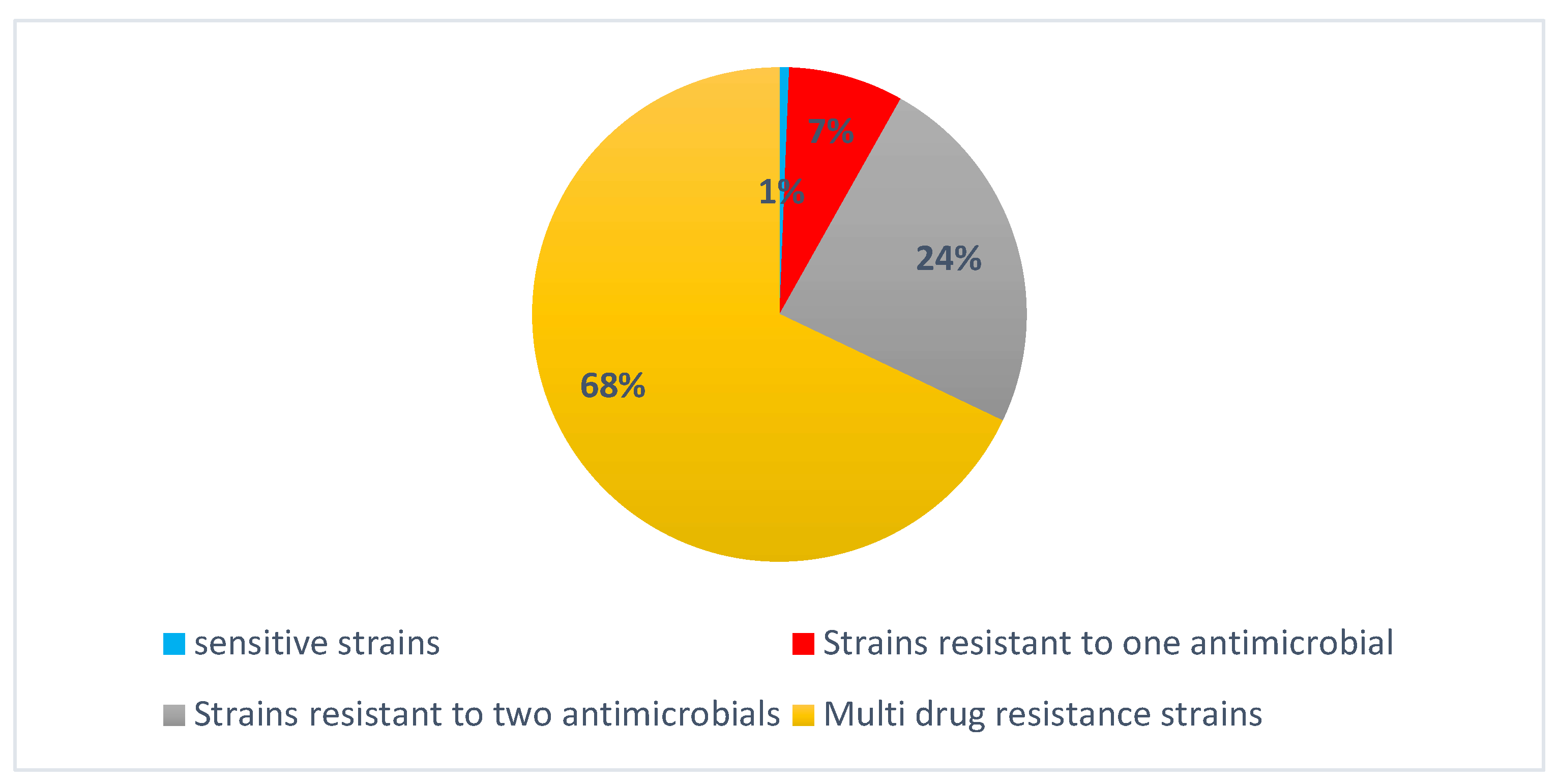
Strains of Campylobacter analyzed for antimicrobial susceptibility revealed a diverse resistance profile (Figure 6). Of the total isolates, 1% demonstrated full susceptibility to all tested antibiotics, while 7% exhibited resistance to a single antibiotic. A further 28% were resistant to two antibiotics. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains accounted for a substantial 68% of the isolates for fluoroquinolone, macrolide, β-lactam, and tetracycline (Table 3).
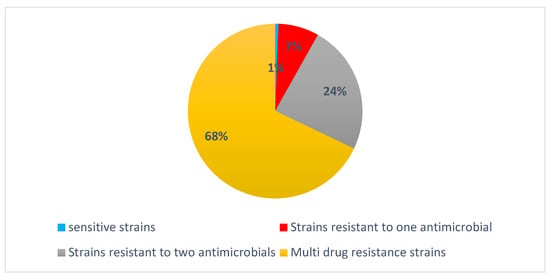
Figure 6.
Distribution of antibiotic resistance among Campylobacter spp. isolates.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance profile of strains isolated.
3.4. Molecular Detection of Tetracycline Resistance
A total of 130 phenotypically resistant Campylobacter strains were examined for the presence of the tet(O) gene using a conventional PCR assay. The results demonstrated the presence of this gene in 104 out of 130 (80%) Campylobacter strains.
4. Discussion
Campylobacteriosis is not a novel disease. However, it remains a significant challenge for poultry producers, food processors, and retailers. Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli are prevalent causative agents of human enteritis globally. The widespread occurrence of these infections is associated with substantial economic burdens. In the present study, the findings demonstrated that the occurrence of Campylobacter species in the poultry samples analyzed was 28.7%, including 133 isolates of Campylobacter coli and 26 isolates of Campylobacter jejuni according to biochemical and MALDI-TOF identification. This indicates a dominance of Campylobacter coli, consistent with the results of a study conducted by El Baaboua et al. [14], which reported a predominance of Campylobacter coli (108 isolates) compared to Campylobacter jejuni (22 isolates). Similarly, Pillay et al. [15], in a study conducted in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, found a distribution of 57% of Campylobacter coli and 43% of Campylobacter jejuni. The presence of Campylobacter in these poultry samples at such a high level suggests that this bacterium is widespread in this population, which may raise concerns for both food safety and public health, given that poultry products are the most widely consumed products in Morocco by the population as a whole due to their low price compared with red meat.
Regarding caecum colonization, Campylobacter was detected in 57.65% of the samples, with a notably higher occurrence in chicken caecum (64.86%) compared to turkey caecum (50.45%) (Figure 1). Generally, this occurrence rate can be considered as moderate compared to the study carried out in the Casablanca Settat region of Morocco by Es-Soukratti et al. [16] on 140 samples of chicken droppings, which revealed an occurrence of 73%. However, Asmai et al. [17] reported a contamination rate of up to 71% in 105 cloacal swabs tested in the Marrakesh Safi region of Morocco.
Comparing the incidence of Campylobacter in caecum samples from slaughterhouses and traditional markets, the Campylobacter rate was higher in traditional markets (78.43%) than in slaughterhouses (40%).
Furthermore, concerning carcass contamination with Campylobacter, the slaughterhouses showed a positivity rate of 6.66% in neck skin, while 0% was detected in muscle samples. However, in traditional markets, the prevalence was 17.39% and 15% in neck skin and muscle samples, respectively. Meanwhile, the findings in the traditional markets aligned with the results of a study in Spain by Bort et al. [18] involving 430 samples from a slaughterhouse (including chicken carcasses and neck skin), who reported 28.2% of Campylobacter spp. in neck skin and 19% in carcasses.
The observed disparity in the occurrence rates of Campylobacter in samples collected from slaughterhouses (19.85%) and traditional markets (41.33%) can largely be attributed to the hygienic measures that prevent contamination of poultry in slaughterhouses.
Modern slaughterhouses are subjected to stringent sanitary standards, encompassing the design, facilities, and equipment, as well as quality procedures of poultry slaughter, handling, packaging, and labeling of poultry products. These resulted in a reduced occurrence of Campylobacter compared to traditional markets. In the absence of biosecurity measures during the slaughtering process, cross-contamination between poultry flocks becomes highly likely. This, in turn, can lead to the contamination of the equipment, posing an increased risk of carcass contamination, particularly during the scalding, feather removal, and evisceration stages.
Interestingly, an elevated occurrence of Campylobacter in chicken samples (16.98% in neck skin and 16.66% in muscle) was observed compared to turkey samples (3.77% in neck skin and 13.33% in muscle) (Figure 1). A similar investigation conducted in Washington by Zhao et al. [19] involving 172 turkey breasts found a Campylobacter contamination rate of 14%, which closely aligns with our results. Interestingly, the same study indicated a significantly higher occurrence of Campylobacter in chicken meat, with 71% contamination, highlighting that the prevalence of Campylobacter is considerably higher in chicken compared to turkey.
The analysis of antimicrobial susceptibility showed a high resistance of Campylobacter, with 73% of isolates showing resistance to ampicillin. The common and most important mechanism of this resistance, according to the literature, is the production of β-lactamase [20]. The gene responsible for β-lactamase production in Campylobacter, blaOXA-61, is chromosomally encoded [21], but the action of this enzyme can be counteracted by β-lactamase inhibitors. The most well-known inhibitor is clavulanic acid [22]. The result of testing clavulanic acid combined with amoxicillin on our isolates showed 0% of resistant isolates. That finding led us to hypothesize that the primary mechanism of resistance to ampicillin in our isolates is indeed the production of β-lactamase.
However, it is important to note that different mechanisms may also be at play, such as the poor ability of this bacterium to bind penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) or the inability of β-lactams to penetrate the outer membrane porins [20,23]. Our results indicate a slightly lower rate compared to other recent studies that reported a high resistance to ampicillin among Campylobacter species, reaching 85% and 95.2% [16,17]. Moreover, a study conducted in Tunisia revealed the presence of the blaOXA-61 resistance gene, associated with ampicillin resistance, in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli, with prevalence rates of 81% and 93%, respectively [24]. This reduction in resistance to this antimicrobial is promising and indicates that the antimicrobial has been used with caution. However, the rate of resistance remains high, requiring ongoing monitoring to track the evolution of antimicrobial resistance.
The resistance to ciprofloxacin in our study was also notably high, reaching 99% of resistant isolates, making its use ineffective. Consequently, it is imperative to stop using this antimicrobial immediately. Regular monitoring of resistance status will be essential to ensure that sensitivity to this antimicrobial is restored after a prolonged period of restricted use. Moreover, erythromycin resistance was observed in 29% of isolates. According to EUCAST, if a bacterium exhibits resistance to erythromycin, it is also likely to be resistant to azithromycin and clarithromycin. The resistance mechanisms for both ciprofloxacin and erythromycin were associated with specific genetic mutations. Ciprofloxacin resistance was associated with a threonine-to-isoleucine mutation at amino acid position 86 of the gyrA protein (Thr-86-Ile) [25]. For macrolide resistance in Campylobacter, point mutations at positions 2074 and 2075 in domain V of the 23S rRNA were identified as the most prevalent mechanisms [26].
The resistance rate to tetracycline reached 82% among Campylobacter isolates. Previous studies by Es-Soukratti et al. [16] and Asmai et al. [17] reported an alarming prevalence of tetracycline resistance in Campylobacter, reaching 100% and 92.8%, respectively. Furthermore, tetracycline resistance in Campylobacter may result from specific genetic mechanisms. The study by Zhao et al. [27] identified the tet(O) resistance gene, and it was recognized as a primary mechanism of resistance due to its encoding of a protective ribosomal protein. This protein appears to facilitate the access of amino acids and tRNAs (transfer ribonucleic acids) to the ribosome, even when tetracycline normally blocks this interaction. This allows the bacterium to continue producing essential proteins for its survival despite the presence of tetracycline [28].
None of the isolates in our study exhibited resistance to gentamicin, which means that this antimicrobial remains highly effective against infections caused by these bacteria. However, it is important to use it with care to avoid the emergence of future resistance and preserve its long-term efficacy. Previous studies [16,17] reported resistance rates of 12.2% and 7.1%, respectively, to gentamicin. The resistance profiles of both C. coli and C. jejuni are largely similar. However, notable differences exist in their resistance to specific antimicrobials. For instance, C. jejuni exhibited a higher prevalence of resistance to tetracycline, ampicillin, and erythromycin (80.45%, 71.18%, 35.33%, respectively) compared to C. coli (96.15%, 61.53%, 19.23%, respectively).
In a study led by Gharbi et al. [24], it was observed that C. jejuni showed a higher prevalence of resistance to tetracycline (100%) than C. coli (80%). Conversely, 81% of C. jejuni were resistant to ampicillin, whereas 93% of C. coli demonstrated resistance.
Additionally, the findings from a study conducted by Schreyer et al. [29] indicated that C. jejuni had a higher prevalence of the bla OXA-61 gene compared to C. coli. Conversely, C. coli had a higher prevalence of tetracycline resistance-associated genetic determinants when compared to C. jejuni. It is important to note that these variations in resistance may be influenced by various factors, including geographic location, antimicrobial usage patterns, and strain-specific differences.
Finally, multi-resistant strains were highly observed (68%) (Figure 4) for fluoroquinolone, macrolide, β-lactam, and tetracycline, which are among the three families of antimicrobials most commonly used in the poultry sector to prevent and treat bacterial infections, and authorized by the Division of Pharmacy and Veterinary Inputs in Morocco. However, the lack of authorized use, the presumed absence of exposure to gentamicin, and the association of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid in Moroccan poultry may explain the observed absence of resistance in Moroccan Campylobacter strains.
The PCR assay identified the tet(O) gene in 104 out of 130 (80%) Campylobacter phenotypically resistant strains. This finding is consistent with the literature, which indicates that tet(O) is the most frequently reported gene conferring tetracycline resistance in the Campylobacter genus [30]. Previous studies have also detected this gene at high rates in tetracycline-resistant Campylobacter species. For example, in Peru, Benites et al. [31] detected the tet(O) gene in 76.9% of C. coli strains from skin samples and 66.0% from meat samples, noting that all Campylobacter species isolated from these samples were phenotypically resistant to tetracycline. Furthermore, in Vietnam, Nguyen et al. [25] found that all resistant isolates in the study were carrying tet(O). Similarly, in Argentina, Schreyer et al. [29] detected the presence of the tet(O) gene in 100% of the C. coli isolates. In Tunisia, Gharbi et al. [24] found that 100% and 80% of C. jejuni and C. coli carried the tet(O) gene.
The fact that 20% of strains exhibiting phenotypic resistance to tetracycline do not harbor the tet(O) gene suggests that additional resistance mechanisms may be involved. Therefore, evaluating other genes involved in tetracycline resistance is crucial to fully understanding the diversity and mechanisms of resistance beyond just tet(O).
5. Conclusions
In this study, the occurrence of Campylobacter species in samples collected in the Rabat-Salé-Kénitra region of Morocco was estimated at 28.7%, both in traditional markets (28.7%) and in slaughterhouses (19.85%). Out of a total of 554 poultry samples analyzed, 159 strains of Campylobacter species were isolated, highlighting the presence of this bacterium in the poultry production chain.
This study also uncovered a concerning prevalence of antibiotic resistance, especially to ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, and ampicillin, with 68% of Campylobacter strains exhibiting resistance to three or more antibiotics. These results suggest that the inappropriate use of these antibiotics could contribute to the emergence and spread of resistant strains, compromising food safety and animal health. The implications of these results are significant for the poultry production sector. A better understanding of resistance mechanisms may enable farmers to adopt more effective management strategies to limit this phenomenon. In addition, these data can inform regulatory policies in traditional markets and abattoirs by encouraging safer handling and processing practices that comply with public health standards. Finally, the results obtained may also help to improve the management of patients suffering from campylobacteriosis and provide valuable insight into the state of antibiotic resistance in Morocco, thereby facilitating the development of appropriate control strategies.
Author Contributions
Z.S.: writing, original draft preparation, and methodology. N.Z.: conceptualization, methodology, reviewing, and editing. R.R.: methodology. N.A.: supervision. B.A.: supervision. S.D.: reviewing and editing. S.F.: methodology, reviewing, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by International Atomic Energy Agency under research project (CRP) D52044. IAEA provided all the necessary materials for the study, including supplies for bacterial isolation, culture media, reagents for bacterial identification, and related resources. No financial support was provided.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study used post-mortem animal samples obtained exclusively from carcasses originally intended for human consumption, in accordance with Moroccan food safety law 28-07. As no live animals were involved, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) approval was not required. Samples were sourced from government-approved slaughterhouses and traditional markets. No animals were sacrificed for this research. To ensure data reliability and public health safeguards, sample collection and handling followed internationally recognized protocols ISO10272-1(2017) to prevent cross-contamination. This approach aligns with replacement principle of 3Rs (replacement), promoting the ethical use of by-products from the food industry.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
All authors would like to thank Ali TALMI, head of Control and Expertise Service of DPIV/ONSSA, and are thankful to IAEA for supporting this research under the coordination research project (CRP) D52044.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no financial, personal, or professional interests that could influence the content of the research.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| AMC | Amoxicilin/Clavulanic acid |
| BTS | Bacterial Test Standard |
| CN | Gentamicin |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| E | Erytromycin |
| TE | Tetracyclin |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| MALDI TOF MS | Matrix-Assisted Lazer Desorption Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry |
References
- Interprofessional Poultry Industry Sectors Confederation. Statistics of the Sector. 2017. Available online: https://www.fisamaroc.org.ma (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Law no. 49-99. The health protection of poultry farms and the control of the production and marketing of poultry products. 2002. Bulletin Official no.5036, 5 September 2002; pp. 901–903.
- Gahamanyi, N.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Matee, M.I.; Mutangana, D.; Komba, E.V.G. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Thermophilic Campylobacter Species in Humans and Animals in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 12, 2092478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baaboua, A.E.; Maadoudi, M.E.; Bouyahya, A.; Abrini, J. Intestinal infections of Campylobacter: A review. Microbiol. Res. J. Int. 2017, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). EFSA Explains Zoonotic Diseases: Campylobacter; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2014. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsatopics/topic/campylobacter (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Atanassova, V.; Reich, F.; Beckmann, L.; Klein, G. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. in turkey meat from a slaughterhouse and in turkey meat retail products. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz, Y.; Zarazaga, M.; Lantero, M.; Gastanares, M.J.; Baquero, F.; Torres, C. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter strains isolated from animals, foods, and humans in Spain in 1997–1998. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithole, V.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Perrett, K.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Occurrence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of Campylobacter spp. In intensive pig production in South Africa. Pathogens 2021, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, S.N.; Hilty, M.; Perreten, V.; Endimiani, A. Extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant gram-negative organisms in livestock: An emerging problem for human health. Drug Resist. Updates 2014, 16, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10272-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- French Society for Microbiology (SFM). Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of the French Society for Microbiology (CASFM)–EUCAST 2023. V1.0; SFM: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/CASFM2023_V1.0.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Düpre, S.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H.; Hafez, H.M. Determination of Antimicrobial Sensitivities of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated from Commercial Turkey Farms in Germany. Avian Diseases 2012, 56, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baaboua, A.; El Maadoudi, M.; Bouyahya, A.; Kounnoun, A.; Bougtaib, H.; Belmehdi, O.; SkaliSenhaji, N.; Abrini, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial profiling of Campylobacter spp. isolated from meats, animal, and human feces in Northern of Morocco. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 349, 109202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Somboro, A.M.; Shobo, C.O.; Perrett, K.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Characterisation of Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Poultry in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Soucratti, K.; Hammoumi, A.; Bouchrif, B. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from poultry in Casablanca-Settat, Morocco. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2020, 9, 8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmai, R.; Karraouan, B.; Es-Soucratti, K.; En-Nassiri, H.; Bouchrif, B.; Karib, H.; Triqui, R. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Campylobacter coli isolated from broiler farms in the Marrakesh Safi region, Morocco. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bort, B.; Martí, P.; Mormeneo, S.; Mormeneo, M.; Iranzo, M. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Broilers Throughout the Supply Chain in Valencia, Spain. Foodborne Pathog. 2022, 19, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Ge, B.; De Villena, J.; Sudler, R.; Yeh, E.; Zhao, S.; White, D.G.; Wagner, D.; Meng, J. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella Serovars in Retail Chicken, Turkey, Pork, and Beef from the Greater Washington, DC, Area. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5431–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajada, P.; Gomez-Graces, J.L.; Alós, J.I.; Balas, D.; Cogollos, R. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to 12 beta-lactam agents and combinations with beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 1924–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, D.A.; Korolik, V. Isolation and Expression of a Novel Molecular Class D β-Lactamase, OXA-61, from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2515–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreau, C.L.; Lariviere, L.A.; Lauzer, J.C.; Turgeon, F.F. Effect of clavulanic acid on susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to eight beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovine, N.M. Resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni. Virulence 2013, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, M.; Béjaoui, A.; Hamda, C.B.; Ghedira, K. Distribution of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from broiler chickens in Tunisia. J. Microbiol. 2022, 55, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Hotzel, H.; El-Adawy, H.; Tran, H.; Le, M.T.H.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H.; Hafez, H.M. Genotyping and antibiotic resistance of thermophilic Campylobacter isolated from chicken and pig meat in Vietnam. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Mateo, E.; Churruca, E.; Martinez, I.; Girbau, C.; Fernandez-Astorga, A. MAMA-PCR assay for the detection of point mutations associated with high-level erythromycin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli strains. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Tyson, G.H.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Young, S.; Lam, C.; Folster, J.P.; Whichard, J.M.; McDermott, P.F. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis Accurately Predicts Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotypes in Campylobacter spp. ASM J. 2016, 82, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.E.; Jerome, L.J.; Grewal, J.; Chang, N. Tet(O), a protein that mediates ribosomal protection to tetracycline, binds, and hydrolyses GTP. Can. J. Microbiol. 1995, 41, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, M.E.; Olivero, C.R.; Rossler, E.; Soto, L.P.; Frizzo, L.S.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Signorini, M.L.; Virginia, Z.M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli identified in a slaughterhouse in Argentina. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Hachesoo, B.; Khoshbakht, R.; Sharifiyazdi, H.; Tabatabaei, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Asasi, K. Tetracycline Resistance Genes in Campylobacter jejuni and C.coli Isolated From Poultry Carcasses. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, e12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benites, C.; Anampa, D.; Torres, D.; Avalos, I.; Rojas, M.; Conte, C.; Lázaro, C. Prevalence, Tetracycline Resistance and Tet(O) Gene Identification in Pathogenic Campylobacter Strains Isolated from Chickens in Retail Markets of Lima, Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).