A Comprehensive Review of Generative AI in Finance
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1. What are the current trends and advancements in the application of GAI within the financial sector?
- RQ2. How does GAI, beyond LLMs, contribute to solving financial tasks and challenges?
- RQ3. How can BERTopic be used to systematically classify and analyze research on GAI in finance?
- RQ4. What are the risks and challenges associated with the use of GAI in finance, and how have these been addressed in the literature?
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
- Data Preprocessing: First, we convert all text to lowercase to ensure uniformity and reduce redundancy; second, we use nltk.word_tokenize() to split the text into individual tokens and WordNetLemmatizer() to reduce words to their base or root form; finally, we use stopwords.words(‘english’) to eliminate the common stopwords, as they usually do not contribute significantly to the meaning of the text.
- Fit the Model and Transform Documents: We use BERTopic and ClassIFidTransformer to fit the model to our data and transform to discover topics.
- Topics Exploration: After fitting the model, we explore the topics generated by various tools of BERTopic.
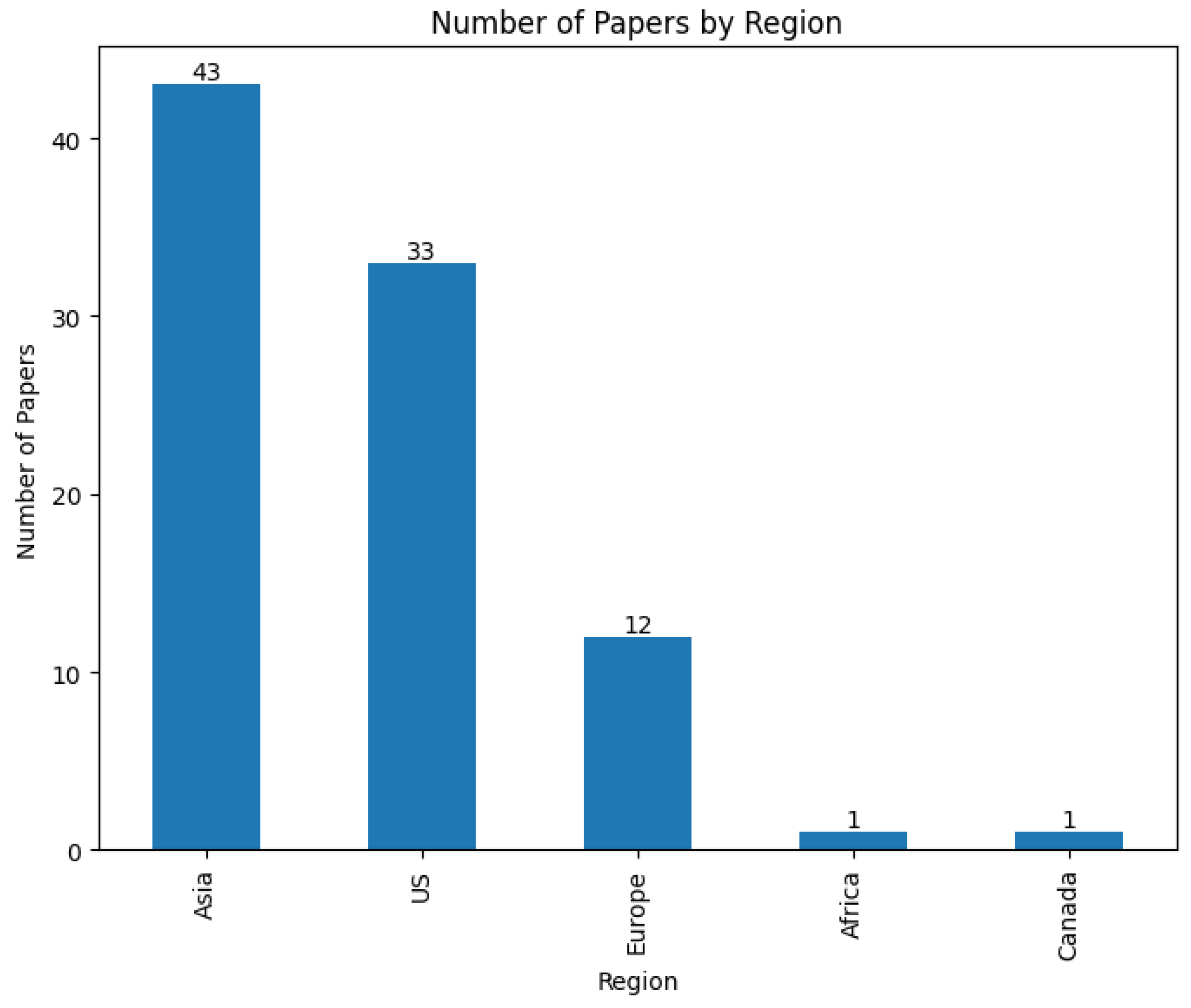
4. Results
- “-1_chatbots_credit_reliable_chatgpt”;
- “0_llm_financial_model_task”;
- “1_ai_generative_risk_challenge”;
- and “2_data_stock_synthetic_market”.
5. Discussion
5.1. LLMs for Financial Tasks
5.1.1. General-Purpose LLMs
5.1.2. Finance-Specific LLMs
5.1.3. Benchmarks of LLMs in Finance
5.2. The Risk and Challenge of Generative AI
5.2.1. Hallucination
5.2.2. Ethical and Social Impact
5.2.3. Financial Regulation
5.3. Synthetic Financial Data Generation
5.3.1. Challenges of Generating Synthetic Data
- Realistic synthetic dataset generation;
- Similarity calculation between real and generated datasets;
- Ensuring privacy constraints with the generative process.
5.3.2. Existing Works by VAE, GAN, and Diffusion Models
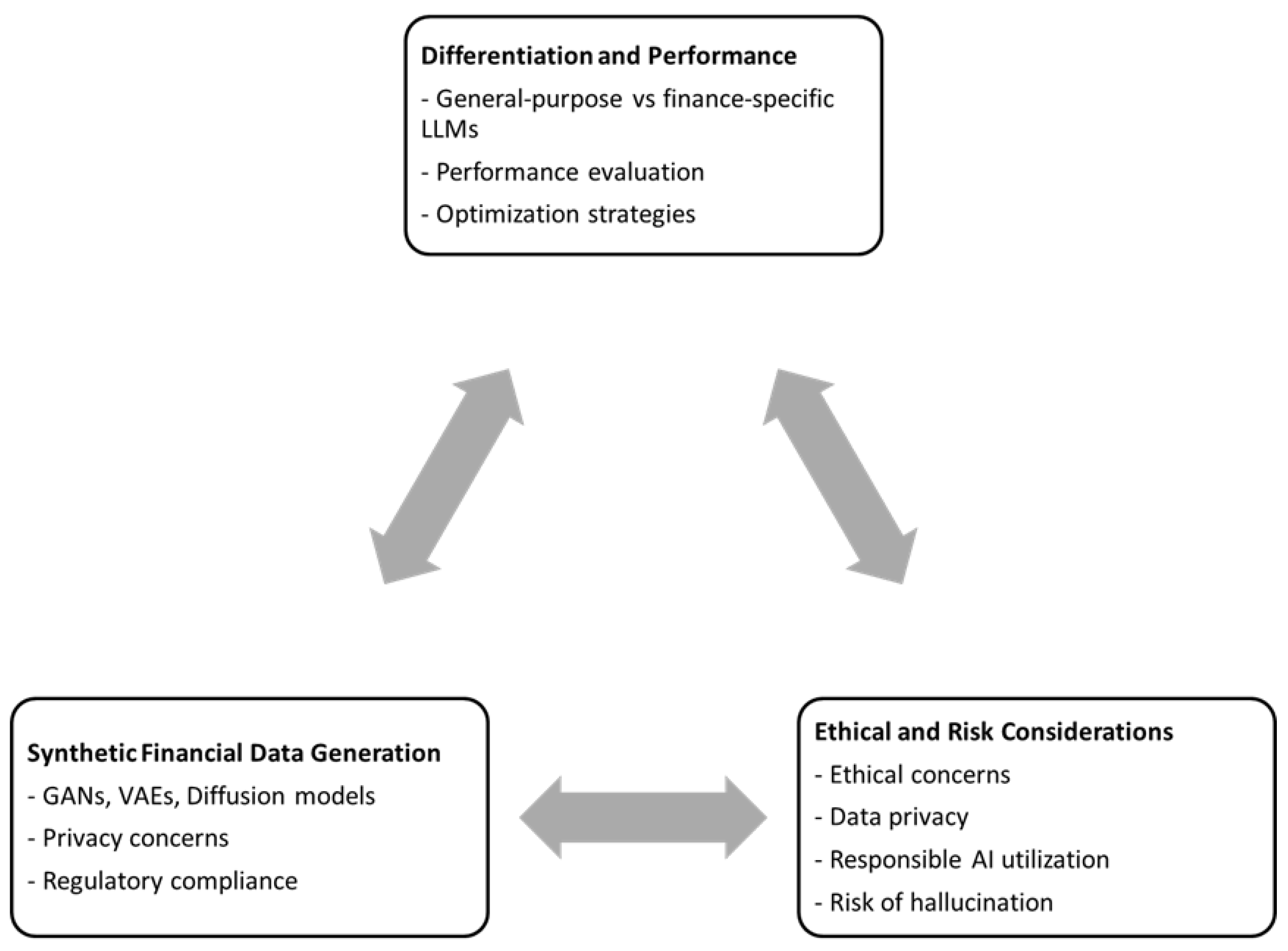
6. Contribution and Future Research Agenda
6.1. Theoretical Contribution
6.2. Managerial Implications
6.3. Future Research Agenda
6.3.1. Intertwined Ethics and Performance Optimization
6.3.2. Synthetic Data: A Boon for Performance Benchmarking
6.3.3. Ethical Considerations in Synthetic Data Generation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatemi, S.; Hu, Y. A Comparative Analysis of Fine-Tuned LLMs and Few-Shot Learning of LLMs for Financial Sentiment Analysis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.08725. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Ding, D.; Wang, Y.; Guan, C.; Ding, B. Unraveling the landscape of large language models: A systematic review and future perspectives. J. Electron. Bus. Digit. Econ. 2023, 3, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.; Chen, H. Large language models in finance: A survey. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, Brooklyn, NY, USA, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Stevens, N.; Han, S.C.; Song, M. A Survey of Large Language Models in Finance (FinLLMs). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02315. [Google Scholar]
- Barde, K.; Kulkarni, P.A. Applications of Generative AI in Fintech. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on AI-ML Systems, Bangalore, India, 25–28 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, D. Large Language Models and Generative AI in Finance: An Analysis of ChatGPT, Bard, and Bing AI. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4511540 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Mbanyele, W. Generative AI and ChatGPT in Financial Markets and Corporate Policy: A Comprehensive Review. 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4745990 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; The MIT Press: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; NeurIPS Foundation: Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018. Available online: https://hayate-lab.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/43372bfa750340059ad87ac8e538c53b.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, J.; Mao, H.; Zeng, X. Twitter mood predicts the stock market. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, T.P.; Yekini, L.S. Stock market returns and the content of annual report narratives. In Proceedings of the Accounting Forum; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 39, pp. 281–294. [Google Scholar]
- McGurk, Z.; Nowak, A.; Hall, J.C. Stock returns and investor sentiment: Textual analysis and social media. J. Econ. Financ. 2020, 44, 458–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U. Gpt-investar: Enhancing stock investment strategies through annual report analysis with large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chan, S.; Zhu, X.; Pei, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Shah, S. Are ChatGPT and GPT-4 General-Purpose Solvers for Financial Text Analytics? A Study on Several Typical Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 408–422. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlyshenko, B.M. Financial News Analytics Using Fine-Tuned Llama 2 GPT Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.13032. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F. Designing Heterogeneous LLM Agents for Financial Sentiment Analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.05799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, G.; Zha, D. Fingpt: Democratizing internet-scale data for financial large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.10485. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, C.D. Fingpt: Open-source financial large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.06031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q. FinPT: Financial Risk Prediction with Profile Tuning on Pretrained Foundation Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.00065. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, N. Role and Challenges of ChatGPT and Similar Generative Artificial Intelligence in Finance and Accounting. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4603206 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Reimers, N. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Astels, S. hdbscan: Hierarchical density based clustering. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Févotte, C.; Idier, J. Algorithms for nonnegative matrix factorization with the β-divergence. Neural Comput. 2011, 23, 2421–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.C.; Marar, V.; Yazdanpanah, H.; Pezente, A.; Ghassemi, M. Enhancing Credit Risk Reports Generation using LLMs: An Integration of Bayesian Networks and Labeled Guide Prompting. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, Brooklyn, NY, USA, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, D. Proper Generative AI Prompting for Financial Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4453664 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Rane, N.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. Gemini or ChatGPT? Efficiency, Performance, and Adaptability of Cutting-Edge Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Finance and Accounting. 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4731283 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Callanan, E.; Mbakwe, A.; Papadimitriou, A.; Pei, Y.; Sibue, M.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Shah, S. Can gpt models be financial analysts? an evaluation of chatgpt and gpt-4 on mock cfa exams. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.08678. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Shu, P.; Xu, S.; Dai, H.; Zhao, L.; Mai, G.; et al. Revolutionizing finance with llms: An overview of applications and insights. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.11641. [Google Scholar]
- Niszczota, P.; Abbas, S. GPT has become financially literate: Insights from financial literacy tests of GPT and a preliminary test of how people use it as a source of advice. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkaraju, K.; Vuruma, S.K.R.; Pallagani, V.; Muppasani, B.; Srivastava, B. Can llms be good financial advisors?: An initial study in personal decision making for optimized outcomes. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07422. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Che, C.; Zheng, H.; Li, C. Research on Generative Artificial Intelligence for Virtual Financial Robo-Advisor. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 10, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Analysis of Financial Market using Generative Artificial Intelligence. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Huang, L.; Li, S. ChatGPT, Generative AI, and Investment Advisory. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Papers.cfm?abstract_id=4519182 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Khashanah, K. Tradinggpt: Multi-agent system with layered memory and distinct characters for enhanced financial trading performance. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03736. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, R.; Suchow, J.W.; Khashanah, K. FinMem: A performance-enhanced LLM trading agent with layered memory and character design. Proc. AAAI Symp. Ser. 2024, 3, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkaraju, K.; Jones, S.E.; Vuruma, S.K.R.; Pallagani, V.; Muppasani, B.C.; Srivastava, B. LLMs for Financial Advisement: A Fairness and Efficacy Study in Personal Decision Making. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, Brooklyn, NY, USA, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand, L.; Berger, A.; Deußer, T.; Dilmaghani, T.; Khaled, M.; Kliem, B.; Loitz, R.; Pielka, M.; Leonhard, D.; Bauckhage, C.; et al. Improving zero-shot text matching for financial auditing with large language models. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Document Engineering 2023, Limerick, Ireland, 22–25 August 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Feinstein, Z. Large Language Model in Financial Regulatory Interpretation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06808. [Google Scholar]
- de Zarzà, I.; de Curtò, J.; Roig, G.; Calafate, C.T. Optimized financial planning: Integrating individual and cooperative budgeting models with llm recommendations. AI 2023, 5, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, R. From fiction to fact: The growing role of generative AI in business and finance. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2023, 21, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Generative AI in Operational Risk Management: Harnessing the Future of Finance. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4452504 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Leippold, M. Thus spoke GPT-3: Interviewing a large-language model on climate finance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 53, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y. Harnessing LLMs for temporal data-a study on explainable financial time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 739–753. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Ling, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. Temporal Data Meets LLM–Explainable Financial Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.11025. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.; Malik, M.; Ganu, T. Assessing LLMs’ Mathematical Reasoning in Financial Document Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.11194. [Google Scholar]
- Sikiru, R.D.; Adekanmbi, O.; Soronnadi, A. Comparative Study of LLMs for Personal Financial Decision in Low Resource Language. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on African Natural Language Processing, Vienna, Austria, 11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Tong, W.; Walid, A. FinGPT-HPC: Efficient Pretraining and Finetuning Large Language Models for Financial Applications with High-Performance Computing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13533. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Irsoy, O.; Lu, S.; Dabravolski, V.; Dredze, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Kambadur, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Mann, G. BloombergGPT: A Large Language Model for Finance. arXiv 2024. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.17564.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Xie, Q.; Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Lai, Y.; Peng, M.; Lopez-Lira, A.; Huang, J. Pixiu: A large language model, instruction data and evaluation benchmark for finance. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.05443. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bian, Y.; Wang, G.; Lei, Y.; Cheng, D.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, C. Cfgpt: Chinese financial assistant with large language model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.10654. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.Y. Instruct-fingpt: Financial sentiment analysis by instruction tuning of general-purpose large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tam, K.Y. Investlm: A large language model for investment using financial domain instruction tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.13064. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Q.; Long, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Bai, X.; Huang, X.; et al. Disc-finllm: A chinese financial large language model based on multiple experts fine-tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.15205. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, H.; Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Cui, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Data-centric financial large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.17784. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Soon, J.; Zhang, X. Finvis-gpt: A multimodal large language model for financial chart analysis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.01430. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, G.; Nagoudi, E.M.B.; Cavusoglu, H.; Abdul-Mageed, M. FinTral: A Family of GPT-4 Level Multimodal Financial Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10986. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, M.; Imajo, K. Construction of Domain-specified Japanese Large Language Model for Finance through Continual Pre-training. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiang, R.; Yuan, C.; Feng, D.; Han, W.; Lopez-Lira, A.; Liu, X.Y.; Ananiadou, S.; Peng, M.; Huang, J.; et al. Dólares or Dollars? Unraveling the Bilingual Prowess of Financial LLMs Between Spanish and English. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.07405. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, W.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dai, W.; Liao, Y.; Qin, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Fineval: A chinese financial domain knowledge evaluation benchmark for large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.09975. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y. Is chatgpt a financial expert? evaluating language models on financial natural language processing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.12664. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, R.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Xiao, M.; Li, D.; Dai, Y.; Feng, D.; et al. The FinBen: An Holistic Financial Benchmark for Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.12659. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, M.; Hu, J.; Cheng, D.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, C. Cfbenchmark: Chinese financial assistant benchmark for large language model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.05812. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, P.; Kannappan, A.; Kiela, D.; Qian, R.; Scherrer, N.; Vidgen, B. Financebench: A new benchmark for financial question answering. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.11944. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Mao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Mi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Lou, D.; Lin, J. FinSQL: Model-Agnostic LLMs-based Text-to-SQL Framework for Financial Analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10506. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, C.; Xu, Y.; Du, Q.; Tan, M.; Huang, J.; Lin, W. AlphaFin: Benchmarking Financial Analysis with Retrieval-Augmented Stock-Chain Framework. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.12582. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, M. Construction of a japanese financial benchmark for large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.15062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Y.; Xue, H. SuperCLUE-Fin: Graded Fine-Grained Analysis of Chinese LLMs on Diverse Financial Tasks and Applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19063. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Liu, X.Y. Deficiency of Large Language Models in Finance: An Empirical Examination of Hallucination. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.15548. [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury, S. Journey of hallucination-minimized generative ai solutions for financial decision makers. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Mérida, Mexico, 4–8 March 2024; pp. 1180–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, S. Potential Impact of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the Financial Industry. Int. J. Cybern. Inform. 2023, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. LLM potentiality and awareness: A position paper from the perspective of trustworthy and responsible AI modeling. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D. Mitigating Risks for Financial Firms Using Generative AI Tools. 2023. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4452600 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Remolina, N. Generative AI in Finance: Risks and Potential Solutions; Singapore Management University School of Law Research Paper Forthcoming, SMU Centre for AI & Data Governance Research Paper Forthcoming: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, A.W.; Ross, J. Can ChatGPT Plan Your Retirement?: Generative AI and Financial Advice. 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4722780 (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Yusof, S.A.B.M.; Roslan, F.A.B.M. The Impact of Generative AI in Enhancing Credit Risk Modeling and Decision-Making in Banking Institutions. Emerg. Trends Mach. Intell. Big Data 2023, 15, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Caspi, I.; Felber, S.S.; Gillis, T.B. Generative AI and the Future of Financial Advice Regulation. In Proceedings of the Generative AI and Law Workshop at ICML 2023, Hawaii Convention Center, Honolulu, HI, USA, 28–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, S.A.; Dervovic, D.; Mahfouz, M.; Tillman, R.E.; Reddy, P.; Veloso, M. Generating synthetic data in finance: Opportunities, challenges and pitfalls. In Proceedings of the First ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, New York, NY, USA, 15–16 October 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhong, G.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Stock market prediction based on generative adversarial network. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 147, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Chen, Y.; Tanaka-Ishii, K. Modeling financial time-series with generative adversarial networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 527, 121261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, A.; Firoozye, N.; Treleaven, P. Generative adversarial networks for financial trading strategies fine-tuning and combination. Quant. Financ. 2021, 21, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzina, P. Improving Portfolio Construction Using Deep Generative Machine Learning Models Applying Generative Models on Financial Market Data. Master’s Thesis, University of Malta, Msida, Malta, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzan, F.; Sartori, C.; Consoli, S.; Reforgiato Recupero, D. Generative Adversarial Networks for Synthetic Data Generation in Finance: Evaluating Statistical Similarities and Quality Assessment. AI 2024, 5, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuletić, M.; Prenzel, F.; Cucuringu, M. Fin-GAN: Forecasting and classifying financial time series via generative adversarial networks. Quant. Financ. 2024, 24, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, M. Synthetic Data Generation for the Financial Industry Using Generative Adversarial Networks. 2021. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1591892/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- He, B.; Kita, E. Stock price prediction by using hybrid sequential generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Sorrento, Italy, 17–20 November 2020; pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmasso, N.; Tillman, R.E.; Reddy, P.; Veloso, M. Payvae: A generative model for financial transactions. In Proceedings of the AAAI 2021 Workshop on Knowledge Discovery from Unstructured Data in Financial Services Workshop, Virtual, 9 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chen, M.; Qiao, X. Generative Learning for Financial Time Series with Irregular and Scale-Invariant Patterns. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Ding, D.; Gupta, P.; Hung, Y.C.; Jiang, Z. A Systematic Review of Research on ChatGPT: The User Perspective. In Exploring Cyber Criminals and Data Privacy Measures; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 124–150. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Ding, D.; Ren, J.; Guo, J. Unveiling the aesthetic “wow factor”: The role of aesthetic incongruity and image quality in NFT art valuation with computer vision. Electron. Mark. 2024, 34, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajath, K. Fintech’s Generative AI Revolution How AI is shaping the Future of Banking and Financial Services. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 5, 1812–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Li, S.; Katsikis, V.; Khan, A.T.; He, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C. Empowering financial futures: Large language models in the modern financial landscape. EAI Endorsed Trans. AI Robot. 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranković, M.; Gurgu, E.; Martins, O.; Vukasović, M. Artificial intelligence and the evolution of finance: Opportunities, challenges and ethical considerations. EdTech J. 2023, 3, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

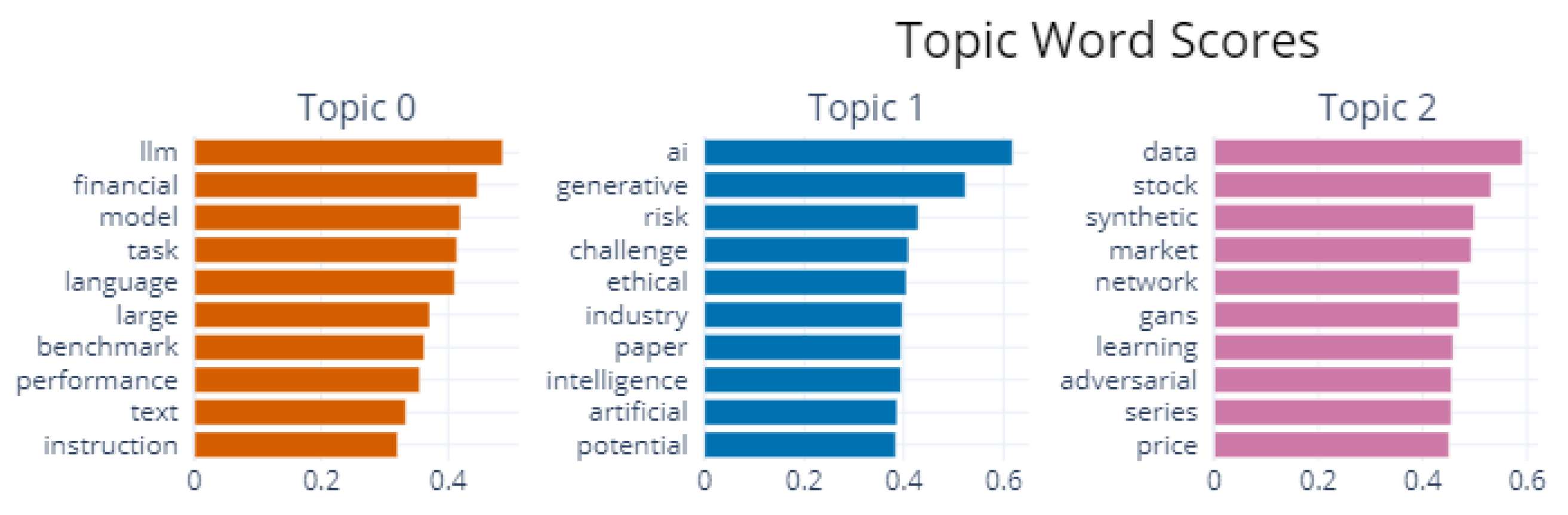

| Count | Name | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | -1_chatbots_credit_reliable_chatgpt | [‘chatbots’, ‘credit’, ‘reliable’, ‘chatgpt’, ‘lgp’, ‘payment’, ‘user’, ‘transaction’, ‘individual’, ‘process’] |
| 47 | 0_llm_financial_model_task | [‘llm’, ‘financial’, ‘model’, ‘task’, ‘language’, ‘large’, ‘benchmark’, ‘performance’, ‘text’, ‘instruction’] |
| 20 | 1_ai_generative_risk_challenge | [‘ai’, ‘generative’, ‘risk’, ‘challenge’, ‘ethical’, ‘industry’, ‘paper’, ‘intelligence’, ‘artificial’, ‘potential’] |
| 12 | 2_data_stock_synthetic_market | [‘data’, ‘stock’, ‘synthetic’, ‘market’, ‘network’, ‘gans’, ‘learning’, ‘adversarial’, ‘series’, ‘price’] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.K.C.; Guan, C.; Yu, Y.; Ding, Q. A Comprehensive Review of Generative AI in Finance. FinTech 2024, 3, 460-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech3030025
Lee DKC, Guan C, Yu Y, Ding Q. A Comprehensive Review of Generative AI in Finance. FinTech. 2024; 3(3):460-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech3030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, David Kuo Chuen, Chong Guan, Yinghui Yu, and Qinxu Ding. 2024. "A Comprehensive Review of Generative AI in Finance" FinTech 3, no. 3: 460-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech3030025
APA StyleLee, D. K. C., Guan, C., Yu, Y., & Ding, Q. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Generative AI in Finance. FinTech, 3(3), 460-478. https://doi.org/10.3390/fintech3030025







