Pre-Sowing Treatments, Seed Components and Water Imbibition Aids Seed Germination of Gloriosa superba
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Electrical Conductivity and Viability Test of G. superba Seeds
2.3. Seed Surface Sterilization
2.4. Pre-Sowing Seed Treatments
2.4.1. Mechanical Scarification and Water Soaking
2.4.2. GA3 Treatment
2.4.3. Sulfuric Acid Treatment
2.5. Seed Germination Procedure
2.6. Estimation of Abscisic Acid by LC-MS
2.7. Seed Water Imbibition Capacity
2.8. BET Surface Area Analysis of Seeds by N2-Adsorption-Desorption
2.9. 3D micro-T Imaging of G. Superba Seed Structure
2.10. Seedling Growth Performance
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
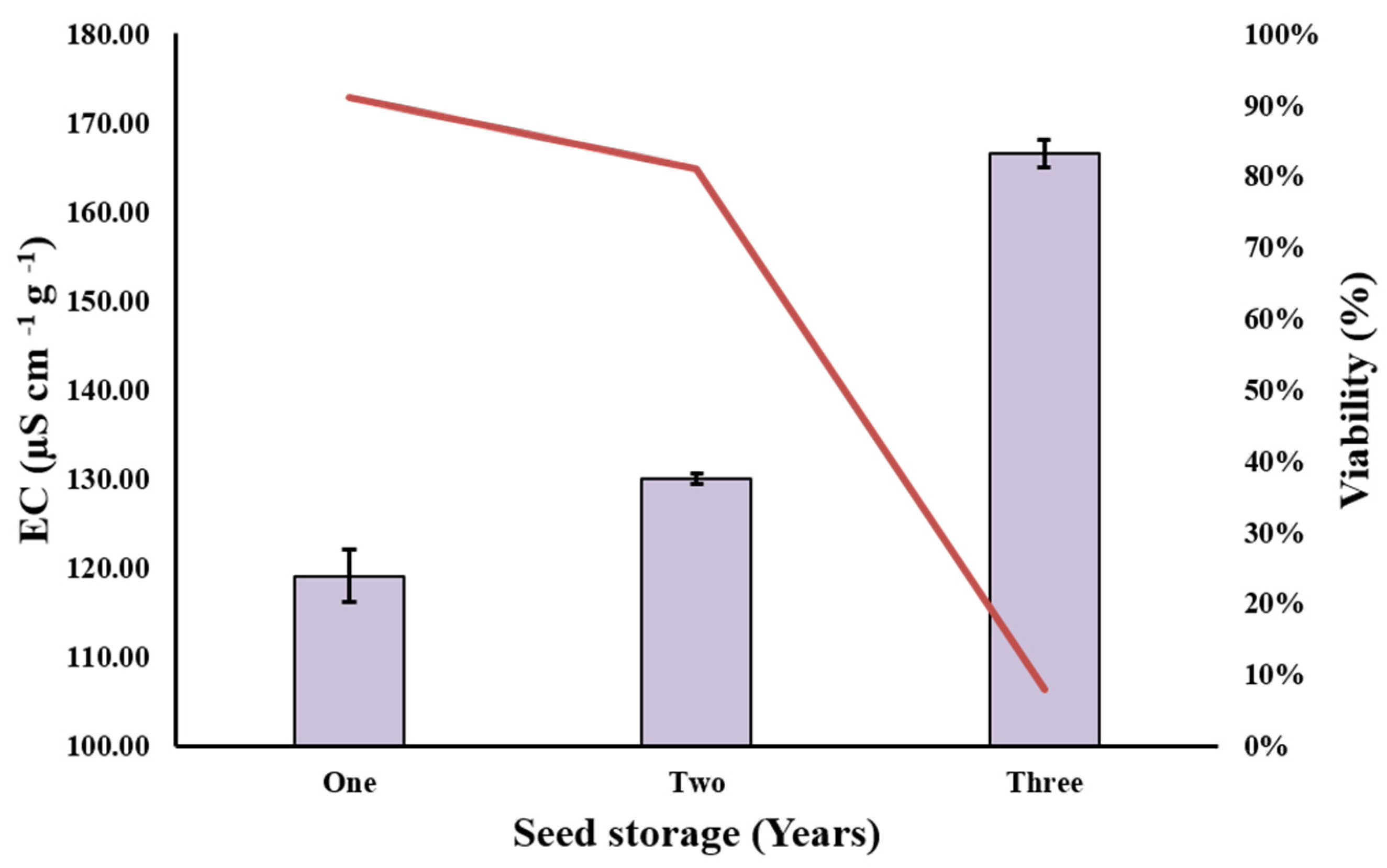
3.1. Seed EC and Viability Test
3.2. Pre-Sowing Seed Treatments
3.2.1. Mechanical Scarification and Water Soaking
3.2.2. GA3 Treatment
3.2.3. Sulfuric Acid Treatment
3.3. ABA Quantification
3.4. Water Uptake Capacity of G. Superba Seeds
3.5. Porosity Analysis of G. Superba Seeds by BET
3.6. 3D Micro-T Imaging of G. superba Seed Structure
3.7. Seedling Growth Performance of G. superba
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gama-Arachchige, N.S.; Baskin, J.M.; Geneve, R.L.; Baskin, C.C. Acquisition of Physical Dormancy and Ontogeny of the Micropyle-Water-Gap Complex in Developing Seeds of Geranium carolinianum (Geraniaceae). Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, G.K.; Song, D.; Liu, W.; Han, Y.; Liu, B. Relationship between Seed Moisture Content and Acquisition of Impermeability in Nelumbo nucifera (Nelumbonaceae). Acta Bot. Bras. 2017, 31, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, G.K.; Li, J.; Biddick, M.; Han, K.; Song, D.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, B. Mechanisms Underpinning the Onset of Seed Coat Impermeability and Dormancy-Break in Astragalus Adsurgens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lush, M.; Evans, T. The Seed Coats of Cowpea and other Grain Legumes: Structure in Relation to Function. Field Crop. Res. 1980, 3, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavaleta-Medina, F.; Snyder, H. Water Imbibition by Normal and Hard Soybeans. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 58, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Cholewa, E.; Mohamed, T.; Peterson, C.A.; Gijzen, M. Cracks in the Palisade Cuticle of Soybean Seed Coats Correlate with Their Permeability to Water. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed Dormancy and the Control of Germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolston, P.; Rolston, M. Water Impermeable Seed Dormancy. Bot. Rev. 1978, 44, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Cavanagh, A.K. Structural Aspects of Dormancy. In Seed physiology, Vol. 2. Germination and Reserve Mobilization; Murray, D., Ed.; Academic Press: Sydney, Australia, 1984; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C.; Li, X. Taxonomy, Anatomy and Evolution of Physical Dormancy in Seeds. Plant Species Biol. 2000, 15, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. A Classification System for Seed Dormancy. Seed Sci. Res. 2004, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasuriya, K.; Wijetunga, A.; Baskin, J.; Baskin, C. Seed Dormancy and Storage Behaviour in Tropical Fabaceae: A Study of 100 Species from Sri Lanka. Seed Sci. Res. 2013, 23, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroyi, A. The Genus Gloriosa (Colchicaceae)—Ethnobotany, Phylogeny and Taxonomy The Genus Gloriosa (Colchicaceae)—Ethnobotany, Phylogeny and Taxonomy. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J. Propagation of Gloriosa from Seeds. Acta Hortic. 1988, 226, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, B.; Jha, S. In Vitro Tuberisation of Gloriosa superba L. on Basal Medium. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 114, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.N.; Jadhav, S.K.; Tiwari, K.L.; Afaque, Q. In Vitro Tuberization and Colchicine Content Analysis of Gloriosa superba L. Biotechnology 2015, 14, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Subiramani, S.; Sundararajan, S.; Govindarajan, S.; Sadasivam, V.; Ganesan, P.K.; Packiaraj, G.; Manickam, V.; Thiruppathi, S.K.; Ramalingam, S.; Narayanasamy, J. Optimized in Vitro Micro-Tuber Production for Colchicine Biosynthesis in Gloriosa superba L. and Its Anti-Microbial Activity against Candida Albicans. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 139, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, L.G.; Robbertse, P.J. Aspects Relating to Seed Production in Gloriosa superba L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 1997, 63, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.R.; Rodrigues, B.F. Enhancement of Seed Germination in Macaranga Peltata for Use in Tropical Forest Restoration. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, A.; Vancauwenberghe, V.; Van De Looverbosch, T.; Verboven, P.; Nicolaï, B. X-Ray Computed Tomography for 3D Plant Imaging. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondt, S.; Vanhaeren, H.; Van Loo, D.; Cnudde, V.; Inzé, D. Plant Structure Visualization by High-Resolution X-Ray Computed Tomography. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Verboven, P.; Nicolai, B. Contrast-Enhanced 3D Micro-CT of Plant Tissues Using Different Impregnation Techniques. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, L.; Leonarduzzi, C.; Mele, G. Micro-CT Imaging of Tomato Seeds: Predictive Potential of 3D Morphometry on Germination. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 200, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloetens, P.; Mache, R.; Schlenker, M.; Lerbs-Mache, S. Quantitative Phase Tomography of Arabidopsis Seeds Reveals Intercellular Void Network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14626–14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.D.Q.; Alvarado, C.; Girousse, C.; Legland, D.; Chateigner-Boutin, A.-L. Use of X-Ray Micro Computed Tomography Imaging to Analyze the Morphology of Wheat Grain through Its Development. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.S.K.; Al Shoaibi, A.; Srinivasakannan, C. Preparation of Porous Carbon from Date Palm Seeds and Process Optimization. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, J.; Sokołowska, Z.; Witkowska-Walczak, B.; Skic, K. Adsorption of Water Vapour and the Specific Surface Area of Arctic Zone Soils (Spitsbergen). Int. Agrophysics 2018, 32, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismadji, S.; Sudaryanto, Y.; Hartono, S.B.; Setiawan, L.E.K.; Ayucitra, A. Activated Carbon from Char Obtained from Vacuum Pyrolysis of Teak Sawdust: Pore Structure Development and Characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, A.H.; Rashid, R.A.; Ismail, K.; Sabar, S. High Surface Area Mesoporous Activated Carbon Developed from Coconut Leaf by Chemical Activation with H3PO4 for Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 74, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, Y.A.; Shinde, B.A.; Mulani, F.A.; Gade, A.B.; Kasodekar, A.K.; Thulasiram, H.V.; Kadoo, N.Y.; Nikam, T.D. Diversity Assessment of Gloriosa Superba Accessions from Western Ghats of India Based on Morphological Traits, ISSR Markers and Metabolite Content. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2022, 30, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.; Mavi, K.; Kenanoglu, B.B.; Matthews, S. Prediction of Germination and Vigour in Naturally Aged Commercially Available Seed Lots of Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea Var. Capitata) Using the Bulk Conductivity Method. Seed Sci. Technol. 2008, 36, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Powell, A. Electrical Conductivity Vigour Test: Physiological Basis and Use. Seed Test. Int. 2006, 131, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Mishra, M.; Yadav, A. Standardizing the Methods for Breaking Seed Dormancy to Enhance Germination of Gloriosa Superba Seeds. Expert Opin. Environ. Biol. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.N.; Dadlani, M. Tetrazolium Test for Seed Viability and Vigour. Available online: https://seednet.gov.in/pdffiles/chapter14.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Perin, E.C.; Crizel, R.L.; Galli, V.; da Silva Messias, R.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Chaves, F.C. Extraction and Quantification of Abscisic Acid and Derivatives in Strawberry by LC-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, R.; Siril, E.A. Assessment of Different Pretreatments to Breakage Dormancy and Improve the Seed Germination in Elaeocarpus serratus L.—An Underutilized Multipurpose Fruit Tree from South India. For. Sci. Technol. 2018, 14, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.D.; Mohamed, M.H.; Headley, J.V. Surface Area and Pore Structure Properties of Urethane-Based Copolymers Containing β-Cyclodextrin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Sabar, S.; Ishak, M.; Wilson, L.; Norrahma, S.; Talari, M.; Farhan, A. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Mesoporous-Activated Carbon from Coconut (Cocos Nucifera) Leaf by H3PO4 Activation for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.D.; Patil, V.D.; Sapre, A.A.; Ambone, T.S.; Torris, A.T.; Shukla, P.G.; Shanmuganathan, K. Tuning Controlled Release Behavior of Starch Granules Using Nanofibrillated Cellulose Derived from Waste Sugarcane Bagasse. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9208–9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, P.M.; Sharif-zadeh, F.; Janmohammadi, M. Influence of Priming Techniques on Seed Germination Behavior of Maize Inbred Lines (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2008, 3, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.F.; Shen, Y.B.; Shi, F.H. Germination of Tilia Miqueliana Seeds Following Cold Stratification and Pretreatment with GA3 and Magnetically-Treated Water. Seed Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Liu, X.D.; Xie, Q.; He, Z.H. Two Faces of One Seed: Hormonal Regulation of Dormancy and Germination. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Chin, D.; Govinden-Soulange, J. Germination Profile of Selected Plants from Mauritius—Towards a Conservation Strategy. Seed Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. The Great Diversity in Kinds of Seed Dormancy: A Revision of the Nikolaeva–Baskin Classification System for Primary Seed Dormancy. Seed Sci. Res. 2021, 31, 249–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louf, J.F.; Zheng, Y.; Kumar, A.; Bohr, T.; Gundlach, C.; Harholt, J.; Poulsen, H.F.; Jensen, K.H. Imbibition in Plant Seeds. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 042403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama-Arachchige, N.S.; Baskin, J.M.; Geneve, R.L.; Baskin, C.C. Identification and Characterization of Ten New Water Gaps in Seeds and Fruits with Physical Dormancy and Classification of Water-Gap Complexes. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivakumar, R.; Maitra, S. Evaluation of Pore Size and Surface Morphology during Devolatilization of Coconut Fiber and Sugarcane Bagasse. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192, 2326–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckhoven, C.; du Plessis, A.; le Roux, S.G.; Mouton, P.l.F.N.; Hui, C. Beauty Is More than Skin Deep: A Non-Invasive Protocol for in Vivo Anatomical Study Using Micro-CT. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.H.; Fortune, J.A.; Gallagher, J. Anatomical Structure and Nutritive Value of Lupin Seed Coats. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2001, 52, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hradilová, I.; Trněný, O.; Válková, M.; Cechová, M.; Janská, A.; Prokešová, L.; Aamir, K.; Krezdorn, N.; Rotter, B.; Winter, P.; et al. A Combined Comparative Transcriptomic, Metabolomic, and Anatomical Analyses of Two Key Domestication Traits: Pod Dehiscence and Seed Dormancy in Pea (Pisum Sp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.S.; Xiong, J.; Gillikin, J.W. Purification and Developmental Analysis of a Metalloendoproteinase from the Leaves of Glycine Max. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishima, N.; Takeda, Y.; Hirose, R.; Kalasová, D.; Šalplachta, J.; Omote, K. Visualization of Internal 3D Structure of Small Live Seed on Germination by Laboratory-Based X-Ray Microscopy with Phase Contrast Computed Tomography. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Jin, J.; Li, D.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, X. High-Throughput Phenotyping of Morphological Seed and Fruit Characteristics Using X-Ray Computed Tomography. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korban, S.S.; Coyne, D.P.; Weihing, J. Evaluation, Variation, and Genetic Control of Seed Coat Whiteness in Dry Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1981, 106, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, G.N.; Hosfield, G.L.; Uebersax, M.A.; Klomparens, K. Seed Microstructure and Its Relationship to Water Uptake in Isogenic Lines and a Cultivar of Dry Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Struct. 1987, 6, 91–102. [Google Scholar]





| Treatment | Treatment Time (min/h) | Germination (%) 30 DAS (Mean ± SE) $ | Minimum Time Required for Germination (days) (days ± SE) $ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (without MS and WS) * | 0 h | 23 g ± 2.98 | 34 h ± 3 |
| MS (without WS) | 0 h | 56 d ± 1.50 | 17 d ± 2 |
| MS + WS | 24 h | 81 a ± 2.31 | 11 a ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 48 h | 79 a ± 1.30 | 13 b ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 72 h | 77 b ± 1.01 | 11 a ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 96 h | 70 c ± 1.52 | 11 a ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 120 h | 57 d ± 1.61 | 11 a ± 2 |
| GA3 (100 ppm) | 60 min | 35 e ± 1.23 | 14 c ± 2 |
| GA3 (200 ppm) | 60 min | 28 f ± 1.09 | 18 d ± 3 |
| GA3 (300 ppm) | 60 min | 28 f ± 1.51 | 24 f ± 1 |
| H2SO4 (25%) | 30 min | 41 e ± 2.12 | 20 e ± 3 |
| H2SO4 (50%) | 30 min | 20 g ± 0.98 | 37 i ± 4 |
| H2SO4 (75%) | 30 min | 8 h ± 1.23 | 29 g ± 3 |
| Treatment | Treatment Time (min/h) | Germination (%) 30 DAS (Mean ± SE) $ | Minimum Time Required for Germination (days) (days ± SE) $ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (without MS and WS) * | 0 h | 33 f ± 1.56 | 37j ± 1 |
| MS (without WS) | 0 h | 65 c± 1.23 | 09 d ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 24 h | 85 a± 3.21 | 06 b ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 48 h | 80 a± 2.09 | 08 c ± 2 |
| MS + WS | 72 h | 73 b ± 1.81 | 05 a ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 96 h | 65 c ± 1.72 | 06 b ± 1 |
| MS + WS | 120 h | 59 d ± 1.31 | 06 b ± 2 |
| GA3 (100 ppm) | 60 min | 65 c ± 1.23 | 11 f ± 2 |
| GA3 (200 ppm) | 60 min | 70 b± 1.29 | 07 bc ± 2 |
| GA3 (300 ppm) | 60 min | 69 b± 1.21 | 10 e ± 1 |
| H2SO4 (25%) | 30 min | 46 e ± 2.12 | 18 g ± 1 |
| H2SO4 (50%) | 30 min | 25 g ± 0.98 | 19 h ± 2 |
| H2SO4 (75%) | 30 min | 10 h ± 1.23 | 20 i ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahajan, Y.A.; Shinde, B.A.; Torris, A.; Gade, A.B.; Patil, V.S.; John, C.K.; Kadoo, N.Y.; Nikam, T.D. Pre-Sowing Treatments, Seed Components and Water Imbibition Aids Seed Germination of Gloriosa superba. Seeds 2023, 2, 15-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010002
Mahajan YA, Shinde BA, Torris A, Gade AB, Patil VS, John CK, Kadoo NY, Nikam TD. Pre-Sowing Treatments, Seed Components and Water Imbibition Aids Seed Germination of Gloriosa superba. Seeds. 2023; 2(1):15-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahajan, Yogesh Ashok, Balkrishna Ankush Shinde, Arun Torris, Akshay Baban Gade, Vipul Subhash Patil, C. K. John, Narendra Yeshwant Kadoo, and Tukaram Dayaram Nikam. 2023. "Pre-Sowing Treatments, Seed Components and Water Imbibition Aids Seed Germination of Gloriosa superba" Seeds 2, no. 1: 15-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010002
APA StyleMahajan, Y. A., Shinde, B. A., Torris, A., Gade, A. B., Patil, V. S., John, C. K., Kadoo, N. Y., & Nikam, T. D. (2023). Pre-Sowing Treatments, Seed Components and Water Imbibition Aids Seed Germination of Gloriosa superba. Seeds, 2(1), 15-29. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds2010002









