On-Chip Adaptive Implementation of Neuromorphic Spiking Sensory Systems with Self-X Capabilities
Abstract
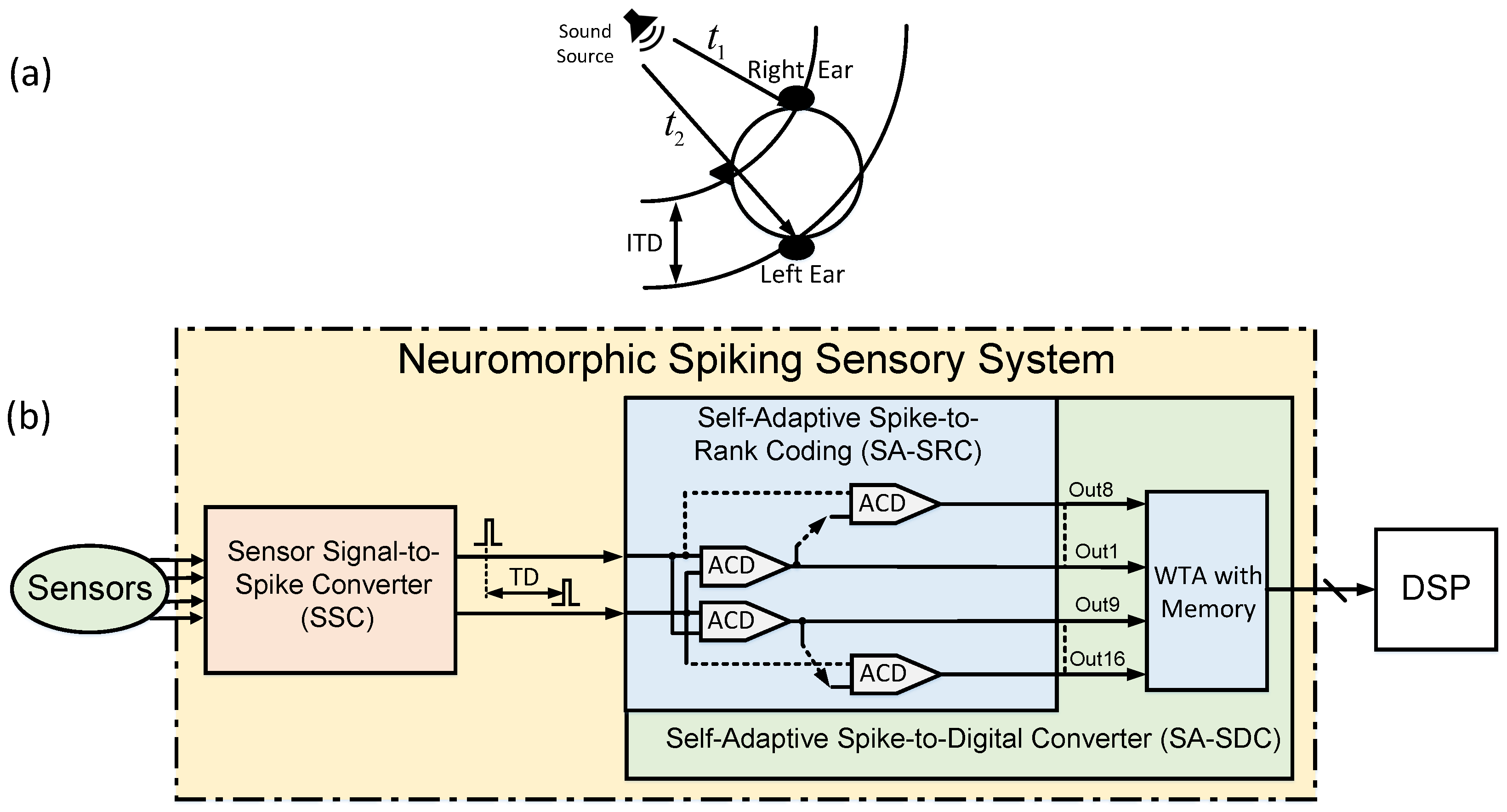
:1. Introduction
2. Inspirations from Biological Sensory Systems
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Sensor Signal-to-Spike Converter (SSC)
3.2. Self-Adaptive Spike-to-Digital Converter (SA-SDC)
4. Experimental Setup
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFE | Analog front-ends |
| USIX | Universal-sensor-interface-with-self-X-properties |
| AFEX | Analog front-ends with self-X properties |
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converters |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| RRAM | Resistive random-access memory |
| ITD | Interaural time differences |
| WTA | Winner-takes-all |
| MPC | Multi-project-chip |
| GMR | Giant magnetoresistance |
| TMR | Tunnel magnetoresistance |
| SSDC | Sensor to spike to digital converter |
| SSC | Sensor-to-spike converter |
| SDC | Spike-to-digital converter |
| TD | Time differences |
| SA-SDC | Adaptive spike-to-digital converter |
| SA-SRC | Self-adaptive spike-to-rank coding |
| ACD | Adaptive coincidence detection |
| NOB | Number of bits |
| LIF | Leaky integrate and fire |
| PVT | Process, voltage, and temperature |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| NUS | Nonuniform sampling |
References
- Weaver, S.; Hershberg, B.; Kurahashi, P.; Knierim, D.; Moon, U.K. Stochastic flash analog-to-digital conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2010, 57, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.; Hershberg, B.; Moon, U.K. Digitally synthesized stochastic flash ADC using only standard digital cells. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2013, 61, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Sobue, K.; Hamashita, K.; Moon, U.K. An oversampling stochastic ADC using VCO-based quantizers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 4037–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, X.; Sanyal, A.; Yoon, Y.; Cong, J.; Sun, N. A 0.7-V 0.6-μW 100-kS/s Low-Power SAR ADC With Statistical Estimation-Based Noise Reduction. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Amirsoleimani, A.; Xu, J.; Azghadi, M.R.; Genov, R. A subranging nonuniform sampling memristive neural network-based analog-to-digital converter. Mem.-Mater. Devices Circuits Syst. 2023, 4, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; He, X.; Chakrabarti, A.; Zhang, X. NeuADC: Neural network-inspired synthesizable analog-to-digital conversion. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 39, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; He, X.; Chakrabarti, A.; Zhang, X. NeuADC: Neural network-inspired RRAM-based synthesizable analog-to-digital conversion with reconfigurable quantization support. In Proceedings of the 2019 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Florence, Italy, 25–29 March 2019; pp. 1477–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Henzler, S. Time-to-digital converter basics. In Time-to-Digital Converters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Recent advances and trends in voltage-time domain hybrid ADCs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2575–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, C.G.; Partzsch, J.; Noack, M.; Schüffny, R. Configurable analog-digital conversion using the neural engineering framework. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kammara, A.; König, A. SSDCα–Inherently robust integrated biomimetic sensor-to-spike-to-digital converter based on peripheral neural ensembles. Tm-Tech. Mess. 2016, 83, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, N.; Santosh, M.; Bose, S.; Karmakar, A. Low-Current Sensing Analog-to-Digital Converter with Tuneable Resolution for Biomedical Applications. IEEE J. Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 16, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, S.; Woo, S.Y.; Kwon, D.; Im, J.; Hwang, J.; Bae, J.H.; Park, B.G.; Lee, J.H. Spiking Neural Networks With Time-to-First-Spike Coding Using TFT-Type Synaptic Device Model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78098–78107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Plank, P.; Wild, A.; Maass, W. A long short-term memory for AI applications in spike-based neuromorphic hardware. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogginger, B.; Kreutz, F.; López-Randulfe, J.; Liu, C.; Dietrich, R.; Gonzalez, H.A.; Scholz, D.; Reeb, N.; Auge, D.; Hille, J.; et al. Automotive radar processing with spiking neural networks: Concepts and challenges. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alraho, S.; Zaman, Q.; Abd, H.; König, A. Integrated Sensor Electronic Front-Ends with Self-X Capabilities. Chips 2022, 1, 83–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, H.; König, A. Adaptive Spiking Sensor System Based on CMOS Memristors Emulating Long and Short-Term Plasticity of Biological Synapses for Industry 4.0 Applications. tm-Tech. Mess. 2021, 88, s114–s119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, H.; König, A. Design of a CMOS memristor emulator-based, self-adaptive spiking analog-to-digital data conversion as the lowest level of a self-x hierarchy. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2022, 11, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, H.; König, A. D10. 3 Adaptive Spiking Sensor Electronics Inspired by Biological Nervous System Based on Memristor Emulator for Industry 4.0 Applications. In Proceedings of the SMSI 2021—Sensors and Instrumentation, Virtual Event, 3–6 May 2021; pp. 232–233. [Google Scholar]
- Abd, H.; König, A. A Compact Four Transistor CMOS-Design of a Floating Memristor for Adaptive Spiking Neural Networks and Corresponding Self-X Sensor Electronics to Industry 4.0. Tm-Tech. Mess. 2020, 87, s91–s96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffress, L.A. A place theory of sound localization. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1948, 41, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashida, G.; Carr, C.E. Sound localization: Jeffress and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doge, J.; Schonfelder, G.; Streil, G.T.; Konig, A. An HDR CMOS image sensor with spiking pixels, pixel-level ADC, and linear characteristics. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog. Digit. Signal Process. 2002, 49, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Q.; Alraho, S.; König, A. Low-Cost Indirect Measurements for Power-Efficient In-Field Optimization of Configurable Analog Front-Ends with Self-X Properties: A Hardware Implementation. Chips 2023, 2, 102–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.; Gautrais, J. Rank order coding. In Computational Neuroscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, S.; Delorme, A.; Van Rullen, R. Spike-based strategies for rapid processing. Neural Netw. 2001, 14, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indiveri, G. A low-power adaptive integrate-and-fire neuron circuit. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS’03, Bangkok, Thailand, 25–28 May 2003; Volume 4, p. IV. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Pipelined Memristive Analog-to-Digital Converter With Self-Adaptive Weight Tuning. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2022, 12, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Ke, L.; Chakrabarti, A.; Zhang, X. Evaluating neural network-inspired analog-to-digital conversion with low-precision RRAM. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 40, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, N.; Santosh, M.; Bose, S.; Karmakar, A. Neuromorphic approach based current sensing analog to digital converter for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th India Council International Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 10–13 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]












| vg1 | vg2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 V | 2 V | 0.45 V | 0.78 V |
| Time Difference * | 15 ns | 32 ns | 40 ns | 55 ns | 70 ns | 95 ns | 107 ns | 120 ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Output | 0000 | 0001 | 0010 | 0011 | 0100 | 0101 | 0110 | 0111 |
| SA-SRC Outputs | Spikes Order | |||||||
| out1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| out2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| out3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| out4 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| out5 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| out6 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| out7 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
| out8 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| out9 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| out10 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| out11 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| out12 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| out13 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| out14 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| out15 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| out16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Time Difference * | 16 ns | 30 ns | 42 ns | 53 ns | 74 ns | 90 ns | 105 ns | 124 ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary Output | 1000 | 1001 | 1010 | 1011 | 1100 | 1101 | 1110 | 1111 |
| SA-SRC Outputs | Spikes Order | |||||||
| out1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| out2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 10 |
| out3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| out4 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| out5 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| out6 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| out7 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| out8 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| out9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| out10 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| out11 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| out12 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| out13 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| out14 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| out15 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
| out16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| Before Adaptation | After Adaptation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Difference * | 16 ns | 55 ns | 16 ns | 55 ns |
| Binary Output | 1000 ** | 1011 ** | 1000 | 1011 |
| SA-SRC Outputs | Spikes Order | |||
| out1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 |
| out2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 7 |
| out3 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 9 |
| out4 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 11 |
| out5 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 13 |
| out6 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 14 |
| out7 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 15 |
| out8 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| out9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| out10 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| out11 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| out12 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 4 |
| out13 | 9 | 5 | 9 | 6 |
| out14 | 12 | 7 | 11 | 8 |
| out15 | 13 | 9 | 13 | 10 |
| out16 | 14 | 11 | 15 | 12 |
| [6] | [28] | [5] | [29] | [30] | [11] | This Work * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution (bits) | 6 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 4 |
| Technology | 130 nm | Off-the-shelf | 180 nm | 130 nm | 180 nm | 350 nm | 350 nm |
| CMOS | Components | CMOS | CMOS | CMOS | CMOS | CMOS | |
| Power Supply (V) | No data | ||||||
| Power Consumption (mW) | 18 | 25 | No data | ||||
| Area (mm2) | No data | ||||||
| Sampling Frequency (MHz) | 1000 | 10 | NUS ** | 1000 | 20 | ||
| Nyquist Bandwidth (MHz) | 500 | 5 | No data | 500 | 10 | ||
| Adaptable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd, H.; König, A. On-Chip Adaptive Implementation of Neuromorphic Spiking Sensory Systems with Self-X Capabilities. Chips 2023, 2, 142-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/chips2020009
Abd H, König A. On-Chip Adaptive Implementation of Neuromorphic Spiking Sensory Systems with Self-X Capabilities. Chips. 2023; 2(2):142-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/chips2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd, Hamam, and Andreas König. 2023. "On-Chip Adaptive Implementation of Neuromorphic Spiking Sensory Systems with Self-X Capabilities" Chips 2, no. 2: 142-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/chips2020009
APA StyleAbd, H., & König, A. (2023). On-Chip Adaptive Implementation of Neuromorphic Spiking Sensory Systems with Self-X Capabilities. Chips, 2(2), 142-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/chips2020009





