Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning of C45 Steel: An Experimental Investigation on Surface Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Results
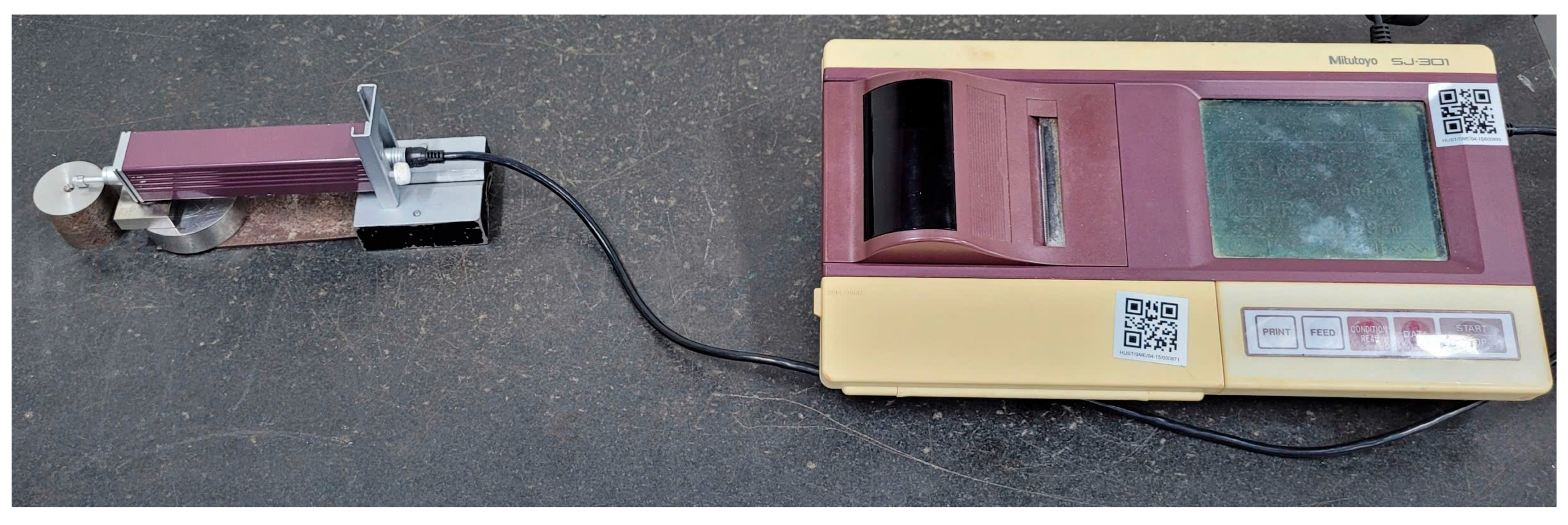
2.1. Experimental Setup
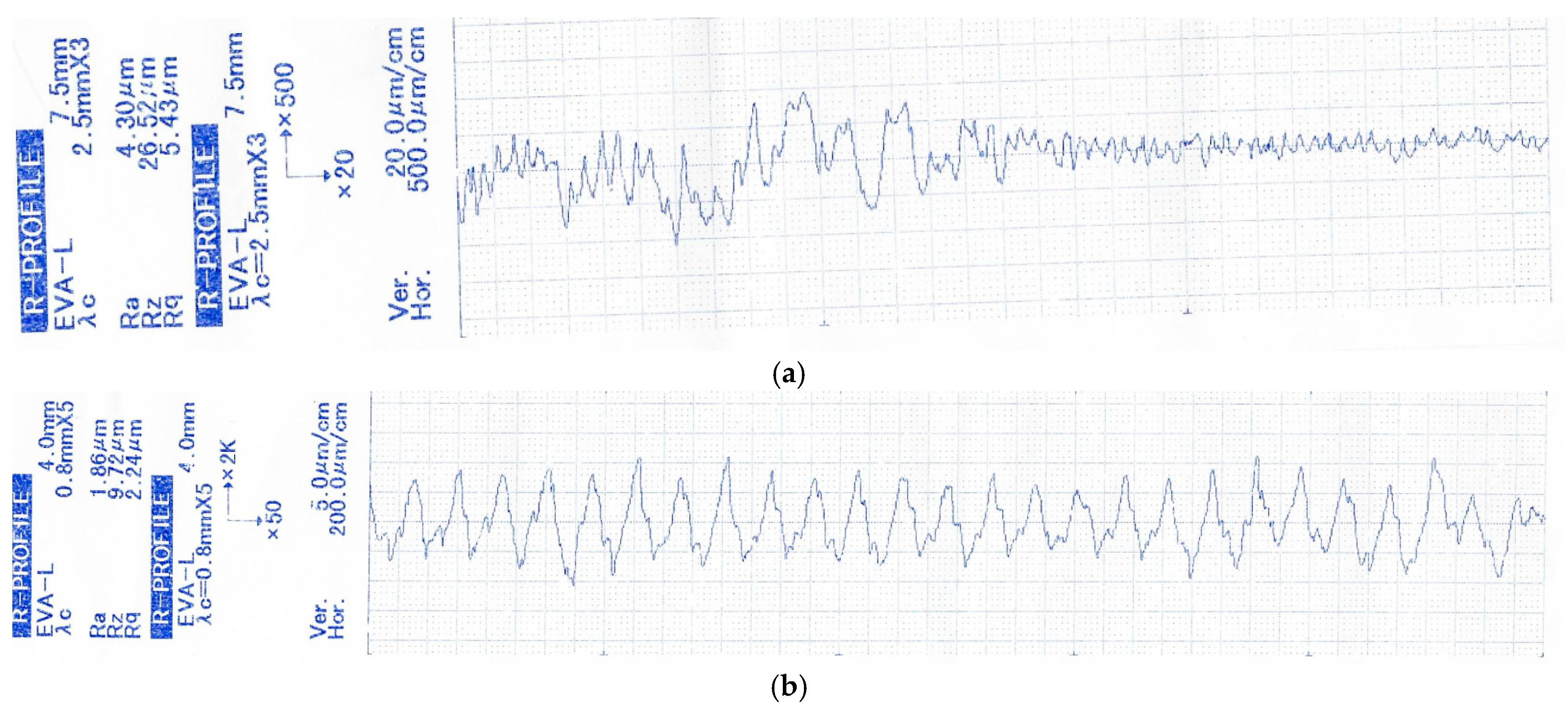
2.2. Surface Roughness
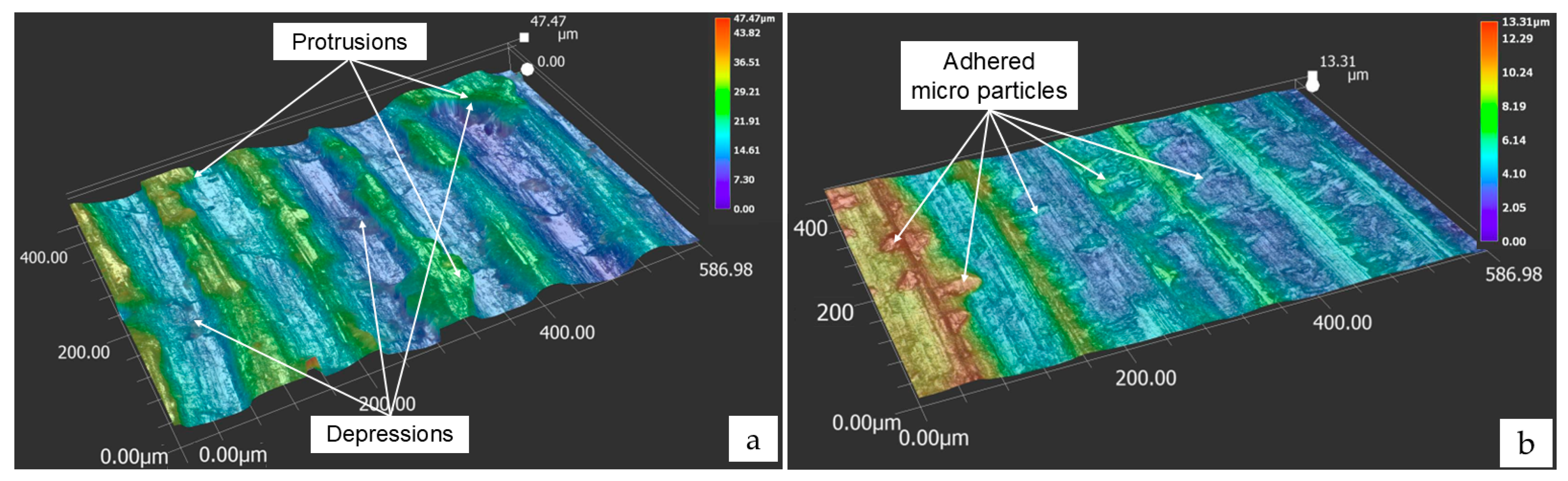
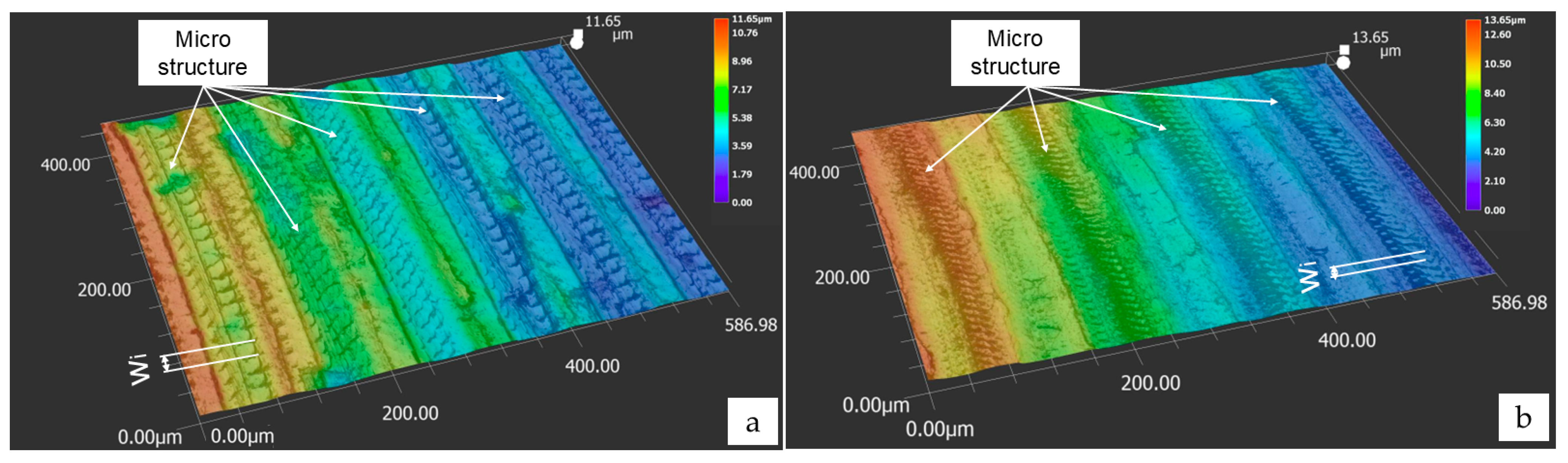
2.3. Surface Topography
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Ultrasonic vibration amplitude (µm) |
| f | Frequency of ultrasonic vibration (Hz) |
| fr | Feed rate in Conventional Turning (CT) (mm/rev) |
| Ra | Arithmetic Mean Height (µm) |
| Rz | Ten-point Mean Height (µm) |
| vc | Cutting speed in Conventional Turning (m/min) |
| vins | Instantaneous cutting speed with ultrasonic vibration assistance |
| vcritical | Critical cutting speed (m/min) |
| n | Spindle speed of lathe (r/min) |
| ap | Depth of cut |
| Rc | Nose radius of turning insert |
| wi | The wavelength of the periodic microstructure |
Abbreviations
| UAFT | Ultrasonic Assisted Face Turning |
| CT | Conventional Turning |
References
- Muñoz-Escalona, P.; Cassier, Z. Influence of the critical cutting speed on the surface finish of turned steel. Wear 1998, 218, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves Correia, A.; Paulo Davim, J. Surface roughness measurement in turning carbon steel AISI 1045 using wiper inserts. Measurement 2011, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frăţilă, D.; Caizar, C. Investigation of the Influence of Process Parameters and Cooling Method on the Surface Quality of AISI-1045 during Turning. Mater. Manuf. Process 2012, 27, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y. Experimental Study on Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of GH4068 Superalloy. Materials 2023, 16, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Airao, J.; Nirala, C.K.; Krolczyk, G.M. Novel sustainable cryo-lubrication strategies for reducing tool wear during ultrasonic-assisted turning of Inconel 718. Tribol. Int. 2022, 174, 107728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, R.; Andrea, G.; Alagan, N.T.; Bruschi, S. Tool wear reduction in ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of SiC-reinforced metal-matrix composite. Wear 2023, 523, 204785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Hu, G.; Lv, Y.; Li, H. Ultrasonic elliptic vibration assisted turning SiCp/Al composite surface morphology. J. Manuf. Process 2025, 141, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, B.; Li, L. Experimental investigation on tool wear in ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 3081–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, A.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Le, T.K.; Nguyen, T.-H. Investigation of surface topography in ultrasonic-assisted turning of C45 carbon steel. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 63, 016501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.; Nestler, A.; Pinternagel, S.; Zeidler, H. Influence of ultrasonic vibration assistance on the surface integrity in turning of the aluminium alloy AA2017. Materials. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 42, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.K.; Jain, V.K. Modeling of material removal in mechanical type advanced machining processes: A state-of-art review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 1573–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bilga, P.S.; Singh, S. Multi objective optimization using different methods of assigning weights to energy consumption responses, surface roughness and material removal rate during rough turning operation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, F.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, F. Theoretical and experimental investigations of surface roughness, surface topography, and chip shape in ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of Inconel 718. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 3791–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehzadeh, M.; Boostanipour, O.; Razfar, M.R. Finite element simulation and experimental investigation of residual stresses in ultrasonic assisted turning. Ultrasonics 2020, 108, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Pandey, P.M. Optimization of machining and vibration parameters for residual stresses minimization in ultrasonic assisted turning of 4340 hardened steel. Ultrasonics 2016, 70, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Ni, C.; Lin, B. Review of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining in advanced materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 156, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabagherian, M.; Amini, S.; Bayat, M. Investigation of the Effects of Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning with CO2 Cooling on Cutting Forces, Residual Stress, and Surface Quality. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Hosseinabadi, H.N.; Sajjady, S.A. Experimental study on effect of micro textured surfaces generated by ultrasonic vibration assisted face turning on friction and wear performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiselt, P.; Hirsch, S.J.; Ozdemir, I.; Nestler, A.; Grund, T.; Schubert, A.; Lampke, T. Ultrasonic-Vibration-Superimposed Face Turning of Aluminium Matrix Composite Components for Enhancing Friction-Surface Preconditioning. J. Manuf. Mater. Process 2024, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Farahnakian, M.; Elhami, S. Experimental study on the wettability of microtextured surfaces generated by the ultrasonic-assisted face turning. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, S.Y.; Djamil, S.; Zebua, Y.K. Effect of cutting speed in the turning process of AISI 1045 steel on cutting force and built-up edge (BUE) characteristics of carbide cutting tool. Sinergi 2020, 24, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Parra, A.; Álvarez-Alcón, M.; Salguero, J.; Batista, M.; Marcos, M. Analysis of the evolution of the Built-Up Edge and Built-Up Layer formation mechanisms in the dry turning of aeronautical aluminium alloys. Wear 2013, 302, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga; Hélder; Grilo, J.; Carneiro, V.H. Ultrasonic assisted turning of Al alloys: Influence of material processing to improve surface roughness. Surfaces 2019, 2, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjady, S.A.; Abadi, H.N.H.; Amini, S.; Nosouhi, R. Analytical and experimental study of topography of surface texture in ultrasonic vibration assisted turning. Mater. Des. 2016, 93, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.D. Surface Topography in Cutting-Speed-Direction Ultrasonic-Assisted Turning. Micromachines 2024, 15, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, T.H.C. Towards simulating built-up-edge formation in the machining of steel. CIRP. J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Beauchamp, Y.; Youssef, A.Y.; Masounave, J. An experimental design for surface roughness and built-up edge formation in lathe dry turning. Int. J. Qual. Sci. 1997, 2, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Guo, S.; Hu, Z.; Sun, T. Study on ultra-precision processing of Ti-6Al-4V with different ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting modes. Mater. Manuf. Process 2019, 34, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, G.; Knight, A. Fundamentals of Machining and Machine Tools, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
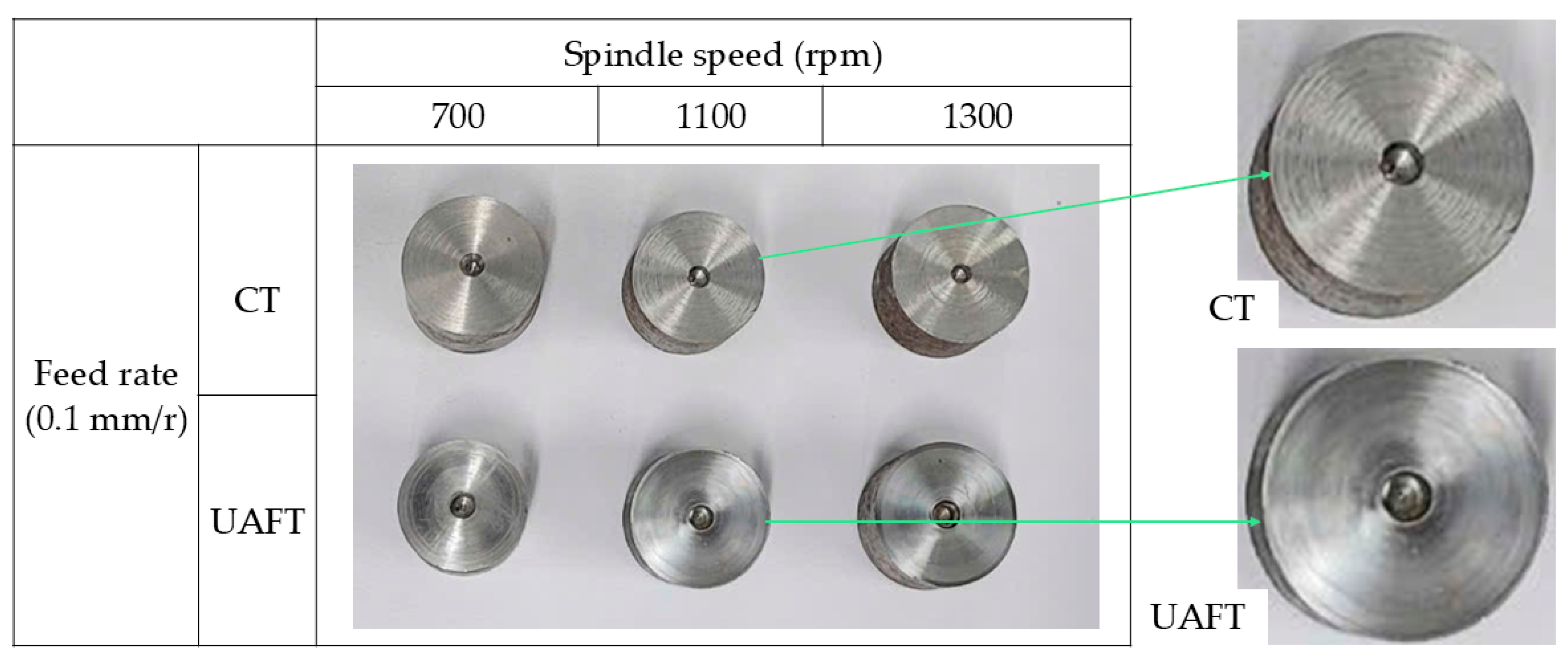

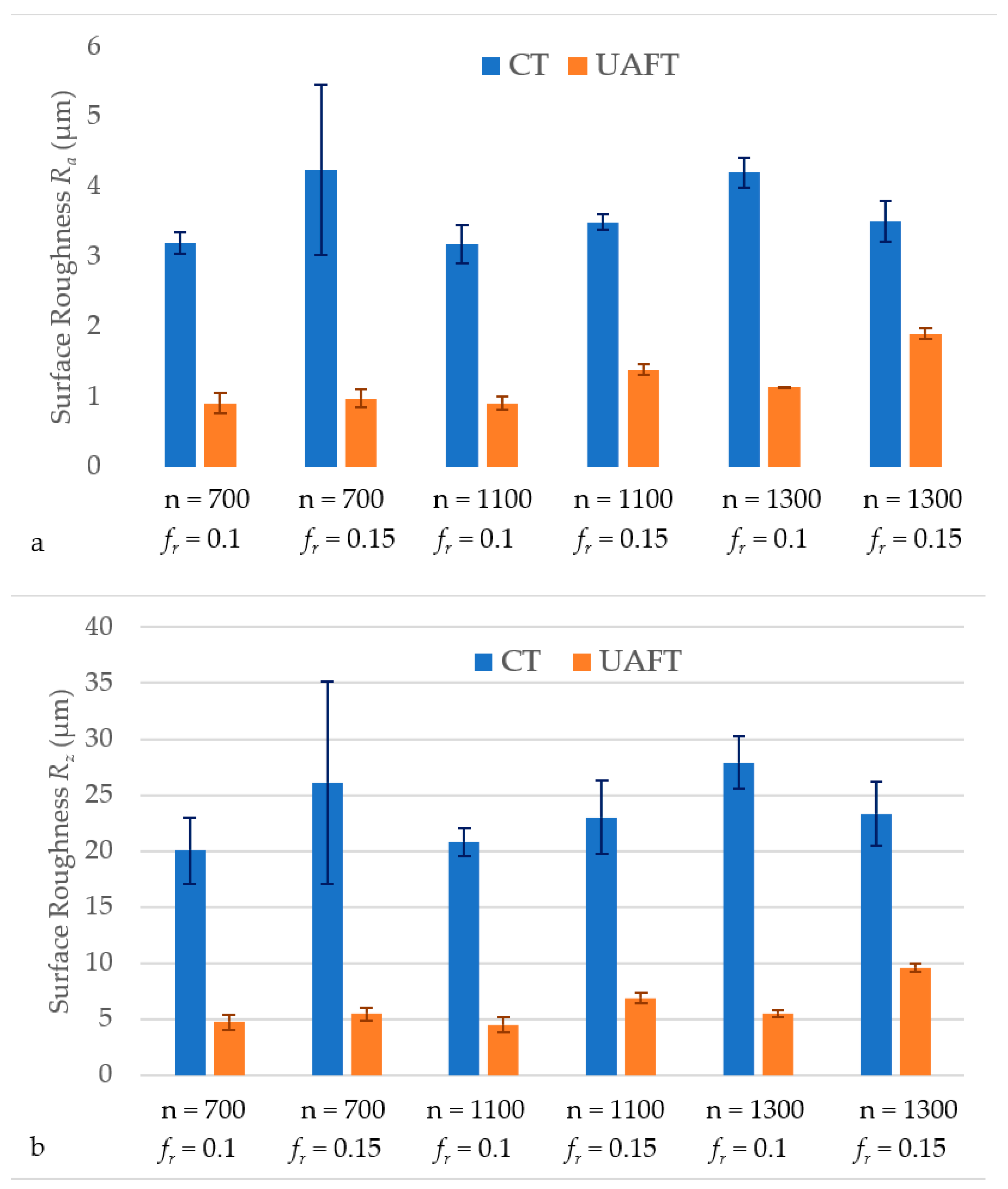

| No. | Spindle Speed, n (rpm) | Feed Rate, fr (mm/r) | Depth of Cut, ap (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 700 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 700 | 0.15 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 1100 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 1100 | 0.15 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 1300 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 6 | 1300 | 0.15 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.-T. Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning of C45 Steel: An Experimental Investigation on Surface Integrity. Alloys 2025, 4, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4030013
Nguyen T-T. Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning of C45 Steel: An Experimental Investigation on Surface Integrity. Alloys. 2025; 4(3):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thanh-Trung. 2025. "Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning of C45 Steel: An Experimental Investigation on Surface Integrity" Alloys 4, no. 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4030013
APA StyleNguyen, T.-T. (2025). Ultrasonic-Assisted Face Turning of C45 Steel: An Experimental Investigation on Surface Integrity. Alloys, 4(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys4030013






