Abstract
In this work, the refractory complex concentrated alloy (RCCA) 3.5Al–4Cr–6Ge–1Hf–5Mo–36Nb–22Si–1.5Sn–20Ti–1W (at.%) was studied in the as cast and heat treated conditions (100 h or 200 h at 1500 °C). There was strong macrosegregation of Si in the 0.6 kg button/ingot of the cast alloy, in which A2 solid solution, D8m βNb5Si3, C14-NbCr2 Laves phase and Tiss and a ternary eutectic of the A2, D8m and C14 phases were formed. The partitioning of Ti in the as cast and heat treated microstructure and its relationships with other solutes was shown to be important for the properties of the A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3, which were the stable phases at 1500 °C. The near surface microstructure of the alloy was contaminated with oxygen after heat treatment under flowing Ar. For the aforementioned phases, it was shown, for the first time, that there are relationships between solutes, between solutes and the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ, between the said parameters, and between parameters and phase properties. For the contaminated with oxygen solid solution and silicide, trends in relationships between solutes, between solutes and oxygen content and between the aforementioned parameters and oxygen content also were shown for the first time. The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3 of the as cast and heat-treated alloy were measured using nanoindentation. Changes of nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and D8m βNb5Si3 per solute addition for this multiphase RCCA were discussed. The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the solid solution and the βNb5Si3, respectively, were 9.5 ± 0.2 GPa and 177.4 ± 5.5 GPa, and 17.55 ± 0.5 GPa and 250.27 ± 6.3 GPa after 200 h at 1500 °C. The aforementioned relationships and properties of the two phases demonstrated the importance of synergy and entanglement of solutes, parameters and phases in the microstructure and properties of the RCCA. Implications of synergy and entanglement for the design of metallic ultra-high temperature materials were emphasised.
1. Introduction
Metallic ultra-high temperature materials (UHTMs) that could replace Ni-based superalloys in a “beyond Nickel superalloys era” could be refractory metal (RM) intermetallic composites (RMICs), RM high entropy alloys (RHEAs), or RM complex concentrated alloys (RCCAs) [1,2,3] (see Abbreviations). Alloys for high temperature applications are known to be sensitive to contamination by interstitials, e.g., [4,5,6,7,8]. Metallic UHTMs also will be contaminated with interstitials. The effects of the latter on the properties of constituent phases and on the properties and in-service life of ultra-high temperature material systems cannot be ignored [9].
In aerofoil applications in aeroengines, the new materials will be used as part of an ultra-high temperature material system comprising a metallic UHTM substrate plus an environmental coating [9,10,11]. The metallic substrate should have “adequate” resistance to oxidation and interstitial contamination, and the environmental coating should also “protect” the substrate from interstitial contamination [12,13,14]. It is important to know how individual phases in a metallic UHTM are contaminated. Such knowledge is essential for the design and development of the material/material system, and for predicting the performance and survivability of the material/material system in-service [9].
Alloying with Al, Cr, Ge, Hf, Si, Sn, or Ti can enhance the resistance of the metallic UHTM substrate to oxidation and interstitial contamination, e.g., see [15,16,17,18,19]. The A2 solid solution in the metallic UHTMs is the Achilles’ heel regarding oxidation, creep and interstitial contamination. To design and develop metallic UHTMs we need data about the properties of contaminated phases, in particular A2 solid solutions and tetragonal or hexagonal M5Si3 silicides. Presently, such data is limited, e.g., see [9,19,20].
Current research focusses on substrate metallic UHTMs, in particular on A2 solid solution RHEAs or RCCAs, e.g., [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], or (i) on RHEAs and RCCAs with A2 + B2 two-phase microstructure, e.g., [22,29,30], or (ii) on multiphase RMICs, RHEAs and RCCAs with microstructures that consist of intermetallics such as silicides, aluminides, Laves phases and A15 compounds with/without A2 solid solution(s), e.g., [1,2,19,21,22,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Research focussing on material systems for a “beyond Nickel superalloys era”, though essential [9,19], is still in its infancy [10,11].
The constituent phases in the aforementioned multiphase metallic UHTMs can be “conventional” or high entropy (HE) or complex concentrated/compositionally complex (CC) [20,40]. In other words, in these materials, HE and/or CC phases can co-exist with “conventional” phases and vice versa. Furthermore, depending on their location in the microstructure, the said phases can be contaminated with interstitials, some more severely than others, in particular A2 solid solution(s) [9,20]. Whereas there is experimental data about the room temperature hardness and the room and high temperature yield strength of solid solution phase RHEAs and RCCAs, e.g., [25,27,32,41,42,43], experimental data about the properties of the phases in multiphase metallic UHTMs is limited for A2 solid solutions and M5Si3 silicides in RM(Nb)ICs and RCCAs/RM(Nb)ICs or RHEAs/RM(Nb)ICs (see Abbreviations), e.g., [1,11,18,19,24,44].
Previous research has reported experimental results for the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of A2 Nbss and tetragonal or hexagonal Nb5Si3 in RM(Nb)ICs with/without Sn [45,46] or Ge [47] addition. The experimental data for properties of Nb5Si3 is for the αNb5Si3, βNb5Si3 [46] or γNb5Si3 [45], and is for RM(Nb)ICs with no CC or HE phases in their microstructures. Also, previous research has reported calculated data about the Young’s modulus of unalloyed α, β and γ Nb5Si3 [48,49,50,51], and of alloyed α, β and γ Nb5Si3 where Nb has been substituted with Ti up to 12.5 at.% [49].
One motivation for this work was to study the microstructure, nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of tetragonal beta M5Si3 silicide (tI32, W5Si3 type-D8m) and A2 solid solution in a RCCA that (a) had “conventional” phases co-existent with CC phases, (b) contained Al, Cr, Ge, Hf, Si, Sn and Ti, and RMs, namely Mo, Nb and W additions, simultaneously, which are key for room temperature and high temperature strength, creep and oxidation resistance, and (c) had stable intermetallic(s) only M5Si3 silicide(s). Another motivation for this work was to discover new relationships between solutes and parameters of uncontaminated and contaminated by interstitial phases guided by the alloy design methodology NICE (Niobium Intermetallic Composite Elaboration) [9,19], and to demonstrate the significance of synergy, entanglement and material-environment interactions [9] for the development of metallic UHTMs.
The design/selection of the RCCA of this work (alloy NT 1.2) was guided by the design and experimental results reported for the UHTM alloys ZF9 (RCCA/RM(Nb)IC) [52], ZX7 (RM(Nb)IC) [53], OHS1 (RCCA/RM(Nb)IC) [54], and JZ3 (RM(Nb)IC), JZ3+, JZ4 and JZ5 (RCCAs/RM(Nb)ICs) [55,56] (see Appendix A for alloy compositions), and the alloy design methodology NICE [9]. The chemical composition of NT1.2 was 3.5Al–4Cr–6Ge–1Hf–5Mo–36Nb–22Si–1.5Sn–20Ti–1W (at.%).
2. Experimental
The alloy was produced as 0.6 kg buttons/ingots using clean melting (plasma melting with water cooled copper crucible) and high purity elements (purity better than 99.99%, with the exception of Nb which had purity 99.8%). Niobium was provided in lump and wire form, Ti in sheet and rod form, Si in small pieces, Al in bar form, Cr and Mo as flakes, Hf and Ge as chips, and W and Sn in powder and slug form. The Al, Ge and Sn charges were packed in a folded Ti sheet, which was placed at the bottom of the crucible, and the Mo, Nb and W charges were placed at the top of the crucible.
For the characterisation of the alloy, specimens were cut and mounted in conductive bakelite. Grinding was done using silicon carbide sand paper with successive grit of P800-P1200-P2400-P4000, and polishing was performed with 1 μm diamond suspension, followed by a final polish using 50 nm diamond suspension.
The alloy was heat treated under flowing inert Ar atmosphere at 1500 °C for 100 and 200 h. The alloy was wrapped in Ta foil during the heat treatment process, and Ti sponge was placed at the Ar gas entrance as oxygen getter. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed to identify the phases present in the as cast (AC) and heat treated (HT) microstructures. For the XRD experiments, alloy samples were crushed with mortar and pestle and then filtered through a sieve with 63 μm aperture. The XRD was performed under Bragg–Brentano geometry with 2θ range of 20° to 90°, with increments of 0.02° per second. A D5000 GA-XRD diffractometer equipped with Kristallo-Flex 710D X-ray generator (Siemens/Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) operating at 40 kV and 40 mA was used with Cu Kα radiation. The detector had fixed slit geometry of 0.2 mm. For analysis of the data, ICDD’s SIeve+ and PDF-4+ database were used.
Nanoindentation was performed using a Bruker Hysitron Ti Premier instrument with diamond Berkovich indenter. Calibration was performed using an H pattern on a fused quartz sample with a reduced modulus of 69.6 GPa, as instructed by the manufacturer. Indent spacing was set at 5 μm with a serpentine pattern. A load of 10,000 μN was used with 60 s time delay between indents.
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) equipped with back-scatter detector and energy dispersive detector were used for imaging and quantitative analysis. XL30 Philips FEG (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) and InspectF FEG SEMs (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) were used. The EDS with standards (elemental standards for all elements and Forsterite (O: 45.5%, Mg: 34.5%, Si: 20.0%) for oxygen) was performed on the XL30 using INCA Oxford Instruments analysis software package, with 20 kV per channel. Acquisition duration and processing time were optimised to maintain good spectral resolution with count rate of 40 kcps and a dead time of up to 20%. Both for EDS and BSE imaging, the aperture was set to three and the spot size to five.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
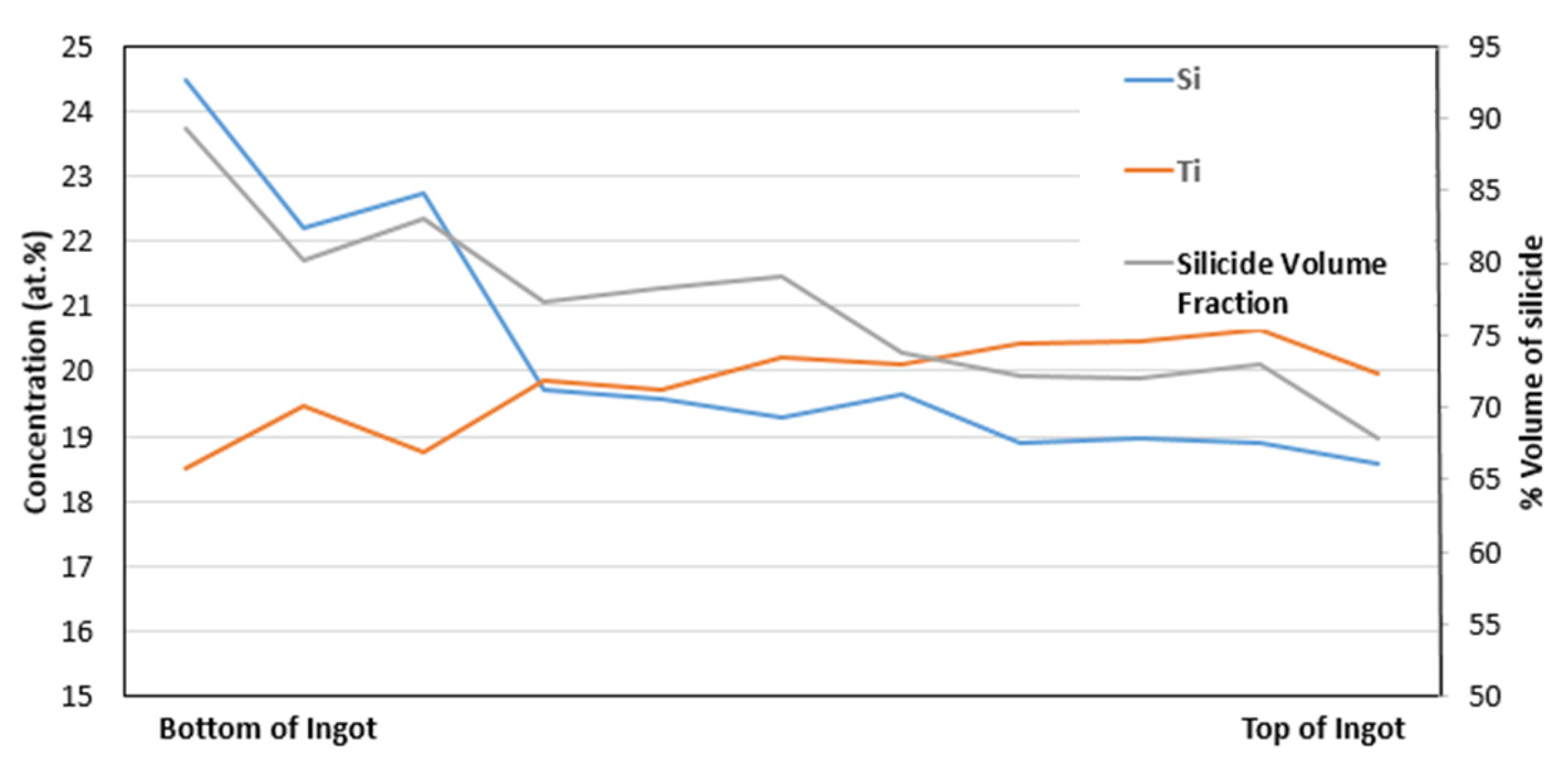
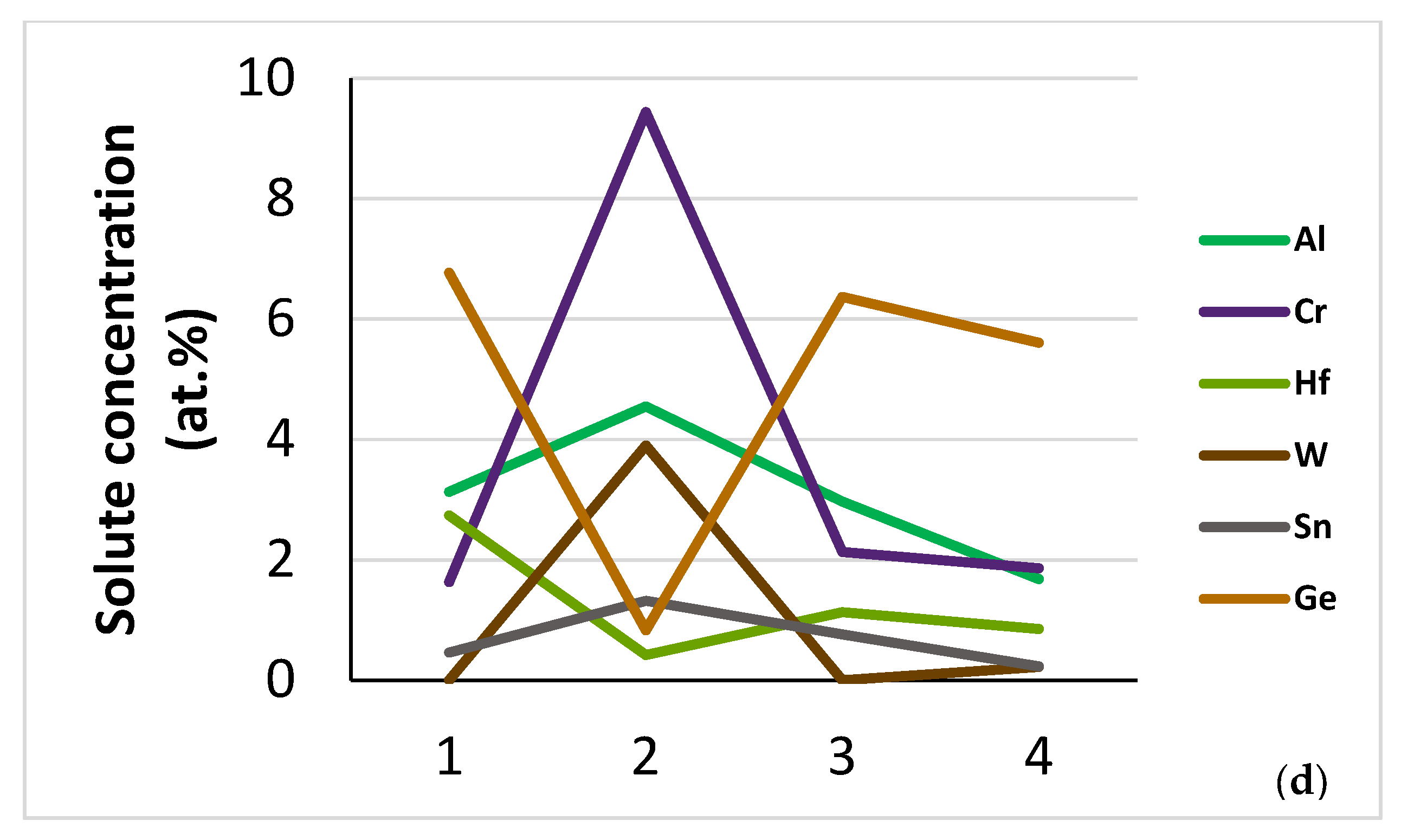
As cast: The average composition (at.%) of NT 1.2-AC was (36.3 ± 2)Nb–(19.6 ± 2.7)Ti–(22.4 ± 6.7)Si–(3.5 ± 1.7)Al–(3.8 ± 2.4)Cr–(1 ± 0.8)Hf–(5 ± 1.7)Mo–(1 ± 0.4)W–(1.2 ± 0.3)Sn–(6.2 ± 1)Ge, where in the parentheses are given the average value and the standard deviation for each element. There was strong macrosegregation of Si between the top and bottom of the button/ingot as well as macrosegregation of Ti; see Figure 1. The reader should also note that there was macrosegregation of Al, Cr, Ge and Mo.
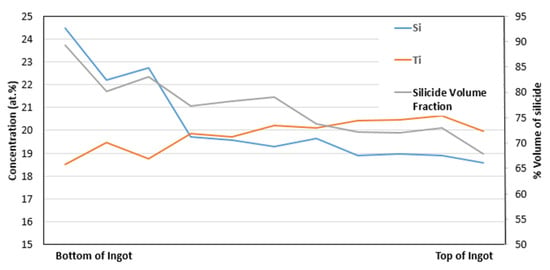
Figure 1.
Concentration of Si and Ti and vol.% of βNb5Si3 between the bottom and top of the button/ingot of NT 1.2-AC. Thickness (bottom to top) of button/ingot about 5 cm.
The microstructure of the as cast alloy consisted of A2 solid solution, D8m βNb5Si3 silicide and C14-NbCr2 Laves phase (Figure 2a) and a very low vol.% of hafnia. A ternary eutectic of solid solution, silicide and Laves phase, with average composition (at.%) (34.6 ± 2.1)Nb–(23.2 ± 1.5)Ti–(10.9 ± 1.1)Si–(6.6 ± 0.8)Al–(7.8 ± 0.9)Cr–(2.3 ± 0.8)Hf–(7.9 ± 0.5)Mo–(1.1 ± 0.4)W–(1.3 ± 0.2)Sn–(4.3 ± 0.4)Ge formed in-between βNb5Si3 grains (Figure 3a) in parts of the microstructure. In some eutectic areas Ti rich solid solution (Tiss), see Table 1, was observed (Figure 3b). The hafnia grains were observed in the eutectic. The vol.% of Tiss was very low (<2%).
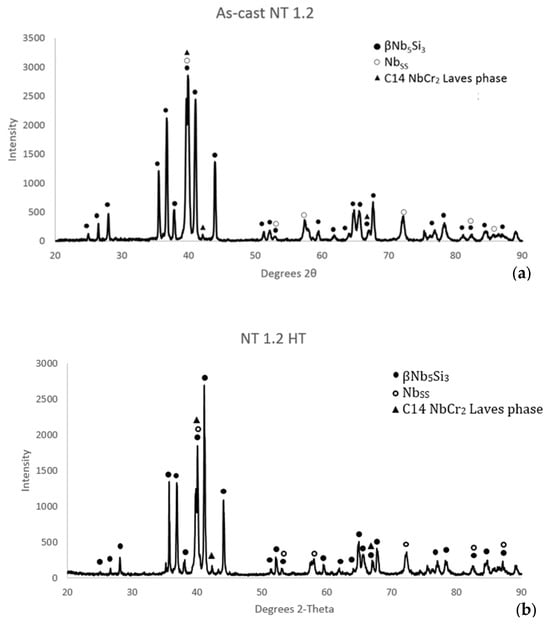
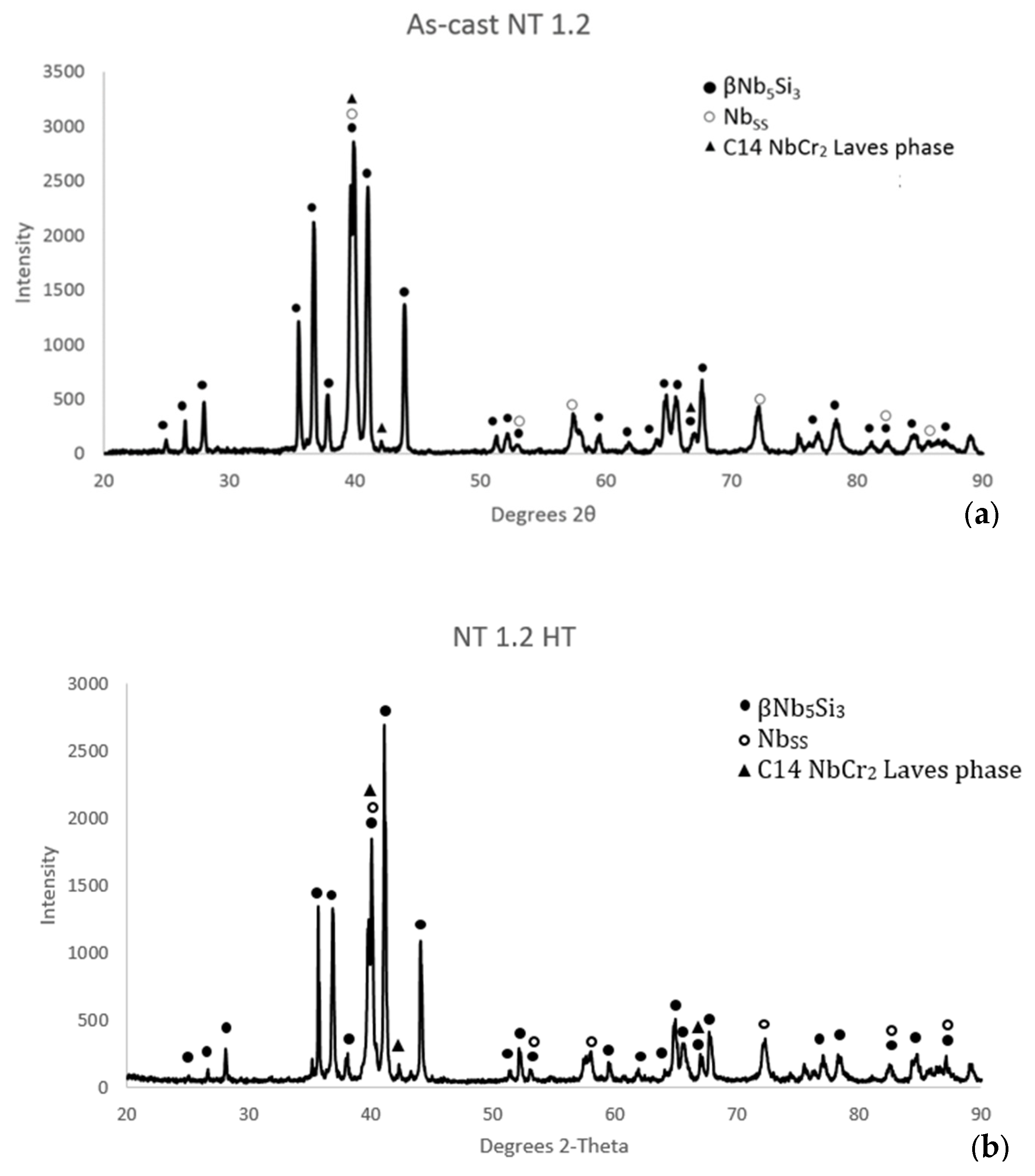
Figure 2.
X ray diffractograms of (a) as cast and (b) heat treated (1500 °C/200 h) NT1.2.
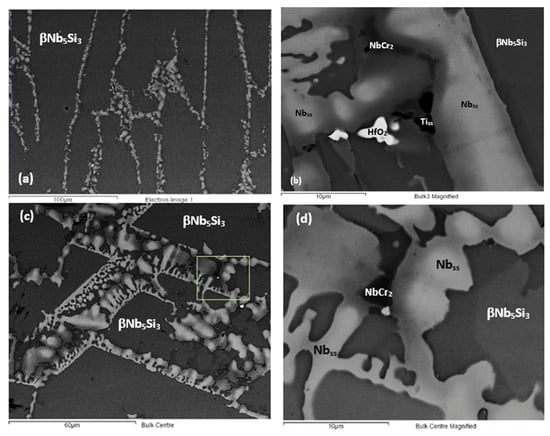
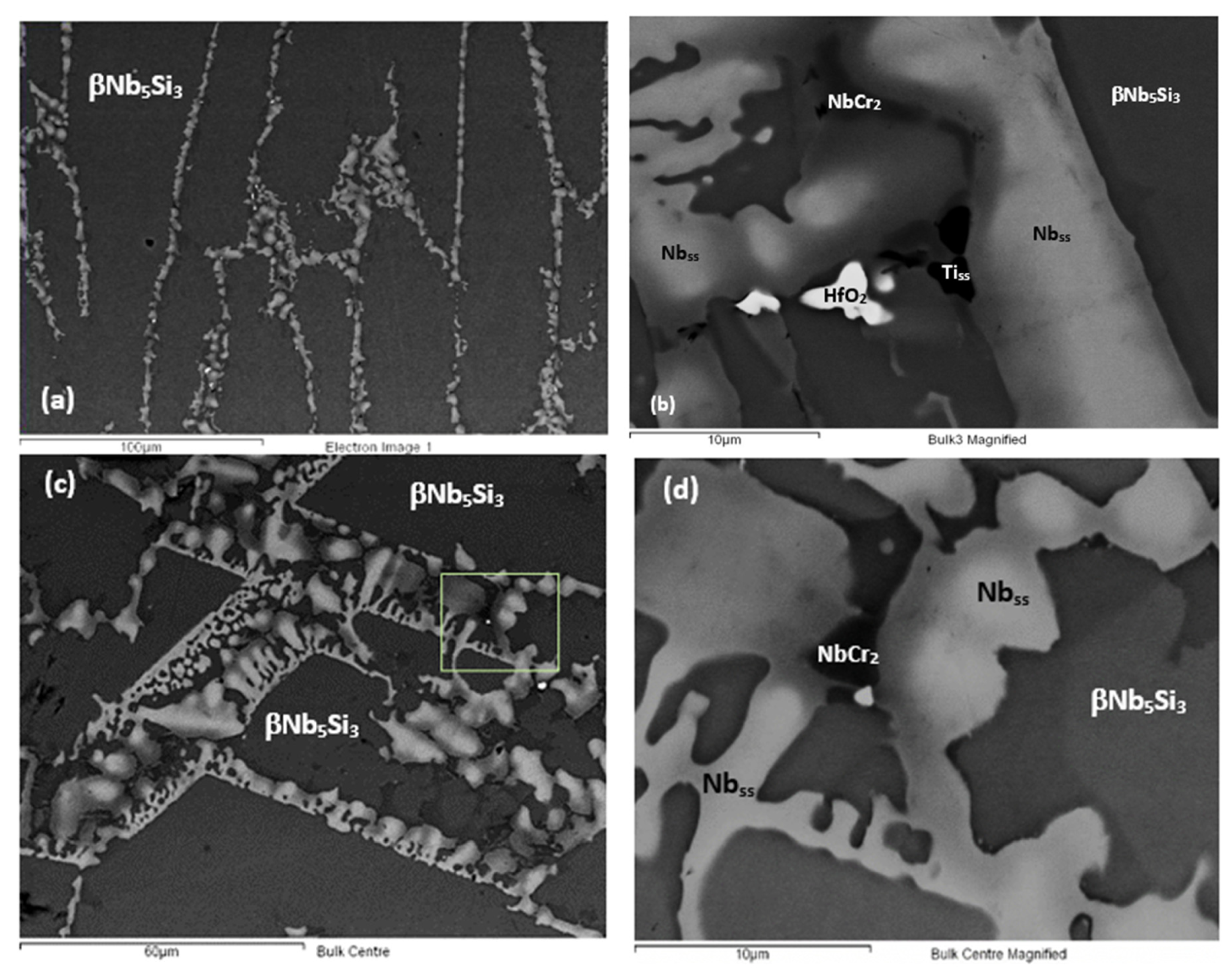
Figure 3.
Back scatter electron (BSE) images of NT 1.2-AC showing (a) microstructure in the bottom of the button/ingot consisting of βNb5Si3 and eutectic, (b) microstructure of eutectic with Tiss (very dark contrast), (c) microstructure in the bulk with βNb5Si3 and eutectic, and (d) magnified image of selected area in (c). The light phase is A2 solid solution (Nbss), the grey phase is βNb5Si3 silicide, and the dark contrast phase is the C14-NbCr2 Laves phase. Note strong solute partitioning in A2 and the silicide, exhibited by the darker areas in the solid solution in (b,d), and by the darker areas in the silicide in (d). For microstructure where no eutectic was formed, see Section 3.2.

Table 1.
Chemical analysis (at.%) data (average composition and standard deviation) of the phases in NT 1.2-AC.
Many of the A2 solid solution grains were Si free. The strong partitioning of Ti between the solid solution and silicide resulted in darker contrast areas of the solid solution next to silicide and vice versa, see Figure 3b,d. The chemical composition of Ti rich Nbss and Ti rich Nb5Si3 is given in Table 1. The chemical analysis data for the aforementioned phases in NT 1.2-AC showed strong partitioning of solutes. Indeed, the Ti rich solid solution was poorer in Mo and W and richer in Al, Cr, Hf, Si and Sn than the “normal” solid solution, and the Ti rich silicide was poorer in Mo, Si and W and richer in Al, Cr, Ge and Sn than the “normal” silicide.
Heat treated: After the heat treatments at 1500 °C for 100 h and 200 h (NT 1.2-HT100 and NT 1.2-HT200, respectively) the microstructure consisted only of βNb5Si3 and A2 solid solution (Figure 2b). There was no evidence of the eutectic that was observed in NT 1.2-AC. Detailed study of the heat treated microstructures using EDS did not confirm the presence of the C14-Laves phase, which was suggested by the XRD data (Figure 2b), and the Tiss. Furthermore, the XRD data for NT 1.2-HT200 did not show peaks for tetragonal D8l αNb5Si3 or hexagonal D88 γNb5Si3. In other words, the D8m βNb5Si3 was the stable silicide in NT 1.2. The near surface areas for the alloy were contaminated with oxygen after both heat treatments, even though these were performed under flowing Ar. The average chemical composition of the alloy and its phases after the heat treatment for 200 h is given in Table 2. The solid solution was Si free, and its contamination with oxygen was more severe than the silicide.

Table 2.
Average composition (at.%) and standard deviation of NT 1.2-HT200 and its phases in near surface and bulk areas.
There was precipitation of a second phase in the silicide (Figure 4a) both in the near surface areas and in the bulk. This precipitation occurred in areas of the silicide (labelled 3 in Figure 4b) that were next to solid solution. We shall refer to this part of the silicide as the “boundary” Nb5Si3. It corresponded to the Ti-rich Nb5Si3 in NT 1.2-AC. The precipitates in the silicide exhibited the same contrast as the solid solution (labelled 2 in Figure 4b). In-between the solid solution grains formed a very dark contrast phase (labelled 1 in Figure 4b), the composition of which corresponded to silicide that was very rich in Ti (Table 2). The “core” of the silicide (labelled 4 in Figure 4b) was precipitate free.
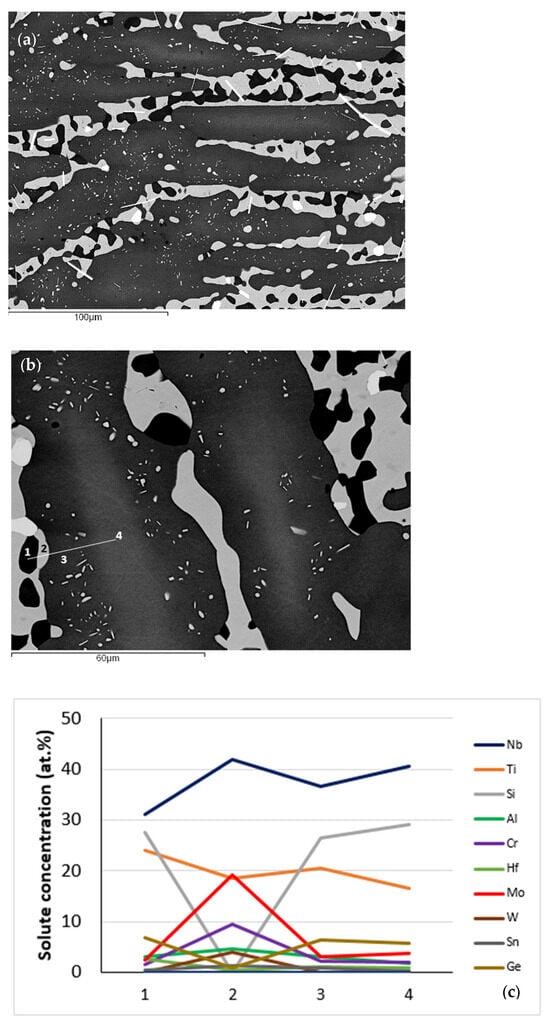
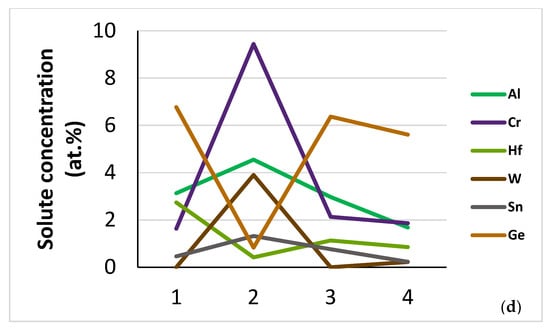
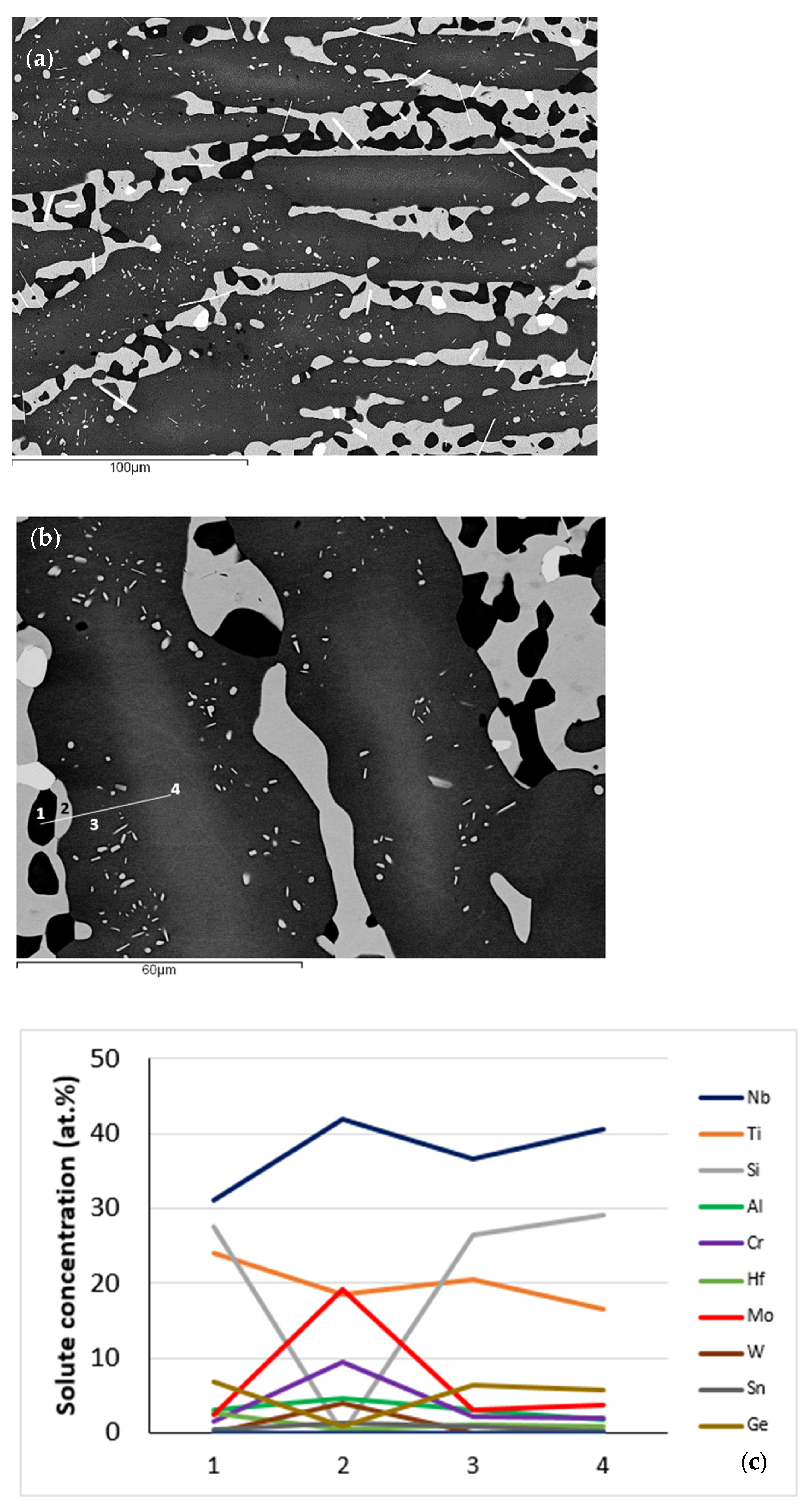
Figure 4.
Bulk microstructures of NT 1.2-HT after (a) 100 h, (b) 200 h at 1500 °C, and (c,d) solute concentrations along the line 1234 in (b) where 1 = Nb5Si3 very rich in Ti, 2 = A2 solid solution, 3 = “boundary” Nb5Si3, 4 = “core” Nb5Si3. In (a) the thin white contrast needle like phase is hafnia.
After the heat treatment for 200 h, of which the objective was to grow precipitates in silicide grains and to clarify the stability of βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2, in some areas of the microstructure few precipitates in “boundary” Nb5Si3 had grown to a size that made their analysis possible. The latter gave their average composition as (41.4 ± 1.1)Nb–(18.9 ± 0.9)Ti–0Si–(4.8 ± 0.5)Al–(9.6 ± 0.6)Cr–0.3Hf–(18.9 ± 0.9)Mo–(3.8 ± 0.4)W–(1.3 ± 0.2)Sn–(1 ± 0.2)Ge (at.%) in the bulk microstructure. Also, it was possible to analyse precipitates in the “boundary” Nb5Si3 in the near surface areas. The average composition of these precipitates was (39.3 ± 0.9)Nb–(17.9 ± 0.8)Ti–0Si–(4.5 ± 0.7)Al–(8.9 ± 0.8)Cr–0.4Hf–(17.7 ± 1)Mo–(3.6 ± 0.5)W–(1.4 ± 0.3)Sn–(1.1 ± 0.2)Ge–(5.2 ± 1.9)O (at.%).
Bulk microstructures similar to that shown in Figure 4b were analysed after the heat treatments at 100 and 200 h and the chemical analysis data are given in Table 3 and Table 4 for the two heat treatment times, respectively. As the data in these two tables show, changes in the chemical composition of the phases were marginal. The solid solution was Si free after both heat treatments, slightly poorer in Ti and richer in Sn in NT 1.2-HT200. The very rich in Ti silicide was richer in Si and Hf in NT 1.2-HT100 and richer in Ti in NT 1.2-HT200, and the “boundary” Nb5Si3 was richer in Hf in NT 1.2-HT100 and richer in Sn in NT 1.2-HT200.

Table 3.
Chemical analysis data (at.%, average value and standard deviation) of phases in the bulk of NT 1.2-HT100.

Table 4.
Chemical analysis data (at.%, average value and standard deviation) of phases in the bulk of NT 1.2-HT200.
3.2. Properties
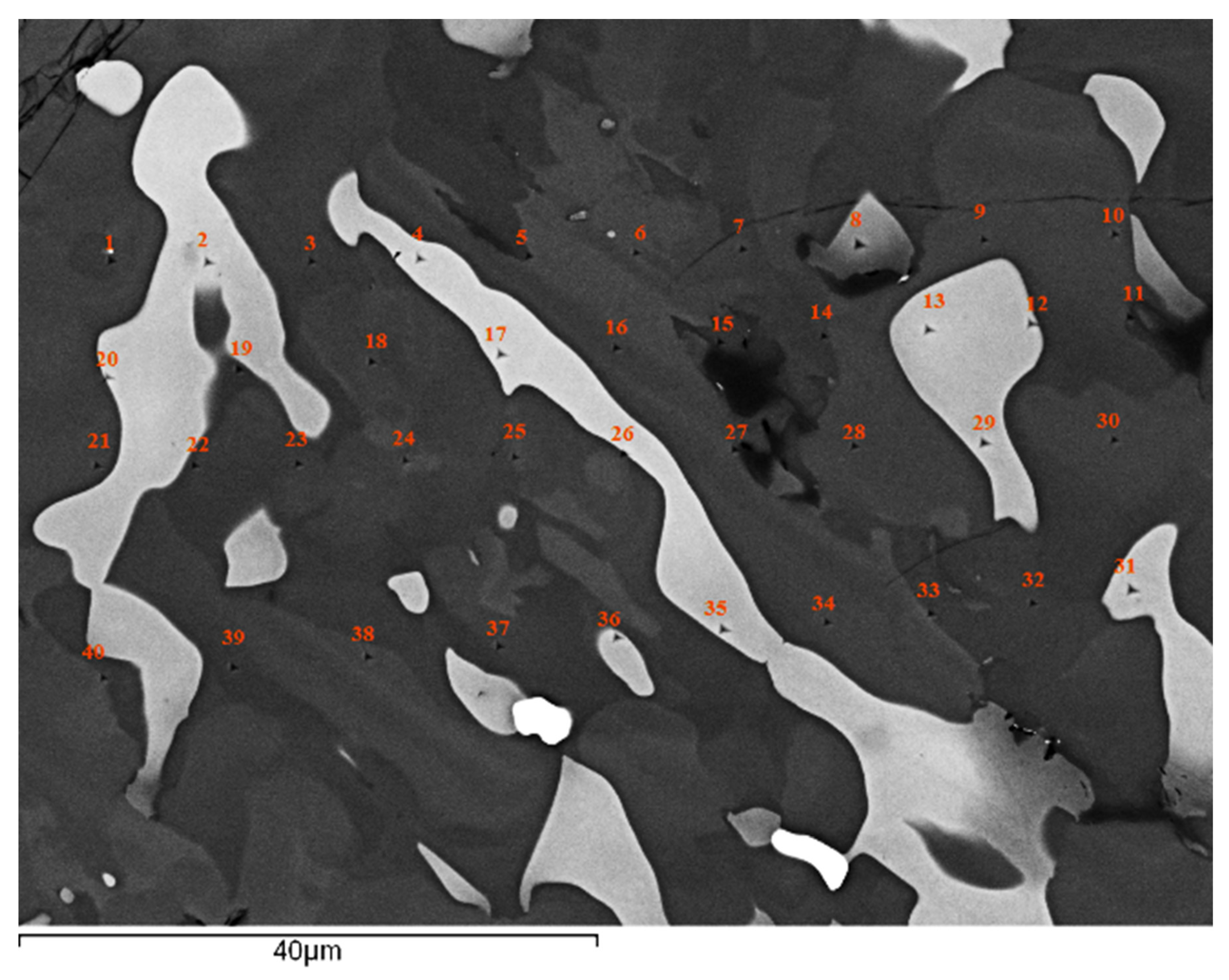
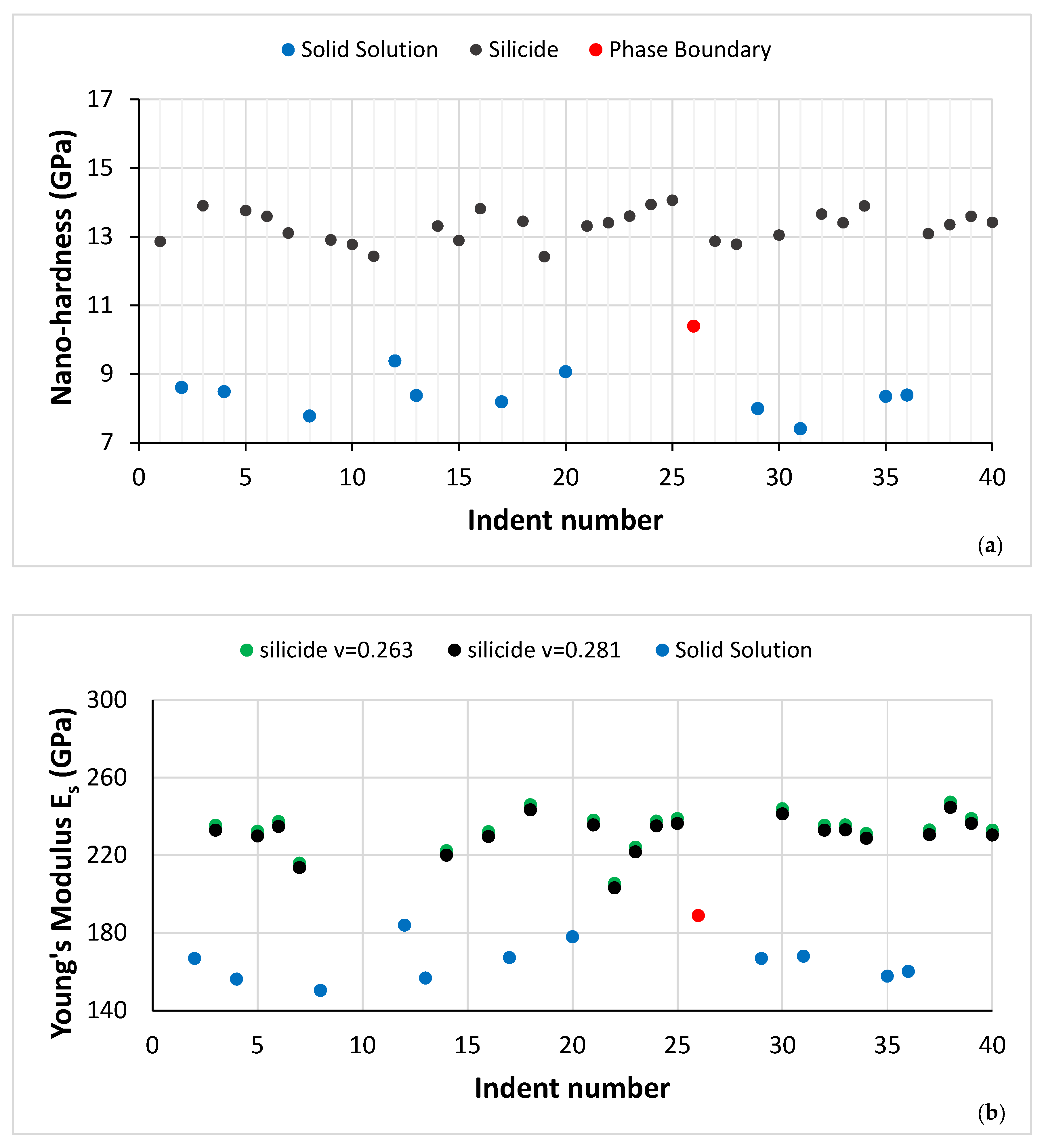
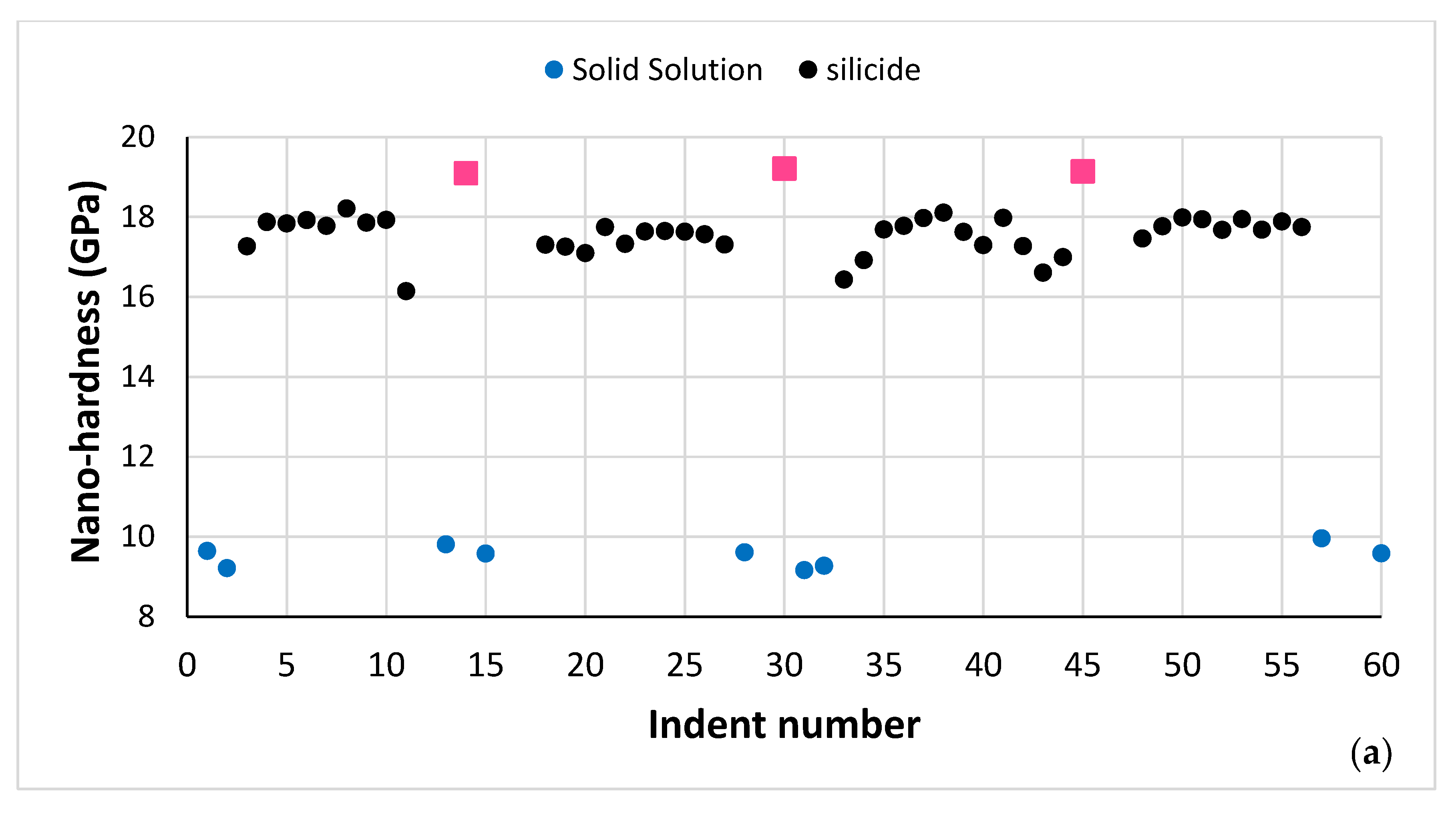
As cast alloy: Nano-indentation was used to measure the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the solid solution and silicide in NT 1.2-AC. A microstructure where the eutectic was absent was chosen for the nano-indentation experiments. Figure 5 shows the eutectic free microstructure with the indentation numbers. The same area where the nano-indentation was performed was subsequently studied using EDS. The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus data are shown in Figure 6. The red data point in Figure 6a and b is for the interface area between the A2 solid solution and the Nb5Si3, nanoindentation point 26 in Figure 5.
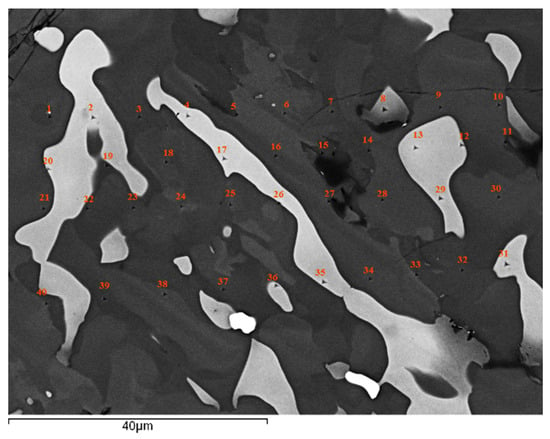
Figure 5.
Microstructure of NT 1.2-AC without eutectic. The indentations are numbered. Light contrast phase is the solid solution, grey contrast phase is the βNb5Si3, darker contrast areas in the silicide were Ti rich.
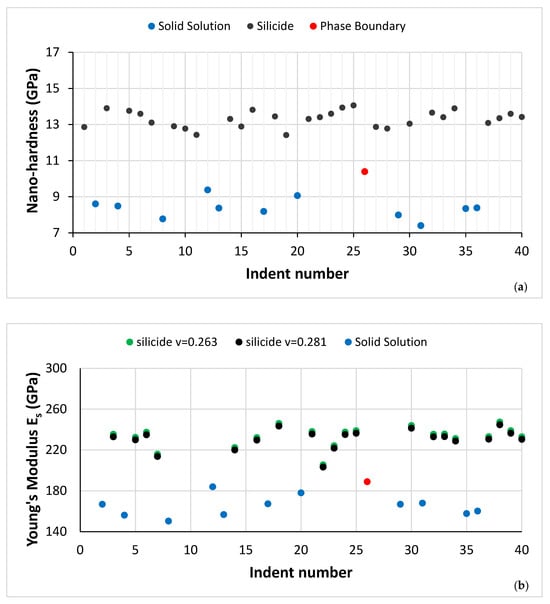
Figure 6.
(a) Nano-hardness and (b) Young’s modulus data for the microstructure of NT 1.2-AC shown in Figure 5. In both figures the red data point is for a measurement of the interface/boundary “area” between the solid solution and silicide (see text).
In nanoindentation, from the unloading curve the stiffness, S, of the phase can be measured. The stiffness is correlated with the reduced modulus Er with the equation
where P is the load, h is the displacement, and A is the projected surface area of the indentation. The reduced modulus Er accounts for the effects of a non-rigid indenter during loading and is given by the equation
where Es and νs are the Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the phase and Ei, νi are the parameters for the indenter [57]. A rearrangement of the last equation gives the actual modulus, Es, of the phase as
The values of Ei and νi were specified in the TriboScope manual [58] as 1140 GPa and 0.07, respectively. The Es was calculated for three different values of νs, namely 0.38 for the A2 solid solution, and 0.263 and 0.281 for the silicide, see [48,49].
The average chemical composition of the solid solution and silicide in the microstructure shown in Figure 5 is given in Table 5.

Table 5.
Chemical analysis data (at.%, average value and standard deviation) of the solid solution and silicide in the microstructure shown in Figure 5.
The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and βNb5Si3 in the microstructure shown in Figure 5 were 8.2 ± 0.4 GPa and 160.4 ± 6.4 GPa for the former, and 13.5 ± 0.3 GPa and 231.4 ± 9 for the latter. The data for the interface/boundary “area” between the A2 and βNb5Si3 were 10.4 GPa and 188.8 GPa, respectively, for nano-hardness and Young’s modulus.
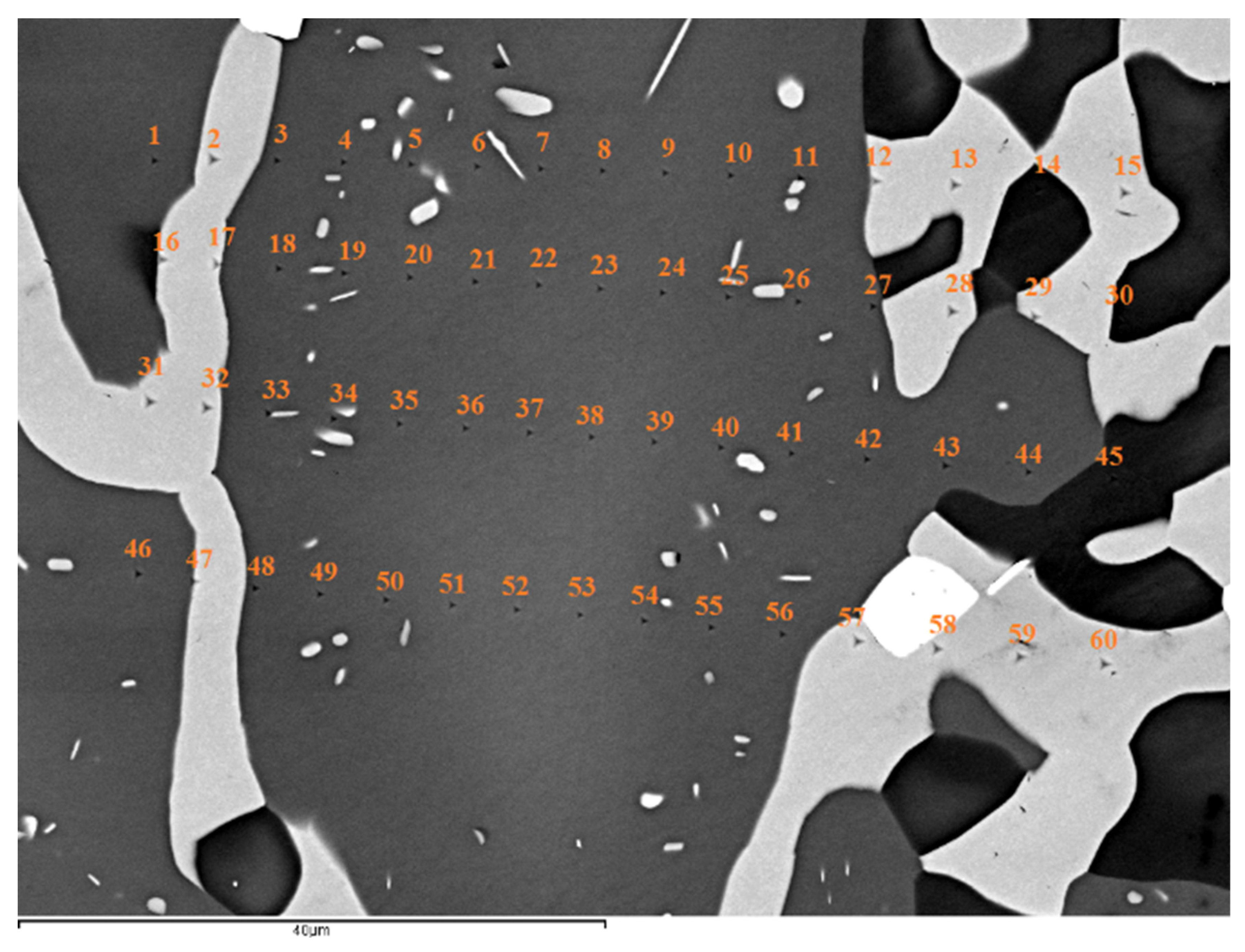
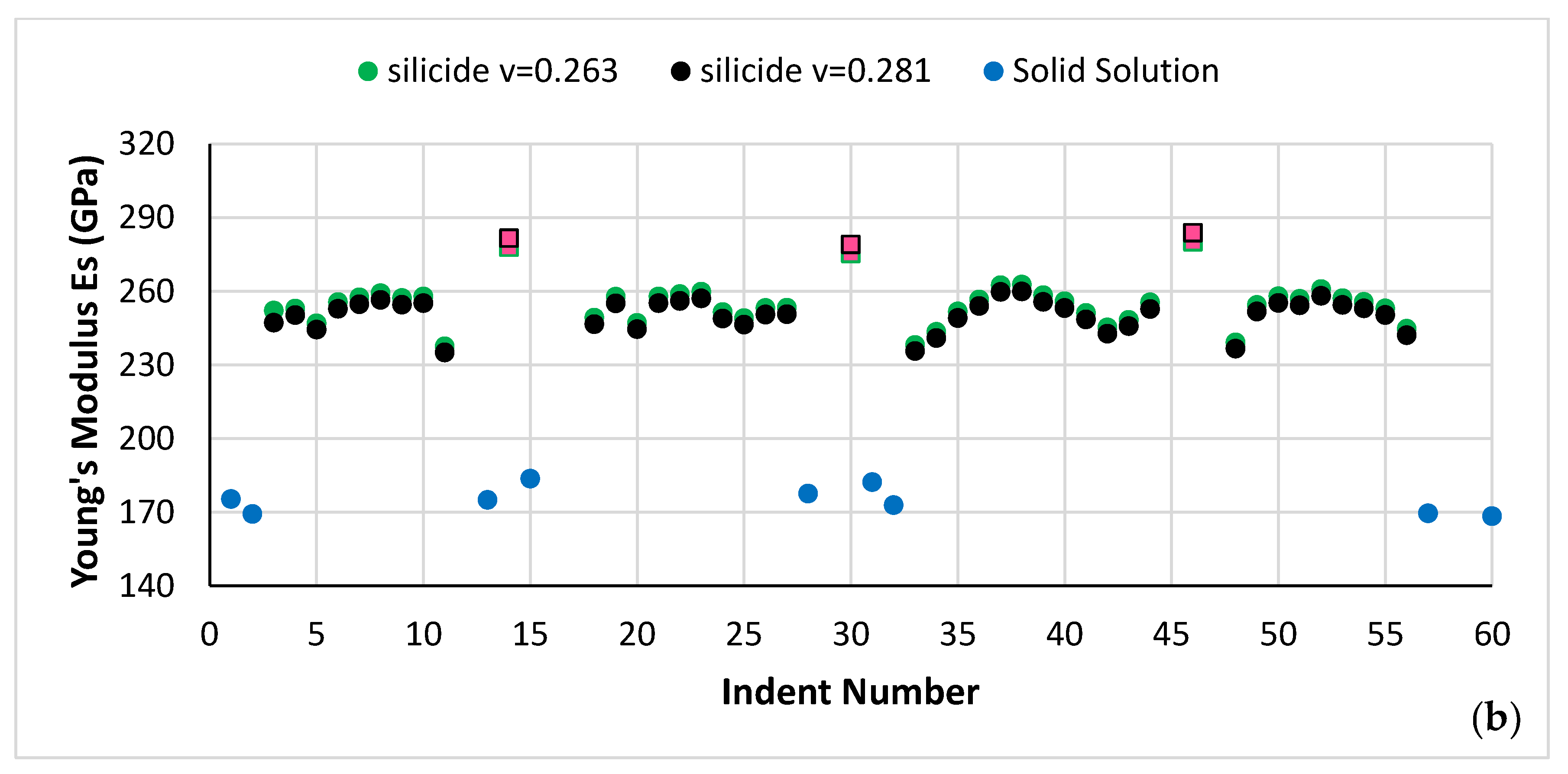
Heat treated alloy: Nanoindentation also was used to measure the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and silicide in NT 1.2-HT200 for a microstructure with solid solution precipitates in the silicide. Figure 7 shows the microstructure and the nanoindentation numbers. The same area where the nanoindentation was performed was subsequently studied using EDS. The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus data are shown in Figure 8.
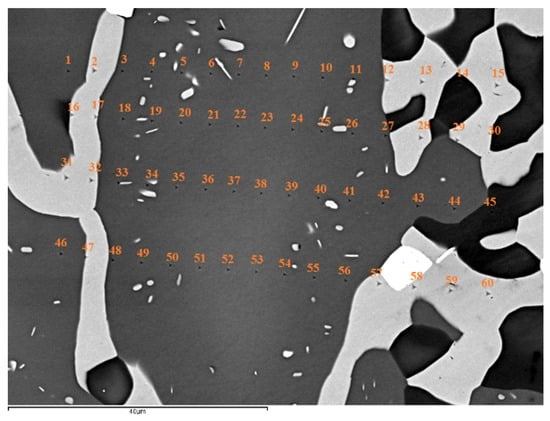
Figure 7.
Microstructure of NT1.2-HT200. The nanoindentations are numbered. Light contrast phase is the solid solution, grey contrast phase is the βNb5Si3, very dark contrast areas show the silicide that was very rich in Ti, and the bright phase near indent numbers 57 and 58 is hafnia.
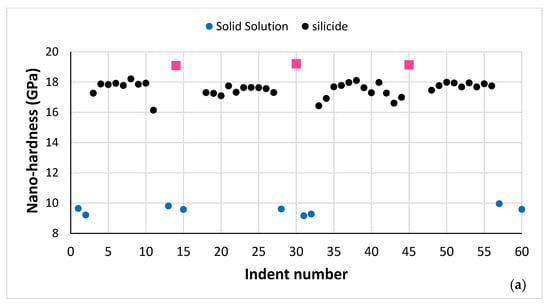
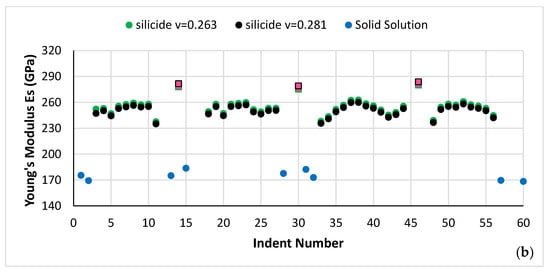
Figure 8.
(a) Nano-hardness and (b) Young’s modulus data for the microstructure shown in Figure 7. Red data points correspond to silicide that was very rich in Ti.
The average chemical composition of the solid solution and silicide in the microstructure shown in Figure 7 is given in Table 6.

Table 6.
Chemical analysis data (at.%, average value and standard deviation) of the solid solution and silicide in the microstructure shown in Figure 7.
The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-HT100, respectively was 10.1 ± 0.2 GPa and 187.1 ± 13.8 GPa, and in NT 1.2-HT200 was 9.5 ± 0.2 GPa and 177.4 ± 5.5 GPa. The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2-HT100, respectively, was 19.5 ± 1.6 GPa and 240.3 ± 10.2 GPa, and in NT 1.2-HT200 was 17.55 ± 0.5 GPa and 250.27 ± 6.3 GPa. For the silicide that was very rich in Ti the average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus in NT 1.2-HT200, respectively, was 19.15 ± 0.05 GPa and 281.5 ± 2 GPa.
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructure
As cast alloy: The actual composition of NT 1.2-AC corresponded to that of a RCCA (HEAs and HE phases are those alloys and phases where the maximum and minimum concentrations of elements are not above or below, respectively, 35 and 5 at.%, whereas RCCAs alloys and CC phases are those where the maximum and minimum concentrations of elements are above 35 at.% (up to about 40 at.% and below 5 at.%), and also corresponded to a RM(Nb)IC. In other words, the alloy NT 1.2 was a RCCA/RM(Nb)IC [3,9] (see Abbreviations). Owing to its Si concentration and the strong Si macrosegregation, and the resultant variation in vol.% silicide between the bottom and top of the button/ingot (Figure 1), the RM(Nb)IC was an intermetallic matrix in situ composite [59]. Thus, the alloy NT 1.2 also can be classified as a refractory intermetallic matrix complex concentrated in situ composite. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first report in the literature of such a RCCA/RM(Nb)IC metallic UHTM. In the as cast microstructure, complex concentrated (CC) A2 and βNb5Si3 co-existed with “conventional” C14-Laves and Tiss phases.
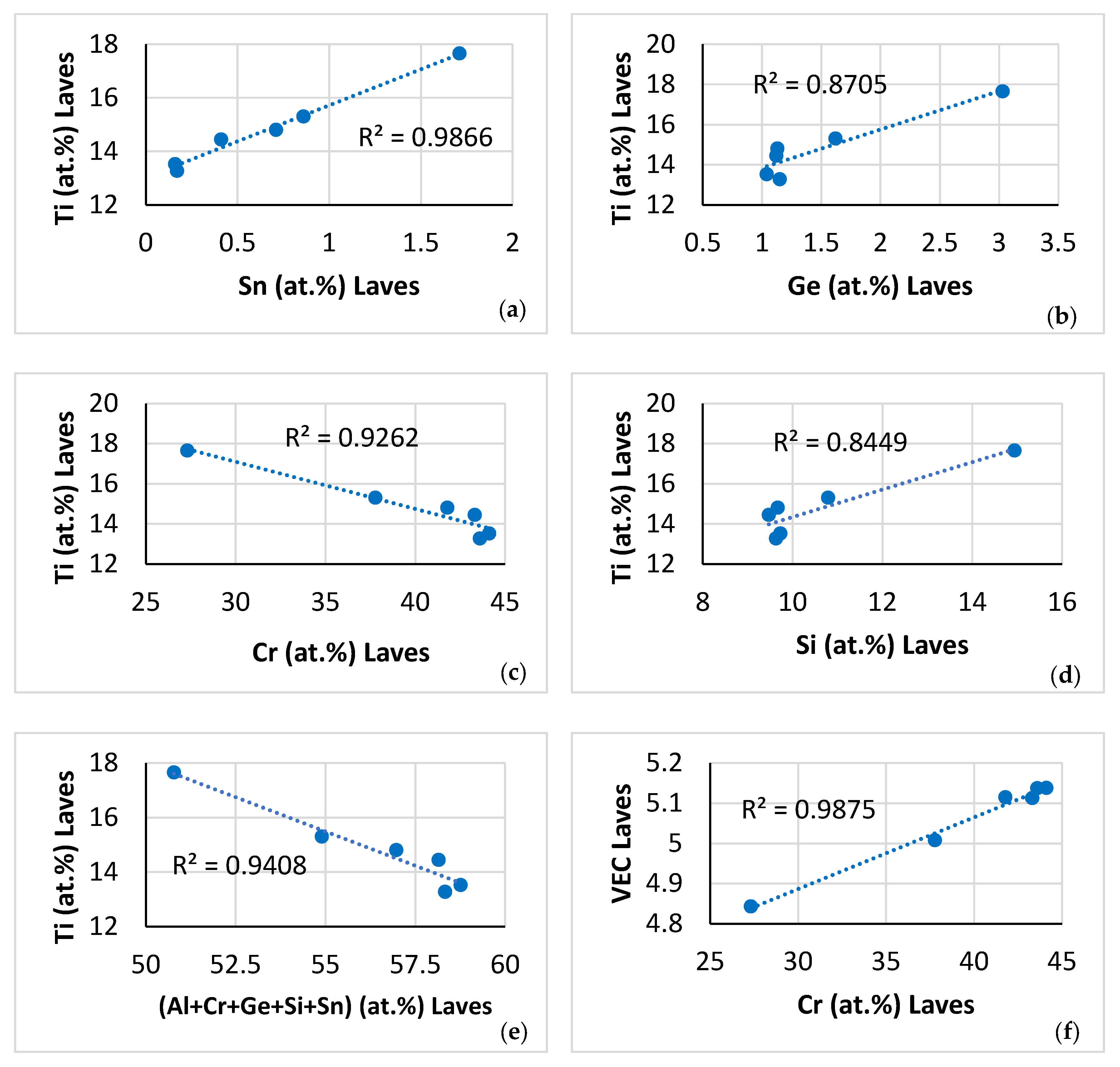
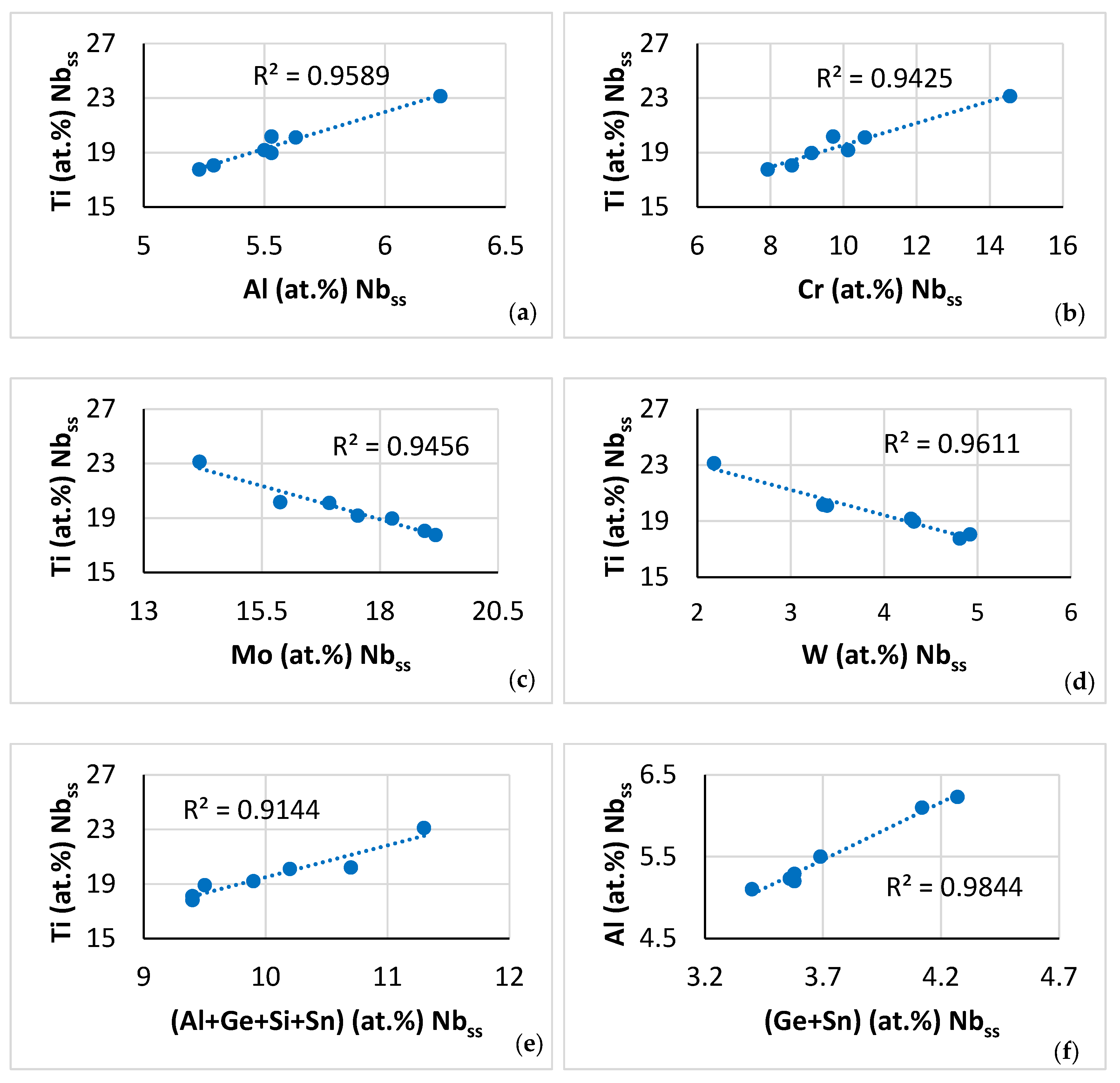
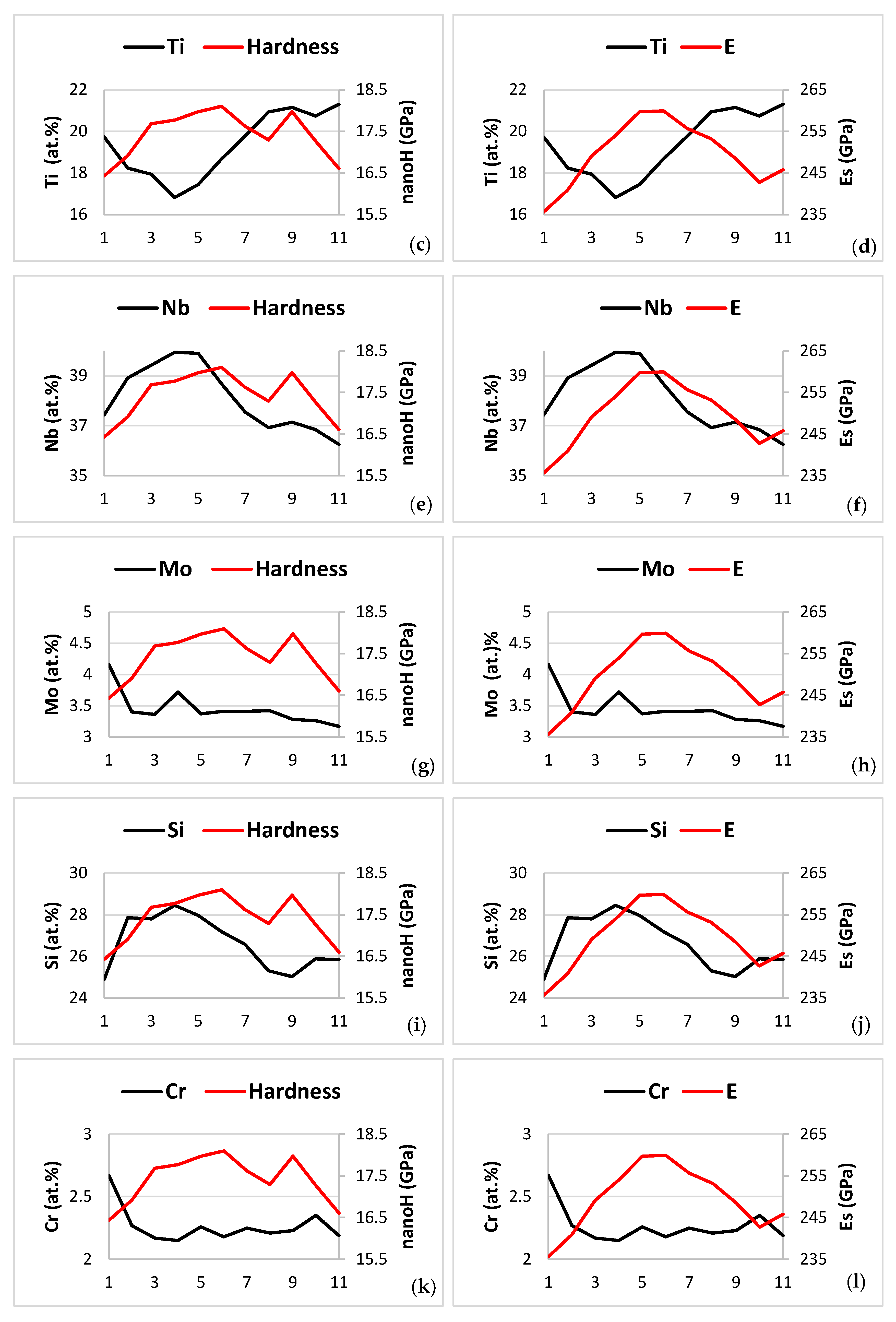
The partitioning of Ti was critical in NT 1.2-AC. Indeed, the Ti “pulled with it” Ge, Si and Sn and “pushed out” Cr in the C14-Laves phase (Figure 9a–d), meaning as the Ti concentration increased in the Laves phase so did the concentrations of Ge, Si and Sn, whereas the concentration of Cr decreased. Also, the Ti “pulled with it” Al and Cr and “pushed out” Mo and W in the A2 solid solution (Figure 10a–d) and “pulled in” Al and Cr in the βNb5Si3 (Figure 11a,b) and Hf. Furthermore, the Ti “pushed out” <Cr> = Al + Cr + Ge + Si + Sn in the C14-Laves phase (Figure 9e) [60], and “pulled with it” <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn in the A2 solid solution (Figure 10e). Also, in the A2 solid solution, the Al “pulled with it” Ge and Sn (Figure 10f), in agreement with [20]. In other words, Ti “worked” in synergy and intricateness (see Appendix A in [9]) with the other solutes and vice versa, and the aforementioned CC and “conventional” phases were entangled. The significance of synergy and entanglement for the design and development of metallic UHTMs was recently discussed by one of the authors in [9].
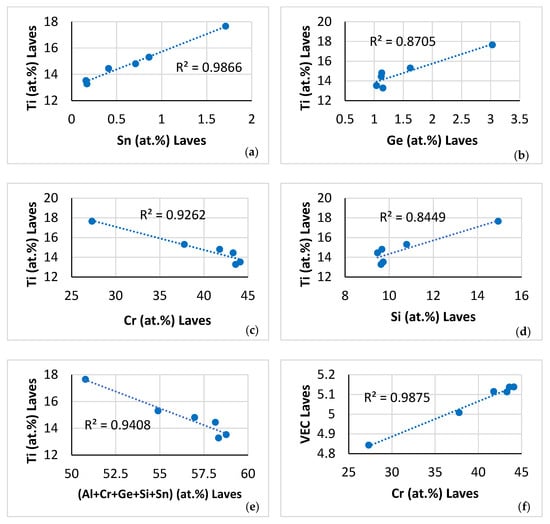
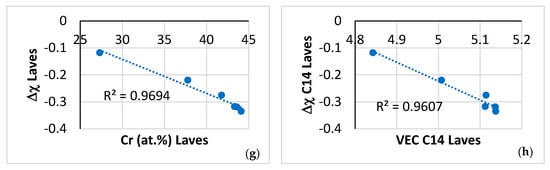
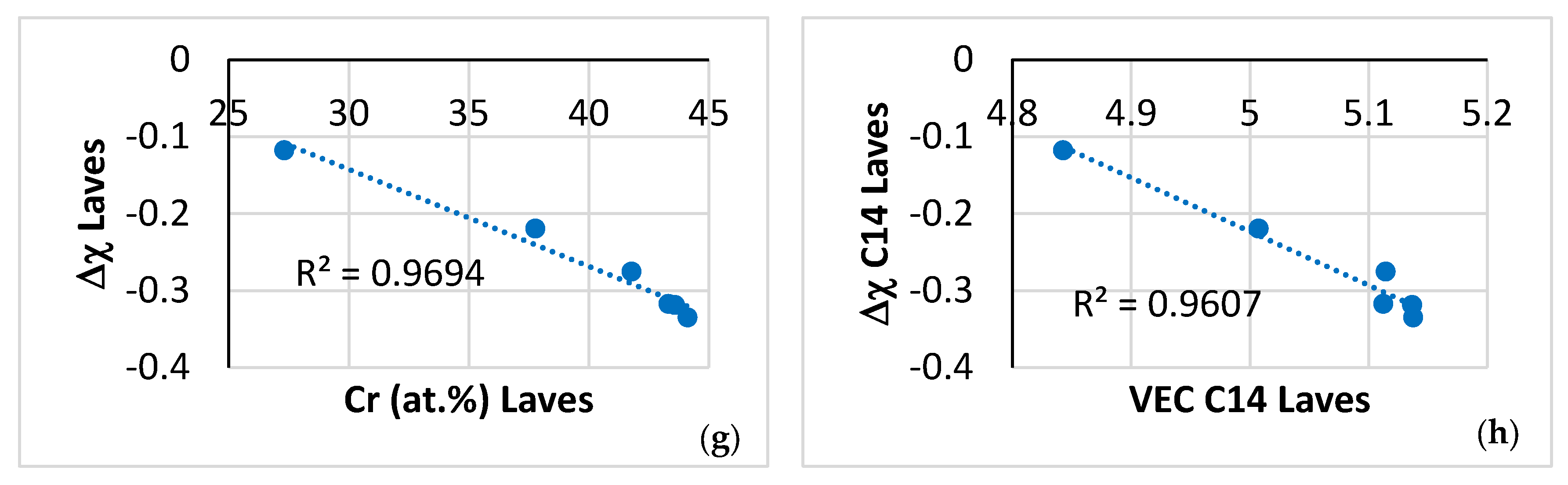
Figure 9.
Data for the C14-NbCr2 Laves phase in NT 1.2-AC. Relationships between solutes, between the parameters VEC and Δχ, and between Cr and the said parameters. (a) Ti versus Sn, (b) Ti versus Ge, (c) Ti versus Cr, (d) Ti versus Si, (e) Ti versus (Al + Cr + Ge + Si + Sn), (f) VEC versus Cr, (g) Δχ versus Cr, and (h) Δχ versus VEC.
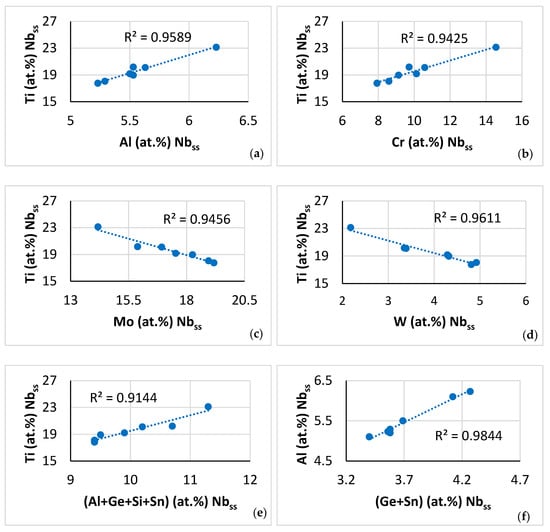
Figure 10.
Relationships between solutes in the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-AC. (a) Ti versus Al, (b) Ti versus Cr, (c) Ti versus Mo, (d) Ti versus W, (e) Ti versus Al + Ge + Si + Sn, and (f) Al versus Ge + Sn.
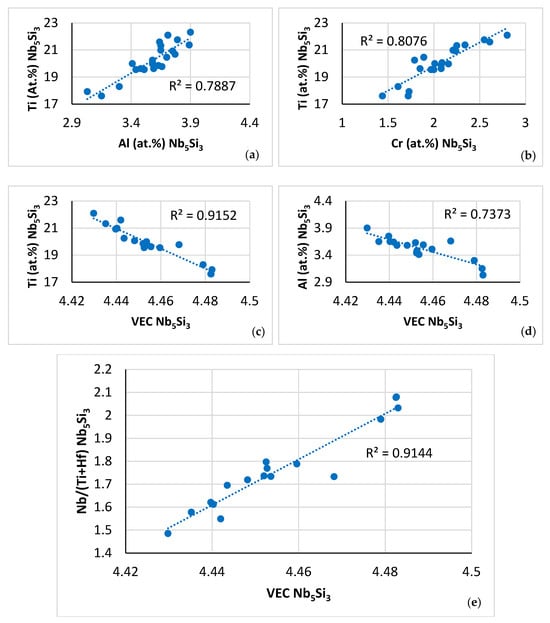
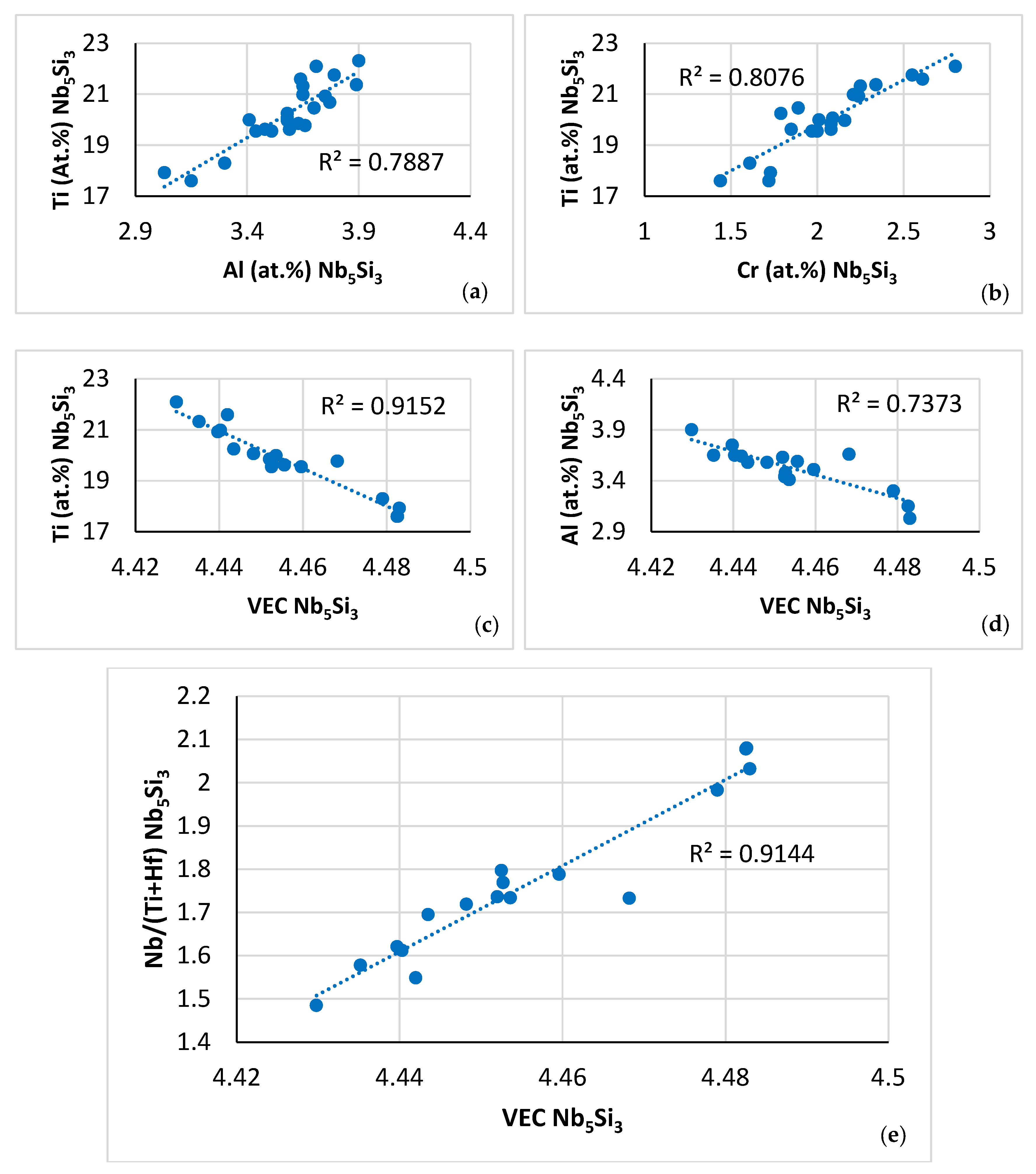
Figure 11.
Data for the βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2-AC. Relationships between solutes and between solutes and the parameter VEC. (a) Ti versus Al, (b) Ti versus Cr, (c) Ti versus VEC, (d) Al versus VEC, and (e) relationship between the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio and the parameter VEC.
The βNb5Si3 was the primary phase and solidification continued with the formation of the A2 solid solution or the eutectic in-between the silicide grains. There was strong partitioning of solutes, as demonstrated by the different contrasts in the microstructure in Figure 3b–d. According to the literature, the synergy of Ge with Si and Ti promoted the partitioning of Ti in the silicide, see [9], the synergy of Ge with Al, Cr, Si, Ti promoted the formation of Tiss, see [47], and the synergy of Ge and Sn with Al, Cr, Si and Ti promoted the formation of (Ti,Nb)ss (i.e., Ti rich solid solution) in the heat treated alloy OHS1 [54]. The primary βNb5Si3 and the formation of the C14-Laves phase was in agreement with the results of the alloys ZX7 [53], ZF9 [52], OHS1 [54] (see Appendix A for alloy compositions), which would suggest that formation of the C14-Laves phase in solidification was promoted by the synergy (i) of low Sn content or (ii) of high Ge content with Al and Cr. Note that the A2 solid solution formed in the aforementioned as cast alloys, but was stable only in ZF9-HT. Also, note that eutectic with the Nbss and Nb5Si3 formed only in ZX7-AC [53], which would suggest that Mo and W in synergy with the microsegretation of solutes “controlled” the formation of eutectic in parts of NT 1.2-AC.
Relationships between solutes in the C14-NbCr2 Laves phase, such as those shown in Figure 9a–e, have not been reported before. Also, the relationships between the Ti, Al and Cr contents of the βNb5Si3 (Figure 11a,b) complement the data for the silicide in [61] (Figure 21), [46] (Figure 8), [55] (Figure 13a,e), and together with the aforementioned data confirm the synergy of solutes in M5Si3 silicides (see [9]).
The partitioning of solutes in the A2 solid solution and the silicide that was discussed in this section was in agreement with previous research for the solid solution [20,46,55,56] and the silicide [46]. In the solid solution, the <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn content increased from 7.6 at.% in the “normal” solid solution to 14.4 at.% in the Ti rich solid solution (changes that are expected to have an effect both on the toughness and the oxidation resistance of the A2 phase [19]), whereas the Mo + W content decreased from 22.2 to 8.8 at.% (changes that are expected to affect the yield strength, toughness, oxidation resistance and contamination (see below section “contaminated microstructure”) of the A2 phase [11,19]). In the silicide, the <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn content increased from 36.4 at.% in the “normal” silicide to 38.9 at.% in the Ti rich Nb5Si3, i.e., the solubility range of <Si> shifted to higher values, in agreement with [61], and the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio was larger than one (2.1 and 1.37, respectively), which is indicative of tetragonal Nb5Si3 [62], in agreement with the XRD data (Figure 2a). In the C14-NbCr2 Laves phase the <Cr> = Al + Cr + Ge + Si + Sn content was 57.5 at.%, in agreement with [60]. In the eutectic, the Mo and <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn contents were in agreement with [63].
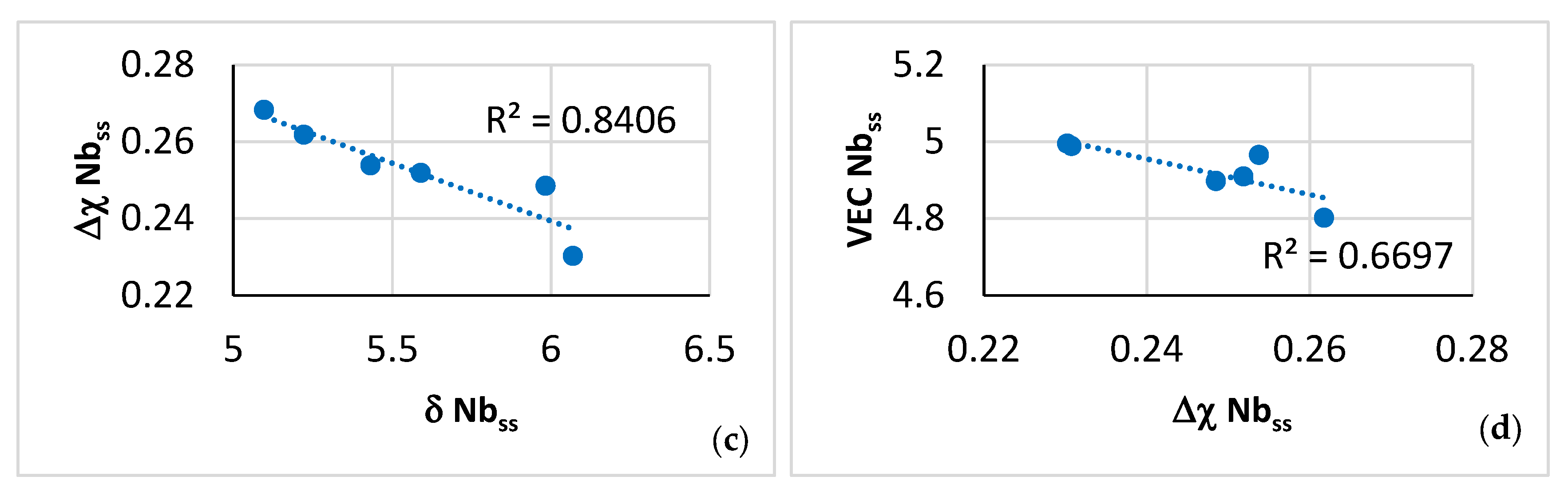
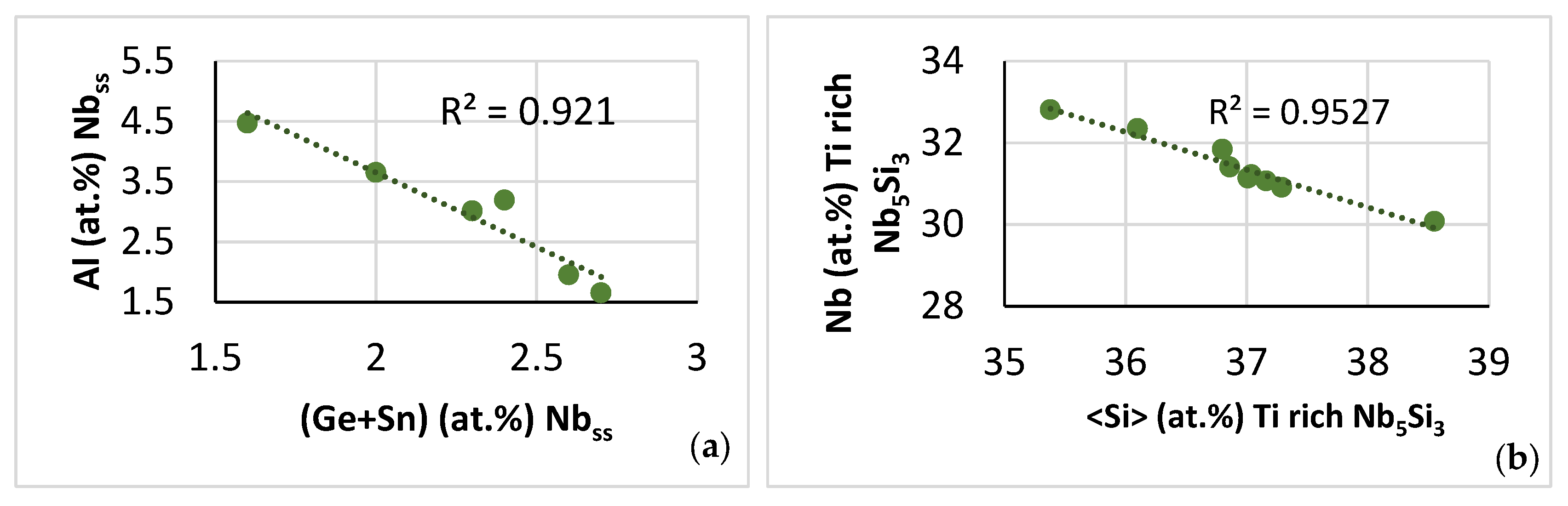
The relationships between solutes and the parameters VEC and Δχ for the C14-Laves phase, or the parameter VEC of the βNb5Si3, or the parameters δ and Δχ of the A2 solid solution, that are shown, respectively, in Figure 9f and g, Figure 11c and d and Figure 12a and b, are in agreement with [46,55,60,61].
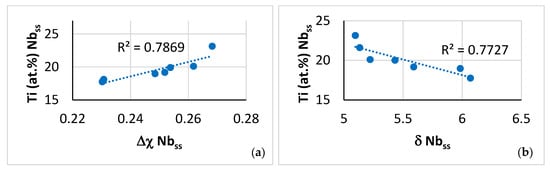
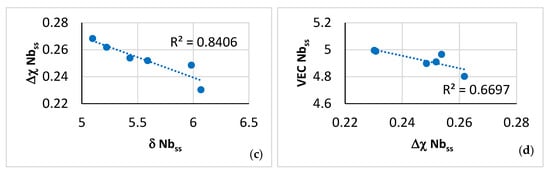
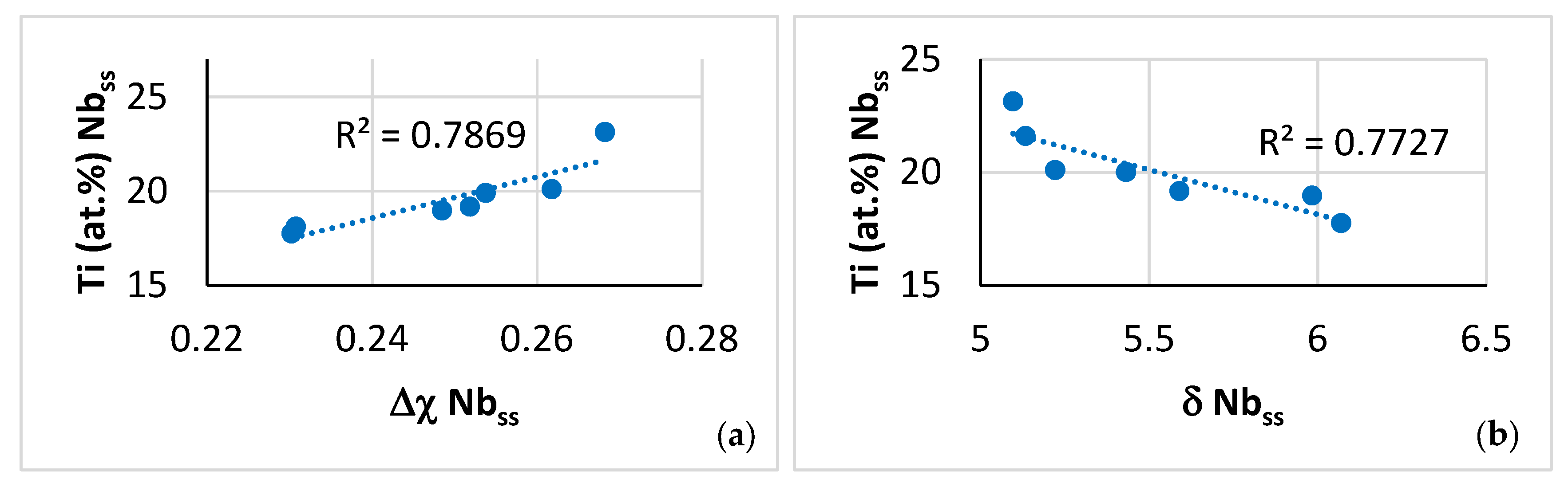
Figure 12.
Data for the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-AC. Relationships between Ti content of the A2 solid solution and its parameters (a) Δχ and (b) δ and between the parameters (c) Δχ versus δ and (d) VEC versus Δχ.
Relationships between parameters of the C14-Laves phases and the A2 solid solution are shown, respectively, in Figure 9h, which is in agreement with [60], and in Figure 12c and d. Furthermore, the parameter VEC of the βNb5Si3 increased as its Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio increased. The latter relationship plus the aforementioned relationships between (i) solutes and parameters and (ii) parameters, (iii) the map of the A2 solid solution, C14-Laves phase and D8m βNb5Si3 silicide shown in Figure 13a, and (iv) relationships between the Ti concentrations in the A2 solid solution, βNb5Si3, and C14-Laves phase, shown in Figure 13b–d, are further evidence of the synergy and entanglement of solutes and phases in the microstructure of NT 1.2-AC, see [9].
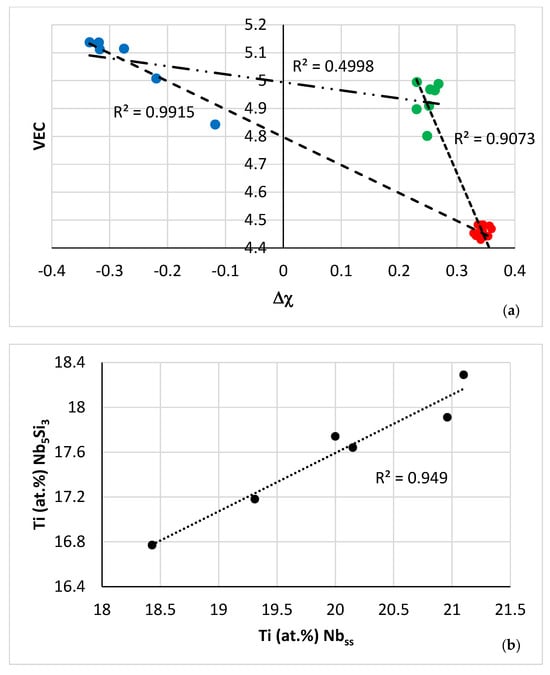
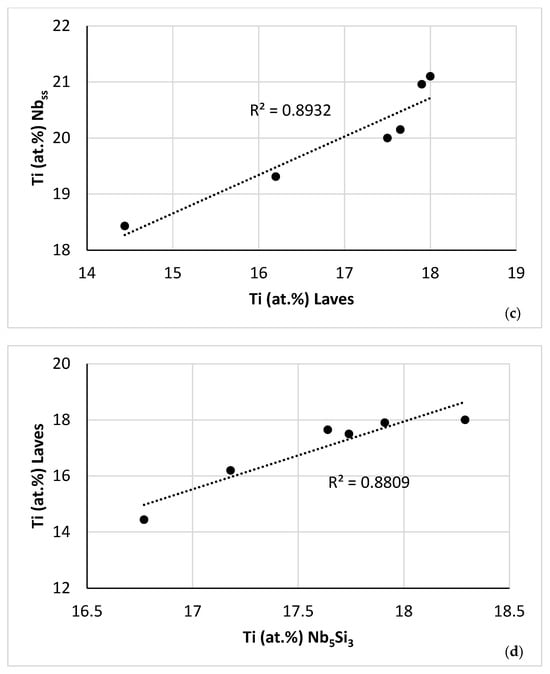
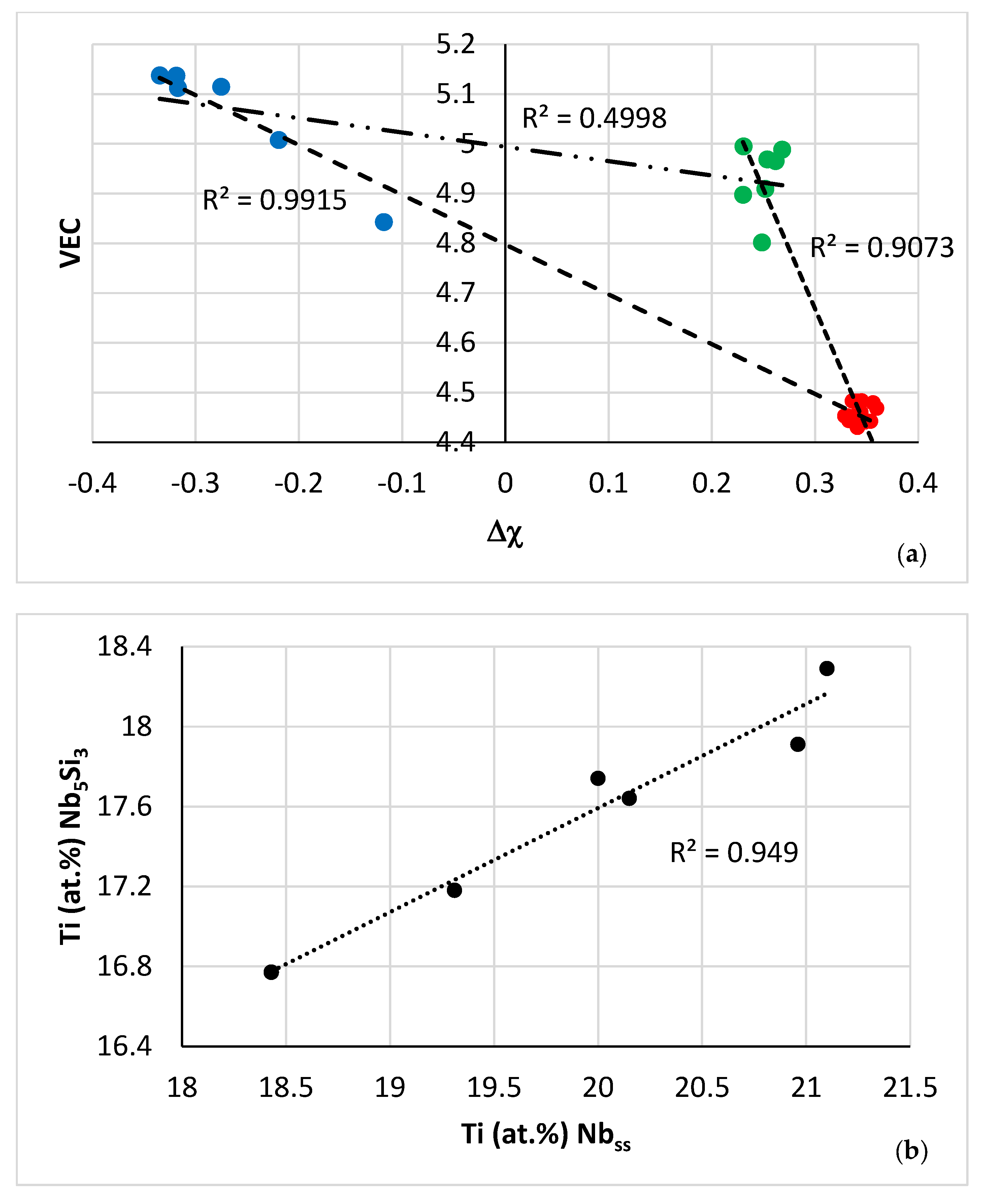
Figure 13.
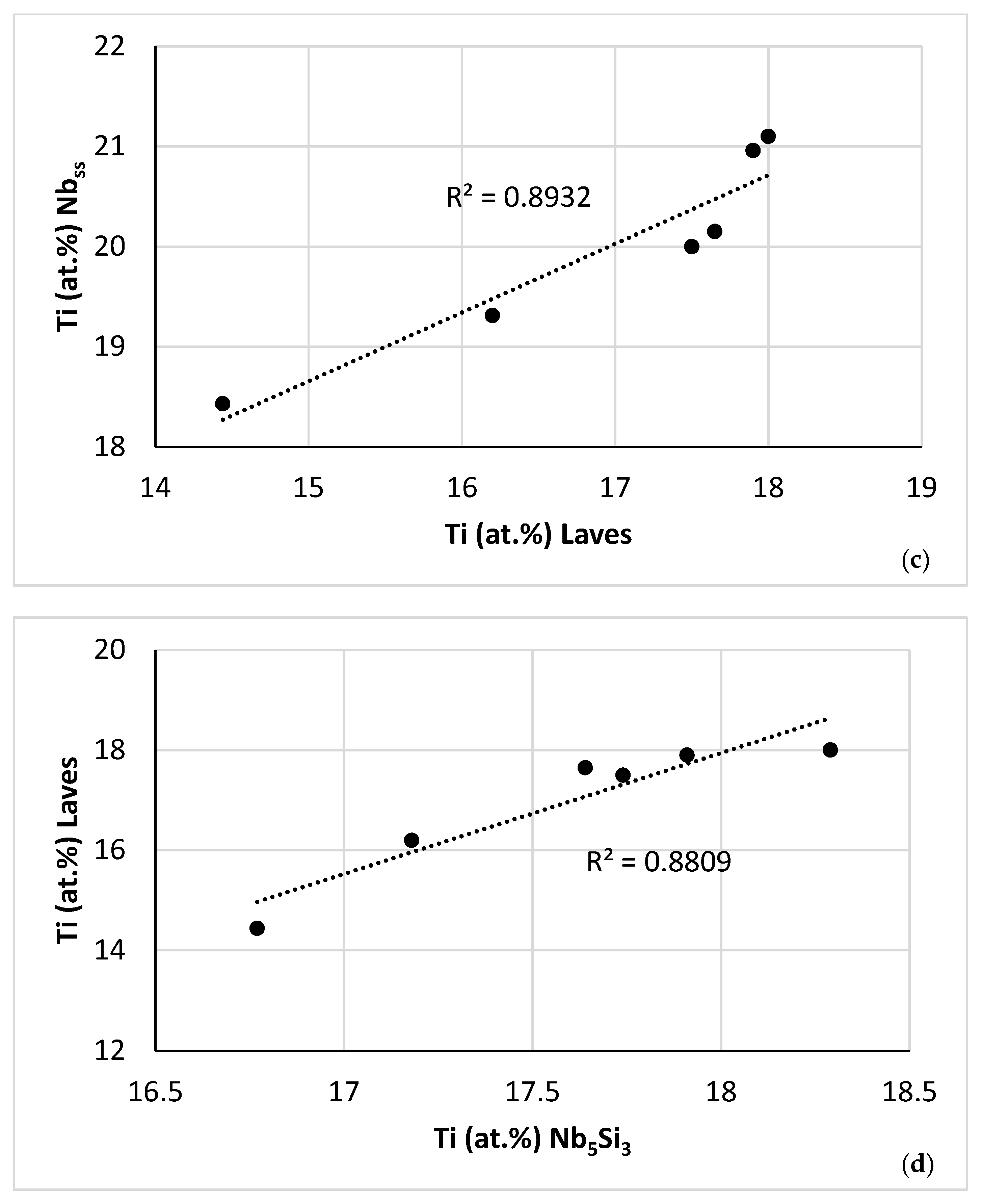
(a) Map of the parameters VEC and Δχ for the A2 solid solution (green data), C14-Laves phase (blue data) and D8m βNb5Si3 silicide (red data) in NT 1.2-AC. R2 = 0.9915 for correlation between C14-NbCr2 Laves phase and βNb5Si3, R2 = 0.9073 for the correlation between βNb5Si3 and A2 solid solution, and R2 = 0.4998 for the correlation between A2 solid solution and C14-NbCr2 Laves phase. (b–d) Relationships between Ti concentrations in the A2 solid solution, C14-Laves phase and D8m βNb5Si3 silicide. (b) Ti in Nb5Si3 versus Ti in Nbss, (c) Ti in Nbss versus Ti in Laves, (d) Ti in Laves versus Ti in Nb5Si3.
Heat treated alloy: Following the heat treatments, the areas of the microstructure near the surface of NT 1.2-HT were contaminated with oxygen but not the bulk (Table 2). The chemical composition of the alloy near the surface areas and in the bulk still corresponded to that of a RCCA. The βNb5Si3 and the A2 solid solution were the stable phases (Figure 2b) both in the near surface areas and in the bulk. Furthermore, both phases were contaminated with oxygen in the near surface areas and their chemical composition corresponded to that of a CC phase (Table 2). In the bulk, the CC A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3 silicide co-existed with “conventional” A2 solid solution. The dissolution of the C14-Laves phase and Tiss, and the accompanying redistribution/partitioning of solutes resulted to the formation of silicide very rich in Ti in-between A2 solid solution areas (Figure 7 and Table 5) and to changes in relationships between some solutes in the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-HT. In NT 1.2-AC many A2 solid solution grains were Si free, and the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-HT was Si free, in agreement with previous research on RM(Nb)ICs and RM(Nb)ICs/RCCAs with Mo, Nb and W additions, e.g., [56].
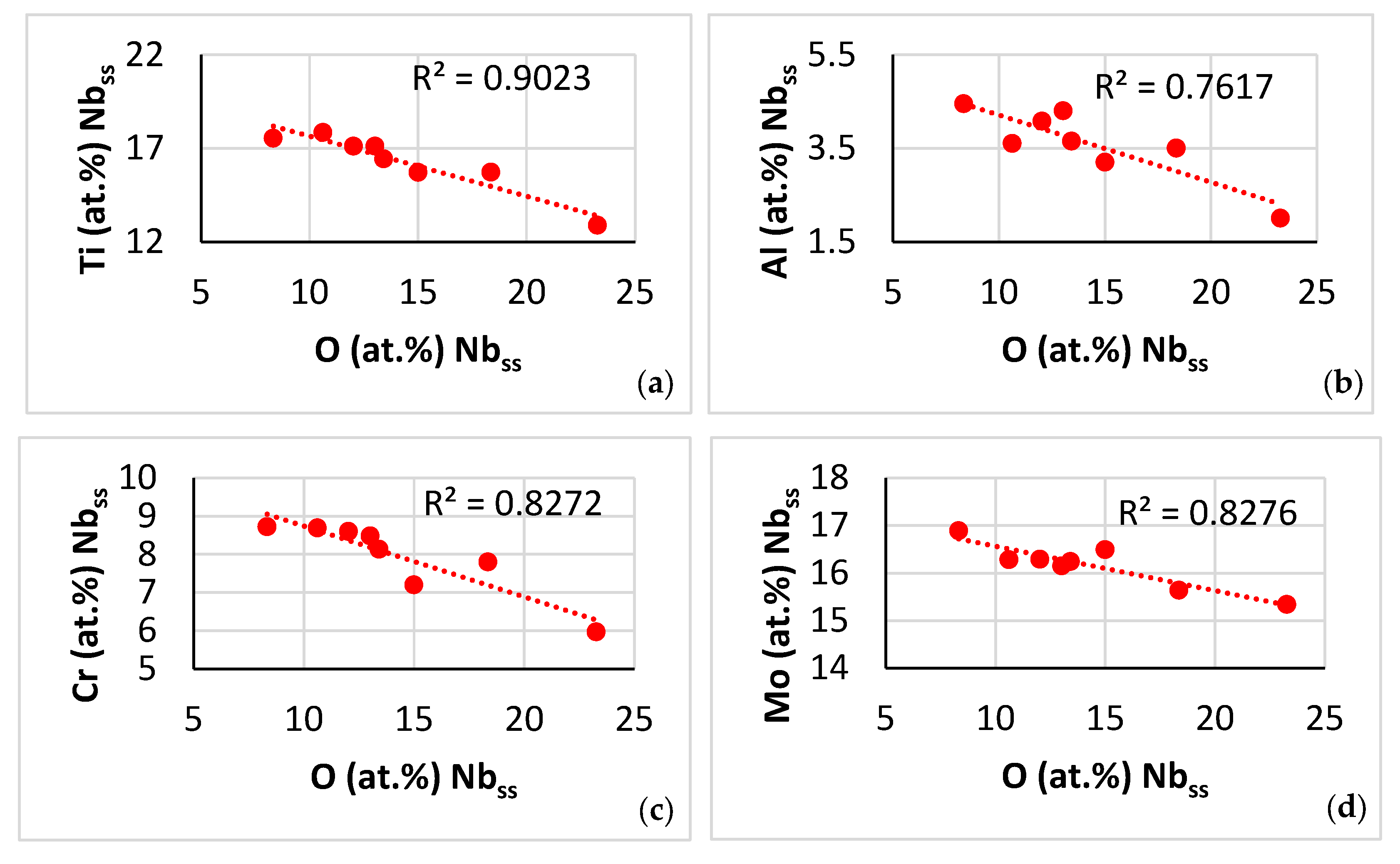
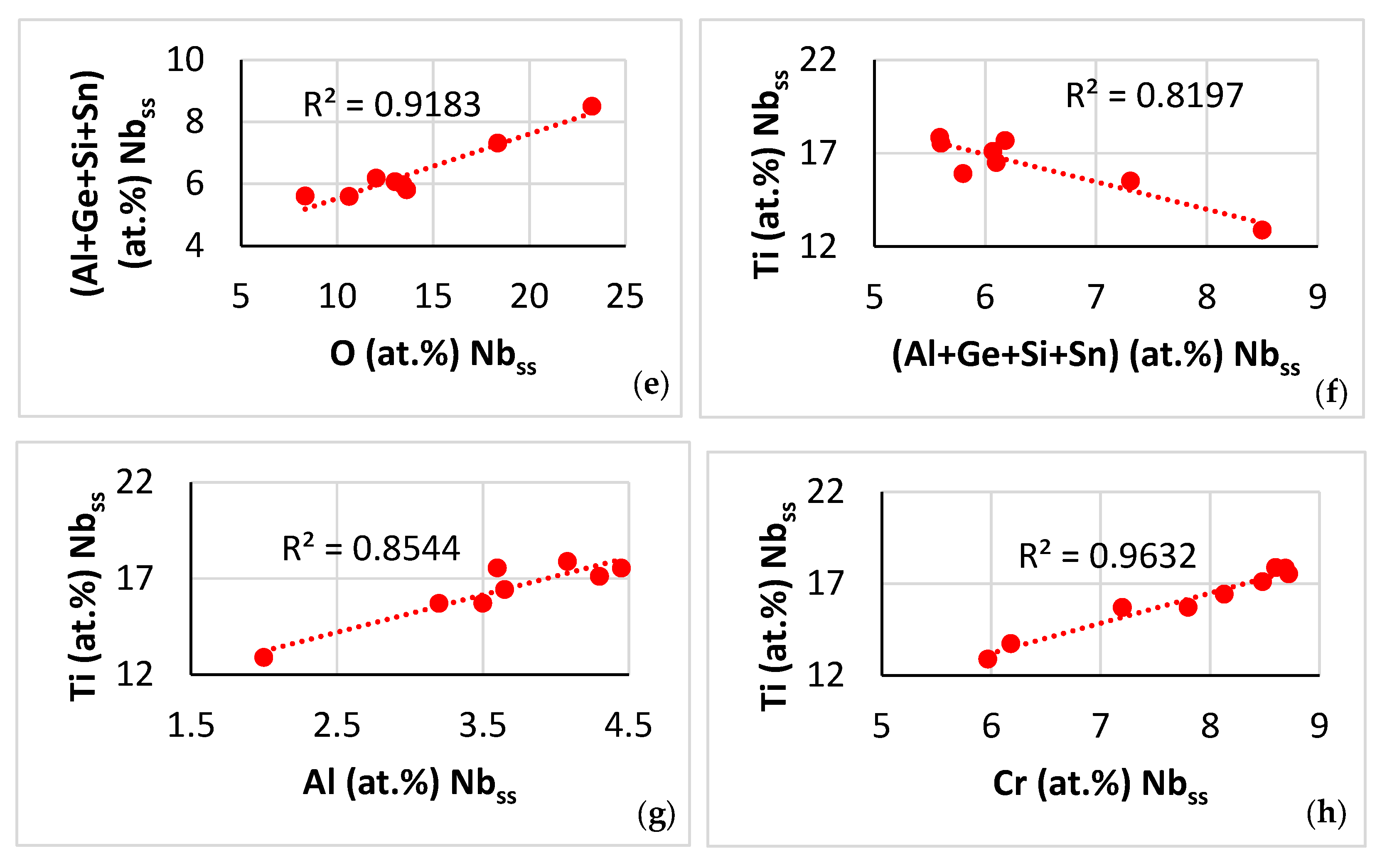
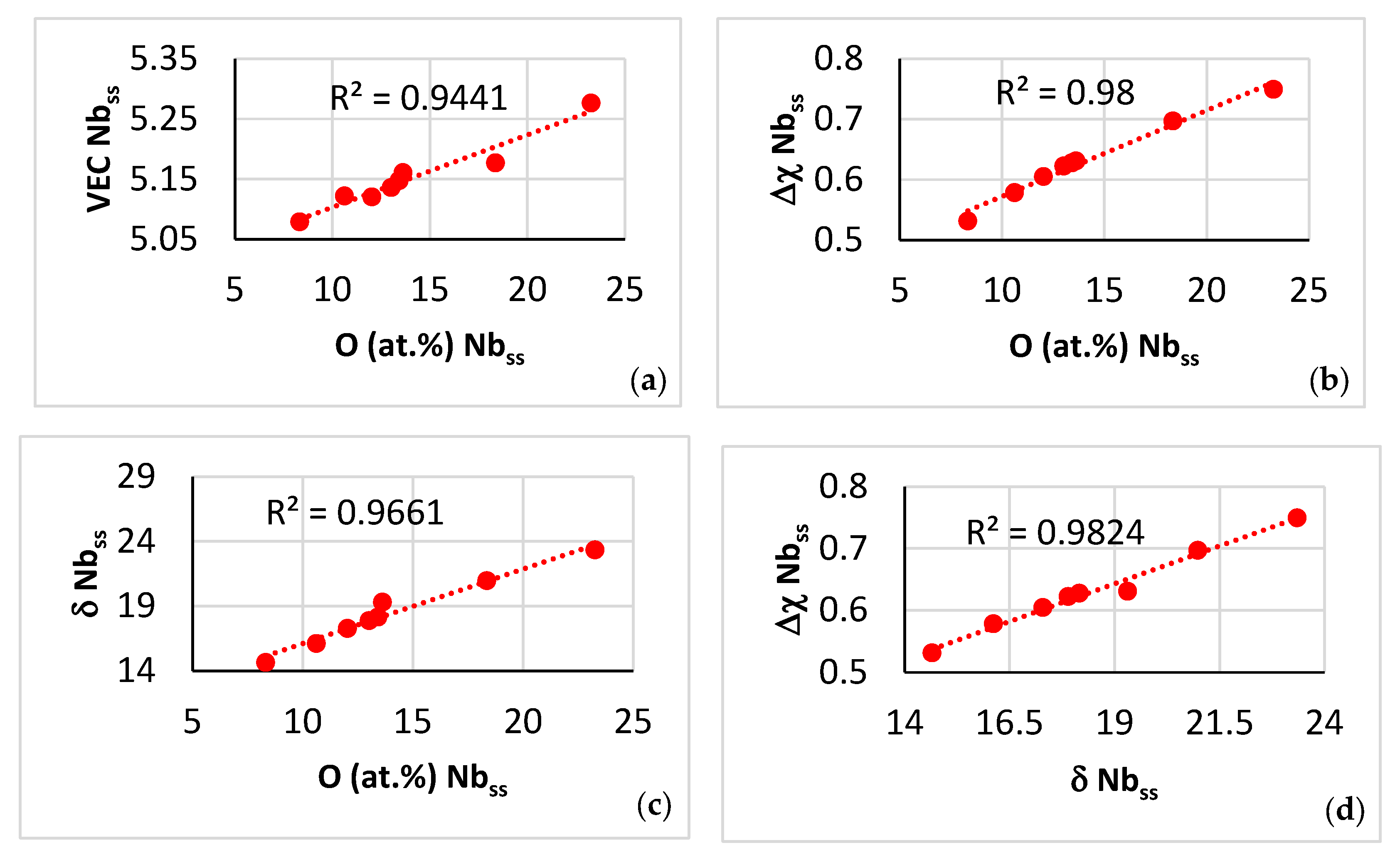
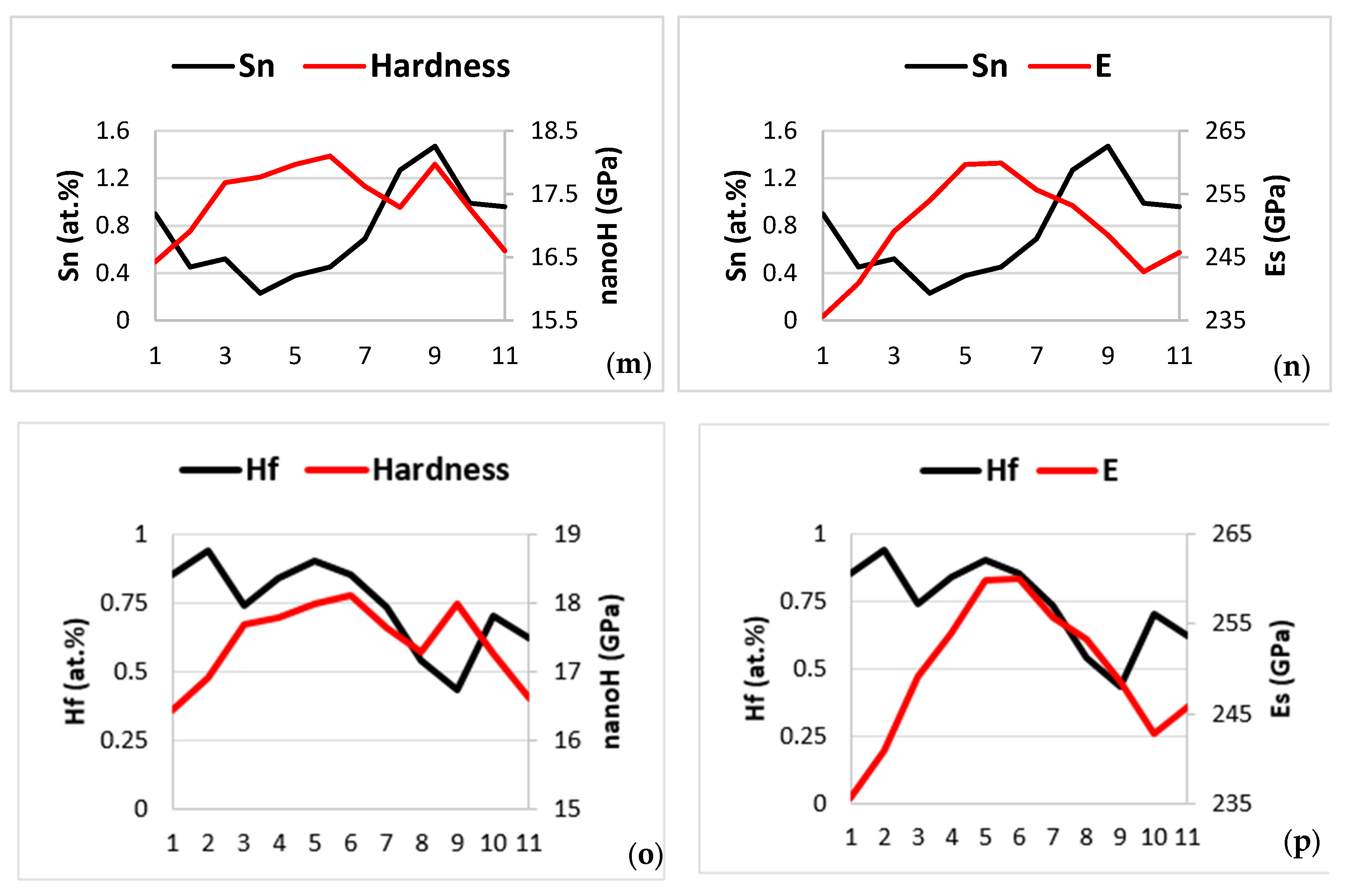
Contaminated microstructure: In this section, the contamination of the A2 solid solution and the βNb5Si3 silicide is discussed with the help of Figure 14, Figure 15, and Figure 16 and Figure 17, respectively. Note that in this work the oxygen content of phases was analysed using EDS with standards (see Section 2), not using EPMA, thus Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 17 show trends in relationships between solutes, between solutes and oxygen content and between parameters and oxygen content and the R2 values shown in the said figures are for these trends. The concentration of different solutes in the A2 solid solution “controlled” the severity of its contamination with oxygen, which was low when the Al, Cr, Mo and Ti concentrations were high (Figure 14a–d). The contamination with oxygen of the A2 solid solution increased with its <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn content (Figure 14e), which was consistent with the trends in the Ti versus the <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn content data (Figure 14f) and the Ti versus O (Figure 14a) data. Note that the trend shown in Figure 14f is different from that in the solid solution in NT 1.2-AC (Figure 10e), whereas the trends between Ti and Al (Figure 14g) and Ti and Cr (Figure 14h) are the same as those in the NT 1.2-AC shown in Figure 10a,b. The aforementioned difference is attributed to the trend between Al and Ge + Sn content of the A2 solid solution in the near surface contaminated areas and in the bulk of NT 1.2-HT (see below). To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time that trends showing how the contamination of the A2 solid solution in a RCCA depends on different solutes in the A2 solid solution, i.e., Figure 14a–e, have been reported in the literature. Also, this is the first time that trends between solutes in contaminated with oxygen A2 solid solution in a RCCA, i.e., Figure 14f–h, have been presented.
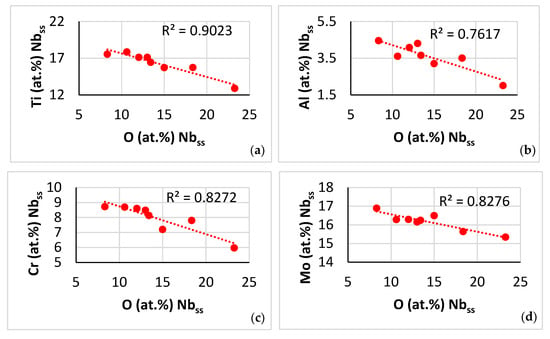
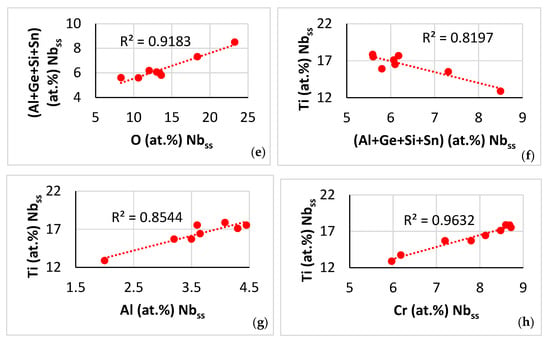
Figure 14.
Data for the contaminated-with-oxygen A2 solid solution in the near surface areas of NT 1.2-HT200. (a–e) Trends in relationships between solutes and oxygen and (f–h) between solutes. (a) Ti versus O, (b) Al versus O, (c) Cr versus O, (d) Mo versus O, (e) <Si> = (Al + Ge + Si + Sn) versus O, (f) Ti versus <Si> = (Al + Ge + Si + Sn), (g) Ti versus Al, and (h) Ti versus Cr.
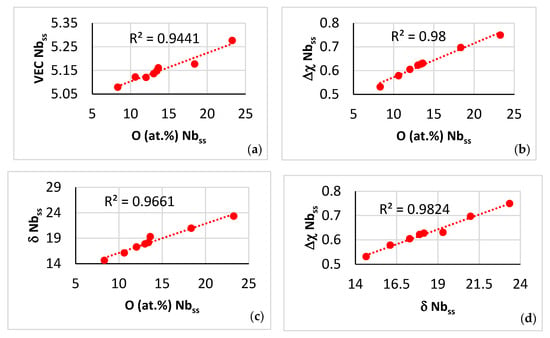
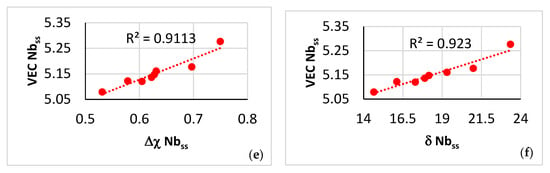
Figure 15.
Data for the contaminated with oxygen A2 solid solution in the near surface areas of NT 1.2-HT200. (a–c) Trends in relationships between the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ and the oxygen concentration, (d–f) trends in relationships between the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ. (a) VEC versus O, (b) Δχ versus O, (c) δ versus O, (d) Δχ versus δ, (e) VEC versus Δχ, (f) VEC versus δ.
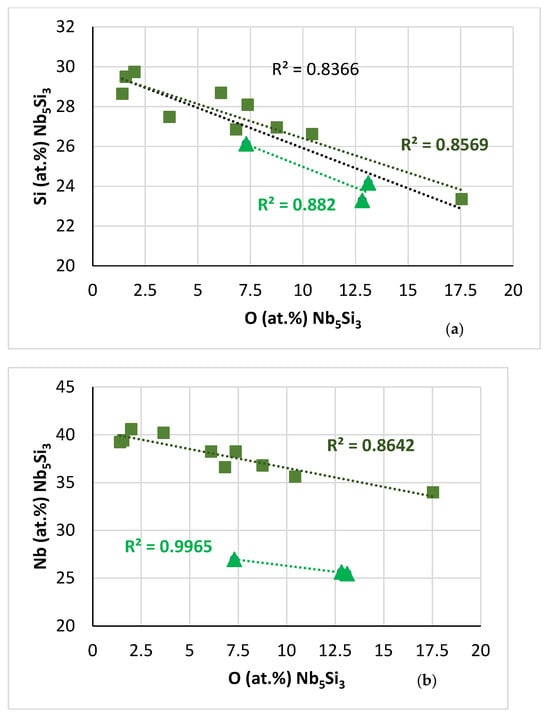
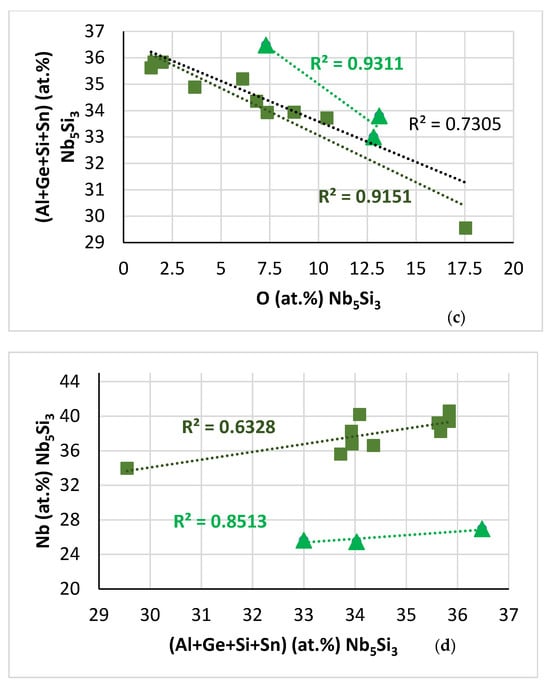
Figure 16.
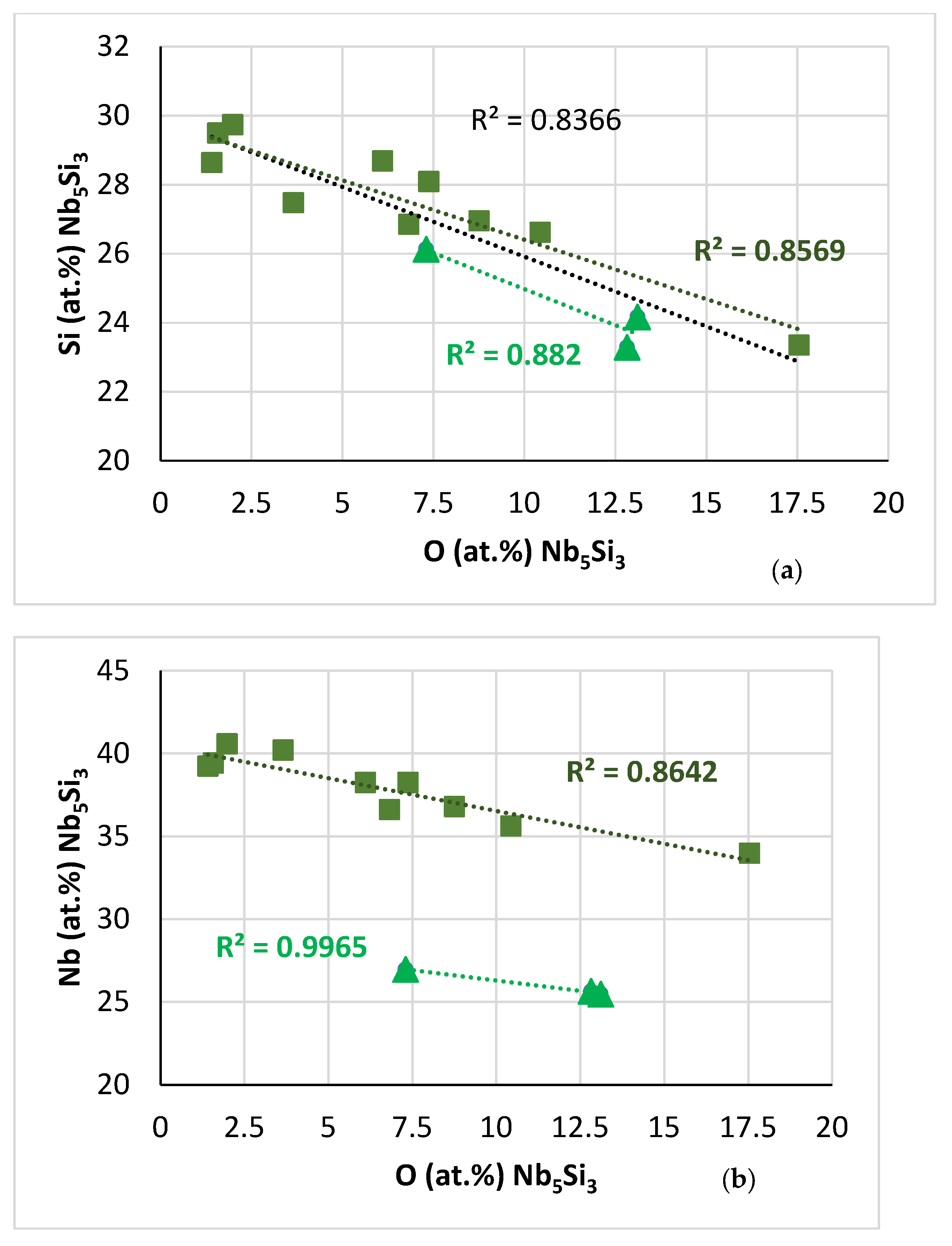
Data for the contaminated with oxygen Nb5Si3 in the near surface areas of NT 1.2-HT200. Squares for “normal” Nb5Si3, triangles for Nb5Si3 very rich in Ti. (a–c) Trends in relationships between solutes and oxygen. (a) Si versus O, R2 = 0.8366 for all data, R2 = 0.8569 for “normal” Nb5Si3, R2 = 0.882 for silicide rich in Ti, (b) Nb versus O, R2 = 0.8642 for “normal” Nb5Si3, R2 = 0.9965 for silicide rich in Ti. (d) Nb versus Al + Ge + Si + Sn in Nb5Si3.
The value of each of the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ of the contaminated with oxygen A2 solid solution increased as the contamination became more severe (Figure 15a–c), in agreement with [20] (see Figure 11). Furthermore, the trends between the aforementioned parameters that are shown in Figure 15d–f were in agreement with [20] (see Figure 10a–c). In other words, the data in Figure 15 complements the data in [20]. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time that comprehensive data has been published for the solutes and parameters of a contaminated with oxygen A2 solid solution in a RCCA with simultaneous addition of transition and refractory metals (Cr, Hf, Mo, Nb, Ti, W) and simple metals and metalloid element (Al, Ge, Si, Sn) that are known to benefit both mechanical properties and oxidation resistance in the same metallic UHTM [19].
In the contaminated microstructure of NT 1.2-HT, the contaminant (oxygen) “worked” in synergy and intricateness (see Appendix A in [9]) with other solutes in the A2 solid solution. The data in Figure 14 and Figure 15 demonstrate how correlative environment–material interactions (CEMI, see [9]) produce changes (in this case in the solid solution phase) that are interrelated with the use of the material in-service, as was recently discussed by one of the authors; see Section 7 in [9].
In both the “normal” Nb5Si3 and the Nb5Si3 that was very rich in Ti the contamination decreased with increasing Si or Nb or <Si> = (Al + Ge + Si + Sn) concentration in the silicide; see Figure 16. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time that data that show how the contamination of an M5Si3 silicide with oxygen in a RCCA depends on different solutes in the silicide has been reported in the literature.
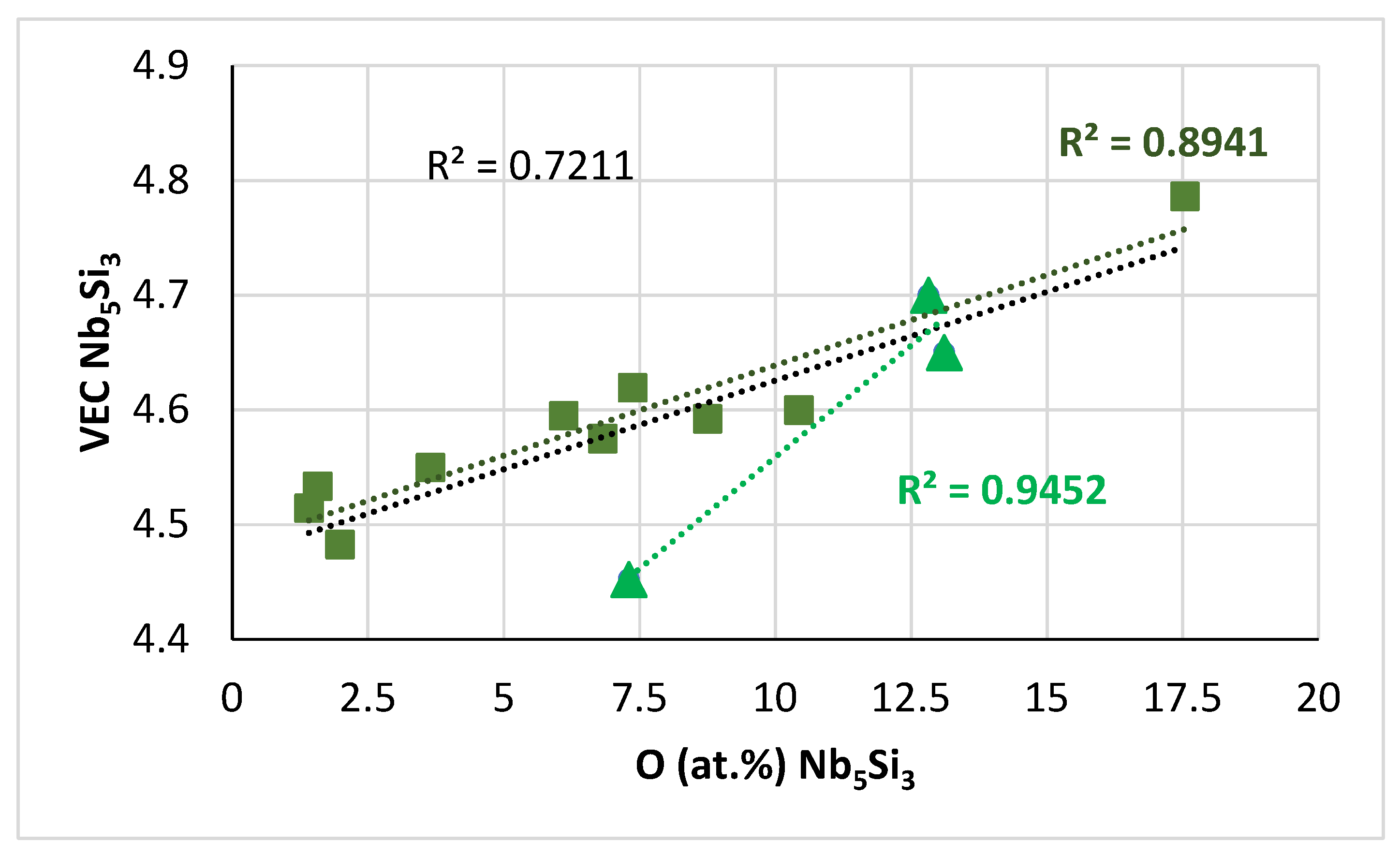
The αNb5Si3 (tI32 Cr5B3-type, D8l) and βNb5Si3 (tI32 W5Si3-type, D8m) are the M5Si3 silicides in the Nb-Si binary equilibrium phase diagram [64]. Their tetragonal crystal structure contains 20 atoms of Nb and 12 atoms of Si, but the two silicides crystalize in different atomic arrangements. Interstitials like oxygen may have environments of both Nb and Si atoms in both the αNb5Si3 and βNb5Si3 [65]. Experiments would suggest that oxygen is less efficient than carbon in stabilising the hexagonal γNb5Si3 (Mn5Si3 type-D88) [64,66]. The parameter VEC of both the “normal” Nb5Si3 and Nb5Si3 that was very rich in Ti increased with contamination with oxygen; see Figure 17. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time that experimental data have shown how contamination of the βNb5Si3 silicide with oxygen in a RCCA changes the parameter VEC of the βNb5Si3 silicide.
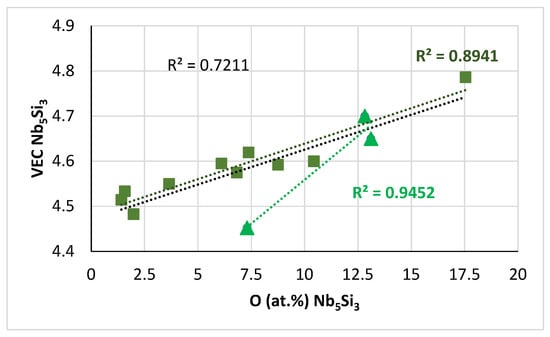
Figure 17.
Data for the contaminated with oxygen Nb5Si3 in the near surface areas of NT 1.2-HT200. VEC versus O, R2 = 0.7211 for all data, squares for “normal” Nb5Si3, triangles for Nb5Si3 very rich in Ti. The parameter VEC of the silicide was calculated as described in [66].
Figure 17.
Data for the contaminated with oxygen Nb5Si3 in the near surface areas of NT 1.2-HT200. VEC versus O, R2 = 0.7211 for all data, squares for “normal” Nb5Si3, triangles for Nb5Si3 very rich in Ti. The parameter VEC of the silicide was calculated as described in [66].
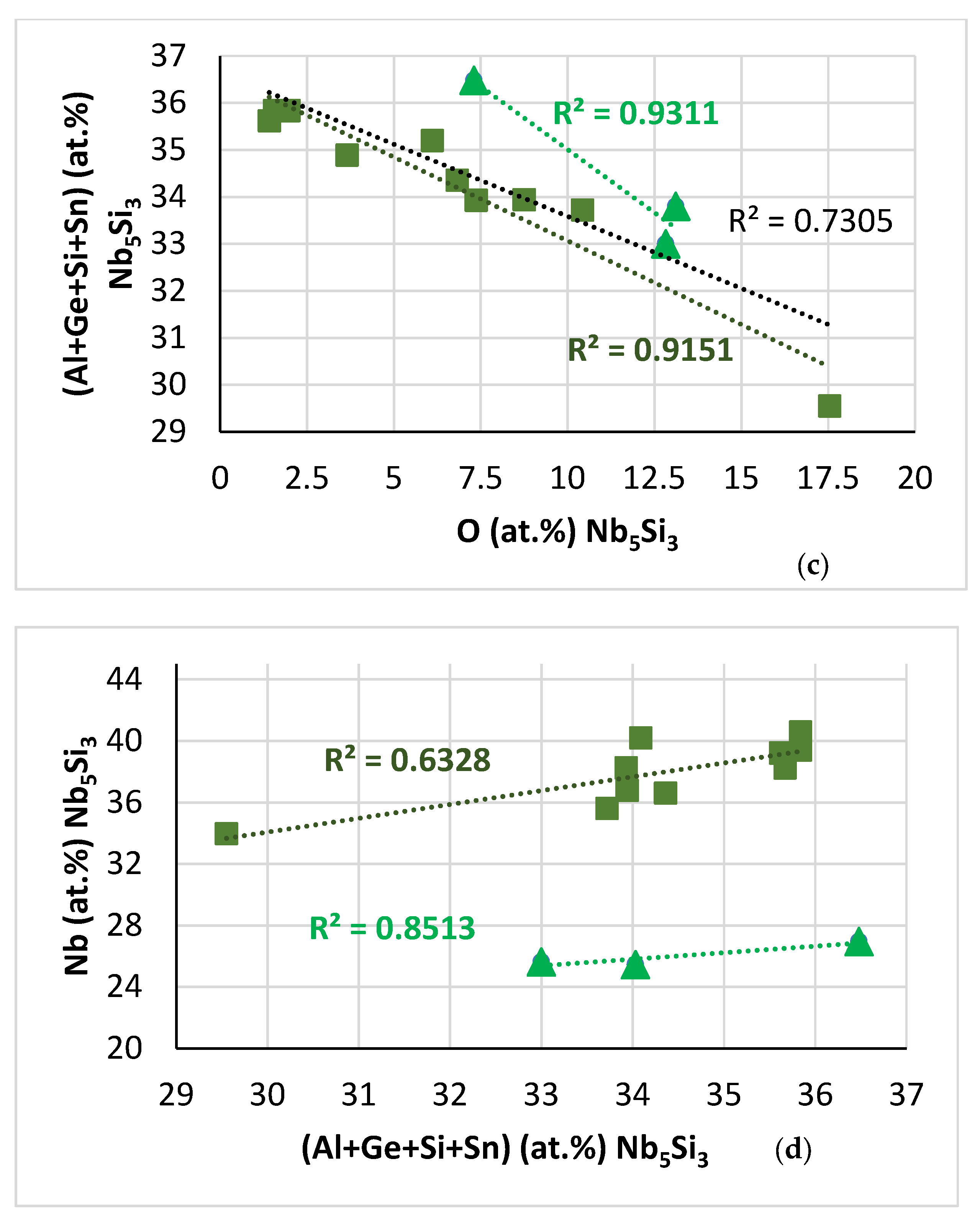
Uncontaminated microstructure near the surface and in the bulk: Both in the near surface areas and in the bulk of NT 1.2-HT200, the Ti concentration of the solid solution corresponded to “normal” solid solution rather than Ti rich solid solution. In the bulk microstructure, for the A2 solid solution the <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn and Mo + W contents were 6.9 at.% and 23.2 at.%, respectively, and for the “normal” silicide and the silicide that was very rich in Ti the <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn content and the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio was 37.3 and 36.8 at.%, and 1.84 and 1.18, respectively. The ratio values were indicative of tetragonal silicide [44], which is in agreement with the XRD data (Figure 2b). However, the trend of the relationship of the Al versus Ge + Sn data of the A2 solid solution was opposite to that shown in NT 1.2-AC (see Figure 10f), and the Al and Ge + Sn contents were lower (Figure 18a). Also, the trend in the relationship of Nb versus <Si> content of the silicide that was very rich in Ti (Figure 18b) was opposite to that shown in Figure 16d. These changes were attributed to the redistribution/partitioning of solutes in NT 1.2-HT following the dissolution of the C14-Laves and Tiss phases and the destabilisation of the prior eutectic, as well as to the contamination of the near surface areas with oxygen.
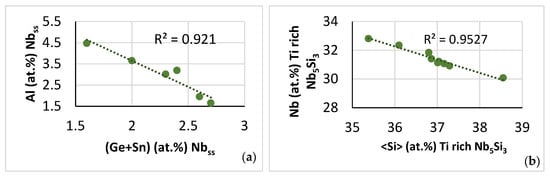
Figure 18.
Solute relationships in the A2 solid solution and silicide very rich in Ti in uncontaminated microstructures in NT 1.2-HT200. (a) Al versus Ge + Sn in A2, (b) Nb versus <Si> = Al + Ge + Si + Sn in Nb5Si3 very rich in Ti.
Solid solution precipitated in the silicide (Figure 4a) both in the near surface areas and in the bulk. The precipitates were observed in the “boundary” Nb5Si3, next to solid solution (labelled 3 in Figure 4b). In-between A2 solid solution grains formed the silicide that was very rich in Ti (Table 2), in agreement with [56]. This silicide is labelled 1 in Figure 4b. The “core” of the silicide (labelled 4 in Figure 4b) was precipitate free. The Al + Ge + Si + Sn and Mo + W content of the precipitates did not change in the bulk and near surface areas microstructures (was 7.1 and 7 at.%, and 22.7 and 21.3 at.%, respectively). The chemical composition of the solid solution precipitates in both the near surface areas and in the bulk, corresponded to that of CC phases.
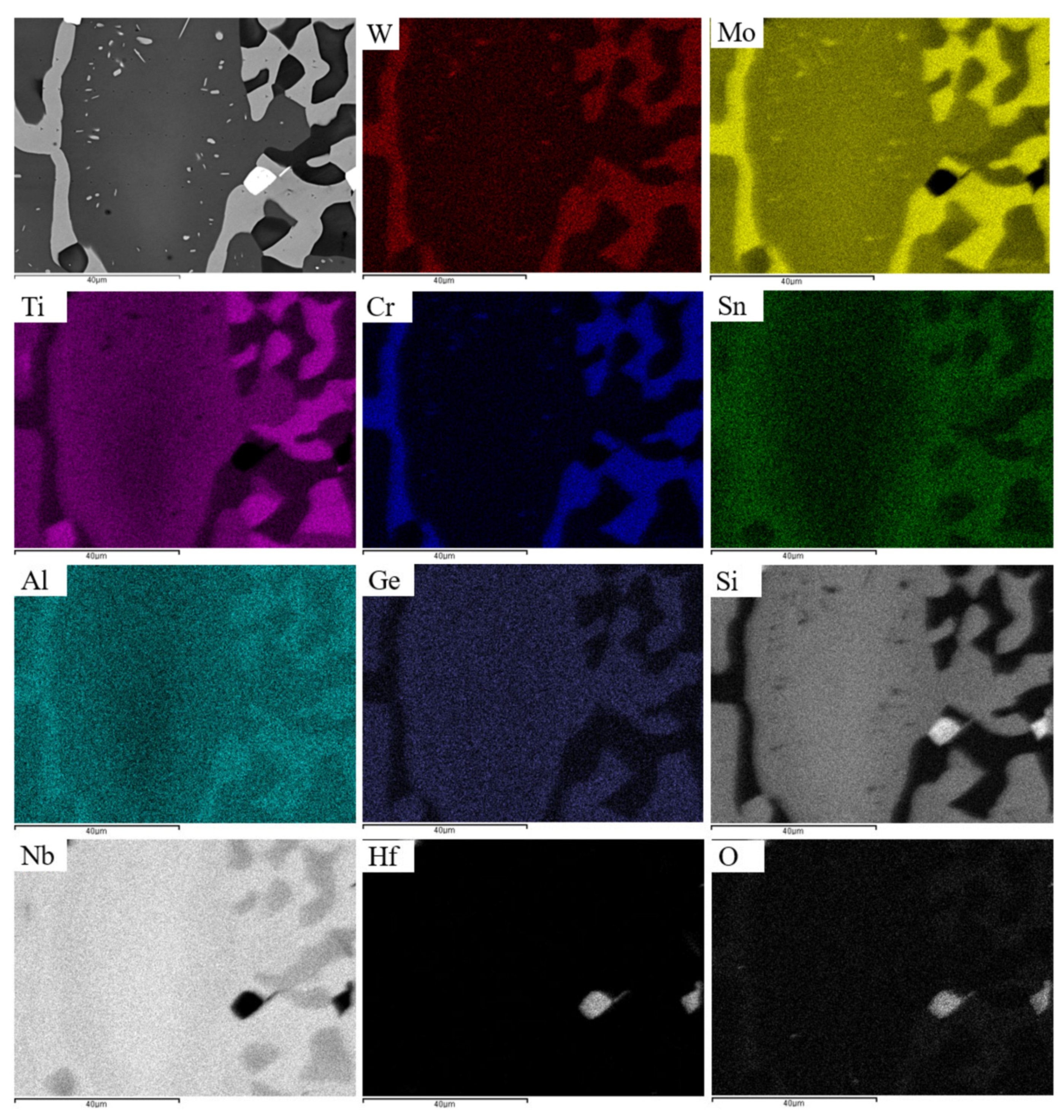
We can follow the partitioning of solutes that accompanied the changes in the microstructure after the heat treatments with the help of Figure 4c,d. This figure shows changes in solute concentration along the line 1234 in Figure 4b. From the Nb5Si3 that was very rich in Ti (labelled 1 in Figure 4c,d) and moving towards the “core” of Nb5Si3 (labelled 4 in Figure 4c,d) there was decrease of Ti and increase of Nb concentration, the solid solution (labelled 2 in Figure 4c,d) was rich in Al, Cr, Mo and W and poor in Ge and Si, in the “boundary” Nb5Si3 (labelled 3 in Figure 4c,d) the concentrations of Ge, Si and Ti increased and that of Nb decreased and in the “core” Nb5Si3 there was increase of the Mo, Nb and Si concentrations and decrease of the Ti concentration. Element maps showing the partitioning of solutes in the microstructure in Figure 7 are shown in Figure 19.
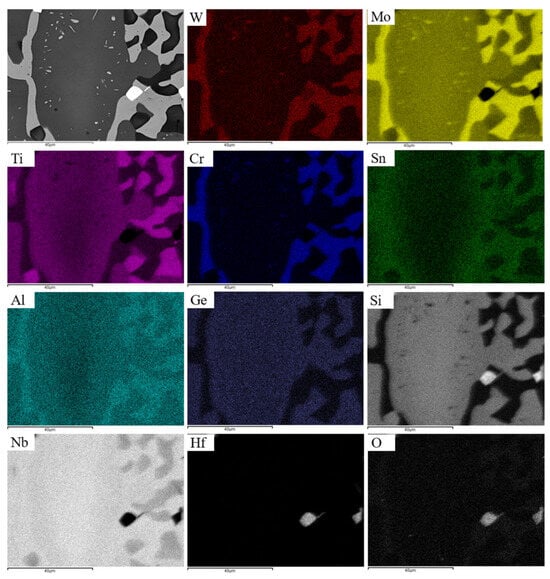
Figure 19.
The microstructure shown in Figure 7 (top left) and element maps.
In the solid solution, the Al + Ge + Sn content had increased from 6.7 ± 0.4 in NT 1.2-HT100 to 7.7 ± 0.5 at.% in NT 1.2-HT200 and the Mo + W content was about 23 ± 0.5 at.%. These values were consistent with those of the “normal” solid solution in NT1.2-AC (Table 1) and NT 1.2-HT (Table 2). In the silicide that was very rich in Ti, the Al + Ge + Si + Ge content and the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio was 37.9 and 37.5 at.%, and 1.16 and 1.1, respectively, in NT 1.2HT-100 and NT 1.2-HT200. The ratio values indicated tetragonal silicide, in agreement with the XRD data (Figure 2b). In the “boundary” Nb5Si3 the Al + Ge + Si + Ge content and the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio was 36.7 and 36.5 at.%, and 1.7 and 1.75, respectively, in NT 1.2HT-100 and NT 1.2-HT-200. The ratio values also indicated tetragonal silicide. In the “core” Nb5Si3 the Al + Ge + Si + Ge content and the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio was 36.6 and 36.5 at.%, and 2.34 and 2.38, respectively in NT 1.2HT-100 and NT 1.2-HT-200. The ratio values again were indicative of tetragonal silicide [62]. In other words, from the “core” to the “boundary” to the very rich in Ti silicide the value of the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio decreased in both heat treatments, but for each type of silicide, the ratio did not change as the heat treatment duration increased.
The data in Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19 are another example (a) of the synergy and intricateness of solutes and phases and (b) of the importance (i) of their entanglement (see Appendix A in [9]) in the microstructure of a metallic UHTM, and (ii) of correlative environment–material interactions (CEMI) in the metallurgy (design, development and use) of RCCA/RMICs (see Section 7 in [9]).
4.2. Properties
In the literature, we can find data about the Vickers hardness of solid solution and/or intermetallic phases in metallic UHTMs, e.g., [11,19,32,40,60,61,67,68,69,70,71,72]. The hardness of a phase that is measured using nanoindentation can be different from its Vickers hardness, meaning a correction factor must be applied. Such correction factors for the phases in the alloy NT 1.2 are not available. However, there is nanoindentation data for the properties of A2 solid solution and αNb5Si3 or βNb5Si3 silicides in other metallic UHTMs that can allow one to infer how specific solutes affect properties.
The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus data of the solid solution and the silicide in the alloy NT 1.2 that was shown in Section 3.2 is summarised in Table 7. Compared with the data for NT 1.2-AC, both properties of the two phases increased after heat treatment, in particular the increase of the nano-hardness of the silicide was remarkable. Furthermore, the difference of the properties of βNb5Si3 and the silicide that was very rich in Ti was significant, primarily the Young’s modulus. The solutes in the A2 solid solution and the change of its chemical composition after the heat treatments resulted to very significant increases of its Young’s modulus compared with that of “pure” Nb (about 102 to 105 GPa, depending on purity).

Table 7.
Average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of solid solution and silicide in NT 1.2. For the standard deviation numbers see Section 3.2.
Data for the average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of solid solutions in heat treated KZ series alloys, i.e., metallic UHTMs/RM(Nb)ICs (Nb silicide in situ composites) based on Nb–24Ti–18Si with addition of Al and/or Cr with/without addition of Ge or Hf (each solute at 5 at.% addition, nominal) is summarised in Table 8. Using the data for the solid solution in the alloy KZ7-HT as reference, the data in Table 8 show that the synergy of Al and Cr increased the nano-hardness and reduced the Young’s modulus (compare the data for the alloys KZ5 and KZ7), whereas when Hf was included in the said synergy, the nano-hardness was reduced but not the Young’s modulus (compare the data for the alloys KZ5 and JN1). The addition of Ge increased the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the solid solution when Ge was in synergy with Al or with Al and Cr (compare the alloys KZ7 and ZF5, and KZ5 and ZF6). However, when Ge was in synergy with Al, Cr and Hf the nano-hardness increased slightly, whereas the Young’s modulus decreased substantially (compare the alloys JN1 and ZF9).

Table 8.
Average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of solid solution in some KZ series alloys.
Keeping in mind that the alloy NT 1.2 cannot be classified as a KZ series alloy, comparison of the data for the solid solution in NT 1.2-HT in Table 7 with the data for the solid solution in heat treated KZ series alloys in Table 8 would suggest that the simultaneous addition of Ge and Sn with Mo and W, and the synergy of these elements with Al, Cr, Hf, Si and Ti resulted to increases both of the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution. In actual fact, the Young’s modulus of the solid solution in NT 1.2-HT100 was the same as that of binary (unalloyed) γNb5Si3 [49].
The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the solid solution in the as cast RM(Nb)IC (Nb silicide in situ composite) Nb-–22Ti–16Si–2Al–2Cr–xGe (x = 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 at.%) increased as the Ge concentration increased, and for x = 5 at.% they were 9.6 GPa and 185.6 GPa, respectively, and for x = 7 at.% they were 11.6 GPa and 194.9 GPa, respectively [47], compared with E = 155.5 GPa for x = 0. This data also confirmed the strong effect that the addition of Ge has on the aforementioned properties, in particular on the Young’s modulus of the solid solution.
The Young’s modulus of unalloyed Nb5Si3, respectively, is 291, 268.9, and 188.5 GPa for the αNb5Si3, βNb5Si3 and γNb5Si3 polymorphs according to first-principles calculations [49]. Also, for αNb5Si3 calculated Young’s moduli of 314.3 and 325 GPa have been reported, respectively, in [50,51]. In Nb5Si3, the Si can be substituted by other simple metal and metalloid element additions and Nb by other TM and RM additions (e.g., see Table 2 in [61]). The data in [49] show that the alloying of Nb5Si3 with Ti increases the Young’s modulus of α(Nb,Ti)5Si3 and γ(Nb,Ti)5Si3 and decreases the Young’s modulus of β(Nb,Ti)5Si3. For 12.5 at.% Ti addition in the silicide the calculated Young’s moduli of α(Nb,Ti)5Si3, β(Nb,Ti)5Si3 and γ(Nb,Ti)5Si3, respectively, were 313.8, 238.5 and 207.1 GPa [49].
To the authors’ knowledge, experimental data for the properties of specific alloyed Nb5Si3 polymorphs are limited. For the α(Nb,Ti)5(Al,Si)3 in KZ7-HT the average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus was 18.7 GPa and 283.8 GPa, respectively, whereas for the β(Nb,Cr,Hf,Ti)5(Al,Si)3 in JN1-HT was 17.4 GPa and 241.4 GPa, respectively [46]. Furthermore, for the β(Nb,Cr,Ti)5(Al,Ge,Si)3 in the as cast RM(Nb)IC (Nb silicide in situ composite) Nb–22Ti–16Si–2Al–2Cr–xGe, for x = 5 at.% the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus was 21.46 GPa and 279.2 GPa, respectively, and for x = 7 at.% was 21.25 GPa and 293.7 GPa, respectively [51].
The properties of the interface “area” between the A2 solid solution and the βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2-AC were 10.4 GPa and 188.8 GPa, respectively, for nano-hardness and Young’s modulus, significantly higher than 7.1 GPa and 144.5 GPa for the solid solution/silicide interface “area” in the alloy NV1-AC (see Appendix A for chemical composition) [45].
The nano-hardness of βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2-AC decreased with increasing VECNb5Si3, in agreement with [11,61]. The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus values of the βNb5Si3 in NT 1.2-HT (Table 7) were consistent with those of the alloyed beta tetragonal silicide reported in [46,49] (see above). The average nano-hardness and Young’s modulus values of the silicide that was rich in Ti in NT 1.2-HT200 (Table 7) were close to those of the alloyed alpha tetragonal 5-3 silicide reported in [46] (see above), but also were close, in particular the Young’s modulus, to the values reported for the β(Nb,Cr,Ti)5(Al,Ge,Si)3 in [47] for the alloy with x = 5 at.% Ge, and close to the modulus of binary αNb5Si3 reported in [49]. The XRD data (Figure 2) did not confirm the presence of αNb5Si3 in the as cast and heat treated microstructures of NT 1.2. The XRD also verified the absence of hexagonal γNb5Si3. This was supported by the values of the Nb/(Ti + Hf) ratio [62], which provided further support for tetragonal silicide. On the basis of the currently available data, we cannot confirm whether the silicide that was rich in Ti was tetragonal αNb5Si3.
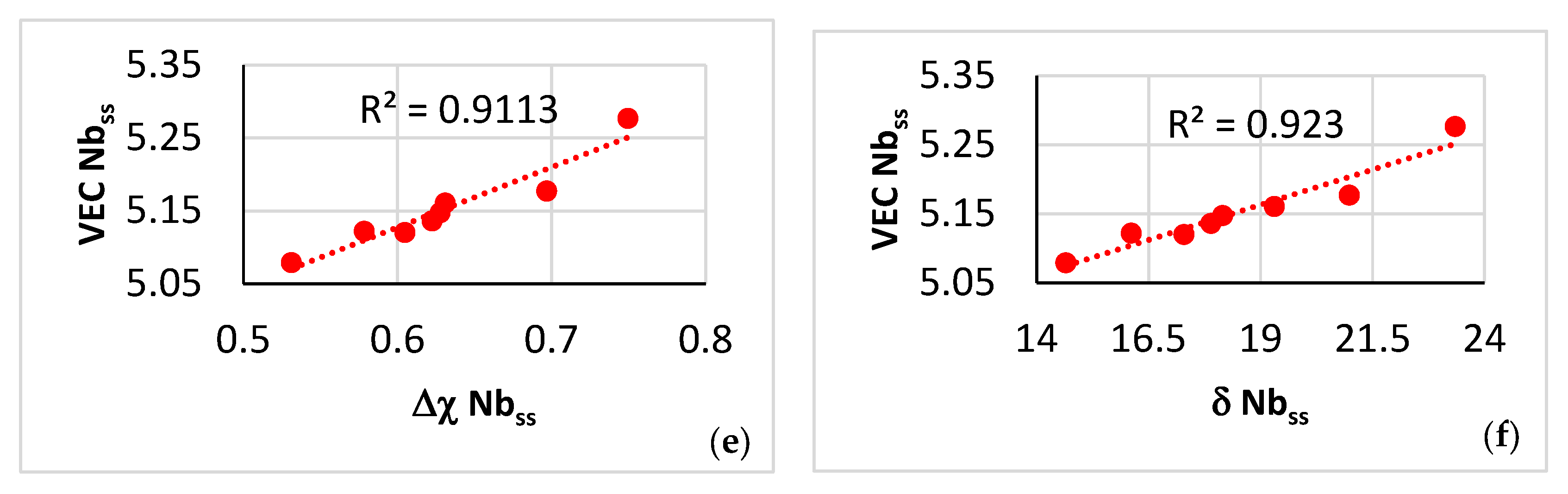
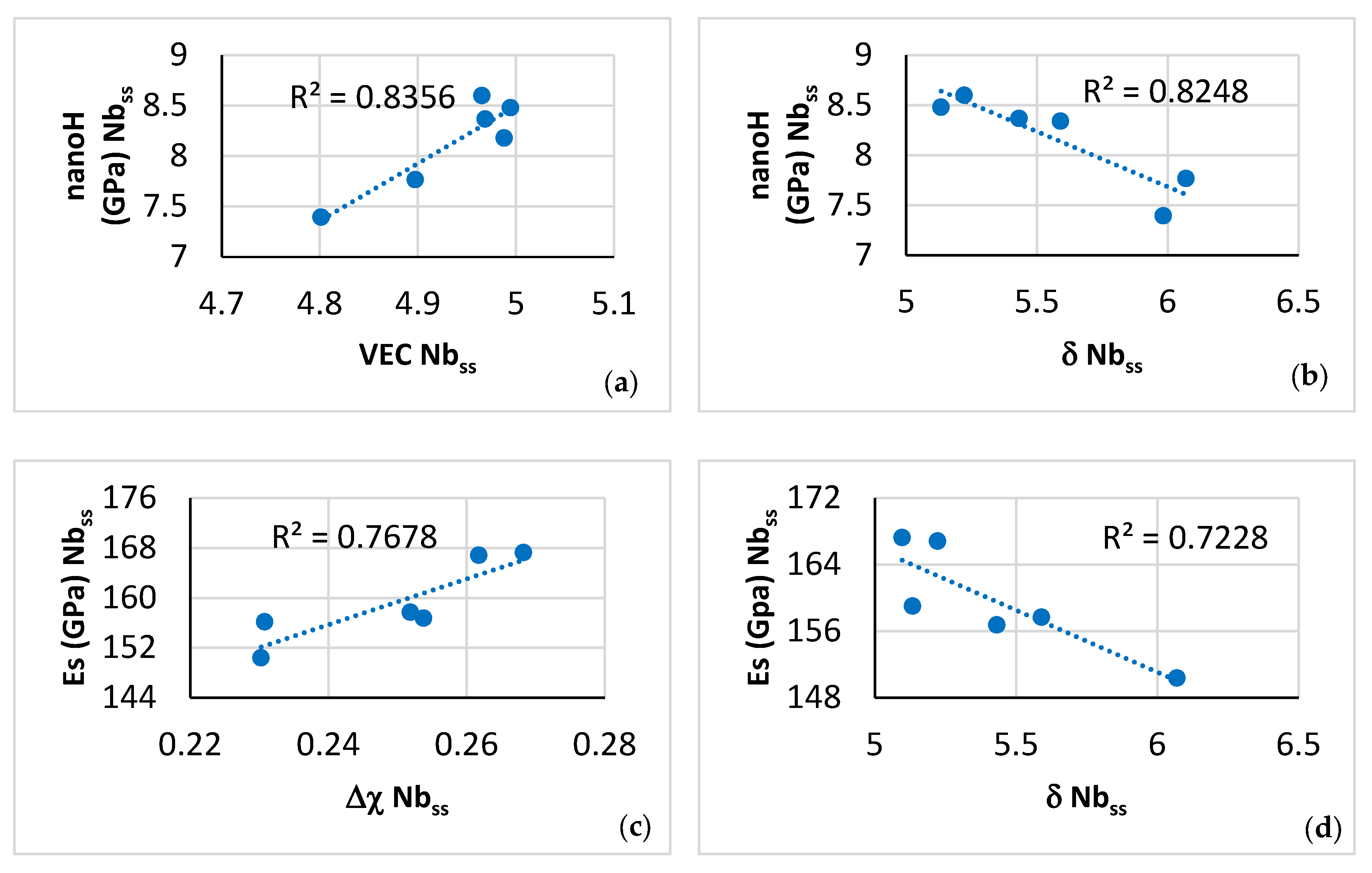
For the microstructure shown in Figure 5, the nano-hardness of the solid solution increased and decreased, respectively, with the parameter VECss and δss of the A2 solid solution (Figure 20a,b), whereas its Young’s modulus increased and decreased, respectively, with its parameter Δχss and δss (Figure 20c,d). The change of nano-hardness with the parameter δss exhibited the same trend as the change of Vickers hardness of Nbss in Boron containing RM(Nb)ICs/RCCAs [11,19]. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time that experimental data about the dependence of the Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution on its parameters Δχss and δss is reported for a CC A2 solid solution in a multiphase RCCA.
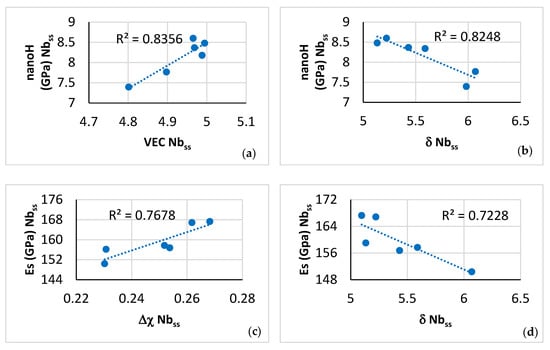
Figure 20.
Data for nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-AC.
The substitution of Nb by Ti in Nb5Si3 changes the properties of the silicide, for example, according to the first-principles calculations in [49], the Young’s modulus of αNb5Si3 increases whereas that of βNb5Si3 decreases. If the change of modulus is calculated using as reference the modulus of the binary (unalloyed) silicide, then the change per atomic percent addition of Ti is as shown in Table 9. However, if the change of modulus is calculated using as reference the modulus value at each increment of Ti concentration in the silicide then the change per atomic percent addition of Ti is as shown in Table 10. The ΔEs/(at.% Ti) value of a specific polymorph of (Nb,Ti)5Si3 depends on how the calculation is approached. The absolute |ΔEs/(at.% Ti)| change for β(Nb,Ti)5Si3 is more than that for α(Nb,Ti)5Si3 when it is calculated between increments of Ti concentration.

Table 9.
Change of Young’s modulus of Nb5Si3 per at.% Ti addition using as reference the modulus of the binary silicide [49].

Table 10.
Change of Young’s modulus of Nb5Si3 per at.% Ti addition using as reference the modulus of the silicide at each increment of Ti addition [49].
In the alloy NT 1.2-AC the silicide was the β(Nb,Cr,Hf,Mo,Ti,W)5(Al,Ge,Si,Sn)3, and the Nb was substituted not only with Ti but also with Cr, Hf, Mo and W, and the Si was substituted with Al, Ge and Sn. Above, we discussed how the synergy of specific alloying elements affected the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and the βNb5Si3 and correlations of these properties with parameters of the solid solution. If we were to use the experimental nanoindentation and chemical analysis data for the solid solution and silicide grains in NT 1.2-AC and calculate the change of a property or parameter per atomic percent addition of solute X (i.e., calculate ΔP/X) using the maximum and minimum concentration values of X (i.e., Cmax. X and Cmin. X, respectively) and the corresponding property or parameter values for the aforementioned concentrations, we get the data for the A2 solid solution and the alloyed βNb5Si3 shown in Table 11 and Table 12, respectively. In other words ΔP/X = (Pmax. X − Pmin. X)/(Cmax. X − Cmin. X), where P is (i) a property, namely Young’s modulus or nano-hardness, or (ii) a parameter, namely VEC, Δχ or δ. (The same approach to the calculation of ΔEs/Ti in (Nb,Ti)5Si3 with the data in [49] gave the values +1.824 GPa/at.% and −2.432 GPa/at.%, respectively for α(Nb,Ti)5Si3 and β(Nb,Ti)5Si3; see Table 9).

Table 11.
Data for properties and parameters of the A2 solid solution in NT 1.2-AC. Average change of Es, nano-hardness, VEC, Δχ and δ per change of concentration of solute X.

Table 12.
Data for properties and parameters of the alloyed βNb5Si3 in NT1.2-AC. Average change of Es, nano-hardness, VEC and Δχ per change of concentration of solute X.
To understand the data in Table 11 and Table 12, we must consider the microstructure of NT 1.2-AC, relationships between solutes, between solutes and parameters, between parameters of specific phases and between phases. We shall make use of the discussion in Section 4.1 and also of the concepts of synergy and entanglement that were discussed in [9].
Regarding the A2 solid solution, the concentrations of its solutes, e.g., Al, Cr, Mo, W, (Ge + Sn), (Al + Ge + Si + Sn) changed with its Ti or Al content, see Figure 10, its parameters Δχ and δ also changed with its Ti concentration (Figure 12a,b) and its parameters VEC, Δχ and δ were related (Figure 12c,d). The solutes in the A2 solid solution were in synergy and entangled with parameters (Figure 10 and Figure 12a,b) and the solid solution was in synergy and entangled with the other two phases, namely the C14-Laves phase and the βNb5Si3 silicide, see Figure 13. In the latter two phases, also, there were relationships between solutes, between solutes and parameters and between parameters (see Figure 9 and Figure 11), and similarly they were in synergy and entanglement with the A2 solid solution (Figure 13). Owing to synergy and entanglement, a change of the concentration of solute element X brought changes to properties and parameters of the solid solution, namely the changes ΔES/X, Δ[nano-H]/X, Δ[VEC]/X, Δ[Δχ]/X and Δ[δ]/X given in Table 11. The same was the case for the βNb5Si3 silicide; see Figure 11 and Figure 13, and Table 12. We note that for Ti in the β(Nb,Cr,Hf,Mo,Ti,W)5(Al,Ge,Si,Sn)3 silicide the ΔEs/Ti was positive and equal to +6.28 GPa/at.% (Table 12), whereas was negative for β(Nb,Ti)5Si3 (Table 9 and Table 10). This is attributed to the synergy of Ti with other solutes.
The value of a property of a phase, say the Young’s modulus of the (Nb,Ti,Al,Si,Cr,Ge,Hf,Mo,Sn,W)ss A2 solid solution or of the β(Nb,Cr,Hf,Mo,Ti,W)5(Al,Ge,Si,Sn)3 silicide, would depend on its actual chemical composition. A change of the concentration of a solute X, say Ti, would bring with it changes of the concentrations of the other solutes in the phase, and owing to the synergy and entanglement of solutes and phases a new value of the property would arise. For example, in NT 1.2-AC the 40.3Nb–17.8Ti–0.6Si–5.2Al–7.9Cr–0.6Hf–19.2Mo–4.8W–2.2Sn–1.3Ge and the 34.1Nb–23.1Ti–0.8Si–6.2Al–14.6Cr–0.6Hf–14.2Mo–2.2W–3.1Sn–1.2Ge solid solutions had Young’s modulus 167.2 GPa and 150.4 GPa, respectively, and the 35.8Nb–21Ti–24.3Si–3.7Al–2.2Cr–1.3Hf –3.7Mo–0W–2.1Sn–6Ge and the 36.4Nb–20Ti–24.6Si–3.6Al–2.2Cr–1.1Hf–4Mo–0.2W–1.8Sn–6.3Ge beta silicides had Young’s modulus 231.6 GPa and 244.7 GPa, respectively.
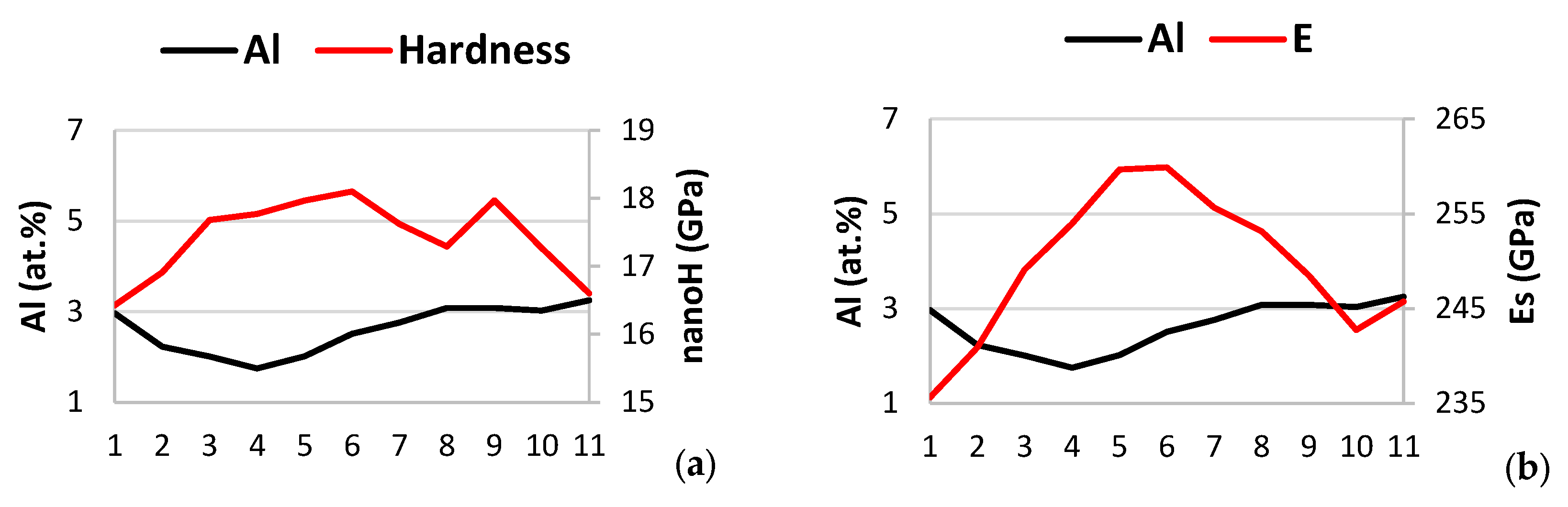
In Figure 21, it is shown the change of the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus (Es) only of the βNb5Si3 silicide with solute concentration over a length of 40 μm along the third line of nano-indentations in Figure 7 (nanoindentation numbers 31 to 45). In Figure 21, the abscissa numbers 1 to 11 correspond to the nanoindentation numbers 34 to 44 in Figure 7. The nano-hardness and Young’s modulus values of the silicide were low in and close to the areas of the silicide where solid solution had precipitated (nanoindentation numbers 34, 35, or abscissa numbers 1 and 2), and were the highest in the “core” of the silicide grain, which was free of solid solution precipitates. Increase of the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus was associated with decrease of the Al, Ti, Cr and Sn content, and increase of the Nb and Si content of the silicide.
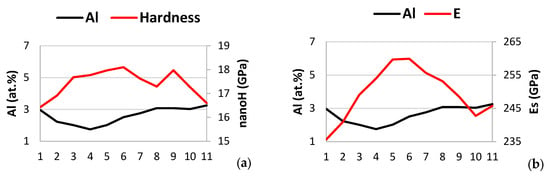
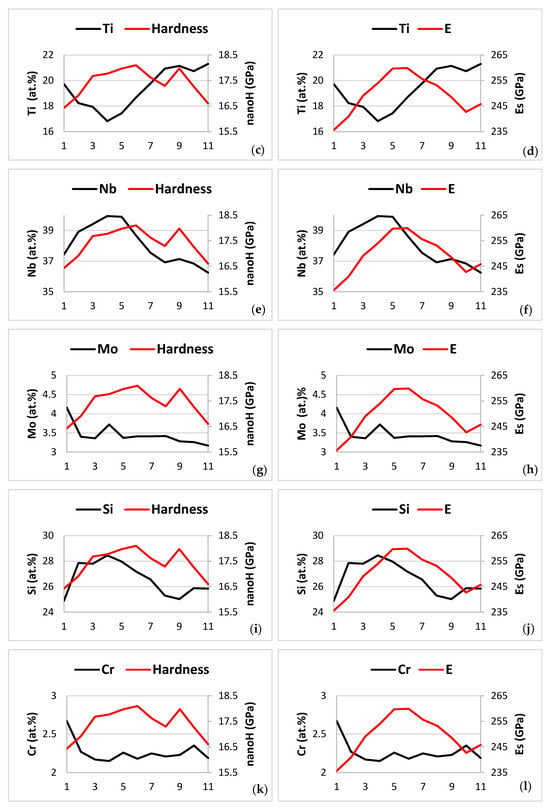
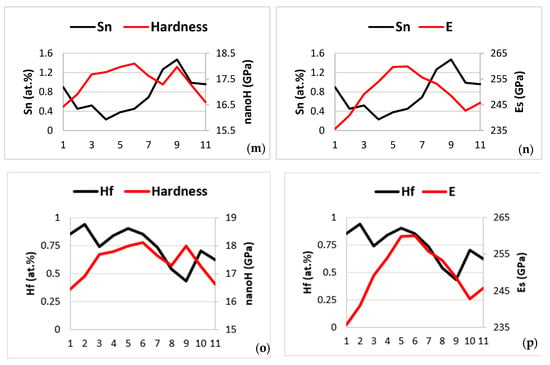
Figure 21.
Data showing how the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus (Es) of βNb5Si3 changed with solute concentration along the third line of nanoindentations (numbers 34 to 44 in Figure 7) of the microstructure shown in Figure 7. Note that no data for the properties of the A2 solid solution is included in this figure, and that the element maps shown in Figure 19 correspond to the microstructure shown in Figure 7. (a,c,e,g,i,k,m,o) Solute versus nano-hardness for Al, Ti, Nb, Mo, Si, Cr, Sn, and Hf, respectively, and (b,d,f,h,j,l,n,p) solutes versus Young’s modulus for Al, Ti, Nb, Mo, Si, Cr, Sn, and Hf, respectively.
The nano-hardness decreased and then increased as the nano-indenter moved from solid solution precipitate free area (“core” of silicide) to solid solution precipitate containing area to solid solution precipitate free area, nanoindentation numbers 39 (nanoindentation in the “core” of the silicide, where the nano-hardness value was the highest) to 42 (abscissa numbers 6 to 9), and continued to decrease to nanoindentation numbers 43 and 44 (abscissa numbers 10 and 11). However, this was not the case for the Young’s modulus, which decreased continuously from the maximum value in the “core”, nanoindentation numbers 38 and 39, (abscissa numbers 5 and 6) to a minimum value at nanoindentation number 43 (abscissa number 10), and then increased again at nanoindentation number 44 (abscissa number 11).
From nanoindentation number 39 to number 44 (abscissa numbers 6 to 11) (i) the concentrations of Ti and Nb, respectively increased and decreased significantly, (ii) the concentrations of Al and Mo, respectively increased and decreased slightly, (iii) the concentration of Cr also changed slightly with a high value at nanoindentation number 43 (abscissa number 10), after which (iv) the concentrations of Si and Sn essentially did not change, having previously decreased and increased between nanoindentation numbers 39 to 42 (abscissa numbers 6 to 9), respectively and (v) the trend in the concentration change of Hf was opposite that of Sn.
From the nanoindentation number 34 to the number 44 (abscissa numbers 1 to 11) in the silicide grain shown in Figure 7, i.e., over a distance of 40 μm, the nano-hardness changed from 16.4 GPa to 16.6 GPa with maximum 18.1 GPa at nanoindentation number 39 (abscissa number 6), and the Young’s modulus changed from 235.6 GPa to 245.8 GPa with maximum 259.9 GPa. At the maximum nano-hardness and Young’s modulus values, i.e., at the nanoindentation number 39 (abscissa number 6) the concentrations were 2.5, 18.7, 38.7, 3.4, 27.2, 2.2, 0.5 and 0.9 at.%, respectively, for Al, Ti, Nb, Mo, Si, Cr, Sn and Hf.
From nanoindentation numbers 34 to 39 (abscissa numbers 1 to 6) ΔP1 to 6/X1 to 6 = (P6 − P1)/(X6 − X1) and from nanoindentation numbers 39 to 44 (abscissa numbers 6 to 11) ΔP6 to 11/X6 to 11 = (P11 − P6)/(X11 − X6), where P is property, namely nano-hardness (nH) or Young’s modulus (Es). Furthermore, ΔnH1 to 6/μm = + 0.08 GPa/μm, ΔnH6 to 11/μm = −0.07 GPa/μm, ΔEs1 to 6/μm = 1.11 GPa/μm and ΔEs6 to 11/μm = −0.64 GPa/μm. For the aforementioned changes of Young’s modulus and nano-hardness with distance along the third line of nanoindentations in Figure 7, the change of property value per atomic percent solute is shown in Table 13.

Table 13.
Change of Young’s modulus and nano-hardness per at.% addition of solute X from abscissa numbers 1 to 11 in Figure 21.
The data in Table 13 shows that along the third line of nanoindentations in Figure 7 and for the abscissa numbers 1 to 6 in Figure 21 the Young’s modulus or nano-hardness decreased per at.% addition of Ti, Mo, Al and Sn, and increased per addition of Si and Nb and that for the abscissa numbers 6 to 11 decreased per addition of Ti, Al and Sn and increased per addition of Nb, Si and Mo.
The data for the alloy NT 1.2 presents some challenges for alloy designers using “alloy design landscapes” [9] to design metallic UHTMs. A challenge is to calculate the chemical composition of an A2 solid solution with the solutes that are essential to get a balance of properties for a single phase metallic UHTM, namely the transition metals Cr, Hf, Mo, Nb, Ti, W and the simple metal and metalloid elements Al, Ge, Si, Sn [11,19,20,40,59]. It should be possible to calculate properties of a multicomponent A2 solid solution with specific solute concentrations, say a (Nb,Ti,Al,Si,Cr,Ge,Hf,Mo,Sn,W)ss. Another challenge is to calculate the chemical composition of a single phase intermetallic material with the solutes that are essential to get a balance of properties in a metallic UHTM, namely the transition metals Cr, Hf, Mo, Nb, Ti, W and the simple metal and metalloid elements Al, Ge, Si, Sn, though with some difficulty owing to the current lack of thermodynamic data. It should be possible, but considerably more difficult, owing to the crystal structure of M5Si3 silicides, to calculate properties of a multicomponent silicide with specific solute concentrations, say β(Nb,Cr,Hf,Mo,Ti,W)5(Al,Ge,Si,Sn)3. Another challenge would be how to model and calculate the microstructure and properties (including oxidation resistance) of a multiphase multicomponent metallic UHTM with solutes that are essential to get a balance of properties, say with the aforementioned elements, and with a microstructure in which the aforementioned A2 solid solution and beta silicide, whether “conventional” or CC, co-exist with other “conventional” or CC/HE phases (e.g., the C14-Laves phase in NT 1.2-AC), and where solutes partition within and between phases, and interstitials contaminate phases, some more severely than others. The said challenges are manageable with the NICE methodology for the design of metallic UHTMs because of the centrality of the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ in the NICE “alloy design landscape”, the relationships of the latter with solutes, phase properties and alloy properties [59], the synergy and entanglement of solutes and phases and the significance of the environment and contamination with interstitials in the NICE “alloy design landscape” [9].
The experimental results for NT 1.2-HT present another challenge regarding the modelling and calculation of mechanical properties, e.g., creep, toughness, of multiphase metallic UHTMs with M5Si3 silicides in which precipitation of a second phase occurs in silicide grains, as demonstrated in this work with the results for the βNb5Si3 silicide. In such metallic UHTMs, the silicide actually is a CC composite phase and exhibits significant variations in properties (nano-hardness, Young’s modulus), owing to the precipitation of a second phase, accompanied with changes of solute concentrations (in the composite phase itself), owing to solute partitioning (Figure 4 and Figure 19), and different properties of M5Si3 silicide/A2 solid solution interface “area” (Figure 4 and Figure 6).
5. Conclusions
In the RCCA that was studied in this work, the A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3 were the stable phases after 200 h at 1500 °C. The partitioning of Ti in the as cast and heat treated microstructure and its relationships with other solutes was important for the properties of the A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3. For these phases, and for the C14-NbCr2 Laves phase that was observed only in the as cast alloy, as well as for the contaminated with oxygen solid solution and silicide in the heat treated alloy, for the first time, it was shown that there are relationships/trends between solutes, between solutes and the parameters VEC, Δχ and δ, between the said parameters, and between parameters and phase properties. The aforementioned relationships/trends, and the nano-hardness and Young’s modulus of the A2 solid solution and the D8m βNb5Si3 in the as cast and heat treated alloy, demonstrated the significance and importance of synergy and entanglement of solutes, parameters and phases (a) for the microstructure and properties of this RCCA and (b) for the design of metallic UHTMs, and for the modelling of their microstructures and properties.
Author Contributions
Experimental work N.T, Supervision C.U. and P.T., Formal analysis N.T., C.U. and P.T., Draft preparation N.T., Review C.U. and P.T., Final paper N.T., C.U. and P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the EPSRC (EP/H500405/1, EP/L026678/1) and Polls-Royce Plc.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AC | as cast |
| CC | complex concentrated (also compositionally complex) |
| HE | high entropy |
| HT | heat treated |
| NICE | Niobium Intermetallic Composite Elaboration |
| RM | refractory metal |
| RMIC | refractory metal intermetallic composite |
| RHEA | refractory metal high entropy alloy |
| RCCA | refractory metal complex concentrated alloy |
| RMIC/RHEA | RMIC that also meets the definition of RHEA |
| RM(Nb)IC | refractory metal intermetallic composite based on Nb |
| RM(Nb)IC/RCCA | RM(Nb)IC that also meets the definition of RCCA |
| RM(Nb)IC/RHEA | RM(Nb)IC that also meets the definition of RHEA |
| TM | transition metal |
| UHTM | ultra-high temperature material |
Appendix A. Nominal Alloy Compositions (at.%)
| (Actual compositions for the alloys JZ3, JZ3+, JZ4 and JZ5) | |
| KZ5 | 48Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr |
| KZ7 | 53Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al |
| JN1 | 43Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr–5Hf |
| JZ3 | 41.8Nb–12.4Ti–17.7Si–4.7Al–5.2Cr–1Hf–4.8Ge–6Ta–3.7Sn–2.7W |
| JZ3+ | 38.7Nb–12.4Ti–19.7Si–4.6Al–5.2Cr–0.8Hf–4.9Ge–5.7Ta–5.7Sn–2.3W |
| JZ4 | 38.9Nb–12.5Ti–17.8Si–5Al–5.2Cr–1.1Hf–5.2Ge–6.2Mo–5.8Sn–2.3W |
| JZ5 | 32Nb–20.4Ti–19.2Si–4.5Al–4.7Cr–0.9Hf–5.2Ge–6.3Mo–5.7Sn–1.1W |
| NV1 | 53Nb–23Ti–5Si–5Al–2Cr–5Hf–5V–2Sn |
| OHS1 | 38Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr5–Ge–5Sn |
| ZF5 | 48Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Ge |
| ZF6 | 43Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr–5Ge |
| ZF9 | 38Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr–5Ge–5Hf |
| ZX7 | 46Nb–24Ti–18Si–5Al–5Cr–2Sn |
References
- Bewlay, B.P.; Jackson, M.R.; Gigliotti, M.F.X. Chapter 6: Niobium silicide high temperature in situ composites. In Intermetallic Compounds: Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 541–560. [Google Scholar]
- Aeronautical Materials for Today and Tomorrow; Forum organised by the Air and Space Academy (AAE), French Aerospace Society (3AF) and Academy of Technologies; SAGEM: Paris, France, 2012; ISBN 978-2-913331-56-3/979-10-92518-09-2.
- Senkov, O.N.; Tsakiropoulos, P.; Couzinié, J.-P. Special Issue “Advanced Refractory Alloys”: Metals, MDPI. Metals 2022, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabol, S.M.; Randall, B.T.; Edington, J.D.; Larkin, C.J.; Close, B.J. Barrier Coatings for Refractory Metals and Superalloys; Bechtel: Reston, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T. Environmental embrittlement and grain-boundary fracture in Ni3Al. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1992, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.F.; Simmons, G.W.; Wei, R.P. Evidence for internal oxidation during oxygen enhanced crack growth in P/M Ni-based superalloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Hegde, S.; Reed, R.C. The oxidation of single-crystal nickel-based superalloys. JOM 2006, 58, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, D.A. Gas phase embrittlement and time dependent cracking of nickel based superalloys. Energy Mater. 2006, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. A Perspective of the Design and Development of Metallic Ultra-High Temperature Materials: Refractory Metal Intermetallic Composites, Refractory Complex Concentrated Alloys and Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Alloys 2023, 2, 184–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewlay, B.P.; Jackson, M.R.; Subramanian, P.R.; Zhao, J.-C. A review of very-high-temperature Nb-silicide-based composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. Refractory Metal Intermetallic Composites, High-Entropy Alloys, and Complex Concentrated Alloys: A Route to Selecting Substrate Alloys and Bond Coat Alloys for Environmental Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.R. Protective Alloy Coatings Comprising Cr-Al-Ru Containing One or More or Y, Fe, Ni and Co. U.S. Patent 4,980,244, 25 December 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.-C.; Jackson, M.R. Diffusion Barrier Coatings and Related Articles and Processes. U.S. Patent 6,746,782 B2, 8 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bewlay, B.A.; Darolia, R.; Dheeradhada, S.; DiDomizio, R.; Gigliotti, M.F.X.; Rigney, J.D.; Subramanian, P.R. Nb-Si Based Alloy Having Al-Containing Coating: Articles and Processes. U.S. Patent 8,039,116 B2, 18 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Fu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, K. Microstructure and Oxidation Behavior of Nb-Si-Based Alloys for Ultrahigh Temperature Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Jia, L.; Hong, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H. Improvement of oxidation resistance of Nb–Ti–Si based alloys with additions of Al, Cr and B at different temperatures. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 31, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Jia, L.; Weng, J.; Hong, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H. Improvement in the oxidation resistance of Nb–Ti–Si–Cr–Al–Hf alloys containing alloyed Ge and B. Corros. Sci. 2014, 88, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Guo, X. Influence of molybdenum contents on the microstructure, mechanical properties and oxidation behaviour of multi-elemental Nb–Si based ultrahigh temperature alloys. Intermetallics 2021, 129, 107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. Alloys for application at ultra-high temperatures: Nb-silicide in situ composites. Challenges, breakthroughs and opportunities. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 123, 100714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Stability of Complex Concentrated (CC)/High Entropy (HE) Solid Solutions and the Contamination with Oxygen of Solid Solutions in Refractory Metal Intermetallic Composites (RM(Nb)ICs) and Refractory Complex Concentrated Alloys (RCCAs). Materials 2022, 15, 8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrica, D.; Badea, I.C.; Serban, B.A.; Olaru, M.T.; Vonica, D.; Burada, M.; Piticescu, R.-R.; Popov, V.V. Complex Concentrated Alloys for Substitution of Critical Raw Materials in Applications for Extreme Conditions. Materials 2021, 14, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.-S.; Zhou, W.-Z.; Tan, Q.-B.; Wu, M.-X.; Qiao, S.; Zhu, G.-L.; Dong, A.-P.; Shu, D.; Sun, B.-D. A review of refractory high-entropy alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 3487–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Qiao, J.; Wu, Y. Excellent room-temperature tensile ductility in as-cast Ti37V15Nb22Hf23W3 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2022, 151, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Juan, C.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Yeh, J.-W. Effect of Al addition on mechanical properties and microstructure of refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 624, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.S.; Li, X.Z.; Su, Y.Q.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory MoNbHfZrTi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.S.; Li, X.Z.; Chen, R.R.; Su, Y.Q.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ MC-carbide particulates-reinforced refractory high entropy Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi matrix alloy composite. Intermetallics 2016, 69, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, N.D.; Yurchenko, N.Y.; Skibin, D.V.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. Structure and mechanical properties of the AlCrxNbTiV (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5) high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 652, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.M. Senary refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaTiVW. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laube, S.; Kauffmann, A.; Schellert, S.; Seils, S.; Tirunilai, A.S.; Greiner, C.; Eggeler, Y.M.; Gorr, B.; Christ, H.-J.; Heilmaier, M. Formation and thermal stability of two-phase microstructures in Al-containing refractory compositionally complex alloys. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2022, 23, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Soni, V.; Sharma, A.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Fraser, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, R. Concomitant Clustering and Ordering Leading to B2 + BCC Microstructures in Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmaier, M.; Krüger, M.; Saage, H.; Rösler, J.; Mukherji, D.; Glatzel, U.; Völkl, R.; Hüttner, R.; Eggeler, G.; Somsen, C.; et al. Metallic materials for structural applications beyond nickel-based superalloys. JOM 2009, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J. Development and exploration of refractory High entropy alloys—A review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, N.; Panina, E.; Tikhonovsky, M.; Salishchev, G.; Zherebtsov, S.; Stepanov, N. Structure and mechanical properties of an in situ refractory Al20Cr10Nb15Ti20V25Zr10 high entropy alloy composite. Mater. Lett. 2020, 264, 127372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.S.; Li, X.Z.; Chen, R.R.; Su, Y.Q.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory high entropy (Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi)BCC/M5Si3 in-situ compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, J.; Peng, S.; An, F.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. Improving oxidation resistance of TaMoZrTiAl refractory high entropy alloys via Nb and Si alloying. Corros. Sci. 2023, 223, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.; Peterlechner, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wilde, G.; Ye, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Si micro-alloyed (Ti28Zr40Al20Nb12)100-xSix (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5) high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2023, 161, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Qin, G.; Chen, R.; Guo, J. Achieving excellent specific yield strength in non-equiatomic TiNbZrVMo high entropy alloy via metalloid Si doping. Mater. Lett. 2023, 335, 133832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ma, Z.L.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, X.W. Designing TiVNbTaSi refractory high-entropy alloys with ambient tensile ductility. Scr. Mater. 2022, 206, 114230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress with BCC-Structured High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Nb5Si3 Silicide in Metallic Ultra-High Temperature Materials. Metals 2023, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Luan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Li, X.Y.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Ultra-high strength WNbMoTaV high-entropy alloys with fine grain structure fabricated by powder metallurgical process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Cai, Y.H.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, T.; Si, J.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.D.; Hui, X.D. Phase composition and solid solution strengthening effect in TiZrNbMoV high-entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory HfMo0.5NbTiV0.5Six high-entropy composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellios, N.; Keating, P.; Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Microstructure and Properties of the Nb-23Ti-5Si-5Al-5Hf-5V-2Cr-2Sn (at.%) Silicide-Based Alloy—RM(Nb)IC. Metals 2021, 11, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.; Ghadyani, M.; Utton, C.; Tsakiropoulos, P. A Study of the Effects of Al, Cr, Hf, and Ti Additions on the Microstructure and Oxidation of Nb-24Ti-18Si Silicide Based Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, B.; Su, B.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Effect of Ge addition on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of quinary Nb-16Si-22Ti-2Al-2Cr alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mat. 2023, 116, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, I.; Utton, C.; Scott, A.; Tsakiropoulos, P. Ab initio study of the intermetallics in Nb–Si binary system. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, I.; Utton, C.; Tsakiropoulos, P. The impact of Ti and temperature on the stability of Nb5Si3 phases: A first-principles study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hammerschmidt, T.; Pettifor, D.G.; Shang, J.; Zhang, Y. Influence of vibrational entropy on structural stability of Nb-Si and Mo-Si systems at elevated temperatures. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhu, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Ab initio study of alloying effects on structure stability and mechanical properties of Nb5Si3. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2015, 108, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tsakiropoulos, P. On the microstructure and hardness of the Nb-24Ti-18Si-5Al-5Cr-5Ge and Nb-24Ti-18Si-5Al-5Cr-5Ge-5Hf (at.%) silicide based alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Utton, C.; Tsakiropoulos, P. A study of the effect of 2 at.% Sn on the microstructure and isothermal oxidation at 800 and 1200 °C of Nb-24Ti-18Si based alloys with Al and/or Cr additions. Materials 2018, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Negrete, O.; Tsakiropoulos, P. On the microstructure and isothermal oxidation at 800 and 1200 °C of the Nb-24Ti-18Si5Al-5Cr-5Ge-5Sn (at.%) silicide based alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Utton, C.; Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Microstructure and Properties of Nb-12Ti-18Si-6Ta-5Al-5Cr-2.5W-1Hf (at.%) Silicide-Based Alloys with Ge and Sn Additions. Materials 2020, 13, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Utton, C.; Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Microstructure and Properties of Nb-18Si-6Mo-5Al-5Cr-2.5W-1Hf Nb-Silicide Based Alloys with Ge, Sn and Ti Additions (at.%). Materials 2020, 13, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus Using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triboscope User Manual; Hysitron Ltd.: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 2005.
- Tsakiropoulos, P. On Nb Silicide Based Alloys: Alloy Design and Selection. Materials 2018, 11, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. Alloying and Properties of C14–NbCr2 and A15–Nb3X (X = Al, Ge, Si, Sn) in Nb–Silicide-Based Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. On the Alloying and Properties of Tetragonal Nb5Si3 in Nb-Silicide Based Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewlay, B.P.; Sitzman, S.D.; Brewer, L.N.; Jackson, M.R. Analyses of eutectoid phase transformations in Nb-silicide in-situ composites. Microsc. Microanal. 2004, 10, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiropoulos, P. Alloying and Hardness of Eutectics with Nbss and Nb5Si3 in Nb-silicide Based Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M.E.; Okamoto, H.; Gokhale, A.B.; Abbaschian, R. The Nb-Si (Niobium-Silicon) System. J. Phase Equilib. 1993, 14, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, N.A.; Eremin, N.N.; Marchenko, E.I.; Svetlov, I.L.; Muromtsev, N.A.; Neuman, A.V.; Yakushev, D.A. Diffusion Paths for Interstitial Impurities in Different Polymorphic Modifications of Niobium Silicide Nb5Si3. Crystallogr. Rep. 2018, 63, 319–326, Original Russian Text published in Kristallografiya 2018, 63, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Ye, Y.Y.; Kramer, M.J.; Ho, K.M.; Hong, L.; Fu, C.L.; Malik, S.K. Theoretical calculations and experimental measurements of the structure of Ti5Si3 with interstitial additions. Intermetallics 2000, 8, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-W.; Lin, C.-M.; Wang, W.-R.; Yang, C.-C.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2015, 62, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.M. Senary refractory high-entropy alloy CrxMoNbTaVW. CALPHAD Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2015, 51, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.M. Senary refractory high-entropy alloy HfNbTaTiVZr. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.W.; Qiao, J.W.; Hawk, J.A.; Zhou, H.F.; Chen, M.W.; Gao, M.C. Mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloys: Experiments and modelling. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.W.; Qiao, J.W.; Gao, M.C.; Hawk, J.A.; Ma, S.G.; Zhou, H.F. MoNbTaV medium-entropy alloy. Entropy 2016, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.W.; Qiao, J.W.; Gao, M.C.; Hawk, J.A.; Ma, S.G.; Zhou, H.F.; Zhang, Y. NbTaV–(Ti,W) refractory high entropy alloys: Experiments and modelling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T. Study of the Effect of Interstitial Element Contamination on the Properties of Nbss and Nb5Si3 in Nb Silicide Based Alloys; Final Year Project; University of Sheffield: Sheffield, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).