Powder Metallurgy Processing and Characterization of the χ Phase Containing Multicomponent Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
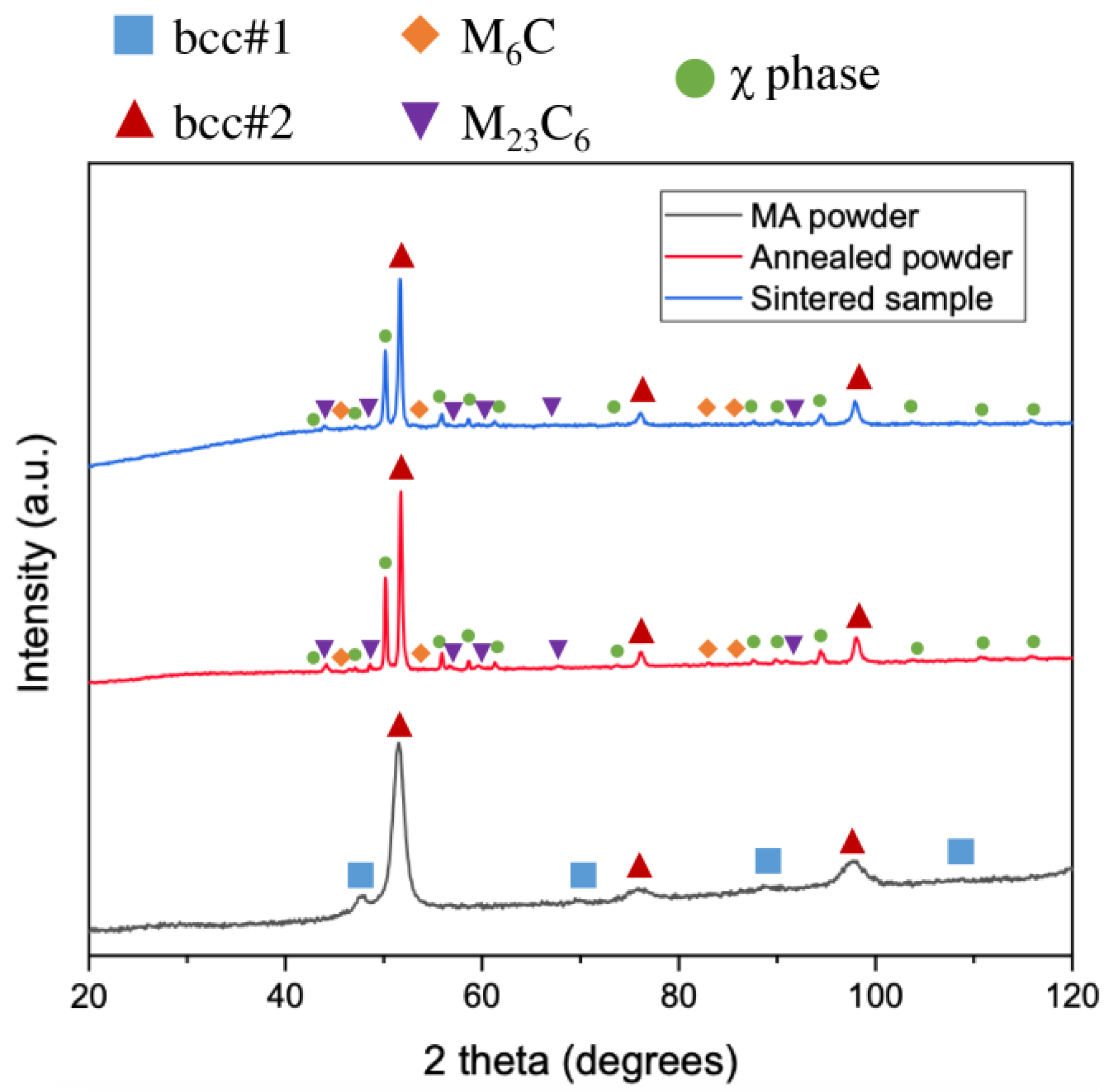
3.1. Structure
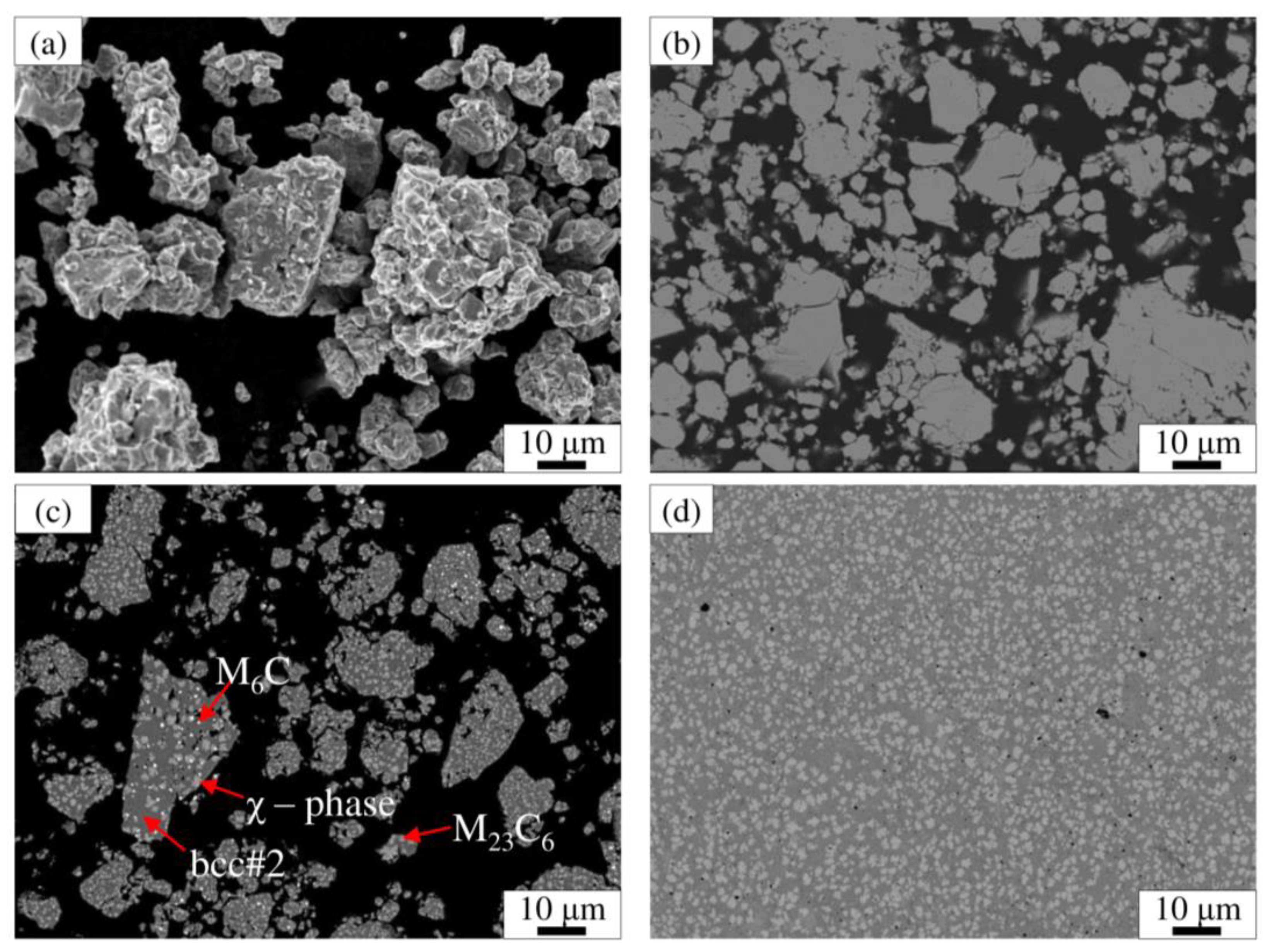
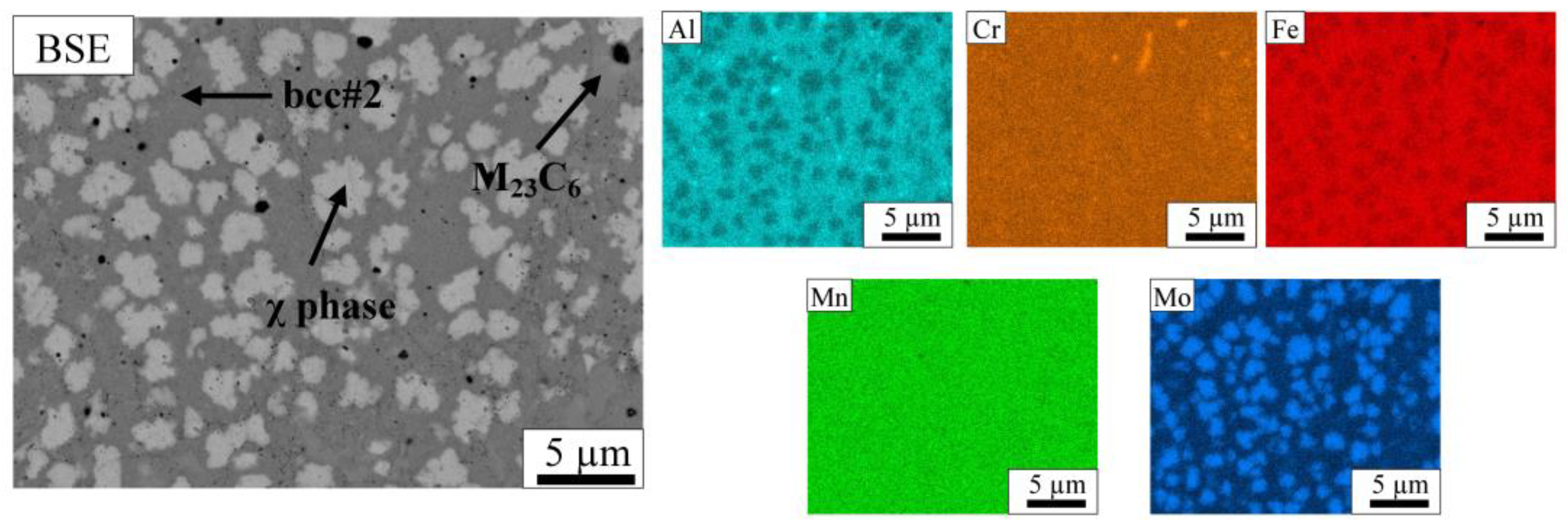
3.2. Microstructure
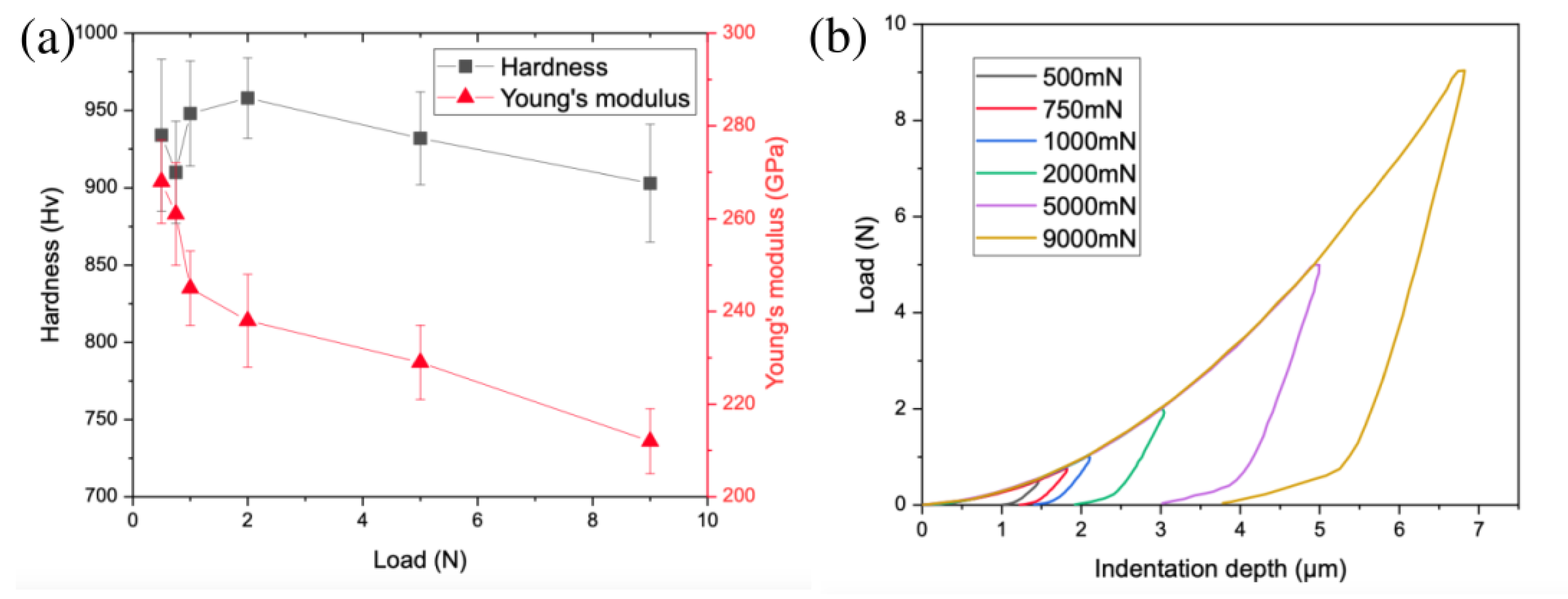
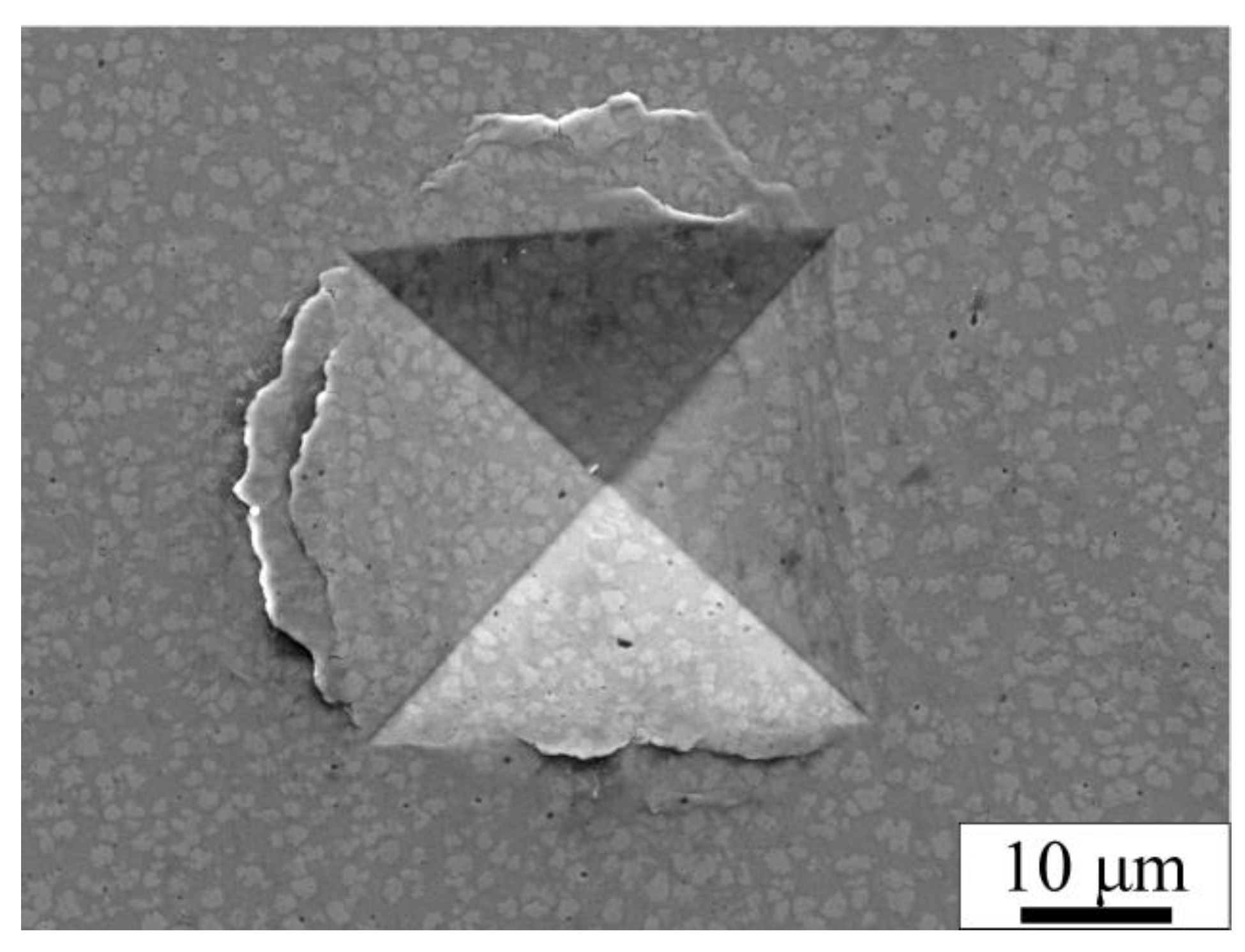
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-Entropy Alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. Mapping the World of Complex Concentrated Alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 135, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Nadzri, N.I.; Halin, D.S.C.; Al Bakri Abdullah, M.M.; Joseph, S.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.A.; Vizureanu, P.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.P.; Sandu, A.V. High-Entropy Alloy for Thin Film Application: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves De Oliveira, T.; Fagundes, D.V.; Capellato, P.; Sachs, D.; Augusto, A.; Pinto Da Silva, A. A Review of Biomaterials Based on High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Liaw, P.K.; Yeh, J.W.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319270135. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.-W. Recent Progress in High Entropy Alloys. Ann. Chim.—Sci. Matériaux 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowa, J.; Zajusz, M.; Kucza, W.; Cieślak, G.; Berent, K.; Czeppe, T.; Kulik, T.; Danielewski, M. Demystifying the Sluggish Diffusion Effect in High Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, O.; Shaburova, N.; Ostovari Moghaddam, A.; Trofimov, E. Al0.25CoCrFeNiSi0.6 High Entropy Alloy with High Hardness and Improved Wear Resistance. Mater. Lett. 2022, 328, 133190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, W.B.; Chen, H.; Brechtl, J.; Song, W.; Yin, W.; He, Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. A Low-Density High-Entropy Dual-Phase Alloy with Hierarchical Structure and Exceptional Specific Yield Strength. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 66, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Oka, H. Study on Irradiation Effects of Refractory Bcc High-Entropy Alloy. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2022, 31, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif El-Eskandarany, M. Mechanical Alloying; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9781455777525. [Google Scholar]
- Torralba, J.M.; Alvaredo, P.; García-Junceda, A. High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated via Powder Metallurgy. A Critical Review. Powder Metall. 2019, 62, 84–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Muralikrishna, G.M.; Murty, B.S. High-Entropy Alloys by Mechanical Alloying: A Review. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, R.C.; Chang, T.; Huang, W.F. Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloys: Statistical Analysis of Their Prevalence and Structural Inheritance. Metals 2019, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Chang, K.C.; Li, J.H.; Tsai, R.C.; Cheng, A.H. A Second Criterion for Sigma Phase Formation in High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Res. Lett. 2015, 4, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lau, K.B.; Teh, W.H.; Lee, J.J.; Wei, F.; Lin, M.; Wang, P.; Tan, C.C.; Ramamurty, U. Compositionally Graded CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion: A Combinatorial Assessment. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Ayyagari, A.V.; Choudhuri, D.; Scharf, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Gibson, M.; Banerjee, R. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of an Intermetallic-Based Al0.25Ti0.75CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Fan, A.C.; Wang, H.A. Effect of Atomic Size Difference on the Type of Major Intermetallic Phase in Arc-Melted CoCrFeNiX High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendejas Medina, L.; Riekehr, L.; Jansson, U. Phase Formation in Magnetron Sputtered CrMnFeCoNi High Entropy Alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 403, 126323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendejas Medina, L.; Tavares da Costa, M.V.; Paschalidou, E.M.; Lindwall, G.; Riekehr, L.; Korvela, M.; Fritze, S.; Kolozsvári, S.; Gamstedt, E.K.; Nyholm, L.; et al. Enhancing Corrosion Resistance, Hardness, and Crack Resistance in Magnetron Sputtered High Entropy CoCrFeMnNi Coatings by Adding Carbon. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cong, W. Laser Remelting of CoCrFeNiTi High Entropy Alloy Coatings Fabricated by Directed Energy Deposition: Effects of Remelting Laser Power. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 158, 108871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.H.; Guo, H.K.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, W.Q.; Li, J.C.; Liang, W. Microstructural Evolution, Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of Hot Rolled 27Cr-4Mo-2Ni Ferritic Steel during 800 °C Aging. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.H.; Luo, Y.; Guo, H.K.; Li, W.Q.; Li, J.C.; Liang, W. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of 27Cr-4Mo-2Ni Ferritic Stainless Steel during Isothermal Aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.W. A New Intermetallic Phase in Alloy Steels. Nature 1949, 164, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miller, J.D.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C. Accelerated Exploration of Multi-Principal Element Alloys for Structural Applications. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2015, 50, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, R. Understanding Phase Equilibria in High-Entropy Alloys: I. Chemical Potentials in Concentrated Solid Solutions—Atomic-Scale Investigation of AlCrFeMnMo. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 872, 159745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, R. Understanding Phase Equilibria in High-Entropy Alloys: II. Atomic-Scale Study of Incorporation of Metallic Elements in Cr Carbides—Application to Equilibrium with AlCrFeMnMo. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 874, 159959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, R. Ordering and Phase Separation in Multi-Principal-Element Metallic Alloys: Contribution from Mean-Field Atomic-Scale Modelling and Simulation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 898, 162842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekkal, W.; Besson, R.; Legris, A. Atomic Scale Modeling of Structural Phase Transformations in AlCrFeMnMo High-Entropy Alloys during Thermal Treatments. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, T.; Kumaran, S.N.; Touzin, M.; Béclin, F.; Cordier, C. Novel Multicomponent Powders from the AlCrFeMnMo Family Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, T.; Aly Sow, M.; Addad, A.; Touzin, M.; Bé Clin, F.; Cordier, C. Processing and Characterization of a Mechanically Alloyed and Hot Press Sintered High Entropy Alloy from the Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Family. JOM 2022, 74, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, T.; Sow, M.A.; Touzin, M.; Béclin, F.; Cordier, C. Preparation and Characterisation of the Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo High-Entropy Alloy Reinforced by in-Situ Formed Carbides. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2022, 102, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, Y.Y.; Sow, M.A.; Nouvellon, C.; Cordier, C.; Beclin, F.; Touzin, M.; Tromont, A.; Noirfalise, X.; Boilet, L.; Trelcat, J.F.; et al. Influence of Powder Mixing Method on Properties of High Entropy Alloys of FeCrMnAlMo Thin Coatings Obtained by Magnetron Sputtering. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2022, 446, 128744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, P.; Xi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, X. A New Type of High Entropy Alloy Composite Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNb3C2 Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Hot Pressing Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 728, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S. Effect of Molybdenum and Niobium on the Phase Formation and Hardness of Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8106–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Anupam, A.; Tilak, R.; Kottada, R.S. Phase Evolution and Thermal Stability of AlCoCrFe High Entropy Alloy with Carbon as Unsolicited Addition from Milling Media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, D.; Luo, Y.; Xia, T.; Zeng, W.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D. Fabrication of CoCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites by Thermomechanical Consolidation of a Mechanically Milled Powder. Mater. Charact. 2019, 148, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xie, Y.C.; Tang, Q.H.; Rao, C.; Dai, P.Q. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Produced by Mechanical Alloying and Vacuum Hot Pressing Sintering. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 28, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriljuk, V.G.; Berns, H. High Nitrogen Steels: Structure, Properties, Manufacture, Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Llorca-Isern, N.; López-Luque, H.; López-Jiménez, I.; Biezma, M.V. Identification of Sigma and Chi Phases in Duplex Stainless Steels. Mater. Charact. 2016, 112, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; San Martin, D.; Rivera Díaz del Castillo, P.E.J.; van der Zwaag, S. Modelling and Characterization of Chi-Phase Grain Boundary Precipitation during Aging of Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 467, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Li, Y. Energy-Balance Analysis for the Size Effect in Low-Load Hardness Testing. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Gavendova, P.; Sheikh, S.; Guo, S.; Dlouhy, I. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 174, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourmont, A.; Le Gallet, S.; Politano, O.; Desgranges, C.; Baras, F. Effects of Planetary Ball Milling on AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering: Experiments and Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 153448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.J.; Kostka, A.; Jimenez, J.A.; Choi, P.; Klemm, J.; Crespo, D.; Raabe, D.; Renner, F.U. Crystallization, Phase Evolution and Corrosion of Fe-Based Metallic Glasses: An Atomic-Scale Structural and Chemical Characterization Study. Acta Mater. 2014, 71, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.; Dołżańska, B. Hardness to Toughness Relationship on WC-Co Tool Gradient Materials Evaluated by Palmqvist Method. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 43, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
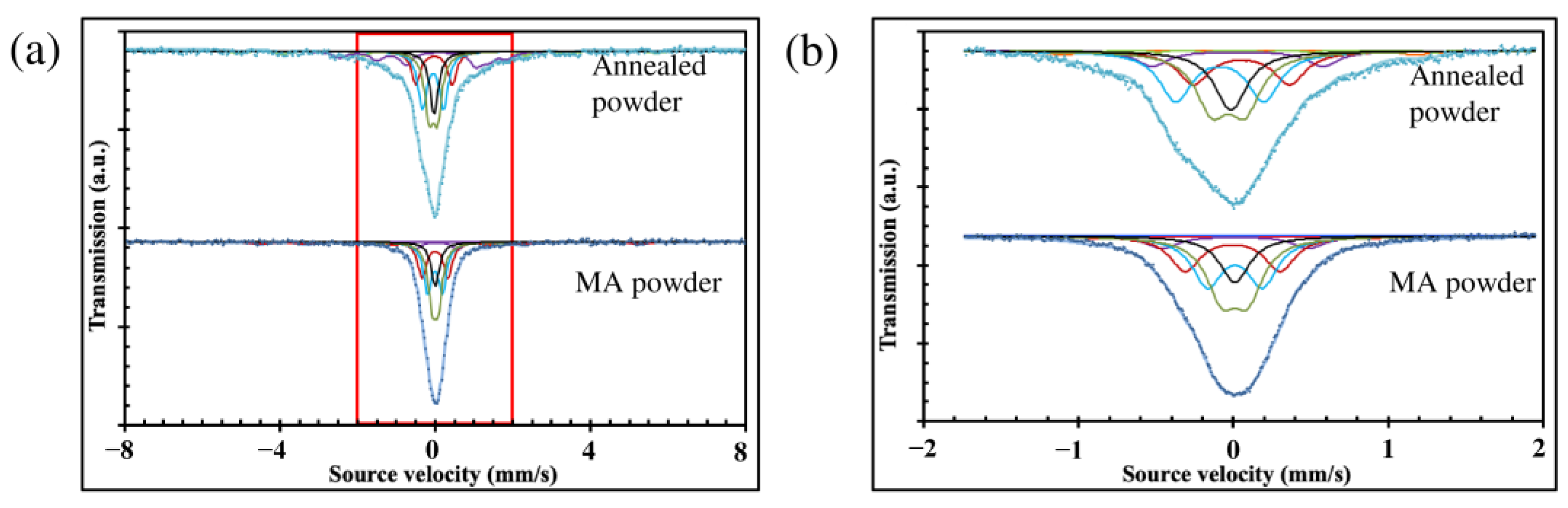

| Sample | Iron Site | H (T) | IS (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | W (mm/s) | A (%) | Magnetic Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annealed powder | Site 1 | 33.6 ± 1 | 0.03 ± 0.08 | 0.28 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 5.75 ± 0.65 | Magnetic: 29.82 ± 1.79% Non-magnetic: 70.18 ± 1.79% |
| Site 10 | 13.5 ± 1 | −0.19 ± 0.02 | −0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 17.60 ± 1.02 | ||
| Site 11 | - | −0.08 ± 0.11 | 1.46 ± 0.36 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 6.47 ± 0.12 | ||
| Site 5 | - | 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.77 ± 0.31 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 13.55 ± 0.04 | ||
| Site 6 | - | −0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 21.44 ± 1.11 | ||
| Sites 9 + 12 | - | −0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 22.91 ± 0.47 | ||
| Site 8 | - | −0.02 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 12.28 ± 0.02 | ||
| MA powder | Sites 2 + 3 | 30.5 ± 1 | −0.08 ± 0.08 | 0.46 ± 0.15 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 6.44 ± 1.03 | Magnetic: 9.93 ± 4.53% Non-magnetic: 90.07 ± 4.53% |
| Sites 4 + 5 | - | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.08 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 5.94 ± 1.05 | ||
| Site 6 | - | −0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 19.48 ± 0.86 | ||
| Site 7 | - | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 26.19 ± 0.36 | ||
| Site 12 | - | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 29.61 ± 0.04 | ||
| Site 8 | - | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 12.34 ± 1.06 |
| Phase | Volume Fraction [%] | Atomic Concentration [at.%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Cr | Fe | Mn | Mo | ||
| bcc#2 | 71 ± 2 | 19.1 | 19.4 | 39.2 | 18.3 | 4.0 |
| χ phase | 26 ± 2 | 13.5 | 22.0 | 34.7 | 18.9 | 10.9 |
| M6C | 1 ± 1 | 13.1 | 15.6 | 24.2 | 10.8 | 36.3 |
| M23C6 | 2 ± 1 | 4.3 | 55.5 | 17.0 | 14.2 | 9.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stasiak, T.; Sow, M.A.; Touzin, M.; Béclin, F.; Cordier, C. Powder Metallurgy Processing and Characterization of the χ Phase Containing Multicomponent Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Alloy. Alloys 2023, 2, 44-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys2010003
Stasiak T, Sow MA, Touzin M, Béclin F, Cordier C. Powder Metallurgy Processing and Characterization of the χ Phase Containing Multicomponent Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Alloy. Alloys. 2023; 2(1):44-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleStasiak, Tomasz, Mourtada Aly Sow, Matthieu Touzin, Franck Béclin, and Catherine Cordier. 2023. "Powder Metallurgy Processing and Characterization of the χ Phase Containing Multicomponent Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Alloy" Alloys 2, no. 1: 44-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys2010003
APA StyleStasiak, T., Sow, M. A., Touzin, M., Béclin, F., & Cordier, C. (2023). Powder Metallurgy Processing and Characterization of the χ Phase Containing Multicomponent Al-Cr-Fe-Mn-Mo Alloy. Alloys, 2(1), 44-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/alloys2010003






