Abstract
Statins are effective drugs for lowering cholesterol and reducing cardiovascular risk. Rarely, they can trigger autoimmune myopathies like immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), associated with anti-HMGCR antibodies. This condition may persist after statin discontinuation and requires immunosuppressive treatment. Despite these rare side effects, the benefits of statins outweigh the risks for most patients.
1. Introduction
Statins inhibit a critical step in cholesterol synthesis, transforming 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) into mevalonate via the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. This mechanism gives statins their potent lipid-lowering effects, reducing cardiovascular risk and mortality. Furthermore, the mevalonate pathway influences endothelial function, inflammatory responses, and coagulation, making the effects of statins extend beyond cholesterol reduction.
However, these side effects are rare, and in carefully selected patient populations, the benefits of statins significantly outweigh their potential risks.
Statins are a widely used group of drugs, primarily because they are the first-line treatment for coronary heart disease. Although highly effective and generally safe, their potential for myopathic toxicity is a well-documented side effect [1,2,3].
In 2010, an autoantibody against HMGCR was identified, enabling the detection of statin-associated autoimmune myopathy, which is clinically identical to immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) [4].
Autoimmune myopathies are rare diseases, with a prevalence of just 9–14 cases per 100,000 people. Of these, only ~10% are associated with either anti-SRP or anti-HMGCR myopathy [5,6].
Our objective is to present a rare case of myositis. While limited cases are described in the literature, this form of myopathic toxicity can occasionally manifest, triggering an autoimmune myopathy that persists even after statin discontinuation [7,8].
2. Case Report
Case 1.
A 74-year-old woman with a history of chronic ischemic heart disease, treated with atorvastatin 80 mg for 3 years, presented for consultation. She had undergone cataract and pterygium surgery and reported no known drug allergies.
The patient complained of pain in the left gluteal region and a sensation of a gluteal mass persisting for several months. On physical examination, Trendelenburg gait was noted; there was noticeable soft tissue swelling in the left gluteal region with increased tension but no palpable, well-defined masses. No signs of inflammation were observed. Joint and muscle function were normal, with no significant alterations. The FABERE maneuver was non-painful, but the FADIR maneuver elicited pain localized to the gluteal area.
Complementary Test Results (Table 1): Laboratory analysis: ESR: 80 mm/h; Hemoglobin: 12.8 g/dL; Urea: 57 mg/dL; Creatinine: 0.93 mg/dL; GOT (AST): 16 U/L; GPT (ALT): 10 U/L; GGT: 13 U/L; CRP: 1.8 mg/dL; CPK: 563 U/L; Aldolase: 3.6 U/L (<7.6). Imaging studies: Ultrasound: Altered signal in the gluteus maximus and medius muscles. MRI: Signal abnormalities with enhancement involving the gluteus maximus and medius, consistent with findings of myositis. Etiologies considered include infectious or inflammatory origins, with traumatic causes deemed less likely (Figure 1a,b).

Table 1.
Analytical values of the two cases.
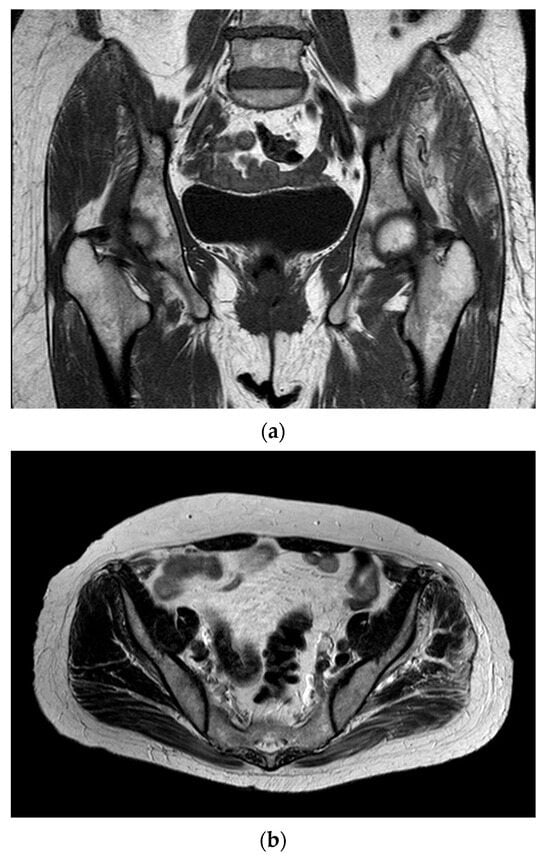
Figure 1.
FSE STIR MRI of the left thigh in coronal view demonstrating patchy feathery STIR signal intensity seen throughout the left thigh in gluteus musculature with minimal superficial perifacial STIR signal within the superficial soft tissues. (a) Coronal section and (b) transverse section.
The analytical study was expanded with a myositis profile, which revealed positive autoantibodies against HMGCR (>200 U/mL). No other myositis-related autoantibodies were detected, including Mi-2, Ku, PM-Scl100, Jo-1, SRP, PI-12, EJ, Oh, and Ro-52. Based on these results, a muscle biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis of statin-induced immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) (Figure 2), established approximately one year after symptom onset.
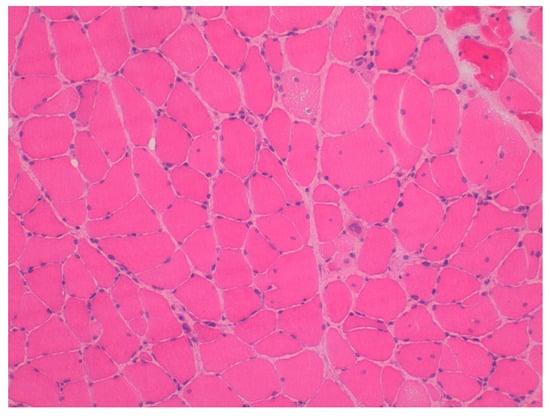
Figure 2.
Pathological image HE ×20, presence of necrotic and regenerative fibers. Very mild endomysial lymphocytic inflammation.
Treatment and Outcome: Statins were discontinued, leading to a reduction in pain and improved muscle strength in the following weeks, although weakness persisted in the thigh and gluteal muscles. Blood tests showed a decline in creatine kinase (CK) levels and liver transaminases.
Treatment was initiated with Prednisone 30 mg/day for three weeks, followed by a tapering regimen over five months. This resulted in the resolution of pain and swelling, with full recovery of functionality. The corticosteroid was then discontinued.
The patient has remained asymptomatic, with no recurrence of muscle symptoms for the past three years.
Case 2.
A 76-year-old woman with a personal history of dyslipidemia, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease was being treated with atorvastatin 20 mg daily as secondary prevention following an ischemic stroke a year earlier.
She presented to our clinic with complaints of pain, swelling, and functional impairment preventing full extension of the left elbow that had persisted for several months. Additionally, she reported intermittent symptoms of paresthesia and dysesthesia in all fingers of the ipsilateral hand.
Physical examination revealed swelling in the proximal region of the left forearm with an increase in perimeter, though the swelling was poorly defined. Muscle strength and joint range of motion were otherwise unaffected.
An ultrasound suggested a possible intramuscular hematoma due to a rupture of the proximal third of the brachioradialis muscle. The patient was referred to the Rehabilitation Service and received local treatment, which provided temporary and slight improvement.
After one year, swelling and functional impairment persisted, prompting additional analytical and imaging studies:
Laboratory analysis (Table 1): ESR: 61 mm/hr; Hemoglobin: 12.8 g/dL; Urea: 57 mg/dL; Creatinine: 0.93 mg/dL; GOT (AST): 8.9 U/L; GPT (ALT): 11 U/L; GGT: 13 U/L; CRP: 1.6 mg/dL; CPK: 343 U/L; Aldolase: 3.5 U/L (<7.6). Myoglobin: 2375 μg/L Imaging studies: Serology tests: Negative for hepatitis, Epstein–Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and Lyme disease. Autoimmune markers: Negative for antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) and extractable nuclear antigen antibodies (anti-ENAs).
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: Signal alteration with enhancement mainly in the flexor carpi radialis muscle. Findings in relation to myositis (Figure 3).
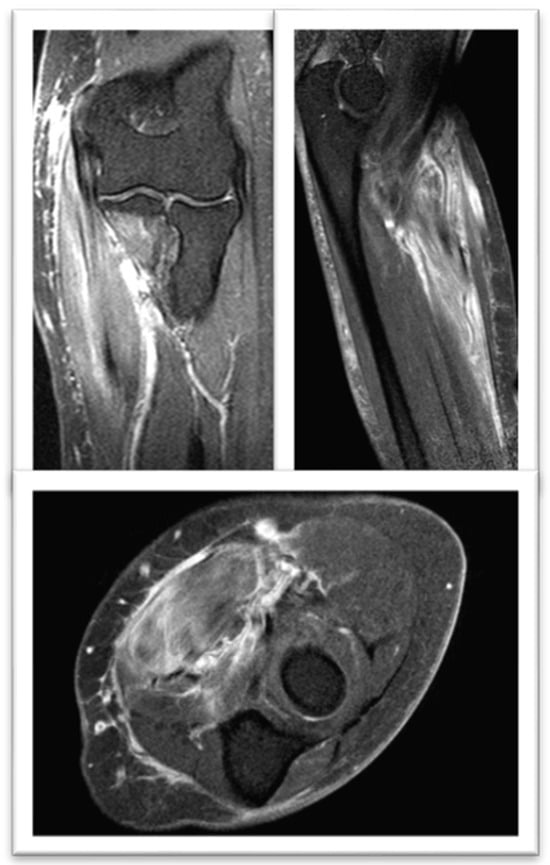
Figure 3.
FSE STIR MRI of the left thigh in coronal view demonstrating patchy feathery STIR signal intensity seen throughout the left proximal third of the left brachioradialis muscle.
An analytical study was completed with the myositis profile: IMNM secondary to statins was confirmed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with positive autoantibodies (AK) against HMGCR (>200 U/mL).
Given the findings, it was decided to perform a muscle biopsy, which showed necrotizing myopathy with the regeneration of muscle fibers, a large number of necrotic muscle fibers, and few inflammatory cells, as in Figure 2, compatible with necrotizing inflammatory myopathy. There was marked diffuse overexpression of HLA/MHC-I on the sarcolemma (Figure 4).
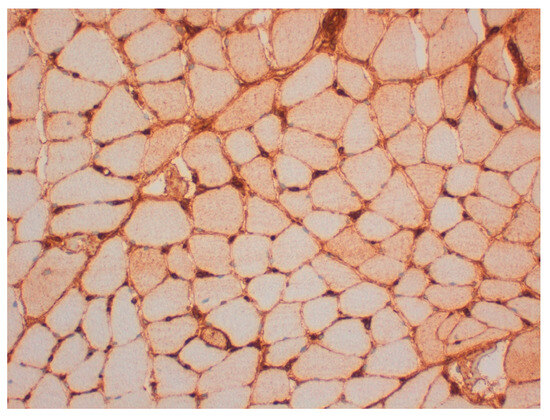
Figure 4.
HLA: (MHC-I 20x) marked diffuse overexpression of HLA/MHC-I on the sarcolemma.
Given the diagnostic criteria of IMNM secondary to statins, it was decided to withdraw cholesterol-lowering treatment. After three months, despite the improvement in her symptoms, and the altered signal in the affected muscles in the control MRI (Figure 5), the persistence of muscle weakness did not improve and the CK values increased, so treatment was started with prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day.
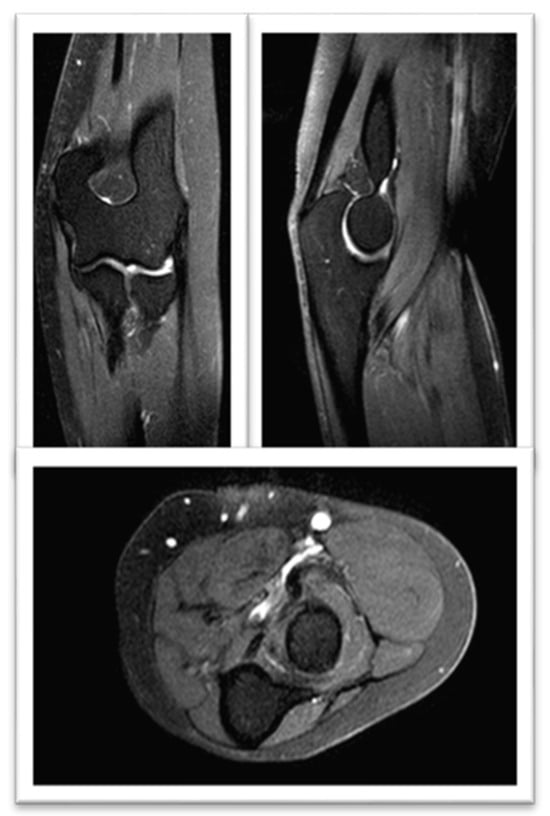
Figure 5.
FSE STIR MRI of the left thigh in coronal view at three months treatment, demonstrating normal STIR signal intensity seen throughout the left proximal third of the left brachioradialis muscle.
After several years of changing lipid-lowering treatments, she remains asymptomatic.
3. Discussion
Statins, hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A-reductase (HMGCR) inhibitors, significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and are generally safe but are associated with muscle side effects, which are usually transient [9].
Statins are among the most effective treatments for the primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Since the introduction of lovastatin in 1987, an estimated 25 million patients worldwide use these drugs. However, statin-induced myopathy (SIM) is a known adverse reaction that limits their use [4]. Myalgia caused by statin use is more common and challenging to quantify, affecting an estimated 2–20% of treated patients
Most statins have been found to possess the potential to cause muscle damage [7]. Myalgia is the most frequently reported and limiting symptom of statin use [8]. Muscle symptoms, especially at high doses, may be more common and impactful on daily life than previously recognized. Clinical signs of myopathy include pain, weakness, stiffness, and muscle cramps, which may or may not be associated with elevations in serum CK levels [1,2,3].
In addition to the described muscular involvement, the incidence of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) is estimated at 9–14 cases per 100,000 exposed patients [6] and, in contrast, IMNM associated with statins is exceptionally rare, at 2–3 per 100,000 treated patients [10]. A review of patients with IMNM revealed that, unlike statin-induced rhabdomyolysis, which typically occurs early in treatment, IMNM symptoms emerged after a median of 38–40 months on statin treatment [5]; this finding suggests that long-term exposure to statins is likely to trigger an autoimmune response in most cases [11].
Myositis has been reported in 0.5% of patients, particularly those on high doses of statins. The mechanism by which statins induce toxicity is not fully understood. Statins inhibit the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a key step in cholesterol synthesis. They also reduce the synthesis of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), which plays an essential role in muscle cell energy production. It is hypothesized that this reduction in CoQ10 may contribute to muscle damage. Treatment with simvastatin (10–40 mg daily for over 12 months) has been shown to reduce CoQ10 levels and impair mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation capacity in skeletal muscle. Regarding the pathophysiology of IMNM, it is not entirely understood. Current hypotheses suggest that muscle damage is mediated by anti-HMGCR antibodies, which target the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme expressed in muscle cells [12]. This enzyme becomes more abundant in muscle cells after statin use. The human leukocyte antigen DRB1×11:01 allele has been associated with a higher incidence of anti-HMGCR antibodies, suggesting a genetic predisposition to this condition.
Some statins, particularly atorvastatin [12], are more frequently associated with IMNM compared to others. Pravastatin and fluvastatin, which are more hydrophilic and have lower muscle penetration, appear to carry a lower risk. Additionally, these statins interact less with other medications as they are not extensively metabolized through CYP3A4.
Risk factors for statin-associated myopathy include hypothyroidism, acute or chronic renal failure, obstructive liver disease, and the use of certain medications or substances such as alcohol. Some authors suggest that genetic factors and ethnicity also influence its appearance as a predisposing element; for example, some authors suggest that Chinese patients take lower doses, particularly of simvastatin [8], although there is no evidence or epidemiological study in that country that shows greater affectation in this race.
The European Neuromuscular Centre criteria recognize anti-SRP myopathy, anti-HMGCR myopathy, and autoantibody-negative IMNM as three distinct subtypes of IMNM. Anti-HMGCR myopathy is a distinct subtype of IMNM, often associated with statin exposure and linked to HLA-DRB111:01 and HLA-DRB107:01. The CK levels may not always reflect disease activity, as muscle strength recovery can lag behind biochemical improvement [6,13].
The clinical presentation of anti-HMGCR myopathy includes subacute, progressive, symmetrical muscle weakness with markedly elevated CK levels, which persist despite statin discontinuation [14]. Medical providers should consider IMNM in statin-exposed patients presenting with proximal muscle weakness and very high CK levels, even after discontinuing statins. The asymmetric presentation in our patients, in addition to being a peculiarity, suggests localized rather than systemic involvement. We do not know why the antibody lesion affects one muscle group and not another in an asymmetrical manner.
Myalgia may or may not be present: approximately one-third of patients may experience myalgia and dysphagia [15]. CK levels are correlated with muscle strength and can serve as surrogate markers of disease activity, although serum CK levels may not accurately reflect disease activity [13].
Muscle MRI has only limited value in diagnosing patients with IMNM because it discriminates poorly between patients with IMNM compared to other types of myositis; Intramuscular hyperintensities on the STIR sequences reflect active muscle edema associated with inflammation or myofiber necrosis. Muscle MRI may be a useful tool for monitoring the evolution of muscle disease over time [5,6,13], but it is impossible to make a differential diagnosis if it is not supported by a clinical history and complementary laboratory studies.
The detection of anti-HMGCR autoantibodies is diagnostic, with high sensitivity and specificity for statin-induced IMNM (94.4% and 99.3%, respectively). These antibodies are not associated with self-limited statin myopathy or genetic muscle diseases [6,13].
In patients with persistent muscle weakness despite statin discontinuation, testing for anti-HMGCR antibodies is recommended to differentiate this condition from more common statin-related myotoxicities. For antibody-negative cases, alternative diagnoses should be considered.
Histopathological findings typically include necrotic and regenerating muscle fibers with minimal inflammation [16]. Other characteristic findings include the upregulation of MHC class I in muscle fibers and the deposition of membrane attack complexes on blood vessels and non-necrotic muscle fibers [17].
The differential diagnosis includes other inflammatory myopathies, metabolic and genetic muscle disorders, and toxic statin myopathy [18]. For example, dermatomyositis can be ruled out by the absence of skin lesions and perifascicular atrophy on biopsy. The absence of significant endomysial mononuclear infiltrates makes polymyositis less likely, while the lack of vacuoles excludes inclusion body myositis.
Prompt and immediate discontinuation of the statin drug is required if the patient is being treated for IMNM [9]. Treatment for IMNM typically requires immunosuppression in addition to discontinuing statins [19]. High-dose corticosteroids are often used initially, followed by steroid-sparing agents such as mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, or methotrexate. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is effective, particularly in HMGCR IMNM, and may even be used as a monotherapy. In refractory cases, rituximab has shown promise [20].
Patients often require prolonged immunosuppressive therapy, and relapses are common during tapering. The optimal treatment duration remains unknown [13], but consensus suggests maintaining the lowest effective steroid dose and tapering steroid-sparing agents after at least two years of disease control. Chronic IVIG therapy may be necessary for many patients [19].
Unfortunately, clinical trials are lacking, and treatment strategies rely on observational studies and expert opinion [21,22]. Approximately 50% of patients continue to experience muscle weakness after two years of treatment [23]. Younger patients tend to have worse prognoses and more severe disease.
4. Conclusions
Statin-associated immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy is a rare form of autoimmune inflammatory myopathy. Unlike statin self-limited myopathy, it is more severe and persistent despite the withdrawal of statins. Clinically, it is characterized by muscle weakness and elevated CK levels. In the last decade, an autoantibody against hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase has been identified, which is diagnostic of statin-triggered immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. The optimal treatment strategy is unclear, but early and intensive immunosuppression has been shown to be effective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A.M.F.; methodology, L.A.M.F.; software, L.A.M.F.; validation, L.A.M.F. and C.F.P.; data curation, L.A.M.F. and C.F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.M.F. and B.S.M.T.; writing—review and editing, C.F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval of this study was waived due to the fact that it involved two clinical cases under regulated medical care and in accordance with the current knowledge of science. Authorization for the publication of their clinical episode was requested from the patients.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study, and written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon request due to restrictions (e.g., privacy, legal or ethical reasons).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Koppel, C. Clinical features, pathogenesis and management of drug-induced rhabdomyolysis. Med. Toxicol. Adverse Drug Exp. 1989, 4, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaist, D.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Huerta, C.; Hallas, J.; Sindrup, S.H. Lipid-lowering drugs and risk of myopathy: A population-based follow-up study. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.D.; Clarkson, P.; Karas, R.H. Statin-associated myopathy. JAMA 2003, 289, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, T.; Wagner, H. Immunmedierad nekrotiserande myopati utlöst av statinbehandling [Two cases of statin-induced immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy]. Lakartidningen 2021, 118, 21110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Casal-Dominguez, M.; Mammen, A.L. Statins: Pros and cons. Med. Clin. 2018, 150, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Casal-Dominguez, M.; Mammen, A.L. Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Baker, S.K.; Jacobson, T.A.; Kopecky, S.L.; Parker, B.A. An assessment by the Statin Muscle Safety Task Force: 2014 update. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, C.H.; Yaakub, A.; Wang, M.C.L.; Shim, S.A.; Chong, P.L.; Khalil, M.A.M.; Telisinghe, P.U.; Lim, K.C.; Tan, J.; Chong, V.H. Refractory Statin-Induced Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myositis: Challenges and Perils in Its Management. Cureus 2022, 14, e24778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuing, W.J.; Dadhania, F.B.; Bankole, A.A. Statin-Related Necrotizing Autoimmune Myositis: More Than Myalgia. Cureus 2022, 14, e22654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammen, A.L. Statin-Associated Autoimmune Myopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, P.; Lahouti, A.H.; Paik, J.J.; Albayda, J.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Bichile, T.; Lloyd, T.E.; Danoff, S.K.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Mammen, A.L.; et al. Statin-Induced Anti-HMGCR-Associated Myopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisrimaneepan, N.; Thongpiya, J.; Yingchoncharoen, P.; Saowapa, S. An atorvastatin-induced positive anti-HMGCR immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy case. Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Casal-Dominguez, M.; Carrino, J.A.; Lahouti, A.H.; Basharat, P.; Albayda, J.; Paik, J.J.; Ahlawat, S.; Danoff, S.K.; Lloyd, T.E.; et al. Thigh muscle MRI in immune-mediated necrotising myopathy: Extensive oedema, early muscle damage and role of anti-SRP autoantibodies as a marker of severity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Amato, A.A. Management of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Muscle Nerve. 2024, 70, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milone, M. Diagnosis and Management of Immune-Mediated Myopathies. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Abu-Abaa, M.; Mousavi, F. Seronegative Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e27824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vlekkert, J.; Maas, M.; Hoogendijk, J.E.; De Visser, M.; Van Schaik, I.N. Combining MRI and muscle biopsy improves diagnostic accuracy in subacute-onset idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Muscle Nerve. 2015, 51, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.; Nadais, G.; Pinto, M.; Taipa, R.; Costa, L.; Pimenta, S. Progressive proximal muscle weakness with subacute onset in an elderly patient: A case report. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 76, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirlis, E.; Obholz, J.; Eineichner, T.; Adio, B. Correction: A Case of Suspected Statin-Related Delayed Onset Necrotizing Myositis. Cureus 2022, 14, c62, Erratum in Cureus 2022, 14, e22893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon-Cardinal, O.; Allenbach, Y.; Soulages, A.; Rigolet, A.; Hervier, B.; Champtiaux, N.; Monzani, Q.; Solé, G.; Benveniste, O. Rituximab in the Treatment of Refractory Anti-HMGCR Immune-mediated Necrotizing Myopathy. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeding, E.; Tiniakou, E. Therapeutic management of immune-mediated necrotizing myositis. Curr. Treatm. Opt. Rheumatol. 2021, 7, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Brady, S.; Kuttikat, A. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of immune-mediated necrotising myopathy (IMNM) in a patient on long-term statins. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upreti, S.; Fayyaz, B.; Bongu, R.P. Anti-HMG-CoA reductase myopathy, an undesirable evolution of statin induced myopathy: A case report. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2019, 9, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).