Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors of Malignant Tumors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
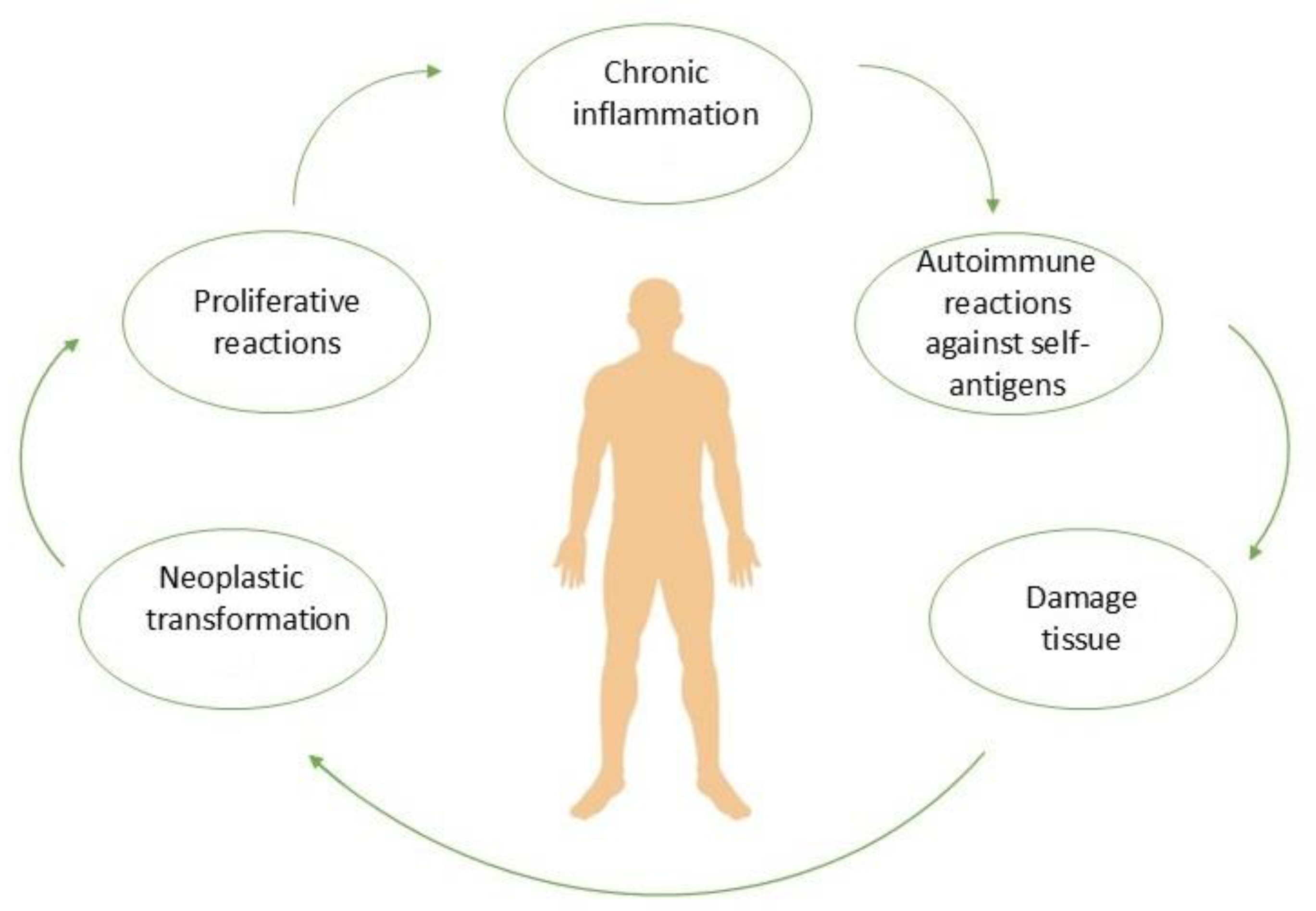
2. Pathogenesis
3. Epidemiology
4. Protective Factors of Malignant Tumors Associated with SLE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladouceur, A.; Tessier-Cloutier, B.; Clarke, A.E.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Gordon, C.; Hansen, J.E.; Bernatsky, S. Cancer and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 46, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.E.; Pooley, N.; Marjenberg, Z.; Langham, J.; Nicholson, L.; Langham, S.; Embleton, N.; Wang, X.; Desta, B.; Barut, V.; et al. Risk of Malignancy in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tselios, K.; Gladman, D.D.; Sheane, B.J.; Su, J.; Urowitz, M. All-Cause, Cause-Specific and Age-Specific Standardised Mortality Ratios of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Ontario, Canada over 43 Years (1971–2013). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariniemi, S.; Rantalaiho, V.; Virta, L.J.; Kautiainen, H.; Puolakka, K.; Elfving, P. Malignancies among Newly Diagnosed Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients and Their Survival. Lupus 2022, 31, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, W. Exploring the Causality and Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Breast Cancer Based on Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Data Analyses. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1029884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Jung, S.Y.; Jang, E.J.; Cho, S.K.; Sung, Y.K. Increased Risk of Malignancy in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, M.; Salmaso, L.; Barbiellini Amidei, C.; Fedeli, U.; Bellio, S.; Iaccarino, L.; Doria, A.; Saia, M. Mortality and Causes of Death in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus over the Last Decade: Data from a Large Population-Based Study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 112, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of Health. Cell 2021, 184, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Chan, T.A.; Kroemer, G.; Wolchok, J.D.; López-Soto, A. The Hallmarks of Successful Anticancer Immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahouel, K.; Younes, L.; Danilova, L.; Giardiello, F.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Groopman, J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Geman, D.; Tomasetti, C. Revisiting the Tumorigenesis Timeline with a Data-Driven Generative Model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, J.; Paillet, J.; Plantureux, C.; Kroemer, G. Beneficial Autoimmunity and Maladaptive Inflammation Shape Epidemiological Links between Cancer and Immune-Inflammatory Diseases. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Mou, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. Identification of Monocyte-Associated Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Their Pan-Cancer Analysis. Lupus 2023, 32, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Flood, K.; Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Clarke, A.E. A Review on SLE and Malignancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 373–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. Should Mutant TP53 Be Targeted for Cancer Therapy? Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, J.P.; Bonavita, E.; Chakravarty, P.; Blees, H.; Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Sammicheli, S.; Rogers, N.C.; Sahai, E.; Zelenay, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. NK Cells Stimulate Recruitment of CDC1 into the Tumor Microenvironment Promoting Cancer Immune Control. Cell 2018, 172, 1022–1037.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markmann, C.; Bhoj, V.G. On the Road to Eliminating Long-Lived Plasma Cells—"are We There Yet?”. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 303, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiß, C.; Steinmann, S.; Lohse, A.W.; Binder, M. B Cells in Autoimmune Hepatitis: Bystanders or Central Players? Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Li, S.; Fu, X.Q.; Zhao, Z.J.; Xing, S. Bioinformatics Analyses of Combined Databases Identify Shared Differentially Expressed Genes in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the Immune System in Cancer: From Tumor Initiation to Metastatic Progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finisguerra, V.; Di Conza, G.; Di Matteo, M.; Serneels, J.; Costa, S.; Thompson, A.A.R.; Wauters, E.; Walmsley, S.; Prenen, H.; Granot, Z.; et al. MET Is Required for the Recruitment of Anti-Tumoural Neutrophils. Nature 2015, 522, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showalter, A.; Limaye, A.; Oyer, J.L.; Igarashi, R.; Kittipatarin, C.; Copik, A.J.; Khaled, A.R. Cytokines in Immunogenic Cell Death: Applications for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cytokine 2017, 97, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, L.; O’Dwyer, T.; Petri, M. Management Strategies and Future Directions for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.; Delatorre, N.; Hurst, C.; Rodgers, K.E. Targeting the Protective Arm of the Renin-Angiotensin System to Reduce Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Related Pathologies in MRL-Lpr Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krovi, S.H.; Kuchroo, V.K. Activation Pathways That Drive CD4+ T Cells to Break Tolerance in Autoimmune Diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 307, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Noel, F.; Grandclaudon, M.; Massenet-Regad, L.; Michea, P.; Sirven, P.; Faucheux, L.; Surun, A.; Lantz, O.; Bohec, M.; et al. PD-L1 and ICOSL Discriminate Human Secretory and Helper Dendritic Cells in Cancer, Allergy and Autoimmunity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Policheni, A.N.; Teh, C.E.; Robbins, A.; Tuzlak, S.; Strasser, A.; Gray, D.H.D. PD-1 Cooperates with AIRE-Mediated Tolerance to Prevent Lethal Autoimmune Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120149119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thien, A.; Prentzell, M.T.; Holzwarth, B.; Kläsener, K.; Kuper, I.; Boehlke, C.; Sonntag, A.G.; Ruf, S.; Maerz, L.; Nitschke, R.; et al. TSC1 Activates TGF-β-Smad2/3 Signaling in Growth Arrest and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-H.; Oh, A.-Y.; Park, S.; Kang, S.-M.; Yoon, M.-H.; Woo, T.-G.; Hong, S.-D.; Hwang, J.; Ha, N.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; et al. Loss of NF2 Induces TGFβ Receptor 1-Mediated Noncanonical and Oncogenic TGFβ Signaling: Implication of the Therapeutic Effect of TGFβ Receptor 1 Inhibitor on NF2 Syndrome. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bian, Y.; Contag Wise, S.; Burnett, J.; Coupar, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. TGF-β and NF-ΚB Signal Pathway Cross-Talk Is Mediated through TAK1 and SMAD7 in a Subset of Head and Neck Cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.K.-K.; Chung, J.Y.-F.; Tang, P.C.-T.; Chan, A.S.-W.; Ho, J.Y.-Y.; Lin, T.P.-T.; Chen, J.; Leung, K.-T.; To, K.-F.; Lan, H.-Y.; et al. TGF-β Signaling Networks in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2022, 550, 215925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-M.; Tang, P.M.-K.; Lian, G.-Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Huang, X.-R.; To, K.-F.; Lan, H.-Y. Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy with Smad3-Silenced NK-92 Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the NFκB-Signaling Pathway in Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaptulbarova, K.A.; Tsyganov, M.M.; Pevzner, A.M.; Ibragimova, M.K.; Litviakov, N.V. NF-KB as a Potential Prognostic Marker and a Candidate for Targeted Therapy of Cancer. Exp. Oncol. 2020, 42, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzella, D.; Pescatore, A.; Capece, D.; Vecchiotti, D.; Ursini, M.V.; Franzoso, G.; Alesse, E.; Zazzeroni, F. Life, Death, and Autophagy in Cancer: NF-ΚB Turns up Everywhere. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Follicular Lymphoma. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Locquenghien, M.; Rozalén, C.; Celià-Terrassa, T. Interferons in Cancer Immunoediting: Sculpting Metastasis and Immunotherapy Response. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhu, B.; Chen, D. Type I Interferon-Mediated Tumor Immunity and Its Role in Immunotherapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocher, A.M.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Interferon-γ: Teammate or Opponent in the Tumour Microenvironment? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilmen, G.; Glon, D.; Siracusano, G.; Lussignol, M.; Shao, Z.; Hernandez, E.; Perdiz, D.; Quignon, F.; Mouna, L.; Poüs, C.; et al. BHRF1, a BCL2 Viral Homolog, Disturbs Mitochondrial Dynamics and Stimulates Mitophagy to Dampen Type I IFN Induction. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1296–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackov, G.; Tavakoli Zaniani, P.; Colomo del Pino, S.; Shokri, R.; Monserrat, J.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Martinez-A, C.; Balomenos, D. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Is Critical for IL-12/IL-18-Induced IFN-γ Production by CD4+ T Cells and Is Regulated by Fas/FasL Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymaker, C.; Johnson, D.H.; Murthy, R.; Bentebibel, S.E.; Uemura, M.I.; Hudgens, C.W.; Safa, H.; James, M.; Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Tilsotolimod with Ipilimumab Drives Tumor Responses in Anti–Pd-1 Refractory Melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1996–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cader, R.A.; Yee, A.K.M.; Yassin, A.; Ahmad, I.; Haron, S.N. Malignancy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 3551–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Peng, Z.; Lin, Z.; Lin, X.; Lin, W.; Deng, Y.; Yang, S.; Wei, S. Identification of Prognostic Genes for Breast Cancer Related to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Integrated Analysis and Machine Learning. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, P.W.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Hansen, J.E. DNA-Damaging Autoantibodies and Cancer: The Lupus Butterfly Theory. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Chan, G.; Liu, Y.; Hegan, D.C.; Dalal, S.; Dray, E.; Kwon, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Peterson-Roth, E.; et al. Targeting Cancer with a Lupus Autoantibody. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 157ra142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouceur, A.; Clarke, A.E.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Bernatsky, S. Malignancies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardenbergh, D.; Molina, E.; Naik, R.; Geetha, D.; Chaturvedi, S.; Timlin, H. Factors Mediating Cancer Risk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2022, 31, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Duan, L.; Gao, J.; Si, J.; Feng, C.; Hu, J.; Zheng, X. Bioinformatics-Based Analysis of the Roles of Basement Membrane-Related Gene AGRN in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Pan-Cancer Development. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1231611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo-Ibáñez, T.; Urruticoechea-Arana, A.; Rúa-Figueroa, I.; Martín-Martínez, M.A.; Ovalles-Bonilla, J.G.; Galindo, M.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Olivé, A.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Menor-Almagro, R.; et al. Hormonal Dependence and Cancer in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Labrecque, J.; Joseph, L.; Boivin, J.F.; Petri, M.; Zoma, A.; Manzi, S.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.; et al. Cancer Risk in Systemic Lupus: An Updated International Multi-Centre Cohort Study. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 42, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Ding, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L. Trans-Ethnic Mendelian Randomization Study of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Common Female Hormone-Dependent Malignancies. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 2609–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Foulkes, W.D.; Gordon, C.; Clarke, A.E. Breast, Ovarian, and Endometrial Malignancies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, N.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y. The Risks of Cancer Development in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.Y. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Pathogenic Link between Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, F. Cancer Occurrence after SLE: Effects of Medication-Related Factors, Disease-Related Factors and Survival from an Observational Study. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Joseph, L.; Boivin, J.F.; Costenbader, K.H.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.D.; Fortin, P.R.; Nived, O.; Petri, M.A.; et al. Lymphoma Risk in Systemic Lupus: Effects of Disease Activity versus Treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, W.C.; Ko, H.J.; Ju, J.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.H. Incidence of Cancer among Female Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Korea. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, R.; Zobbe, K.; Cordtz, R.; Haugaard, J.H.; Dreyer, L. Increased Cancer Risk in Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Compared with the General Population: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study. Lupus 2021, 30, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertz-Archambault, N.; Kosiorek, H.; Taylor, G.E.; Kelemen, K.; Dueck, A.; Castro, J.; Marino, R.; Gauthier, S.; Finn, L.; Sproat, L.Z.; et al. Association of Therapy for Autoimmune Disease with Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Zhen, K.; Wu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bi, H.; Tian, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, C. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Prostate Cancer Risk: A Pool of Cohort Studies and Mendelian Randomization Analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 9517–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, A.; Ohmori, K.; Yoneda, T.; Tsuyuoka, K.; Hasegawa, A.; Kiso, M.; Kannagi, R. Contribution of Carbohydrate Antigens Sialyl Lewis A and Sialyl Lewis X to Adhesion of Human Cancer Cells to Vascular Endothelium. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Chen, Z. Causal Associations of Hyperthyroidism with Prostate Cancer, Colon Cancer, and Leukemia: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1162224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, W.D.; Preen, D.B.; Keen, H.I.; Inderjeeth, C.A.; Nossent, J.C. Cancer Development in Patients Hospitalized with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Population-Level Data Linkage Study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 26, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfström, B.; Backlin, C.; Sundström, C.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Ekbom, A.; Lundberg, I.E. Myeloid Leukaemia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Nested Case-Control Study Based on Swedish Registers. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Yu, Z. The Relationship between Cancer and Medication Exposure in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nested Case-Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, K.; Sato, S.; Igawa, T.; Okamoto, M.; Takatani, A.; Endo, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Shimizu, T.; Sumiyoshi, R.; Koga, T.; et al. Evaluating the Safety Profile of Calcineurin Inhibitors: Cancer Risk in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from the LUNA Registry—A Historical Cohort Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Urowitz, M.B.; Hanly, J.G.; Gordon, C.; Petri, M.A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Wallace, D.J.; Bae, S.C.; Romero-Diaz, J.; et al. Cancer Risk in a Large Inception Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Cohort: Effects of Demographic Characteristics, Smoking, and Medications. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Su, Y.J.; Cheng, T.T.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiu, W.C.; Chen, T.H. Cumulative Immunosuppressant Exposure Is Associated with Diversified Cancer Risk among 14 832 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nested Case-Control Study. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Qiu, L.-J.; Hu, L.-F.; Cen, H.; Zhang, M.; Wen, P.-F.; Wang, X.-S.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Lung, Liver, Prostate, Bladder Malignancies Risk in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. Lupus 2014, 23, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.; Seo, M.S.; Hwang, I.C.; Shim, J.Y. An Updated Meta-Analysis on the Risk of Urologic Cancer in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.-H.; Kuo, C.-F.; Huang, L.H.; Huang, W.-K.; See, L.-C. Cancer Risk in Patients With Inflammatory Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Nationwide Population-Based Dynamic Cohort Study in Taiwan. Medicine 2016, 95, e3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardenbergh, D.; Naik, R.; Manno, R.; Azar, A.; Monroy Trujillo, J.M.; Adler, B.; Haque, U.; Timlin, H. The Cancer Risk Profile of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. J. Clin. Rheumatol. Pract. Rep. Rheum. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 28, e257–e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, S.W. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Is a Risk Factor for Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea. Lupus 2019, 28, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Zhang, W. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals a Protective Association between Genetically Predicted Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Renal Cell Carcinoma. Medicine 2024, 103, E37545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallbacka, K.R.; Pettersson, T.; Pukkala, E. Increased Incidence of Cancer in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Finnish Cohort Study with More than 25 Years of Follow-Up. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 47, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, A.P.; Filippucci, E.; McVeigh, C.M.; Grassi, W. An Electronic Logbook for Rheumatologists Performing Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goobie, G.C.; Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Clarke, A.E.; Centre, H.S. HHS Public Access: Malignancies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A 2015 Update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Liang, X.; Lin, X.; Lin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wei, S. Exploration of the Molecular Mechanisms, Shared Gene Signatures, and MicroRNAs between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma by Bioinformatics Analysis. Lupus 2022, 31, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Igusa, T.; Goldman, D.; Li, J.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Rosen, A.; Petri, M. Association of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Autoantibody Diversity with Breast Cancer Protection. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Qian, J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, H. Durable Benefit from Immunotherapy and Accompanied Lupus Erythematosus in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma with DNA Repair Deficiency. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Almeida Gomes, L.; Werth, A.J.; Thomas, P.; Werth, V.P. The Impact of Hormones in Autoimmune Cutaneous Diseases. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2024, 35, 2312241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.L.; Hsu, H.-T.; Weng, S.F.; Lin, Y.S. Impact of Head and Neck Malignancies on Risk Factors and Survival in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Acta Otolaryngol. 2013, 133, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Petri, M.; Manzi, S.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.; Fortin, P.R.; Ginzler, E.M.; Yelin, E.; et al. Non-Lymphoma Hematological Malignancies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Oncology 2013, 85, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadström, H.; Arkema, E.V.; Sjöwall, C.; Askling, J.; Simard, J.F. Cervical Neoplasia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide Study. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.R.S.; Ferraz, D.L.F.; de Oliveira, C.R.G.; Evangelista, K.; Silva, M.A.G.; Silva, F.P.Y.; de Silva, B.S.F. Risk and Prevalence of Oral Cancer in Patients with Different Types of Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2023, 136, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Shang, J.; Feng, X.; Yu, L.; Fan, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. Identification of the Shared Gene Signatures and Molecular Pathways in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Gene Med. 2023, 25, e3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-López, M.; Galindo, M.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Jiménez, N.; Olivé Marqués, A.; Tomero, E.; Freire, M.; Martínez-Barrio, J.; Boteanu, A.; Salgado-Perez, E.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors Associated with Lymphoma in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Wang, W.M.; Lin, S.H.; Shieh, C.C. Bidirectional Relationship between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, L.; Sheikh, M.; Kosaraju, N.; Smedby, K.E.; Bernatsky, S.; Berndt, S.I.; Skibola, C.F.; Nieters, A.; Wang, S.; McKay, J.D.; et al. Genetic Overlap between Autoimmune Diseases and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Subtypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2019, 43, 844–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, R.; Devaragudi, S.; Kaur, L.; Singh, K.; Bawa, J.; Theik, N.W.Y.; Palisetti, S.; Jain, A. SLE and Multiple Myeloma: An Underlooked Link? A Review of Case Reports from the Last Decade. J. Med. Life 2024, 17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh-Patel, A.; White, R.H.; Allen, M.; Cress, R. Cancer Risk in a Cohort of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in California. Cancer Causes Control 2008, 19, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Petri, M.; Urowitz, M.B.; Gladman, D.D.; Fortin, P.R.; Yelin, E.H.; Ginzler, E.; Hanly, J.G.; Peschken, C.; et al. Smoking Is the Most Significant Modifiable Lung Cancer Risk Factor in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Ho, C.M.; Huang, C.J.; Hsu, S.S.; Jiann, B.P.; Chen, J.S.; Huang, J.K.; Chang, H.T.; Lo, Y.K.; Yeh, J.H.; et al. Defect in Regulation of Ca2+ Movement in Platelets from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pharmacology 2005, 73, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblom-Kullberg, S.; Kautiainen, H.; Alha, P.; Leirisalo-Repo, M.; Julkunen, H. Smoking and the Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, P.; Bromberg, J. Environment, Inflammation, and Cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, M.; Gai, J.; Zhang, R.; Du, T.; Li, Q. SPOCK2 Serves as a Potential Prognostic Marker and Correlates with Immune Infiltration in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 588499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, V.; Rondaan, C.; Heijstek, M.W.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Van Assen, S.; Bijl, M.; Breedveld, F.C.; D’amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; et al. 2019 Update of EULAR Recommendations for Vaccination in Adult Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Fei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. The Five Major Autoimmune Diseases Increase the Risk of Cancer: Epidemiological Data from a Large-Scale Cohort Study in China. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Oshima, K.; Singleton, M.; Thomason, J.; Currier, C.; McCartney, S.; Singh, N. Determinants of Cervical Cancer Screening Patterns Among Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohrmann, G.; Hengstler, J.G.; Hofmann, T.G.; Endele, S.U.; Lee, B.; Stelzer, C.; Zabel, B.; Brieger, J.; Hasenclever, D.; Tanner, B.; et al. SPOC1, a Novel PHD-Finger Protein: Association with Residual Disease and Survival in Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, L. Tumour-Associated Antigens in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Clinical Manifestations and Serological Indicators. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, E.L.; Appleby, P.N.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Chan, J.M.; Chen, C.; Cohn, B.A.; Cook, M.B.; Flicker, L.; Freedman, N.D.; et al. Low Free Testosterone and Prostate Cancer Risk: A Collaborative Analysis of 20 Prospective Studies. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbs, R.W.; Malhotra, N.R.; Greenwald, D.T.; Wang, A.Y.; Prins, G.S.; Abern, M.R. Estrogens and Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandolara, T.B.; Panis, C. Neutrophil Traps, Anti-Myeloperoxidase Antibodies and Cancer: Are They Linked? Immunol. Lett. 2020, 221, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, D.; Wang, M.; Li, E.; Hou, C.; Su, Y.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X. RACGAP1 Modulates ECT2-Dependent Mitochondrial Quality Control to Drive Breast Cancer Metastasis. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 400, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, F.; He, Z.; Mei, L.; de Garibay, G.R.; Herranz, C.; García, N.; Lorentzian, A.; Baiges, A.; Blommaert, E.; Gómez, A.; et al. Modification of BRCA1-Associated Breast Cancer Risk by HMMR Overexpression. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaczek, A.J.; Markiewicz, A.; Seroczynska, B.; Skokowski, J.; Jaskiewicz, J.; Pienkowski, T.; Olszewski, W.P.; Szade, J.; Rhone, P.; Welnicka-Jaskiewicz, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of TOP2A Gene Dosage in HER-2-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2012, 17, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, K.P.; Ni, J.J.; Saavedra, H.I.; Dong, J.-T. TTK Promotes Mesenchymal Signaling via Multiple Mechanisms in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, G. KIF15 Contributes to Cell Proliferation and Migration in Breast Cancer. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Geng, M.; Ye, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. IRF7 Inhibits the Warburg Effect via Transcriptional Suppression of PKM2 in Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Q.; Peyvandi, S.; Duffey, N.; Huang, Y.T.; Barras, D.; Held, W.; Richard, F.; Delorenzi, M.; Sotiriou, C.; Desmedt, C.; et al. Type I Interferon/IRF7 Axis Instigates Chemotherapy-Induced Immunological Dormancy in Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2814–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreal, L.; Piva, M.; Fernández, S.; Revandkar, A.; Schaub-Clerigué, A.; Villanueva, J.; Zabala-Letona, A.; Pujana, M.; Astobiza, I.; Cortazar, A.R.; et al. Targeting PML in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Elicits Growth Suppression and Senescence. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1186–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampakaki, M.; Oraiopoulou, M.-E.; Tzamali, E.; Tzedakis, G.; Makatounakis, T.; Zacharakis, G.; Papamatheakis, J.; Sakkalis, V. PML Differentially Regulates Growth and Invasion in Brain Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, S. Hematological Malignancies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Prognosis—A Case-Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Zheng, X.; Chu, Y.; Xiong, S. Anti-tumor effect of anti-dsDNA autoantibodies. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2005, 27, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Ugarte, A.; Egurbide, M.V.; Garmendia, M.; Pijoan, J.I.; Martinez-Berriotxoa, A.; Aguirre, C. Antimalarials May Influence the Risk of Malignancy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, T.A.; Bansal, R.; Su, G.H.; Murphy, K.M.; Kern, S.E. Erratum: High-Throughput Measurement of the Tp53 Response to Anticancer Drugs and Random Compounds Using a Stably Integrated Tp53-Responsive Luciferase Reporter. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, G.; Dong, H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B.; Chen, X. Targeting Autophagy Augments In Vitro and In Vivo Antimyeloma Activity of DNA-Damaging Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Shang, D.; Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Xiong, J. Autophagy Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Invasion through Activation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.S.; Yeo, J.; Hwang, I.C.; Shim, J.Y. Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Malignant Tumor | SIR (95% CI) | Prevalence in SLE Compared to the General Population |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 1.18 (1.00–1.38) | 1.5 to 2 times higher risk |
| Hematologic | 3 to 4 times higher risk | |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) | 4.32 (3.4–5.47) | 4 to 5 times more often |
| Hodgkin lymphoma, lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma | 2.71 (1.68–4.36) | 2 to 3 times higher risk |
| The respiratory system | 1.53 (1.11–2.11) | |
| Lung | 1.75 (1.37–2.24) | 1.5 times higher risk; in case of smoking, the risk increases 7 times |
| Larynx | 4.22 (1.97–9.03) | 2 times higher risk |
| Oropharynx | 7.35 (1.12–48.36) | Increased risk |
| The digestive system | 1.15 (0.97–1.37) | |
| Oral | 2.69 (1.75–4.16) | 3 times higher risk |
| Oesophagus | 1.73 (1.04–2.89) | Increased risk |
| Liver | 2.81 (1.72–4.59) | 2 times higher risk |
| Gallbladder | 1.83 (1.76–1.90) | Increased risk |
| Hepatobiliary tract | 2.07 (1.37–3.12) | Increased risk |
| Stomach | 1.34 (1.05–1.72) | 1.3 times higher risk |
| Pancreatic | 1.26 (0.97–1.63) | Increased risk |
| Colorectal | 1.65 (1.23–2.22) | Increased risk |
| Anal | 5.69 (1.62–19.94) | |
| The cardiovascular system | NR | NR |
| The musculoskeletal system | NR | NR |
| The urogenital system | 3.41 (1.86–6.23) | |
| Bladder and kidney | 1.80 (1.04–3.11) | 1,5-krotnie wyższe ryzyko |
| Ovarian | 0.86 (0.68–1.10) | Reduced risk |
| Endometrial | 0.64 (0.49–0.83) | Reduced risk |
| Cervical | 1.66 (1.16–2.36) | 1.5 times higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma and squamous intraepithelial lesions |
| Vulva/vagina | 3.63 (2.54–5.20) | 3 times higher risk |
| Prostate | 0.80 (0.65–0.99) | Reduced risk |
| The nervous system and brain | 1.41 (1.02–1.93) | 1.3 times higher risk |
| The skin tumors | ||
| Nonmelanoma skin | 1.24 (0.98–1.57) | Increased risk |
| Melanoma skin | 0.69 (0.53–0.90) | Reduced risk |
| Others malignant tumors | ||
| Head and neck | NR | Increased risk |
| Thyroid | 1.50 (1.34–1.68) | 1.5 times higher risk |
| Breast | 0.87 (0.76–1.00) | Reduced risk |
| Type of Malignant Tumor | Protective Factors of Malignant Tumors | Risk Factors for Malignant Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | Immunosuppressive therapies (excluding antimalarials and steroids); cyclophosphamide; disease activity; acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) | |
| Hematologic | Antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL); immunosuppressive therapies (excluding antimalarials and steroids); cyclophosphamide; presence of BAFF, APRIL, and 3E10 antibody; TNFAIP3 or A20 rs77191406 polymorphism; increased levels of IL-6 and IL-10; EBV; | |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) | Male gender; Sjogren’s syndrome; CD40 allele rs4810485 (chromosome 20q13); HLA allele rs1270942 (chromosome 6p21.33); cyclophosphamide | |
| Hodgkin lymphoma, lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma | ||
| The respiratory system | ||
| Lung | Smoking; lung fibrosis; rs13194781 and rs1270942 (chromosome 6p21-22) | |
| The digestive system | Acetylsalicylic acid | Smoking, alcohol consumption, diet, obesity, low physical activity, diabetes, |
| Liver | HBV, HCV, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | |
| Stomach | ||
| Pancreatic | Ro60/SSA antigen reduction, acetylsalicylic acid, melatonin, statins, curcumin, and flavonoids | |
| The musculoskeletal system | The presence of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) | |
| The urogenital system | ||
| Bladder and kidney | Age, diet, low physical activity, cyclophosphamide; TNFAIP3 or A20 rs77191406 polymorphism | |
| Ovarian, Endometrial | less exposure to endogenous and/or exogenous hormones | |
| Cervical | HPV vaccination and cytology every year; | Immunosuppressive therapies (excluding antimalarials and steroids); HPV; cyclophosphamide |
| Vulva/vagina | HPV vaccination | HPV; cyclophosphamide |
| Prostate | Low levels of heat shock protein 27, reduced testosterone levels | Glucocorticosteroids |
| The skin tumors | ||
| Nonmelanoma skin | Antimalarials | Cyclophosphamide |
| Melanoma skin | Use of UV filter, avoiding solar radiation | The presence of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) |
| Others malignant tumors | ||
| Head and neck | Smoking; HPV, EBV | |
| Thyroid | Thyroid antibodies | |
| Breast | Less exposure to endogenous and/or exogenous hormones; antimalarials; presence of anti-double-stranded DNA and 5C6 antibody; regulatory T cells (Tregs); low levels of heat shock protein 27 | rs9888739 (chromosome 16p11.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blachut, D.; Przywara-Chowaniec, B.; Tomasik, A. Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors of Malignant Tumors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumato 2024, 4, 209-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040017
Blachut D, Przywara-Chowaniec B, Tomasik A. Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors of Malignant Tumors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumato. 2024; 4(4):209-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlachut, Dominika, Brygida Przywara-Chowaniec, and Andrzej Tomasik. 2024. "Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors of Malignant Tumors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" Rheumato 4, no. 4: 209-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040017
APA StyleBlachut, D., Przywara-Chowaniec, B., & Tomasik, A. (2024). Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Risk Factors of Malignant Tumors in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumato, 4(4), 209-221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040017







