Abstract
This work aimed to investigate a potential link between serum IL-1β levels in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) and their responsiveness to combined anti-IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and glucocorticoid (GC) treatments within the context of two separate clinical trials. IL-1β levels were analyzed in serum samples of two prospective clinical trials investigating tocilizumab in GCA patients using quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) based Proximity Ligation Assays (PLA). In the phase II randomized controlled trial, serum samples from five patients were quantified at two critical time points: the commencement of the trial (Week 2) and the conclusion of the trial (Week 52). In the GUSTO trial, serum samples from nine patients were similarly analyzed using PLA at Day 0 and Week 52. Furthermore, for the GUSTO trial, serum samples from 18 patients were assessed for IL-1β and IL-1RN at six time points: days 0, 3, and 10, weeks 4, 24, and 52 by a second assay (Proximity Extension Assay, PEA). PLA results from both studies indicated that IL-1β levels were below 1 pg/mL in most of the patients, resulting in notable signal deviations within the same samples. In the analysis of the GUSTO trial, both PLA and PEA exhibited similar trends in IL-1β variations among patients from day 0 to week 52. Notably, the PEA analysis did not show significant variation over time. Furthermore, we did not find a correlation of IL-1β levels with active disease as compared to remission, but interestingly, the measurement of IL-1β receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) revealed a substantial decrease over time. Our study shows that IL-1RN but not IL-1β concentration in serum samples could be directly related to anti-IL-6R treatment in patients diagnosed with GCA.
1. Introduction
Interleukin (IL)-1β is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine implicated in various diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, cardiac disease, cancer, or autoinflammatory syndromes [1]. IL-1 β is initially synthesized as an inactive precursor and requires proteolytic cleavage by the inflammasome complex to become biologically active. Once liberated, it acts as a potent mediator, triggering a cascade of events that coordinate both innate and adaptive immune responses thereby causing a potent pro-inflammatory response. The release of IL-1β prompts the secretion of other pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and IL-6. Notably, IL-6 subsequently induces the production of C-reactive protein (CRP), further amplifying the inflammatory response. Uncontrolled action of these cytokines exacerbates the inflammatory reaction, resulting in disease, sepsis, and eventually death. Therefore, understanding the interplay between these cytokines and their inhibitory counterparts is crucial for the development of targeted therapies for various inflammatory conditions.
Anakinra [2], the IL-1 receptor antagonist, canakinumab [3], a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-1β, and rilonacept [4], an Fc fusion molecule containing parts of the IL-1R and the IL-1R accessory protein, have all demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials for a range of conditions including rheumatoid arthritis [5], cryopyrin-associated syndromes (CAPS) [6], familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) [7], Still’s disease [8] or COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure and pneumonia [9]. Furthermore, a large randomized clinical trial (RCT) of canakinumab has shown modest efficacy in the context of cardiovascular disease [10].
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common vasculitis in individuals over the age of 50, affecting medium and large-sized arteries. GCA is characterized by the presence of infiltrates in arterial walls, composed of activated T cells, macrophages, and giant cells, which release various chemokines, cytokines, growth factors, and enzymes. Chemokines such as CCL9 and CCL21 trigger the recruitment of immune cells, while inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) induce local vascular injury and contribute to systemic inflammatory response [11]. Additionally, growth factors like platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and VEGF promote neo-angiogenesis and the activation of vascular cells, ultimately leading to hyperplasia. Enzymes like matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) contribute to tissue damage, facilitating the migration and activation of immune cells and resulting in luminal narrowing [12].
Currently, glucocorticoids are the standard treatment for GCA preventing serious vascular complications. However, this treatment is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. IL-6, produced by granuloma cells in GCA, plays a key role in the development of systemic symptoms in GCA [13]. Tocilizumab (TCZ), a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-6 receptor, has been shown to induce and maintain remission in patients with GCA. In a first phase 2, double-blind, randomized-controlled trial (RCT) [14], it was demonstrated that incorporating TCZ as an adjunct therapy in GCA could reduce the use of glucocorticoids by at least 50%. Based on the successful phase 3 RCT, TCZ became approved for the treatment of GCA [15]. The efficacy of this drug was further examined in the follow-up GUSTO (GCA treatment with ultra-short glucocorticoids and TCZ) trial [16] for patients with newly diagnosed GCA. Despite the encouraging results of this therapy, studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as described by Villiger’s group [17] have documented the persistency of inflammation, the clinical significance of which remains uncertain. These findings may suggest the presence of subclinical disease activity that has yet to be fully detected [18]. As conventional markers of systemic inflammation such as CRP and ESR are under the control of IL-6, blockade of this pathway using TCZ renders the markers unreliable. Therefore, a broad range of biomarkers was subsequently analysed and proposed to mirror disease activity. A recent proteome analysis identified chemokines as potential candidates [19].
Tocilizumab which targets the IL-6 pathway might potentially lead to a dysregulation of other inflammatory pathways, including the IL-1β pathway [20]. This opens the possibility of using serum IL-1β levels as a marker for subclinical disease activity in TCZ-treated patients. However, the serum concentration of IL-1β is generally very low and difficult to assess (on average it is between 0 to 5 pg/mL) [21].
The main objective of this study was to perform a comparative analysis of results obtained from two highly sensitive methodologies: Proximity Extension Assay (PEA) [22], and Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA) [23], for detecting IL-1β. These selected immunoassays offer a combination of highly specific antibody-antigen binding and the integration of reliable genomic tools like quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) technology. PLA serves as a quantification tool for IL-1β detection, allowing us to assess a patient’s inflammation state by detecting low protein levels using small sample sizes. This technology utilizes two antibodies, requiring a dual binding event, thereby minimizing the possibility of false positive results and reducing background noise. After binding, the proximity of the two ends of the nucleotides permits a second hybridization with a splint that is subsequently amplified. In PEA, two single-stranded oligonucleotides contain complementary sites for pair-wise annealing with each other, allowing extension by a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase. This method allows us to determine IL-1β serum level changes over time by comparing multiple samples with high sensitivity and specificity. Similar to PLA, PEA used PCR amplification for IL-1β detection. One of the significant advantages of the PEA method over PLA is the replacement of the ligation event with a DNA polymerization step and its ability to approach multiplexing [24]. However, it lacks the capability of quantification, which is a clear limitation if one wants to establish the inflammatory state of patients.
This study aims to establish a possible correlation between the concentration levels of IL-1β in serum samples from both the phase II RCT and GUSTO trials and the deliberate progression or remission of the disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phase II RCT for GCA
The phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University Hospital Bern, Switzerland, and recruited patients over 50 years old who were diagnosed with GCA as described [14]. A total of 30 patients were enrolled, including those with new-onset or relapsing disease, in this clinical trial and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive oral glucocorticoids and either 8 mg of TCZ/kg of body weight or placebo. The regimen of administration included 13 TCZ infusions administered at 4-week intervals intravenously until week 52. Prednisolone therapy started with a dose of 1 mg/kg per day and was continuously reduced until 0 mg by the end of the trial. Additionally, patients were allowed to receive prednisolone up to 1 mg/kg body weight for a maximum of 10 days between inclusion in the trial and the first infusion. In the TCZ group, 18 patients completed the follow-up until week 52 while 2 patients withdrew from the trial before week 12. Among the placebo group, 5 patients completed the follow-up by week 52, with 3 patients withdrawing before week 12 and 2 patients withdrawing between week 12 and week 52. Blood samples were collected from 4 patients of the TCZ group and 1 patient from the placebo group, both at weeks 2 and 52, for measuring IL-1β.
2.2. The GUSTO Trial
In this investigator-initiated, single-arm, single-center, open-label clinical trial a total of eighteen patients with newly diagnosed GCA were enrolled [16]. All patients received 500 mg methylprednisolone intravenously for three consecutive days. After discontinuing glucocorticoid treatment, TCZ was administered intravenously at a dosage of 8 mg/kg body weight, followed by weekly subcutaneous TCZ injections (162 mg dose) starting from day 10 and continuing until week 52. The primary endpoint assessed the proportion of patients who had remission within 31 days and showed no relapse at week 24. Out of the 18 patients enrolled, 13 completed the follow-up until week 52, while 5 patients discontinued the trial (2 due to adverse events and 3 due to non-response). Blood samples were collected at day 0 and week 52 for measuring IL-1β.
2.3. Measurement of Serum IL-1β Using Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
To enable the quantification of IL-1β in the serum samples, we employed the Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA). This assay was chosen because it allows the investigation of antibody-antigen interaction with a high degree of specificity and sensitivity. It effectively combines the specificity of the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the sensitivity of quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR). This combination enables the detection of low levels of proteins even when using small sample sizes, reducing the need for extensive sample dilutions.
In this measurement, we used fourteen serum samples from both the phase II RCT (5 samples) and the GUSTO trial (9 samples) at day 0 and week 52 were quantified for IL-1β using a cytokine-specific ProQuantum immunoassay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). This assay was conducted according to the manufacturer’s protocol, as illustrated in Figure 1.
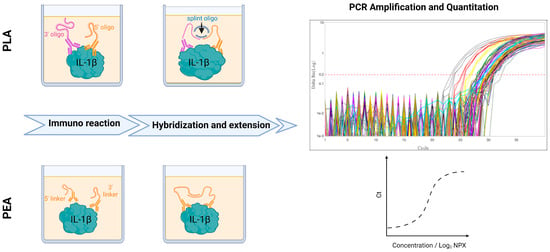
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of IL-1β quantification in serum using PLA and PEA. PLA-Proximity Ligation assay. Two antibodies, each tagged with a short DNA sequence bind to two distinct epitopes on IL-1β within serum samples. This binding brings the two DNA sequences in close proximity. The addition of a ligation mixture containing DNA ligase and a third splint oligonucleotide connector allows the connection of the two ends of the conjugated oligonucleotide. The ligation product is subsequently amplified by 40 cycles of PCR. PEA-Proximity Extension Assay (PEA) is an alternative to PLA, the ligation step is replaced by a DNA polymerization step. Single-strand oligonucleotides linked to antibodies hybridize together, allowing extension by a DNA polymerase. This extension process generates a template for amplification through PCR assay. The amount of fluorescence is directly proportional to the quantity of PCR product molecules that are generated. The results are expressed in NPX (arbitrary unit in log2 scale) and are proportional to the presence of each gene in the sample.
To establish a standard curve, an IL-1β sample, included in the kit at a concentration of 5000 pg/mL, was used. This standard sample was first diluted at 100 pg/mL and then to 1:3 dilutions. Before analysis, serum samples were diluted five-fold and then diluted 1:2 with the antibody-conjugate mixture included in the kit.
To perform qPCR procedure, the samples diluted at 1:5 in assay dilution buffer (5 μL), were added to a 96-well plate containing a 5 μL antibody conjugation mixture and to a 40 μL reaction mixture with ligase, as provided in the kit. The samples were amplified through 40 cycles of TaqMan fluorescence-based qPCR. The amount of amplified DNA was measured after each cycle via fluorescent dyes whose fluorescence is directly proportional to the amount of PCR molecules amplified.
2.4. Measurement of Serum IL-1β Using Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
Serum samples were collected according to standard operating procedures (processed 30 min after venipuncture, centrifugation at 2730 r.p.m. for 10 min). Samples were obtained at the following time points: before treatment or with minimal prior GC exposure (referred to as day 0), at day 3 (following GC treatment), and during TCZ monotherapy at day 10 and weeks 4, 24, and 52.
All 13 patients who completed the study were analyzed at 6 time points. Additionally, two samples (day 0, week 4) from one patient who discontinued the study due to diverticulitis after achieving remission, and six samples (day 0, 3, and 10, each) from two patients who discontinued the study after day 10 due to persistent cranial symptoms were included. In total, 86 samples were assessed [19].
Serum samples were analyzed using Olink Explore 1536 platform (Uppsala, Sweden), a proximity extension assay (PEA) multiplex immunoassay system capable of capturing 1463 proteins. Initially, in the PEA method, specific probes are mixed with the serum samples. During sample incubation, all proximity probe pairs bound their corresponding antigens, which brings the probe oligonucleotides in close proximity for hybridization. The addition of a DNA polymerase led to an extension and joining of the two oligonucleotides, forming a PCR template. Each DNA sequence was then detected and quantified using specific primers in microfluidic qPCR.
2.5. Statistics
All statistical analyses for PLA measurements were conducted using ThermoFisher software, calculating the calibration curve for the standards used in the experiment, and fitting the experimental points from each serum sample. PEA levels of proteins are displayed as log2 normalized protein expression (NPX), a doubling in the relative protein concentration equals a unit increase.
3. Results
3.1. Proof of Concept: Analysis of IL-1β in Phase II RCT for GCA Using PLA
In our study, we first examined serum samples of patients participating in the phase II RCT for GCA. Four out of the five patients were assigned to the anti-IL-6R treatment group (3/4 with new-onset GCA, 1/4 with relapsing GCA) and 1/5 to the placebo group (Figure 2B). We first established a standard curve by serially diluting IL-1β protein, starting with a concentration of 100 pg/mL and decreasing to 0.137 pg/mL. Subsequently, we used this standard curve to quantify the levels of IL-1β in the serum samples. Our analysis of the serum samples, conducted at week 2 after the trial’s start and at week 52, at the trial’s conclusion, consistently revealed IL-1β levels below 1pg/mL for four of the patients. In contrast, one patient (patient no. 2) exhibited a measured concentration of 4 pg/mL at week 52 (Figure 2C). However, we found no clear evidence that the presence of increased IL-1β in the serum sample of this patient had any clinical significance.
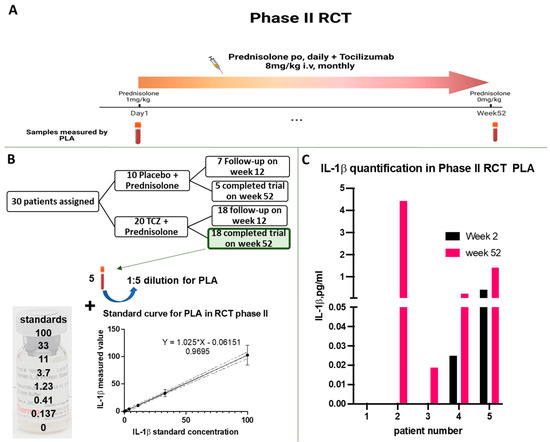
Figure 2.
Analysis of IL-1β amount in phase II RCT for GCA by PLA. (A) Dose regimen and indication of the time points at which serum samples were collected for analysis. (B) Out of 30 patients, 5 individuals from the TCZ or placebo group who completed the 52-week follow-up were selected for analysis. Serum samples were diluted 1:5 for PLA analysis and results were interpolated using the standard curve created by analysing indicated standard concentrations. (C) Analysis of IL-1β concentration levels in serum samples of the phase II RCT for GCA. The Limit of Detection (LOD) for the assay was achieved for the standards at 0.68 pg/mL and samples displayed minimal concentration variation from the beginning to the end of the trial.
3.2. Comparison of IL-1β Serum Levels in the GUSTO Trial Using PLA and PEA
Since we were unable to establish a correlation between the quantity of IL-1β and the response to TCZ treatment in the initial 5 patients, we conducted further testing to assess the reliability of the PLA test in another clinical trial. Therefore, we examined serum samples obtained from the GUSTO trial using PLA and compared the results with those obtained using an alternative assay, PEA, as shown in Figure 3A. For the PLA analysis, we selected 9 patient samples based on sample quality and collection date. These samples were examined at two-time points: at the trial’s initiation, when patients were enrolled, and at week 52 (end of study treatment). As depicted in Figure 3C, 3 patients (GUSTO 01, 02, and 04) exhibited concentrations of IL-1β ranging from 2 pg/mL to as high as 12 pg/mL (GUSTO 02). Notably, a comparison of the IL-1β levels revealed a down-regulation at week 52 in two patients, 01 and 02. In contrast, during the same period, there was a noticeable trend of up-regulation in IL-1β levels for patient 04.
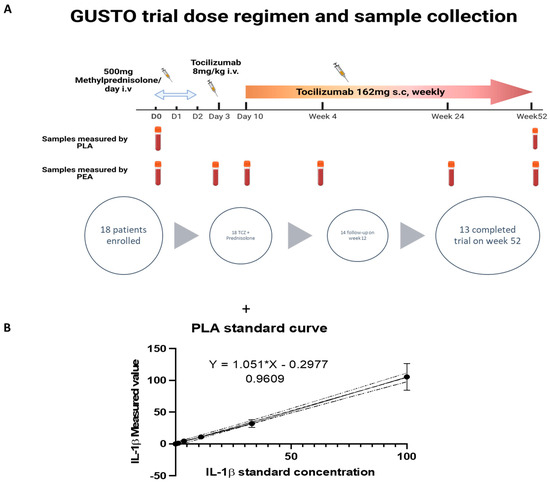
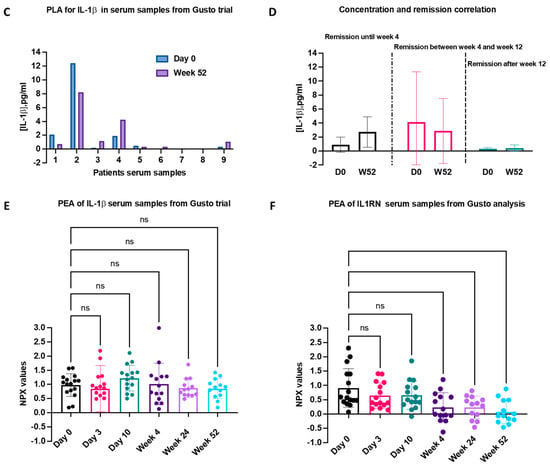
Figure 3.
Analysis of IL-1β amount in samples from GUSTO Trial by PLA and PEA. (A) Dose regimen and the time points of sample collection for PLA and PEA analysis; (B) Standard curve for PLA analysis of serum samples that were diluted 1:5; (C) PLA analysis results of IL-1β concentration in serum samples are shown, with an assay limit of detection (LOD) of 0.02 pg/mL; (D) IL-1β concentration values at day 0 and week 52 are plotted on the right and they are correlated with the patients’ time for remission based on the GUSTO trial analysis [16]; (E) PEA serum samples analysis of IL-1β; (F) PEA analysis of IL1RN variation in samples according to the regimen from reference [16]. Serum samples from six different time points were tested for the presence of IL-1β and IL1RN. The results are shown in NPX (arbitrary unit in log2 scale). IL-1β displays lower variation until the end of the study, while IL1RN consistently shows a decrease in protein expression. ns: non-significant.
We then examined a possible relationship between the presence of IL-1β in serum samples and the time it took for patients to achieve remission (Figure 3D). The serum levels of IL-1β were correlated with three remission points, namely remission within the first 4 weeks of the trial, remission occurring between weeks 4 and 12, and remission achieved after week 12 of the trial. Four patients who entered remission after week 12 of the trial began the study with low levels of IL-1β, and they maintained these low levels at the trial’s conclusion. In contrast, three patients who achieved remission between weeks 4 and 12, including GUSTO 04, experienced a considerable decrease in IL-1β levels by week 52. As for the two patients in remission within the initial 4 weeks of the trial, their IL-1β levels, which were initially below 5 pg/mL on day 0, exhibited an upward trend by the end of the trial. Based on these results, serum IL-1β levels failed to reliably predict the efficacy of TCZ treatment.
To corroborate the results obtained from the PLA assay, we conducted a Proximity Extension Assay (PEA). PEA shares comparable advantages with PLA, though it cannot absolutely quantify cytokine levels, focusing solely on monitoring protein fluctuations over time. In this test, patient samples from the GUSTO trial were assessed at six distinct time points spanning the 52-week trial duration. Figure 3E reveals the fluctuations in IL-1β expression, with an average maximum variation of 1.2-fold observed at day 10, while showing minimal variation during the remaining time points. These PEA data confirm our previous PLA findings, specifically that IL-1β exhibited small up- and downregulations over time, but these fluctuations could not be correlated with TCZ treatment.
With the same patient group, we analyzed IL-1RN, the IL-1 receptor antagonist, at various time points. Remarkably, we observed substantial changes over time, with values reaching zero by the 52nd week, as illustrated in Figure 3F.
4. Discussion
IL-1β, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory response, orchestrating various reactions such as fever, cell activation, and the induction of acute phase proteins [25]. Previous research has established a connection between IL-1β and IL-6. Particularly, IL-6, working in conjunction with IL-1β, contributes to the production of fever, especially in response to immune challenges. This would imply that TCZ, an antibody targeting the IL-6 pathway, should induce changes in serum IL-1β levels, potentially reflecting the effectiveness of TCZ therapy.
In the field of the currently used methodologies, PCR-based techniques emerged as some of the most reliable tools available to date for detecting exceedingly low concentrations of proteins, such as IL-1β. A challenge related to IL-1β is that in healthy individuals the serum IL-1β concentration typically falls within the range of 0.5 to 12 pg/mL [21]. This wide range of concentration levels makes the detection level of IL-1β difficult, primarily due to the limited sensitivity of standard tests [26].
In this study, we used two specific PCR-based tests to detect serum IL-1β: PLA and PEA. Both of these tests are characterized as dual-recognition assays, distinguished by their capacity to specifically and sensitively detect one or more analytes [27]. This unique feature enables a better tracking of disease progression by flowing cytokine profiles. We utilized PLA to measure IL-1β in serum samples obtained from two clinical trials, achieving a remarkable sensitivity level as low as 0.01 pg/mL. Previous studies have demonstrated higher plasma IL-1β levels in patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica or GCA (median 4 pg/mL) as compared to control subjects (median 0 pg/mL) [28]. These findings have been subsequently validated by immunohistochemical analyses, which revealed increased expression of IL-1β as well as TNF in tissue sections from temporal arteries of GCA patients. This heightened expression was found to be directly correlated with the intensity of the systemic inflammatory response and the response to glucocorticoid therapy [29].
Despite a potential role for IL-1β in GCA, in our study analyzing two clinical trials where IL-6 signaling was blocked, we did not observe any correlation between IL-1β levels and the treatment involving glucocorticoids and TCZ. In the phase II RCT trial, the PLA analysis revealed IL-1β levels below 1 pg/mL for 4 out of 5 patients at the beginning and after 52 weeks of the trial. Similarly, the analysis of serum samples from the GUSTO trial indicated an absence of correlation between IL-1β concentration levels and disease activity. When comparing IL-1β levels at different time points using the PEA assay in the GUSTO trial, we observed no significant variations. However, interestingly, using the same assay, we noted a decrease in IL-1RN over time, with values below detection levels at week 52. This observation indicates a correlation between IL-6 inhibition and the levels of IL-1RN. Blocking IL-6 therefore affects the IL-1β signaling, but via the antagonist and not via IL-1β itself. This decline is consistent with the analysis of different inflammatory markers in the same serum proteins [17], showing once again the synergetic effect of IL-6 downregulation. Hence, the blockade of IL-6 production might have a similar effect as the blockade of IL-1β, essentially disrupting the positive feedback loop for IL-1RN production [30]. Former studies using knockout mouse models have shown that IL-1RN is required to prevent the development of lethal arteritis. This highlights the specific function of IL-1RN in regulating inflammation and reinforces the crucial role of IL-1 in causing damage to the artery wall [31]. Notably, in the previous study of serum proteomics (Table S1), the analysis of other biomarkers revealed that one-third of the proteins changed in response to glucocorticoid treatment followed by TCZ within 10 days of starting treatment. Some of these proteins (CCL-7, CXCL9, and MMP12) have been proposed as biomarkers of disease activity. We extend these findings here to IL-1RN, which may serve as a general systemic parameter for increased local inflammation.
It is plausible that IL-1sR (soluble IL-1 receptor) levels increased with IL-6 receptor blocker therapy, potentially leading to downregulation of the IL-1 effect. This could occur concomitantly with a decrease in the levels of the IL-1β receptor antagonist (IL-1RN) [32], as observed in our study. This scenario aligns with findings from tissue cultures of temporal arteries, where exogenous IL-6 did not induce increased levels of IL-1. Thus, our observation of no significant changes in IL-1 levels following IL-6 receptor blocker therapy is consistent with this existing evidence [33].
However, despite the lack of direct modulation of IL-1 levels by IL-6 receptor blockade, the effectiveness of anti-IL-1 therapies in GCA suggests that IL-1 still plays a crucial role in the disease process. This implies the involvement of indirect mechanisms, possibly related to interactions between IL-1 and other cytokines or pathways implicated in GCA pathology. Therefore, while IL-6 may not directly regulate IL-1 levels, the efficacy of anti-IL-1 therapies underscores the continued importance of IL-1 in GCA pathogenesis [34,35].
Approaching this study’s limitations requires careful consideration of various factors, particularly regarding the exploratory nature of the research. One notable limitation is the absence of an analysis of potential confounding factors, such as concomitant medications, comorbidities, and specific disease characteristics of the patients, including different forms of GCA. While this limitation is partially justifiable given the exploratory nature of the study, it underscores the need for future research to incorporate these variables for a more comprehensive understanding of the observed associations.
Furthermore, it is essential to acknowledge the intrinsic challenges in defining disease activity in GCA, which complicates the interpretation of marker levels in patients. During anti-IL6 therapy, discerning disease activity can be particularly challenging due to subtle symptoms, uninformative laboratory tests, and the influence of organ involvement on imaging results. Given the absence of a gold standard for defining disease remission in GCA, validating a marker as a response predictor becomes inherently complex. In the phase II RCT study was also analyzed one patient from the placebo group, received only standard glucocorticoid treatment. However, the comparison with the treatment group did not provide further insights into the specificity of the observed marker responses to TCZ therapy. Additionally, it is noteworthy that all patients underwent follow-up imaging, including MRI (phase II) and MRI and ultrasound (GUSTO), to monitor disease activity in addition to clinical and laboratory assessment.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study was not able to qualify IL-1β as a possible marker for detecting disease activity in GCA. However, due to the limited number of patients tested and the lack of a control population, the effect of TCZ on serum IL-1β levels should be further explored. Nonetheless, the discovery that disease activity and treatment influence IL-1RN may offer new possibilities for investigating deeper into crucial pathophysiological mechanisms at play within vasculitis and exploring IL-1RN as a predictive biomarker.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rheumato4020006/s1, Table S1: Immunological markers studied from phase II RCT.
Author Contributions
J.J.d.C. designed, performed, interpreted experiments, and wrote the manuscript. L.C. and P.M.V. contributed the patient samples from the GUSTO trial and Phase II RCT; M.F.B. and M.V. supervised, and interpreted experiments, and wrote and revised the manuscripts. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by funding from the following grants: SNF grant 310039_185114 to Martin F. Bachmann. The phase 2 and GUSTO trial were funded by the Research Funds of the Department of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergology, University Hospital and University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland, and by F. Hoffmann-La Roche.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Bern, Switzerland (NCT01450137 and NCT03745586 and ethics number 2008-00845).
Informed Consent Statement
The studies (NCT01450137, NCT03745586) were approved by the local ethics committee, Bern, Switzerland and written informed consent for participation was provided by all patients (number 2018–00845).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Marianne Zwicker, Aleksandra Nonic, and Gilles Augusto for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
M.F.B. is a shareholder and board member of Saiba Animal Health AG. L.C. reports research/non-financial support, advisory fees, and stock ownership from Gilead Sciences, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Vifor, and Sanofi. P.M.V. has received consultancy fees, honoraria, and travel expenses from F. Hoffmann-La Roche, MSD, Abbvie, Grünenthal, Vifor, GSK, AstraZeneca, and Janssen. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Legge, W. The Journal. Br. Med. J. 1859, s4-1, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcicek, F.; Kara, A.V.; Akbas, E.M.; Kurt, N.; Yazici, G.N.; Cankaya, M.; Mammadov, R.; Ozcicek, A.; Suleyman, H. Effects of anakinra on the small intestine mucositis induced by methotrexate in rats. Exp. Anim. 2020, 69, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhimolea, E. Canakinumab. MAbs 2010, 2, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M. Rilonacept in the treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders. Drugs Today 2009, 45, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Masedu, F.; Alvaro, S.; Airò, P.; Battafarano, N.; Cantarini, L.; Cantatore, F.P.; Carlino, G.; D’Abrosca, V.; Frassi, M.; et al. Anti-interleukin-1 treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes (TRACK): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Walker, U.; Tilson, H.H.; Hawkins, P.N.; van der Poll, T.; Noviello, S.; Levy, J.; Vritzali, E.; Hoffman, H.M.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.B. Long-term safety and effectiveness of canakinumab therapy in patients with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome: Results from the β-Confident Registry. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharouf, F.; Tsemach-Toren, T.; Ben-Chetrit, E. IL-1 inhibition in familial Mediterranean fever: Clinical outcomes and expectations. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galozzi, P.; Bindoli, S.; Doria, A.; Sfriso, P. Progress in Biological Therapies for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Biologics 2022, 16, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haibel, H.; Poddubnyy, D.; Angermair, S.; Allers, K.; Vahldiek, J.L.; Schumann, M.; Schneider, T. Successful treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia, a case series with simultaneous interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 blockade with 1-month follow-up. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Everett, B.M.; Libby, P.; Thuren, T.; Glynn, R.J.; Kastelein, J.; Koenig, W.; Genest, J.; Lorenzatti, A.; et al. Relationship of C-reactive protein reduction to cardiovascular event reduction following treatment with canakinumab: A secondary analysis from the CANTOS randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pla, A.; Bosch-Gil, J.A.; Rosselló-Urgell, J.; Huguet-Redecilla, P.; Stone, J.H.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in Giant Cell Arteritis. Circulation 2005, 112, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilie, D.; Liozon, E.; Crevon, M.-C.; Lavignac, C.; Portier, A.; Liozon, F.; Galanaud, P. Production of interleukin 6 by granulomas of giant cell arteritis. Hum. Immunol. 1994, 39, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villiger, P.M.; Adler, S.; Kuchen, S.; Wermelinger, F.; Dan, D.; Fiege, V.; Bütikofer, L.; Seitz, M.; Reichenbach, S. Tocilizumab for induction and maintenance of remission in giant cell arteritis: A phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Tuckwell, K.; Dimonaco, S.; Klearman, M.; Aringer, M.; Blockmans, D.; Brouwer, E.; Cid, M.C.; Dasgupta, B.; Rech, J.; et al. Trial of Tocilizumab in Giant-Cell Arteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, L.; Seitz, L.; Scholz, G.; Sarbu, A.-C.; Amsler, J.; Bütikofer, L.; Tappeiner, C.; Kollert, F.; Reichenbach, S.; Villiger, P.M. Tocilizumab monotherapy after ultra-short glucocorticoid administration in giant cell arteritis: A single-arm, open-label, proof-of-concept study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e619–e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloor, A.D.; Yerly, D.; Adler, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Kuchen, S.; Seitz, M.; Villiger, P.M. Immuno-monitoring reveals an extended subclinical disease activity in tocilizumab-treated giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Régent, A.; Mouthon, L. Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, L.; Gloor, A.D.; Kollert, F.; Gaber, T.; Buttgereit, F.; Reichenbach, S.; Villiger, P.M. Serum proteomics in giant cell arteritis in response to a three-day pulse of glucocorticoid followed by tocilizumab monotherapy (the GUSTO trial). Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1165758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, C.M.; Lu, C.; Corbin, K.L.; Sharma, P.R.; Dula, S.B.; Carter, J.D.; Ramadan, J.W.; Xin, W.; Lee, J.K.; Nunemaker, C.S. Circulating Levels of IL-1B+IL-6 Cause ER Stress and Dysfunction in Islets From Prediabetic Male Mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Holmquist, G.; Björkesten, J.; Thorsen, S.B.; Ekman, D.; Eriksson, A.; Dickens, E.R.; Ohlsson, S.; Edfeldt, G.; et al. Homogenous 96-Plex PEA Immunoassay Exhibiting High Sensitivity, Specificity, and Excellent Scalability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, S.; Gullberg, M.; Jarvius, J.; Olsson, C.; Pietras, K.; Gústafsdóttir, S.M.; Östman, A.; Landegren, U. Protein detection using proximity-dependent DNA ligation assays. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, C.; Ruff, D.; Kirvell, S.; Johnson, G.; Dhillon, H.S.; Bustin, S.A. Proximity assays for sensitive quantification of proteins. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 4, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. A clinical perspective of IL-1β as the gatekeeper of inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platchek, M.; Lu, Q.; Tran, H.; Xie, W. Comparative Analysis of Multiple Immunoassays for Cytokine Profiling in Drug Discovery. SLAS Discov. Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2020, 25, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedin, F.; Benoit, V.; Ferrazzi, E.; Aufradet, E.; Boulet, L.; Rubens, A.; Dalbon, P.; Imbaud, P. Procalcitonin detection in human plasma specimens using a fast version of proximity extension assay. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pountain, G.; Hazleman, B.; Cawston, T.E. Circulating levels of IL-1beta, IL-6 and soluble IL-2 receptor in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez, J.; Segarra, M.; Vilardell, C.; Sánchez, M.; García-Martínez, A.; Esteban, M.J.; Queralt, C.; Grau, J.M.; Urbano-Márquez, A.; Palacín, A.; et al. Tissue production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6) correlates with the intesity of the systemic inflammatory response and with corticosteroid requirements in giant-cell arteritis. Rheumatology 2003, 43, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimbo, K.; Park, J.S.; Yokosuka, K.; Sato, K.; Nagata, K. Positive feedback loop of interleukin-1β upregulating production of inflammatory mediators in human intervertebral disc cells in vitro. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2005, 2, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin, M.J.; Hughes, D.E.; Barton, J.L.; Ure, J.M.; Duff, G.W. Arterial Inflammation in Mice Lacking the Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist Gene. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, D.; Chicheportiche, R.; Giri, J.G.; Dayer, J.M. The Inhibitory Activity of Human Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Is Enhanced by Type 11 Interleukin-1 Soluble Receptor and Hindered by Type I Interleukin-1 Soluble Receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’neill, L.; McCormick, J.; Gao, W.; Veale, D.J.; McCarthy, G.M.; Murphy, C.C.; Fearon, U.; Molloy, E.S. Interleukin-6 does not upregulate pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in an ex vivo model of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2019, 3, rkz011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, K.-H.; Stirnemann, J.; Liozon, E.; Michel, M.; Fain, O.; Fauchais, A.-L. Interleukin-1 blockade in refractory giant cell arteritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshayes, S.; Ly, K.H.; Rieu, V.; Maigné, G.; Martin Silva, N.; Manrique, A.; Monteil, J.; de Boysson, H.; Aouba, A.; French Study Group for Large Vessel Vasculitis (GEFA). Steroid-sparing effect of anakinra in giant-cell arteritis: A case series with clinical, biological and iconographic long-term assessments. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).