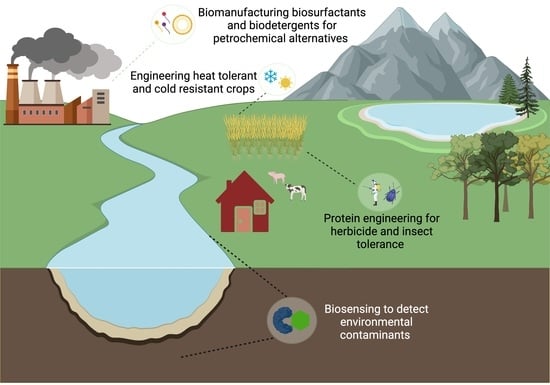
Proteins in Synthetic Biology with Agricultural and Environmental Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Food Safety and Security
2.1. Herbicide Tolerance
2.2. Insecticidal Activity
2.3. Environmental Change Tolerance
3. Environmental Sensing
3.1. Enzyme Based Sensing
3.2. Binding Affinity-Based Sensing
4. Biomanufacturing
4.1. Naturally Occurring Proteins for Biomanufacturing
4.2. Optimizing Protein Activity within a Pathway
4.3. Strategically Modulating Structural Moieties within a Protein
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Synthetic Biology Market Size, Share, Trends, by Technology, by Tools, by Application, by End-Use, and by Region Forecast to 2030; Synthetic Biology Market; Research and Markets. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5648701/synthetic-biology-market-size-share-trends-by (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- USDA ERS-Key Statistics & Graphics. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-u-s/key-statistics-graphics/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Daramola, O.S.; Adigun, J.A.; Olorunmaiye, P.M. Challenges of weed management in rice for food security in Africa: A review. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 2020, 53, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Heng, Y.; Li, J.; Pei, J.; Cao, Y.; Deng, X.W.; Ma, L. Generation of a series of mutant lines resistant to imidazolinone by screening an EMS-based mutant library in common wheat. Crop J. 2020, 9, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozi, A. New Standards to Curb the Global Spread of Plant Pests and Diseases; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.P.; Tranel, P.J. Target-Site Mutations Conferring Herbicide Resistance. Plants 2019, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acetohydroxyacid Synthase Inhibitors (AHAS/ALS). Modern Crop Protection Compounds; Jeschke, P., Witschel, M., Krämer, W., Schirmer, U., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2019; pp. 33–171. ISBN 978-3-527-69926-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Wan, C.; Wang, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X. Engineering Herbicide-Tolerance Rice Expressing an Acetohydroxyacid Synthase with a Single Amino Acid Deletion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, E.C.M.; da Costa, K.S.; Lameira, J.; Alves, C.N.; Lima, A.H. Investigation of the target-site resistance of EPSP synthase mutants P106T and T102I/P106S against glyphosate. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44352–44360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achary, V.M.M.; Sheri, V.; Manna, M.; Panditi, V.; Borphukan, B.; Ram, B.; Agarwal, A.; Fartyal, D.; Teotia, D.; Masakapalli, S.K.; et al. Overexpression of improvedEPSPSgene results in field level glyphosate tolerance and higher grain yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2504–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.L.; Rajapakse, W.; Bagga, S.; Apodaca, K.; Lucero, Y.; Sengupta-Gopalan, C. An intragenic approach to confer glyphosate resistance in chile (Capsicum annuum) by introducing an in vitro mutagenized chile EPSPS gene encoding for a glyphosate resistant EPSPS protein. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z.; Yin, Y.; Xi, J.; Liu, Q.; Yan, W.; Song, X.; Zhao, F.; et al. Engineered chimeric insecticidal crystalline protein improves resistance to lepidopteran insects in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and maize (Zea mays L.). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Cong, R.; Izumi-Willcoxon, M.; Ali, H.; Zheng, Y.; Bermudez, E.; McDonald, M.; Nelson, M.; Yamamoto, T. Engineering of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Proteins to Enhance the Activity against Western Corn Rootworm. Toxins 2019, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomis-Cebolla, J.; dos Santos, R.F.; Wang, Y.; Caballero, J.; Caballero, P.; He, K.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.; Ferré, J. Domain Shuffling between Vip3Aa and Vip3Ca: Chimera Stability and Insecticidal Activity against European, American, African, and Asian Pests. Toxins 2020, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, J.G.; Wisniewski, M.J. The use of antifreeze proteins for frost protection in sensitive crop plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 106, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juurakko, C.L.; Dicenzo, G.C.; Walker, V.K. Cold acclimation and prospects for cold-resilient crops. Plant Stress 2021, 2, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yao, S. A point mutation in LTT1 enhances cold tolerance at the booting stage in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, R.; Carrillo, N.; Morelli, M.P.; Tula, S.; Shahinnia, F.; Hajirezaei, M.-R.; Lodeyro, A.F. Faster photosynthetic induction in tobacco by expressing cyanobacterial flavodiiron proteins in chloroplasts. Photosynth. Res. 2017, 136, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, U.M.; Majeed, S.T.; Raja, V.; Wani, Z.A.; Jan, N.; Andrabi, K.I.; John, R. Ectopic expression of a novel cold-resistance protein 1 from Brassica oleracea promotes tolerance to chilling stress in transgenic tomato. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selahle, S.K.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. A review of extraction, analytical, and advanced methods for the determination of neonicotinoid insecticides in environmental water matrices. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 40, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Shi, X.-C.; Liu, F.-Q.; Laborda, P. Chromatographic Methods for Detection and Quantification of Carbendazim in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11880–11894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsidar, A.; Siddiquee, S.; Shaarani, S.M. A review of extraction, analytical and advanced methods for determination of pesticides in environment and foodstuffs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.P.F. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical biosensors: An exhaustive and comprehensive review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, V.K.; Shukla, P. Enzyme Based Biosensors for Detection of Environmental Pollutants-A Review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, P. Biosensors and their applications–A review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2016, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahu, S.; Roy, R.; Anand, R. Harnessing the Potential of Biological Recognition Elements for Water Pollution Monitoring. ACS Sensors 2022, 7, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, L.S.B.; Verma, N. Enzyme Inhibition Based Biosensors: A Review. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, U.; Bhardwaj, P.; Agarwal, R.; Rawat, P.; Agarwal, R.; Gupta, I.; Panjwani, M.; Singh, S.; Ahuja, C.; Selvaraj, S.K.; et al. Recent progress and growth in biosensors technology: A critical review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadurmus, L.; Kaya, S.I.; Ozkan, S.A. Recent advances of enzyme biosensors for pesticide detection in foods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4582–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshvar, S.; Sudhakumari, C.C.; Senthilkumaran, B.; Prakash, H. Recent Advances in Biosensor Technology for Potential Applications—An Overview. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, F.; Zhu, A.; Shi, H. Recent Advances in Optical Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring and Early Warning. Sensors 2013, 13, 13928–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucherenko, I.S.; Soldatkin, A.; Kucherenko, D.Y.; Soldatkina, O.V.; Dzyadevych, S.V. Advances in nanomaterial application in enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4560–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.C.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.; She, Y.; Ye, J.; El-Aty, A.M.A.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Wang, J.; Lao, S. An Overview on the Mechanisms and Applications of Enzyme Inhibition-Based Methods for Determination of Organophosphate and Carbamate Pesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7298–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.O.; Singh, B. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of Pesticides and Heavy Metal Toxicants in Water: Recent Trends and Progress. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, A.; Ghazizadeh, A.J.; Hashemi, P.; Afkhami, A.; Arduini, F.; Bagheri, H. An overview to electrochemical biosensors and sensors for the detection of environmental contaminants. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 2429–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, Y.; Park, S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Ju, Y.; Yeon, K.-M.; Kim, J. Tyrosinase-immobilized CNT based biosensor for highly-sensitive detection of phenolic compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, D.; Su, Z.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Recent advances in enzyme immobilization based on novel porous framework materials and its applications in biosensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 459, 214414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Yin, N.; Song, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, D. Recent advances in carbon nanomaterials-based electrochemical sensors for phenolic compounds detection. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Rout, C.S. Electrochemical biosensors based on Ti3C2Tx MXene: Future perspectives for on-site analysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 30, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltaninejad, K.; Shadnia, S. History of the Use and Epidemiology of Organophosphorus Poisoning. In Basic and Clinical Toxicology of Organophosphorus Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4471-5625-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway, J.; Hawkes, N.J.; McCarroll, L.; Ranson, H. The molecular basis of insecticide resistance in mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, B.H.; Deng, J.F.; Ger, J.; Tsai, W.J. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and the Extrapyramidal Syndrome: A Review of the Neurotoxicity of Organophosphate. Neurotoxicology 2001, 22, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassall, K.A. Biochemistry and Uses of Pesticides; Macmillan Press Ltd.: Basingstoke, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, S.; Rao, G.R.; Sharma, M.K.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Rao, V.K.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Immobilization of acetylcholineesterase–choline oxidase on a gold–platinum bimetallic nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides, carbamates and nerve agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Shojaosadati, S.; Ranaie, S.; Mousavi, S. Optimization and evaluation of acetylcholine esterase immobilization on ceramic packing using response surface methodology. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, J. Use of biosensors for detecting organophosphorus agents. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 126, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran-Minh, C.; Pandey, P.C.; Kumaran, S. Studies on acetylcholine sensor and its analytical application based on the inhibition of cholinesterase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1990, 5, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Thiocholine-triggered reaction in personal glucose meters for portable quantitative detection of organophosphorus pesticide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1060, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council 2005. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/396/2022-09-19 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Su, L.; Jia, W.; Hou, C.; Lei, Y. Microbial biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1788–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, H.; Tan, L.L.; Ta, G.C.; Heng, L.Y. Detection of halogenated hydrocarbon pollutants using enzymatic reflectance biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Das, A.; Sarkar, D.J.; Weerathunge, P.; Parida, P.K.; Das, B.K.; Thavamani, P.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in inland aquatic ecosystems: Perils and remedies through biosensors and bioremediation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikova, E.G.; Shumkova, E.S.; Shumkov, M.S. Whole-cell bacterial biosensors for the detection of aromatic hydrocarbons and their chlorinated derivatives (Review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.; Ng, L.C.; Sze, C.C.; Shingler, V. Aromatic ligand binding and intramolecular signalling of the phenol-responsive σ54-dependent regulator DmpR: Ligand Binding and Intramolecular Signalling of DmpR. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Gunzburg, M.J.; Wilce, M.; Panjikar, S.; Anand, R. Structural Basis of Selective Aromatic Pollutant Sensing by the Effector Binding Domain of MopR, an NtrC Family Transcriptional Regulator. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.C.; O’Neill, E.; Shingler, V. Genetic Evidence for Interdomain Regulation of the Phenol-responsive 54-dependent Activator DmpR. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17281–17286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.; Dixon, R. The Role of Bacterial Enhancer Binding Proteins as Specialized Activators of σ54-Dependent Transcription. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 497–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, S.; Panjikar, S.; Anand, R. Structure Guided Design of Protein Biosensors for Phenolic Pollutants. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Senapati, T.; Sahu, S.; Bandyopadhyaya, R.; Anand, R. Design of Ultrasensitive Protein Biosensor Strips for Selective Detection of Aromatic Contaminants in Environmental Wastewater. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8960–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Ray, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Anand, R. Tunable Multiplexed Whole-Cell Biosensors as Environmental Diagnostics for ppb-Level Detection of Aromatic Pollutants. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleja, N.; Jairajpuri, M.A.; Queen, A.; Mohsin, M. Genetically encoded FRET-based optical sensor for Hg2+ detection and intracellular imaging in living cells. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Liu, D.; Tian, J. Construction of a mApple-D6A3-mediated biosensor for detection of heavy metal ions. AMB Express 2020, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattocks, J.A.; Ho, J.V.; Cotruvo, J.A. A Selective, Protein-Based Fluorescent Sensor with Picomolar Affinity for Rare Earth Elements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2857–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, H.; Kang, Y.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, Y. A Biosensor Platform for Metal Detection Based on Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein. Sensors 2019, 19, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.; Kang, Y.; Lee, W.; Oh, K.-C.; Jang, G.; Kim, B.-G. Modulating the Properties of Metal-Sensing Whole-Cell Bioreporters by Interfering with Escherichia coli Metal Homeostasis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, M.M.; Tang, J.D.; Berger, B.W. Engineering human liver fatty acid binding protein for detection of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Guetta, P.-E.Y.; Fink, M.M.; Rizk, S.S. Engineering a fluorescence biosensor for the herbicide glyphosate. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2020, 33, gzaa021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahay, S.; Chouhan, D. Study on the potential of cold-active lipases from psychrotrophic fungi for detergent formulation. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; Ye, H.; Jiang, C. Effects of inoculation of biosurfactant-producing Bacillus sp. J119 on plant growth and cadmium uptake in a cadmium-amended soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.; Shanthi, C. Alkaline Thermostable Cold Active Lipase from Halotolerant Pseudomonas sp. VITCLP4 as Detergent Additive. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, J.; Özkaya, Ö.; Kümmerli, R. Bacterial siderophores in community and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 18, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Huang, Y.C.; Wei, Y.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Biosurfactant-enhanced removal of total petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.N.; Yong, R.N.; Gibbs, B.F. Heavy metal removal from sediments by biosurfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 85, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Cameotra, S.S. Efficiency of lipopeptide biosurfactants in removal of petroleum hydrocarbons and heavy metals from contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7367–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Han, S.J.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, D. Characterization of an Antarctic Alkaline Protease, a Cold-Active Enzyme for Laundry Detergents. Korean J. Microbiol. 2018, 54, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kan, G.; Ren, X.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.; Xie, Q.; Wen, H.; Betenbaugh, M. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Novel α-Amylase from Antarctic Sea Ice Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. M175 and Its Primary Application in Detergent. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Wilson, L.M.; Yan, Y. Protein Engineering for Improving and Diversifying Natural Product Biosynthesis. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Ma, T.; Liu, M.; Qu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shi, B.; Fu, S.; Ma, J.; Lai, L.T.F.; et al. Modular enzyme assembly for enhanced cascade biocatalysis and metabolic flux. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for Production of 2-phenylethanol from Renewable Glucose. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 172, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Ravn, M.M.; Coates, R.M. Synthesis and characterization of abietadiene, levopimaradiene, palustradiene, and neoabietadiene: Hydrocarbon precursors of the abietane diterpene resin acids. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6155–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, E.; Ajikumar, P.K.; Thayer, K.; Xiao, W.-H.; Mo, J.D.; Tidor, B.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Prather, K.L.J. Combining metabolic and protein engineering of a terpenoid biosynthetic pathway for overproduction and selectivity control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13654–13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Tovilla-Coutiño, D.B.; Eiteman, M.A. Engineered citrate synthase improves citramalic acid generation in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibik, J.D.; Weraduwage, S.M.; Banerjee, A.; Robertson, K.; Espinoza-Corral, R.; Sharkey, T.D.; Lundquist, P.K.; Hamberger, B.R. Pathway Engineering, Re-targeting, and Synthetic Scaffolding Improve the Production of Squalene in Plants. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, D.H.; Schulz, F. The Stereochemistry of Complex Polyketide Biosynthesis by Modular Polyketide Synthases. Molecules 2011, 16, 6092–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, G.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Hindra; Ma, M.; Yang, D.; Zhou, H.; Gansemans, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Discovery of the leinamycin family of natural products by mining actinobacterial genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E11131–E11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDaniel, R.; Thamchaipenet, A.; Gustafsson, C.; Fu, H.; Betlach, M.; Betlach, M.; Ashley, G. Multiple genetic modifications of the erythromycin polyketide synthase to produce a library of novel “unnatural” natural products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobsen, J.R.; Hutchinson, C.R.; Cane, D.E.; Khosla, C. Precursor-Directed Biosynthesis of Erythromycin Analogs by an Engineered Polyketide Synthase. Science 1997, 277, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Type I Polyketide Synthase Requiring a Discrete Acyltransferase for Polyketide Biosynthesis. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0537286100 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Li, W. An Unusual Type II Polyketide Synthase System Involved in Cinnamoyl Lipid Biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Whicher, J.R.; Hansen, D.A.; Hale, W.A.; Chemler, J.A.; Congdon, G.R.; Narayan, A.R.H.; Håkansson, K.; Sherman, D.H.; Smith, J.L.; et al. Structure of a modular polyketide synthase. Nature 2014, 510, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, A.A.; Schmidt, J.J.; Lowell, A.N.; Hansen, D.A.; Coburn, K.M.; Chemler, J.A.; Sherman, D.H. Probing Selectivity and Creating Structural Diversity Through Hybrid Polyketide Synthases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13575–13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, T.; Kamlet, A.S.; Ritter, T. Catalysis for fluorination and trifluoromethylation. Nature 2011, 473, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirirungruang, S.; Ad, O.; Privalsky, T.M.; Ramesh, S.; Sax, J.L.; Dong, H.; Baidoo, E.E.K.; Amer, B.; Khosla, C.; Chang, M.C.Y. Engineering site-selective incorporation of fluorine into polyketides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mann, M.M.; Vigil, T.N.; Felton, S.M.; Fahy, W.E.; Kinkeade, M.A.; Kartseva, V.K.; Rowson, M.-J.C.; Frost, A.J.; Berger, B.W. Proteins in Synthetic Biology with Agricultural and Environmental Applications. SynBio 2023, 1, 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/synbio1010006
Mann MM, Vigil TN, Felton SM, Fahy WE, Kinkeade MA, Kartseva VK, Rowson M-JC, Frost AJ, Berger BW. Proteins in Synthetic Biology with Agricultural and Environmental Applications. SynBio. 2023; 1(1):77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/synbio1010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMann, Madison M., Toriana N. Vigil, Samantha M. Felton, William E. Fahy, Mason A. Kinkeade, Victoria K. Kartseva, Mary-Jean C. Rowson, Abigail J. Frost, and Bryan W. Berger. 2023. "Proteins in Synthetic Biology with Agricultural and Environmental Applications" SynBio 1, no. 1: 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/synbio1010006
APA StyleMann, M. M., Vigil, T. N., Felton, S. M., Fahy, W. E., Kinkeade, M. A., Kartseva, V. K., Rowson, M.-J. C., Frost, A. J., & Berger, B. W. (2023). Proteins in Synthetic Biology with Agricultural and Environmental Applications. SynBio, 1(1), 77-88. https://doi.org/10.3390/synbio1010006