Fast Synthesis of Fine Boron Carbide Powders Using Electromagnetic Induction Synthesis Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ignition of the Reaction, Temperature-Time Profiles, and Mass Loss during Synthesis
3.2. Characterization of the Synthesized B4C
3.2.1. Phase Composition
3.2.2. Microstructure and Particle Size
3.2.3. Specific Surface Area
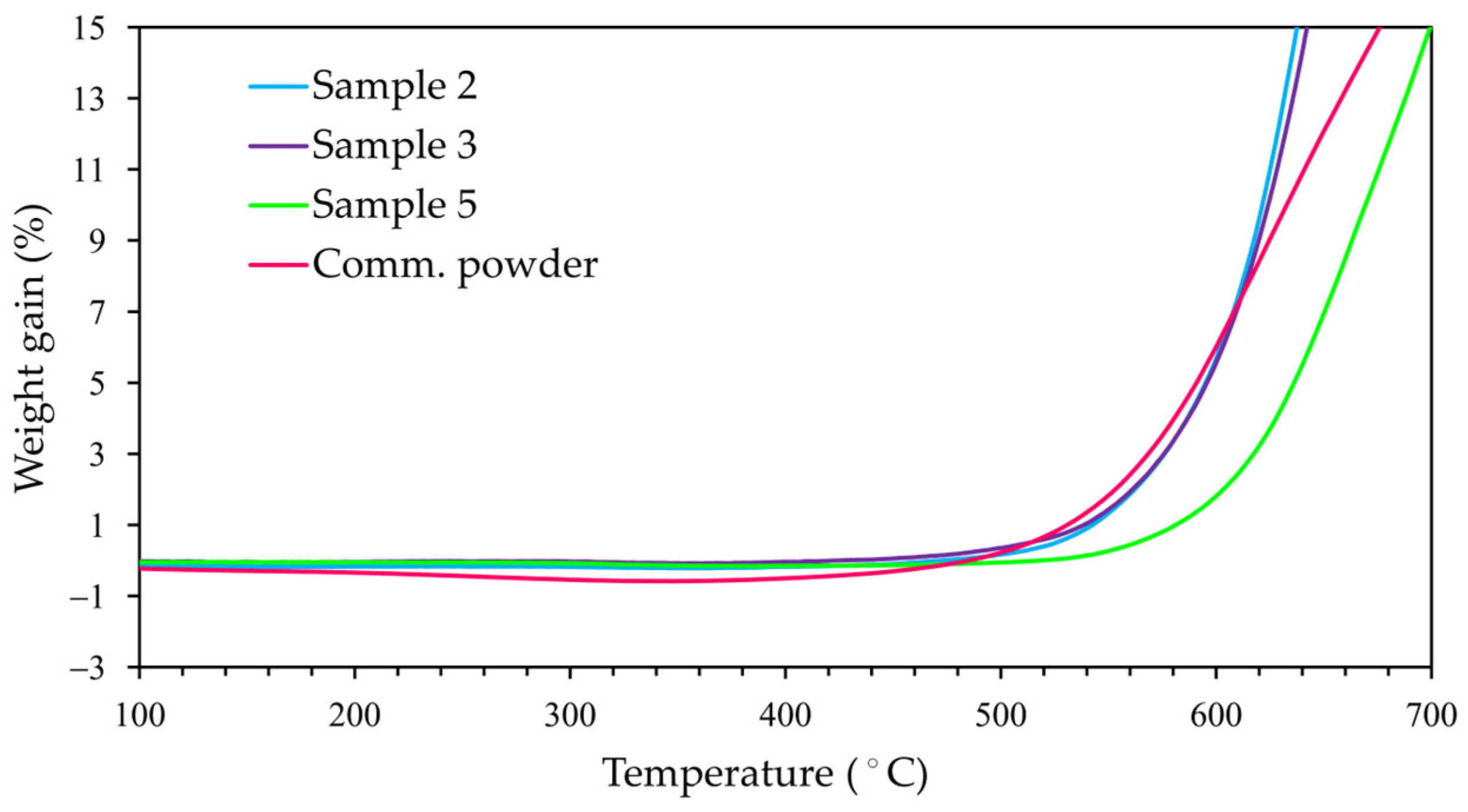
3.3. Non-Isothermal Oxidation of B4C Powders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Domnich, V.; Reynaud, S.; Haber, R.A.; Chhowalla, M. Boron carbide: Structure, properties, and stability under stress. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 3605–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, F. Boron carbide—A comprehensive review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 6, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, A.K.; Subramanian, C.; Sonber, J.K.; Murthy, T.C. Synthesis and consolidation of boron carbide: A review. Int. Mat. Rev. 2010, 55, 4–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajar, M.; Gubarevich, A.; Maki, R.S.S.; Uchikoshi, T.; Suzuki, T.S.; Yano, T.; Yoshida, K. Effect of Al2O3 addition on texturing in a rotating strong magnetic field and densification of B4C. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 18222–18228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stodolak-Zych, E.; Gubernat, A.; Ścisłowska-Czarnecka, A.; Chadzińska, M.; Zych, Ł.; Zientara, D.; Nocuń, M.; Jeleń, P.; Bućko, M. The influence of surface chemical composition of particles of boron carbide powders on their biological properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 582, 152380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.N.; Chen, X.M.; Liu, P. Microwave absorbing properties of FeB/B4C nanowire composite. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4020–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wen, S.; Hou, Y.; Zuo, F.; Beran, G.J.; Feng, P. Boron carbides as efficient, metal-free, visible-light-responsive photocatalysts. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3241–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chkhartishvili, L.; Mikeladze, A.; Tsagareishvili, O.; Kvatchadze, V.; Tavkhelidze, V.; Mestvirishvili, Z.; Driaev, D.; Barbakadze, N.; Nadaraia, L.; Sarajishvili, K.; et al. Advanced Boron Carbide Matrix Nanocomposites Obtained from Liquid-Charge: Focused Review. Condens. Matter 2023, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.C.; Aruna, S.T.; Mimani, T. Combustion synthesis: An update. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mat. Sci. 2002, 6, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubarevich, A.V.; Watanabe, T.; Nishimura, T.; Yoshida, K. Combustion synthesis of single-phase Al4SiC4 powder with assistance of induction heating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovskikh, D.O.; Paramonov, K.A.; Nepapushev, A.A.; Shkodich, N.F.; Mukasyan, A.S. Bulk boron carbide nanostructured ceramics by reactive spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 8190–8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, I.D.; Ponomarev, V.I.; Konovalikhin, S.V.; Kovalev, D.Y.; Vershinnikov, V.I. SHS of boron carbide: Influence of combustion temperature. Int. J. SHS 2015, 24, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Munir, Z.A.; Kodera, Y.; Imai, T.; Ohyanagi, M. Influence of synthesis temperature on the defect structure of boron carbide: Experimental and modeling studies. J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chkhartishvili, L.; Mikeladze, A.; Chedia, R.; Tsagareishvili, O.; Bugdayci, M.; Karagoz, I.; Maras, T.; Jalabadze, N.; Kvatchadze, V. Combustion Synthesis of Boron Carbide Matrix for Superhard Nanocomposites Production. Adv. Combust. Synth. Technol. 2022, 1, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubarevich, A.V.; Tamura, R.; Yoshida, K. Combustion synthesis of high yield Ti3SiC2 from TiC0.67 with induction heating assistance. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 23887–23892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucía, O.; Maussion, P.; Dede, E.J.; Burdío, J.M. Induction heating technology and its applications: Past developments, current technology, and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electr. 2014, 61, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnev, V.; Loveless, D.; Cook, R.L. Handbook of Induction Heating, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gubarevich, A.V.; Homma, G.; Yoshida, K. Boron carbide with improved mechanical properties fabricated via rapid pressureless densification with electromagnetic induction assistance. Scr. Mater. 2024, 238, 115731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.W.; McCauley, J.W.; LaSalvla, J.C.; Hemker, K.J. Microstructural characterization of commercial hot-pressed boron carbide ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Guan, P.; Madhav Reddy, K.; Hirata, A.; Guo, J.; Chen, M. Asymmetric twins in rhombohedral boron carbide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 021907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Chou, K.C. Quantitative investigation of oxidation behavior of boron carbide powders in air. J. Alloys Comp. 2013, 573, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

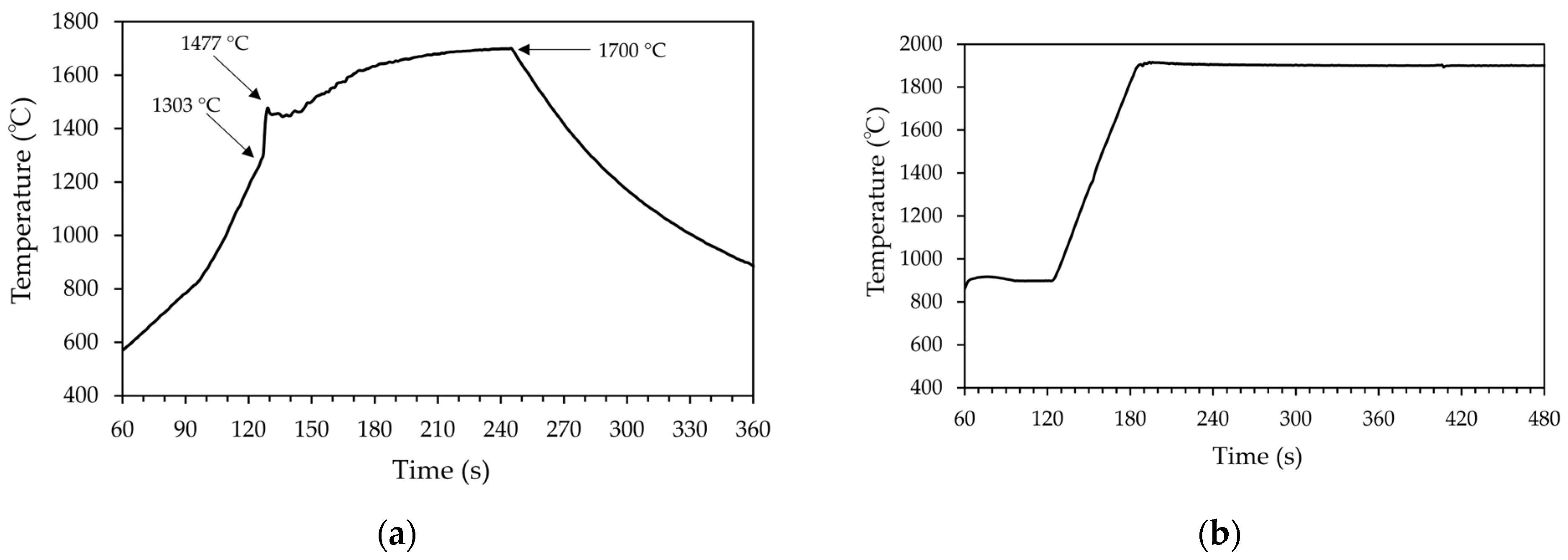
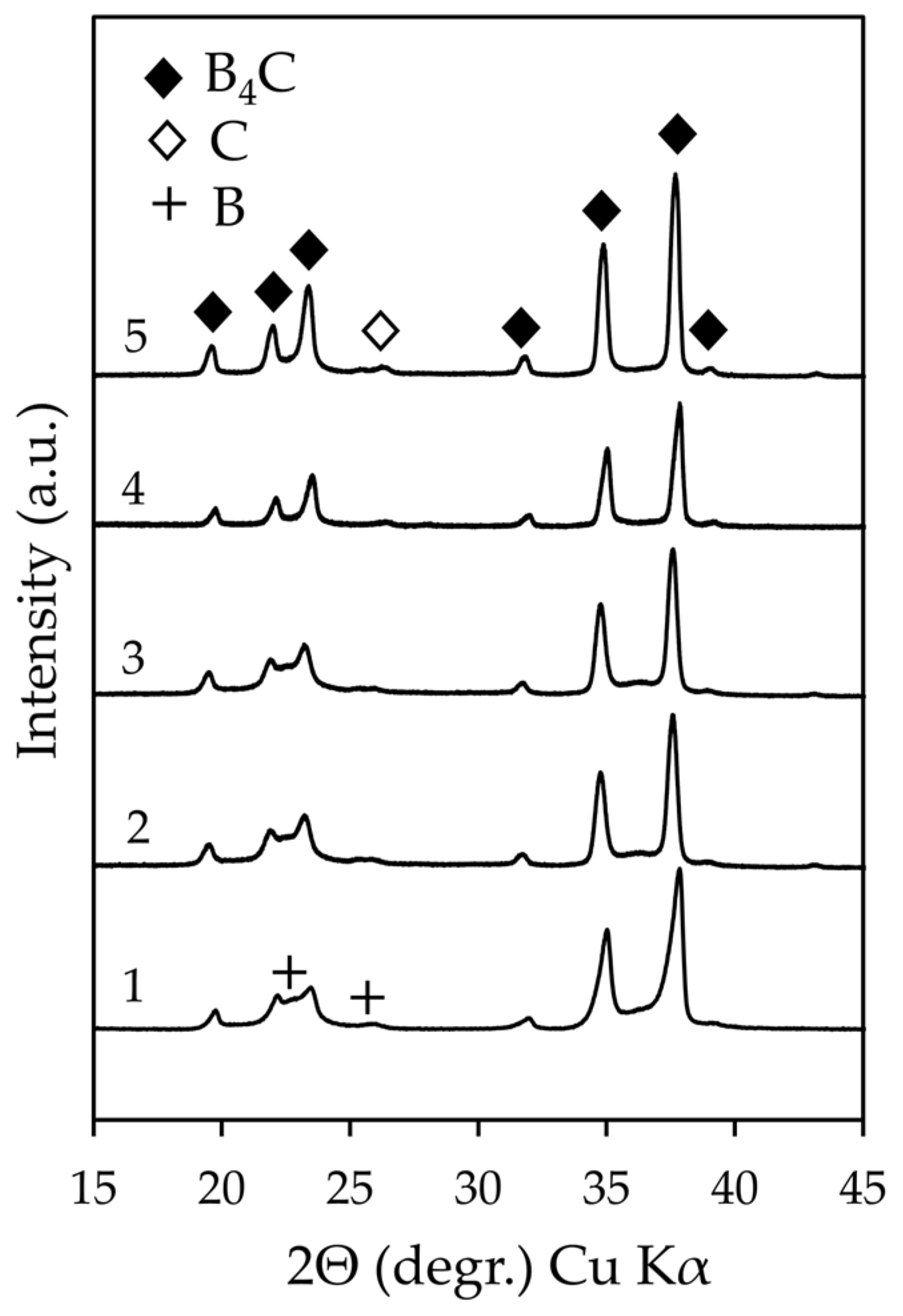

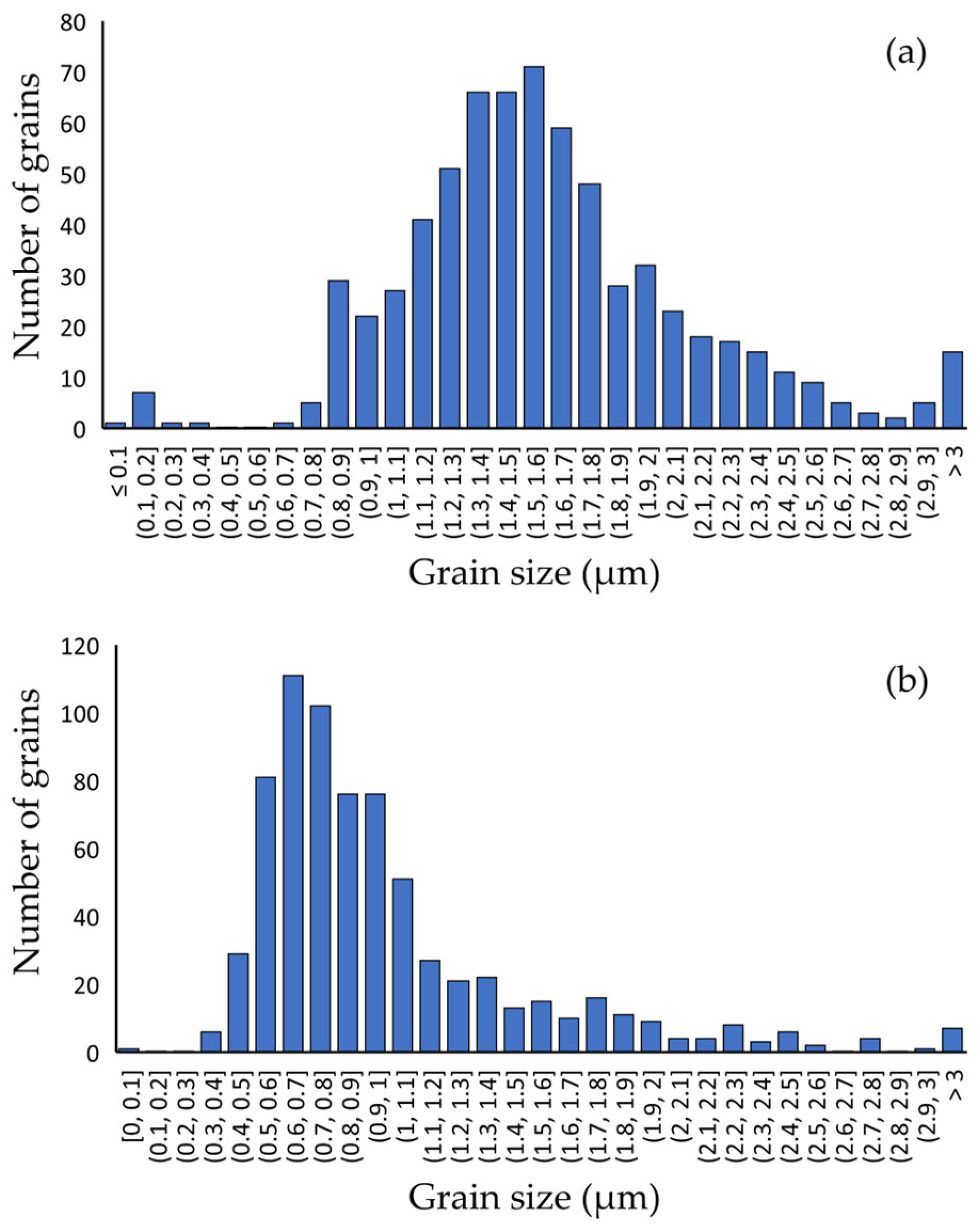
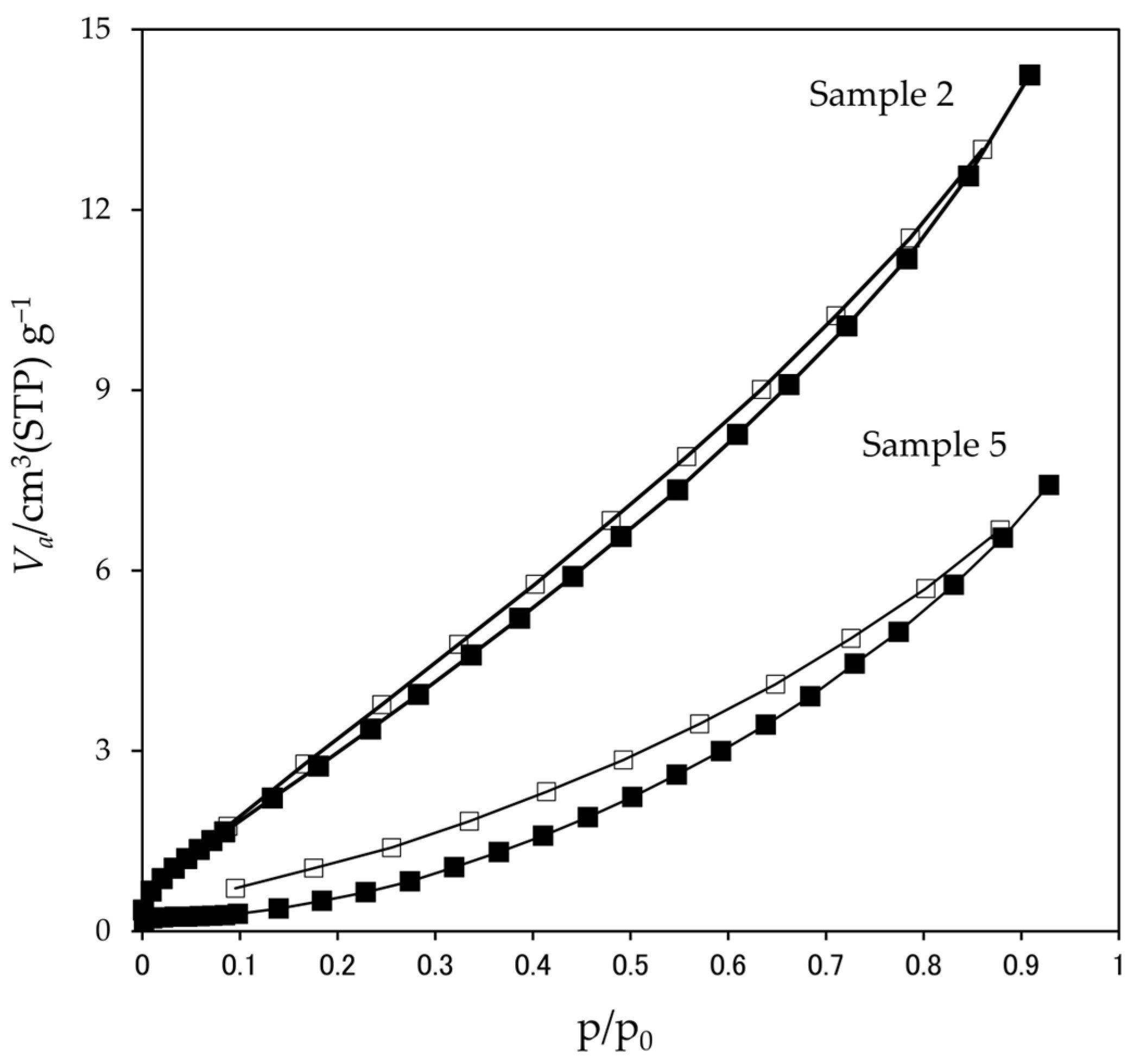
| Tmax (°C) | Point of T Measurement | Holding Time at Tmax (min) | Sample ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 | Sample | 0 | 1 |
| 1900 | Graphite lid | 3 | 2 |
| 1900 | 5 | 3 | |
| 1950 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1970 | 0 | 5 |
| Sample ID | Oxygen Content | B2O3 Content | Mass Loss (w%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w% | at% | (w%) | ||
| 1 | 1.18 | 0.82 | 5.13 | 4.2 |
| 2 | 0.64 | 0.44 | 2.78 | 6.9 |
| 3 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 3.87 | 6.8 |
| 4 | 0.84 | 0.58 | 3.65 | 6.9 |
| 5 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 2.52 | 6.5 |
| Boron | 3.08 | 2.10 | 14.0 | 9.2 (1) |
| B4C comm. | 0.7 | 0.48 | 3.04 | - |
| Sample ID | SBET (m2·g−1) | Average Particle Size (nm) 1 | SEM Grain Size (nm) 2 | OOT (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 17.2 | 138 | 450 | 521 |
| 3 | 11.0 | 216 | 480 | 521 |
| 4 | 2.3 | 1035 | 1600 | 584 |
| 5 | 1.5 | 1550 | 990 | 550 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gubarevich, A.V.; Yoshida, K. Fast Synthesis of Fine Boron Carbide Powders Using Electromagnetic Induction Synthesis Method. Powders 2024, 3, 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders3010002
Gubarevich AV, Yoshida K. Fast Synthesis of Fine Boron Carbide Powders Using Electromagnetic Induction Synthesis Method. Powders. 2024; 3(1):17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders3010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGubarevich, Anna V., and Katsumi Yoshida. 2024. "Fast Synthesis of Fine Boron Carbide Powders Using Electromagnetic Induction Synthesis Method" Powders 3, no. 1: 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders3010002
APA StyleGubarevich, A. V., & Yoshida, K. (2024). Fast Synthesis of Fine Boron Carbide Powders Using Electromagnetic Induction Synthesis Method. Powders, 3(1), 17-27. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders3010002






