Hot Consolidation of Titanium Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
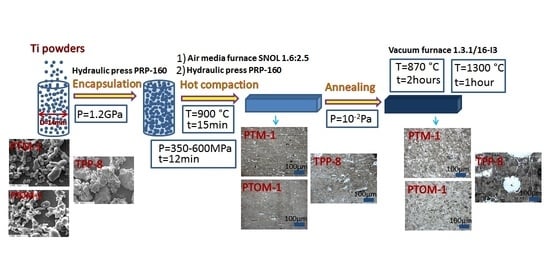
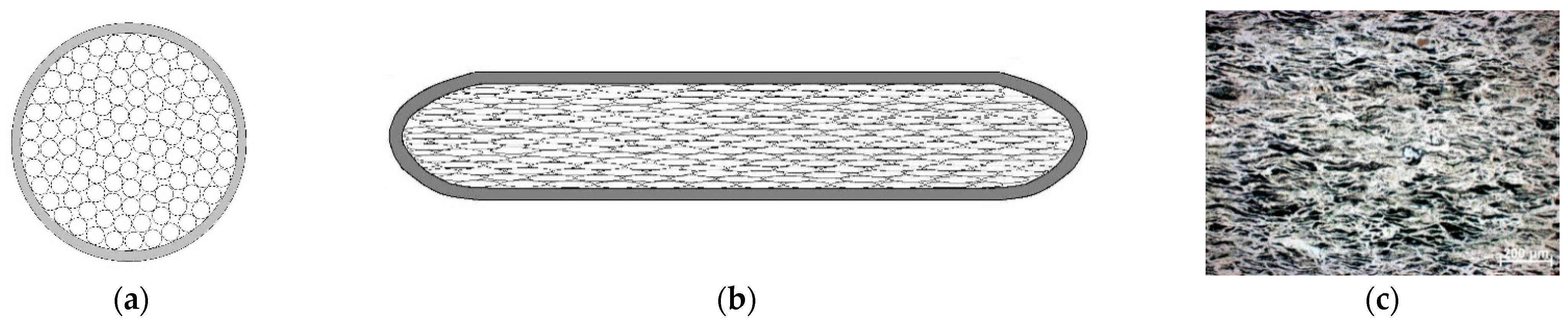
2. Materials and Experimental Technique
3. Results and Discussion
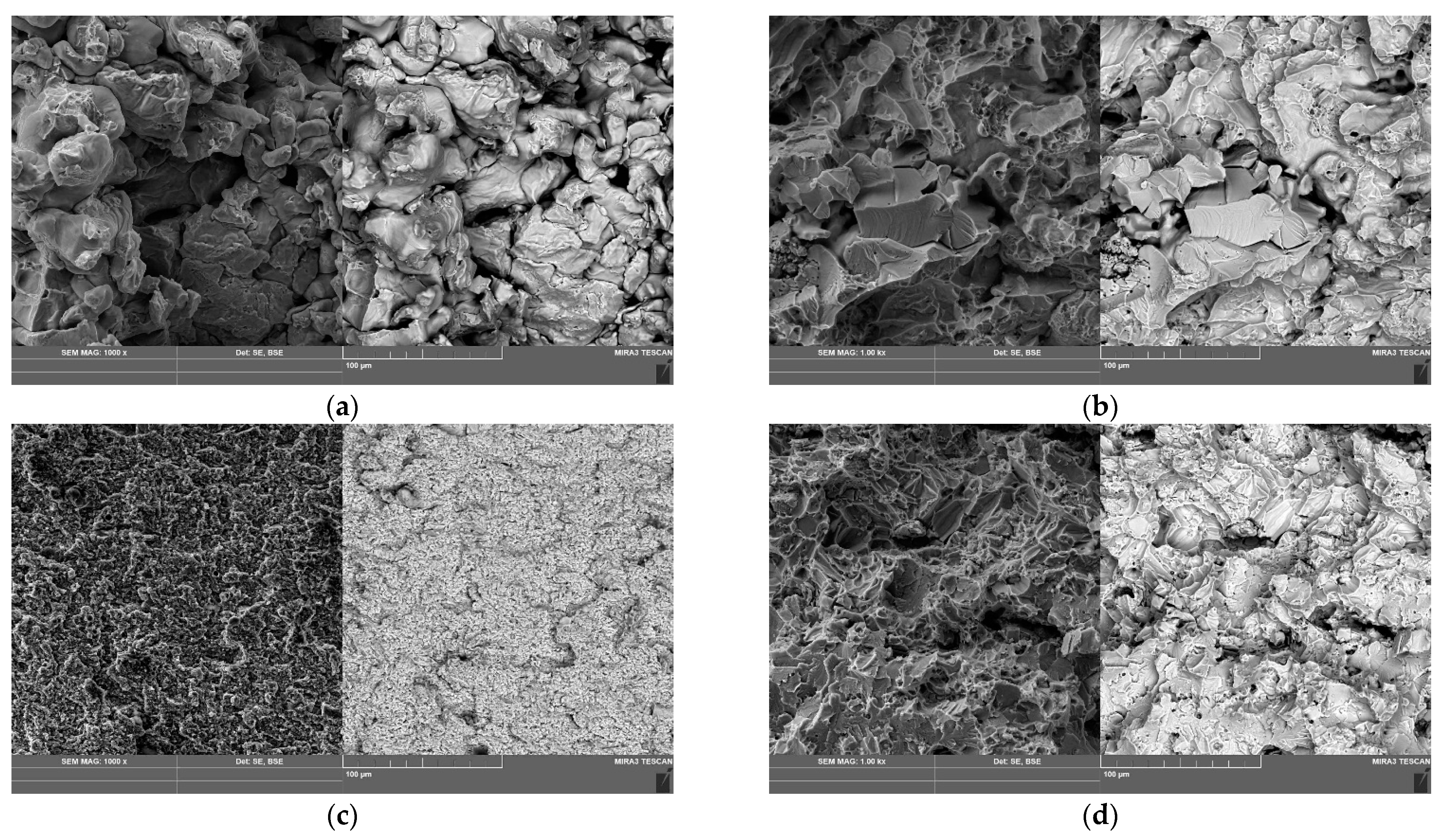
3.1. Structure of the Consolidated Powders
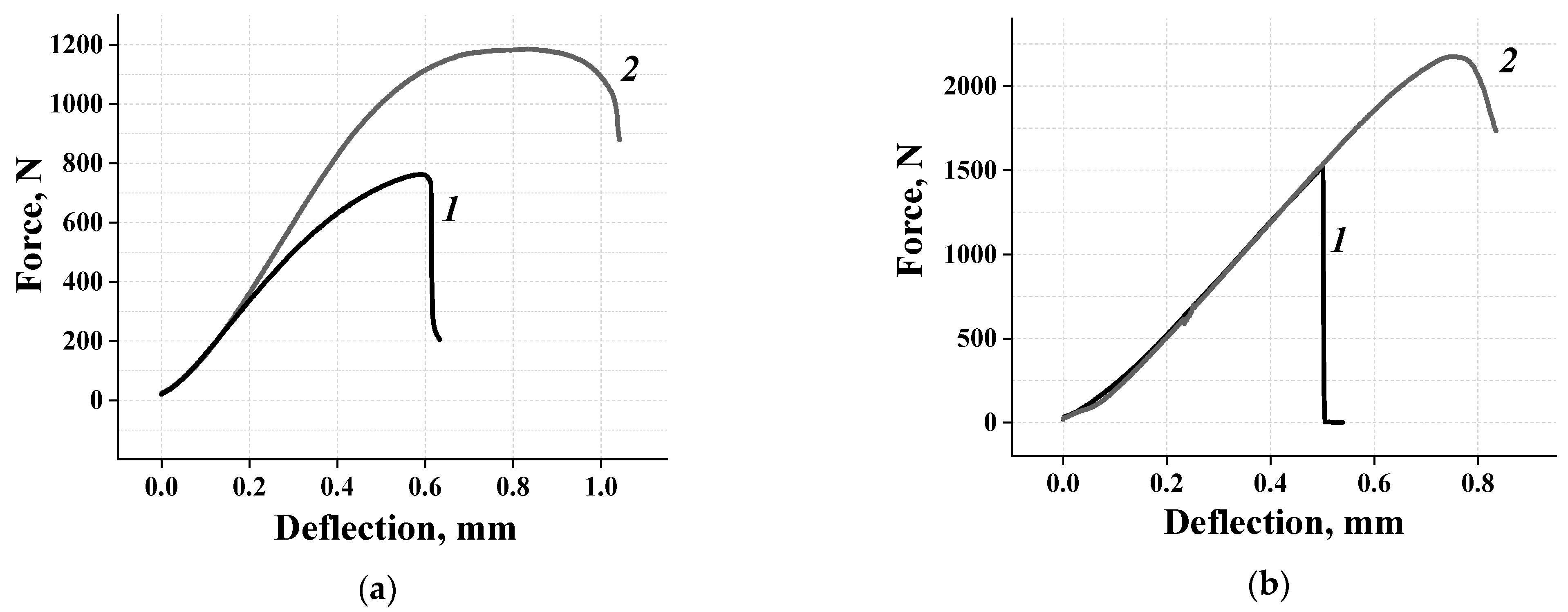
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Fracture Features of the Consolidated Powders
4. Conclusions
- A method of hot compaction of titanium powders using shear deformation is proposed. The method promotes the removal of oxide films from the surfaces of adjacent particles, prevents peripheral cracking and provides residual porosity by not more than 1.0–1.5%;
- The hardness and bending strength of the resulting compacts depend on the dispersivity and hydrogen content of the titanium powder. The highest values of hardness and bending strength have compacts pressed from fine PTOM-1 grade titanium powder, which contains 0.32% hydrogen. The annealing of PTOM-1 compacts at a temperature below α → β transformation temperature increases the bending strength by 60% and moves the fracture from brittle area to brittle—ductile area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HP | hot pressing. |
| HIP | hot isostatic pressing. |
| HC | hot compaction. |
| SE | secondary electron image. |
| BSE | back-scattered electron image. |
References
- Crowley, G. How to extract low-cost titanium. Adv. Mater. Process. 2003, 161, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Froes, F.H.S.; Gungor, M.N.; Imam, M.A. Cost-affordable titanium: The component fabrication perspective. JOM 2007, 59, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlenko, D.V. Technological methods of sealing sintered titanium billets. [Tekhnologicheskiye metody uplotneniya spechennykh titanovykh zagotovok]. Her. Aeroenginebuild. [Vestnik Dvigatelestroeniya] 2015, 1, 87–93. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, G.; Myers, N.S.; German, R.M. An overview of dynamic compaction in powder metallurgy. Int. Mater. Rev. 2008, 53, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y. High-velocity compaction of titanium powder and process characterization. Powder Technol. 2011, 208, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y.; Yin, J. Influence of particle size on property of Ti−6Al−4V alloy prepared by high-velocity compaction. T. Nonferr. Metal. SOC 2013, 23, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Huang, X.; Cui, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, H. Effect of aspect ratio on the compaction characteristics and micromorphology of copper powders by magnetic pulse compaction. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4354–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, A.; Defouw, J.D.; Daehn, G.S. Dynamic compaction of titanium powder by vaporizing foil actuator assisted shearing. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensburger, D.S. Sinter ability of titanium powder. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1970, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensburger, D.S.; Pugin, B.C.; Fedorchenko, I.M. Properties of electrolytic and reduced titanium powders and sinter ability of porous compacts from such powders. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1968, 7, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagliuk, G.A.; Stern, M.B.; Yurchuk, V.L. A comparative analysis of loading modes in the hot re-pressing of a porous blank in a closed die. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1989, 28, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sypko, A.V.; Dolgii, N.I.; Gavrilov-Kryamichev, N.L. Dynamic forging of parts from titanium powder with counter pressure. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1978, 17, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagliuk, G.A. Technological problems of the processes of hot stamping porous blanks [Tekhnologicheskiye problemy protsessov goryachey shtampovki poristykh zagotovok]. J. Mech. Eng. NTUU “Kyiv Polytech. Ins. [Vísnik Natsíonal’nogo Tekhníchnogo Uníversitetu Ukraîni «Kiîvs’kiy Polítekhníchniy Institut». Seriya: Mashynobuduvannya 2009, 56, 93–100. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bagliuk, G.A. Influence of deformation parameters on the structure and properties of hot-forged powder materials [Vliyaniye deformatsionnykh parametrov na strukturu i svoystva goryacheshtampovannykh poroshkovykh materialov]. Press. Mat. Process. [Obrabotka Materialov Davleniyem] 2011, 26, 139–145. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Obodovskii, E.S.; Laptev, A.M. Effect of technological factors on the properties of high-density titanium sponge compacts. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1987, 26, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Nosenko, M.I.; Karlov, L.A. Thermomechanical regime of hot forgine of titanium powder preform. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1991, 30, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovskii, V.S.; Borzetsovskaya, K.M.; Olenina, N.S.; Bolotina, T.A. Hot deformation of sintered titanium powder preforms. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1973, 12, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashenko, A.P.; Pavlov, V.A.; Boguslaev, V.A.; Karlov, L.A.; Avrunina, G.V. Production of P/M titanium materials by hot forging. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1984, 12, 85–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeev, G.A.; Lad’yanov, V.I.; Lubnin, A.N.; Mukhgalin, V.V.; Kanunnikova, O.M.; Mikhailova, S.S.; Aksenova, V.V. Mechanochemical interaction of titanium powder with organic liquids. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9690–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltsev, V.Y.; Osintsev, A.V.; Plotnikov, A.S. Determination of the material elasticity modulus in bending. Lett. Mater. 2017, 2, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Ti Powder | Fe | Ni | Ti | C | Si | Cl | H | N | O | HV200, MPa | Dispersivity, µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP-8 | 0.29 | - | basis | 0.05 * | - | 0.13 | -/0.01 * | 0.025/0.006 * | 1.04 * | 146 | <160 |
| PTM-1 | 0.19 | 0.20 | basis | 0.06 * | - | - | 0.32/0.29 * | 0.07/0.01 * | 1.06 * | 250 | <40 (60%) |
| PTOM-1 | 0.18 | 0.14 | basis | 0.04 * | 0.10 | 0.003 | 0.35/0.32 * | 0.08/0.01 * | 0.97 * | - | <45 |
| Ti Powder | Processing | HV200, MPa | E, GPa | σf, MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP-8 | HC | 2079 ± 210 | 39 ± 4 | 509 ± 23 |
| HC+annealing 870 °C, 2 h | 2174 ± 195 | 47 ± 2 | 712 ± 25 | |
| PTOM-1 | HC | 3688 ± 220 | 55 ± 2 | 723 ± 20 |
| HC+annealing 870 °C, 2 h | 3288 ± 206 | 64 ± 2 | 1148 ± 55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pribytkov, G.A.; Firsina, I.A.; Baranovskiy, A.V.; Krivopalov, V.P. Hot Consolidation of Titanium Powders. Powders 2023, 2, 484-492. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2020029
Pribytkov GA, Firsina IA, Baranovskiy AV, Krivopalov VP. Hot Consolidation of Titanium Powders. Powders. 2023; 2(2):484-492. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2020029
Chicago/Turabian StylePribytkov, Gennady A., Irina A. Firsina, Anton V. Baranovskiy, and Vladimir P. Krivopalov. 2023. "Hot Consolidation of Titanium Powders" Powders 2, no. 2: 484-492. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2020029
APA StylePribytkov, G. A., Firsina, I. A., Baranovskiy, A. V., & Krivopalov, V. P. (2023). Hot Consolidation of Titanium Powders. Powders, 2(2), 484-492. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2020029