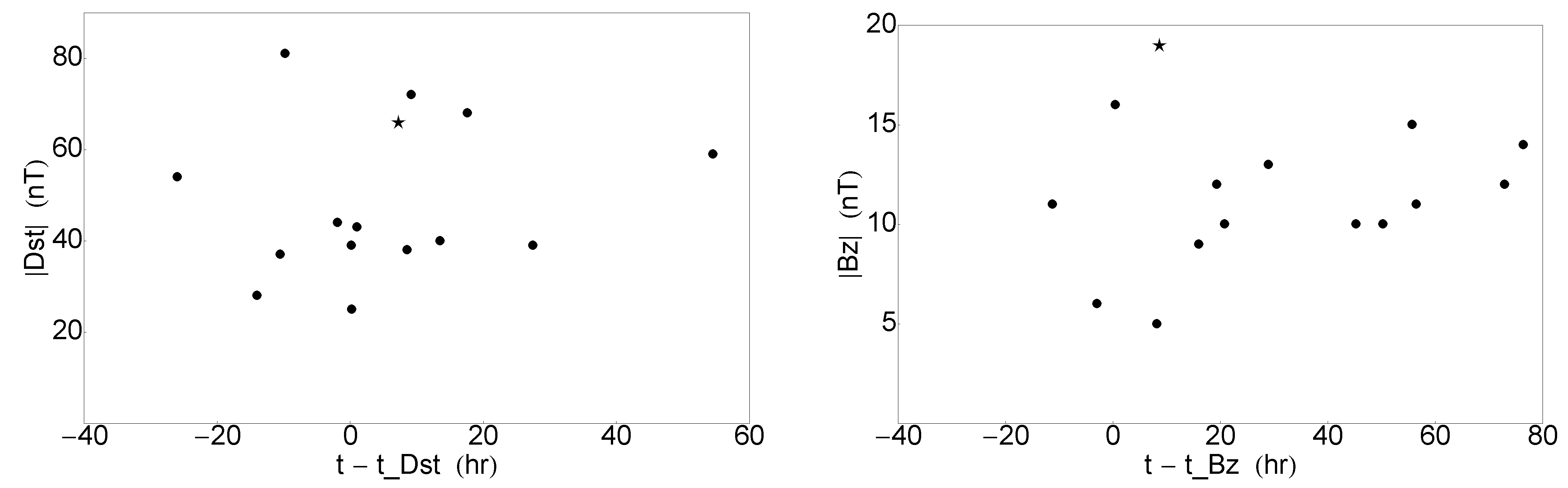Abstract
The study presents a concise overview on the main effects on satellites due to space weather drivers compared to the well-known interplanetary, magnetospheric and ground-based consequences. The solar-activity-driven influences include specific physics-based effects on the spacecraft surface and on-board electronics due to electromagnetic emission and energetic particles as well as complex effects due to geomagnetic storms which may endanger the mission performance and spacecraft longevity. We select as test examples the Starlink satellites in the period 2019–2022 and present the temporal correspondence between their launches and the space weather phenomena. Based on comparative analysis, we discuss whether the occurrence vs. the intensity of solar and interplanetary drivers of space weather can be considered as a cause for orbital stability problems and satellite loss. The results suggest that a sequence of geomagnetic disturbances together with multiple weak space weather events could lead to severe levels of atmospheric drag ending in a service or satellite loss.
1. Introduction
The term ‘space weather’ (SW) first appeared in the scientific literature in 1968; see [1] for a historical review of the relevant terminology. Nowadays, the SW concept includes a multitude of solar drivers and their environmental, technological, and biological effects via different physical mechanisms and a chain of processes. A widely-circulated definition of SW from the 1995 issue of the US National Space Weather Program, The Strategic Plan of Space Weather, reads as ‘conditions on the Sun and in the solar wind, magnetosphere, ionosphere and thermosphere that can influence the performance and reliability of space-borne and ground-based technological systems and can endanger human life or health’ [2]. This multi-disciplinary sphere of research is gaining attention in both academic and commercial aspects due to its social relevance and the high economic costs of extreme SW events [3,4,5].
The solar drivers of SW can be summarized as electromagnetic (EM) emissions by solar flares (SFs); pressure and magnetic field interaction of the coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and fast-speed solar wind streams: co-rotating interaction regions (CIRs)/streaming interaction regions (SIRs); and radiation by solar energetic particles: protons (SEPs) and electrons (SEEs). All these solar activity drivers are known as the solar perspective of SW [6,7,8].
SFs are the most violent explosions in the solar system, releasing up to J of energy, causing magnetic field line re-configurations in the corona, mass motion, and particle acceleration [9,10]. Their EM radiation is the first to arrive at Earth (in about 8 min) and cause SW effects. In contrast, CMEs are the last to arrive (up to 3–5 days after the SF flash phase) and cause a disturbance. The CMEs are large magnetized clouds of plasma expelled from the corona into the interplanetary (IP) space. Single-spacecraft observations provide their on-sky projected speeds which range from a few hundred to over 3000 km s [11,12]. The CMEs are the drivers of the geomagnetic storms (GSs) occurring when a southward-directed IP magnetic field (termed -component) and the day-side of the terrestrial magnetosphere undergo a process known as magnetic reconnection [13,14]. The magnetic reconnection is the underlying process that powers the SFs as well. Nowadays, the chain of processes that takes place in the magnetosphere is well established, leading to the development of ring current systems that eventually causing a decrease in the terrestrial magnetic field. The CMEs near the Sun and their IP counterparts (ICMEs) and their link to GSs have been the topic of numerous research studies, e.g., [15,16,17,18] and the references therein. Apart from the ICME arrivals, high-speed solar wind streams can cause the so-called recurrent GSs, which are usually weaker than the ICME-driven ones, e.g., [19,20].
The intermediate, in time scale, SW effects are those from energetic particles. SEEs arrive shortly after the SF brightening (10s of minutes), whereas SEPs can take hours to be recorded at the spacecraft, usually situated at the first Lagrange point (L1), constantly facing the Sun. These in situ observed electrons, protons, and heavy ions, with keV up to hundreds of MeV energies, show a velocity dispersion in their intensity–time profiles (e.g., the high-energy particle channels peak earlier in time), which is taken as an evidence for their solar origin [21,22]. Despite the ongoing debate in the literature, nowadays both SFs and CMEs are considered as their solar origin [23,24]. The in situ particles can have important SW effects on technology in the IP space. For example, during strong SEP events the spacecraft optical systems can be saturated due to the impact of particles on the CCD matrix, leading to so-called snow-like effects. The images are thus highly degraded in quality, and usually the spacecraft is switched off into a safe mode. Alternatively, permanent damage on the optical system is possible, as well as loss of position/control of the entire spacecraft because the stability is ensured by the pointing towards a few (fixed) stars. The loss of stability can be easily corrected when the spacecraft is relatively near, as in the case on for STEREO mission during the solar storm on 2014-09-01. However, if the satellites are traversing the solar system any misalignment could lead to their loss since longer times are needed to register the problem and send a correcting command. In addition to the limited reaction time, the lack of well-developed mission scenarios for trouble-shooting could be another reason for spacecraft loss.
The galactic counterpart of the energetic particle populations, know as galactic cosmic rays (GCRs, consisting of high-energy particles accelerated at shock fronts of distant supernova explosions) is modulated inversely with the strength of solar activity [25]. This is why, weak solar cycles are accompanied by increased fluxes of GCRs. Their SW effects can be traced to enhanced levels of the total ionization dose received by astronauts [26] and aircrews [27]. The solar energetic particles can contribute by adding extra doses during their sporadic occurrences [28,29]. The danger of radiation exposure to humans in space is considered as the primary obstacle of space travel. Recently, the radiation dose received during a single flight to Mars and back is estimated to contribute up to 60% of the lifelong limit of astronauts [30].
When ICMEs, fast solar wind plasma streams, and/or IP shocks reach the planetary magnetospheres, various atmospheric (and ground-based) effects are possible [31], auroras being the most spectacular ones. Apart from Earth, auroras have been observed around the magnetic poles of Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. Due to the localized (surface) magnetic field on Mars, none on Venus, and lack of atmosphere on Mercury, large scale SW effects are not expected there.
The planetary (with a focus here on the terrestrial) perspective of SW [32] refers to the effects of the solar activity drivers from the magnetosphere down to ground. If the ICME magnetic field is oppositely directed to the one of the planetary magnetosphere, a process of magnetic reconnection can take place. During the field line reconstruction, injected streams of electrons and protons form a ring current, which finally leads to a depression of the horizontal terrestrial magnetic field [33]. This cascade of processes is known as a GS with ICME or fast solar wind stream as its primary driver [34].
Apart from changes in the surface magnetic field, other ground-based effects are also known as a consequence of SW phenomena. One such type is termed ground-level enhancement (GLE) [35], which is the secondary particle products (i.e., neutrons, muons) of high-energy SEP events after their interactions with atmospheric atoms and molecules. Thus, particle events can be the driver of atmospheric radiation storms as they can generate a shower of secondary particles in the Earth’s atmosphere down to lower altitudes. The high-energy secondary particles cause additional radiation dose at the cruising altitudes for aircraft [5].
The consequences of SW can be traced to different (conducting) devices located on/under the ground [32]. The problems experienced in these equipment systems include telluric currents in pipelines, induced effects in submarine cables, and ground-based magnetic interference. Due to their practical importance, a large amount of research is devoted to the geomagnetically induced currents (GICs) [36], which are intense, low-frequency currents induced in large conductive systems like power lines and pipelines [37]. In rare cases, transformer damage also occurred, as, for example, during the GS in March 1989 in Quebec, Canada.
The SW severity ranges from weak to extreme events [38] without strict definitions, as large intensity in one of the parameters does not ensure large values for the accompanied phenomena. Although intense SW events rarely occur [39], they can have substantial influence on our technology-dependent society [40,41]. The largest GS (or/and SW) event on record is the Carrington–Hodgson event (1859-09-01) [42,43], estimated to cause devastating effects in the current technological age [44,45]. As SW is in essence a multi-disciplinary research topic, reviewing the representative literature is a challenging task that goes beyond the scope of our concise report. Instead, many reviews have been preferred here which contain many relevant references. The aim here is to outline the main SW effects with a special focus on the spacecraft anomalies.
2. SW Drivers and Their Effects on Spacecraft Technology
In this report we focus on the effects experienced by satellites during SW events [46], either in the IP space or in the terrestrial magnetosphere and atmosphere. The SW effects vary depending on the local environment surrounding the spacecraft. Several locations are used for satellites orbiting the Earth. Stationary positioning at the Lagrange points is common for many astronomical and solar-dedicated missions (e.g., on the Sun–Earth line, at about 1.5 million km, either always facing the Sun at L1 or hiding in the Earths’ shadow at L2). In contrast, the other common orbits are geostationary (GEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), low Earth orbit (LEO), and polar and Sun-synchronous orbits (https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Types_of_orbits, accessed on 17 August 2023). Each of them experiences a different space and terrestrial environment, or a combination of both. Thus, the spacecraft will be subject to different plasma, particle, and EM influences which require different sets of observations, models, and forecasting tools. Below, we compose a concise review on the SW effects according to the essence of the driver (https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/noaa-scales-explanation, accessed on 17 August 2023) in terms of light, magnetized plasma, or energetic particles, e.g., [2,8,45] and the references therein.
2.1. EM Emission
The photons of different energies can interact with the hardware and software systems aboard the spacecraft. These sporadic bursts of additional EM radiation are due to the SF eruptions.
Enhanced ultraviolet (UV), extreme ultraviolet (EUV), and X-ray radiation are known to affect the upper atmosphere, namely the ionosphere heats and expands. Ionospheric disturbances have several consequences on the satellites and their work performance, and the effects are known for many decades [47]. The perturbed ionosphere can cause delay, distortion, and absorption of radio signals during their propagation. The delay occurs since the ionosphere increases the propagation path for the signal, thus affecting the quality of satellite communication, navigation, and positioning. Ionospheric density inhomogeneities lead to the so-called scintillation patterns. SF emission can be also the reason of day-side radio blackouts due to plasma density increases known as sudden ionospheric disturbances. Less common are the direct interferences with the radar systems due to solar radio bursts (e.g., air traffic control problems in Sweden on 2015-11-04). The largest SFs can also cause a minor disturbance (magnetic crochet) of the magnetic field.
The spacecraft-related effects of the EM emission can be summarized as follows:
- Satellite signal degradation and loss;
- Radio blackouts;
- Increased atmospheric drag.
2.2. Magnetized Plasma Structures
Incoming fast-speed plasma structures with magnetic field orientation opposite to the terrestrial dipole are the drivers of geomagnetic sub-storms (due to CIRs/SIRs) and storms (due to ICMEs) in the magnetosphere. These are complex events, often preceded by increased EM emission and accompanied by fluxes of energetic particles. Their combined effects lead to an expansion of the upper atmosphere. The related frequent collisions with neutral atoms cause an increased atmospheric drag, affecting mostly LEO satellites [48,49] as well as the Starlink constellations of spacecraft at very low Earth orbit (VLEO), e.g., [50]. As a result, the altitude decreases gradually, which requires re-entry boosts in order to avoid tracking loss. That leads to premature fuel exhaustion and shortens the lifetime of the mission. Their increased fuel requirements mean heavier spacecraft and thus larger costs for the spacecraft owners.
Another major consequence of the GSs is the ground-level effects, namely GICs, that carry significant risk for ground-based, marine, and underground infrastructure, e.g., [2].
2.3. Energetic Particles
SEPs, SEEs, heavy ions, and neutrons which are energized in an SF reconnection event and/or a CME-driven shocks [22,51] may have a direct impact on the Earth and near-Earth environment as well as an immediate impact on satellite operations [52,53]. They can cause many deleterious effects and accelerate material aging by altering their electrical and optical properties, which may gradually reduce the performance of solar cells by up to ∼10%. Also, they may cause device leakage and power consumption and, eventually, can decrease the overall functionality of the space systems [32]. The particle effects as a function of energy, species, and origin are given in more detail in [8], in their Table 3, whereas the spacecraft anomalies as a function of the their orbits are explored by [54] with high-altitude and high-inclination being the most vulnerable ones.
The physical principle of the high-energy particle interaction with various substances is based on the energy deposition (e.g., total ionizing dose effects) and the creation of a charge in the material of the spacecraft (or in the semiconductor lattice structure, e.g., due to displacement damage dose effects) or its electronics, such as the single event effects. The latter are mostly software related and in the extreme cases may require power reset of the system, but some of the particle-related effects can be destructive and irreversible. The surface charging effects can cause charge build-up leading to high-voltage potential differences between different parts of the spacecraft and thus are considered as a serious risk. Alternatively, the deep dielectric charging effects are due to high-energy particles causing discharges inside the spacecraft components. These and other engineering aspects have been investigated in detail, e.g., [52,53,55,56], either for the preparation of space-hardened materials or for the development of various mitigation strategies.
Below are given the main spacecraft-related effects due to energy deposition of energetic particles, as already described above:
- Single-event upsets/single-event effects;
- Cumulative radiation effects (total ionizing dose and displacement damage dose);
- Surface discharges;
- Deep dielectric charging;
- Solar cell degradation, material aging/surface damage to materials.
3. Notable Satellite Failures
3.1. Historical Overview
Since the satellite malfunctions are not subject to public disclosure, the academic investigation of direct or indirect SW effects on satellites is hindered to a large degree. An incomplete list of known satellite failures is provided in Table 1 (see e.g., https://swe.ssa.esa.int/TECEES/spweather/workshops/esww/proc/brekke_stoa5.pdf, https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19810005468/downloads/19810005468.pdf, accessed on 17 August 2023). We add significant radio blackouts reported by [8] and some major SW-driven failures on ground due to GICs, as outlined by [45].

Table 1.
A list of known satellite/ground-based failures: date (the format yyyy-mm-dd is used here and also in the text); satellite name or type of infrastructure; orbit or location; type of the anomaly; probable cause for the anomaly.
3.2. The ‘SpaceX’ Storm: 2022-02-03
The most recent example of destructive SW influence on technology is the loss of 38 out of 49 Starlink satellites during the so-called ‘SpaceX’ storm [50,57]. The overall conditions were estimated as a modest SW event [50] and minor (G1) to moderate (G2) GS [58], according to the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center G-scale metric (https://www.swpc.noaa.gov/noaa-scales-explanation, accessed on 17 August 2023). The general guidance issued indicated probable corrective actions to orientation and predicted a possible orbital drag. Based on the issued forecast and the empirical thermospheric neutral density model used, the launch proceeded as planned at 18:11 UT on 2022-02-03 with an initial orbit of 210 km perigee. The launch occurred on the recovery phase of G1 and a few hours before a subsequent G1 GS. Based on an alternative geomagnetic indices, the first storm reached Dst nT (11 UT; the exact values of Dst in 2022 may be subject to change, https://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dst_realtime/, accessed on 17 August 2023) and Kp of 5+ on 2022-02-03 and followed by another GS with Dst nT (21 UT) and Kp = 5+ on 2022-02-04, respectively. Despite the modest strength of the GSs, it was noted that the launch took place at the time when the thermosheric neutral density had reached its maximum increase [59]. This was the first time for a Starlink constellation to experience an enhanced level of atmospheric drag (reported by the operator as 50% higher than previous launches) that ultimately led to the loss of most spacecraft by 2022-02-07. The next scheduled launch by SpaceX used a 300 km initial orbit in order to minimize such risks [50].
The solar origin of the GSs as well as the IP conditions (solar wind, shock, ICME, , F10.7) are described in great detail in [59,60,61] and can be summarized as follows: a series of SFs (e.g., M1.1/2022-01-29/23:29 and C5/2022-01-30/01:29 from the same active region 12396 with location N17E11) and multiple CMEs occurred over a period of several days prior the launch. Among the CMEs, we note a halo one on 2022-01-29 that had a projected speed of 530 km s and a second one on 2022-02-01 that was faster than 1000 km s, based on information from https://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/, accessed on 17 August 2023. [59] reported 637 and 791 km s from the CACTUS CME catalog, https://www.sidc.be/cactus/catalog.php, accessed on 17 August 2023, whereas [61] estimated speeds from the Graduated Cylindrical Shell model to 777 and 420 km s for the CMEs on 2022-01-30 and 2022-01-31, respectively. These CMEs merged into the IP space and led to a complex ICME/shock signatures at Earth causing a double GS with a complex profile: (1) a two-step decrease can be noticed on 2022-02-03 with a minimum Dst index of nT at 11 UT and a second step of nT at 15–16 UT on the recovery phase and (2) an extended minimum over many hours over 2022-02-04 reaching nT at 21 UT. The detailed analysis of the IP data also reveals signatures of magnetic flux rope and long-lasting periods of fast solar wind and negative .
The majority of the previous research on the Starlink failure focuses on evaluating the increase in the neutral density at the spacecraft orbit of 210 km. These studies use observational data [62] and empirical [59] or physics-based models [57,58,60] to test in more detail the performance of the simulations and forecasts currently in use. In summary, the studies all point towards an increased atmospheric drag due to the enhanced neutral density in the thermosphere. However, a different magnitude of the enhancement is reported by the different teams, ranging from 20–30% [59,61] at the lowest end, 50% [60], 40–60% [62], 50–125% [58], with up to ∼150% [57] as the highest reported value.
The increased atmospheric drag described above is the primary suspect for the notable Starlink failure. In addition, an increased EUV irradiance months prior to the storm [59], emissions from long-duration SFs [60], as well as radiation exposure due to solar energetic particles might also be contributing factors to the satellite failure.
4. Results
Instead of focusing on the Starlink launch on 2022-02-03, as the majority of the previous research noted above, we prefer to consider all SpaceX launches in the period 2019–2022, since the information on the timing and number of satellites still in orbit is freely available. The aim of our analysis is to identify the geomagnetic disturbances which are well known to endanger the satellite performance. We start by identifying the value of the Dst index (as one proxy for the GS strength) at the time of the launches. A focus is then put on the cases occurring during the strongest geomagnetic disturbances. We consider the conditions not only before and after the launch time but also co-temporal with the launch. The event on 2022-02-03 is depicted with a different symbol in the plots for comparative purposes.
4.1. Space Weather Conditions during Starlink Launches
We complement our brief literature overview of the SW effects with the analysis of Starlink satellite launches in about three-year period (2019–2022) as listed in Appendix A. We identified first the Dst index at the nearest hour to the launch time, as provided by the Kyoto (provisional and real-time) database, https://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dstdir/index.html, accessed on 17 August 2023. Based on the Dst values, none of the cases qualified as a GS, as all values were ≤−50 nT.
Thus, we increased the time window of interest of about 1–2 days around the spacecraft launch in order to capture any GSs. From the entire list, we selected 15 Starlink launches accompanied by geomagnetic disturbances with Dst index down to nT, Table 2. The threshold is, however, to some degree subjectively chosen. Nevertheless, we do not expect SW effects due to geomagnetic disturbances weaker than this limit.

Table 2.
Starlink launches and accompanied magnetospheric and IP phenomena: date (yyyy-mm-dd) and time (hh:mm) of the Starlink launches; day (dd), nearest hour (hh), and value (in nT) of the Dst index of the GS; day/time/speed (in km s) of the ICME; day/time/speed (in km s) of the IP shock, density jump at the shock surface (in cm); day/time/value (in nT) for component. All times are in UT. No reported events are denoted with ‘no’.
None of the remaining GSs has the double profile and complexity as the case of GSs on 2022-02-03 and 04, described earlier. Some of the launches occur around times of long-lasting but always weak geomagnetic disturbances. Despite the step-like recovery profile, the strongest GS in Table 2 also shows a single drop in the Dst index.
We focus on the IP conditions (presence or not of ICMEs, IP shocks and -values) occurring close in time to the Starlink launches. The events are listed chronologically in Table 2. Only six cases have been accompanied by ICMEs, and only four of them have an IP shock with reported speeds ranging between ∼340 and 820 km s. ICME information is adopted from the online list, https://izw1.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/icmetable2.htm, accessed on 17 August 2023. IP shock information is collected from the Wind spacecraft, https://lweb.cfa.harvard.edu/shocks/wi_data/, accessed on 17 August 2023, due to the larger data coverage of the database.
The strongest value ( nT) of the southward magnetic field component () of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) is for the Starlink failure case. Interestingly, at the time of the second weakest ( nT), we observe the fastest IP ejecta in the list, reaching 820 km s for the shock speed. The fast (projected) speeds for the incoming ejecta at the Earth are not a determining factor for the GS strength, whereas the GSs (here minor to moderate) are usually related to large values of . The component is identified from the data provided by https://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/form/dx1.html, accessed on 17 August 2023. All the IP data is inspected for abrupt changes from about a two-day period before to one day after the spacecraft launch. The exact timings are given in Table 2.
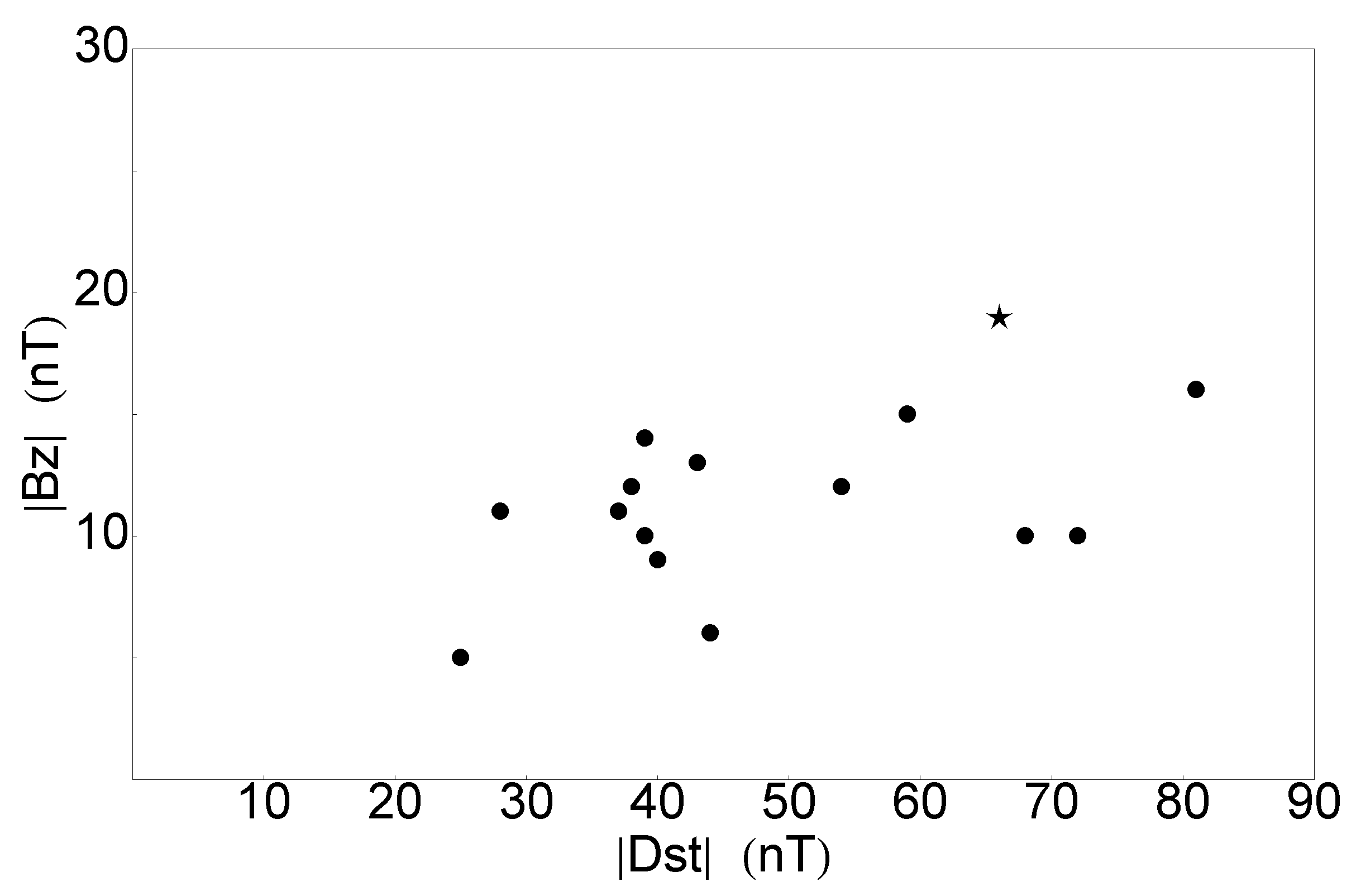
The magnitude of the does not seem to be an ordering parameters in terms of identifiable ICME at Earth, see Table 2, as the second weakest ( nT) is also related to the fastest ICME in our list (610 km s). The positive trend known to exist between the Dst index and -component is also examined for the above sample and given in Figure 1. Due to the fewer event pairs, the reliability of any type of correlation coefficients (e.g., Pearson, with a value of 0.52) is highly questionable as the scatter plots are subject to statistical noise.
Figure 1.
Scatter plot of the modulus of Dst index and component of the events in Table 2. The 2022-02-03 case is shown with a star symbol.
We continue by evaluating both the SFs and particle fluxes co-occurring with the spacecraft launch. Any effects due to EM emission, particle radiation and/or ejecta/shock arrival at Earth could be considered as a potential, additional risk for the spacecraft stability in addition to the (ongoing) geomagnetic disturbance. Namely, we provide information about the solar emission in terms of soft X-rays (SXRs), e.g., ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/warehouse/ and https://www.solarmonitor.org/, accessed on 17 August 2023. Additionally, the SEP and SEE fluxes are inspected by us from the Wind/EPACT and ACE/EPAM data, provided by https://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html, accessed on 17 August 2023, in a similar way as provided for the proton [23] and electron catalog [24]. The SFs and particle events are selected only if they occur simultaneously or in a period of several hours from the spacecraft launch. The results are summarized in Table 3 for the same event sample as in Table 2.

Table 3.
Starlink launches and accompanied solar/SW phenomena: date (yyyy-mm-dd) and time (hh:mm) of the Starlink launches; SF day/start/peak/end time/class; SEP day/peak time; SEE day/peak time. All times are in UT. Abbreviations: on: ongoing; pr: preceding; s: start time; su: succeeding.
Only for six launches, there is SXR emission found, started either before or, in one case, shortly after the launch. Compared with the IP conditions summarized in Table 2, we obtained coincidence only for two cases: 2021-05-26 and 2022-02-03. In both cases, the SFs are of the negligible (B7) or weak (C1.1) classes. Several hours following the launch on 2022-02-03, there are in situ electrons detected at L1. The only event with both proton and electron fluxes in addition to an ongoing C3-class SF is the launch on 2022-04-29; however, the GS is negligible with a Dst index of nT, and there are no IP signatures.
The accompanied EM emission and particle flux is expected to affect the mission performance when the timing of arrival at Earth overlaps with the launch time. During 2020 and 2021, there are no strong SFs or particle events. During 2022, there are more instances when the EM emission from an SF might add to the SW pre-conditioning during the spacecraft launch. The emission in SXRs is, however, rather weak; namely, the strongest is a C5 class (or W m). With respect to the radiation environment, only a single SEP and three SEEs could be identified, which confirms the relatively quiet background during the selected examples in Table 3. The SEE event at the Starlink failure case starts several hours after the actual launch. However, since the spacecraft failure occurred several days after the launch, 2022-02-07, the radiation exposure effect (from delayed solar or magnetospheric origin) may still have contributed to the hazardous environment at the satellite orbit.
For completeness, we show the time differences between the Starlink launches and Dst time (Figure 2, left) and Starlink launches and time (on the right). Positive numbers denote GSs occurring before the launches (preceding or ongoing at the time of spacecraft deployment), which is the majority of the cases, whereas negative times denote successive events (which take place after the spacecraft has been launched). The Starlink failure is a GS-preceding case but relatively close to the launch time in both cases. Its accompanied GS (denoted as nT) is among the largest GSs in the list but not the strongest, which occurred on 2022-07-07 with Dst nT (we have identified an ICME, but no IP shock, SF or particle events in this case).
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of the difference between Starlink spacecraft launch (t) and Dst time (on the left) or time (on the right). The 2022-02-03 case is shown with a star symbol.
4.2. A Comparative Analyses on the Starlink Failure Event
Among the set of events from Table 2, the case of Starlink failure coincides with a preceding SF. Despite the weak flare strength in SXRs (C1.1 class ending one day prior the launch), the terrestrial ionosphere could still be disturbed due to an increased UV emission. Such preconditioning coincides with the arrival of an IP disturbance with southward , the development of dual minor-to-medium GSs, and a subsequent flux of energetic electrons (but not protons). No other events in Table 2 and Table 3 have such a set of SW phenomena. The visual inspection of the Dst profiles of the other 14 GSs also singles out the SpaceX storm. Due to the limited event sample, we could only speculate whether a spacecraft launch that occurs between GSs (and accompanied by an ICME, IP shock and negative beyond certain threshold) in addition to an SF and particle radiation component is the right mix of preconditions that could lead again to a spacecraft failure in the future. Increased atmospheric drag and compromised electronics on board due to radiation exposure by increased particle precipitation could be an additional cause for the failure.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Although the majority of the previous research [57,58,59,60,61,62] concluded that the notable Starlink failure was due to the increased atmospheric drag, ranging from 20–30% up to 150% at the staging orbit of 210 km, some doubts are raised if that it is the sole cause [63]. Despite the fact that the latter also estimated an increased thermospheric mass density by 35%, these authors proposed that GSs occurring in close succession (within about one day) are accountable for more negative SW effects on spacecraft operation and stability. The effects of the atmospheric drag on LEO satellites has been the topic of intense research, e.g., [48,49] and the references therein. Although it is well known that GSs lead to a global increase in the thermospheric neutral density, Joule heating due to EUV flare emission, and particle precipitation cause additional expansion in the 100−200 km region (or VLEO) [62]. There are several existing models, both empirical and physics-based, of the magnetospheric response during GSs, e.g., [64,65]. Due to the lack of operational schemes (forecasting and nowcasting) on the coupling between thermosphere–ionosphere–atmosphere [59], however, the danger of similar satellite failures is still present. Further research into the satellite failures due to SW impacts will contribute to a better quantification of the economic losses and raise the importance of proper forecasting and nowcasting services to the benefit of satellite owners.
In contrast with a detailed magnetospheric or in situ data analysis of the SpaceX storm, we present in this study the solar and near-Earth IP contributions at the time of selected Starlink launches in order to evaluate the additional impact of the EM and radiation environment. The intensity of these solar and IP phenomena can be considered to be of minor to moderate importance compared to the largest values on record. In the current understanding of the SW effects, the observed weak-to-moderate SFs, particle events, and IP phenomena (e.g., strength of IMF -component) are not expected to be responsible for the poor spacecraft performance, even less for its failure. Our results support the search for additional causes of the failure of Starlink satellites launched during an ongoing GS on 2022-02-03 and confirms that the cumulative effects of multiple weak SW events carry a hidden risk to (V)LEO satellites. With the increase in commercial constellations and expected growth of the in orbit satellite services (IoS) industry, there will be a need faced by satellite owners to protect their satellites in orbit from SW events in order to mitigate the economic losses incurred by such SW anomalies.
This study offers a concise summary of known SW effects on satellites, including solar activity and magnetospheric, ionospheric, and atmospheric effects. We performed a comparative analysis of Starlink spacecraft launches based on the largest Dst index within about one-day period around the time of launch. The notable failure of the 2022-02-03 Starlink launch (the SpaceX storm) coincides with minor GSs preceding and following the launch (with the related arrival of IP ejecta and shock wave), a preceding weak SF, and an increased flux of energetic electrons following the launch by several hours. The radiation environment (both by in situ energetic particles and by increased particle fluxes in the van Allen belts) might be a contributing factor to the satellite’s overall performance and ability to maintain orbital stability. The usage of radiation-hardened satellite components even for LEO and VLEO may well minimize future failure risks, which should be taken into consideration especially during solar activity maximum periods. Spacecraft operators and owners could consider the following mitigation strategies, particularly in view of the fact that 43% of GEO and 6% of LEO satellites are insured (data from 2018, https://payloadspace.com/the-space-insurance-landscape/, accessed on 17 August 2023): a delay in the launch in order to avoid ongoing GS or multiple GS-arrival; development of physics-based forecasting schemes tailored to the specific operational needs; consideration of a higher staging orbit (currently being implemented); and investment in the development of improved propulsion systems to counteract the atmospheric drag. Such strategies aim at utilizing in full the nominal lifetime of the spacecraft in order to ensure reliable services but also to regulate space debris pollution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.; methodology, R.M., S.W.S. and S.T.; software, R.M.; validation, R.M. and S.W.S.; formal analysis, R.M. and S.W.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.; writing—review and editing, R.M., S.W.S. and S.T.; visualization, R.M.; project administration, R.M. and S.W.S.; funding acquisition, R.M. and S.W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Bulgarian-Egyptian inter-academy project by the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences IC-EG/08/2022-2024 and Egyptian Academy of Scientific Research and Technology (ASRT)/NRIAG (ASRT/BAS/2022-2023/10116). The authors thank Arno Wielders for the valuable discussions.
Data Availability Statement
Data and results from open access databases have been used in this work and the links are provided in the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The views expressed in this paper are the sole responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Innovation Council and SME Executive Agency. The Authors are not liable for any consequence stemming from the reuse of this publication.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CCD | Charge-coupled device |
| CIR | Co-rotating interaction region |
| CME | Coronal mass ejection |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| EUV | Extreme ultraviolet |
| GCR | Galactic cosmic rays |
| GEO | Geostationary Earth orbit |
| GIC | Geomagnetically induced current |
| GLE | Ground-level enhancement |
| GS | Geomagnetic storm |
| ICME | Interplanetary CME |
| IMF | Interplanetary magnetic field |
| IP | Interplanetary |
| LEO | Low Earth orbit |
| MEO | Medium Earth orbit |
| SEE | Solar energetic electron |
| SEP | Solar energetic proton |
| SF | Solar flare |
| SIR | Stream interaction region |
| SSC | Sudden storm commencement |
| SW | Space weather |
| SXR | Soft X-ray |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VLEO | Very low Earth orbit |
Appendix A. Starlink Launch Information (2019–2022)
The table lists all Starlink launches in the period 2019–2022, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Starlink_and_Starshield_launches (accessed on 17 August 2023) and the Dst index as reported by the https://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dst_provisional/index.html and https://wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dst_realtime/index.html (accessed on 17 August 2023) at the nearest full hour and closest to the launch time. Such a procedure confirms the overall quiet time at the time of the spacecraft launches that took place in a period of the solar minimum.

Table A1.
Starlink launch information: Date (yyyy-mm-dd), Time (hh:mm); Orbit (altitude, in km)/orbital inclination, in deg), Number (of deployed/working satellites), Dst index (in nT) at the nearest hour of the launch.
Table A1.
Starlink launch information: Date (yyyy-mm-dd), Time (hh:mm); Orbit (altitude, in km)/orbital inclination, in deg), Number (of deployed/working satellites), Dst index (in nT) at the nearest hour of the launch.
| Date | Time | Orbit | Number | Dst | Date | Time | Orbit | Number | Dst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-11-09 | 14:56 | 550/53 | 60/43 | 2022-01-06 | 21:49 | 540/53.2 | 49/49 | −4 | |
| 2020-01-07 | 02:19 | 550/53 | 60/43 | 2022-01-19 | 02:03 | 540/53.2 | 49/49 | ||
| 2020-01-29 | 14:06 | 550/53 | 60/48 | 2022-02-03 | 18:13 | 540/53.2 | 49/10 | ||
| 2020-02-17 | 15:05 | 550/53 | 60/48 | 0 | 2022-02-21 | 14:44 | 540/53.2 | 46/46 | |
| 2020-03-18 | 12:17 | 550/53 | 60/53 | 5 | 2022-02-25 | 17:12 | 540/53.2 | 50/50 | 7 |
| 2020-04-22 | 19:31 | 550/53 | 60/51 | 2022-03-03 | 14:25 | 540/53.2 | 47/47 | 14 | |
| 2020-06-04 | 01:25 | 550/53 | 60/54 | 2022-03-09 | 13:45 | 540/53.2 | 48/47 | ||
| 2020-06-13 | 09:21 | 550/53 | 58/42 | 2022-03-19 | 04:43 | 540/53.2 | 53/47 | ||
| 2020-08-07 | 05:12 | 550/53 | 57/54 | 2022-04-21 | 17:52 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | ||
| 2020-08-18 | 14:31 | 550/53 | 58/53 | 4 | 2022-04-29 | 21:27 | 540/53.2 | 53/52 | |
| 2020-09-03 | 12:46 | 550/53 | 60/52 | 0 | 2022-05-06 | 09:42 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | |
| 2020-10-06 | 11:30 | 550/53 | 60/51 | 2022-05-13 | 22:08 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | ||
| 2020-10-18 | 12:26 | 550/53 | 60/47 | 2 | 2022-05-14 | 20:41 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | 19 |
| 2020-10-24 | 15:32 | 550/53 | 60/44 | 2022-05-18 | 11:00 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | ||
| 2020-11-25 | 02:13 | 550/53 | 60/42 | 2022-06-17 | 16:09 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | ||
| 2021-01-20 | 13:02 | 550/53 | 60/57 | 2 | 2022-07-07 | 13:11 | 540/53.2 | 53/52 | 29 |
| 2021-01-24 | 15:00 | 560/97.5 | 10/0 | 12 | 2022-07-11 | 01:40 | 560/97.6 | 46/46 | |
| 2021-02-04 | 06:19 | 550/53 | 60/56 | 0 | 2022-07-17 | 14:20 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | |
| 2021-02-16 | 04:00 | 550/53 | 60/57 | 4 | 2022-07-22 | 17:40 | 560/97.6 | 46/46 | |
| 2021-03-04 | 08:25 | 550/53 | 60/56 | 2022-07-24 | 13:38 | 540/53.2 | 53/51 | ||
| 2021-03-11 | 08:13 | 550/53 | 60/60 | 9 | 2022-08-10 | 02:15 | 540/53.2 | 52/51 | |
| 2021-03-14 | 10:01 | 550/53 | 60/58 | 2022-08-12 | 21:40 | 560/97.6 | 46/46 | ||
| 2021-03-24 | 08:28 | 550/53 | 60/45 | 2022-08-19 | 19:21 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | ||
| 2022-08-19 | 19:21 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | 2022-08-28 | 03:41 | 540/53.2 | 54/51 | ||
| 2021-04-07 | 16:34 | 550/53 | 60/60 | 2022-08-31 | 05:40 | 560/97.6 | 46/46 | ||
| 2021-04-29 | 03:44 | 550/53 | 60/60 | 6 | 2022-09-05 | 02:10 | 540/53.2 | 51/46 | |
| 2021-05-04 | 19:01 | 550/53 | 60/60 | 2 | 2022-09-11 | 01:20 | 540/53.2 | 34/31 | |
| 2021-05-09 | 06:42 | 550/53 | 60/58 | 6 | 2022-09-19 | 00:19 | 540/53.2 | 54/53 | 5 |
| 2021-05-15 | 22:56 | 569–582/53 | 52/49 | 2022-09-24 | 23:32 | 540/53.2 | 52/51 | ||
| 2021-05-26 | 18:59 | 550/53 | 60/60 | 40 * | 2022-10-05 | 23:11 | 540/53.2 | 52/52 | |
| 2021-06-30 | 19:31 | 560/97.5 | 3/3 | 2022-10-20 | 14:51 | 540/53.2 | 54/53 | −3 | |
| 2021-09-14 | 03:56 | 570/70 | 51/50 | 2022-10-28 | 01:14 | 540/53.2 | 53/53 | 0 | |
| 2021-11-13 | 11:20 | 540/53.2 | 53/52 | 0 | 2022-12-17 | 21:32 | 540/53.2 | 54/54 | 13 |
| 2021-12-02 | 23:12 | 540/53.2 | 48/48 | 2022-12-28 | 09:34 | 530/43 | 54/54 | ||
| 2021-12-18 | 12:42 | 540/53.2 | 52/50 | 2 | |||||
* SSC.
References
- Cade, W.B., III; Chan-Park, C. The Origin of “Space Weather”. Space Weather 2015, 13, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, R.; Kauristie, K.; Lappalainen, H.; Viljanen, A.; Pulkkinen, A. Space weather risk. Space Weather 2005, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, J.P.; Biffis, E.; Hapgood, M.A.; Green, L.; Bisi, M.M.; Bentley, R.D.; Wicks, R.; McKinnell, L.A.; Gibbs, M.; Burnett, C. The Economic Impact of Space Weather: Where Do We Stand? Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oughton, E.J.; Skelton, A.; Horne, R.B.; Thomson, A.W.P.; Gaunt, C.T. Quantifying the daily economic impact of extreme space weather due to failure in electricity transmission infrastructure. Space Weather 2017, 15, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Wickramasinghe, N.K.; Sato, T.; Shiota, D. Estimate of economic impact of atmospheric radiation storm associated with solar energetic particle events on aircraft operations. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenn, R. Space Weather: The Solar Perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmer, M. Space weather: The solar perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N. The Sun and Space Weather. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, L.; Dennis, B.R.; Hudson, H.S.; Krucker, S.; Phillips, K.; Veronig, A.; Battaglia, M.; Bone, L.; Caspi, A.; Chen, Q.; et al. An Observational Overview of Solar Flares. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 159, 19–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, A.O. Flare Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F. Coronal Mass Ejections: Models and Their Observational Basis. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2011, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.F.; Howard, T.A. Coronal Mass Ejections: Observations. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2012, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungey, J.W. Interplanetary Magnetic Field and the Auroral Zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1961, 6, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, J.T.; Bame, S.J.; McComas, D.J.; Phillips, J.L. Coronal mass ejections and large geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Richardson, I.G.; Webb, D.F.; Gopalswamy, N.; Huttunen, E.; Kasper, J.C.; Nitta, N.V.; Poomvises, W.; Thompson, B.J.; Wu, C.C.; et al. Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (Dst ≤ −100 nT) during 1996–2005. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, A10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N. Solar connections of geoeffective magnetic structures. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 2078–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G.; Cane, H.V. Solar wind drivers of geomagnetic storms during more than four solar cycles. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2012, 2, A01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, S. Geomagnetic storms of cycle 24 and their solar sources. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G.; Webb, D.F.; Zhang, J.; Berdichevsky, D.B.; Biesecker, D.A.; Kasper, J.C.; Kataoka, R.; Steinberg, J.T.; Thompson, B.J.; Wu, C.C.; et al. Major geomagnetic storms (Dst ≤ −100 nT) generated by corotating interaction regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, A07S09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanac, G.; Vršnak, B.; Živković, S.; Hojsak, T.; Veronig, A.M.; Temmer, M. Solar wind high-speed streams and related geomagnetic activity in the declining phase of solar cycle 23. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 533, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Giacalone, J. Large gradual solar energetic particle events. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2016, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.L.; Dalla, S. Acceleration and Propagation of Solar Energetic Particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 1107–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R.; Samwel, S.W.; Costa-Duarte, M.V. The Wind/EPACT Proton Event Catalog (1996–2016). Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwel, S.W.; Miteva, R. Catalogue of in situ observed solar energetic electrons from ACE/EPAM instrument. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 505, 5212–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, R.D.; Leske, R.A.; Rankin, J.S. The Modulation of Anomalous and Galactic Cosmic-Ray Oxygen over Successive Solar Cycle Minima. Astrophys. J. 2023, 944, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Song, X.; Huo, R.; Luo, X. Astronaut Radiation Dose Calculation With a New Galactic Cosmic Ray Model and the AMS-02 Data. Space Weather 2023, 21, e2022SW003285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Kataoka, R.; Sato, T. Cosmic ray modulation and radiation dose of aircrews during the solar cycle 24/25. Space Weather 2017, 15, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkova, J.; Dachev, T.; Koleva, R.; Bankov, N.; Maltchev, S.; Benghin, V.; Shurshakov, V.; Petrov, V. Observation of radiation environment in the International Space Station in 2012–March 2013 by Liulin-5 particle telescope. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2014, 4, A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwadron, N.A.; Cooper, J.F.; Desai, M.; Downs, C.; Gorby, M.; Jordan, A.P.; Joyce, C.J.; Kozarev, K.; Linker, J.A.; Mikíc, Z.; et al. Particle Radiation Sources, Propagation and Interactions in Deep Space, at Earth, the Moon, Mars, and Beyond: Examples of Radiation Interactions and Effects. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 1069–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkova, J.; Koleva, R.; Benghin, V.; Dachev, T.; Matviichuk, Y.; Tomov, B.; Krastev, K.; Maltchev, S.; Dimitrov, P.; Mitrofanov, I.; et al. Charged particles radiation measurements with Liulin-MO dosimeter of FREND instrument aboard ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter during the transit and in high elliptic Mars orbit. Icarus 2018, 303, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witasse, O.; Sánchez-Cano, B.; Mays, M.L.; Kajdič, P.; Opgenoorth, H.; Elliott, H.A.; Richardson, I.G.; Zouganelis, I.; Zender, J.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F.; et al. Interplanetary coronal mass ejection observed at STEREO-A, Mars, comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, Saturn, and New Horizons en route to Pluto: Comparison of its Forbush decreases at 1.4, 3.1, and 9.9 AU. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 7865–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, T. Space Weather: Terrestrial Perspective. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2007, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungey, J.W. The Steady State of the Chapman-Ferraro Problem in Two Dimensions. J. Geophys. Res. 1961, 66, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasofu, S.I. A Historical Review of the Geomagnetic Storm-Producing Plasma Flows from the Sun. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 164, 85–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, M.J.; Barnard, L.A.; Pope, B.J.S.; Lockwood, M.; Usoskin, I.; Asvestari, E. Solar Energetic-Particle Ground-Level Enhancements and the Solar Cycle. Sol. Phys. 2022, 297, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, R. Intense Geomagnetically Induced Currents (GICs): Association with Solar and Geomagnetic Activities. Sol. Phys. 2022, 297, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzaszek, A.; Gil, A.; Modzelewska, R.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Wawrzaszek, R. Analysis of Large Geomagnetically Induced Currents During the 7–8 September 2017 Storm: Geoelectric Field Mapping. Space Weather 2023, 21, e2022SW003383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, R. On extreme space weather events: Solar eruptions, energetic protons and geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 1977–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P. On the probability of occurrence of extreme space weather events. Space Weather 2012, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.; Baker, D.; Liu, Y.D.; Verronen, P.; Singer, H.; Güdel, M. Extreme Space Weather Events: From Cradle to Grave. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliver, E.W.; Schrijver, C.J.; Shibata, K.; Usoskin, I.G. Extreme solar events. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2022, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, R.C. Description of a Singular Appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1859, 20, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, R. On a curious Appearance seen in the Sun. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1859, 20, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapgood, M.; Angling, M.J.; Attrill, G.; Bisi, M.; Cannon, P.S.; Dyer, C.; Eastwood, J.P.; Elvidge, S.; Gibbs, M.; Harrison, R.A.; et al. Development of Space Weather Reasonable Worst Case Scenarios for the UK National Risk Assessment. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzulukova, N.; Tsurutani, B. Space Weather: From Solar Origins to Risks and Hazards Evolving in Time. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.C.; Likar, J.; Shprits, Y. Impact of space weather on the satellite industry. Space Weather 2017, 15, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.P. Ionospheric Effects of Solar Flares; Reidel: Boston, MA, USA, 1974; Volume 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, K.I.; Samwel, S.W. Effect of Air Drag Force on Low Earth Orbit Satellites During Maximum and Minimum Solar Activity. Space Res. J. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.M.; Zesta, E. Satellite Orbital Drag During Magnetic Storms. Space Weather 2019, 17, 1510–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapgood, M.; Liu, H.; Lugaz, N. SpaceX—Sailing Close to the Space Weather? Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottet, G.; Samwel, S.; Klein, K.L.; Dudok de Wit, T.; Miteva, R. Statistical Evidence for Contributions of Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections to Major Solar Energetic Particle Events. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 819–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwel, S.W.; Hady, A.A. Space radiation environment forecast for EGYPTSAT-2 satellite. Space Weather 2009, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwel, S.W.; El-Aziz, E.A.; Garrett, H.B.; Hady, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Amin, M.Y. Space radiation impact on smallsats during maximum and minimum solar activity. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iucci, N.; Levitin, A.E.; Belov, A.V.; Eroshenko, E.A.; Ptitsyna, N.G.; Villoresi, G.; Chizhenkov, G.V.; Dorman, L.I.; Gromova, L.I.; Parisi, M.; et al. Space weather conditions and spacecraft anomalies in different orbits. Space Weather 2005, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, J.L. An Updated Perspective of Single Event Gate Rupture and Single Event Burnout in Power MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1912–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luza, L.M.; Wrobel, F.; Entrena, L.; Dilillo, L. Impact of Atmospheric and Space Radiation on Sensitive Electronic Devices. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE European Test Symposium (ETS), Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wang, W.; Garcia-Sage, K.; Yue, J.; Merkin, V.; McInerney, J.M.; Pham, K.; Sorathia, K. Thermospheric Neutral Density Variation during the “SpaceX” Storm: Implications From Physics-Based Whole Geospace Modeling. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.W.; Kubaryk, A.; Goldstein, D.; Li, Z.; Fuller-Rowell, T.; Millward, G.; Singer, H.J.; Steenburgh, R.; Westerman, S.; Babcock, E. Space Weather Environment During the SpaceX Starlink Satellite Loss in February 2022. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.E.; Dominique, M.; Lucas, G.; Pilinski, M.; Ray, V.; Sewell, R.; Sutton, E.K.; Thayer, J.P.; Thiemann, E. The Thermosphere Is a Drag: The 2022 Starlink Incident and the Threat of Geomagnetic Storms to Low Earth Orbit Space Operations. Space Weather 2023, 21, e2022SW003330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, R.; Shiota, D.; Fujiwara, H.; Jin, H.; Tao, C.; Shinagawa, H.; Miyoshi, Y. Unexpected space weather causing the reentry of 38 Starlink satellites in February 2022. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2022, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Li, X.; Luo, B.; Li, R.; Zhang, B.; Pham, K.; Ren, D.; Chen, X.; Lei, J.; Wang, Y. Unveiling the Space Weather During the Starlink Satellites Destruction Event on 4 February 2022. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Paxton, L.J.; Schaefer, R.; Swartz, W.H. Thermospheric Conditions Associated With the Loss of 40 Starlink Satellites. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, F.; Astafyeva, E.; Fleury, R.; Maletckii, B.; He, J. Did a minor geomagnetic storm really cause the loss of 40 Starlink satellites? In Proceedings of the SF2A-2022: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the French Society of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Societe Francaise d’Astronomie et d’Astrophysique (SF2A) 2022, Besançon, France, 7–10 June 2022; pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.Y.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.J.; Sutton, E.K.; Rotan Hairston, M.; Coley, W.R. Ionosphere-thermosphere (IT) response to solar wind forcing during magnetic storms. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2016, 6, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gomez, I.; Kodikara, T.; Borries, C.; Forootan, E.; Goss, A.; Schmidt, M.; Codrescu, M.V. Improving estimates of the ionosphere during geomagnetic storm conditions through assimilation of thermospheric mass density. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).