Abstract
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) presents diverse challenges that significantly impact feeding, nutrition, growth, and development. The heterogeneity of ASD manifestations adds complexity to assessments due to the broad range of factors to be considered. Moreover, the literature lacks a comprehensive tool specifically addressing nutritional aspects in ASD. Methods: Conducted in two steps, this study first involved researchers selecting evidence-based elements related to ASD and nutrition to develop a preliminary tool. Content validation was subsequently undertaken using a modified Delphi method, whereby expert consensus was sought from 30 dietitians with experience in ASD, who evaluated the tool through a digital questionnaire. Four quality criteria were evaluated: functionality, organization, language and comprehensibility, and comprehensiveness. Results: Levels of strong agreement with the quality criteria ranged from 63.3% to 80%, specifically functionality (76.7%), organization (73.3%), language and comprehensibility (80%), and comprehensiveness (63.3%). Thematic analysis highlighted six key areas for improvement. The instrument assesses nutritional aspects across seven domains: life history, food-related aspects, feeding behavior, dietary intake, daily routines, clinical aspects, and anthropometry. Conclusions: This is the first known tool to comprehensively address the nutritional needs of individuals with ASD, offering a detailed framework for clinical application. It supports initial assessments, ongoing monitoring, and targeted interventions, supporting dietitians worldwide in clinical decision-making.
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has shown an increasing prevalence over time [1,2]. Commonly referred to as autism, ASD is classified as a neurodevelopmental condition [3]. It is characterized by challenges in communication and social interaction, restricted and repetitive behaviors, as well as sensory and motor alterations that vary in intensity. These manifestations are present from early childhood, although they may be identified later in life [4]. Individuals with ASD may face various difficulties, leading to diverse phenotypes and distinct developmental trajectories [3,5]. In addition to core symptoms, co-occurring conditions are frequently observed, significantly impacting the quality of life [6,7]. Among these challenges, feeding difficulties stand out as a significant concern, as they can be exacerbated by autism characteristics, impaired skills, associated health conditions, comorbidities, and medical treatments, significantly affecting nutrition [8,9,10].
Recently, the term “pediatric feeding disorder” was proposed to unify diagnostic criteria, characterized by impaired and age-inappropriate food intake, and associated with medical and nutritional circumstances, feeding skills, and psychosocial dysfunction, including neurodevelopmental conditions like autism [11]. The prevalence of feeding problems in children with ASD is estimated at 46% to 90% [8,12,13]. These issues may manifest as persistent refusal to consume certain foods, difficulty in achieving sufficient intake to support healthy growth and development, and fear or aversion toward trying new or unfamiliar foods—known as food neophobia—which may arise from both behavioral and organic factors [14,15]. Furthermore, motor impairments associated with autism can contribute to feeding difficulties, including problems with chewing and swallowing, as well as challenges in properly handling utensils [16,17,18]. Emotional challenges and internalizing symptoms related to autism can lead to both overfeeding and underfeeding [19,20]. Similarly, when pharmacological intervention becomes necessary, potential metabolic and hormonal changes may further influence the mechanisms that regulate hunger and satiety [21,22,23].
These feeding-related challenges are a significant source of concern for parents regarding their children’s nutrition [14,24]. Parental stress has been positively associated with behavioral feeding issues, such as food refusal and rigidity, in autistic children [25]. Maternal anxiety has also been correlated with children’s feeding difficulties. In some cases, when coupled with less effective coping strategies, this may contribute to the persistence of disruptive feeding behaviors in autistic children [26,27]. Food selectivity can also affect the eating habits of other family members, contribute to increased marital stress among parents [28], and lead to social isolation in families with autistic children [12].
Food selectivity is the most frequently reported feeding issue in ASD [29] and has been defined as rejecting over 33% of offered foods or consuming fewer than 50 distinct foods per year [30]. When associated with autism, food selectivity often reflects preferences based on sensory characteristics, such as type, texture, or presentation [31].
Individuals with ASD and oral hypersensitivity face greater challenges with food acceptance compared to those without this trait [32]. They may also show a preference for specific brands and packaging [13,33], often favoring hyper-palatable foods like fast food and ultra-processed products, which are nutritionally imbalanced [34]. A tendency to refuse fruits and vegetables is also common [8,29], contributing to diets with a high intake of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods and potential macro and micronutrient imbalances, increasing nutritional risks [35]. Food refusal is also linked to altered perception, inflexibility, and challenging behaviors associated with autism [30].
Children with ASD and food selectivity often exhibit behavioral issues such as screaming, crying, and aggression toward caregivers [29,36]. They may also establish meal rituals, including specific food presentation, utensil use, and rigid intake patterns [13]. Feeding problems, such as lack of appetite or inappropriate feeding behavior, can emerge in early childhood [37] and, if untreated, may persist or evolve during adolescence [38,39], continuing into adulthood [40] and potentially leading to health issues due to dysfunctional intake [41,42,43]. Individualized interventions influence the course of these issues [29].
Nutrition is a complex topic in the context of autism. In addition to feeding challenges, individuals with ASD are at increased risk for nutritional imbalances compared to neurotypical peers [8]. A meta-analysis reported significantly lower intakes of several nutrients among children with ASD, including calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. The notably insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D raises concerns regarding bone health and immune function. Although children with ASD also consumed less protein, phosphorus, selenium, thiamine, riboflavin, and vitamin B12 than typically developing children, their intake of these nutrients generally remained adequate or exceeded dietary recommendations [44]. However, when dietary intake becomes insufficient, the prescription of supplements becomes necessary to ensure that nutritional requirements are met [11].
Severe and chronic feeding problems are associated with a broad range of medical complications, including malnutrition, which can hinder growth and development and contribute to psychosocial and academic challenges. In extreme cases, invasive interventions such as enteral feeding may become necessary. Therefore, the routine assessment of pediatric feeding disorders should be an integral part of care in pediatric settings that serve individuals with ASD [8].
To address gaps in the nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD, it is crucial to explore strategies that consider each person’s family and cultural context, as well as etiological factors of feeding and nutritional problems, to develop appropriate interventions [36,45,46]. Studies have shown benefits in conditions associated with autism when individuals receive nutritional treatment [47,48], provided they are under professional clinical supervision [49,50].
Effective clinical practice requires a comprehensive assessment process, which must be rigorously validated and interpreted to accurately determine an individual’s nutritional status. This requires the use of specialized instruments designed to address nutrition-related issues [51]. However, the literature lacks a comprehensive tool capable of adequately capturing the diverse and heterogeneous characteristics of autism that significantly impact feeding and nutrition.
Given that accurate assessment is critical to tailor individualized clinical strategies, the aim of this study was to develop an evidence-based nutritional assessment instrument specifically designed for individuals with ASD. The tool was structured to integrate research and clinical practice by incorporating multiple indicators across clinical, behavioral, physiological, socioeconomic, and feeding domains that may impact nutrition in this population. Rather than focusing exclusively on nutritional status or feeding-related behavioral challenges, the instrument was designed to provide a comprehensive assessment of the individual’s overall nutritional profile, addressing the multifactorial nature of nutritional issues in ASD.
Recognizing the absence of a comprehensive, gold-standard, evidence-based nutritional assessment tool specific to ASD, this study also included a content validation phase. This phase was conducted through expert consensus using a modified Delphi method, a structured and iterative technique widely applied in healthcare research for the development and refinement of clinical instruments, especially in fields where empirical evidence remains limited. Thirty dietitians with expertise in ASD participated in this process, contributing to the refinement of the tool and ensuring its relevance and applicability.
By addressing key dimensions such as behavioral rigidity, gastrointestinal symptoms, and environmental and social conditions, the instrument aims to support clinicians, including those with limited experience in ASD, in performing thorough and individualized assessments. This integrated approach is intended to guide evidence-based interventions and help fill the existing gap in clinical practice regarding the nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD.
2. Materials and Methods
This study aims to develop an evidence-based instrument for the nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD. This descriptive and cross-sectional study combined quantitative and qualitative methods, divided into two steps: (1) development of the instrument and (2) refinement and content validation of the instrument, based on experts’ appraisals, utilizing a modified Delphi method in conjunction with a thematic analysis.
2.1. Step 1: Development and Structuring of the Initial Instrument Version
Based on the clinical and inquiry expertise of the researchers, an investigation of evidence-based studies was conducted to develop the initial version of the instrument. This preliminary version was organized into seven domains: clinical aspects, daily routines, life history, food-related aspects, feeding behavior, dietary intake, and anthropometry. Additionally, validated tools: the Bristol Stool Scale [52,53], the Brussels Infant and Toddler Stool Scale (BITSS) [54], the food diary [55], and anthropometric measurements [56,57] were incorporated. Supporting evidence and details underpinning its creation can be found in the Supplementary Material (Autism Nutritional Assessment (ANA): available in English, Portuguese, and French, with supporting documentation [3,4,5,7,8,9,11,12,13,17,18,19,28,30,31,36,37,43,45,46,47,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161]).
2.2. Step 2: Refinement of the Instrument
Selection of experts: A purposive sampling technique [162] was employed by disseminating the research invitation with specific participation criteria, targeting nutritionists experienced in ASD. The Dietitian Boards of Brazil and the researchers disclosed the invitation via social media and e-mail and later recruited the experts. Participants signed the Informed Consent Form and the Confidentiality Agreement and completed a profile questionnaire to characterize the sample. This approach led to the grouping of 30 expert dietitians from across the country, with a median of two years of clinical experience in providing care to individuals with ASD. The range of expertise varied, with a minimum of 1 year and a maximum of 10 years.
Appraisal of the instrument by experts using a modified Delphi method: After the sample was selected and characterized, each participant was invited to review the initial version of the instrument and appraise it using a digital questionnaire designed to gather their feedback. This variation of the Delphi method [163] facilitated the process and enabled the collection of opinions and recommendations of professionals [163,164].
The modified Delphi method was conducted via a structured digital form to appraise four quality criteria of the instrument: functionality, organization, language and comprehensibility, and comprehensiveness. These criteria were assessed using a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (Strongly Disagree) to 5 (Strongly Agree) and included the following questions:
- Functionality: “The purpose of the instrument is to conduct a nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD. Do you agree that the instrument performs this with excellence?”
- Organization: “The instrument covers seven domains in the following ordinal presentation: clinical aspects, daily routines, life history, food-related aspects, feeding behavior, food intake, and anthropometry. Do you agree that these domains are appropriately presented in the instrument?”
- Language and comprehensibility: “Do you agree that the language used in the instrument is clear and understandable, without requiring further examples or explanations?”
- Comprehensiveness: “Do you agree that the instrument addresses all relevant nutrition aspects for individuals with ASD?”
In addition to these questions, optional open-ended questions solicited recommendations for further refinement of the instrument. To assess the relationship between quality criteria scores and experience with ASD, a two-year cutoff was established to differentiate dietitians with up to two years of experience from those with over two years of experience. Figure 1 shows the flowchart of the instrument’s refinement process.
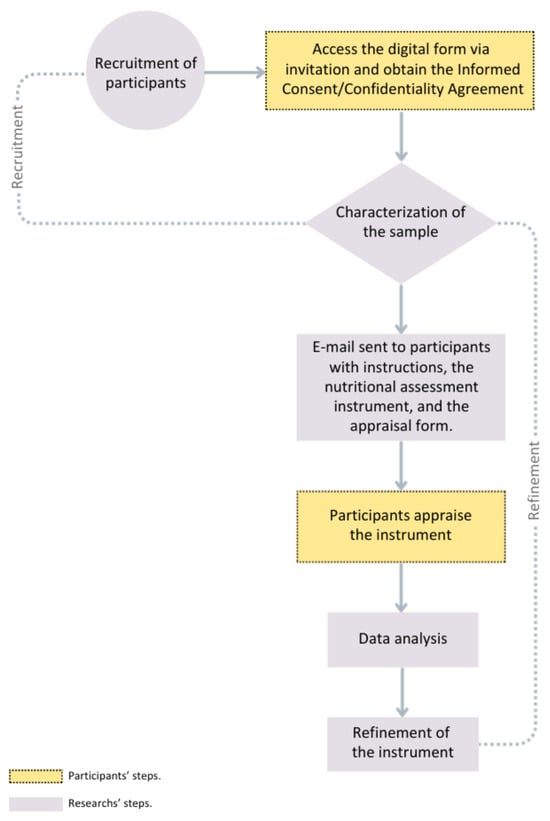
Figure 1.
Refinement Process Flowchart.
2.3. Data Analysis
The four quality criteria for appraising the instrument developed in this study are functionality, organization, language and comprehensibility, and comprehensiveness. These aspects were described using frequency, means, and standard deviations (SD). Fisher’s exact and linear association tests were applied to demonstrate the association between the expert’s experience and the appraisal of the quality criteria. The analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics v. 30 for Windows [165]. Experts’ recommendations were analyzed using thematic analysis [166,167]. This approach enabled a deeper understanding of each expert’s perceptions, contributing to the content validation and refinement of the instrument.
3. Results
An initial version of the evidence-based nutritional assessment instrument was developed, incorporating ASD- and nutrition-related factors identified in previous studies, which were recorded in supporting documentation.
The experts’ appraisal was based on four quality criteria using the modified Delphi method. Regarding the functionality criterion, which evaluates whether the instrument accurately and excellently provides a comprehensive nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD, the mean level of agreement was 4.73 (SD = 0.52), with 76.7% of the sample strongly agreeing. In the ‘organization’ criterion, which stated the adequacy of the ordinal presentation of domains within the instrument, the mean level of agreement was 4.50 (SD = 1.07), with 73.3% strongly agreeing. For the ‘language and comprehensibility’ criterion, which examines whether the instrument uses clear and understandable language, the level of agreement was 4.77 (SD = 0.50), with 80% strongly agreeing. As for comprehensiveness, which assesses whether the instrument covers all relevant nutritional aspects in the context of ASD, the mean level of agreement was 4.60 (SD = 0.56), with 63.3% of the sample strongly agreeing.
Scores for the quality criteria were analyzed to determine their association with experience in ASD, using a cutoff of two years to distinguish professionals with up to two years of experience from those with more than two years. It was observed that the latter gave lower scores for the comprehensiveness criterion, according to Fisher’s exact test (p-value = 0.018) and the linear association test (p-value = 0.011). No significant associations were observed for the other quality criteria.
Following 26 recommendations by the experts, the thematic analysis was converted into six categories, with the number of recommendations in each shown in parentheses: sensory system (n = 6), socialization (n = 2), biochemical markers (n = 5), food selectivity (n = 7), feeding behavior (n = 3), and organization (n = 3). Based on these analyses, the authors critically evaluated the experts’ recommendations and refined the instrument accordingly. This included forming a subdomain on sensory issues related to food within the food-related aspects domain, consisting of eight questions to assess sensory influences on feeding. A question regarding the impact of socialization difficulties in celebratory and/or school contexts involving food was added to the feeding behavior domain. Additionally, two questions regarding restricted interests or behavioral inflexibility in autism, particularly the need for specific places and utensils during meals, were included in this domain. A subdomain on biochemical markers for nutritional assessment was added to the clinical aspects domain. Two questions about food selectivity were added, enabling parent/caregiver perceptions, which can be analyzed in conjunction with other questions in the instrument. Moreover, recommendations for changing the order of domain presentations were implemented. After the identification section, the final sequence of domains was as follows: life history, food-related aspects, feeding behavior, dietary intake, daily routines, clinical aspects, and anthropometry. Table 1 details the experts’ recommendations, along with the corresponding themes and refinement actions. The complete final version is accompanied by supporting documentation and application instructions, provided in three languages (Supplementary Material).

Table 1.
Results of Thematic Analysis of Experts’ Recommendations for the Instrument’s Refinement.
4. Discussion
From 2014 to 2024, the number of publications in PubMed alone exploring the relationship between nutrition and autism increased by approximately 422%, reflecting the growing interest in understanding how dietary factors may influence the development and management of ASD. Researchers are increasingly exploring various nutritional interventions and their potential impacts, contributing to a better understanding of this complex condition. However, much of this information remains largely unstandardized and not synthesized, which can hinder its specific use in nutritional assessments for this population. To our knowledge, there are currently no available questionnaires in the literature that comprehensively assess different nutritional aspects in a single instrument unique to individuals with ASD. Some tools exist for other populations, such as individuals with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) [168], kidney disease [169], pediatric oncology patients [170], children living with human immunodeficiency virus [171], childhood obesity [172], and even the school context [173]. Nevertheless, these instruments are not suitable for individuals with ASD due to the heterogeneous and complex nature of the condition.
In this study, the refined version of the instrument was developed based on expert recommendations and encompasses seven domains: life history, food-related aspects, feeding behavior, dietary intake, daily routines, clinical aspects, and anthropometry. These domains reflect the comprehensive approach needed to adequately evaluate the diverse factors that may influence the nutrition of individuals with ASD. Each domain is discussed in detail, including the rationale for the inclusion of specific items, thereby offering a structured framework to support the tool’s use in clinical practice.
A comprehensive assessment must consider autism characteristics that directly influence skills and competencies related to proper feeding and nutrition, as well as the recognized health conditions and potential challenges associated with ASD, to ensure the healthy development and growth [8].
Life History: This domain is designed to explore prenatal, perinatal, and familial factors that may influence nutritional development. It emphasizes the collection of a detailed developmental history, including both genetic and environmental influences. The domain comprehensively considers the individual’s social context, early development, and family dynamics, elements that are essential for understanding the environmental and relational factors that may affect nutritional status and feeding behaviors in individuals with ASD. It involves gathering information to explore potential genetic influences on health, with inquiries into the health of siblings and parents, as well as data from the pre- and perinatal periods. Inherited genes and environmental factors are important, as they can influence metabolic and immunological health and may be modified by exposure to certain agents, such as nutrition and maternal behaviors. The impact of these influences is particularly significant during the ‘1000 days’ period, which spans from preconception, through pregnancy, into the early years of an individual’s life, operating via epigenetic mechanisms [174,175]. Additionally, some of these factors may increase the likelihood of ASD, such as the mother’s health conditions, events during gestation [176], and factors like prematurity and low or high birth weight [3].
Food-Related Aspects: This domain includes questions from the earliest stages of childhood. Initially centered on breastfeeding and complementary feeding practices, it was expanded to address a broader range of food-related factors, such as the introduction of solid foods, food intolerances, adherence to restrictive diets, use of dietary supplements, and the impact of sensory characteristics on feeding. Based on expert recommendations, items related to sensory experiences, such as texture, temperature, and food aversions, were added, resulting in the development of a dedicated subdomain focused specifically on sensory influences.
Atypical responses to sensory stimuli have recently been included in the diagnostic criteria for ASD [66]. It is estimated that these sensory processing alterations reach 74% of children with autism, manifesting in various ways, such as over-responsiveness, characterized by extreme sensitivity; diminished responsiveness, with little or no reaction to stimuli such as touch or pain; and sensory-seeking behaviors, where the individual actively pursues new sensations [177]. Sensory dysregulation significantly contributes to feeding challenges in individuals with ASD, emphasizing the need to assess their sensory profiles for tailored interventions [142,178]. Hypersensitivity often leads to avoiding foods due to their appearance, texture, smell, or consistency, resulting in selective eating. Hyposensitivity is associated with a preference for intense flavors, difficulty identifying strong odors, messy eating, or retaining food in the mouth. Sensory-seeking behavior includes mouthing objects or licking surfaces for new sensory experiences [179]. To identify each individual’s sensory profile, consulting with professionals from the care team, particularly the occupational therapist, may be necessary, as they are typically responsible for addressing sensory system needs.
Feeding Behavior: In accordance with expert recommendations, this domain was expanded to include additional questions regarding the usual location of meals, preferred utensils used during feeding, more detailed items for identifying food selectivity, and aspects of social interaction during mealtimes. Overall, the domain focuses on examining eating habits and behaviors during meals, as well as caregivers’ perceptions and concerns related to their children’s feeding behavior. Additionally, it is important to understand how the feeding behaviors and dietary patterns of other family members may influence people with ASD. This comprehensive approach enables an evaluation of both individual patterns and the broader context of feeding behaviors to which the individual is exposed [180]. Feeding difficulties can manifest as early as the first few months in children with ASD, encompassing challenges with infant feeding practices, introduction of solid foods, and disruptive behaviors during mealtimes [39]. Feeding behaviors can play a protective role against chronic diseases and eating disorders, shaped by various factors. Therefore, understanding how the autistic individual relates to food is crucial to developing effective management strategies [32]. Several tools are available to assess feeding behavior; but no instrument covers all aspects of feeding problems [181], and few scales or questionnaires specifically address behavioral feeding challenges in individuals with ASD [37]. Thus, the instrument’s feeding behavior domain was developed to encompass the various issues described in the literature, ensuring its applicability within the context of autism. This structure facilitates effective use in clinical practice, supporting professionals’ decision-making during consultations and enabling them to assist parents in managing these challenges and their potential outcomes.
Dietary Intake: This domain focuses on evaluating both the quantity and quality of foods consumed. Various methods can be employed to assess dietary intake, including the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ), which, despite its practicality, tends to overestimate energy and nutrient consumption [182]. Another approach is food recall, which relies on recollecting, during the interview, foods consumed [183], and the food diary, completed at mealtime [55]. The latter provides more accurate data and captures essential nutritional details, making it more reliable. Ideally, it should cover at least three non-consecutive days, including one weekend day, with the recording of all foods, beverages, and snacks consumed, serving as a useful tool in clinical practice [55]. However, in the ASD context, engaging caregivers can be challenging, considering the high caregiving demands they already face [160]. The method incorporated into the instrument involves caregivers completing a food diary. Nevertheless, consideration of the challenges and circumstances faced by each family is essential; accordingly, this method should be applied flexibly and adapted to the specific needs of each individual and their caregiver.
Daily routines: This domain enables a deeper understanding of the daily habits and routines of individuals with ASD, offering valuable insights into how these factors may affect their overall health and nutritional status. Understanding communication difficulties is essential, as half of verbally expressive children with ASD exhibit some degree of language impairment [184], while approximately 25% to 30% do not develop functional language or are minimally verbal [140]. The impact of these challenges extends across multiple areas, potentially affecting quality of life, behavior, daily activities, and academic performance [184]. Regarding nutrition, it is crucial to assess the extent of communication challenges and determine whether the individual can express hunger, satiety, or the desire to eat or drink.
Individuals with ASD may face challenges in performing daily tasks. However, it is important to assess whether direct parental intervention might be seen as unnecessary interference, potentially hindering the development of essential skills for greater autonomy, depending on the individual’s abilities [147]. It is crucial to consider how these difficulties can impact nutrition and explore their relationship with school attendance and participation in celebratory events.
Nutritional factors are closely associated to physical activity in maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. However, individuals with autism tend to engage less in physical activities [47]. Sedentary behavior in children with ASD may contribute to excess weight and obesity, which are associated with adverse health outcomes, such as insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, sleep duration and quality have been linked to an increased risk of being overweight [9], as well as to problematic behaviors and core autism symptoms [108].
Children with ASD are exposed to screens earlier and for longer periods compared to peers from other clinical groups, including those with typical development (TD) [107]. Digital technologies, when used appropriately, hold significant educational value. However, for individuals with ASD, excessive and indiscriminate screen use can result in greater negative effects due to heightened sensitivity to stimuli. These include impaired self-regulation, screen dependence, and nutrition-related issues, often driven by unhealthy food choices influenced by advertising linked to the content viewed, as well as increased sedentary behavior, increasing the risk of excessive weight gain [185]. Additionally, parents may face challenges in managing their children’s screen time, even when they are aware of negative consequences [186]. Therefore, assessing screen time and its impact is essential in the context of nutrition.
Clinical Aspects: This domain encompasses a range of individual characteristics that may influence feeding and nutrition. Considering the unique clinical profiles of individuals with ASD, a detailed examination of these aspects is essential for understanding how they may affect nutritional status and feeding behavior. These influences include associated comorbidities, therapeutic interventions, biochemical markers, and medication use. It is estimated that two-thirds of individuals with autism require medication to manage symptoms such as irritability, aggression, mood issues, and anxiety [21], with up to 42% using psychotropic drugs in combination [79]. This can significantly increase the risk of metabolic abnormalities, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and weight gain [23], which makes rigorous biochemical monitoring crucial [21]. These treatments may contribute to disturbances in hunger and satiety signals and their relationship with food, potentially altering feeding behavior, as evidenced by a greater preference for sweets and salty foods with high energy density [187]. Although hormones like ghrelin, which regulates hunger signals, and leptin, which signals satiety, are not typically monitored in clinical nutrition practice, it is important to highlight that, along with other metabolic and hormonal processes, these hormones may be dysregulated in individuals with ASD, contributing to feeding concerns and difficulty in maintaining adequate weight [188].
In the preliminary version, the assessment of biochemical markers was not included. However, based on expert feedback, a subdomain was incorporated into the clinical aspects domain to encompass laboratory tests relevant to nutritional evaluation. Monitoring these markers is essential, given the risk of nutritional imbalances resulting from feeding difficulties and common deficiencies observed in individuals with ASD, such as iron and calcium [87] and vitamins A and D [189]. Deficiencies in folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12, essential for homocysteine metabolism, have also been observed [93]. Meta-analyses indicate that peripheral blood homocysteine levels are significantly elevated in children with ASD compared to children with TD [86], increasing the risks of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular conditions [190]. Furthermore, an elevated cardiovascular risk has already been reported in individuals with ASD [83].
Gastrointestinal dysfunction is among the most common comorbidities in autism, with a prevalence approximately 2.6 times higher than in the general population, with up to 49% of children with ASD exhibiting one or more chronic gastrointestinal symptoms [191]. Such dysfunctions can significantly impact both behavior and autism manifestations and are associated with increased ASD severity [99]. However, communication difficulties often hinder the identification and characterization of these symptoms, potentially leading to them being overlooked or mistaken for core traits of the condition [192]. Gastrointestinal issues may also correlate with feeding challenges [101]; thus, a comprehensive examination of gastrointestinal aspects, from chewing to elimination and covering the full range of intestinal symptoms and influencing factors, is essential for an accurate nutritional assessment.
Anthropometry: Maintained as a core domain for physical assessment, this section plays a vital role in providing key indicators of health status and developmental progress. The collection of anthropometric data—particularly height and weight, which allow for Body Mass Index (BMI) calculation and growth monitoring—is fundamental to a comprehensive nutritional assessment. However, in the context of autism, obtaining these measurements can present unique challenges. Accordingly, the discussion was expanded to emphasize the importance of a flexible and individualized approach, tailored to each person’s comfort and specific needs. Health professionals are encouraged to avoid unnecessary procedures and to ensure that assessments are conducted in a manner that minimizes discomfort while preserving accuracy and clinical relevance.
The formulation of instruments in healthcare using the Delphi method is widely recognized for its effectiveness, particularly when research is limited or logistical challenges arise. The method is designed to identify priorities, establish guidelines, and develop clinical tools, ideally with input from eight to 23 experts, and can be applied with various modifications [163]. In this study, 30 dietitians specializing in the clinical care of individuals with ASD participated in the content validation, which enabled the refinement of the nutritional assessment instrument, employing a modified Delphi method. Qualitative analysis was used to interpret the recommendations, consistent with other studies in the literature, such as the development of guidelines for diagnosing and supporting autism in women [193], achieving consensus among clinicians on optimal post-diagnostic services for autistic adults [194], and creating sports nutrition questionnaires for athletes [195,196].
Feedback from specialists regarding the first version of the instrument significantly contributed to optimizing the tool. The evaluated domains included quality, functionality, organization, language and comprehension, and comprehensiveness. The selected specialists had different profiles, particularly regarding their experience with individuals with ASD, which may have influenced their responses. All the feedback received was discussed among the authors, and necessary decisions were made to improve the instrument.
To the best of our knowledge, this study presents the first instrument specifically designed for the nutritional assessment of individuals with ASD, integrating science, evidence, and clinical practice. It assesses multiple domains, providing a comprehensive evaluation, and is applicable in clinical practice for initial evaluations, monitoring progress, and addressing specific needs. Further, it can be partially integrated into discussions within multidisciplinary teams. To overcome potential challenges in training clinicians to use the tool, the authors developed a detailed manual alongside the instrument, providing step-by-step guidance on its application. This instrument addresses a critical gap in healthcare by enabling the identification of feeding and nutritional challenges specific to ASD, facilitating targeted interventions, and ultimately improving health outcomes and quality of life for individuals and their families.
The complexity and diversity of needs among individuals with ASD highlight the critical importance of having well-trained and specialized professionals who can deliver effective, individualized interventions that enhance the quality of life for both individuals on the spectrum and their families. Despite this growing need, there remains a significant shortage of clinicians with specialized training in autism-specific care, including the unique nutritional challenges faced by this population.
The evidence-based nutritional assessment instrument developed in this study addresses this gap by providing a comprehensive tool for evaluating key domains that influence the nutrition and feeding behaviors of individuals with ASD. Its structured approach enables even professionals with limited experience in autism to conduct thorough assessments, thereby supporting more informed and effective clinical interventions. By encompassing critical areas such as life history, sensory processing, feeding behavior, dietary intake, and clinical indicators, the instrument facilitates a deeper understanding of the multifactorial elements that affect nutrition in this population.
Moreover, because it can be applied in both initial evaluations and ongoing monitoring, the instrument allows clinicians to track progress longitudinally and adapt care plans to the changing needs of each individual. While cultural and contextual factors will need to be considered during the instrument’s planned validation phase, its current design offers a strong foundation to enhance clinical practice. This tool not only empowers healthcare providers to deliver more personalized and precise nutritional care but also raises awareness of the complex interplay between autism and nutrition, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes for individuals with ASD.
5. Limitations and Future Directions
Despite being grounded in a broad range of scientific evidence, this instrument has not yet undergone a formal validation process with individuals with ASD. It is important to highlight that all items included are evidence-based, as demonstrated by the supporting material used in its development, which provides initial content validation through expert recommendations. However, further studies are needed to assess the instrument’s validity and reliability in clinical settings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/dietetics4030037/s1, Autism Nutritional Assessment (ANA): available in English, Portuguese, and French, with supporting documentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.V., K.C. and R.d.S.R.; methodology, C.V., K.C. and R.d.S.R.; formal analysis, C.V. and K.C.; investigation, C.V.; data curation, C.V.; writing—original draft preparation, C.V. and K.C.; writing—review and editing, C.V., K.C. and R.d.S.R.; supervision, K.C. and R.d.S.R.; project administration, C.V.; funding acquisition, C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES), Financial Code 001, and was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa (FIPE) of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (project number 2022-0322).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (protocol number 61247122.1.0000.5327, approved on 22 September 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants through digital agreement prior to completing the online questionnaire. No identifiable data are included in this publication.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are not publicly available due to ethical and privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| TD | Typical Development |
| SD | Standard Deviations |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
References
- Issac, A.; Halemani, K.; Shetty, A.; Thimmappa, L.; Vijay, V.R.; Koni, K.; Mishra, P.; Kapoor, V. The global prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2025, 16, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A.; Williams, S.; Patrick, M.E.; Valencia-Prado, M.; Durkin, M.S.; Howerton, E.M.; Ladd-Acosta, C.M.; Pas, E.T.; Bakian, A.V.; Bartholomew, P.; et al. Prevalence and Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 and 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 16 Sites, United States, 2022. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2025, 74, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Brugha, T.S.; Charman, T.; Cusack, J.; Dumas, G.; Frazier, T.; Jones, E.J.H.; Jones, R.M.; Pickles, A.; State, M.W.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; text rev. (DSM-5-TR); American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, T.; King, B.H. Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, C.L.; Barreto, I.I.; da Silva, A.C.F.; Soriano, J.F.B.; Castro, J.d.L.S.; Tristão, L.S.; Bernardo, W.M. Behavioral therapies for the treatment of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Clinics 2025, 80, 100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waizbard-Bartov, E.; Fein, D.; Lord, C.; Amaral, D.G. Autism Severity and its Relationship to Disability. Focus 2024, 22, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, W.G.; Berry, R.C.; McCracken, C.; Nuhu, N.N.; Marvel, E.; Saulnier, C.A.; Klin, A.; Jones, W.; Jaquess, D.L. Feeding Problems and Nutrient Intake in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Meta-analysis and Comprehensive Review of the Literature. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2159–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, K.K.; Orsso, C.E.; Richard, C.; Haqq, A.M.; Zwaigenbaum, L. Risk Factors for Unhealthy Weight Gain and Obesity among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Figuerola, P.; Morales-Hidalgo, P.; Arija-Val, V.; Canals-Sans, J. Are there anthropometric and body composition differences between children with autism spectrum disorder and children with typical development? Analysis by age and spectrum severity in a school population. Autism 2021, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goday, P.S.; Huh, S.Y.; Silverman, A.; Lukens, C.T.; Dodrill, P.; Cohen, S.S.; Delaney, A.L.; Feuling, M.B.; Noel, R.J.; Gisel, E.; et al. Pediatric Feeding Disorder: Consensus Definition and Conceptual Framework. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, W.G.; Burrell, T.L.; Jaquess, D.L. The Autism MEAL Plan: A parent-training curriculum to manage eating aversions and low intake among children with autism. Autism 2014, 18, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, S.D.; Zickgraf, H. Atypical eating behaviors in children and adolescents with autism, ADHD, other disorders, and typical development. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2019, 64, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzner, B.; Milano, K.; MacLean, W.C., Jr.; Berall, G.; Stuart, S.; Chatoor, I. A Practical Approach to Classifying and Managing Feeding Difficulties. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.V.S.; Poli, M.C.F.; Petrilli, P.H.; Dornelles, R.C.M.; Turcio, K.H.; Theodoro, L.H. Food selectivity and neophobia in children with autism spectrum disorder and neurotypical development: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 1034–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.L.; Murphy, J.; Catmur, C.; Bird, G. The role of interoception in the overlap between eating disorders and autism: Methodological considerations. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2022, 30, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibrandi, A.; Zirilli, A.; Loschiavo, F.; Gangemi, M.C.; Sindoni, A.; Tribulato, G.; Lo Giudice, R.; Famà, F. Food Selectivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Statistical Analysis in Southern Italy. Children 2023, 10, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacrey, L.-A.; Germani, T.; Bryson, S.; Zwaigenbaum, L. Reaching and Grasping in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Review of Recent Literature. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, A.; Colombo, P.; De Cosmi, V.; Mazzocchi, A.; Scaglioni, S.; Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Bettocchi, S.; D’Oria, V.; Viganò, N.; Mani, E.; et al. Understanding feeding problems in autistic children: Exploring the interplay between internalizing symptoms and sensory features. Autism 2022, 26, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.L.; Richard, E.; Wolff, A.; Nadeau, M.; Zucker, N. Increased emotional eating behaviors in children with autism: Sex differences and links with dietary variety. Autism 2021, 25, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishworiya, R.; Valica, T.; Hagerman, R.; Restrepo, B. An Update on Psychopharmacological Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieiras, C.; Chen, M.H.; Liquitay, C.M.E.; Meza, N.; Rojas, V.; Franco, J.V.A.; Madrid, E. Risperidone and aripiprazole for autism spectrum disorder in children: An overview of systematic reviews. BMJ Evid.-Based Med. 2023, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, R.A.; Storm, A.E.M.; Kloosterboer, S.M.; Hillegers, M.H.J.; Koch, B.C.P.; Dierckx, B.; de Winter, B.C.M. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring to Optimize Risperidone Treatment in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Ther. Drug Monit. 2023, 46, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.M., St.; Ausderau, K.K. The characterization of feeding challenges in autistic children. Autism 2024, 28, 2381–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thullen, M.; Bonsall, A. Co-Parenting Quality, Parenting Stress, and Feeding Challenges in Families with a Child Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázaro, C.P.; Pondé, M.P. Narratives of mothers of children with autism spectrum disorders: Focus on eating behavior. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2017, 39, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlomke, K.; Rossetti, K.; Murphy, J.; Mallicoat, K.; Swingle, H. Feeding Problems and Maternal Anxiety in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Matern. Child. Health J. 2020, 24, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, C.; Hubbard, K.; Anderson, S.E.; Mick, E.; Must, A.; Bandini, L.G. Food Selectivity, Mealtime Behavior Problems, Spousal Stress, and Family Food Choices in Children with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 3308–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Mirizzi, P.; Fadda, R.; Pirollo, C.; Ricciardi, O.; Mazza, M.; Valenti, M. Food Selectivity in Children with Autism: Guidelines for Assessment and Clinical Interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.D.; Souders, M.C.; Kral, T.V.E.; Chao, A.M.; Pinto-Martin, J. Correlates of Feeding Difficulties Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbley, E.; Golds, L.; Sharpe, H.; Gillespie-Smith, K.; Duffy, F. Sensory processing and eating behaviours in autism: A systematic review. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2022, 30, 538–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.; Wallisch, A.; Nowell, S.; Meredith, J.; Boyd, B. Short report: The role of oral hypersensitivity in feeding behaviors of young autistic children. Autism 2023, 27, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postorino, V.; Sanges, V.; Giovagnoli, G.; Fatta, L.M.; De Peppo, L.; Armando, M.; Vicari, S.; Mazzone, L. Clinical differences in children with autism spectrum disorder with and without food selectivity. Appetite 2015, 92, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, K.; Faccioli, L.S.; Baronio, D.; Gottfried, C.; Perry, I.S.; Riesgo, R. Feeding behavior and dietary intake of male children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A case-control study. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2016, 53, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; de Araújo, L.A.; da V, F.; Contini, A.A.; Nogueira-de-Almeida, M.E.; Martinez, E.Z.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.C.J.; Fisberg, M. Nutritional Factors and Therapeutic Interventions in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Narrative Review. Children 2025, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, W.G.; Postorino, V.; McCracken, C.E.; Berry, R.C.; Criado, K.K.; Burrell, T.L.; Scahill, L. Dietary Intake, Nutrient Status, and Growth Parameters in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Severe Food Selectivity: An Electronic Medical Record Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Frye, R.E.; Silva, E.; Vasconcelos, C.; Hoffmann, L.; Riesgo, R.; Vaz, J. Feeding-Related Early Signs of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverill, S.; Smith, I.M.; Duku, E.; Szatmari, P.; Mirenda, P.; Vaillancourt, T.; Volden, J.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Bennett, T.; Elsabbagh, M.; et al. Developmental Trajectories of Feeding Problems in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2019, 44, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margari, L.; Marzulli, L.; Gabellone, A.; de Giambattista, C. Eating and Mealtime Behaviors in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Current Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 2083–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, S.C.; Halkett, A.; Miller, M.; Hinshaw, S.P. Food selectivity and eating difficulties in adults with autism and/or ADHD. Autism 2025, 29, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnaird, E.; Norton, C.; Pimblett, C.; Stewart, C.; Tchanturia, K. Eating as an autistic adult: An exploratory qualitative study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pubylski-Yanofchick, W.; Zaki-Scarpa, C.; LaRue, R.H.; Manente, C.; Kahng, S. Treatment of Food Selectivity in an Adult With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2021, 15, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Richard, E.; Zucker, N.L.; Wallace, G.L. Rigidity and Sensory Sensitivity: Independent Contributions to Selective Eating in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc. Psychol. 2022, 51, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Figuerola, P.; Canals, J.; Fernández-Cao, J.C.; Arija Val, V. Differences in food consumption and nutritional intake between children with autism spectrum disorders and typically developing children: A meta-analysis. Autism 2019, 23, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.N. Feeding and Swallowing Issues in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraskewich, J.; von Ranson, K.M.; McCrimmon, A.; McMorris, C.A. Feeding and eating problems in children and adolescents with autism: A scoping review. Autism 2021, 25, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreswamy, S.; Bashir, A.; Guarecuco, J.E.; Lahori, S.; Baig, A.; Narra, L.R.; Patel, P.; Heindl, S.E. Effects of Diet, Nutrition, and Exercise in Children With Autism and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Literature Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, E.; Zukerman, R.; Eshraghi, R.S.; Mittal, J.; Deth, R.C.; Castejon, A.M.; Trivedi, M.; Mittal, R.; Eshraghi, A.A. Nutritional interventions for autism spectrum disorder. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, J.; Hoffmann, F.; Bachmann, C. Use of complementary and alternative medicine in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Autism 2017, 21, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.S.; Madden, R.F.; Parnell, J.A.; Gibbard, W.B.; Shearer, J. Dietary and Supplement-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use in Pediatric Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, A.; Noel, J.Y. Nutritional Assessment. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.P.; de Azevedo, G.R. The Bristol Stool Form Scale: Its translation to Portuguese, cultural adaptation and validation. Rev. Lat.-Am. Enferm. 2012, 20, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.J.; Heaton, K.W. Stool Form Scale as a Useful Guide to Intestinal Transit Time. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysentruyt, K.; Koppen, I.; Benninga, M.; Cattaert, T.; Cheng, J.; De Geyter, C.; Faure, C.; Gottrand, F.; Hegar, B.; Hojsak, I.; et al. The Brussels Infant and Toddler Stool Scale: A Study on Interobserver Reliability. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, F.E.; Byers, T. Dietary Assessment Resource Manual1. J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 2245s–2317s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, K.; Kiel, J. Anthropometric Measurement. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537315/ (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- World Health Organization. Software for Assessing the Growth and Development of the World’s Children. 2006. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/software (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- de Lima, T.A.; Zuanetti, P.A.; Nunes, M.E.N.; Hamad, A.P.A. Differential diagnosis between autism spectrum disorder and other developmental disorders with emphasis on the preschool period. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, E.A.; Kaiser, A.P. The Effects of Early Intervention on Social Communication Outcomes for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2020, 50, 1683–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, S.L.; Levy, S.E.; Myers, S.M.; Council on Children with Disabilities SODABP; Kuo, D.Z.; Apkon, S.; Davidson, L.F.; Ellerbeck, K.A.; Foster, J.E.A.; Noritz, G.H.; et al. Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallitsounaki, A.; Williams, D.M. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Gender Dysphoria/Incongruence. A systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 3103–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodak, T.; Bergmann, S. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Characteristics, Associated Behaviors, and Early Intervention. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 67, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Charman, T.; Leigh, E.; Russell, A.; Mohamed, Z.; Hollocks, M.J. Examining the relationship between cognitive inflexibility and internalizing and externalizing symptoms in autistic children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 2265–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Elsabbagh, M.; Baird, G.; Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 2018, 392, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, C.; Keehn, B. Implications of Sensory Processing and Attentional Differences Associated With Autism in Academic Settings: An Integrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 695825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ozonoff, S.; Miller, M. Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Assessment 2024, 31, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, H.; Wright, S.; Sargeant, C.; Cortese, S.; Wood-Downie, H. Research Review: A systematic review and meta-analysis of sex differences in narrow constructs of restricted and repetitive behaviours and interests in autistic children, adolescents, and adults. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2024, 65, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich, C.; Pacho, M.; Catalan, A.; Yousaf, N.; Pérez-Rodríguez, V.; Hollocks, M.J.; Parellada, M.; Krebs, G.; Clark, B.; Salazar de Pablo, G. Prevalence and Correlates of the Concurrence of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeard, C.; Picarel-Blanchot, F.; Schmid, R.; Campbell, R.; Buitelaar, J. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Co-morbidities in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 744709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachadourian, V.; Mahjani, B.; Sandin, S.; Kolevzon, A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Reichenberg, A.; Janecka, M. Comorbidities in autism spectrum disorder and their etiologies. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micai, M.; Fatta, L.M.; Gila, L.; Caruso, A.; Salvitti, T.; Fulceri, F.; Ciaramella, A.; D′Amico, R.; Del Giovane, C.; Bertelli, M.; et al. Prevalence of co-occurring conditions in children and adults with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 155, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskens, J.B.; Velders, F.P.; Staal, W.G. Medical comorbidities in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders: A systematic review. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cividini-Motta, C.; Livingston, C.; Efaw, H. Systematic Review of Differential Reinforcement in Skill Acquisition. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2024, 17, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, B.H.A.; Salt, A.T. Autism: The management and support of children and young people on the autism spectrum (NICE Clinical Guideline 170). Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2015, 100, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, K.; Steinbrenner, J.R.; Odom, S.L.; Morin, K.L.; Nowell, S.W.; Tomaszewski, B.; Szendrey, S.; McIntyre, N.S.; Yücesoy-Özkan, S.; Savage, M.N. Evidence-Based Practices for Children, Youth, and Young Adults with Autism: Third Generation Review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 4013–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xiong, S.; Arora, N.; Dubé, L. Using food as reinforcer to shape children’s non-food behavior: The adverse nutritional effect doubly moderated by reward sensitivity and gender. Eat. Behav. 2015, 19, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, A.M.; Ricciardello, A.; Lamberti, M.; Turriziani, L.; Cucinotta, F.; Brogna, C.; Vitiello, B.; Arango, C. The pediatric psychopharmacology of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review—Part I: The past and the present. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 110, 110326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar de Pablo, G.; Pastor Jordá, C.; Vaquerizo-Serrano, J.; Moreno, C.; Cabras, A.; Arango, C.; Hernández, P.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J.; Simonoff, E.; Fusar-Poli, P.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Pharmacological Interventions for Irritability and Emotional Dysregulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Predictors of Response. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 62, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtz, L.; Schwartz, C.; DiStefano, C.; McPartland, J.C.; Levin, A.R.; Dawson, G.; Kleinhans, N.M.; Faja, S.; Webb, S.J.; Shic, F.; et al. Concomitant medication use in children with autism spectrum disorder: Data from the Autism Biomarkers Consortium for Clinical Trials. Autism 2023, 27, 952–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawasdi, P.; Vanwong, N.; Hongkaew, Y.; Puangpetch, A.; Vanavanan, S.; Intachak, B.; Ngamsamut, N.; Limsila, P.; Sukasem, C.; Kroll, M.H. Impact of risperidone on leptin and insulin in children and adolescents with autistic spectrum disorders. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, L.; Charlton, R.A.; McLean, K.J.; McQuaid, G.A.; Lee, N.R.; Wallace, G.L. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Autistic Adults: The Impact of Sleep Quality and Antipsychotic Medication Use. Autism Res. 2023, 16, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celkan, T.T. What does a hemogram say to us? Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 55, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekara, C.S.; Ancona, D.; Cortes, L. Association Between Autism Spectrum Disorders and Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2023, 177, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Carrasco, M.C.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.A.; Bravo-Pastor, M.d.M.; Martin-Castillo, D.; Sánchez-Muñoz, M. Serum Vitamin, D, Folate and Fatty Acid Levels in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 52, 4708–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis-Blake, J.M.; Evans, C.V.; Coppola, E.L.; Redmond, N.; Perdue, L.A. Screening for Lipid Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2023, 330, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, T.; Lai, X.; Lei, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Vitamin A and vitamin D deficiencies exacerbate symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorders. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittana, M.; Ahmadani, A.; Williams, K.E.; Attlee, A. Nutritional Status and Feeding Behavior of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Middle East and North Africa Region: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, L.K. Krause’s Food & the Nutrition Care Process—E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Parellada, M.; Andreu-Bernabeu, Á.; Burdeus, M.; Cáceres, A.S.J.; Urbiola, E.; Carpenter, L.L.; Kraguljac, N.V.; McDonald, W.M.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Rodriguez, C.I.; et al. In search of biomarkers to guide interventions in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Am. J. Psychiatry 2023, 180, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, A.; Ahangari, N.; Hendi, K.; Saleh, F.; Rezaei, N. Status of essential elements in autism spectrum disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Zhu, M.; Fu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Lou, X.; et al. A comparison between children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and healthy controls in biomedical factors, trace elements, and microbiota biomarkers: A meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 1318637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.-T.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Stubbs, B.; Whiteley, P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Li, D.-J.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yang, W.-C.; Tang, C.-H.; et al. Peripheral iron levels in children with autism spectrum disorders vs controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Res. 2018, 50, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, C.; Perry, I.S.; Gottfried, C.; Riesgo, R.; Castro, K. Folic acid and autism: Updated evidences. Nutr. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 273–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-N.; Lei, X.; Xiao, C.-Y.; Li, Y.-M.; Lei, X.-Y. Association between type 1 diabetes and neurodevelopmental disorders in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 982696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierk, J.; Arzideh, F.; Rechenauer, T.; Haeckel, R.; Rascher, W.; Metzler, M.; Rauh, M. Age- and Sex-Specific Dynamics in 22 Hematologic and Biochemical Analytes from Birth to Adolescence. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.C.; Novak, P.; Withrow, N.; Schmidt, B.; Rarback, S.; Feucht, S.; Criado, K.K.; Sharp, W.G. Nutrition Management of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Guideline from an Expert Panel. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, R.S.; Deth, R.C.; Mittal, R.; Aranke, M.; Kay, S.-I.S.; Moshiree, B.; Eshraghi, A.A. Early Disruption of the Microbiome Leading to Decreased Antioxidant Capacity and Epigenetic Changes: Implications for the Rise in Autism. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korteniemi, J.; Karlsson, L.; Aatsinki, A. Systematic Review: Autism Spectrum Disorder and the Gut Microbiota. Focus 2024, 22, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasheras, I.; Real-López, M.; Santabárbara, J. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. An. Pediatría (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 99, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, H. Altered composition and function of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madra, M.; Ringel, R.; Margolis, K.G. Gastrointestinal Issues and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 44, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.E.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Adivi, A.; Pauwels, S.; Godderis, L. Air pollution and endocrine disruptors induce human microbiome imbalances: A systematic review of recent evidence and possible biological mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Liao, X.; Li, Y. Effects of gut microbial-based treatments on gut microbiota, behavioral symptoms, and gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarron, E.; Skafle, I.; Nordahl-Hansen, A.; Wynn, R. Social media interventions for autistic individuals: Systematic review. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1089452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwynette, M.F.; Sidhu, S.S.; Ceranoglu, T.A. Electronic Screen Media Use in Youth With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, G. Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Screen Time: Results From a Large, Nationally Representative US Study. Acad. Pediatr. 2016, 16, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodin, O.; Heffler, K.F.; Davidovitch, M. Screen Media and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2019, 40, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Solmi, M.; Cortese, S.; Smith, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Shin, J.I.; Cheon, K.-A.; et al. Correlations between sleep problems, core symptoms, and behavioral problems in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2024, 33, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodak, T.; Piazza, C.C. Assessment and Behavioral Treatment of Feeding and Sleeping Disorders in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 17, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Larsson, H.; Lundström, S.; Lichtenstein, P.; Butwicka, A. Etiological links between autism and difficulties in initiating and maintaining sleep: A familial co-aggregation and twin study. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2022, 63, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.P.; Zarrinnegar, P. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Sleep. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 47, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Haegele, J.A.; Tse, A.C.-Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, S.X. The impact of the physical activity intervention on sleep in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2024, 74, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, K.; Samulski, B.; Neely, K.A.; Laverdure, P. Physical Activity for Anxiety for Autistic People: A Systematic Review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2025, 55, 2663–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredsson, L.; Armstrong, B.K.; Butterfield, D.A.; Chowdhury, R.; de Gruijl, F.R.; Feelisch, M.; Garland, C.F.; Hart, P.H.; Hoel, D.G.; Jacobsen, R.; et al. Insufficient Sun Exposure Has Become a Real Public Health Problem. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.H.; Norval, M.; Byrne, S.N.; Rhodes, L.E. Exposure to Ultraviolet Radiation in the Modulation of Human Diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboni, G.; Bacherini, A.; Rebecchini, G.; Cagiano, R.; Mancini, A.; Tancredi, R.; Igliozzi, R.; Muratori, F. Individual and Environmental Factors Affecting Adaptive Behavior of Toddlers with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Role of Parents’ Socio-cultural Level. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 3469–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benseny Delgado, E.; Peñate Castro, W.; Díaz Megolla, A. Relationship between Parenting Educational Styles and Well-Being in Families with Autistic Children: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2024, 14, 1527–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.M.Y.; Fang, Y.; Or, P.P.L.; Sun, F.; Poon, E.T.C.; Chan, C.K.M. “Still work?” Design and effect of interventions used to modify feeding problems in children with autism: A systematic review of studies employing group designs. Child. Care Health Dev. 2024, 50, e13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, A.; Happé, F.; Hoekstra, R.A. A conceptual framework for understanding the cultural and contextual factors on autism across the globe. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 1029–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musetti, A.; Manari, T.; Dioni, B.; Raffin, C.; Bravo, G.; Mariani, R.; Esposito, G.; Dimitriou, D.; Plazzi, G.; Franceschini, C.; et al. Parental Quality of Life and Involvement in Intervention for Children or Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Figueroa, K.; Marfo, N.Y.A.; Eigsti, I.-M. Parental Perceptions of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Latinx and Black Sociocultural Context: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2022, 127, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hsu, J.-W.; Tsai, S.-J.; Huang, K.-L.; Bai, Y.-M.; Su, T.-P.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, M.-H. Risk of attention deficit hyperactivity and autism spectrum disorders among the children of parents with autoimmune diseases: A nationwide birth cohort study. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 32, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratesi, C.B.; Garcia, A.B.; Pratesi, R.; Gandolfi, L.; Hecht, M.; Nakano, E.Y.; Zandonadi, R.P. Quality of Life in Caregivers of Children and Adolescents with Autistic Spectrum Disorder: Development and Validation of the Questionnaire. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardes, F.; Pastura, G.M.C. Pediatric Anamnesis: Revising a Tradicional Medical Topic; Residência Pediátrica: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’matuzahroh; Suen, M.-W.; Ningrum, V.; Widayat; Yuniardi, M.S.; Hasanati, N.; Wang, J.-H. The Association between Parenting Stress, Positive Reappraisal Coping, and Quality of Life in Parents with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Children: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2021, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, M.J.; Roman, S.D.; Aitken, R.J.; Nixon, B. Transgenerational inheritance: How impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health. Hum. Reprod. Update 2019, 25, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, T.; Molander, F.; Taylor, M.J.; Jonsson, U.; Bölte, S. Early environmental risk factors for neurodevelopmental disorders—A systematic review of twin and sibling studies. Dev. Psychopathol. 2021, 33, 1448–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuwantono, T.; Aviani, J.K.; Permadi, W.; Achmad, T.H.; Halim, D. Risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in children born from different ART treatments: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, B.; Reissland, N.; Covey, J.; Schaal, B.; Blissett, J. Flavor Sensing in Utero and Emerging Discriminative Behaviors in the Human Fetus. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 33, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, M.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fidler Mis, N.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.M.; Indrio, F.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutel, M.; Mosnaim, G.S.; Bernstein, J.A.; del Giacco, S.; Khan, D.A.; Nadeau, K.C.; Pali-Schöll, I.; Torres, M.J.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M.; Agache, I. The One Health approach for allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy 2023, 78, 1777–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Tong, G.; Sun, Y. Association of food hypersensitivity in children with the risk of autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Jing, J.; Liu, B.; Strathearn, L.; Bao, W. Association of Food Allergy and Other Allergic Conditions With Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Audhya, T.; Geis, E.; Gehn, E.; Fimbres, V.; Pollard, E.L.; Mitchell, J.; Ingram, J.; Hellmers, R.; Laake, D.; et al. Comprehensive Nutritional and Dietary Intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder—A Randomized, Controlled 12-Month Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Rimestad, M.L.; Friis Rohde, J.; Holm Petersen, B.; Bruun Korfitsen, C.; Tarp, S.; Lauritsen, M.B.; Händel, M.N. The Effect of a Combined Gluten- and Casein-Free Diet on Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, N.; Andrews, J.C.; McPheeters, M.L.; Warren, Z.E. Nutritional and Dietary Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20170346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Wang, X.; Pu, L.; Gu, C.; Cai, C. Efficacy and Safety of Diet Therapies in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 844117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, A.J.; Robbins, J. Sensory Integration and the Child: Understanding Hidden Sensory Challenges; Western Psychological Services: Torrance, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, L.; Mandy, W.; Bryant-Waugh, R. Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder and severe food selectivity in children and young people with autism: A scoping review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2022, 64, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignell, A.; Chenausky, K.V.; Song, H.; Zhu, J.; Suo, C.; Morgan, A.T. Communication interventions for autism spectrum disorder in minimally verbal children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD012324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, S.A.; Curtin, C.; Bandini, L.G. Food Selectivity and Sensory Sensitivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, H.E.; Thompson, K.L.; Conklin, J.L.; Watson, L.R. Systematic Review of the Relation Between Feeding Problems and Sensory Processing in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2022, 31, 2875–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri-Destro, M.; Maugeri, F.; Ianni, C.; Corsini, S.; Di Stefano, E.; Scatigna, S.; Crifaci, G.; Bruzzi, G.; Berloffa, S.; Fantozzi, P.; et al. Early Sensory Profile in Autism Spectrum Disorders Predicts Emotional and Behavioral Issues. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flippin, M.; Reszka, S.; Watson, L.R. Effectiveness of the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) on communication and speech for children with autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2010, 19, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilroy, E.; Aziz-Zadeh, L.; Cermak, S. Ayres Theories of Autism and Sensory Integration Revisited: What Contemporary Neuroscience Has to Say. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.E.; Baron-Cohen, S. Sensory perception in autism. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Späth, E.M.A.; Jongsma, K.R. Autism, autonomy, and authenticity. Med. Health Care Philos. 2020, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.; Vi, C.T.; Obrist, M.; Forster, S.; Yeomans, M.R. Ingested but not perceived: Response to satiety cues disrupted by perceptual load. Appetite 2020, 155, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakthavachalu, P.; Kannan, S.M.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Food Color and Autism: A Meta-Analysis. Adv. Neurobiol. 2020, 24, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, B.H.; Guedes, B.d.M.; Santos, T.S.S. Marcadores do consumo alimentar do Sisvan: Estrutura e invariância de mensuração no Brasil. Rev. Saúde Pública 2023, 57, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepper, M.J.; Chai, W. Parents’ barriers and strategies to promote healthy eating among school-age children. Appetite 2016, 103, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, S.; Emmett, P.; Townsend, N.; Biswas, T.; Huda, M.M.; Northstone, K.; Fatima, Y.; McIntyre, H.D.; Al Mamun, A. The myth and reality of familial resemblance in dietary intake: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the resemblance of dietary intake among parent and offspring. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 60, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoori, F.; Norouzzadeh, M.; Farhadnejad, H.; Jahromi, M.K.; Ahmadirad, H.; Saber, N.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Zarkesh, M.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Mirmiran, P. Parent–child correlation in energy and macronutrient intakes: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 2279–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.L.; Smith, I.M.; Duku, E.; Vaillancourt, T.; Szatmari, P.; Bryson, S.; Fombonne, E.; Volden, J.; Waddell, C.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; et al. Behavioral Pediatrics Feeding Assessment Scale in Young Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Psychometrics and Associations With Child and Parent Variables. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2015, 40, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Perry, I.S.; Ferreira, G.P.; Marchezan, J.; Becker, M.; Riesgo, R. Validation of the Brief Autism Mealtime Behavior Inventory (BAMBI) Questionnaire. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukens, C.T.; Linscheid, T.R. Development and Validation of an Inventory to Assess Mealtime Behavior Problems in Children with Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiverling, L.; Hendy, H.M.; Williams, K. The Screening Tool of Feeding Problems applied to children (STEP-CHILD): Psychometric characteristics and associations with child and parent variables. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiverling, L.J.; Williams, K.E.; Hendy, H.M.; Adams, K.; Fernandez, A.; Alaimo, C.; Anderson, K.; Galeano, V.; Yamazaki, H.; Yusupova, S.; et al. Validation of the Brief Assessment of Mealtime Behavior in Children (BAMBIC) for children in a non-clinical sample. Child. Health Care 2016, 45, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, J.; Guthrie, C.A.; Sanderson, S.; Rapoport, L. Development of the Children’s Eating Behaviour Questionnaire. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2001, 42, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Silva, E.; Castro, K.; Valle, S.C.; dos Santos Vaz, J. Dietary Assessment Methods Applied in Clinical and Epidemiological Studies in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024, 11, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Subcommittee on Interpretation and Uses of Dietary Reference Intakes; Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. DRI Dietary Reference Intakes: Applications in Dietary Assessment; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Palinkas, L.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; Green, C.A.; Wisdom, J.P.; Duan, N.; Hoagwood, K. Purposeful Sampling for Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis in Mixed Method Implementation Research. Adm. Policy Ment. Health 2015, 42, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z. Use of Delphi in health sciences research: A narrative review. Medicine 2023, 102, e32829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Reese, C.; Wendler, M.C. Methodology Update: Delphi Studies. Nurs. Res. 2018, 67, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 30.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleberry, A.; Nolen, A. Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds? Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iron-Segev, S.; Best, D.; Arad-Rubinstein, S.; Efron, M.; Serur, Y.; Dickstein, H.; Stein, D. Feeding, Eating, and Emotional Disturbances in Children with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID). Nutrients 2020, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, C.L.; Shaw, V.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Anderson, C.; Desloovere, A.; Haffner, D.; Oosterveld, M.J.S.; Paglialonga, F.; Polderman, N.; Qizalbash, L.; et al. Assessment of nutritional status in children with kidney diseases-clinical practice recommendations from the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, J. Nutritional assessment and intervention in a pediatric oncology unit. Indian. J. Cancer 2015, 52, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, L.; Fox, S.; Hell, K.J.; Church, J.A. Development of an instrument to assess nutritional risk factors for children infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhope, K.K.; Kay, C.; Stevenson, B.; Gazmararian, J.A. Measurement of obesity prevention in childcare settings: A systematic review of current instruments. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 52–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugault-Lafleur, C.N.; Black, J.L.; Barr, S.I. A Systematic Review of Methods to Assess Children’s Diets in the School Context. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Caraballo, L.; Ding, M.; Ferrante, A.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; Hii, C.S.; Irvine, J.; Llinás-Caballero, K.; et al. Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silao, C.L.T. A Child’s Nutrition and Epigenetics. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2023, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Yip, B.H.K.; Windham, G.C.; Sourander, A.; Francis, R.; Yoffe, R.; Glasson, E.; Mahjani, B.; Suominen, A.; Leonard, H.; et al. Association of Genetic and Environmental Factors With Autism in a 5-Country Cohort. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, A.V.; Bilder, D.A.; Wiggins, L.D.; Hughes, M.M.; Davis, J.; Hall-Lande, J.A.; Lee, L.-C.; McMahon, W.M.; Bakian, A.V. Sensory features in autism: Findings from a large population-based surveillance system. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschlager, J.; Cintron, C.; Hall, R.; Shields, T.; Tolbert, G.L.; Woldebirhan, R.; Agarwal, K.; Joseph, P.V. Taste processing in autism spectrum disorder: A translational scoping review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2025, 170, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaware, S.H.; Dubey, S.G.; Kakatkar, V.; Jankar, A.; Pustake, S.; Darekar, A. The Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Oral Sensory Challenges in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2021, 11, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.Ç.; Özcan, Ö. The nutritional behavior of children with autism spectrum disorder, parental feeding styles, and anthropometric measurements. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2022, 76, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destriatania, S.; Februhartanty, J.; Nurwidya, F.; Sekartini, R. Feeding Problems Assessment Tools in Children: A Scoping Review. Children 2025, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Rodrigo, C. Food Frequency Questionnaires. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31 (Suppl. 3), 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, E.; Bradley, J. Methodological considerations and future insights for 24-hour dietary recall assessment in children. Nutr. Res. 2018, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, J.; El-Raziq, M.A.; Castroviejo, E.; Durrleman, S.; Ferré, S.; Grama, I.; Hendriks, P.; Kissine, M.; Manenti, M.; Marinis, T.; et al. Language in autism: Domains, profiles and co-occurring conditions. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westby, C. Screen Time and Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2020, 73, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, R.E.; Bowling, A.; Kaur, R.; Davison, K.K. Promoting Sleep and Balanced Screen Time among School-Aged Children with Neurodevelopmental and Mental Health Disorders: A Parent Perspective. Child. Obes. 2021, 17, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutwalli, H.; Keeler, J.L.; Bektas, S.; Dhopatkar, N.; Treasure, J.; Himmerich, H. Eating cognitions, emotions and behaviour under treatment with second generation antipsychotics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 160, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikkol Sadıç, Ç.; Bilgiç, A.; Kılınç, İ.; Oflaz, M.B.; Baysal, T. Evaluation of Appetite-Regulating Hormones ın Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2021, 51, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.-Q.; Li, H.-B.; Ding, S.-B. Blood homocysteine levels in children with autism spectrum disorder: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 291, 113283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhan, S.C.; Marczewski, S.E. Methionine, homocysteine, one carbon metabolism and fetal growth. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, R.; Ciobica, A.; Timofte, D.; Stanciu, C.; Trifan, A. A Descriptive Review on the Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Disturbances and Their Multiple Associations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Medicina 2019, 56, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holingue, C.; Kalb, L.G.; Musci, R.; Lukens, C.; Lee, L.-C.; Kaczaniuk, J.; Landrum, M.; Buie, T.; Fallin, M.D. Characteristics of the autism spectrum disorder gastrointestinal and related behaviors inventory in children. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumin, J.; Pelaez, S.; Mottron, L. Positive and differential diagnosis of autism in verbal women of typical intelligence: A Delphi study. Autism 2022, 26, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigham, S.; Ingham, B.; Le Couteur, A.; Wilson, C.; Ensum, I.; Parr, J.R. Consensus statements on optimal adult post-autism diagnosis support and services: Delphi process following a UK survey of autistic adults, relatives and clinicians. Autism 2023, 27, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, R.; Beck, K.L.; Gifford, J.A.; Flood, V.M.; O’Connor, H.T. Development of an Electronic Questionnaire to Assess Sports Nutrition Knowledge in Athletes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Espino, K.; Fernández-Tena, C.; Lizarraga-Dallo, M.A.; Farran-Codina, A. Development and Validation of a Short Sport Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire for Athletes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).