1. Introduction
The current technological era promotes the rapid transmission of information worldwide; however, it raises security issues that require the adaptation of traditional security elements (such as signatures and handwriting itself) to new digital writing instruments. In this sense, several studies have explored the eventual equivalence between an individual’s signature and handwriting in both supports (paper and digital), with the aim of developing tools and methodologies that assist in graphoscopic analysis. In general, differences have been described, for example, in terms of speed (faster in the digital support), size (larger in the digital support) and pressure (lower in the digital support) [
1,
2]. In addition to these differences, significant differences between handwriting/signatures have also been reported when written on different software and hardware resources, which makes standardization difficult when it comes to digital samples, especially when the individual writes/signs in different positions [
3,
4,
5]. Thus, the present work aims to contribute to the description of the common and particular characteristics of handwriting in each medium (paper and digital).
2. Materials and Methods
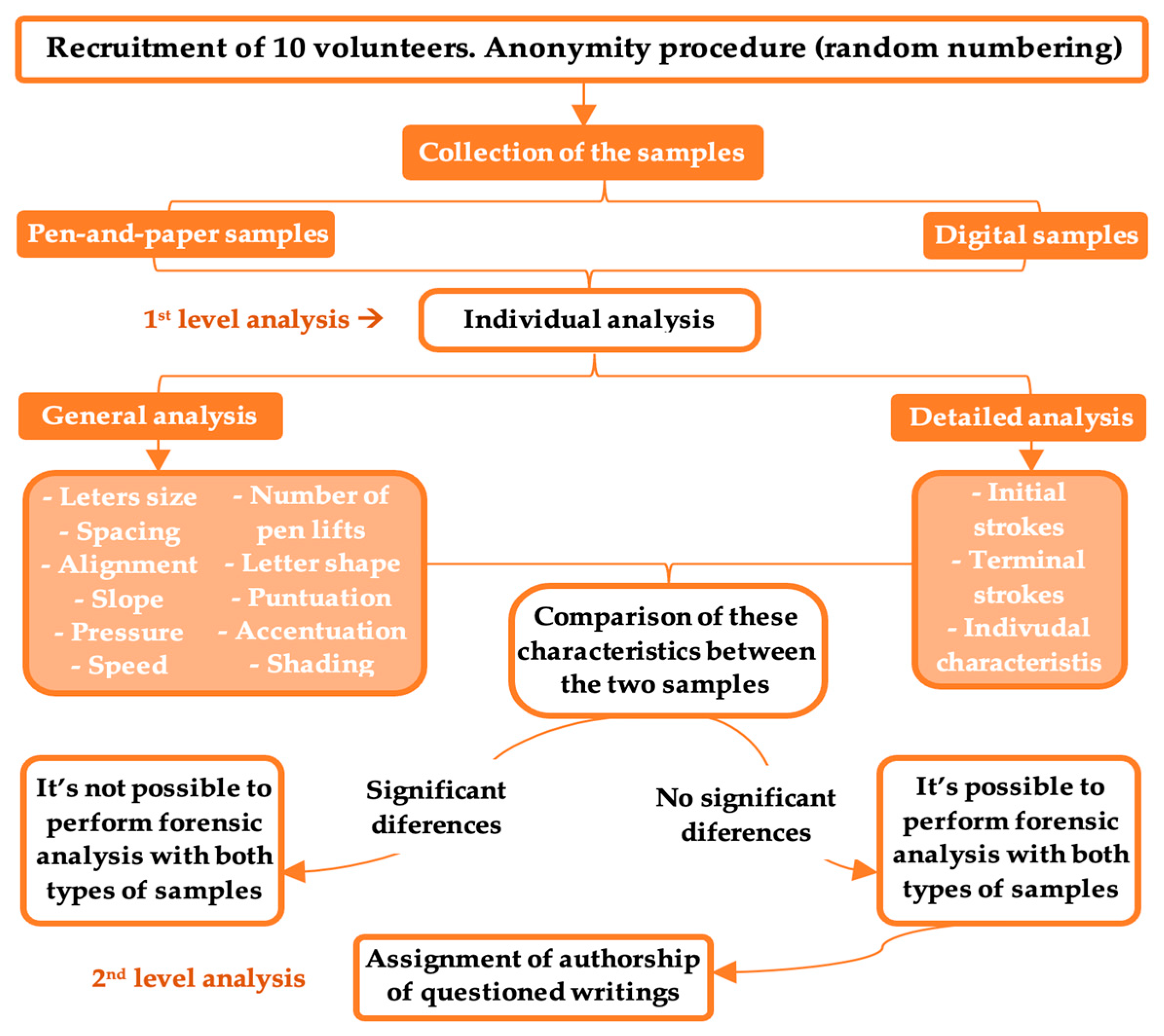
This pilot study adopts a design, presented in
Figure 1, involving 10 forensic students as volunteers, between the ages of 18 and 20. The participants provided handwriting samples, including four anonymous samples for authorship identification (2 positive controls and 2 negative controls). All participants willingly agreed to participate in the study and provided their written informed consent. To ensure anonymity, participants were coded with randomly generated numbers.
Participants were asked to write a text three times (once in uppercase and twice in lowercase) on a piece of paper, and to repeat the process using a digital medium, namely an 8th generation iPad® and an Apple Pencil 1st gen. Blue ink pens and individual sheets of white A4 paper were used, in accordance with the Judiciary Police guidelines (LPC-FEM-MD012, LPC-FEM-MD016 and LPC-FEM-MD017).
Forensic handwriting analysis was performed at two levels by three independent calibrated experts. The first level involved an analysis of the handwriting and comparison of the general and detailed characteristics between the two supports for 8 participants, and the second level involved the graphoscopic analysis on both supports with the aim of assigning the graphic identity of 4 anonymous samples.
3. Results
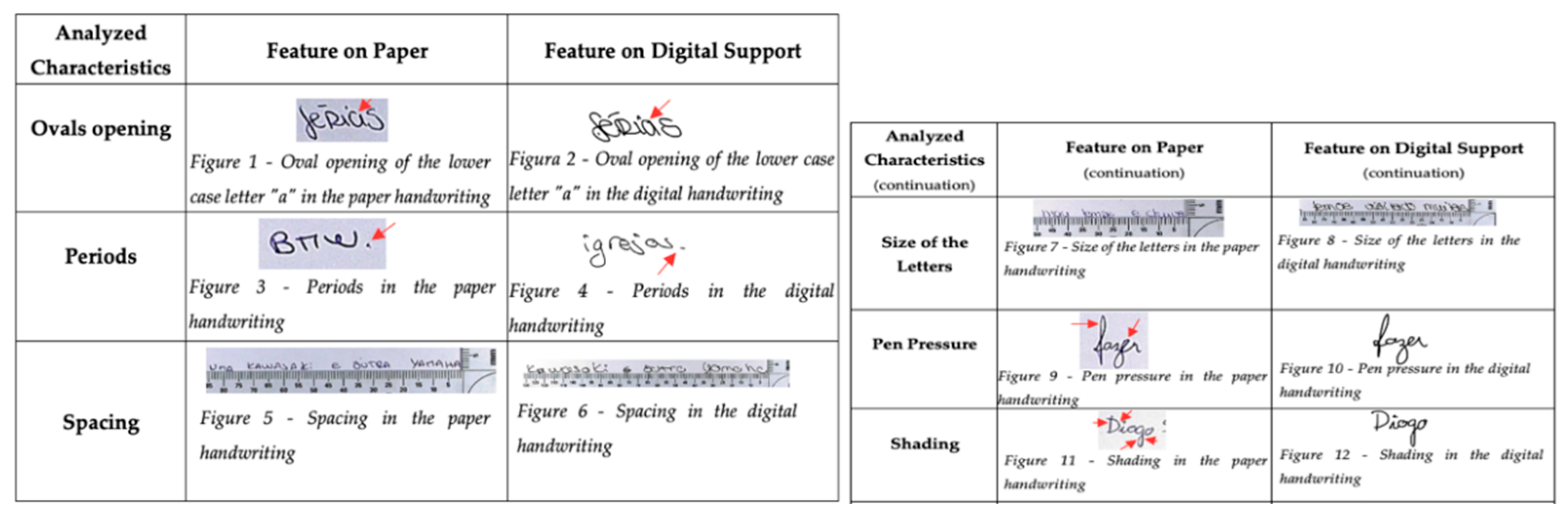
The comparison of the handwriting from eight participants revealed notable differences between the pen-and-paper and digital media. Several recurring differences were observed, including discrepancies in the opening of ovals, periods, spacing, and letter size. The detailed analysis highlighted disparities, particularly in the initial and terminal strokes. It should be noted that no significant changes in digital writing pressure were detected, as indicated by the figures presented in
Figure 2.
For instance, when examining the opening of ovals, a distinct contrast was observed between paper writing and digital support. In paper writing, the oval exhibited an open shape at the top right, while in digital writing, it appeared closed at the top right. Similarly, in the case of periods, the shape differed between paper writing (dot shape) and digital writing (straight line). Furthermore, the comparison indicated that the spacing and letter size in paper handwriting were generally smaller than those in the digital medium. This finding aligns with the observations made by other authors [
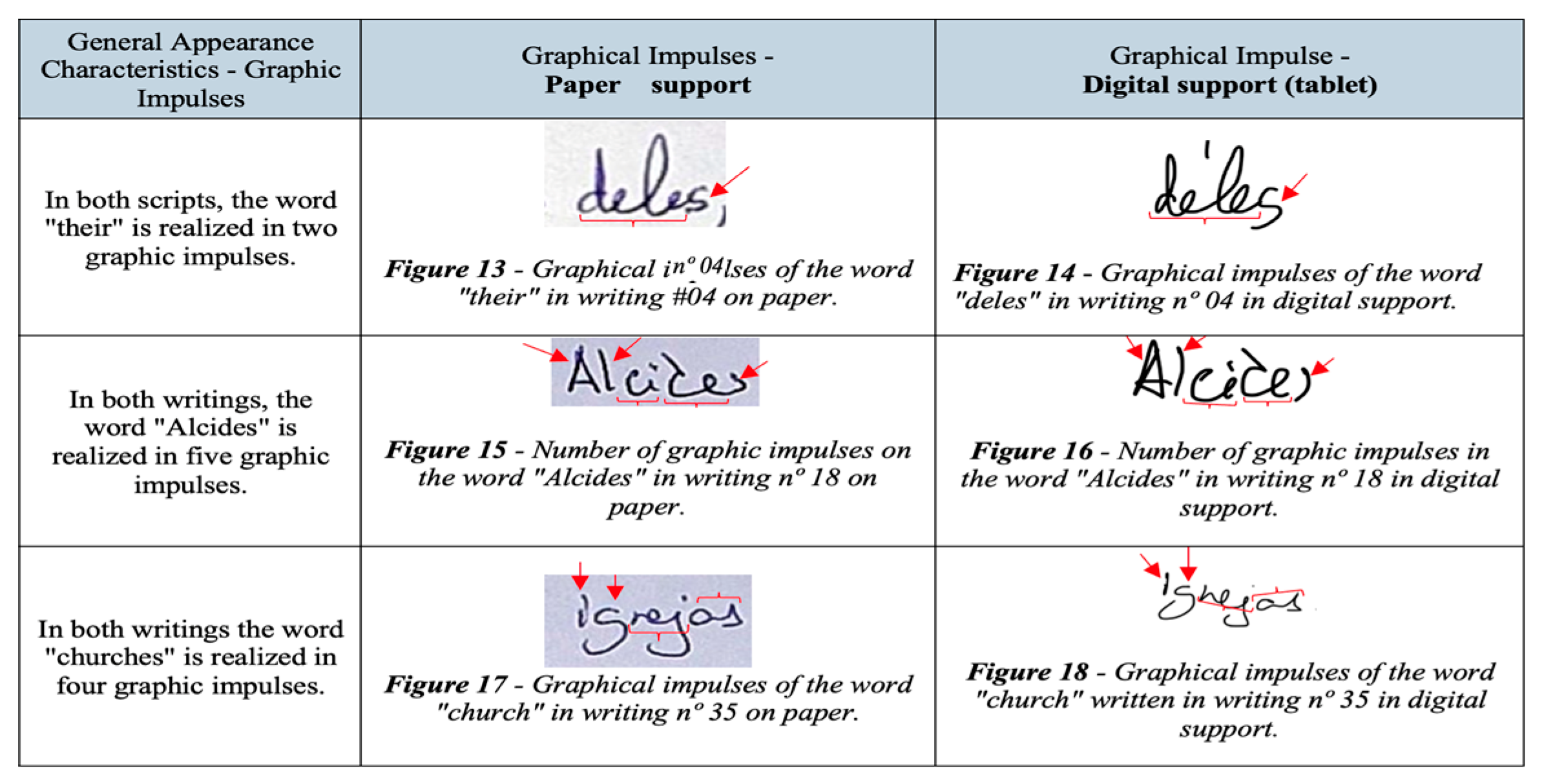
3]. In terms of the initial and terminal strokes, there were a few discernible distinctions. The terminal stroke of certain letters and the initial stroke of dashes exhibited variations between paper handwriting (straight line) and digital writing (hook-shaped). On the other hand, it was possible to establish a similarity relationship between certain graphical and dynamic characteristics of the writings performed on paper and the digital support. Thus, similarities were observed in graphic impulses, inclination, commas, punctuation, accentuation, calligraphic case, baseline, speed, and letter shapes. An example of these similarities can be observed in
Figure 3.
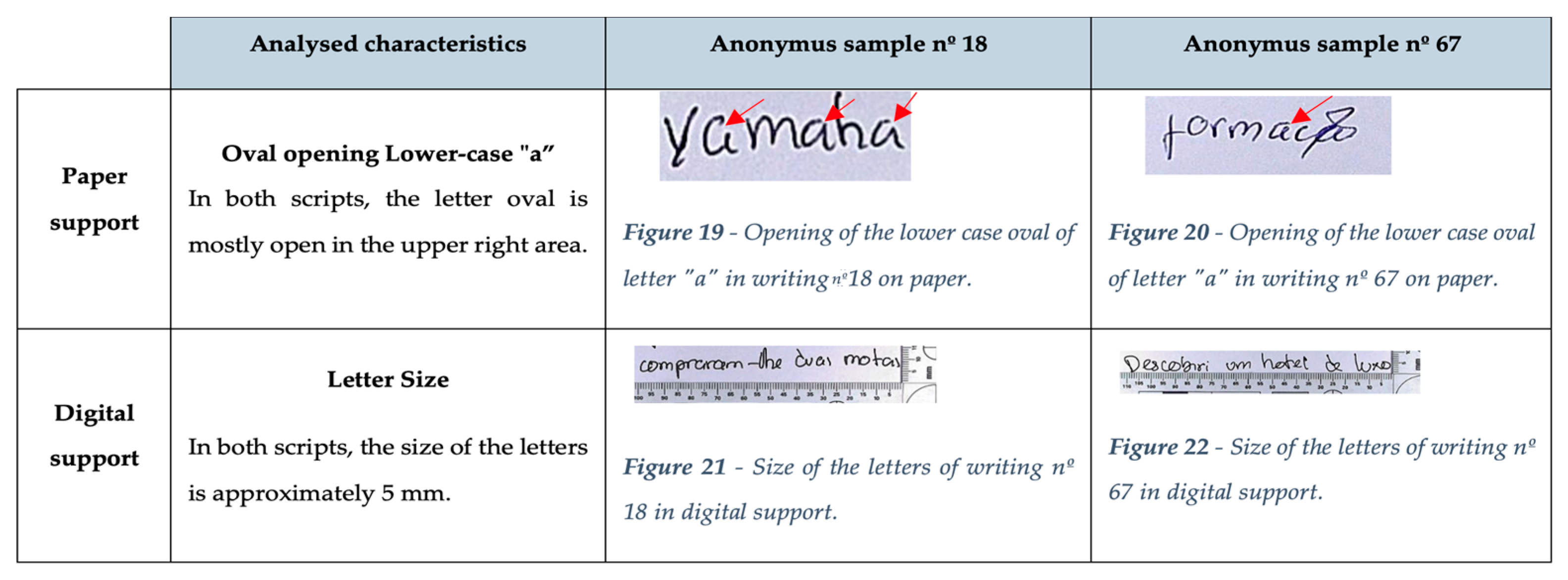
Regarding the second level of graphoscopic analysis, namely the assignment of authorship of questioned writings, it was possible to attribute an identity to one out of four anonymous handwriting samples and conclude that two anonymous samples did not match any of the eight samples previous analyzed. The obtained results suggest that it is possible to compare texts in both formats, as similarities were identified in 16 parameters (inclination, commas, periods, question marks, accentuation, calligraphic style, opening of ovals in lowercase letters “a”, “g”, “p”, and “q”, speed, letter size, letter shape, lowercase letter “d”, lowercase letter “f”, uppercase letter “E”) between the anonymous writing and its corresponding paper and digital formats. Consequently, it is possible to attribute samples 18 and 67 to the same author.
Figure 4 provides two examples of similarities between the two writings concerning appearance characteristics.
4. Conclusions
This pilot study indicates the feasibility of comparing handwriting in both supports and evaluates handwriting authorship with a 75% success rate. However, it is crucial to emphasize that a validated methodology is essential in supporting the comparison between the supports and in the attribution of handwriting authorship.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.; methodology, A.B.; software, M.M.L., D.E. and V.T.; validation, M.M.L., D.E. and V.T.; formal analysis, M.M.L., D.E. and V.T.; investigation, M.M.L., D.E. and V.T.; writing—original draft preparation, V.T.; writing—review and editing, A.B.; supervision, A.B.; project administration, A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to data protection.
Acknowledgments
Laboratório de Ciências Forenses e Criminais Egas Moniz (LCFPEM) and Egas Moniz School of Health & Science.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gerth, S.; Dolk, T.; Klassert, A.; Fliesser, M.; Fischer, M.H.; Nottbusch, G.; Festman, J. Adapting to the surface: A comparison of handwriting measures when writing on a tablet computer and on paper. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2016, 48, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckeroth, J.; Kupferschmid, E.; Dziedzic, T.; Kalantzis, N.; Čakovská, B.G.; Fernandes, C.; Branco, M.J.; Spjuth, K.A.; Kerkhoff, A.; Vaccarone, P.; et al. Features of digitally captured signatures vs. pen and paper signatures: Similar or completely different? Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 318, 110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, J.; Kalantzis, N.; Dziedzic, T.; Heckeroth, J.; Kupferschmid, E.; Fernandes, C.; Čakovská, B.G.; Branco, M.J.; Spjuth, K.A.; Vaccarone, P.; et al. The challenge of comparing digitally captured signatures registered with different software and hardware. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 327, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harralson, H.H. Developments in Handwriting and Signature Identification in the Digital Age; Anderson Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Geistová Čakovská, B.; Kalantzis, N.; Dziedzic, T.; Fernandes, C.; Zimmer, J.; Branco, M.J.; Heckeroth, J.; Spjuth, K.A.; Kupferschmid, E.; Vaccarone, P.; et al. Recommendations for capturing signatures digitally to optimize their suitability for forensic handwriting examination. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).