1. Introduction
Palatal Rugae are disproportionate bilateral protuberances of connective tissue found on both sides of the median palatine raphe posterior to the incisive papilla [
1]. Comparable to fingerprints, PRs appear from birth, are distinctive to each subject, and are noticed in various configurations and forms. The number of PR ranges from three to five on each side of the midpalatine raphe [
1,
2].
PR has a number of physiological functions, such as assisting in suckling in babies and enhancing deglutition, food mastication, and speech [
1,
2].
This cross-sectional observational study aimed to investigate the anatomical morphological pattern and sexual dimorphism of palatal rugae (PR) in Portuguese subjects attending the orthodontic clinic at the Egas Moniz School of Health and Science.
2. Materials and Methods
This sample investigated orthodontic dental casts of 120 Portuguese individuals (mean age 19.9, SD = 6.7 years) attending the Orthodontic Clinic of Egas Moniz School of Health and Science. Each maxillary dental cast was assessed for the prevalence and pattern of PR morphology corresponding to the classification of Thomas and Kotze [
3]: straight, wavy, curved, circular, divergent unification, convergent unification and cross-link.
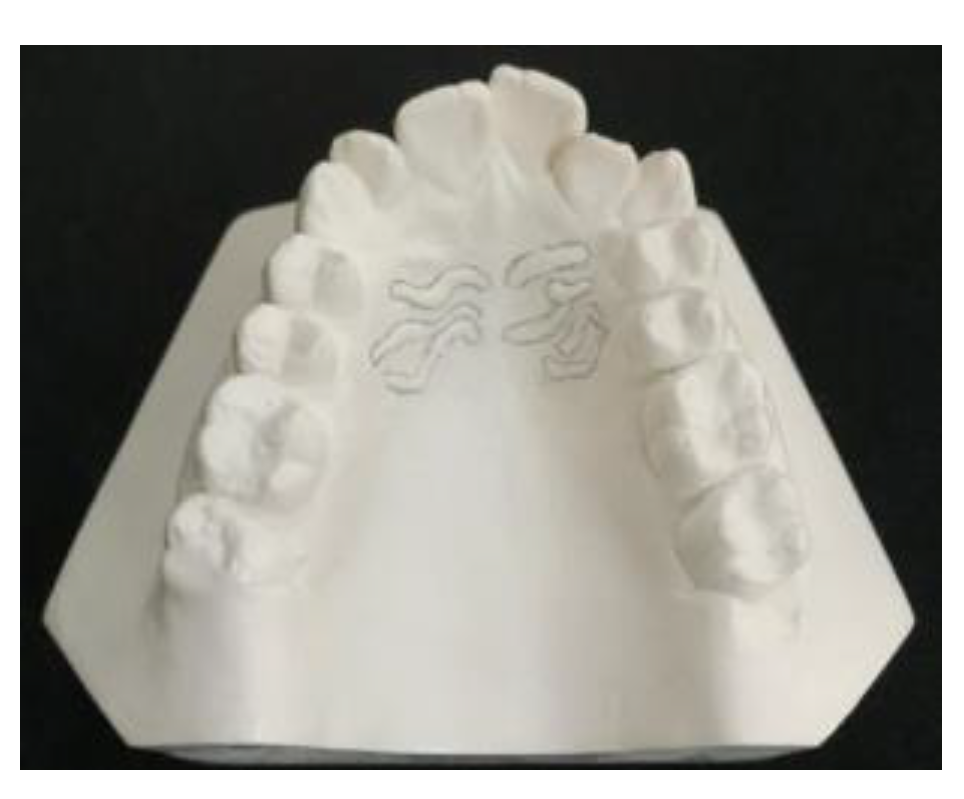
Each PR was determined by one operator using a graphite pencil (0.5 mm) under suitable light and magnification by one operator (
Figure 1). Any PR less than 3 mm were excluded from the study.
An intra-observer reliability test was performed on 15 casts in two-week intervals. The intra-class correlation coefficient revealed an excellent level of reliability (≥0.97).
The data were analysed using Mann–Whitney U and Pearson’s Chi-square test at p < 0.05.
3. Results
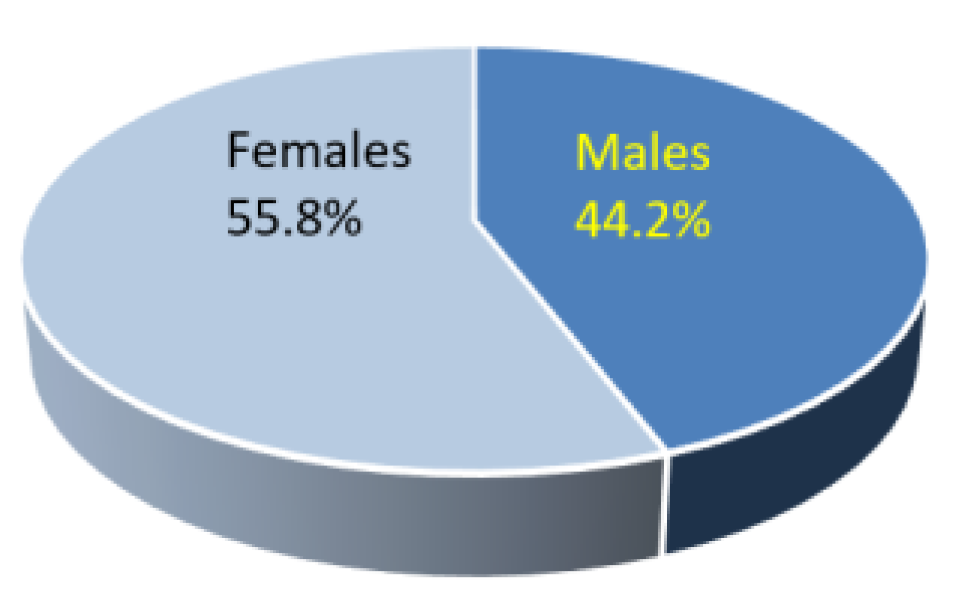
The sample comprised 44.2% males and 55.8% females (
Figure 2). Chi-square tests determined a similar correlation between gender and the frequency of PRs (
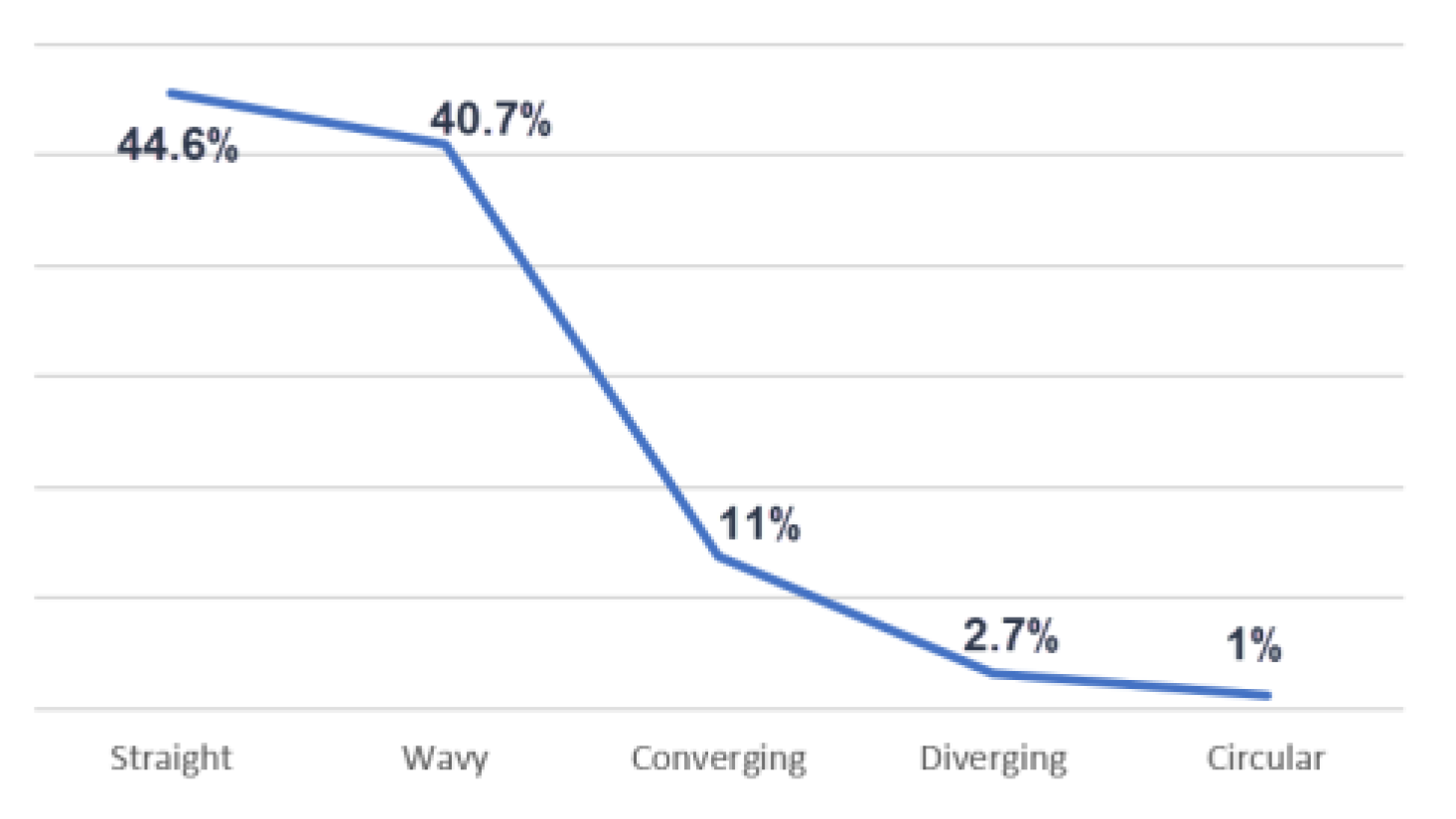
p ≥ 0.372). The total number of PR included in the analysis was 624 rugae. The most frequent PR shape was straight (44.6%), followed by wavy 257 (40.7%) PR (
Figure 3). Likewise, the prevalence of converging (11%), diverging (2.7%) and circular PR (1%) were the least frequent, while cross-linked PR did not exist in our group.
4. Discussion
This retrospective study evaluated the appearance, prevalence and sexual dimorphism of PR in a limited group of Portuguese individuals. Therefore, for the moment, we regard this investigation as a pilot study.
In agreement with our study, several other investigations on Portuguese individuals living in Porto [
4] and other populations reported similar prevalence and distribution of PR in both sexes [
1,
2,
5]. In comparison, sexual dimorphism was observed in other populations [
6,
7].
Straight (44.6%) and wavy (40.7%) PR were the most frequently observed shapes in the Portuguese subjects. Similarly, Santos and Caldas [
4] reported a higher prevalence of straight first PR in their Portuguese sample living in Porto. However, their study analysed only each individual´s 1st and 3rd PRs. The occurrence of straight PRs in our sample was more than in Caucasians (15.2%) [
1] and Libyans (14.28%) [
2]. These variations might be attributed to the different ethnicities of the investigated groups.
The occurrence of diverging and converging PR combined (13.7%) was slightly less than in Caucasians [
1] and relatively more than in Libyans [
2].
This preliminary study explored the morphological discrepancy and sexual dimorphism of PR morphology in Portuguese individuals. A national research initiative involving larger groups is proposed to acquire a clearer picture of the morphological differences of PR in Portuguese individuals.
5. Conclusions
Straight and wavy PRs were the most common in Portuguese individuals. Furthermore, both sexes had a similar PR frequency and morphology; therefore, using PR to determine sex in the Portuguese subjects attending our clinic is not proposed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and I.B.; methodology, M.M. and I.B.; software, M.M., I.B. and G.K.; validation, M.M., I.B. and V.A.; formal analysis, M.M. and I.B.; investigation, M.M., I.B. and V.A.; resources, I.B.; data curation, M.M. and I.B.; writing, original draft preparation, M.M., I.B., G.K. and I.P.; writing, review and editing, M.M., I.B., G.K. and I.P.; visualization, I.B.; supervision, I.B., V.A. and A.D.; project administration, I.B., V.A. and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Egas Moniz School of Health and Science.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kapali, S.; Townsend, G.; Richards, L.; Parish, T. Palatal rugae patterns in Australian aborigines and Caucasians. Aust. Dent. J. 1997, 42, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulmajid, Z.; Bugaighis, I. Evaluation of the morphology of palatal rugae in Libyan school children. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 2, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.J.; Kotze, T.J. The palatal ruga pattern: A new classification. J. Dent. Assoc. S. Afr. 1983, 38, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Caldas, I.M. Palatal rugae pattern in a Portuguese population: A preliminary analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P.; Acharya, A.B.; Padmini, A.T.; Kaveri, H. Differences in the palatal rugae shape in two populations of India. Arch Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, F.M.; Al-Shamrani, S.A.; Talic, Y.F. Rugae pattern in Saudi population sample of males and females. SDJ 2001, 13, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Dohke, M.; Osato, S. Morphological study of the palatal rugae in Japanese. 1. Bilateral differences in the regressive evolution of the palatal rugae. JPN J. Oral. Biol. 1994, 36, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).