Neutrino Mass Ordering with IceCube DeepCore †
Abstract
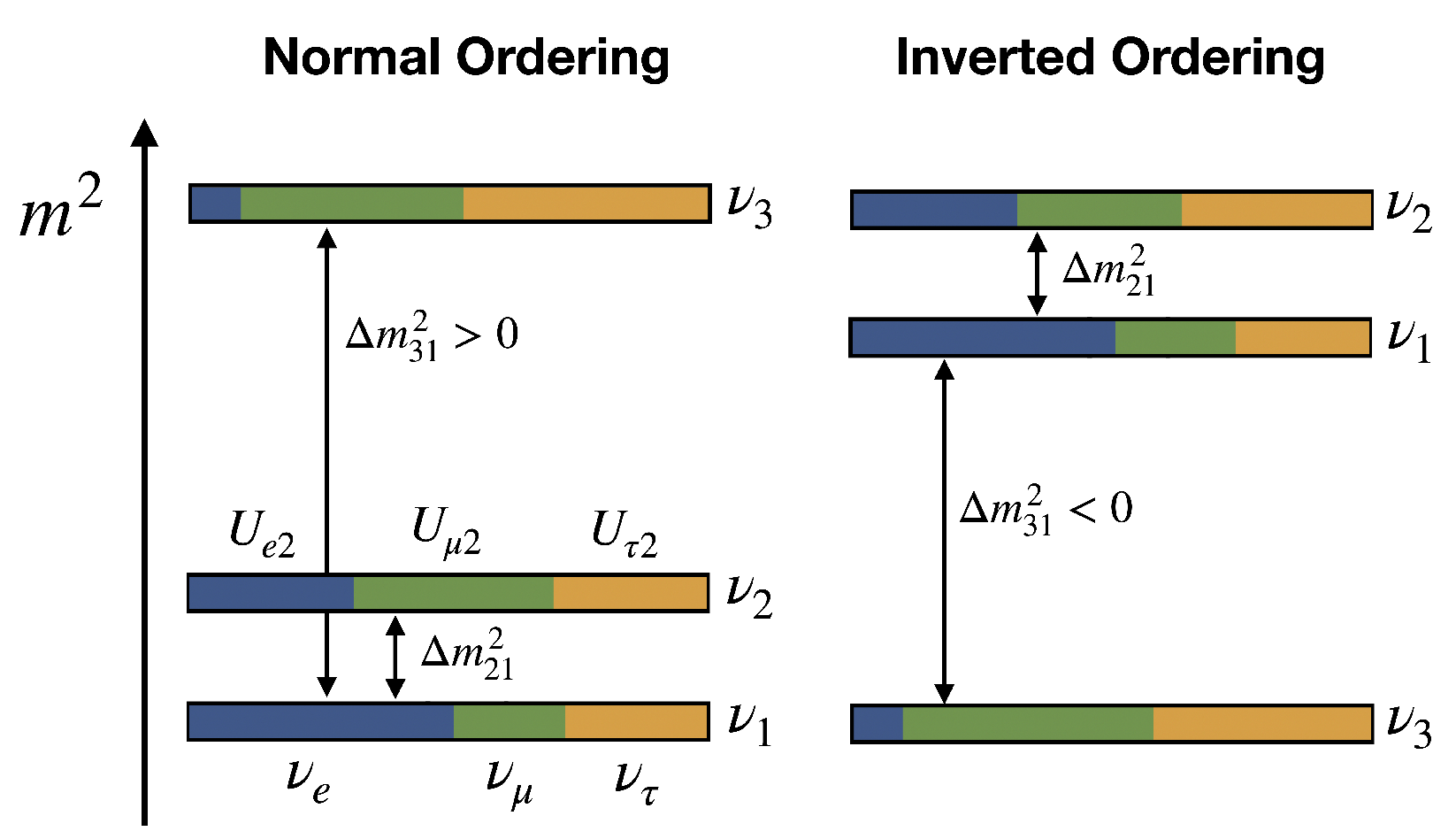
1. Introduction
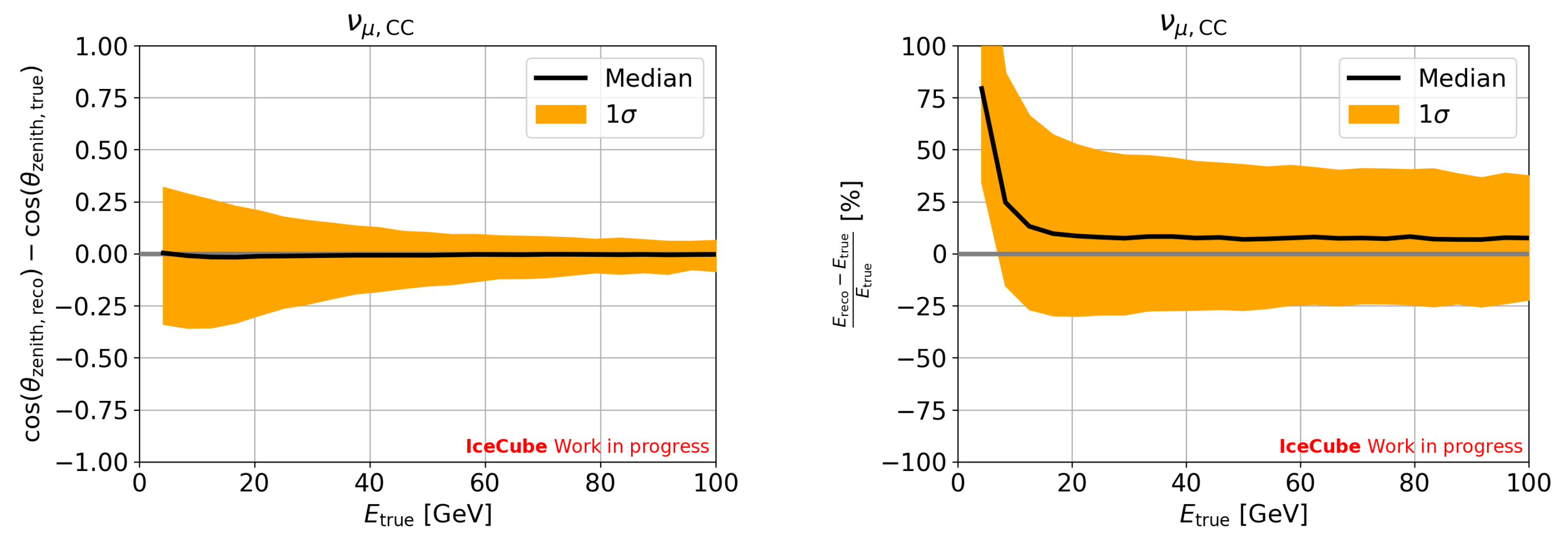
2. Materials and Methods
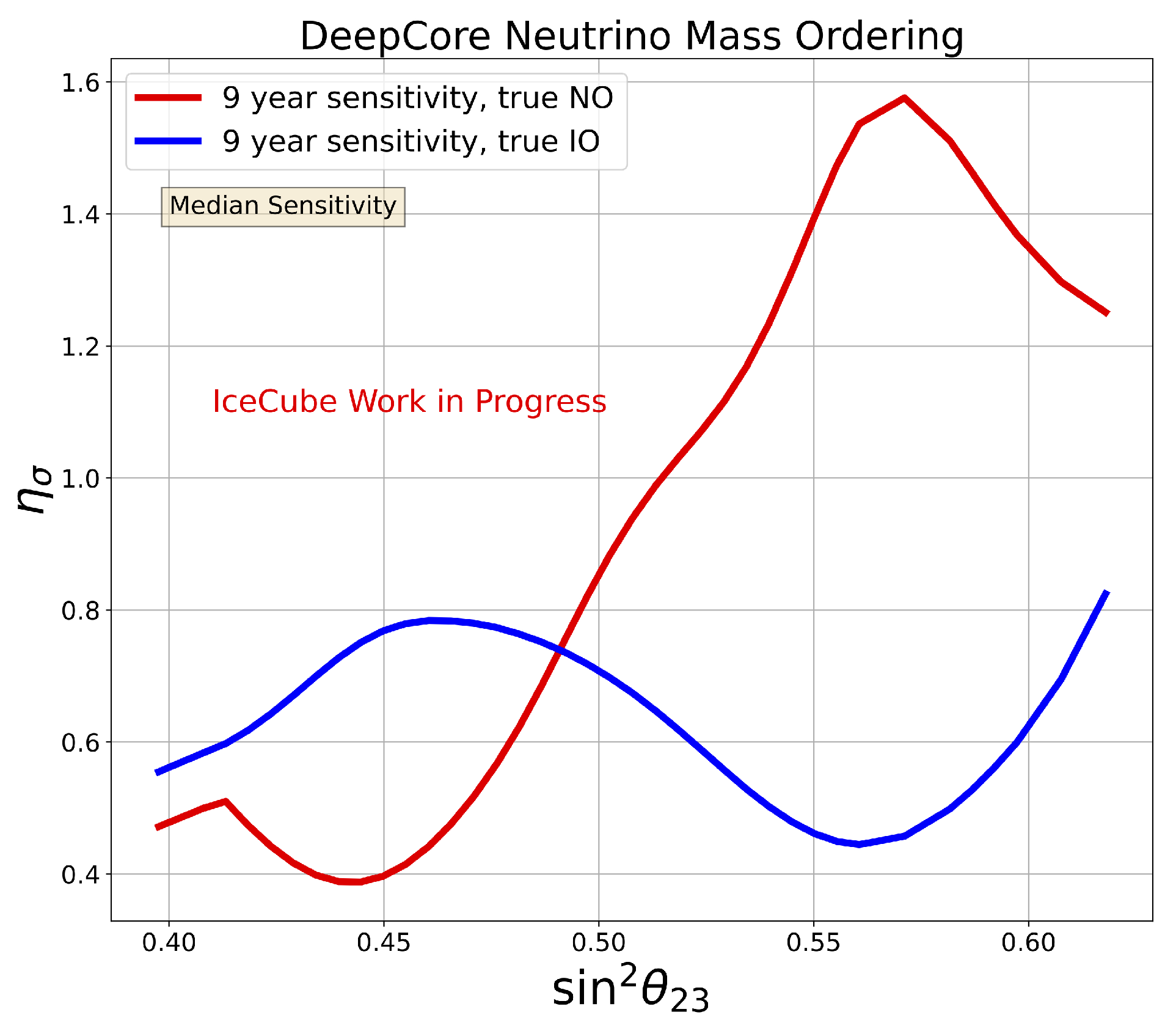
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NuFIT v5.1. Available online: http://www.nu-fit.org/?q=node/238 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Super-Kamiokande Collaboration. Evidence for Oscillation of Atmospheric Neutrinos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SNO Collaboration. Measurement of the Rate of νe + d → p + p + e− Interactions Produced by 8B Solar Neutrinos at the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 071301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory: Instrumentation and online systems. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, P03012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration. The design and performance of IceCube DeepCore. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 35, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NuFIT v4.0. Available online: http://www.nu-fit.org/?q=node/177 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- IceCube Collaboration. Measurement of Atmospheric Neutrino Mixing with Improved IceCube DeepCore Calibration and Data Processing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.12236v1. [Google Scholar]
- IceCube Collaboration. Measurement of atmospheric tau neutrino appearance with IceCube DeepCore. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 032007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration. Low energy event reconstruction in IceCube DeepCore. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Sajjad Athar, M.; Kajita, T.; Kasahara, K.; Midorikawa, S. Atmospheric neutrino flux calculation using the NRLMSISE-00 atmospheric model. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 023004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedynitch, A.; Engel, R.; Gaisser, T.; Riehn, F.; Stanev, T. Calculation of conventional and prompt lepton fluxes at very high energy. EPJ Web Conf. 2015, 99, 08001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, G.D.; Robbins, S.; Gaisser, T.K.; Stanev, T. Uncertainties in atmospheric neutrino fluxes. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 74, 094009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper-Sarkar, A.; Mertsch, P.; Sarkar, S. The high energy neutrino cross-section in the Standard Model and its uncertainty. J. High Energy Phys. 2011, 2011, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulos, C.; Barry, B.; Dytman, S.; Gallagher, H.; Golan, T.; Hatcher, R.; Perdue, G.; Yarba, J. The GENIE Neutrino Monte Carlo Generator: Physics and User Manual. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.05494. [Google Scholar]
- Ciuffoli, E.; Evslin, J.; Zhang, X. Sensitivity to the Neutrino Mass Hierarchy. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1305.5150v4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Agarwalla, S.; Prakash, S.; Uma Sankar, S. Resolving the octant of θ23 with T2K and NOνA. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.2574v2. [Google Scholar]
- An, F.; An, G.; An, Q.; Antonelli, V.; Baussan, E.; Beacom, J.; Bezrukov, L.; Blyth, S.; Brugnera, R.; Avanzini, M.B.; et al. Neutrino physics with JUNO. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 2016, 43, 030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube-Gen2 Collaboration and JUNO Collaboration Members. Combined sensitivity to the neutrino mass ordering with JUNO, the IceCube Upgrade, and PINGU. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 032006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, M.; Schwetz, T. Determination of the neutrino mass ordering by combining PINGU and Daya Bay II. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 2013, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, I.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.C.; Hernandez-Cabezudo, A.; Maltoni, M.; Schwetz, T. Global analysis of three-flavour neutrino oscillations: Synergies and tensions in the determination of θ23, δCP, and the mass ordering. J. High Energy Phys. 2019, 1, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, A.; on behalf of the IceCube Collaboration. The IceCube Upgrade-Design and Science Goals. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019. [Google Scholar]

| Type | Rate [mHz] | Num Events [9.3 yr] | % of Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.162 | 47,541 ± 73 | 23.0 | |
| 0.432 | 126,411 ± 126 | 61.1 | |
| 0.032 | 9510 ± 21 | 4.6 | |
| 0.075 | 21,966 ± 50 | 10.6 | |
| 0.005 | 1463 ± 87 | 0.7 | |
| Total | 0.707 | 206,894 ± 179 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prado Rodriguez, M., on behalf of the IceCube Collaboration. Neutrino Mass Ordering with IceCube DeepCore. Phys. Sci. Forum 2023, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2023008007
Prado Rodriguez M on behalf of the IceCube Collaboration. Neutrino Mass Ordering with IceCube DeepCore. Physical Sciences Forum. 2023; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2023008007
Chicago/Turabian StylePrado Rodriguez, Maria on behalf of the IceCube Collaboration. 2023. "Neutrino Mass Ordering with IceCube DeepCore" Physical Sciences Forum 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2023008007
APA StylePrado Rodriguez, M., on behalf of the IceCube Collaboration. (2023). Neutrino Mass Ordering with IceCube DeepCore. Physical Sciences Forum, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2023008007





