Geometric Variational Inference and Its Application to Bayesian Imaging †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Probabilistic Reasoning
1.2. Posterior Approximation
- Accuracy: The approximation must be accurate even in the case of non-Gaussian and non-conjugate posterior distributions.
- Scalability: Scalability in both the number of data points and the number of DOFs of s are of utmost importance. In practice, only methods with a quasilinear scaling in both are fast enough to cope with the sizes of realistic problems in astrophysical imaging.
- Efficiency: Any method must allow for an efficient implementation that makes use of available computational resources as well as possible, as linear scaling alone does not necessarily yield a fast approximation algorithm, if the resources are not used efficiently.
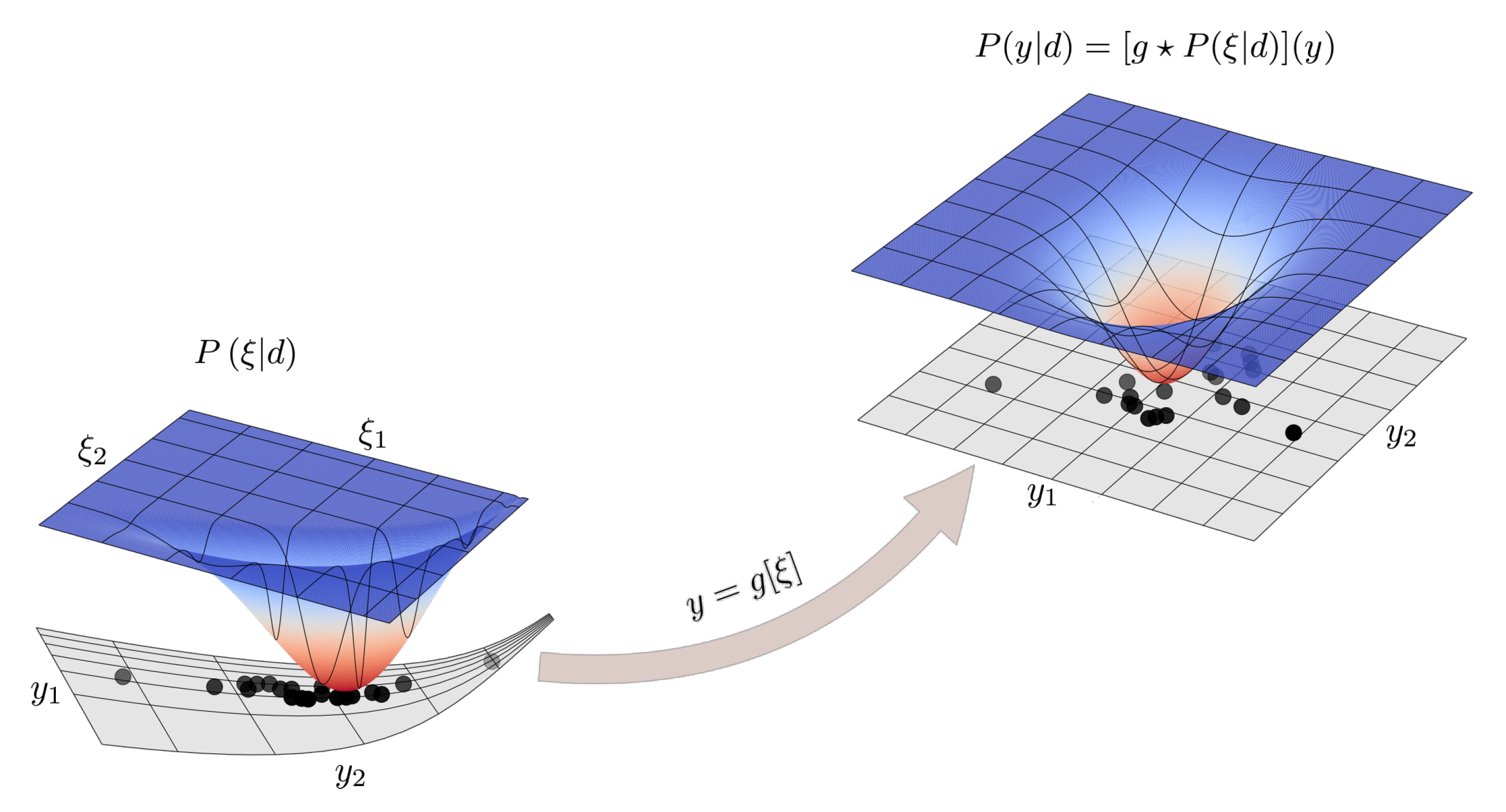
2. Geometric Variational Inference
Coordinate System
Fisher–Rao Metric and Normal Coordinates
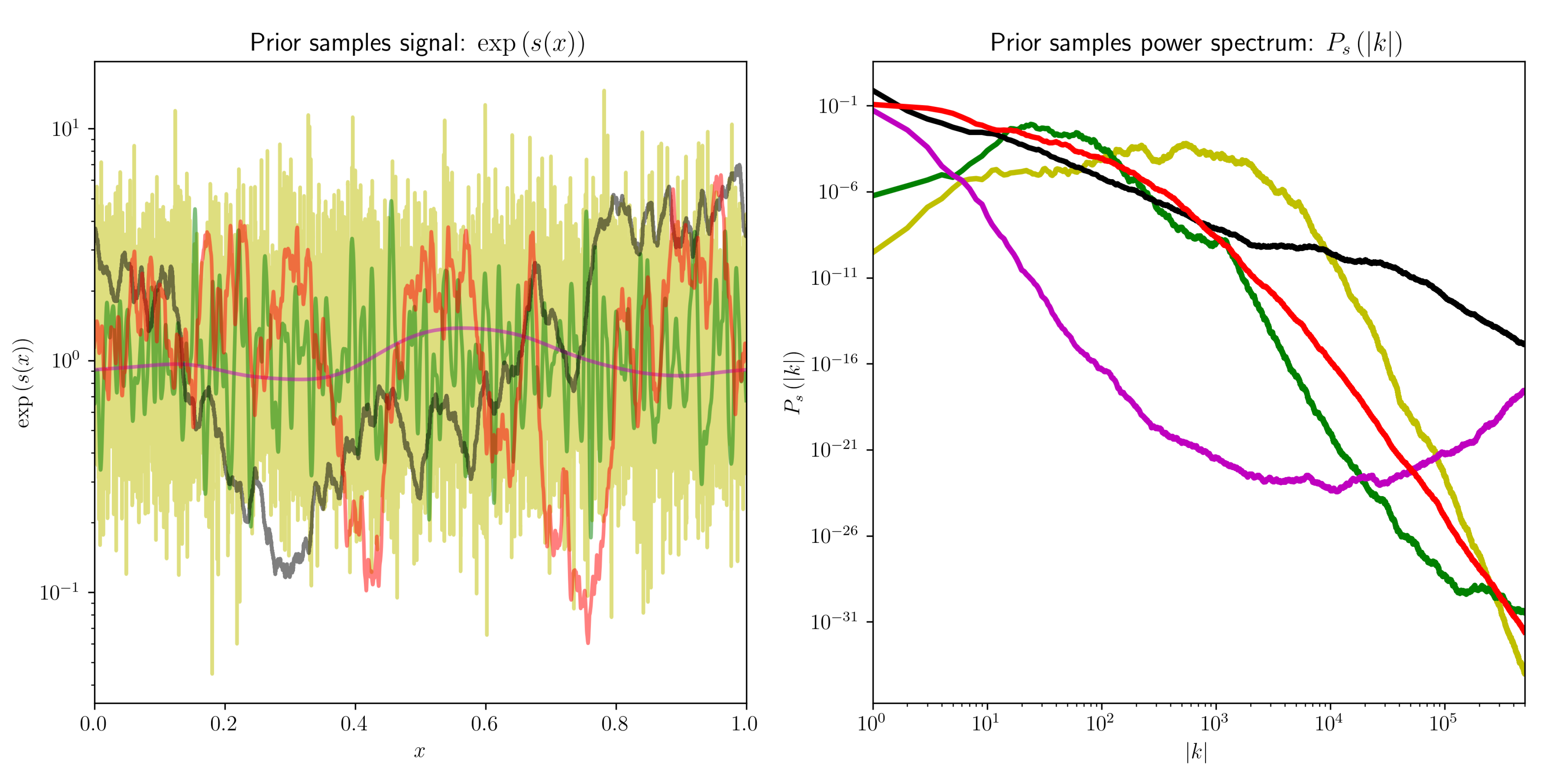
3. A Simple Imaging Example
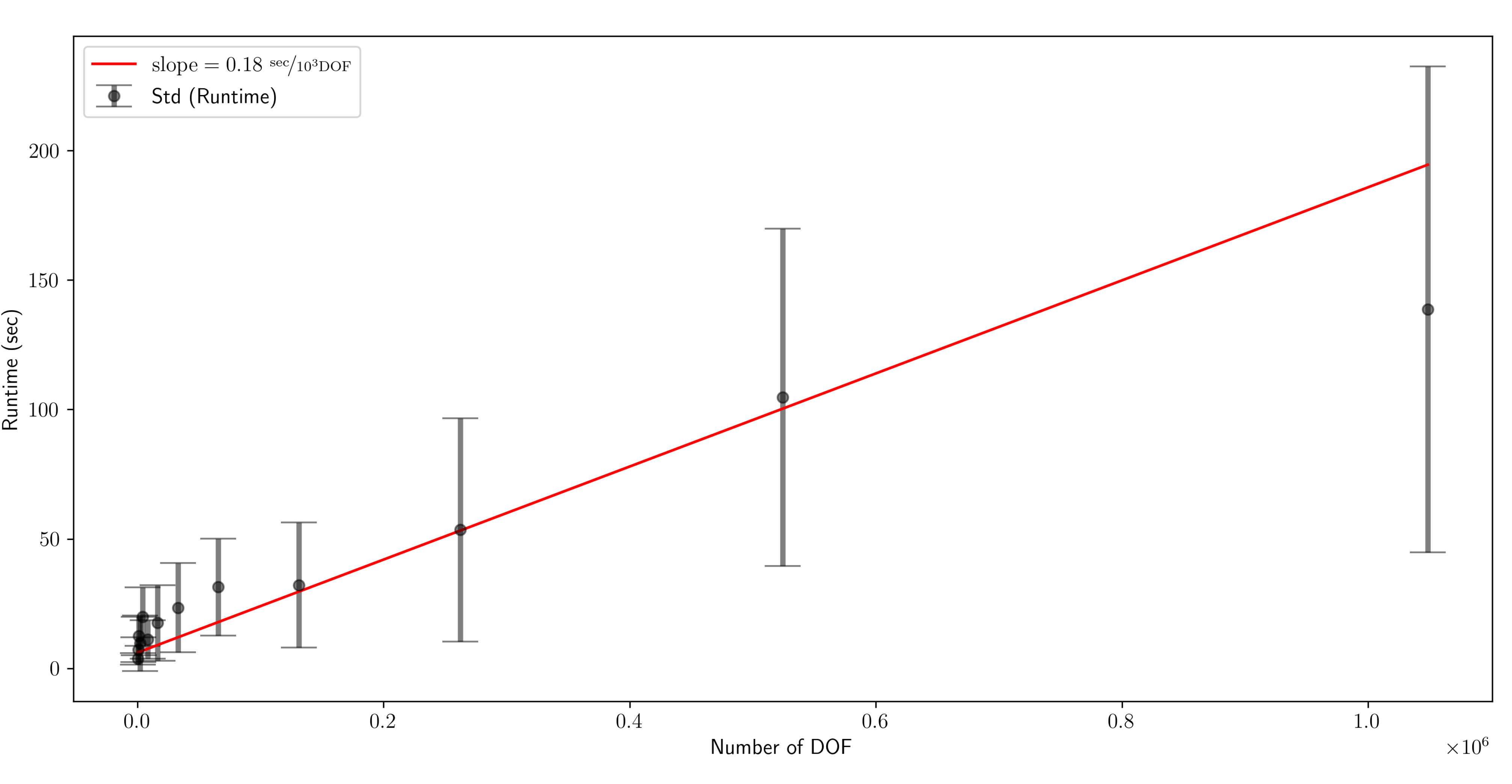
Scaling Behavior
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arras, P.; Baltac, M.; Ensslin, T.A.; Frank, P.; Hutschenreuter, S.; Knollmueller, J.; Leike, R.; Newrzella, M.N.; Platz, L.; Reinecke, M.; et al. Nifty5: Numerical Information Field Theory v5; Astrophysics Source Code Library: Houghton, MI, USA, 2019; p. ascl-1903. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, P.; Leike, R.; Enßlin, T.A. Geometric Variational Inference. Entropy 2021, 23, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutschenreuter, S.; Enßlin, T.A. The Galactic Faraday depth sky revisited. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 633, A150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, B.D.; Larson, D.L.; Lakshminarayanan, A. Global, exact cosmic microwave background data analysis using Gibbs sampling. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 083511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J.B.; Eriksen, H.K.; Wandelt, B.D.; O’Dwyer, I.J.; Huey, G.; Górski, K.M. A Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm for Analysis of Low Signal-To-Noise Cosmic Microwave Background Data. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, B.; Jewell, J.B.; Eriksen, H.K.; Wehus, I.K. Cosmological Parameters from CMB Maps without Likelihood Approximation. Astrophys. J. 2016, 820, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, S.; Frank, P.; Leike, R.H.; Müller, A.; Enßlin, T.A. Bayesian decomposition of the Galactic multi-frequency sky using probabilistic autoencoders. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, A100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, L.I.; Knollmüller, J.; Arras, P.; Frank, P.; Reinecke, M.; Jüstel, D.; Enßlin, T.A. Multi-Component Imaging of the Fermi Gamma-ray Sky in the Spatio-spectral Domain. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.09360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, P.; Frank, P.; Haim, P.; Knollmüller, J.; Leike, R.; Reinecke, M.; Enßlin, T. Variable structures in M87* from space, time and frequency resolved interferometry. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welling, C.; Frank, P.; Enßlin, T.; Nelles, A. Reconstructing non-repeating radio pulses with Information Field Theory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2021, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutschenreuter, S.; Dorn, S.; Jasche, J.; Vazza, F.; Paoletti, D.; Lavaux, G.; Enßlin, T.A. The primordial magnetic field in our cosmic backyard. Class. Quantum Gravity 2018, 35, 154001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leike, R.H.; Glatzle, M.; Enßlin, T.A. Resolving nearby dust clouds. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leike, R.H.; Edenhofer, G.; Knollmüller, J.; Alig, C.; Frank, P.; Enßlin, T.A. The Galactic 3D large-scale dust distribution via Gaussian process regression on spherical coordinates. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenhofer, G.; Leike, R.H.; Frank, P.; Enßlin, T.A. Sparse Kernel Gaussian Processes through Iterative Charted Refinement (ICR). arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasche, J.; Kitaura, F.S. Fast Hamiltonian sampling for large-scale structure inference. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasche, J.; Wandelt, B.D. Bayesian physical reconstruction of initial conditions from large-scale structure surveys. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 894–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasche, J.; Leclercq, F.; Wandelt, B.D. Past and present cosmic structure in the SDSS DR7 main sample. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavaux, G. Bayesian 3D velocity field reconstruction with VIRBIUS. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasche, J.; Lavaux, G. Physical Bayesian modelling of the non-linear matter distribution: New insights into the nearby universe. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 625, A64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porqueres, N.; Jasche, J.; Lavaux, G.; Enßlin, T. Inferring high-redshift large-scale structure dynamics from the Lyman-α forest. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 630, A151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, F.; Heavens, A. On the accuracy and precision of correlation functions and field-level inference in cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, L85–L90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porqueres, N.; Heavens, A.; Mortlock, D.; Lavaux, G. Lifting weak lensing degeneracies with a field-based likelihood. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 509, 3194–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, P.; Frank, P.; Leike, R.; Westermann, R.; Enßlin, T.A. Unified radio interferometric calibration and imaging with joint uncertainty quantification. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, P.; Leike, R.; Enßlin, T.A. Field Dynamics Inference for Local and Causal Interactions. Annalen der Physik 2021, 533, 2000486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Kucukelbir, A.; McAuliffe, J.D. Variational inference: A review for statisticians. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2017, 112, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Blei, D.M.; Wang, C.; Paisley, J. Stochastic variational inference. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 1303–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, D.; Mohamed, S. Variational inference with normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; 37, pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Kucukelbir, A.; Tran, D.; Ranganath, R.; Gelman, A.; Blei, D.M. Automatic differentiation variational inference. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 430–474. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, C.W.; Roberts, S.J. A tutorial on variational Bayesian inference. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2012, 38, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmídl, V.; Quinn, A. The Variational Bayes Method in Signal Processing; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, C.J. Practical markov chain monte carlo. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Gelman, A.; Jones, G.; Meng, X.L. Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marjoram, P.; Molitor, J.; Plagnol, V.; Tavaré, S. Markov chain Monte Carlo without likelihoods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15324–15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, S.; Kennedy, A.D.; Pendleton, B.J.; Roweth, D. Hybrid monte carlo. Phys. Lett. B 1987, 195, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, M. A conceptual introduction to Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.02434. [Google Scholar]
- Skilling, J. Nested sampling. In Proceedings of the 24th International Workshop on Bayesian Inference and Maximum Entropy Methods in Science and Engineering, Garching, Germany, 25–30 July 2004; AIP Publishing LLC.: Melville, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 735, pp. 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Skilling, J. Nested sampling for general Bayesian computation. Bayesian Anal. 2006, 1, 833–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroz, F.; Hobson, M.P. Multimodal nested sampling: An efficient and robust alternative to Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods for astronomical data analyses. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 384, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knollmüller, J.; Enßlin, T.A. Metric gaussian variational inference. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.11033. [Google Scholar]
- Girolami, M.; Calderhead, B. Riemann manifold Langevin and Hamiltonian Monte Carlo methods. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2011, 73, 123–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leike, R.H.; Enßlin, T.A. Optimal belief approximation. Entropy 2017, 19, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. Theory of statistical estimation. In Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1925; Volume 22, pp. 700–725. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frank, P. Geometric Variational Inference and Its Application to Bayesian Imaging. Phys. Sci. Forum 2022, 5, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005006
Frank P. Geometric Variational Inference and Its Application to Bayesian Imaging. Physical Sciences Forum. 2022; 5(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005006
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrank, Philipp. 2022. "Geometric Variational Inference and Its Application to Bayesian Imaging" Physical Sciences Forum 5, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005006
APA StyleFrank, P. (2022). Geometric Variational Inference and Its Application to Bayesian Imaging. Physical Sciences Forum, 5(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2022005006





