Bayesian Surrogate Analysis and Uncertainty Propagation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bayesian Uncertainty Quantification
2.1. General Structure of the Problem
2.2. Bayesian Analysis and Selection of the Surrogate Model
2.3. Bayesian Uncertainty Propagation with Surrogate Models
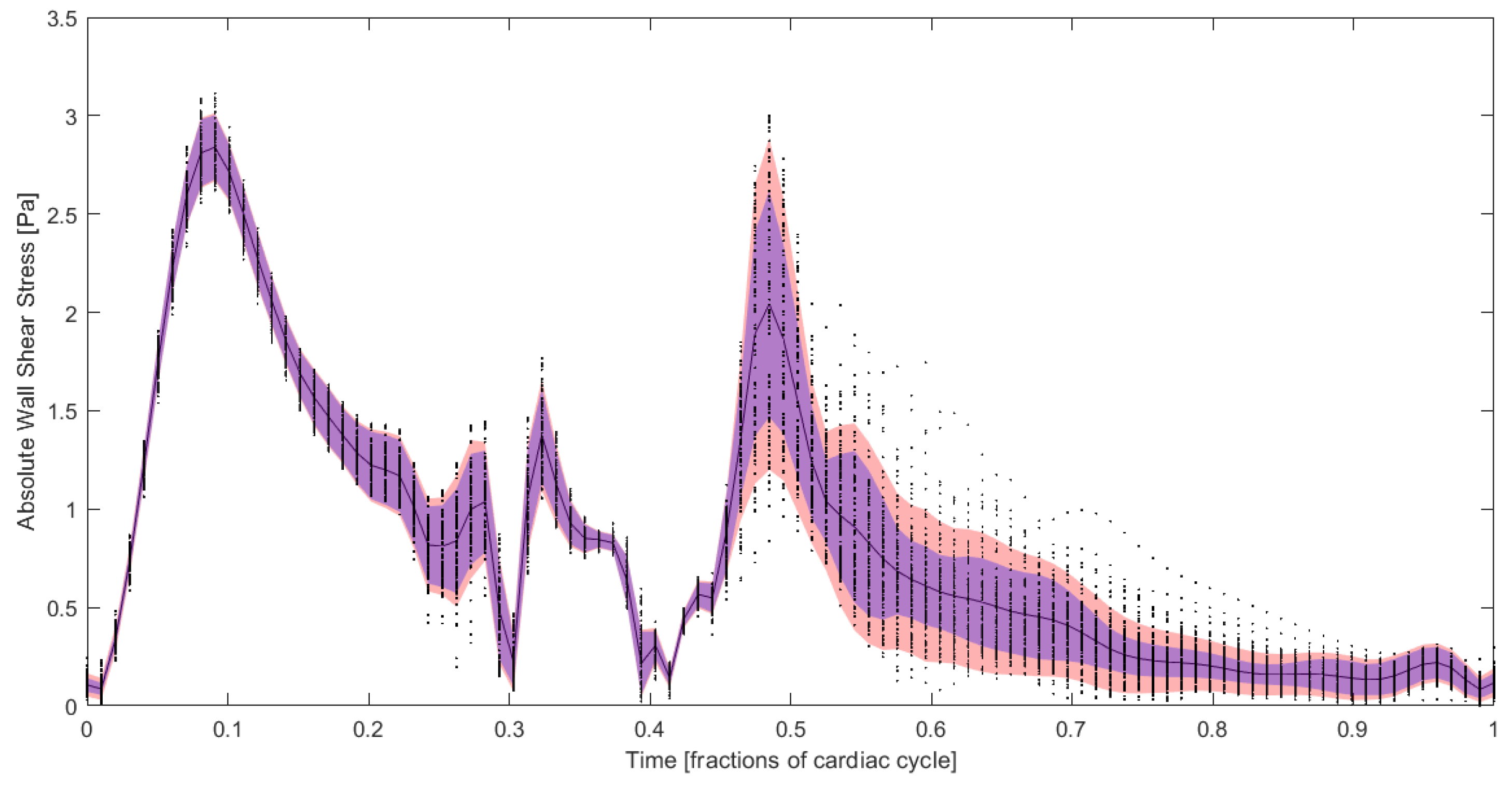
3. Numerical Example
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Mathematical Proofs
Appendix B. The Transformation Invariant Prior for the Surrogate Coefficients
References
- Xiu, D.; Karniadakis, G.E. The Wiener-Askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2005, 27, 1118–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, A. Polynomial Chaos: A Tutorial and Critique from a Statistician’s Perspective. 2013. Available online: http://tonyohagan.co.uk/academic/pdf/Polynomial-chaos.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Crestaux, T.; Le Maître, O.P.; Martinez, J.-M. Polynomial chaos expansion for sensitivity analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2009, 94, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, A. Curve Fitting and Optimal Design for Prediction. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1978, 40, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sraj, I.; Le Maître, O.P.; Knio, O.M.; Hoteit, I. Coordinate transformation and Polynomial Chaos for the Bayesian inference of a Gaussian process with parametrized prior covariance function. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 298, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, A.; Kennedy, M.C.; Oakley, J.E. Uncertainty analysis and other inference tools for complex computer codes. Bayesian Stat. 1999, 6, 503–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, M.C.; O’Hagan, A. Predicting the output from a complex computer code when fast approximations are available. Biometrika 2000, 87, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnst, M.; Ghanem, R.G.; Soize, C. Identification of Bayesian posteriors for coefficients of chaos expansions. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 3134–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madankan, R.; Singla, P.; Singh, T.; Scott, P.D. Polynomial-chaos-based Bayesian approach for state and parameter estimations. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2013, 36, 1058–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, G.; Lin, G. Selection of polynomial chaos bases via Bayesian model uncertainty methods with applications to sparse approximation of PDEs with stochastic inputs. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 259, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Morzfeld, M.; Tu, X.; Chorin, A.J. Limitations of polynomial chaos expansions in the Bayesian solution of inverse problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 282, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwai, M.; Tan, Y. Sequential Bayesian Polynomial Chaos Model Selection for Estimation of Sensitivity Indices. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2015, 3, 146–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.G.; Owhadi, H.; Higdon, D. Handbook of Uncertainty Quantification; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, A. Bayesian analysis of computer code outputs: A tutorial. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Linden, W.; Dose, V.; von Toussaint, U. Bayesian Probability Theory: Applications in the Physical Sciences, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladyshkin, S.; Nowak, W. Data-driven uncertainty quantification using the arbitrary polynomial chaos expansion. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 106, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeman, J.D.; Franzelin, F.; Narayan, A.; Eldred, M.; Plfüger, D. Polynomial chaos expansions for dependent random variables. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 351, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Linden, W.; Preuss, R.; Hanke, W. Consistent Application of Maximum Entropy to Quantum-Monte-Carlo Data. J. Physics: Condens. Matter 1996, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranftl, S.; Müller, T.; Windberger, U.; von der Linden, W.; Brenn, G. Data and Codes for ’A Bayesian Approach to Blood Rheological Uncertainties in Aortic Hemodynamcis’; Zenodo Digital Repository: Genève, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, E.; Marelli, S.; Embrechts, P.; Sudret, B. A general framework for data-driven uncertainty quantification under complex input dependencies using vine copulas. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2019, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranftl, S.; von der Linden, W. Bayesian Surrogate Analysis and Uncertainty Propagation. Phys. Sci. Forum 2021, 3, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2021003006
Ranftl S, von der Linden W. Bayesian Surrogate Analysis and Uncertainty Propagation. Physical Sciences Forum. 2021; 3(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2021003006
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanftl, Sascha, and Wolfgang von der Linden. 2021. "Bayesian Surrogate Analysis and Uncertainty Propagation" Physical Sciences Forum 3, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2021003006
APA StyleRanftl, S., & von der Linden, W. (2021). Bayesian Surrogate Analysis and Uncertainty Propagation. Physical Sciences Forum, 3(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/psf2021003006






