Abstract
Depression is a neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by altered emotion and cognition. Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is a potent natural antioxidant and exhibits neuroprotective effects. However, its antidepressant activity and its mechanism of action in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) need to be evaluated. The rats were divided into six groups. Group, I vehicle control (without stress), II- CUMS, III- fluoxetine (FLX) (50 mg/kg p.o.), IV, V, and VI were treated with ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg, p.o.), respectively. All the groups, except I, were subjected to CUMS + treatments from day 1 to day 42. Body weight and behavioral parameters like sucrose preference test (SPT), Morris water maze (MWM), resident intruder test (RIT), and marble-burying test (MBT) were performed on day 0, day 21, and day 42, and forced swim test (FST) on last day 42 and 43 only. The rats were further sacrificed for biochemical and histopathological evaluation. ALA significantly improved behavioral function, increased antioxidant strength, reduced lipid peroxidation, restored monoamines, and protected CA3 neurons. Further, docking studies revealed strong binding of ALA on the 5HT3 receptor. The study demonstrates that ALA might be exhibiting antidepressant effects in part by restoring monoamines and modulating the 5HT3 receptor.
1. Introduction
Depression is a neuropsychological disorder exhibiting physiological and behavioral distress characterized by persistent sad and empty moods, loss of interest and motivation, melancholy, and anhedonia [1]. It is a primary health concern and globally contributes to significant socioeconomic losses along with disability, morbidity, and mortality. In the last twenty years, depression has evolved from an acute and self-limiting illness to a chronic, lifelong condition. It profoundly affects the elderly with comorbidities like memory, cognitive deficit, and cardiovascular complications [2,3]. It is well established that reduced sensitivity of the dopaminergic system results in cognitive impairment, insomnia, and feelings of guilt [4,5]. Clinical symptoms characteristics include anhedonia, low self-esteem, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness, suicidal thoughts, disturbances in sleep and appetite, as well as anxiety and aggressive behavior [6,7,8].
Chronic stress is the major contributory factor to depression. Chronic or repeated provocative stress alters the autonomic nervous system, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA), and the immune system. Moreover, it affects physical integrity as well as one’s psychological well-being. Chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) is a classical and well-validated animal model to induce a broad spectrum of behavioral deficits, including anhedonia, anxiety, aggression, depression-like behavior, reduced cognition, and altered the level of antioxidants and neurotransmitters like NE, DA, 5HT [9,10].
Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms exist for depression, including impaired HPA axis, glucocorticoid receptor (GR), cortisol resistance, reduced BDNF expression, mitochondrial damage, reduced antioxidant activity, and neuroinflammation [11,12,13]. Traditional antidepressants alleviate the level of monoamines but are also associated with many disadvantages, such as suicidal thoughts, the late onset of action, and cardiac side effects [14,15,16]. Nevertheless, 1/3 of patients still do not respond to it and have a high relapse rate. Notably, the most prescribed SSRI has a black box warning [17,18,19]. The 5HT3 receptors are thus emerging as newer targets for antidepressant compounds. Their antagonists are found reverse depression at a low dose and with a short duration of treatment. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) is also known as thioctic acid (TA) and 1,2 dithiolane -3-pentanoic acid [20,21]. It is naturally present in spinach, broccoli, tomato, and various microorganisms and animal tissues. The ALA contains cysteine, a promising precursor of GSH (Glutathione). GSH, an intracellular non-enzymatic thiol antioxidant system, neutralizes free radicals/ROS. The finding of this investigation is in line with others, showing that stressed mice have lower brain GSH levels indicating an alteration in antioxidant brain defenses in CUMS model of depression [22]. ALA boosts tissue GSH levels and inhibits Ca2+ channel sulfhydryl group modifications [23,24]. It acts as a biological antioxidant and a metal chelator, reducing the oxidized forms of other antioxidant agents, such as vitamins A, C, and E, GSH, and Coenzyme Q10. It improves endothelial dysfunction through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory function [25]. Previously, ALA demonstrated increased BDNF, exhibits neuroprotective effect in traumatic brain injury by inhibiting neural apoptosis [26,27], and improved memory in the senescence-accelerated prone mouse strain 8 (SAMP8) model of Alzheimer’s disease due to its potent antioxidant effect [28]. Given its neuroprotective and potent antioxidant properties, ALA can perhaps prove to be an effective antidepressant in its own right for CUMS-induced depression. An attempt has been made to evaluate the antidepressant effect of ALA on CUMS-induced depression and understand its mechanism of action through brain monoamine estimations and molecular docking study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
Male Wistar rats (36) (weight 240–250 g) were procured from Global Bioresearch Solutions Private Limited, Pune. Animals were maintained under standard laboratory conditions at 23 ± 2 °C with a relative humidity of 55 ± 10% on a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle. Animals had free access to food and water ad libitum. A laboratory diet was provided by VRK Nutrition Pune, India. The animals were moved to the experimental area 1 h before the experiment. All the experiments were performed according to the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) and were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee. The IAEC approval No is PCP/IAEC/PCL 31/2019–2020.
2.2. Drugs and Chemicals
ALA and fluoxetine (FLX) were obtained as a gift sample from Inlife Pharmaceuticals private limited Hyderabad, India and Sun Pharmaceuticals Limited Vadodara, India, respectively. Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) was purchased from Loba Chemie Private Limited (Mumbai, India). The standard biomarkers for HPLC DA, NE, and 5-HT were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Bangalore, India). The other HPLC-grade chemicals and solvents used in the study were procured from local suppliers.
2.3. Experimental design
Thirty-six male Wistar rats aged about (9–10 weeks old) were divided into 6 groups. Group I was vehicle control (VC; 0.2% (w/v) CMC) and was kept under normal conditions with feed and water, Group II was CUMS subjected to stress and vehicle (0.2% (w/v) CMC) (1 mL once a day p.o.), Group III was standard subjected to CUMS treated with FLX (10 mg/kg p.o., for 42 days). Group IV, V, and VI were subjected to CUMS with ALA treatment (50, 100, 200 mg/kg p.o for 42 days). ALA was dissolved in 0.2% (w/v) CMC, and FLX was dissolved in distilled water and administered using oral gavage (gauge size 18) daily at a constant volume according to body weight. The dosages and route of administration for ALA were selected based on the methods used in previous studies [29,30] (Figure 1).
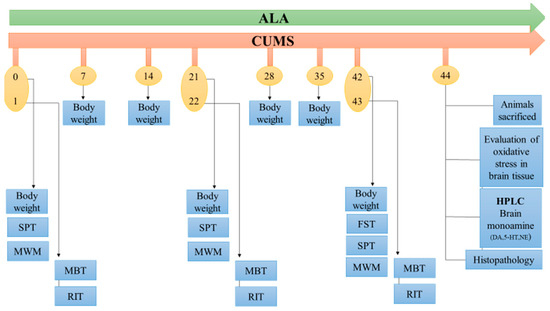
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the protocol and treatment schedule adopted. Abbreviations: CUMS—chronic unpredictable mild stress, Force swim test—FST, Sucrose preference test-SPT, Morris’ water maze—MWM, Marble burying test—MBT, Resident intruder test—RIT.
2.4. CUM-Induced Depression-Like Behaviour in Rats
CUMS method was carried out with minimal modifications, as previously reported with minor modifications [31,32]. The VC group rats were left undisturbed in their cages in a separate room for the next six weeks (42 days), while the other five groups of rats were housed and exposed to various minor stressors from 0 days to 42 days. The stress was given from 0 day to 42 days; however, no stressors were applied during testing of pharmacological behavior on various days, such as days 0, 1, 21, 22, 42, and 43. The stressors were clamped tail (1 h), wet cage (24 h), tilt cage 45° (14 h), novel odor (17 h), overnight illumination, food and water deprivation (24 h), restricted access to food (2 h), limited access to water (2 h), crowding (24 h), clamp tail (1 h), forced running (4 h), white noise 10 m (60 dBA). These stressors were randomly scheduled over one week and repeated throughout the 6-week experiment to maintain the aspect of unpredictability. Each week stressors sequence took place on different days and at other times. All the parameters were recorded by the blind observer, who had no information about the treatment. The sequence of behavior testing was SPT, MWM on the same day, whereas MBT and RIT on the next day. FST was done only once on day 42 before SPT. Care was taken to perform the testing in such a way that one parameter should not interfere with the other.
2.5. Body Weight
Throughout the CUMS phase, the body weights were recorded weekly for 42 days.
2.6. Forced Swim Test (FST)
The FST was performed on 42 and 43 days of study. Rats were individually placed in a water tank made of glass (height, 80 cm; diameter, 30 cm) at 23–25 °C. Experiments were performed in two sessions. In the first session (42 days), animals were trained to swim for 15 m. The second (test) session was conducted 24 h after the training (43 days) and 1 h post-treatment. In this test session, rats were studied for an immobility time of 10 m. Immobility was recorded as floating, with small movements or the head above the water’s surface [33,34].
2.7. Sucrose Preference Test
In depression, anhedonia is a significant symptom observed, characterized by a loss of pleasure. In rats, the sucrose preference test (SPT) measures the anhedonia behavior where they lose interest in sucrose solution. We performed SPT on 0, 21, and 42 days for 1 h in the morning with minimal modification procedures as described [35]. Training phase, seventy-two hours before the test, rats were adapted for 1% (w/v) sucrose solution (100 mL). The two-sucrose solution 1% (w/v) bottles were placed per cage for 24 h. In the next 24 h, one bottle of sucrose solution was replaced with tap water (100 mL). In the test phase, these rats were deprived of food and water for 24 h. The next day morning, rats were housed in individual cages kept in 2 bottles in each cage, one with 1% (w/v) sucrose solution (100 mL) and another with tap water (100 mL). The positions of bottles were interchanged post 30 min to avoid side preference. After 1 h, the sucrose solution and tap water consumed were measured. Sucrose preference (%) was calculated by
2.8. Morris Water Maze
Loss of memory and cognitive decline result from CUMS. Morris water maze (MWM) test was carried out to test spatial memory and long-term memory on 0, 21, and 42 days following SPT [36,37]. The MWM consisted of a black circular tank with a diameter of 150 cm and height of 45 cm filled with clean water up to 35 cm in depth and maintained a temperature of 20–22 °C. The training period was conducted one week before the induction of stress. All the rats were trained to identify the platform. During the 5 days of the training phase, rats were released into the water tank in search of a platform. Four prominent visual clues were colored red, blue, green, and yellow as path indicators for rats. After the training phase, water was made opaque by adding a non-toxic white color dye (food-grade titanium dioxide). A water level above 2 cm was maintained from the platform. Individual rats were placed into the maze and allowed to search the platform for 60 s. The moment when the rat was found and climbed onto the platform, the trial was stopped, and escape latency, distance traveled, and time spent in zones were recorded by a video tracking system (VJ Instruments Maharashtra, India). If a rat could not locate the platform within the 60 s, the experimenter guided the rat to the platform and kept it there for 10 s before removal from the maze. If still during training, the rat could not find the platform, it was not included in further study. Zero days were the baseline reading for all the rats.
2.9. Marble Burying Test (MBT)
The anxiogenic behavior of rats was analyzed by marble-burying test on 1, 22, and 43 days [38]. The rat cage was filled with bedding up to 5 cm. The marbles (20 in number) were put on the surface of the bedding. The individual rat was placed in a cage for 20 m under observation. The deeply buried marbles were counted (3.3 cm).
2.10. Resident Intruder Test (RIT)
RIT occurred after the MBT trial on 1, 22, and 43 days. Resident male rats were tested in their home cages for aggression against 150 s g male Wistar rats aged about (6–7 weeks old) intruders. After placing the intruder rat in the territorial cage, the behavior of the male rat was observed. The time of the first attack latency was noted, and the cut-off time was 5 min [39].
2.11. Brain Tissue Homogenate Preparation for Antioxidant Parameters
At the end of 42 days of the behavioral study protocol, the forebrain region of the rats’ brains was isolated and rinsed with ice-cold saline solution and weighed. The individual 0.15 g of the brain was fragmented and diluted with PBS 10× of brain weight. The diluted brain sections were homogenized in a homogenizer at 1000 rpm for 5 min (Remi motors, Mumbai). Ice-cold conditions were maintained to avoid tissue degradation and were stored in a deep freezer at −80 °C for further analysis.
2.12. Evaluation of Antioxidant Parameters
2.12.1. Assay of GSH
20% TCA, 0.6 M DTNB 5,5′-Dithio-Bis (2-Nitrobenzoic acid) dissolved in 50 mL of phosphate buffer (pH 8) were prepared as per the method described by [40] with slight modification. 200 µL brain tissue homogenate was mixed with 200 µL trichloroacetic acid (TCA) 20% and centrifuged for 15 min, 2500 rpm, at 0 °C. 50 µL of supernatant was separated in an Eppendorf tube and was mixed with 400 µL of DTNB. The final volume comprised 600 µL of PBS (pH 8). Absorbance was recorded at 412 nm. The amount was expressed as a nanogram per gram of tissue weight.
2.12.2. TBARS Assay
200 µL of the sample was mixed with freshly prepared TCA (20%) and was kept in an ice bath for 15 min. The mixture was further centrifuged at 2500 rpm for 15 min, 0 °C, and 200 µL of supernatant was separated. To this supernatant, TBA (20%) was added, and the solution was heated in a water bath for 10 min (95 °C), allowed to cool at room temperature, and placed in an ice-cold bath for 5 min. Absorbance was read at 532 nm, and the amount was expressed as nanomoles/g of tissue weight [41].
2.12.3. Assay of SOD
The previously reported method with slight modifications was used [42]. Carbonate buffer (pH 10.2), EDTA solution (0.4 M), and epinephrine bitartrate (3 mM) solutions were prepared separately. 200 µL of brain tissue homogenate was mixed with 200 µL of cold distilled water, 100 µL of ice-cold ethanol, and 60 µL of ice-cold chloroform. The above solution was mixed well by using a cyclomixer for 5 m and centrifuged at 250 rpm, 15 min, at 0 °C. 200 µL of supernatant was separated out and then mixed with 600 µL carbonate buffer, 200 µL of EDTA solution, and 160 µL of epinephrine bitartrate. Changes in the absorbance were recorded at 480 nm for 1 min at room temperature. The amount was expressed as U/g of tissue weight.
2.12.4. Assay of NO
The Griess reagent determined NO levels per the method described by [43], 2.3 mL of phosphoric acid (85%), 1 g of sulphanilamide, 0.1 g N-1-Naphthylethylenediamine was dissolved in 97.7 mL of distilled water. It was mixed well on the vortex and protected from light. 50 µL of the sample was added in an Eppendorf tube, followed by 50 µL of Griess reagent, and vortexed for 10 min. Absorbance was recorded at 540 nm. Dark conditions were maintained strictly during all steps of the above procedures. The amount was expressed as µg/g of tissue weight.
2.12.5. Assay of Catalase
We prepared 0.01 M phosphate buffer (pH 7) and 2 M hydrogen peroxide separately. Dichromate acetic acid reagent was mixed with 5% potassium dichromate with glacial acetic in a 1:3 ratio. Separately 400 µL of 0.01 M phosphate buffer (pH 7) was mixed with 40 µL of sample and 160 µL H2O2 (2 M). Further, 800 µL of dichromate acetic acid reagent was added, and green and purple coloration was observed. The above mixture was heated in a water bath at 72–90 °C for 10 min, and 160 µL of distilled water was added to the solution. Absorbance was taken at 583 nm, and the amount was expressed as µg/g of tissue weight [44].
2.13. Histopathological Study of Brain Tissues
The part of the brain comprising the dorsal part of the hippocampus of the animals is carefully fixed in the appropriate fixative and processed for histopathology. It was then embedded in formalin (10% v/v) and sliced into 5 μm using the microtome. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for the routine assessment of the histological structure of the hippocampus. CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus were examined [45].
2.14. Monoamine’s Estimations
2.14.1. Tissue Preparation
The ventral hippocampal part of the brain was dissected under ice-cold conditions to avoid tissue degradation and weighed. Perchloric acid (0.2 M) was prepared by adding 3.35 mL of perchloric acid and 36.6 mg of cysteine (3 mM) in 100 mL of distilled water [46]. A hippocampal portion of brain tissue was homogenized in 200 µL of perchloric acid and centrifuged at 1200 rpm, −4 °C for 15 min. The supernatant was used to estimate the monoamines.
2.14.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Conditions
The monoamines were estimated by an HPLC-FD (JASCO-BORWIN version 1.50, Tokyo, Japan). The mobile phase composition consisted of acetate buffer (12 mM acetic acid, 0.26 mM Na2EDTA) at pH 3.5. Methanol was added in the ratio 86:14 v/v. Before use, the mobile phase was passed through a 0.45 mm membrane filter and degassed under a sonicator. A 0.22 µm syringe filter filtered the supernatant of tissue homogenate. 20 µL of the filtrate was injected onto HPLC with autosampler AS-1555, JASCO, Japan. The flow rate was maintained at 1 mL/m. The C18 column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) was deployed, and the temperature was kept at 35 °C run time of 30 min, at an excitation wavelength of 280 nm and an emission wavelength of 315 nm. A standard curve was obtained with different concentrations and used to estimate the levels of noradrenaline (NE), dopamine (DA), and 5-hydroxy tryptamine (5-HT) after separation. Peaks were identified by comparing their retention time in the sample (tissue extracts) solution with that of the standard solution [47].
2.15. Molecular Docking Study
The molecular docking studies were performed by using docking software (Autodock). This study completed the molecular docking using Molegro virtual docker software 2013 version 6.0.0 (MVD), following all standard procedures. MVD is the most widely used and effective tool for determining various ligand-protein interactions and has greater accuracy (87%) than similar docking tools. The 3-D structure of the serotonin receptor in complex with cofactors was gained from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB) Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org/pdb, accessed on 21 December 2021), having PDB id 6Y1Z. The structure was downloaded from the database in .pdb format. The possible orientations and conformations were analyzed by the clustering method implanted in MVD. Docking was completed between the ligands and the receptor’s active site, with Grid resolution of 0.30 Å, MolDock scoring function, and including amino acids within a radius of 20 Å around X: 125.90, Y: 110.83, Z: 168.25 as the active site residues. A docking score (−52.8461) was obtained, the best pose for the Rerank score (−41.6617) for ALA was retained, and the binding geometry or conformation was assessed.
2.16. Statistical Analysis
The data are presented as mean ± SEM and were analyzed statistically using Graph Pad Prism version 8.0 software (GraphPad Software; La Jolla, CA, USA). Statistical comparison was carried out using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett post-test for GSH, MDA, SOD, NO, CAT, NE, DA, 5-HT and repeated measures of two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test were used for body weight, SPT, MWM, RIT, MBT. p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Body Weight
The animals in CUMS group showed a reduction in body weight from day 14 only. Application of two-way ANOVA showed a significant effect of drug treatment on body weight {F (30, 210) = 6.63, p < 0.001}. Significance was obtained after the application of Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons tests. Values were on day 14, day 21 (## p < 0.01), day 28, day 35, and day 42 (### p < 0.001) when compared to the VC group. The animals treated with ALA (200 mg/kg) showed a significant (*** p < 0.001) increase in body weight from day 14 onwards as compared to CUMS group. Treatment with FLX (10) and ALA (200) showed a significant (*** p < 0.001) increase in body weight as compared to CUMS group from day 28 onwards. However, ALA (50) was found to increase in body weight on day 42 (* p < 0.05) (Figure 2). The effects of ALA, thus, were found to be dose-dependent.
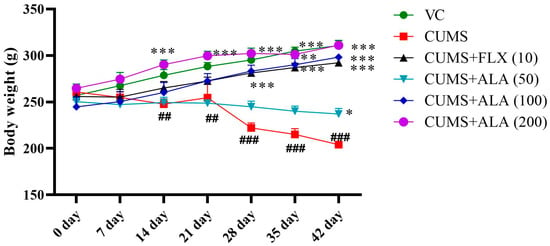
Figure 2.
Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10) on body weight in rats. The above data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical comparison was carried out using repeated measures of two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons tests. ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 as compared to VC. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to CUMS group.
3.2. Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Sucrose Preference
The application of two-way ANOVA showed a significant effect of the drug on the interaction between variables, drug treatment × days {F (10, 60) = 11.47, p < 0.001}. The use of Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test to obtain significance. CUMS group showed a significant reduction in % sucrose preference by rats on day 21 as well as on day 42 (### p < 0.001) when compared to the VC group. The animals treated with ALA (200) (*** p < 0.001) and FLX (10) and ALA (100) improved % sucrose preference significantly and (** p < 0.01) from day 21 onwards. The ALA (50) exhibited an improved % sucrose preference significantly (* p < 0.05) on day 42 (Figure 3). The CUMS animals had 55. 5% reduction in sucrose consumption, as compared to vehicles. FLX treatment had 59.4%, ALA (50, 100, 200) had 40.6%, 59.4%, and 75% improvement in sucrose preference as compared to CUMS group. Therefore, the results for ALA were found to be dose-dependent.
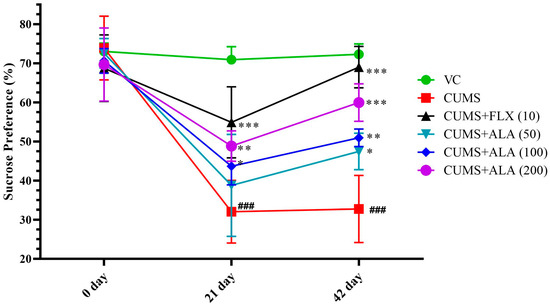
Figure 3.
Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10) on % sucrose preference in CUMS-induced depression-like behavior in rats. The above data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical comparison was carried out using repeated measures of two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons tests. ### p < 0.001 as compared to VC. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to CUMS group.
3.3. Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Escape Latency, Path Length, and Time Spent away from the Target Zone Using MWM
Figure 4 and Table 1 show the effect of various treatments on rats on MWM parameters. According to two-way ANOVA, there was a significant difference in escape latency due to treatment {F (10, 60) = 5.26, p < 0.001} and for path length {F (10, 90) = 3.84, p < 0.001} and for time spent away from target zone {F (10, 90) = 5.392, p < 0.001}. Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test for significance demonstrated that animals in CUMS group showed an increase in escape latency (### p < 0.001) on day 21 as well as on day 42, while treatment with FLX (10) and ALA (100 and 200) reduced it (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). There was an increase in path length and time spent away from the target zone significantly (## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001) on day 21 and day 42 as compared to the VC group. The animals treated with FLX (10), ALA (50), ALA (100), and ALA (200) decreased the escape latency, path length, and time spent away from the target zone. (** p < 0.01, ns, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 for path length), (*** p < 0.001, ns, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 for time spent away from target zone) also on day 42 (*** p < 0.001, ns, *** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.001 for escape latency), (*** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.001 for path length), (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.001 for time spent away from target zone) as compared to CUMS group.
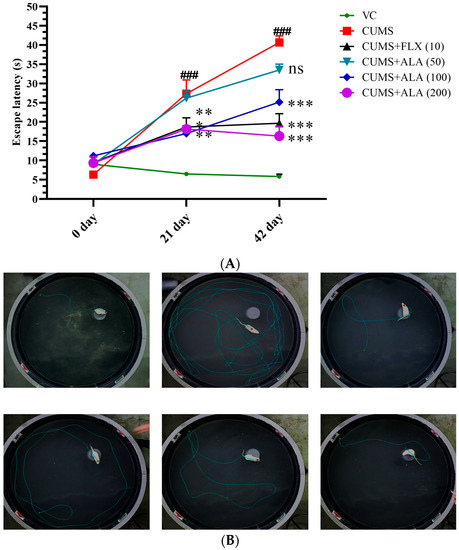
Figure 4.
(A) Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10) on (A) Escape latency using Morris water maze (MWM) in CUMS-induced depression-like behavior in rats. The discrete lines indicate the time of escape latency in seconds. The above data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical comparison was carried out using repeated measures of two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons tests. ### p < 0.001 as compared to VC. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to CUMS group. VC-vehicle control, CUMS-chronic unpredictable mild stress, FLX-fluoxetine, ALA-alpha lipoic acid. (B) Photograph obtained from instrument showing the path followed by rats after treatment with the drugs. VC-vehicle control, CUMS-chronic unpredictable mild stress, FLX-fluoxetine, ALA-alpha lipoic acid.

Table 1.
Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on path length, time spent away from the target zone, number of marbles buried, attack latency, and brain antioxidant parameters, GSH, MDA, SOD, NO, CAT.
3.4. Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on the Number of Marbles Buried Using MBT
Table 1 shows the effect of various treatments on the number of marbles buried by rats. The two-way ANOVA represents the effect of treatment on the number of marbles buried {F (10, 90) = 3.65, p < 0.001}. Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test was applied to obtain significance. It showed that animals under CUMS group buried a significantly greater number of marbles (### p < 0.001) on day 21 and day 42, respectively, as compared to the VC group. The treatment groups, FLX (10) (*** p < 0.001) and ALA (100 and 200) (* p < 0.05), exhibited a significantly lower number of marbles buried on day 21. All the groups (FLX and ALA) buried marbles significantly on day 42 (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) compared to CUMS group. The effects of ALA were dose-dependent.
3.5. Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Attack Latency Using RIT
The RIT paradigm was demonstrated on day 21 and day 42. The two-way ANOVA showed the effect of treatment on attack latency was found to be {F (10, 60) = 17.98, p < 0.001}. The significance was given by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test CUMS group rats’ animals exhibited reduced attack latency significantly (## p < 0.001, ### p < 0.001) as compared to the VC group. The treatment groups FLX (10) and ALA (100 and 200) significantly (** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, * p < 0.05) increased the time for an attack on day 21 as well as on day 42 (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) as compared to CUMS group (Table 1).
3.6. Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Immobility Using FST
The graph showed the effect of various treatments on immobility using FST on day 42 (Figure 5). One-way ANOVA showed the effect of CUMS and treatments on the immobility of rats {F (5, 30) = 16.04, p < 0.001}. The applied Dunnett’s test showed CUMS group exhibited high immobility, which was significant (### p < 0.001) as compared to the VC group. The immobility time in ALA (50, 100, 200) (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) and FLX (10) (*** p < 0.001) was significantly reduced as compared to CUMS group.
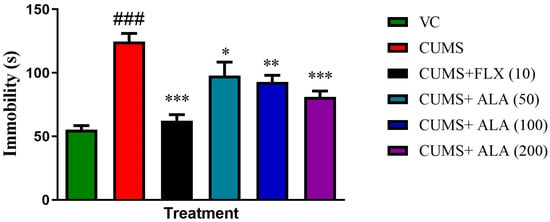
Figure 5.
Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on immobility time. Each bar represents the effect of treatments on immobility in seconds. The above data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test. ### p < 0.001 as compared to the VC group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to CUMS group. VC—vehicle control, CUMS—chronic unpredictable mild stress, FLX—fluoxetine, ALA—alpha lipoic acid.
3.7. Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on Antioxidant Parameters
Treatment with FLX (10), ALA (100 and 200) showed by one-way ANOVA showed GSH {F (5, 30) = 15.15, p < 0.001}, CAT {F (5, 30) = 21.35, p < 0.001}, SOD {F (5, 30) = 29.47, p < 0.001}. Dunnett’s test showed CUMS group had significantly reduced GSH, CAT levels, and SOD (### p < 0.001) in the brain as compared to the VC group. There was significant amelioration of GSH as well CAT levels (*** p < 0.001) as compared to CUMS group. However, SOD levels were restored significantly by FLX and a higher dose of ALA (*** p < 0.001 and * p < 0.05) compared to CUMS group. Similarly, the lipid peroxidation MDA level, NO was higher in animals under CUMS group (## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001) than in the VC group. Treatment with FLX (10) ALA (100 and 200) indicated significant interaction on MDA {F (5, 30) = 8.18, p < 0.001} and NO {F (5, 30) = 101.5, p < 0.001}. The Dunnett’s test demonstrated significant attenuation of MDA level as well as NO by FLX, ALA (100 and 200) (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and ** p < 0.01) as compared to CUMS group (Table 1).
3.8. Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on the Brain Monoamines (DA, NE, 5HT)
The brain hippocampal monoamines were evaluated, as shown in (Figure 6). The one way showed that the effect of treatment and CUMS on monoamines of animal DA levels {F (5, 18) = 109.6, p < 0.0001}, NE levels {F (5, 18) = 68.76, p < 0.001} and on 5HT level {F (5, 18) = 89.34, p < 0.001} was significant. Dunnett post hoc test showed that the concentration of DA, NE, and 5HT in CUMS group reduced significantly (## p < 0.001, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.001) as compared to the VC group. The animals treated with FLX (10), ALA (50, 100 and 200) showed significant (* p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, * p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) elevation in the DA level as compared to CUMS group. The FLX (10) and ALA treatment groups elevated the level of NE significantly (*** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) as compared to CUMS group. Similarly, the animals treated with ALA (all doses) and FLX (10) showed a significant (** p < 0.01 * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.01) rise in 5-HT levels as compared to CUMS group.
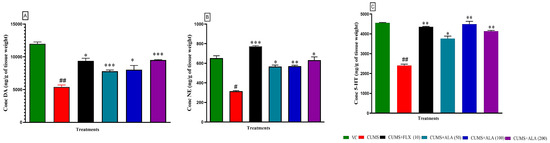
Figure 6.
Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on brain hippocampal (A) DA, (B) NE and (C) 5-HT. Each bar represents the effect of CUMS and treatments on levels of monoamines. The above data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.001 as compared to the VC group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to CUMS group. VC-vehicle control, CUMS-chronic unpredictable mild stress, FLX-fluoxetine, ALA-alpha lipoic acid. HPLC chromatograms show peaks for dopamine (DA), noradrenaline (NE), and serotonin (5-HT).
3.9. Histopathology
Effect of ALA (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on CUMS-induced depressed rats. There were no remarkable neuronal abnormalities in the hippocampus CA3 in the VC group. However, CUMS-treated animals showed degeneration, as observed by eosinophilic pyknotic neurons. The treatment with FLX (10) showed a hippocampus with small dark cells. The ALA (50) exhibited minor neuronal abnormalities, while treatment with ALA higher doses prevented neuronal damage and maintained the neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus (Figure 7).
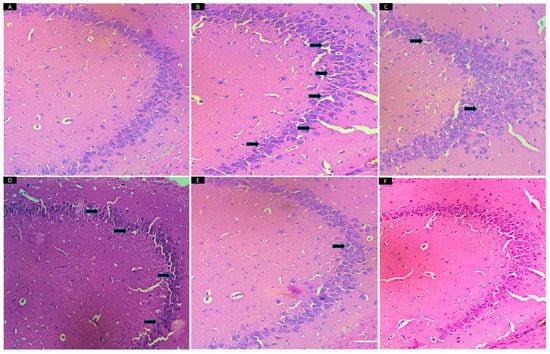
Figure 7.
Effect of ALA (50,100,200 mg/kg) and FLX (10 mg/kg) on brain histopathology in CUMS-induced depressed rats. There were no remarkable neuronal abnormalities in the hippocampus CA3 in (A) VC group. (B) CUMS-treated animals showed degeneration (eosinophilic pyknotic neuron, indicated by arrows). (C) In FLX (10) treated hippocampus, small dark cells were observed (D) ALA (50) minor neuronal abnormalities were observed. The treatment groups (E) ALA (100) and (F) ALA (200) prevented neuronal damage and maintained neuronal strength in the CA3 region of the hippocampus. VC-vehicle control, CUMS-chronic unpredictable mild stress, FLX-fluoxetine, ALA-alpha lipoic acid.
3.10. Molecular Docking Study
Depression has a strong connection with the catecholaminergic neuronal system. The primary neurotransmitter related to depression is serotonin. Seven superfamilies of serotonin receptors have been identified. When it comes to the 5-HT receptor family, the 5-HT3 receptors are the only ionotropic or ligand-regulated ion channel. Serotonin type 3 (5-HT3) are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels belonging to a cys-loop superfamily. Antidepressants, such as SSRIs and TCA, block 5-HT3 receptors. This pharmacological characteristic is also present in antidepressants of the new generation molecule, such as Vortioxetine. Vortioxetine antagonism of the 5-HT3 receptor has been shown to remove GABAergic inhibition. GABAergic neurotransmission’s role in depression is a relatively novel area of study. Variations in GABAergic function have been observed in an animal model of depression, and GABA receptor agonists appear to have antidepressant-like properties. In addition, serotonergic neurons are primarily connected to GABAergic interneurons, indicating an effective connection between the two mechanisms. Standard antidepressants like mirtazapine and mianserin antagonize serotonin type 3 receptors, indicating the possibility that the 5-HT3 receptor blocker has a significant role in managing depression [48].
The method is a powerful computational modeling technique that explains the affinity of receptor/enzyme binding of any molecule. The energy liberated during the interaction is a negative value that can determine the ligand-receptor complex stability and is stated as the docking score. Any compound having a higher (i.e., more negative) docking score represents a more stable complex and is guessed to be a better ligand. The structure of the enzyme was imported into the Molegro Virtual Docker software with all the cofactors and followed by the preparation of the receptor for docking and the addition of the structure of the ALA into the workspace.
The possible orientations and conformations were analyzed by the clustering method implanted in MVD. Docking was completed between the ligands and the receptor’s active site, with Grid resolution of 0.30 Å, MolDock scoring function, and including amino acids within a radius of 20 Å around X: 125.90, Y: 110.83, Z: 168.25 as the active site residues. Once the docking score (−52.8461) was obtained, the best pose in terms of the Rerank score (−41.6617) for ALA was retained, and the binding geometry or conformation was assessed. Compared with the Effective 5HT3 antagonist palonosetron, an antidepressant drug, it has been observed that it has shown Moldock score (−50.706) and Rerank score (−45.3301), which show very considerable similarity.
ALA docked deeply inside the binding pocket with the 5-HT3 serotonin receptor, an ion channel receptor with a binding energy of −5.4 Kcal/mol. We docked our molecule ALA on an enzyme having (PBDID: 6Y1Z). After docking, it was found that the molecule has an excellent binding pattern with various amino acid interactions, including serine, leucine, and phenylalanine. In a nutshell, it can be concluded that the above structure of molecule ALA has the best fitting inside the binding pocket 5HT3 receptor and made hydrogen bond and electrostatic interaction with LEU234, THR257, LEU260, and SER263 (Figure 8).
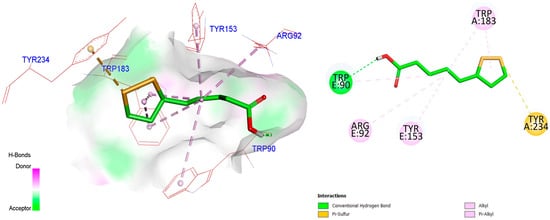
Figure 8.
The figure shows binding patterns with various amino acid interactions, including serine, leucine, and phenylalanine, indicating its interaction with the 5-HT3 receptor.
4. Discussion
In CUMS, animals were exposed to chronic and continuous stressors that mimic those associated with human depression. The current study demonstrated CUMS-induced animals exhibited depression-like behavior, anxiety, aggression, and cognitive deficit along with altered neurotransmission levels, as reported previously [9,10,49]. Therefore, CUMS-induced depression-like behavior model has good model validity and reliable predictability to evaluate potential antidepressants using classical tests, such as SPT, FST, MBT, RIT, and MWM. The body weight in CUMS animals was significantly reduced, corroborating the earlier findings [50] and which was regulated by ALA and FLX. The role of hypothalamic AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), an essential enzyme in the central regulation of food intake and energy expenditure, is known. Previous reports suggest that ALA affects body weight regulation by suppressing hypothalamic AMPK activity [51]. Consequently, it can be hypothesized that ALA inhibits the activity of AMPK and thus regulates body weight and therefore possesses potential nutritional values to prevent weight loss. Furthermore, our results have shown ALA to modulate the 5HT3 receptor, which is consistent with the previously reported study that suggested 5HT3 agonism is responsible for suppressing feeding behavior. As a result, body weight gain in this study may be due to the 5HT3 antagonistic effect. However, other comprehensive studies should be undertaken to understand its mechanism of action for improving body weight and dietary intake [52].
Anhedonia is a hallmark of depressive symptoms and can be assessed in rodents by SPT. CUMS group rats reduced their preference for sucrose and consumed more tap water. In contrast, treatment with FLX or ALA reversed the anhedonia conditions by increasing preference towards sucrose compared to tap water. CUMS alters mesolimbic reward processing in humans and animals, and these changes are linked to anhedonia behavior. Stress also produces dendritic remodeling in mPFC (Prefrontal cortex), and co-occurring functional changes in the mPFC-mesolimbic circuit appear to contribute to anhedonia-like outcomes. Prolonged stress induces ROS that seem to cross the blood-brain barrier to interact with mesolimbic circuitry, increase susceptibility to anhedonia-like behavior, and interfere with dopamine synthesis [53]. The present study indicated that ALA markedly reduces oxidative stress, modulating the mesolimbic reward processing pathway. Further, ALA improves brain dopamine. These factors might be responsible for attenuating anhedonia. Furthermore, FST demonstrated CUMS rats exhibited depression-like behavior alleviated by ALA, which might be attributed to improved neurotransmitter levels.
The hippocampal neurons play a vital role in memory formation. Exposure to chronic stress leads to an imbalanced HPA axis resulting in excessive release of cortisol. During stress, the hippocampus becomes the main target affected by cortisol leading to hippocampal neurodegeneration and cognitive decline [54]. To assess this function MWM paradigm was performed in the present study as described by [55]. Time taken to locate platform escape latency, path length, and away from the target zone were measured as cognition parameters before and after treatment. Impairment of memory was observed in CUMS group, while ALA treatment indicated improved cognition.
It has been established that CUMS is associated with anxiety-like behavior due to dysfunction of the HPA axis and reduced levels of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) [35,56]. We could see similar effects in the present study. The anxiety-like behavior was inhibited by ALA treatment indicating its anxiolytic potential. The present study has demonstrated improved monoamines level by ALA treatment. However, we have not measured GABA. Hence it is difficult to comment on the mechanism of action of ALA as an anxiolytic. Therefore, we recommend the estimation of GABA as well as cortisol in future studies.
As indicated earlier, CUMS is often associated with aggressive behavior. We also have previously reported the association of stress and aggression in socially isolated stressed rats [57]. The current study used RIT to measure aggressive behavior patterns, such as reducing attack latency [58]. We found that ALA could prolong attack latency which can be attributed to its serotonergic effect. ALA has been previously reported to increase tryptophan influx into the brain, thereby increasing serotonin levels in the synapse. This substantiates the previous finding that advocates using ALA as an antidepressant [59,60].
ALA is a potent antioxidant with many benefits due to its free radical scavenging activity. Stress has a causal relationship with depression and neurodegeneration due to the accumulation of free radicals and declines in the endogenous antioxidant defense system, thereby affecting the HPA axis and inducing neuroinflammation and thus disrupting serotonergic pathways [34,61,62]. As reported previously, the forebrain region is the foremost region highly involved in the depression-like behavior of rats due to oxidative stress [63]. We also document similar findings in the forebrain. The increase in oxidative stress is reflected by a decrease in the levels of GSH, SOD, and catalase and an increase in MDA and NO levels were significantly reduced by ALA. Hence, it can be claimed that ALA at different concentrations markedly attenuated CUMS-induced oxidative stress and thereby ameliorated depression-like behavior.
To understand the mechanism of action of ALA, we estimated monoamines in the rat brain. The previous findings suggest that CUMS in rats is associated with significant impairment in monoamine production and neurotransmission. Although ALA has been previously studied as an antidepressant in mice models exposed to CUMS, the present study provides in-depth analyses of various behavioral paradigms as well as it’s the first study to report its serotonergic effect that might be via 5HT3 receptor [54,64,65].
Chronic mild stress alters the synaptic function and cell survival in the ventral hippocampus [66]. These impairments of the hippocampus lead to altered emotionality, cognitive impairment, aggression, anxiety, and disturbed memory [67]. Our study demonstrated that all doses of ALA increased DA and 5-HT to a greater extent than NE and hence found safer than FLX regarding cardiac problems. Overall, ALA improved behaviour deficits associated with CUMS as well as reward functions and augmented anxiety, aggression, and improved memory functions. FLX also significantly elevated 5HT, DA, and NE levels, but very high levels of NE had a detrimental effect on cardiovascular function [68]. Therefore, it can be hypothesized that behavior deficits associated with CUMS are alleviated by ALA by increasing DA, 5-HT, and NE to an optimum level due to its potent antioxidant and neuroprotective effects.
Furthermore, the docking study demonstrated ALA exhibits interaction with 5HT-3 receptors (PDBID:6Y1Z). ALA docked deeply inside the binding pocket 5HT3 receptor and made hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interaction with LEU234, THR257, LEU260, and SER263. This bonding confirms the interaction between ALA and serotonin receptors, showing that it may have some antidepressant properties.
Fourteen subtypes of serotonin receptors have been documented in the brain. Their role in depression and neurological disorders is very much known 5HT-3 receptor is present in different areas of the brain, mainly the amygdala, hippocampus, and cortex. 5-HT-3 antagonism results in antidepressant activity. Various studies show that 5HT-3 antagonist administration improved depression [69,70,71]. Clinical studies have also proposed antagonism of the 5HT-3 receptor in alleviating symptoms of depression. On similar grounds, ALA was found to interact with 5HT-3. Thus, this could be a possible mechanism for it to act as an antidepressant. The receptor is also known to modulate the reward center and dopamine. Hence, strong antioxidant potential improved the DA and serotonin levels and its effect on the 5HT-3 receptor, prompting a clinical study of its effects.
5. Conclusions
The outcome of the present study proposes using ALA as a nutritional supplement to overcome the consequences of daily stressors that humans go through, which for a long time affect the brain resulting in depression-like behavior, anxiety, aggression, and cognitive deficit. ALA exhibited strong antidepressant, antianxiety, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects. It improved the monoamine concentrations in the hippocampus. ALA might be partially showing neuroprotective effects by restoring 5-HT, DA, and NE and acting on the 5HT3 receptor. Thus, the study found ALA a safer alternative for mild stress-induced behavior deficits. However, further molecular and preclinical studies must be designed to study its interaction with the 5HT3 receptor.
Further studies, such as cortisol, GABA estimation, and BDNF mRNA expression, will help in decoding the exact molecular mechanism behind the antidepressant activity of ALA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.A., M.A. and S.G.; Methodology, L.A., R.P. and J.P.; Formal analysis, D.K. and J.P.; Investigation, L.A., R.P. and J.P.; Data curation, D.K.; Writing—review & editing, S.G.; Supervision, S.G.; Project administration, U.A. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All the experiments were performed according to the CPCSEA (The Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) and were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee. The IAEC approval No is PCP/IAEC/PCL 31/2019–2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge A.P. Pawar, Principal, Poona College of Pharmacy, Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), Erandwane, Pune-411038, India, for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Perez-Caballero, L.; Torres-Sanchez, S.; Romero-Lopez-Alberca, C.; Gonzalez-Saiz, F.; Mico, J.A.; Berrocoso, E. Monoaminergic system and depression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinxing, W.; Wei, L.; Lei, W.; Rui, Z.; Baoying, J.; Lingjia, Q. A neuroendocrine mechanism of co-morbidity of depression-like behavior and myocardial injury in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Guo, R. Effect of XingPiJieYu decoction on spatial learning and memory and cAMP-PKA-CREB-BDNF pathway in rat model of depression through chronic unpredictable stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J.; Barrot, M.; DiLeone, R.J.; Eisch, A.J.; Gold, S.J.; Monteggia, L.M. Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 2002, 34, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Grace, A.A. Amygdala-ventral pallidum pathway decreases dopamine activity after chronic mild stress in rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Hidaka, N.; Kawagoe, C.; Odagiri, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Ishizuka, Y.; Hashiguchi, H.; Takeda, R.; Nishimori, T.; et al. Prenatal psychological stress causes higher emotionality, depression-like behavior, and elevated activity in the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patki, G.; Atrooz, F.; Alkadhi, I.; Solanki, N.; Salim, S. High aggression in rats is associated with elevated stress, anxiety-like behavior, and altered catecholamine content in the brain. J. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.H.; Hall, W.A. Anger in the context of postnatal depression: An integrative review. Birth 2018, 45, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chang, X.; Wu, H. Animal models of stress and stress-related neurocircuits: A comprehensive review. Stress Brain 2021, 10, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.X.; Zhang, R.Y.; Rui, W.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Feng, X. Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors by promoting adult hippocampal neurogenesis via FoxG1/CREB/ BDNF signaling pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 406, 113245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Fisar, Z.; Medina, M.; Scapagnini, G.; Nowak, G.; Berk, M. New drug targets in depression: Inflammatory, cell-mediated immune, oxidative and nitrosative stress, mitochondrial, antioxidant, and neuroprogressive pathways. And new drug candidates--Nrf2 activators and GSK-3 inhibitors. Inflammopharmacology 2012, 20, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandam, L.S.; Brazel, M.; Zhou, M.; Jhaveri, D.J. Cortisol and Major depressive disorder-translating findings from humans to animal models and back. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulska, J.; Juszczyk, G.; Gawronska-Grzywacz, M.; Herbet, M. HPA Axis in the Pathomechanism of Depression and Schizophrenia: New Therapeutic Strategies Based on Its Participation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareri, P.; Falconi, U.; De Fazio, P.; De Sarro, G. Conventional and new antidepressant drugs in the elderly. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 61, 353–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Thanacoody, H.K.; Watt, B.E.; Thomas, S.H.; Vale, J.A. Management of the cardiovascular complications of tricyclic antidepressant poisoning: Role of sodium bicarbonate. Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Fornaro, M.; Ostinelli, E.G.; Zangani, C.; Croatto, G.; Monaco, F.; Krinitski, D.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Correll, C.U. Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: A large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, A.J. Limitations in efficacy of antidepressant monotherapy. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68 (Suppl. 10), 8–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fornaro, M.; Anastasia, A.; Valchera, A.; Carano, A.; Orsolini, L.; Vellante, F.; Rapini, G.; Olivieri, L.; Di Natale, S.; Perna, G. The FDA “black box” warning on antidepressant suicide risk in young adults: More harm than benefits? Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuijpers, P.; Quero, S.; Dowrick, C.; Arroll, B. Psychological Treatment of Depression in Primary Care: Recent Developments. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, B.; Rideout, T.C. Anti-obesity and lipid-lowering properties of alpha-lipoic acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.N.; Dandiya, P. Glutathione as a cerebral substrate in depressive behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 48, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Karunakaran, U.; Jeoung, N.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, I.K. Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Ahammad, H.; Bhoumik, N.C.; Shakil, M.S.; Shawan, M.; Morshed, M.; Hossan, T.; Sarker, S.R.; Rahman, M.N.; Rahman, S.B. Extraction and estimation of alpha lipoic acid content in different food samples by reverse phase HPLC: Effect of heat treatment. Int. J. Biosci. 2018, 13, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Badran, M.; Abuyassin, B.; Golbidi, S.; Ayas, N.; Laher, I. Alpha Lipoic Acid Improves Endothelial Function and Oxidative Stress in Mice Exposed to Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4093018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, C.N.; Meneses, L.N.; Vasconcelos, G.S.; Silva, M.C.; da Silva, J.C.; Macedo, D.; de Lucena, D.F.; Vasconcelos, S.M. Reversal of corticosterone-induced BDNF alterations by the natural antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid alone and combined with desvenlafaxine: Emphasis on the neurotrophic hypothesis of depression. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, K.; Li, T.; Cong, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhou, M.; Huang, L.; Ding, H.; et al. Alpha lipoic acid inhibits neural apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in rats following traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 87, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, H.F.; Farr, S.A.; Thongboonkerd, V.; Lynn, B.C.; Banks, W.A.; Morley, J.E.; Klein, J.B.; Butterfield, D.A. Proteomic analysis of specific brain proteins in aged SAMP8 mice treated with alpha-lipoic acid: Implications for aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 46, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, D.S.; Medeiros, C.D.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Sousa, F.C.; Santos, J.V.; Morais, T.A.; Hyphantis, T.N.; McIntyre, R.S.; Quevedo, J.; Carvalho, A.F. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid in an animal model of mania induced by D-amphetamine. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, Y. Effect of alpha lipoic acid on intracerebroventricular streptozotocin model of cognitive impairment in rats. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003, 13, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Dong, H.; Hou, P.; Tang, Y. Chronic mild stress impairs cognition in mice: From brain homeostasis to behavior. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, J.; Haidkind, R.; Harro, M.; Modiri, A.R.; Gillberg, P.G.; Pahkla, R.; Matto, V.; Oreland, L. Chronic mild unpredictable stress after noradrenergic denervation: Attenuation of behavioural and biochemical effects of DSP-4 treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999, 10, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagne, V.; Porsolt, R.D.; Moser, P. Use of latency to immobility improves detection of antidepressant-like activity in the behavioral despair test in the mouse. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 616, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswar, U.; Chepurwar, S.; Shintre, S.; Aswar, M. Telmisartan attenuates diabetes induced depression in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, P.; Scheel-Kruger, J.; Belzung, C. The neurobiology of depression and antidepressant action. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2331–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooge, R.; De Deyn, P.P. Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res. 2001, 36, 60–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Sripanidkulchai, K.; Wyss, J.M.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Curcuma comosa improves learning and memory function on ovariectomized rats in a long-term Morris water maze test. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.L. Evaluation of marble-burying behavior as a model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 38, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Xue, L.; Sun, P.; Chao, Y.; Xue, G.; Qiao, M. Impact of social isolation and resident intruder stress on aggressive behavior in the male rat. Neural Regen Res. 2010, 5, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Moron, M.; Depierre, J.; Mannervik, B. Biochim Biophys Acta. Gen. Subj. 1979, 582, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.S.; Comim, C.M.; Valvassori, S.S.; Reus, G.Z.; Barbosa, L.M.; Andreazza, A.C.; Stertz, L.; Fries, G.R.; Gavioli, E.C.; Kapczinski, F.; et al. Acute administration of ketamine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases BDNF levels in the rat hippocampus. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I. Nitrite and nitrate measurement by Griess reagent in human plasma: Evaluation of interferences and standardization. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 440, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.K. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuob, N.N.; Balgoon, M.J. Histological and molecular techniques utilized to investigate animal models of depression. An updated review. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorré, K.; Pravda, M.; Sarre, S.; Ebinger, G.; Michotte, Y. New antioxidant mixture for long term stability of serotonin, dopamine and their metabolites in automated microbore liquid chromatography with dual electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1997, 694, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benedetto, G.E.; Fico, D.; Pennetta, A.; Malitesta, C.; Nicolardi, G.; Lofrumento, D.D.; De Nuccio, F.; La Pesa, V. A rapid and simple method for the determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin in mouse brain homogenate by HPLC with fluorimetric detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 98, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bétry, C.; Etiévant, A.; Oosterhof, C.; Ebert, B.; Sanchez, C.; Haddjeri, N. Role of 5-HT3 receptors in the antidepressant response. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 603–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhang, B.Y.; Dong, L.M.; Lv, J.W.; Lu, C.; Wang, Q.; Fan, L.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Pan, R.L.; Liu, X.M. Antidepressant effects of dammarane sapogenins in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Shukkoor, M.S.; Baharuldin, M.T.; Mat Jais, A.M.; Mohamad Moklas, M.A.; Fakurazi, S. Antidepressant-Like Effect of Lipid Extract of Channa striatus in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 2986090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-Y.; Namkoong, C.; Jang, P.-G.; Ryu, J.-W.; Song, H.-S.; Yun, J.-Y.; Namgoong, I.-S.; Ha, J.; Park, I.-S. Anti-obesity effects of α-lipoic acid mediated by suppression of hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, W.E.; Lin, P.; Pierce-Messick, Z.; Ilesanmi, A.O.; Clissold, K.A. Contrasting effects of 5-HT3 receptor stimulation of the nucleus accumbens or ventral tegmentum on food intake in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 323, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, C.H.; Holmes, A.J.; Chang, S.W.; Joormann, J. From stress to anhedonia: Molecular processes through functional circuits. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, X.; Xing, N.; Qu, H.; Zhang, K. Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Zhi-Zi-Hou-Po decoction in chronic unpredictable mild stress induced rats through pharmacokinetics, monoamine neurotransmitter and neurogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; He, B.; Wan, S.; Xu, M.; Yang, H.; Xiao, F.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of Schisandra chinensis in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice and its related mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Zhu, X.C.; Han, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Yue, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, R.; Li, B.; Wu, G.C.; Liu, Q.; et al. Ghrelin alleviates anxiety- and depression-like behaviors induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 326, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswar, U.; Shende, H.; Aswar, M. Buspirone, a 5-HT1A agonist attenuates social isolation-induced behavior deficits in rats: A comparative study with fluoxetine. Behav. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.R.; Bai, Y.Y.; Ruan, C.S.; Zhou, H.F.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.F.; Shen, L.J.; Zheng, H.Y.; Zhou, X.F. Enhanced aggressive behaviour in a mouse model of depression. Neurotox. Res. 2015, 27, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.R. Alpha lipoic acid: A novel treatment for depression. Med. Hypotheses 2000, 55, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, C.N.S.; Meneses, L.N.; Vasconcelos, G.S.; da Silva Medeiros, I.; Silva, M.C.C.; Mouaffak, F.; Kebir, O.; da Silva Leite, C.M.G.; Patrocinio, M.C.A.; Macedo, D.; et al. Neuroprotective evidence of alpha-lipoic acid and desvenlafaxine on memory deficit in a neuroendocrine model of depression. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackovic, M.; Rovcanin, B.; Pantovic, M.; LvkovIc, M.; Petronijevic, N.; Damjanovic, A. Association of oxidative stress with the pathophysiology of depresion and bipolar disorder. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2013, 65, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, A.S.; Cardoso, A.; Vale, N. Oxidative Stress in Depression: The Link with the Stress Response, Neuroinflammation, Serotonin, Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, T.; Yu, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, J.; Cai, D. Apocynum venetum leaf extract reverses depressive-like behaviors in chronically stressed rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusha’u, Y.; Muhammad, U.; Mustapha, S.; Umar, A.; Imam, M.; Umar, B.; Alhassan, A.; Saleh, M.; Ya’u, J. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates depressive symptoms in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. J. Afr. Assoc. Physiol. Sci. 2021, 9, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yusha’u, Y.; Adam, U.M.; Wahab, A.A.; Saleh, M.I.A.; Ya’u, J. Alpha-lipoic acid enhances short-term spatial memory of mice in open-space forced swim-induced depression mouse model. Neurosci. Res. Notes 2021, 4, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, A.; Jayatissa, M.N.; Mork, A.; Wiborg, O. Stress sensitivity and resilience in the chronic mild stress rat model of depression; an in situ hybridization study. Brain Res. 2008, 1196, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Araragi, N.; Waider, J.; van den Hove, D.; Gutknecht, L. Targeting brain serotonin synthesis: Insights into neurodevelopmental disorders with long-term outcomes related to negative emotionality, aggression and antisocial behaviour. Philos. Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2426–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.Z.; Huang, K.F.; Hung, S.W.; Kuo, L.T. Chronic fluoxetine treatment enhances sympathetic activities associated with abnormality of baroreflex function in conscious normal rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 811, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.; Devadoss, T.; Manjula, S.N.; Rajangam, J. 5-HT3 receptor antagonism: A potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of depression and other disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, G.; Maswood, S. Acute treatment with 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, tropisetron, reduces immobility in intact female rats exposed to the forced swim test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 85, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Kurhe, Y.; Thangaraj, D.; Prabhakar, V.; Kanade, P. Antidepressant-like effects of a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist 6z in acute and chronic murine models of depression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).