The On/Off History of Hydrogen in Medicine: Will the Interest Persist This Time Around?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hydrogen History
3. Hydrogen in the Genesis and Evolution of Life and Effects in Plants
3.1. Hydrogen Chemistry
3.2. Hydrogen and Genesis and Evolution of Life
3.3. Hydrogen in Plants and Agriculture
4. Hydrogen Use in Humans for Non-Medicinal Purposes
4.1. Biodegradable Implants
4.2. Bodily Wounds
4.3. Diving
4.4. Blood Flow
4.5. Malabsorption
4.6. Detecting Achlorhydria
5. Hydrogen in Natural “Healing” or “Curative” Spring Waters
6. Hydrogen in Alkaline Ionized Water
7. Hydrogen in Therapeutic and Medical Applications
8. Physicochemical Properties of Hydrogen
9. Pharmacological Activities of Hydrogen
10. Methods of Administration
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramachandran, R. An overview of industrial uses of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, D.N. Hydrogen, What a Gas. Hydrocarb. Process. 1993, 72, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, M.; Sobue, S.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Beneficial biological effects and the underlying mechanisms of molecular hydrogen—Comprehensive review of 321 original articles. Med. Gas Res. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.; Ferrige, A.; Moncada, S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 1987, 327, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, K.R. The therapeutic potential of hydrogen sulfide: Separating hype from hope. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R297–R312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.; Ma, L.; Niu, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Liu, R.; Xing, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, H. Protection of donor lung inflation in the setting of cold ischemia against ischemia-reperfusion injury with carbon monoxide, hydrogen, or both in rats. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. The evolution of molecular hydrogen: A noteworthy potential therapy with clinical significance. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Kawamura, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Nakao, A. Recent advances in hydrogen research as a therapeutic medical gas. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.H. Chemistry and cosmology. Faraday Discuss. 2006, 133, 27–32, discussion 83–102, 449–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.; Muller, M. The hydrogen hypothesis for the first eukaryote. Nature 1998, 392, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.; Wachtershauser, G. alpha-Hydroxy and alpha-amino acids under possible Hadean, volcanic origin-of-life conditions. Science 2006, 314, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenfreund, P.; Irvine, W.; Becker, L.; Blank, J.; Brucato, J.R.; Colangeli, L.; Derenne, S.; Despois, D.; Dutrey, A.; Fraaije, H.; et al. Astrophysical and astrochemical insights into the origin of life. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2002, 65, 1427–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, I.P. Hydrogen the fuel for 21st century. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7368–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, K.B.; Ames, B.N. The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 547–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, B.C.; Chang, C.J. Chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species in signaling or stress responses. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, N.S.; Varadharaj, S.; Khanderao, G.D.; Davidson, C.J.; Kannan, S.; Firpo, M.A.; Zweier, J.L.; Benjamin, I.J. Sustained activation of nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element signaling promotes reductive stress in the human mutant protein aggregation cardiomyopathy in mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; Desikan, R.; Neill, S.J. Cytochrome c, glutathione, and the possible role of redox potentials in apoptosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchitti, S.A.; Chen, Y.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Ultraviolet radiation: Cellular antioxidant response and the role of ocular aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes. Eye Contact Lens 2011, 37, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happe, R.P.; Roseboom, W.; Pierik, A.J.; Albracht, S.P.; Bagley, K.A. Biological activation of hydrogen. Nature 1997, 385, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.; Ralphs, J.R.; Harris, J.C. Giardia intestinalis, a eukaryote without hydrogenosomes, produces hydrogen. Microbiology 2002, 148, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahata, S.; Kabayama, S.; Nakano, M.; Miura, T.; Kusumoto, K.; Gotoh, M.; Hayashi, H.; Otsubo, K.; Morisawa, S.; Katakura, Y. Electrolyzed-reduced water scavenges active oxygen species and protects DNA from oxidative damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Tang, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Xiu, Q. Hydrogenase: The next antibiotic target? Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazuru, T.; Sato, E.F.; Nagata, K.; Matsui, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kasahara, E.; Jikumaru, M.; Inoue, J.; Inoue, M. Role of hydrogen generation by Klebsiella pneumoniae in the oral cavity. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstein, J.H.; Akhmanova, A.; Boxma, B.; Harhangi, H.R.; Voncken, F.G. Hydrogenosomes: Eukaryotic adaptations to anaerobic environments. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embley, T.M.; van der Giezen, M.; Horner, D.S.; Dyal, P.L.; Bell, S.; Foster, P.G. Hydrogenosomes, mitochondria and early eukaryotic evolution. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, D.S.; Heil, B.; Happe, T.; Embley, T.M. Iron hydrogenases--ancient enzymes in modern eukaryotes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.F.; Agarwal, A. Hydrogen: Another gas with therapeutic potential. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.T. Harnessing Evolutionary Toxins for Signaling: Reactive Oxygen Species, Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide in Plant Cell Regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballor, N.R.; Leadbetter, J.R. Analysis of extensive [FeFe] hydrogenase gene diversity within the gut microbiota of insects representing five families of Dictyoptera. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Nishimura, N. Suppressive Effect of High Hydrogen Generating High Amylose Cornstarch on Subacute Hepatic Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in Rats. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2012, 31, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaiti, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Cen, Y.P.; Layzell, D.B.; Peoples, M.; Dong, Z. Isolation and characterization of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria induced following exposure of soil to hydrogen gas and their impact on plant growth. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Fang, P.; Zhu, K.; Mao, Y.; Gao, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. Hydrogen-rich water confers plant tolerance to mercury toxicity in alfalfa seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 105, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lai, D.; Wang, Q.; Shen, W. Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Nitric Oxide Production Contributes to Hydrogen-Promoted Stomatal Closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, F.; Cui, W.; Xie, Y.; Shen, W. Hydrogen-rich water regulates cucumber adventitious root development in a heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide-dependent manner. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Shen, W.; Yang, J. Hydrogen-rich water alleviates salt stress in rice during seed germination. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J.; Shen, W.; Xia, K.; Cui, J. Hydrogen-rich water reestablishes ROS homeostasis but exerts differential effects on anthocyanin synthesis in two varieties of radish sprouts under UV-A irradiation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6454–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; Adzavon, Y.M.; Su, Z.; Zhao, Q.; LeBaron, T.W.; Li, Q.; Lyu, B.; Liu, G.; et al. Hydrogen Evolution and Absorption Phenomena in the Plasma Membrane of Vigna radiata and Capsicum annuum. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 42, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; LeBaron, T.W.; May, J.; Thomas, A.; Russell, G. Molecular Hydrogen: Is This a Viable New Treatment for Plants in the UK? Plants 2021, 10, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.T.; Russell, G.; Stratakos, A.C. Molecular Hydrogen: The Postharvest Use in Fruits, Vegetables and the Floriculture Industry. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Cheng, P.; Shen, W. Molecular Hydrogen Improves Rice Storage Quality via Alleviating Lipid Deterioration and Maintaining Nutritional Values. Plants 2022, 11, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mao, Y.; Lai, D.; Zhang, W.; Shen, W. H(2) enhances arabidopsis salt tolerance by manipulating ZAT10/12-mediated antioxidant defence and controlling sodium exclusion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, J.; Bartsch, I.; Willbold, E.; Schuchardt, S.; Holz, O.; Hort, N.; Hoche, D.; Heineman, W.R.; Witte, F. Fast escape of hydrogen from gas cavities around corroding magnesium implants. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8714–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennemeyer, J.J.; Hopkins, T.; Hershcovitch, M.; Little, K.D.; Hagen, M.C.; Minteer, D.; Hom, D.B.; Marra, K.; Pixley, S.K. Initial observations on using magnesium metal in peripheral nerve repair. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 29, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, D.; Paramitha, D.; Ulum, M.F.; Hermawan, H. The effect of hydrogen gas evolution of magnesium implant on the postimplantation mortality of rats. J. Orthop. Transl. 2016, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, R.; Wang, H.; Cai, W.; Ni, J.; Luthringer-Feyerabend, B.J.; Wang, W.; Peng, H.; Ji, W.; Yan, J.; Xia, J. Controlled release of hydrogen by implantation of magnesium induces P53-mediated tumor cells apoptosis. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, N. Rectal insufflation of hydrogen gas an infallible test in the diagnosis of visceral injury of the gastro intestinal canal in penetrating wounds of the abdomen. Read in the Section on Surgery, at the Thirty-ninth Annual Meeting of the American Medical Association, May, 9, 1888, and illuistrated by three experiments on dogs. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1888, 10, 767–777. [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher, J.E. Senn on the Diagnosis of Gastro-Intestinal Perforation by the Rectal Insufflation of Hydrogen Gas. Ann. Surg. 1888, 8, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, E.M.; Haldane, J.B. Human physiology under high pressure: I. Effects of Nitrogen, Carbon Dioxide, and Cold. J. Hyg. 1941, 41, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlman, A.; Kaveeshwar, J.A.; Tikuisis, P.; Kayar, S.R. Calorimetry and respirometry in guinea pigs in hydrox and heliox at 10-60 atm. Pflugers Arch. 2000, 440, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjurstedt, H.; Severin, G. The prevention of decompression sickness and nitrogen narcosis by the use of hydrogen as a substitute for nitrogen, the Arne Zetterstrom method for deep-sea diving. Mil. Surg. 1948, 103, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brubakk, M.; Neuman, T.S. Bennett and Elliott’s Physiology and Medicine of Diving, Alf O. Respir. Care 2004, 49, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Abraini, J.H.; Gardette-Chauffour, M.C.; Martinez, E.; Rostain, J.C.; Lemaire, C. Psychophysiological reactions in humans during an open sea dive to 500 m with a hydrogen-helium-oxygen mixture. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 76, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fife, W. The Use of Non-Explosive Mixtures of Hydrogen and Oxygen for Diving. 1979. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/12070 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Kot, J. Extremely deep recreational dives: The risk for carbon dioxide (CO2) retention and high pressure neurological syndrome (HPNS). Int. Marit. Health 2012, 63, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Perovic, A.; Unic, A.; Dumic, J. Recreational scuba diving: Negative or positive effects of oxidative and cardiovascular stress? Biochem. Med. 2014, 24, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen is a novel antioxidant to efficiently reduce oxidative stress with potential for the improvement of mitochondrial diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.X.; Cai, Z.Y.; Fan, D.F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Liu, S.L.; Kang, Z.M.; Liu, K.; Li, R.P.; Sun, X.J.; et al. Protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline on decompression sickness in rats. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2011, 82, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukland, K.; Berliner, R.W.; Bower, B.F. Measurement of Local Blood Flow with Hydrogen Gas. Fed. Proc. 1963, 22, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenb, I.; Aukland, K. Measurement of Human Uterine Cervical Blood Flow by Local Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1969, 48, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakiyama, T. The cervical blood flow using hydrogen gas clearance method. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 36, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Kamata, T.; Hiratani, S.; Nakatani, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamamoto, S. Trial in determination of the blood flow of the gastric mucosa by a hydrogen gas clearance method--intragastric fixation of an improved electrode. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 1982, 79, 1643. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, L.Y.; Sonnenschein, L.A. Measurement of regional gastric mucosal blood flow by hydrogen gas clearance. Am. J. Surg. 1984, 147, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, S.W.; Cheung, L.Y. Measurements of gastric mucosal blood flow by hydrogen gas clearance. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 247, G339–G345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.W.; Washington, J.; Kauffman, G.; Guth, P.H. Endoscopic Measurement of Gastric-Mucosal Blood-Flow by Hydrogen Gas Clearance in Conscious Dogs. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1984, 30, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Nissenkorn, I.; Kaspi, T.; Shalit, M.; Servadio, C. Use of hydrogen gas clearance for measurement of renal circulation. An experimental study. Urology 1983, 22, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.W. Endoscopic Measurement of Human Gastric-Mucosal Blood-Flow by Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1988, 34, 206–207. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, T.; Yagi, Y.; Tsuru, A.; Izumi, R. Placental and Fetal Tissue Blood-Flow Measurement by Electrolytically Generated Hydrogen Gas Clearance Method. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. Part B-Hypertens. Pregnancy 1984, 3, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Gouma, D.J.; Coelho, J.C.; Schlegel, J.; Fisher, J.D.; Li, Y.F.; Moody, F.G. Estimation of hepatic blood flow by hydrogen gas clearance. Surgery 1986, 99, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri, F.; Kawasuji, M.; Aoyama, T.; Sakakibara, N. Intraoperative Measurement of Myocardial Blood-Flow by Electrolytic Hydrogen Gas Clearance Method. Jpn. Circ. J.-Engl. Ed. 1986, 50, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harakawa, I.; Yano, T.; Sakurai, T.; Nishikimi, N.; Nimura, Y. Measurement of spinal cord blood flow by an inhalation method and intraarterial injection of hydrogen gas. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiwaki, H.; Satake, K.; Koh, I.; Nagai, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Umeyama, K. Pancreatic microcirculation of dogs measured by hydrogen gas generated by electrolysis. Pancreas 1986, 1, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki, H.; Satake, K.; Ko, I.; Tanaka, H.; Kanazawa, G.; Nagai, Y.; Umeyama, K. Measurement of pancreatic microcirculation using hydrogen gas generated by electrolysis in dogs. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1986, 87, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Nohara, S.; Nakamura, H.; Okada, A. Measurement of skin blood flow using inhaled hydrogen gas clearance method. Kokyu To Junkan 1986, 34, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Aukland, K.; Bower, B.F.; Berliner, R.W. Measurement of Local Blood Flow with Hydrogen Gas. Circ. Res. 1964, 14, 164–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukland, K.; Berliner, R.W. Renal Medullary Countercurrent System Studied with Hydrogen Gas. Circ. Res. 1964, 15, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianchuk, P.I.; Palatnyi, T.P.; Rusinchuk Ia, I. Modification of electrode for regional mucose blood flow measurements with the aid of hydrogen gas clearance. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. Im. I. M. Sechenova 2005, 91, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oohata, Y.; Mibu, R.; Hotokezaka, M.; Ikeda, S.; Nakahara, S.; Itoh, H. Comparison of blood flow assessment between laser doppler velocimetry and the hydrogen gas clearance method in ischemic intestine in dogs. Am. J. Surg. 1990, 160, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T. Measurement of hepatic blood flow by the hydrogen gas clearance method. Experimental and clinical observations. Nihon Ika Daigaku Zasshi 1990, 57, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.W. Comparison of blood flow measurements by hydrogen gas clearance and laser Doppler flowmetry in the rat duodenum. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 25, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, H.P. The hydrogen gas clearance method for liver blood flow examination: Inhalation or local application of hydrogen? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1989, 248, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, F.W. Intravenous Corticotropin Releasing-Factor Significantly Increases Duodenal Mucosal Blood-Flow Measured by Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Clin. Res. 1988, 36, A132. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki, S. An experimental study on the tissue blood flow under hyperthermia in the normal rat bladder and bladder tumor--a hydrogen gas clearance method. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 1988, 79, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Koji, T.; Morita, O. Measurement of blood flow rate of oral mucosa using the electrolytic regional blood flowmeter. Part 1. Studies on electrifying conditions and diffusion of hydrogen gas. Shigaku 1988, 76, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Soybel, D.I.; Wan, Y.L.; Ashley, S.W.; Yan, Z.Y.; Ordway, F.S.; Cheung, L.Y. Endoscopic Measurements of Canine Colonic Mucosal Blood-Flow Using Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, H.; Sakamoto, W.; Nishijima, T.; Yasumoto, R.; Kobayakawa, H.; Umeda, M.; Maekawa, M. The local blood flow of the rabbit bladder measured by electrochemically generated hydrogen gas. Hinyokika Kiyo 1987, 33, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, K.; Watanabe, J.; Atsumi, F. Effects of urethane anesthesia and age on organ blood flow in rats measured by hydrogen gas clearance method. J. Pharmacobiodyn. 1987, 10, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gana, T.J.; Huhlewych, R.; Koo, J. Focal gastric mucosal blood flow by laser-Doppler and hydrogen gas clearance: A comparative study. J. Surg. Res. 1987, 43, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Ueda, S.; Machida, J.; Soejima, H.; Ikegami, K. Studies on the regional blood flow of the rabbit kidney by means of electrolytic hydrogen gas clearance method. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 1986, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Washabau, R.J.; Strombeck, D.R.; Buffington, C.A.; Harrold, D. Use of Pulmonary Hydrogen Gas Excretion to Detect Carbohydrate Malabsorption in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 189, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, F.W.; Morishita, T.; Guth, P.H. Comparison of Reflectance Spectrophotometry with Invivo Microscopy and Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 1518. [Google Scholar]
- Aukland, K. Citation-Classic—Measurement of Local Blood-Flow with Hydrogen Gas. Cc/Life Sci. 1986, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, S.; Isshiki, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Nose, K.; Nishimura, R. Measurement of cutaneous blood flow by clearance of hydrogen gas generated by electrolysis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1985, 15, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.W.; Guth, P.H.; Scremin, O.; Golanska, E.; Kauffman, G. Comparison of Blood-Flow Measurements by Aminopyrine Clearance, Hydrogen Gas Clearance and Electromagnetic Flow Probe in the Rabbit. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 1160. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, H.; Kato, M.; Akimoto, K.; Miyashige, M.; Sekiguchi, H.; Fujino, Y.; Mikuniya, A.; Onodera, K. Evaluation for Effects of Partial Coronary-Occlusion and or Intravenous Nitroglycerin Administration on Transmural Distribution of Coronary Blood-Flow by Hydrogen Gas Clearance Method. Jpn. Circ. J. -Engl. Ed. 1983, 47, 993–994. [Google Scholar]
- Koshu, K.; Kamiyama, K.; Oka, N.; Endo, S.; Takaku, A.; Saito, T. Measurement of regional blood flow using hydrogen gas generated by electrolysis. Stroke 1982, 13, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, K.; Whiteside, L.A.; Lesker, P.A. Subchondral route for nutrition to articular cartilage in the rabbit. Measurement of diffusion with hydrogen gas in vivo. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1978, 60, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordby, H.K.; Flood, S. A long term observation of local cerebral blood flow using the hydrogen gas clearance technique. Acta Neurochir. 1976, 35, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sem-Jacobsen, C.W.; Styri, O.B.; Mohn, E. Measurements in man of focal intracerebral blood flow around depth-electrodes with hydrogen gas. Prog. Brain Res. 1972, 35, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuiki, K.; Tominaga, S. Non-nutritional blood flow in skeletal muscle determined with hydrogen gas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1972, 106, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbmann, M.R.; Williams, S.N.; Booth, A.N. The quantitative collection and determination of hydrogen gas from the rat and factors affecting its production. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1971, 137, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, S. Transperitoneal exchange. II. Peritoneal blood flow estimated by hydrogen gas clearance. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1970, 5, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Meyer, J.S.; Kitamura, A.; Toyoda, M.; Ryu, T. Measurement of cerebral hemispheric blood flow by intracarotid injection of hydrogen gas. Validation of the method in the monkey. Circ. Res. 1969, 25, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.J.; Fife, W.P.; Corbett, T.H.; Schabel, F.M., Jr. Response of five established solid transplantable mouse tumors and one mouse leukemia to hyperbaric hydrogen. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1978, 62, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Ashikawa, K.; Inooka, E.; Yanagiya, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Ishide, N.; Isoyama, S.; Takishima, T.; Suzuki, N. Quantitative-Analysis of Heterogenous Distribution of Myocardial Blood-Flow by Coronary Sinus Hydrogen Gas Clearance. Jpn. Circ. J. -Engl. Ed. 1975, 39, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Wodick, R.; Lubbers, D.W.; Grunewald, W. Evaluation procedure for the determination of organ blood flow after breathing hydrogen gas mixtures. Pflugers Arch. 1969, 307, R51. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpure, B.; Bian, J.-S. Interaction of hydrogen sulfide with nitric oxide in the cardiovascular system. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6904327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fox, B.; Keeble, J.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Wood, M.E.; Moore, P.K.; Whiteman, M. The complex effects of the slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide donor GYY 4137 in a model of acute joint inflammation and in human cartilage cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Lin, H.C.; McSweeney, C.S.; Mackie, R.I.; Gaskins, H.R. Mechanisms of microbial hydrogen disposal in the human colon and implications for health and disease. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 363–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, J.W.; Maier, R.J. Molecular hydrogen as an energy source for Helicobacter pylori. Science 2002, 298, 1788–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calloway, D.H.; Murphy, E.L.; Bauer, D. Determination of lactose intolerance by breath analysis. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1969, 14, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, M.D. Production and excretion of hydrogen gas in man. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969, 281, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.C.; Schoeller, D.A.; Klein, P.D. Improved gas chromatographic quantitation of breath hydrogen by normalization to respiratory carbon dioxide. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1979, 94, 755–763. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, E.A.; Bloch, K.J.; Cohen, S.; Isselbacher, K.J.; Walker, W.A. Use of hydrogen gas (H2) analysis to assess intestinal absorption. Studies in normal rats and in rats infected with the nematode, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Gastroenterology 1981, 81, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, G.C.; Kwong, L.K.; Morrill, J.S.; Vreman, H.J.; Stevenson, D.K. Hydrogen gas excretion after sucrose gavage in the fasted rat. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washabau, R.J.; Strombeck, D.R.; Buffington, C.A.; Harrold, D. Evaluation of intestinal carbohydrate malabsorption in the dog by pulmonary hydrogen gas excretion. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1986, 47, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Oku, T.; Nakamura, S. Comparison of digestibility and breath hydrogen gas excretion of fructo-oligosaccharide, galactosyl-sucrose, and isomalto-oligosaccharide in healthy human subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerlin, P.; Wong, L. Breath hydrogen testing in bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine. Gastroenterology 1988, 95, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urita, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Maeda, T.; Arita, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Ishii, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Kugahara, A.; Nakayama, A.; Nanami, M.; et al. Extensive atrophic gastritis increases intraduodenal hydrogen gas. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2008, 2008, 584929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Shi, D.; Ye, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Kang, Z.; Bi, H.; et al. Lactulose ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inducing hydrogen by activating Nrf2 expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y. Increased concentrations of breath hydrogen gas in Japanese centenarians. Anti-Aging Med. 2013, 10, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sack, D.A.; Stephensen, C.B. Liberation of hydrogen from gastric acid following administration of oral magnesium. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1985, 30, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephensen, C.B.; Leon-Barua, R.; Sack, R.B.; Sack, D.A. Comparison of noninvasive breath hydrogen test for gastric acid secretion to standard intubation test in adults. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1987, 32, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, P.; Lopez de Soria, P.; Fernandez-Banares, F.; Junca, J.; Boix, J.; Planas, R.; Quer, J.C.; Domenech, E.; Gassull, M.A. Magnesium hydrogen breath test using end expiratory sampling to assess achlorhydria in pernicious anaemia patients. Gut 1994, 35, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, A.D.; Sarker, S.; Bauerfeind, P.; Drewe, J.; Meier, R.; Gyr, K. Assessment of gastric acid output by H2 breath test. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 29, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Ito, M. Molecular hydrogen as an emerging therapeutic medical gas for neurodegenerative and other diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 353152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, G.A. Water and health: A forgotten connection? Perspect Public Health 2010, 130, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, E.W. The fountain of youth. J. Am. Orient. Soc. 1905, 26, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.M. Mineral springs and miracles. Can. Fam. Physician 1994, 40, 729–737. [Google Scholar]
- Baudish, O. Magic and science of natural healing waters. J. Chem. Educ. 1939, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaud, C. Indications for alkaline mineral water cure in diabetes mellitus. Toulouse Med. 1951, 52, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, R.H. Remedial effects of mineral waters, home and foreign. Assoc. Med. J. 1854, 2, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Chambron, J. Physico-Chemical, Biological and Therapeutic Characteristics of Electrolyzed Reduced Alkaline Water (ERAW). Water 2013, 5, 2094–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Teruya, K.; Katakura, Y.; Kabayama, S.; Otsubo, K.; Morisawa, S.; Ishii, Y.; Gadek, Z.; Shirahata, S. Effect of reduced water on the apoptotic cell death triggered by oxidative stress in pancreatic b HIT-T15 cell. Anim. Cell Technol. Meets Genom. 2005, 2, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata, S.; Hamasaki, T.; Teruya, K. Advanced research on the health benefit of reduced water. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.; Qu, K.; Wang, R.; Tai, M.H.; Lei Lei, J.C.; Wu, Q.F.; Wang, Z.X. A review of hydrogen as a new medical therapy. Hepatogastroenterology 2012, 59, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Teruya, K.; Maki, T.; Komatsu, T.; Hamasaki, T.; Kashiwagi, T.; Kabayama, S.; Shim, S.Y.; Katakura, Y.; et al. Protective mechanism of reduced water against alloxan-induced pancreatic beta-cell damage: Scavenging effect against reactive oxygen species. Cytotechnology 2002, 40, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirahata, S.A.N.E.T.A.K.A. Reduced water for prevention of diseases. Anim. Cell Technol. Basic Appl. Asp. 2002, 12, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Amitani, H.; Asakawa, A.; Cheng, K.; Amitani, M.; Kaimoto, K.; Nakano, M.; Ushikai, M.; Li, Y.; Tsai, M.; Li, J.B.; et al. Hydrogen improves glycemic control in type1 diabetic animal model by promoting glucose uptake into skeletal muscle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadek, Z.; Li, Y.; Shirahata, S. Changes in the Relevant Test Parameters of 219 Diabetes Patients under the Influence of the So Called “Nordenau—Phenomenon” in the Prospective Observation Procedure. In Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects; Yagasaki, K., Miura, Y., Hatori, M., Normura, Y., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Gadek, Z.; Shirahata, S. Changes in the Relevant Test Parameters of 101 Diabetes Patients under the Influence of the So-Called “Nordenau-Phenomenon”. In Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects; Shirahata, S., Teruya, K., Katakura, Y., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Gadek, Z.; Li, Y.; Shirahata, S. Influence of natural reduced water on relevant tests parameters and reactive oxygen species concentration in blood of 320 diabetes patients in the prospective observation procedure. In Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects; Iijima, S., Nishijima, K., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Gadek, Z.; Hamasaki, T.; Shirahata, S. Therapy. In Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects; Shirahata, S., Ikura, K., Nagao, M., Ichikawa, A., Teruya, K., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata, S.; Li, Y.; Hamasaki, T.; Gadek, Z.; Teruya, K.; Kabayama, S.; Otsubo, K.; Morisawa, S.; Ishi, Y.; Katakura, Y. Redox Regulation by Reduced Waters as Active Hydrogen Donors and Intracellular ROS Scavengers for Prevention of type 2 Diabetes. In Cell Technology for Cell Products; Smith, R., Ed.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, D.J. The Nordenau-Phenomenon—Facts and Hypotheses. In Animal Cell Technology: Products from Cells, Cells as Products, Proceedings of the 16th ESACT Meeting, Lugano, Switzerland, 25–29 April 1999; Bernard, A., Griffiths, B., Noé, W., Wurm, F., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 525–527. [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata, S. Anti-Oxidative Water Improves Diabetes. 2001. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-010-0369-8_137 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Spear, J.R.; Walker, J.J.; McCollom, T.M.; Pace, N.R. Hydrogen and bioenergetics in the Yellowstone geothermal ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, M.; Blake, D.; Hoehler, T.; McCollom, T. Serpentinization and its implications for life on the early Earth and Mars. Astrobiology 2006, 6, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.O.; McKinley, J.P. Lithoautotrophic Microbial Ecosystems in Deep Basalt Aquifers. Science 1995, 270, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.T.; del Valle, D.A.; Robidart, J.C.; Zehr, J.P.; Karl, D.M. Dissolved hydrogen and nitrogen fixation in the oligotrophic North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scranton, M.; Novelli, C.P.; Loud, A.P. The distribution and cycling of hydrogen gas in the waters of two anoxic marine environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.; Bonjour, F.; Aragno, M. Aerobic and anaerobic microbial consumption of hydrogen in geothermal spring water. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1985, 29, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S.; Hamilton, T.L.; Spear, J.R.; Lavin, M.; Peters, J.W. [FeFe]-hydrogenase in Yellowstone National Park: Evidence for dispersal limitation and phylogenetic niche conservatism. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.; Aragno, M.; Seiler, W. Production and consumption of hydrogen in a eutrophic lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.-H.; Slater, G.F.; Sherwood Lollar, B.; Lacrampe-Couloume, G.; Onstott, T.C. The yield and isotopic composition of radiolytic H2, a potential energy source for the deep subsurface biosphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.; Parnell, J.; Blamey, N.J. Evidence for Seismogenic Hydrogen Gas, a Potential Microbial Energy Source on Earth and Mars. Astrobiology 2016, 16, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Are there natural spring waters rich in molecular hydrogen? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinka, T.; Bergmann, H.; Garche, J.; Kusnezoff, M. Chapter 4—The history of water electrolysis from its beginnings to the present. In Electrochemical Power Sources: Fundamentals, Systems, and Applications; Smolinka, T., Garche, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 83–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zoulias, E.; Varkaraki, E.; Lymberopoulos, N.; Christodoulou, C.N.; Karagiorgis, G.N. A review on water electrolysis. Tcjst 2004, 4, 41–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama, Y.; Kitahora, T. Alkaline electrolytic water (alkali ions water) for drinking water in medicine. Mizu No Tokusei Atarashii Riyo Gijutsu Enu-Ti-Esu Tokyo 2004, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro, H.; Kitahora, T.; Fujiyama, Y.; Banba, T. Clinical evaluation of alkali-ionized water for chronic diarrhea-placebo-controlled double blind study. Dig. Absorpt. 2000, 23, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Daliri, E.B.; Oh, D.H. New Clinical Applications of Electrolyzed Water: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R.; Ohno, K. Electrolyzed Reduced Water: Review I. Molecular Hydrogen Is the Exclusive Agent Responsible for the Therapeutic Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R. ORP should not be used to estimate or compare concentrations of aqueous H2: An in silico analysis and narrative synopsis. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R.; Ohno, K. Electrolyzed Reduced Water: Review II: Safety Concerns and Effectiveness as a Source of Hydrogen Water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, T. An Essay on the Medicinal Properties of Factitious Airs: With an Appendix on the Nature of Blood; Gale: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 1798. [Google Scholar]
- Dole, M.; Wilson, F.R.; Fife, W.P. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: A possible treatment for cancer. Science 1975, 190, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, R.J. Dietary fibre and health: The role of hydrogen production. Med. Hypotheses 1988, 27, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, M.; Sato, K.; Silva, M.J.; Ouhara, K.; Do, P.M.; Shanmugam, K.T.; Kawai, T. Hydrogen from intestinal bacteria is protective for Concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sano, M.; Hayashida, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S.; Fukuda, K. Are the effects of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors on cardiovascular events related to elevated levels of hydrogen gas in the gastrointestinal tract? FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2157–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, J.L.; Josse, R.G.; Gomis, R.; Hanefeld, M.; Karasik, A.; Laakso, M.; Group, S.-N.T.R. Acarbose treatment and the risk of cardiovascular disease and hypertension in patients with impaired glucose tolerance: The STOP-NIDDM trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimouchi, A.; Nose, K.; Takaoka, M.; Hayashi, H.; Kondo, T. Effect of dietary turmeric on breath hydrogen. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimouchi, A.; Nose, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ishiguro, H.; Kondo, T. Breath hydrogen produced by ingestion of commercial hydrogen water and milk. Biomark. Insights 2009, 4, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: From bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, N.; Tanabe, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Makita, Y.; Ohata, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Asano, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kiriyama, S. Pectin and high-amylose maize starch increase caecal hydrogen production and relieve hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D. Gas Therapy. Nature 1996, 383, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, B.; Hanna, S.; Abdallahi, O.M.; Lepidi, H.; Gardette, B.; De Reggi, M. Anti-inflammatory properties of molecular hydrogen: Investigation on parasite-induced liver inflammation. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. III 2001, 324, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y.; Sharma, P.; Evans, M.; Guthrie, N. Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label pilot study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Singh, R.B.; Fatima, G.; Kartikey, K.; Sharma, J.P.; Ostojic, S.M.; Gvozdjakova, A.; Kura, B.; Noda, M.; Mojto, V.; et al. The Effects of 24-Week, High-Concentration Hydrogen-Rich Water on Body Composition, Blood Lipid Profiles and Inflammation Biomarkers in Men and Women with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiyama, S.; Hasegawa, G.; Asano, M.; Hosoda, H.; Fukui, M.; Nakamura, N.; Kitawaki, J.; Imai, S.; Nakano, K.; Ohta, M.; et al. Supplementation of hydrogen-rich water improves lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, M.; Sang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yao, S.; Yu, Y.; Zong, C.; Xue, Y.; Qin, S. Hydrogen-rich water decreases serum LDL-cholesterol levels and improves HDL function in patients with potential metabolic syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoritaka, A.; Takanashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nakahara, T.; Ohta, S.; Hattori, N. Pilot study of H(2) therapy in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimaki, K.; Asada, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Nakajima, E.; Ikejima, C.; Yokota, T.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Effects of Molecular Hydrogen Assessed by an Animal Model and a Randomized Clinical Study on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Sato, B.; Rikitake, M.; Seo, T.; Kurokawa, R.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y.; Hara, H.; Nagao, T. Consumption of water containing a high concentration of molecular hydrogen reduces oxidative stress and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An open-label pilot study. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhu, L.; Sun, X.; Sun, X. Effect of hydrogen-rich water on oxidative stress, liver function, and viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2013, 6, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Sato, B.; Hara, K.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y.; Koyanagi, S.; Hara, H.; Nagao, T.; Ishibashi, T. Consumption of water containing over 3.5 mg of dissolved hydrogen could improve vascular endothelial function. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojić, S.M.; Stojanović, M.D.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Obrenović, M.D.; Veljović, D.; Međedović, B.; Kanostrevac, K.; Stojanović, M.; Vukomanović, B. Drinks with alkaline negative oxidative reduction potential improve exercise performance in physically active men and women: Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial of efficacy and safety. Serb. J. Sport. Sci. 2011, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Laher, I.; Kura, B.; Slezak, J. Hydrogen gas: From clinical medicine to an emerging ergogenic molecule for sports athletes (1). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kinone, K.; Horikosi, T.; Tamaki, M.; Takeshita, H.; Futatuki, T.; Ohishi, W.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Treatment in Acute Cerebral Infarction: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study on Safety and Neuroprotection. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Tribulova, N.; Slezak, J. A New Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders. Molecular Hydrogen Significantly Reduces the Effects of Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Hayashida, K.; Sano, M.; Onuki, S.; Suzuki, M. Efficacy of inhaled HYdrogen on neurological outcome following BRain Ischemia During post-cardiac arrest care (HYBRID II trial): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.; Rehman, M.; LeBaron, T.W.; Veal, D.; Adukwu, E.; Hancock, J.T. An Overview of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection: The Importance of Molecular Hydrogen as an Adjunctive Therapy. React. Oxyg. Species 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwazeer, D.; Liu, F.F.; Wu, X.Y.; LeBaron, T.W. Combating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in COVID-19 by Molecular Hydrogen Therapy: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 5513868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.T.; LeBaron, T.W.; Russell, G. Molecular Hydrogen: Redox Reactions and Possible Biological Interactions. React. Oxyg. Species 2021, 11, m17–m25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Akiyama, E.; Wang, Y.; Song, X. Review of hydrogen embrittlement in metals: Hydrogen diffusion, hydrogen characterization, hydrogen embrittlement mechanism and prevention. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2020, 33, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Seike, T.; Yutsudo, N.; Ohno, M.; Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sakumi, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Kido, M.A.; Takaki, A.; et al. Hydrogen in drinking water reduces dopaminergic neuronal loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Gong, W.; Ding, W.; He, Q. Fe-porphyrin: A redox-related biosensor of hydrogen molecule. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ohta, S.; Zhang, J.H. Discovery of a hydrogen molecular target. Med. Gas Res. 2023, 13, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryugina, A.V.; Danilova, D.A.; Pichugin, V.V.; Brichkin, Y.D. The Effect of Molecular Hydrogen on Functional States of Erythrocytes in Rats with Simulated Chronic Heart Failure. Life 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kura, B.; Bagchi, A.K.; Singal, P.K.; Barancik, M.; LeBaron, T.W.; Valachova, K.; Soltes, L.; Slezak, J. Molecular hydrogen: Potential in mitigating oxidative-stress-induced radiation injury (1). Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, J.; Kura, B.; LeBaron, T.W.; Singal, P.K.; Buday, J.; Barancik, M. Oxidative Stress and Pathways of Molecular Hydrogen Effects in Medicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; Russell, G.; Craig, T.J.; May, J.; Morse, H.R.; Stamler, J.S. Understanding Hydrogen: Lessons to Be Learned from Physical Interactions between the Inert Gases and the Globin Superfamily. Oxygen 2022, 2, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Sano, M.; Ohsawa, I.; Shinmura, K.; Tamaki, K.; Kimura, K.; Endo, J.; Katayama, T.; Kawamura, A.; Kohsaka, S.; et al. Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kato, S.; Matsuoka, D.; Tanaka, H.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen water intake via tube-feeding for patients with pressure ulcer and its reconstructive effects on normal human skin cells in vitro. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ji, M.; Jia, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Duan, M. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates neuronal ischemia--reperfusion injury by protecting mitochondrial function in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakano, H.; Hamada, H.; Itami, N.; Nakazawa, R.; Ito, S. A novel bioactive haemodialysis system using dissolved dihydrogen (H2) produced by water electrolysis: A clinical trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Saitoh, Y.; Iwai, K.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen-rich electrolyzed warm water represses wrinkle formation against UVA ray together with type-I collagen production and oxidative-stress diminishment in fibroblasts and cell-injury prevention in keratinocytes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2012, 106, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.W.; Tao, H.; Sun, X.; Kang, Z. Lactulose mediates suppression of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colon inflammation by increasing hydrogen production. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Vukomanovic, B.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Hoffman, J.R. Effectiveness of oral and topical hydrogen for sports-related soft tissue injuries. Postgrad. Med. 2014, 126, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Korovljev, D.; Stajer, V.; Javorac, D. 28-days Hydrogen-rich Water Supplementation Affects Exercise Capacity in Mid-age Overweight Women: 2942 Board# 225. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2018, 50, 728–729. [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Kharman, J.; McCullough, M.L. An H2-infused, nitric oxide-producing functional beverage as a neuroprotective agent for TBIs and concussions. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
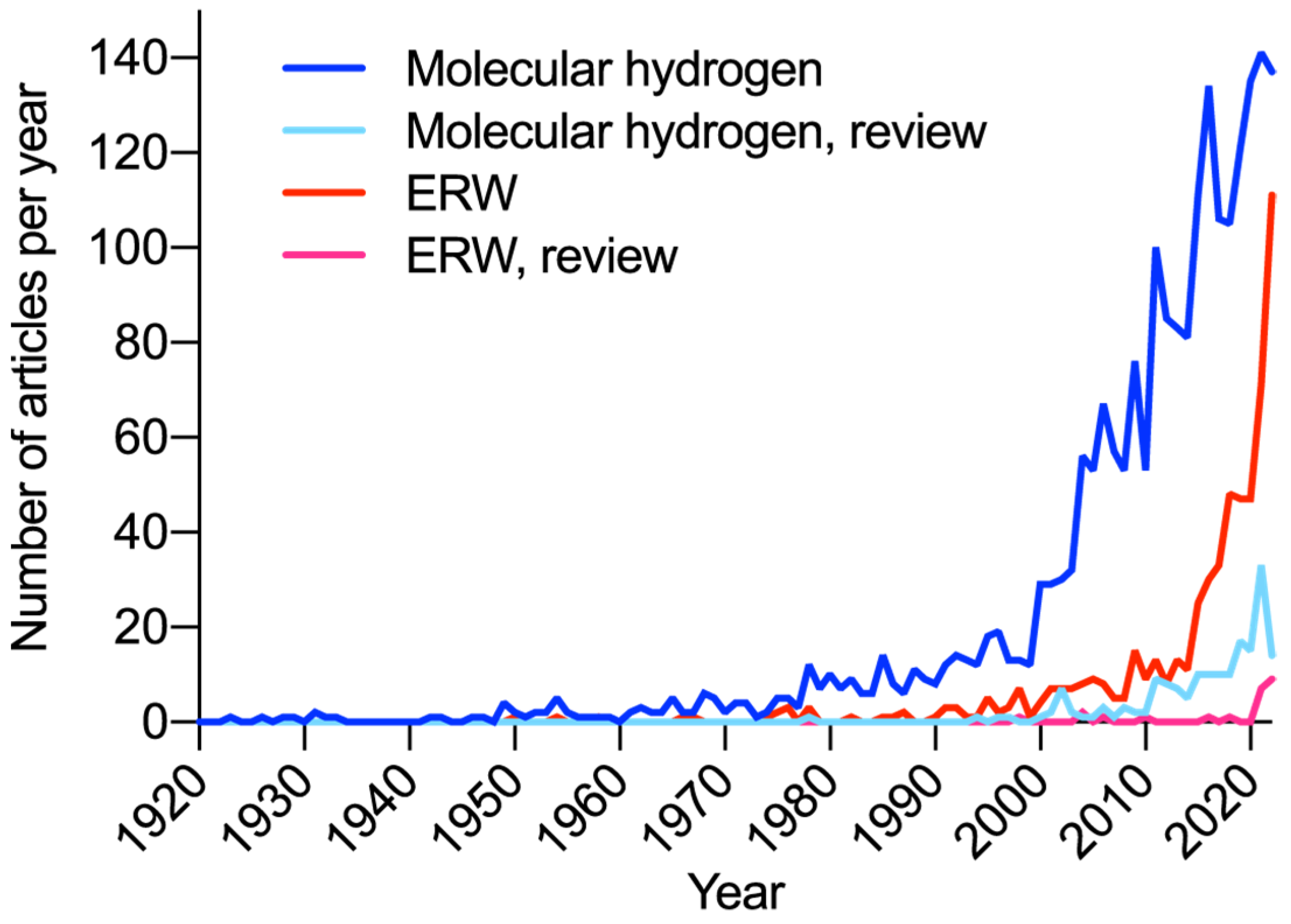
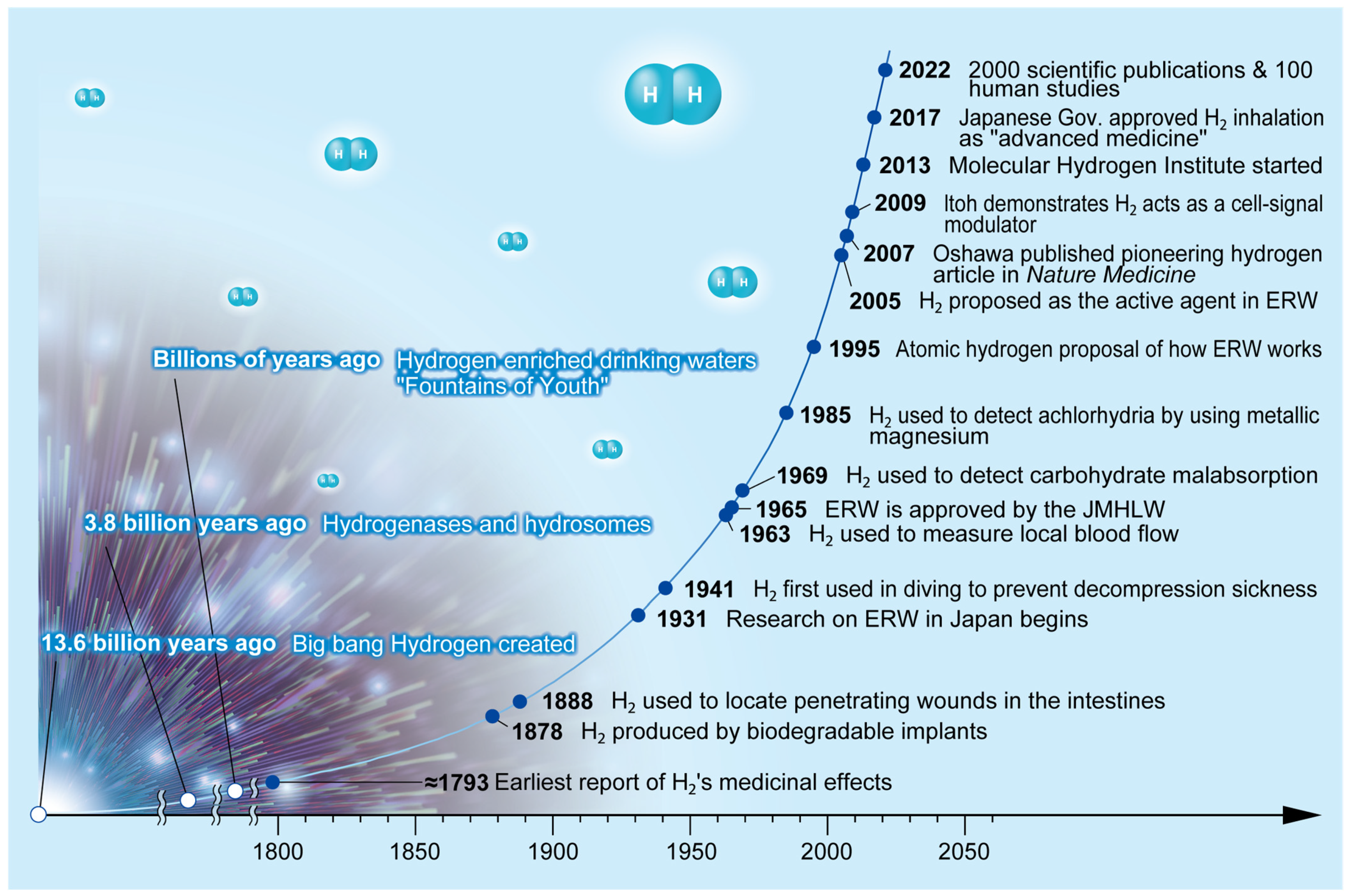
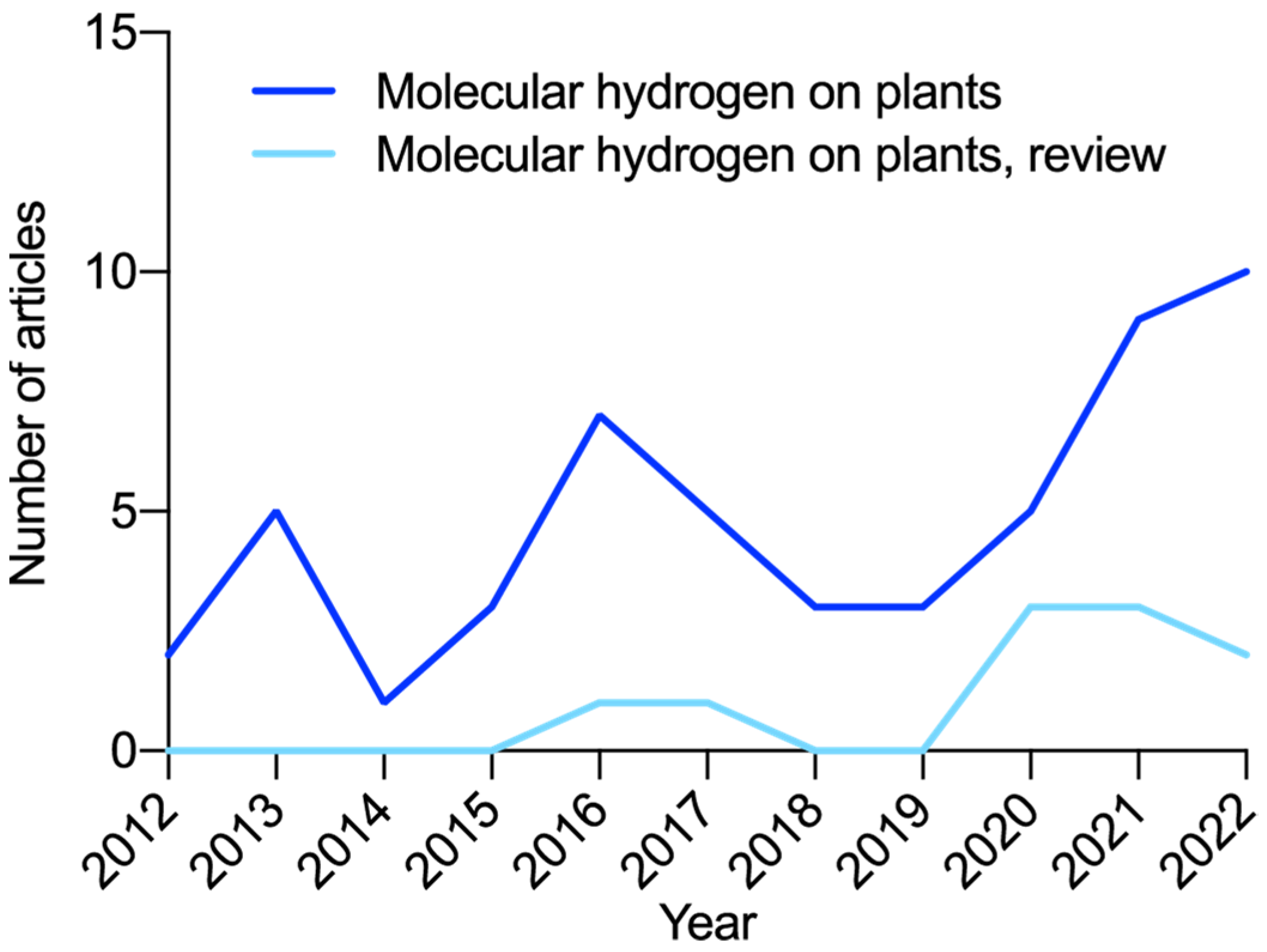
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LeBaron, T.W.; Ohno, K.; Hancock, J.T. The On/Off History of Hydrogen in Medicine: Will the Interest Persist This Time Around? Oxygen 2023, 3, 143-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen3010011
LeBaron TW, Ohno K, Hancock JT. The On/Off History of Hydrogen in Medicine: Will the Interest Persist This Time Around? Oxygen. 2023; 3(1):143-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen3010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeBaron, Tyler W., Kinji Ohno, and John T. Hancock. 2023. "The On/Off History of Hydrogen in Medicine: Will the Interest Persist This Time Around?" Oxygen 3, no. 1: 143-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen3010011
APA StyleLeBaron, T. W., Ohno, K., & Hancock, J. T. (2023). The On/Off History of Hydrogen in Medicine: Will the Interest Persist This Time Around? Oxygen, 3(1), 143-162. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen3010011







